Abstract
Glioblastoma (GB) is the most common and most aggressive primary brain tumor in adults, with an overall survival almost 14.6 months. Optimal resection followed by combined temozolomide chemotherapy and radiotherapy, also known as Stupp protocol, remains the standard of treatment; nevertheless, resistance to temozolomide, which can be obtained throughout many molecular pathways, is still an unsurpassed obstacle. Several factors influence the efficacy of temozolomide, including the involvement of other DNA repair systems, aberrant signaling pathways, autophagy, epigenetic modifications, microRNAs, and extracellular vesicle production. The blood–brain barrier, which serves as both a physical and biochemical obstacle, the tumor microenvironment’s pro-cancerogenic and immunosuppressive nature, and tumor-specific characteristics such as volume and antigen expression, are the subject of ongoing investigation. In this review, preclinical and clinical data about temozolomide resistance acquisition and possible ways to overcome chemoresistance, or to treat gliomas without restoration of chemosensitinity, are evaluated and presented. The objective is to offer a thorough examination of the clinically significant molecular mechanisms and their intricate interrelationships, with the aim of enhancing understanding to combat resistance to TMZ more effectively.
1. Introduction
Glioblastoma (GB) is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults, comprising roughly 50% of gliomas [1]. Tumors previously called glioblastoma are, in the 2021 World Health Organization (WHO) classification, divided into two separate diagnoses based primarily on isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation status: a. Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype, CNS WHO grade 4; b. Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, CNS WHO grade 4 [2]. For the purposes of this review, GB refers to IDH-wildtype glioblastoma unless specifically stated otherwise. High-grade gliomas originate from neural progenitor cells. The precise stage of differentiation of such target cells remains under investigation. Mouse models and molecular genetic studies of patient GB tissue, adjacent subventricular zone (SVZ) biopsies, and normal tissue indicate that astrocyte-like neural stem cells, which contain low-level somatic driver mutations and are in the SVZ, are the cells of origin. Over time, these cells may migrate and acquire additional somatic mutations, ultimately leading to the development of IDH-wildtype glioblastoma in distant brain regions. These multipotent tumor stem cells may have therapeutic implications, since therapeutic agents that fail to eliminate the tumor stem cells will be ineffective in eradicating the tumor. PTEN inactivation, TERT promoter mutation EGFR, PDGFR, or MET amplification, or in rare cases an oncogenic chromosomal translocation fusing the tyrosine kinase coding domains of FGFR1 or FGFR3 to transforming acidic coiled-coil 1 or 3 (TACC1/3), are associated with GB formation. The wingless (WNT) signaling pathway may also be aberrant in glioblastoma [3,4].
Histopathologic hallmarks include increased cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism, frequent mitoses, necrosis, and neovascularization. The presence of either TERT promoter mutation, EGFR gene amplification, or combined gain of entire chromosome 7 and loss of entire chromosome 10 (17/10) allows for a molecular diagnosis of glioblastoma, IDH wild-type, even in the absence of the characteristic GB histologic features [2,5].
Even with maximal therapy, glioblastoma has a less favorable prognosis and is less responsive to chemotherapy. The 5-year survival rate is less than 7%, with a median overall survival (mOS) of approximately 12 to 15 months with standard treatment [6]. Resistance to temozolomide (TMZ) therapy is a major cause of treatment failure. Therefore, overcoming TMZ resistance can be critical to improving treatment outcomes [1,7,8].
