Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviate Salt Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Adjusting Na+/K+ Ratio and Antioxidative Ability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cotton Materials and Treatments
2.2. Determination of Agronomic Traits
2.3. Determination of Chlorophyll Content and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
2.4. Determination of Elements
2.5. Measurement of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA, H2O2, O2−, Pro, Protein, and AA Contents
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing (RNA-Seq)
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
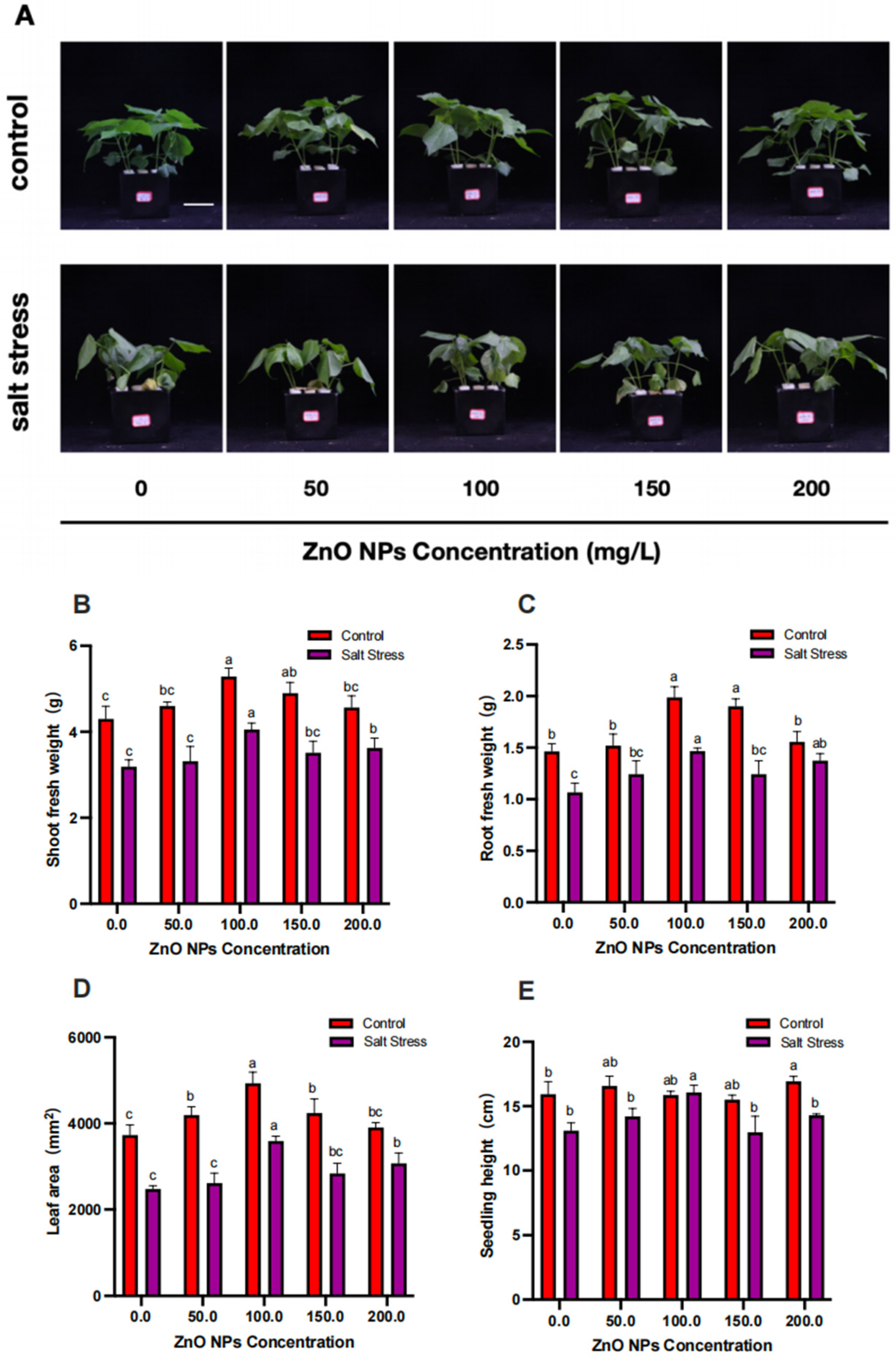
3.1. Effects of ZnO NPs on Phenotypic Characteristics of Cotton Seedlings under Salt Stress
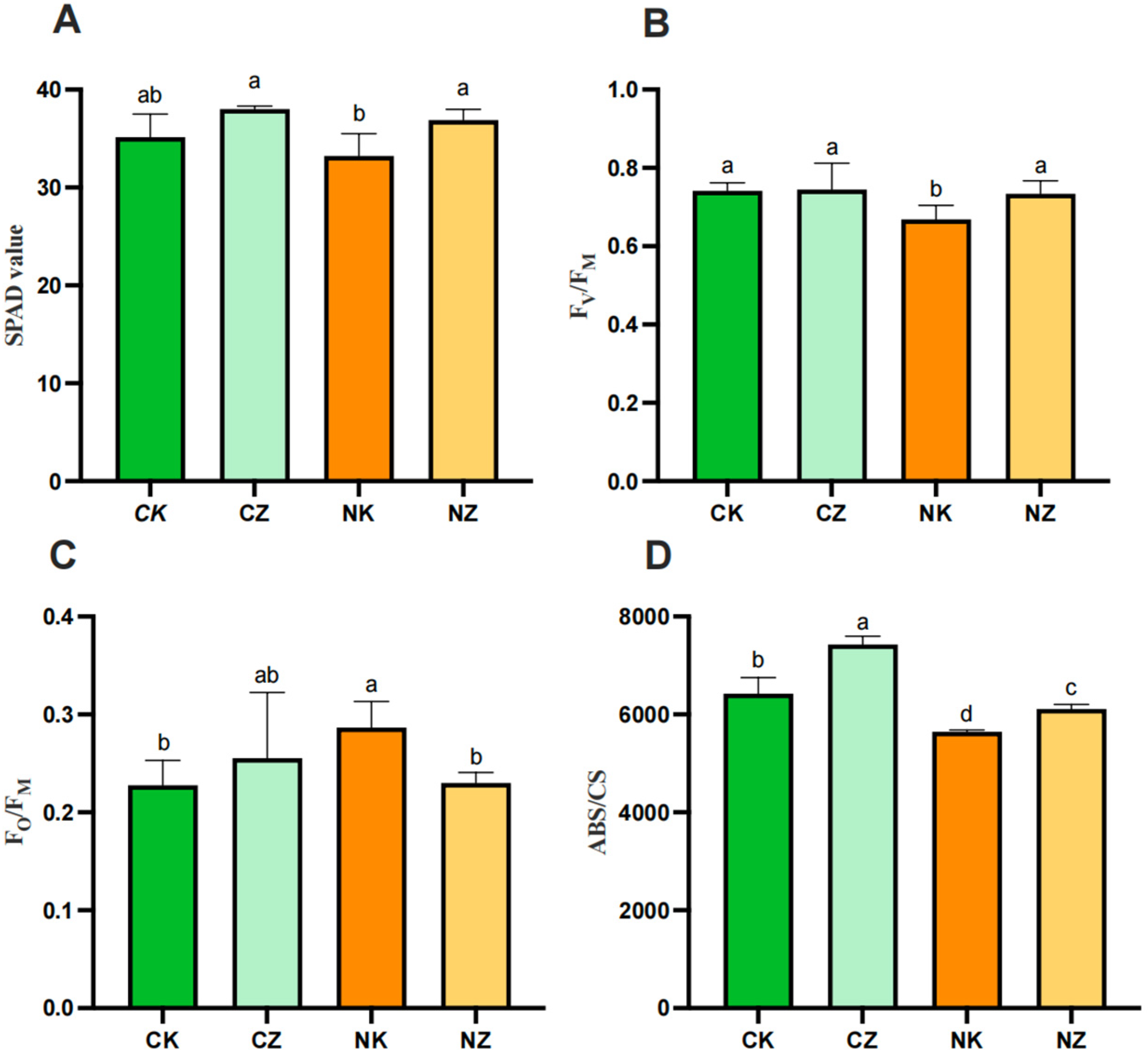
3.2. Effects of ZnO NPs on Chlorophyll Content and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters of Cotton Seedlings under Salt Stress
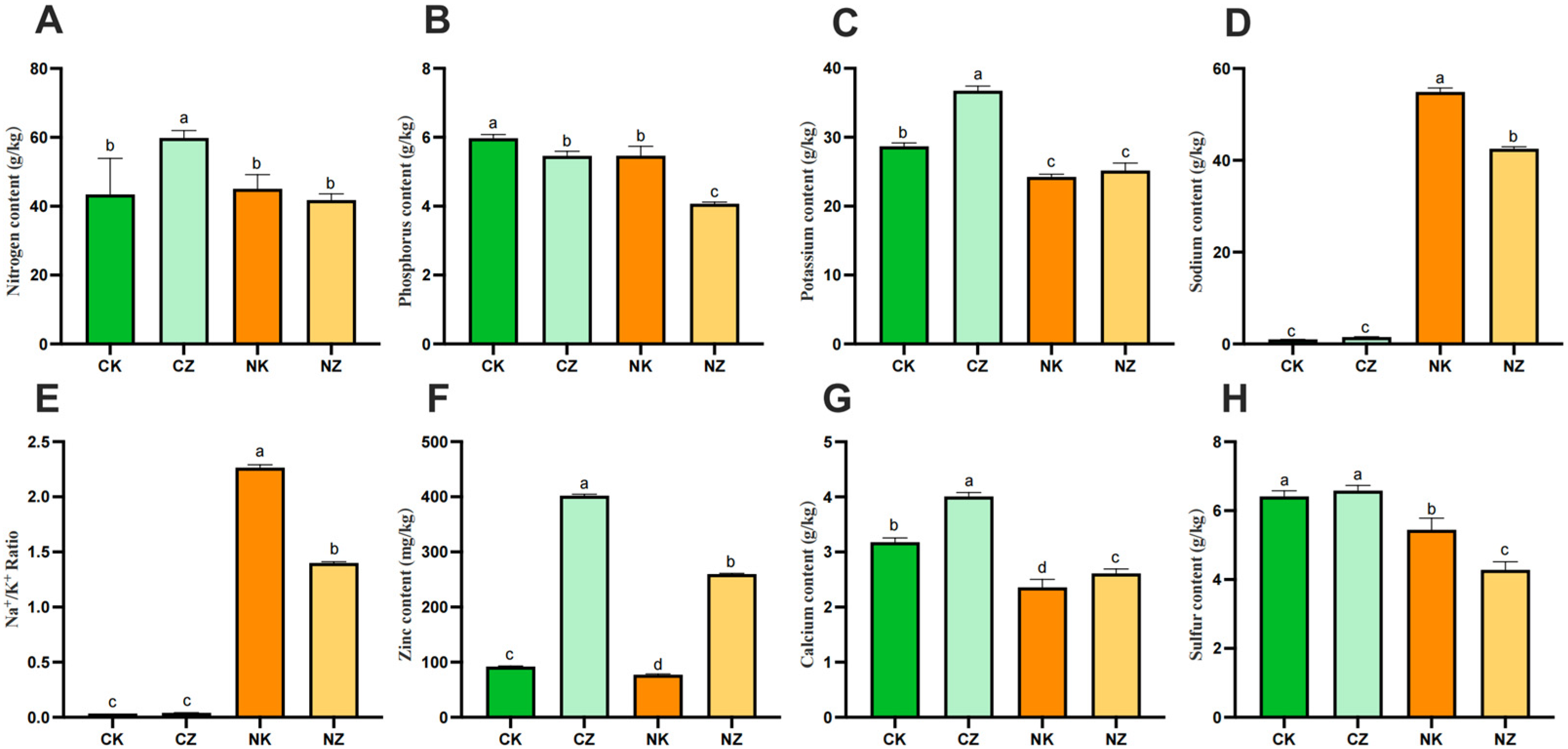
3.3. Effects of ZnO NPs on Elemental Contents of Cotton Seedlings under Salt Stress
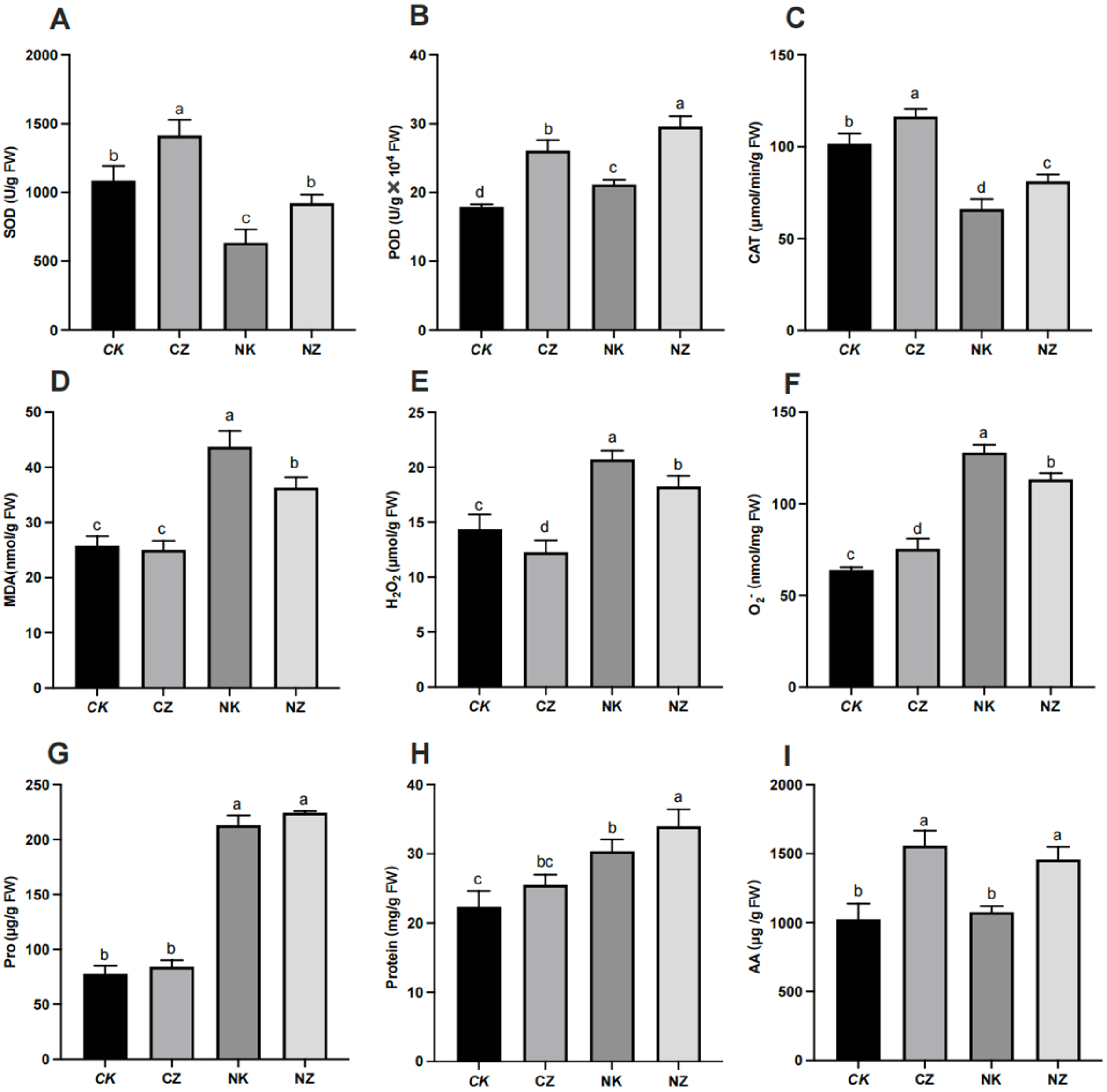
3.4. Spraying of ZnO NPs Alleviated Salt Stress-Induced Oxidative Stress
3.5. Analysis of the Effects of ZnO NPs on Gene Expression in the Salt-Responsive Transcriptome of Cotton
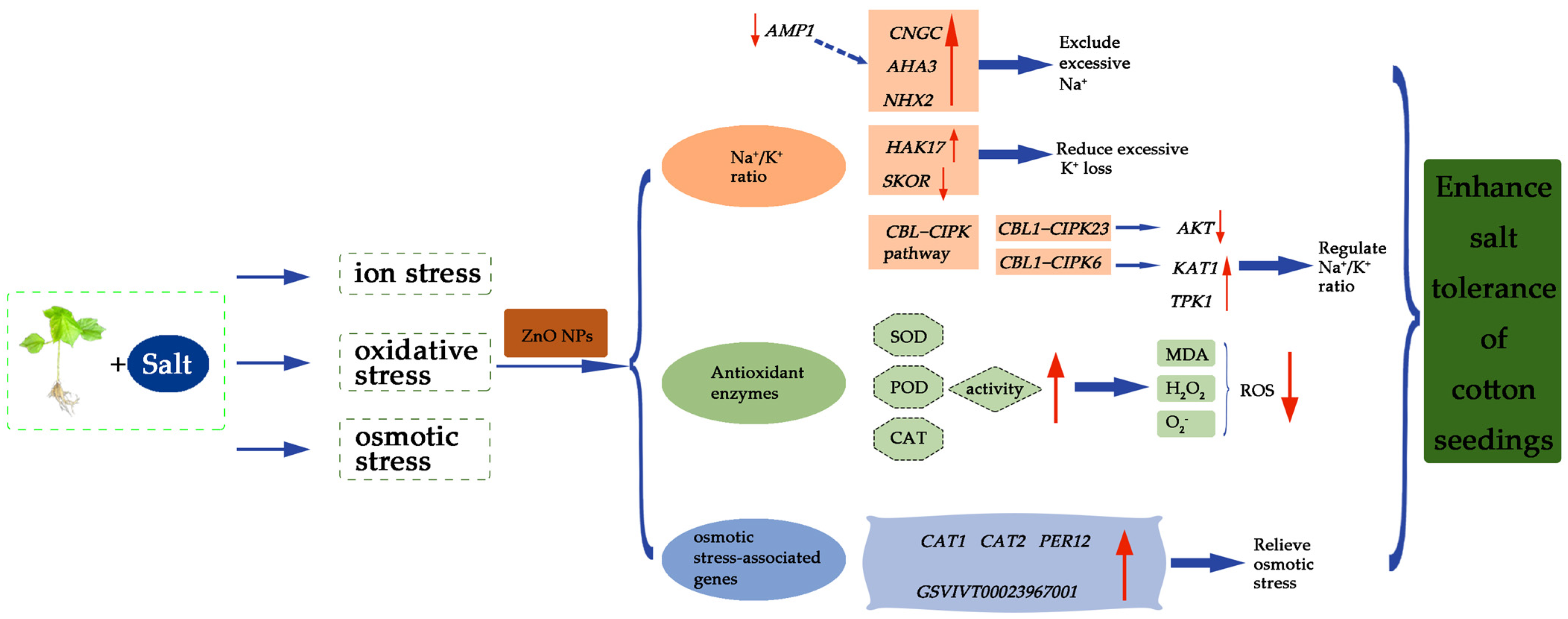
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopecká, R.; Kameniarová, M.; Černý, M.; Brzobohatý, B.; Novák, J. Abiotic Stress in Crop Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, Z.; Tang, Z.H.; Arif, M.; Ye, Z. An Insight into Abiotic Stress and Influx Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants to Cope in Saline Environments. Biology 2022, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Ali, A.; Safdar, L.B.; Zafar, M.M.; Rui, Y.; Shakeel, A.; Shaukat, A.; Ashraf, M.; Gong, W.; Yuan, Y. Salt stress induces physiochemical alterations in rice grain composition and quality. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Yan, L.; Riaz, M.; Babar, S.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C. Exogenous boron alleviates salt stress in cotton by maintaining cell wall structure and ion homeostasis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, W.; Waheed, A.; Naveed, H.; Zeng, F. MicroRNAs Mediated Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Cells 2022, 11, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xiao, F.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Fu, C.; Lin, H. PAMP-INDUCED SECRETED PEPTIDE 3 modulates salt tolerance through RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 7 in plants. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 927–944, Erratum in Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3148–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, G.; Song, X.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Salih, E.G.I.; Hussain, S.; Younas, M.U. Pivotal Role of Phytohormones and Their Responsive Genes in Plant Growth and Their Signaling and Transduction Pathway under Salt Stress in Cotton. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, A.; Cheng, B.; Wu, J. OsASR6 Enhances Salt Stress Tolerance in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.; Li, F.; Yang, Z. Regulatory Network of Cotton Genes in Response to Salt, Drought and Wilt Diseases (Verticillium and Fusarium): Progress and Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 759245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, I.; Aleem, S.; Farooq, J.; Rizwan, M.; Younas, A.; Sarwar, G.; Chohan, S.M. Salinity stress in cotton: Effects, mechanism of tolerance and its management strategies. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2019, 25, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryum, Z.; Luqman, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, S.M.U.D.; Wang, B.; Ditta, A.; Khan, M.K.R. An overview of salinity stress, mechanism of salinity tolerance and strategies for its management in cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 907937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, P.