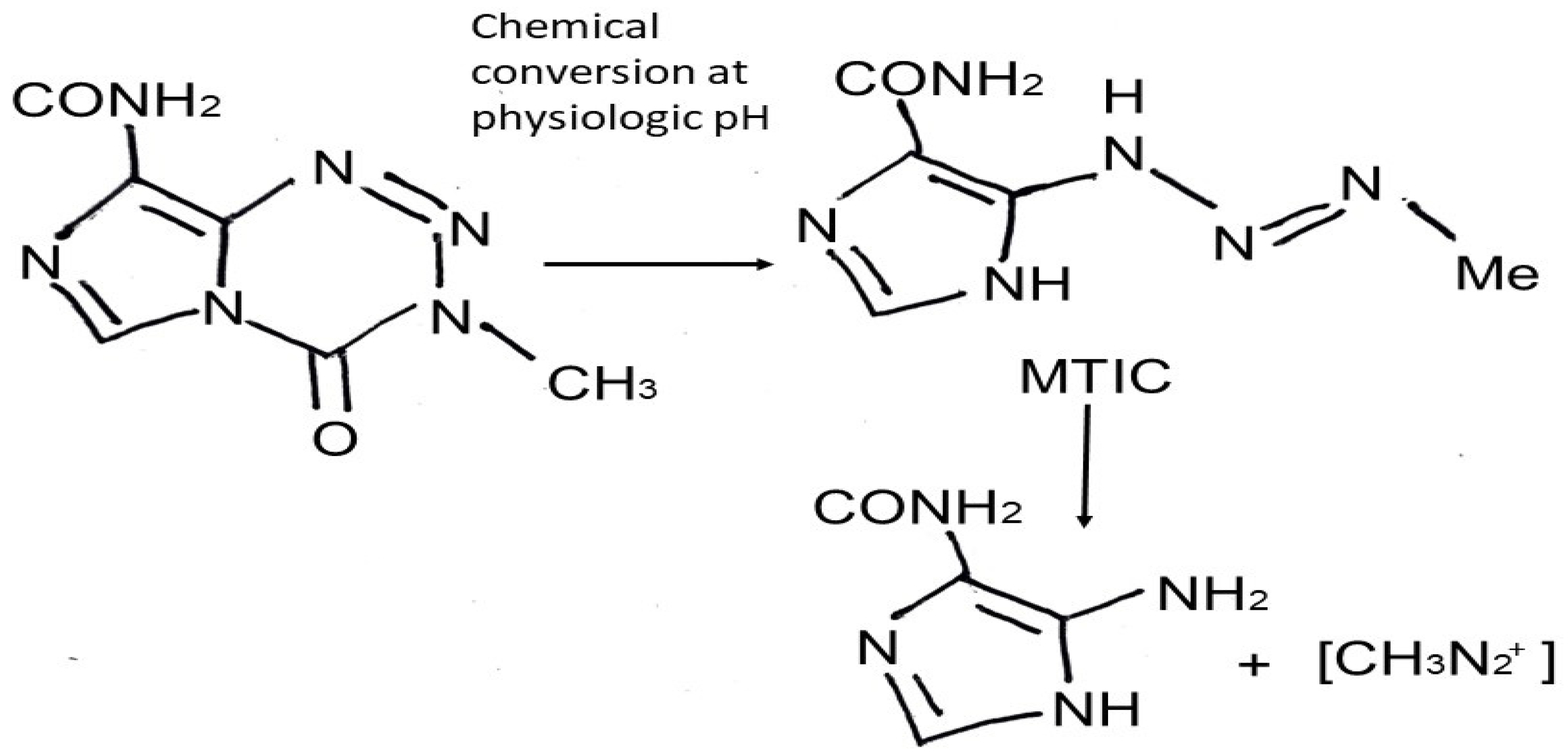
TMZ is an imidazotetrazine lipophilic prodrug [9] which is rapidly and nonenzymatically converted to the active alkylating metabolite MTIC [(methyl-triazene-1-yl)-imidazole-4-carboxamide]; this conversion occurs under physiologic pH in all tissues to which it distributes [9,10] (Figure 1). Pharmacologically, after per os administration, TMZ takes approximately 0.5 to 1.5 h to reach its greatest plasma concentration. In its majority, it remains unbounded in the central circulation and demonstrates high bioavailability [11]. The cytotoxic effects of MTIC are manifested through alkylation (methylation) of DNA at the O6, N7 guanine positions, which leads to depletion of the DNA-repair enzyme O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), DNA double strand breaks, and apoptosis [10]. DNA repair mechanisms, such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, recognize the DNA damage caused by TMZ, leading to cell cycle arrest and cells’ death [12]. Gliomas present a more alkaline environment compared to surrounding healthy brain cells, leading to drug activation [1,3,4,7,8] almost exclusively in the tumor cells [1,7,8,13,14]. Moreover, senescence induced by TMZ is another phenomenon that should also be mentioned. TMZ senescent GB cells overexpress NF-kB and lead to inflammatory cytokines’ production, such as IL6 and IL8; thus, these cells seem not to be eliminated after TMZ and radiotherapy and tend to be present even in recurrence of the tumor, with a not yet fully clarified role [15].
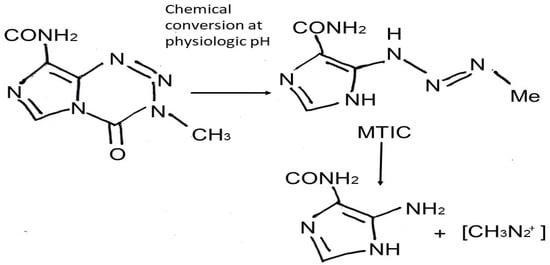
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of temozolomide and mechanism of action (MTIC: monomethyl 5-triazino imidazole carboxamide).
Due to the highly heterogeneous and mutation-prone nature of GB, resistance to TMZ is developed and accounts for over 50% of GB patients that eventually fail to respond to the therapy [16]. The demethylating enzyme O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) has been implicated in intrinsic TMZ resistance (TMZ-R) and recurrence by removing alkyl groups from the O6 position of guanine directly [17]. Herein, we present the most recent preclinical and clinical data about TMZ resistance acquisition and possible ways to overcome this resistance. This review aims to help physicians choose the best evidence-based therapy for chemoresistant glioblastomas based on the existing literature.
2. Preclinical Data
Preclinical data evaluating possible mechanisms of overcoming temozolomide resistance are presented below; a summary is presented in Supplementary Materials Tables S1–S6.
- A.
- Targeting DNA repair mechanisms
- MGMT
The most common mechanism of TMZ resistance has been associated with MGMT DNA repair enzyme. This enzyme removes the methyl groups attached to O6 guanine position, correcting the lesions formed by TMZ. Molecules that inhibit MGMT, such as O6-Benzyl guanine (O6-BG) and O6-(4-bromothenyl) guanine, have been tested in animal models and in vitro, enhancing TMZ action, but their pronounced bone marrow toxicity challenges their integration into clinical practice [1,7,18,19].
- MMR mutations
In some cases, TMZ-related DNA products can be combined with thymine, allowing the cell cycle to continue. The DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system removes thymine, arresting tumor growth. Mutations in MMR genes may lead to loss of apoptosis and cell regeneration, lowering the effectiveness of TMZ. Hunter et al. (2006) noticed MSH6 mutations in recurrent GB cell lines which were not mutated before TMZ treatment, demonstrating a potential role in TMZ resistance acquirement [20]. Li et al. (2022) proved that concomitant administration of TMZ, NAD+ precursor dihydronicotinamide riboside (NRH), and a poly(ADP-ribose) glycol hydrolase inhibitor resulted in poly(ADP-ribose) hyperaccumulation and DNA repair mechanisms such as MMR and BER knockdown, leading to an increase in TMZ cytotoxicity and effectiveness [1,7,19,21,22,23,24,25].
- BER
The base excision repair (BER) system repairs damage caused by oxidizing agents, radiation, and alkylating factors, including N3 and N7 methylation caused by TMZ. BER component inhibitors (for example, PARP inhibitors) may be effective; however, BER’s significance in TMZ resistance is still not clear. Zampieri et al. (2021) proved that upregulation of oxidative activity in tumor cells’ mitochondria is a main cause of TMZ resistance and suppression of oxidative phosphorylation or autophagy may promote chemosensitivity [26]; olaparib, unexpectedly, seems to inhibit mitochondrial complex I, suggesting that its use should be further tested in advanced TMZ-resistant GBs [1,7,23,25,26,27].
- B.
- Survival and metastasis regulation proteins (Galectin-1, ID1)
- Galectin
Galectin-1 is a member of the lectin protein family, with both intracellular and extracellular functions. It is related to tumor cell migration, formation of metastases, T-cell apoptosis, and chemotherapy and radiotherapy resistance. Davanat, a galactomannan which binds to galectin-1 at carbohydrate recognition domain, has been approved for colorectal cancer; it is not yet evaluated in GB in clinical trials [1,28].
- The role of ID1
The inhibitors of DNA binding proteins (ID) are a family of proteins that promote cells’ survival and homeostasis. More specifically, ID1 has been found to contribute in plenty of cancer’s hallmarks, such as angiogenesis, migration, and survival of malignant cells, and its overexpression leads to EGFR dysregulation, resulting in the development of TMZ resistance. Sachdeva et al. (2019) managed to enhance sensitivity to TMZ with the concomitant use of pimozide, an FDA-approved dopamine receptor antagonist, in vitro. Pimozide seems to inhibit pEGFR and USP1, which stabilizes—via deubiquitination—the ID1 protein, and has proved its efficacy against multiple tumor pathways at in vivo mouse models too, underlying a new potential drug combination against TMZ-resistant GBs [29,30].