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Q.; Han, J.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Protoplast Dissociation and Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights to Salt Stress Response in Cotton. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldivar, R.H.L.; Argüello, B.M.; Reyes, I.V.; de los Santos Villarreal, G. Agronanotecnología: Una nueva herramienta para la agricultura moderna. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Agrar. 2018, 50, 395–411. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Khan, M.I.; Patel, M.; Alreshidi, M.; Moin, A.; Singh, R.; Snoussi, M.; Adnan, M. Innovations in nanoscience for the sustainable development of food and agriculture with implications on health and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Moneim, D.A.; Dawood, M.F.A.; Moursi, Y.S.; Farghaly, A.A.; Afifi, M.; Sallam, A. Positive and negative effects of nanoparticles on agricultural crops. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Liu, Y.; Geng, J.; Kou, X.; Xin, Z.; Yang, D. Engineering nanomaterials-based biosensors for food safety detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Lee, H.V.; Juan, J.C.; Phang, S.M. Production of new cellulose nanomaterial from red algae marine biomass Gelidium elegans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Almutairi, K.F.; Alotaibi, M.; Shami, A.; Alhammad, B.A.; Battaglia, M.L. Nano-Fertilization as an Emerging Fertilization Technique: Why Can Modern Agriculture Benefit from Its Use? Plants 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Mobin, M.; Abbas, Z.K.; AlMutairi, K.A.; Siddiqui, Z.H. Role of nanomaterials in plants under challenging environments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Hayat, Z.