- C.
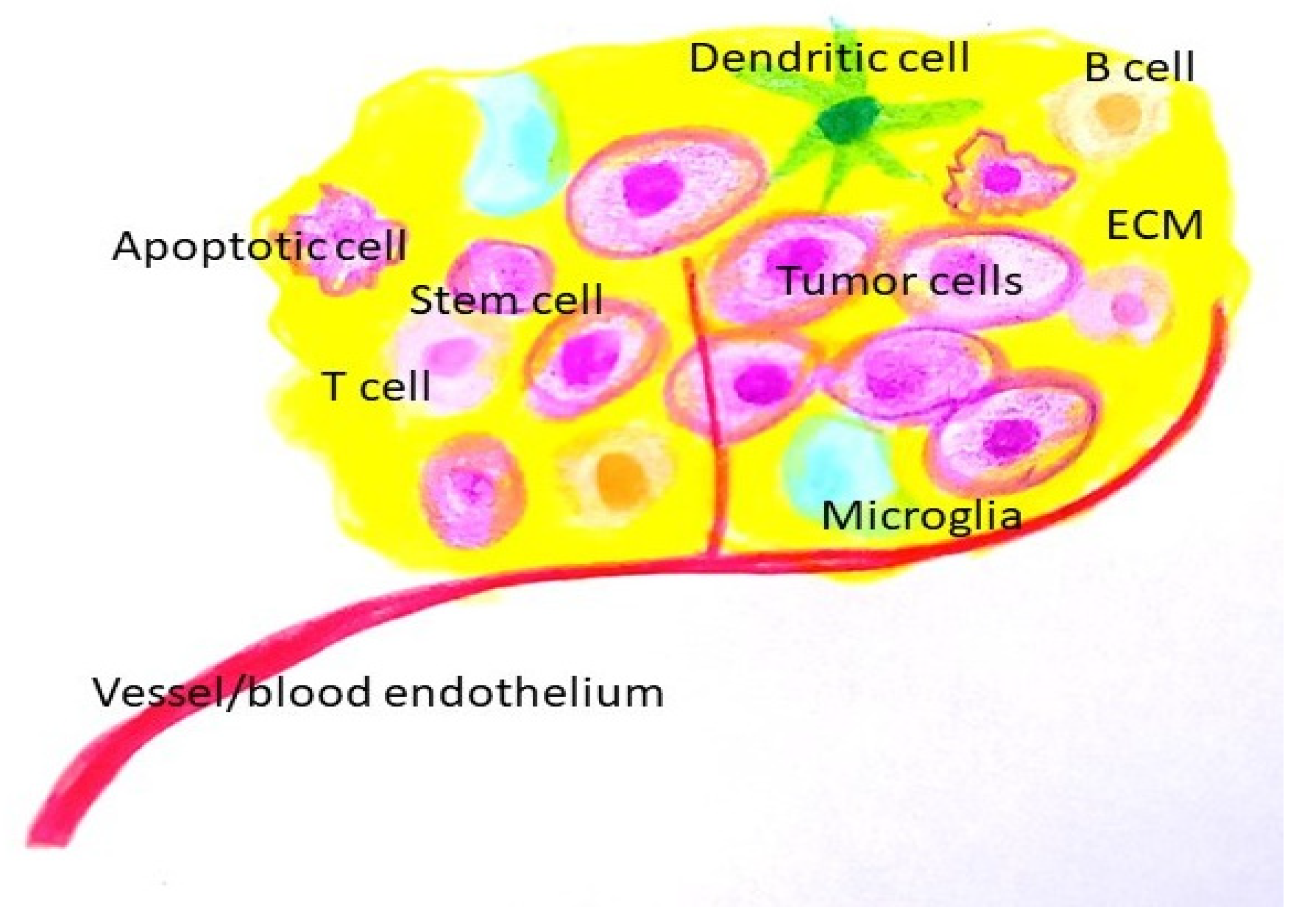
- The role of the tumor microenvironment (TME) (Figure 2)
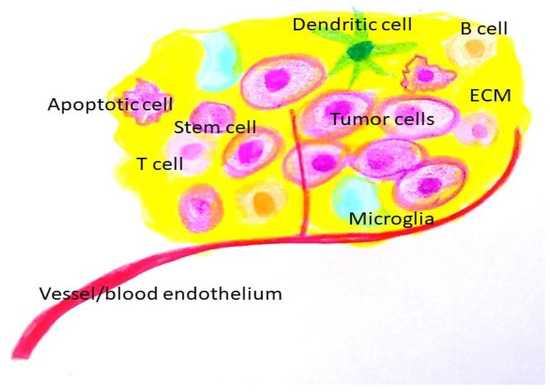 Figure 2. Tumor microenvironment. (ECM: extracellular matrix).