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, M.Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, Q.; Cao, Y.F.; Yuan, Y. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Modification, and Applications in Food and Agriculture. Processes 2023, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Nian, H.; Lian, T. Plants and rhizospheric environment: Affected by zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs). A review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 185, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Liu, C.; Fan, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, X. Preventing viral disease by ZnONPs through directly deactivating TMV and activating plant immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2019, 6, 3653–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Zia ur Rehman, M.; Adrees, M.; Arshad, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ali, L.; Hussain, A.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Imran, M. Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Noureen, S.; Anwar, S.; Ali, B.; Naveed, M.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Ahmad, P. Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11288–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizan, M.; Bhat, J.A.; Chen, C.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Ahmad, P.; Yu, F. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) induce salt tolerance by improving the antioxidant system and photosynthetic machinery in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakgotho, T.; Ndou, N.; Mulaudzi, T.; Iwuoha, E.; Mayedwa, N.; Ajayi, R.F. Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Mitigate Salt Stress in Sorghum bicolor. Agriculture 2022, 12, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.; Sagir, M.; Tahir, M.B.; Qureshi, K.A.; Jaremko, M.; Selim, S.; Hussain, A.; et al. Mitigation of salinity stress in barley genotypes with variable salt tolerance by application of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 973782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.; Abou-Baker, N.H. The contribution of nano-zinc to alleviate salinity stress on cotton plants. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Gu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Cerium oxide nanoparticles improve cotton salt tolerance by enabling better ability to maintain cytosolic K+/Na+ ratio. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; He, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Su, B.; Mei, L.; et al. Melatonin enhances cotton immunity to Verticillium wilt via manipulating lignin and gossypol biosynthesis. Plant J. 2019, 100, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmin, S.; Lipka, U.; Polle, A.; Eckert, C. The influence of transpiration on foliar accumulation of salt and nutrients under salinity in poplar (Populus × canescens). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.-M.; Gao, H.-Y.; Strasser, R.-J. Application of the fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction dynamics analysis in photosynthesis study. Zhiwu Shengli Yu Fenzi Shengwuxue Xuebao 2005, 31, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Shabala, S.; Cuin, T.A. Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Du, L. Research progress of CNGC function in plants. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2021, 48, 895–903. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; He, J. Arabidopsis AMP1 Negatively Modulates Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Biotechnol. Bull. 2015, 31, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Leidi, E.O.; Barragán, V.; Rubio, L.; El-Hamdaoui, A.; Ruiz, M.T.; Cubero, B.; Fernández, J.A.