Figure 2. Tumor microenvironment. (ECM: extracellular matrix).
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is comprised of a cellular component (glioma cells, immune cells), and non-cellular components (extracellular vesicles, extracellular matrix (ECM) components, and secreted ECM remodeling enzymes). Due to its diverse components and dynamic nature, the TME plays a vital role in the survival of cancer cells and their response to therapy.
- Targeting the cellular component of TME
- Endothelial cells and blood–brain barrier (BBB)
The tumor’s endothelial cells are resistant to chemotherapy, while possessing a high rate of migration and growth factor expression, and a lower proliferation rate. Tumor endothelial cells express VEGF receptors, creating a paracrine loop wherein tumor cells stimulate vascular proliferation. In GB, the microenvironment plays a crucial role, with areas of neovascularization frequently encircling necrotic zones. Additionally, other proangiogenic signal transduction pathways are heightened, including the PDGF pathway involving PDGFR-beta on endothelial cells, angiopoietin-2 and its receptor Tie-2, the fibroblast growth factor family and its receptors, and stromal-cell derived factor-one alpha. In addition, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is made up of microvascular endothelial cells separating blood from brain interstitial fluid, while communicating with astrocytes and pericytes [31]. In GB, some areas of a tumor have BBB breakdown and increased permeability, whereas others do not. The invasive perimeters of GB consist of normal brain tissue infiltrated by cancer cells. Within this area, the BBB remains intact, limiting the delivery of drugs to these invasive margins, which harbor a distinct immune microenvironment and are the primary sites for tumor recurrences following treatment [13,32].
- Astrocytes
- Astrocyte-induced chemoresistance
Astrocytes are the most multitudinous glial cell population, occupying approximately 50% of the human brain’s volume. They often communicate through gap junctions, promoting astrocyte–astrocyte and astrocyte–glioma cell intercommunication, contributing to malignant cell invasion by mediating microRNA signaling. It is also believed that astrocyte-mediated transfer of protective mitochondria is involved in TMZ chemoresistance; thus, this hypothesis needs to be further verified [13,32].
- Astrocytes and stem cancer cells
Overexpression of some transcription factors, such as Nanog, in p53-negative astrocytes, has been linked to dedifferentiation to cancer progenitor cells or cancer stem cells, retaining a possible pathway to the TMZ resistance. Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) possess a crucial role in TMZ resistance development due to their differentiation capacity and induction of tumor heterogeneity [23]. New therapeutic approaches targeting specific GSCs markers have emerged; CD133 is one of the most commonly used cell surface markers for GSCs, and targeted therapies towards CD133-positive cells have been developed, such as chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cell therapy [23]. Moreover, autophagic cell death of CD133+ cells may become activated after sonic hedgehog signaling inhibition, through mTOR-independent pathways [33]. In previous research, the Notch pathway seemed to be upregulated in GSCs, and γ-secretase inhibitors inhibited both Notch and VEGF signaling pathways, highlighting their potential usage in TMZ-resistant GBs [34]. Lastly, GSCs are located in niches whose viability depends on their abnormal vascularity; antiangiogenic agents are thought to play a critical role in GSC survival and distribution to TMZ resistance [35,36].
- Microglia/Macrophages
Microglia consists of CNS macrophages. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) release plenty of factors that seem to contribute to glioma cell proliferation, survival, and migration. Microglia synthesizes and releases stress-inducible protein 1 (STI1), endothelial growth factor (EGF), colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1), CCL2 receptor (CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, is expressed by GB cells), TGF-β, membrane type 1–matrix metalloproteinase (MT1–MMP), and signaling through Toll-like receptors, which seem to retain the most critical role among others [32,37,38]. Bowman and Joyce (2014) demonstrated in preclinical stages that the use of CSF-1 inhibitors, along with TMZ and radiotherapy, may improve TMZ-resistant GB prognosis [39].
- Targeting non-cellular components of TME
- a.
- The role of extracellular matrix and interstitial fluid pressure
The extracellular matrix (ECM) and interstitial fluid pressure play a role in drug distribution, from noncellular factors to the glioma cells, possessing a possible role in chemoresistance. A great number of the ECM’s components conduce to malignant cell survival through a variety of molecules: tenascin-C (TN-C), a member of the tenascin glycoprotein family, fibronectin, an ECM glycoprotein which conduces to p53 suppression, fibulin 3, another glycoprotein acting through Notch and NF-kB signaling pathways, and hyaluronic acid, a high-molecular-weight glycosaminoglycan; all of them lead to GB cell proliferation, survival, neovascularization, and chemoresistance [40,41].
- b.
- The role of extracellular vesicles
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are a family of cell-derived structures possessing a role in cell-to-cell communication. They may become involved in plenty of pathological conditions and they can even be used as potential therapeutic approaches. EVs help tumor cells to communicate and secrete significant molecules for glioma cells’ survival [42,43].
Nandhu et al. (2018) were the first to develop an anti-fibulin 3 monoclonal antibody, giving promising results, while inducing cancer cell apoptosis and inflammatory cell proliferation of the tumor cells [44]. Radioimmunotherapy targeting the extra domain B of fibronectin [45], antibodies against tenascin-C [46], double-specific tenascin-C and fibronectin targeted peptide [47], double-stranded RNA with a nucleotide sequence homologous to tenascin-C mRNA [48], oncolytic herpes simplex virus (oHSV) armed with MMP-9 [49], HSP47 by modifying the TGF-β pathway [50], chondroitinase, riving chondroitin sulfate disaccharide chains from chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in the tumor’s ECM [51], lumefantrine, through inhibition of the heat shock proteins-MMPs circuit [52], and tetraarsenic oxide, via decreasing MMPs and protein kinase B phosphorylation [53], seem to carve the path of new targeted therapies against advanced, chemoresistant GBs.
- D.
- Key molecular pathways in temozolomide resistance
- 1.
- The Akt pathway
The Akt/mTOR (Ak strain transforming/mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway possesses a crucial role in TMZ resistance acquisition, mainly by promoting tumor cell upregulation, proliferation, survival, and apoptosis blockage [54].
- 2.
- The Wnt/β-catenin pathway
The Wnt (Wingless-related integration site)/β-catenin pathway seems to be involved in autophagy-related protein 9B activation, mainly through loss of DOC-2/DAB2-interacting protein (DAB2IP), which is a tumor suppression gene. Genome-wide binding profiles for ASCL1 and the Wnt effector LEF-1 provide mechanistic insight and suggest widespread interactions between the TF module and the signaling pathway. Regulatory connections between ASCL1, Wnt signaling, and collaborating TFs seem to be essential for the maintenance and tumorigenicity of GB cancer stem cells. Blockage of this pathway inhibits TMZ-associated autophagy and sensitizes glioma cells to chemotherapy [55].
- 3.
- The JAK/STAT pathway
The Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway is a very complex signaling pathway; its upregulation induces angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation, and immune blockage and suppression [56]. Kohsaka et al. demonstrated that STAT3 inhibits the degradation of the enzyme MGMT, whose expression is associated with TMZ resistance. In line with that, STAT3 inhibition and radiation in a syngeneic immune-competent glioma mouse model led to immunologic TME reprogramming, with increased dendritic cell–T-cell interaction and antigen presentation. This was correlated with significantly longer animal survival, indicating that a fully functional immune response was required to mediate the therapeutic effects of STAT3 inhibition [50].
- E.
- Cancer cell metabolism and pH regulation
- The role of hypoxia, pH, and glucose
Hypoxia has many roles, including a modulation in phenotype and increasing the migration of glioma cells. Chronic hypoxia may contribute to chemoresistance due to a lack of oxygen, which is necessary for chemotherapeutic drugs to act. Moreover, cycling hypoxia has been proven to increase the delivery of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 (ABCB1), leading to resistance to TMZ as well as the deliverance of Livin, a member of apoptosis proteins, which is overexpressed in both chronic and cycling hypoxia [13,32,57,58].