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Quintero, F.J.; et al. The AtNHX1 exchanger mediates potassium compartmentation in vacuoles of transgenic tomato. Plant J. 2010, 61, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Kong, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Dong, H. Overexpression of TaNHX2 gene improves drought and salt tolerance of transgenic cotton. Northeast Agric. Sci. 2021, 46, 31–35+71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, G. Research progress on high-affinity K+ transporter(HAK)in plants. Plant Physiol. J. 2021, 57, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.J.; Fan, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, R.Z.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.M. A Glycine max sodium/hydrogen exchanger enhances salt tolerance through maintaining higher Na+ efflux rate and K+/Na+ ratio in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shen, L.; Han, X.; He, G.; Fan, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, W.; et al. Phosphatidic acid-regulated SOS2 controls sodium and potassium homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Waadt, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Dominguez-Solis, J.R.; Schültke, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, T.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel cotton CBL-interacting protein kinase gene (GhCIPK6) reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J. HbCIPK2, a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1582–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, J.K.; Hirschi, K.D. CAX-ing a wide net: Cation/H(+) transporters in metal remediation and abiotic stress signalling. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-León, E.; Paradisone, V.; López-Moreno, F.J.; Rios, J.J.; Esposito, S.; Blasco, B. Effect of CAX1a TILLING mutations on photosynthesis performance in salt-stressed Brassica rapa plants. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.A.; Tanveer, M.; Hussain, S.; Bao, M.; Wang, L.; Khan, I.; Ullah, E.; Tung, S.A.; Samad, R.A.; Shahzad, B. Cadmium toxicity in Maize (Zea mays L.): Consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 17022–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sawah, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, G.G.; Holford, P.; Korany, S.M.; Alsherif, E.A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Ulhassan, Z.; Jośko, I.; Ali, B.; Sheteiwy, M.S. Funneliformis constrictum modulates polyamine metabolism to enhance tolerance of Zea mays L. to salinity. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, J.; Shan, R.; Shi, Y.; Li, H.; Xue, L.; Song, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviate Salt Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Adjusting Na+/K+ Ratio and Antioxidative Ability. Life 2024, 14, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14050595
Qian J, Shan R, Shi Y, Li H, Xue L, Song Y, Zhao T, Zhu S, Chen J, Jiang M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviate Salt Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Adjusting Na+/K+ Ratio and Antioxidative Ability. Life. 2024; 14(5):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14050595
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Jiajie, Ren Shan, Yiqi Shi, Huazu Li, Longshuo Xue, Yue Song, Tianlun Zhao, Shuijin Zhu, Jinhong Chen, and Meng Jiang. 2024. "Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviate Salt Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Adjusting Na+/K+ Ratio and Antioxidative Ability" Life 14, no. 5: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14050595
APA StyleQian, J., Shan, R., Shi, Y., Li, H., Xue, L., Song, Y., Zhao, T., Zhu, S., Chen, J., & Jiang, M. (2024). Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviate Salt Stress in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Adjusting Na+/K+ Ratio and Antioxidative Ability. Life, 14(5), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14050595