PH becomes minimized close to the tumor, inhibiting gap junctions, increasing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), carbonic anhydrase, interleukin-8, cathepsin B, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 expression, leading to progression, survival of the tumor cells, and chemoresistance [13,32,59].
- RFP
RET finger protein (RFP) binds to deacetylase 1 in GBs, inducing deacetylation of H3K27 and dysregulation of cis-regulatory elements, leading to resistance in chemotherapy. Knockdown of RFP decreases oxidative stress and modifies the function of BER and, in addition to TMZ, transcends chemoresistance [60,61].
- F.
- Molecules contributing to temozolomide resistance
- The role of miRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRs) are non-coding molecules that negatively affect gene expression by binding to the 3′-untranslated region of messenger RNAs [7]. A suppression of miR-519a has been connected with GB chemoresistance, leading to the collection of more preclinical data about this hypothesis [49]. In vivo and in vitro analysis has demonstrated that miR-519a is able to inhibit the STAT3/Bcl-2/Beclin-1 pathway, giving rise to GB cell apoptosis through autophagy, sensitizing gliomas to TMZ treatment. Cardoso et al. highlighted that overexpression of miR-200c downregulates GB cells’ metabolism, promotes chemosensitivity, and leads to cancer cell cycle arrest [62,63].
- AURKB
Aurora kinase B (AURKB) is a member of the aurora kinases, a family of serine/threonine kinases that contribute to chromatid separation. Moreover, AURKB is already recognized as a possible encoding gene possessing a critical role in TMZ resistance acquisition, glioma cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, and autophagy, by becoming involved in p53/Mdm2 suppression, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, p38 MAPK and AMPK signaling pathway alternation. Its inhibition has been tested both in vitro and in vivo, through transfection via lentivirus and specific small molecules targeted against AURKB, such as Hesperadin. These agents, as monotherapy or concomitant to TMZ (for Hesperadin), led to TMZ sensitivity, and their efficacy should be further examined in clinical trials [54,64,65].
- De novo purine synthesis
Shireman et al. highlighted the importance of ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 13B (ARL13B), a ciliary protein whose epigenetic modification may possess a crucial role in the development of chemoresistance in GBs. It was unveiled that its interaction with inosine-50-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 (IMPDH2), a purine biosynthetic enzyme, reduces the DNA-associated damage caused by TMZ, which downregulates purine salvage; in vivo use of the FDA-approved drug mycophenolate mofetil, which can block IMPDH2’s activity and diminish the efficiency of the ARL13B–IMPDH2 circuit, led to enhancement of TMZ therapeutic efficacy [66]. In addition, Zhou et al. (2020) demonstrated that high activity of GTP synthetase resulted in shortening of overall survival in patients with advanced GBs, and its inhibition may be an auspicious strategy [67].
- NF-kB
The NF-kB family of transcriptional factors controls the expression of plenty of targeted genes that are involved in cell growth, survival, apoptosis, et cetera [68]. Yu et al. demonstrated that high NF-kB activity is associated with oncogenic characteristics of glioma cells that promote GB’s viability; moreover, inhibition of NF-kB resulted in S-cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Furthermore, NF-kB correlates with MGMT expression in gliomas; the use of NF-kB inhibitors, such as parthenolide, leads to MGMT downregulation, resulting in TMZ chemosensitivity restoration [69]. Moreover, Avci et al. (2020) tested in vivo the concurrent administration of an NF-κB inhibitor, BAY 11-7082, with TMZ, which resulted in contiguous outcomes, possibly by modulating the actin cytoskeleton pathway [70].
- LGR6
Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 6 (LGR6) seems to promote cell proliferation and survival in plenty of malignancies, including, for example, colorectal cancer. Cheng et al. proved that LRG6 induces GB survival and chemoresistance, partly by activating the Akt signaling pathway, pointing out the potential benefit from such pathway inhibitors [71].
- Hexokinase 2
Zhang et al. revealed that hexokinase 2 (HK2)-mediated glycolysis is of great importance in TMZ resistance emergence in GBs, resulting in malignant cell proliferation and survival. HOTAIR, a lncRNA, regulates HK2 expression in tumor cells, inhibiting miR-125. This results in HOTAIR shut down and downregulates HK2 expression, inducing chemosensitivity both in vitro and in vivo [72].
- Circular RNA ASAP1 and NRAS/MEK1/ERK 1-2 pathway
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are members of the non-coding RNA family, derived from RNA backsplicing and forming a covalent closed-loop structure. More precisely, circular RNA ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase activating proteins with the Src homology 3 domain, ankyrin repeat and Pleckstrin homology domain 1 (circASAP1) were found highly expressed in recurrent GBs. Wei et al. revealed that eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A3 (EIF4A3) bounds to the 3’ flanking region of circASAP1, winding up its expression. CircRNA’s sponging to miR-502-5p eventually activated NRAS/MEK1/ERK 1-2 signaling pathway, contributing to TMZ resistance by promoting GB cell growth and apoptosis suppression [73].
- PTRF/Cavin-1
Polymerase I and transcript release factor (PTRF), cavin-1, was situated to be involved in extracellular vesicle (EV) formation and excretion emerging from eukaryotic cells; these EVs appear to possess an essential role in GB cells’ communication, by transmitting regulatory RNA, DNA, and proteins. GB cells seem to overexpress PTRF, leading to TMZ resistance through extracellular vehicles [74]. Chloroquine downregulates PTRF expression—with still not completely understood mechanisms—and, sequentially to TMZ chemotherapy, it seems to increase TMZ’s intracellular concentration and sensitivity [75].
- Cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha
Yang et al. demonstrated that cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha (cPLA2a), an intracellular enzyme that delivers arachidonic acid for eicosanoid production, induces TMZ resistance when upregulated, due to PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway overactivation. CPLA2a inhibition, and PI3K’s by extension, restore chemosensitivity in advanced, TMZ-resistant GBs [76].
- Long noncoding RNA
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) transmission via EVs from one cell, cancerous or not, to another may affect a tumor’s expansion and progression [77]. Li et al. revealed through their study that EV-derived TMZ-associated lncRNA in GB (lnc-TALC) is able to promote p38 MAPK pathway activation, inducing C5a release, via microglia M2 macrophage polarization through enolase 1 (ENO1) binding, leading to TMZ resistance. Therefore, this study enlightens the pathway of finding novel therapeutic agents, by blocking the lnc-TALC-mediated communication between GB cells and microglia [78].
3. Clinical Data
One way to ameliorate our therapeutic approach to GB is either to replace temozolomide with a targeted agent to improve the toxicity profile with the same efficacy, or to add a new agent with non-cross toxicities to increase treatment efficacy and overcome acquired resistance. Supplementary Material Table S7 summarizes the clinical data that are discussed below.
3.1. Bevacizumab and Other Antiangiogenic Agents
GB is one of the most vascularized human malignancies due to its wide production of angiogenic factors, such as VEGF. It is proved that VEGF not only induces neovascularization in GBs, but also modifies BBB’s vascular permeability and generates vasogenic edema; its inhibition prevents glioma cells’ growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis [32,75,76]. Bevacizumab is the most thoroughly examined agent in patients with GBs, with a number of clinical trials being completed or recruiting at the moment, testing its efficacy as monotherapy or in combination with standard chemotherapy, mainly irinotecan [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84]. Different combinatorial approaches are currently tested in clinical trials such as of bevacizumab along with marizomib (NCT02330562), bevacizumab, and irinotecan (BI) [85], and TMZ plus apatinib (NCT03741244). In general, bevacizumab has been shown to increase progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS) in patients with firstly recurrent glioblastoma [86].
3.2. EGFR Inhibitors
Endothelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor which is of great importance in migration, proliferation and angiogenesis of malignant cells. Its mutations are encountered at 40% of gliomas, resulting in the production of targeted therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors [1,79,80,81]. The usage of Cetuximab in TMZ-resistant GBs was disappointing in clinical trials (interruption at phase II), while the use of Erlotinib and Gefitinib (and other TKIs, such as Afatinib; Phase II NCT00727506) was found to be effective in a subpopulation of patients with intact PTEN and MGMT promoter methylation [1] (NCT00052208, NCT00525525, NCT00445588).
3.3. The PI3K Pathway
The importance of the PI3K pathway’s dysregulation has been highlighted in the development of multiple cancer types. The PI3K family of intracellular kinases possesses a critical role in cell proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. PI3K/AKT/mTOR and some of the involved proteins, such as p85, PTEN, EGFR, are often negatively alternated in GB [82]. Moreover, BKM120, a pan-PI3K inhibitor, is investigated in concomitant use with bevacizumab in a phase I/II clinical trial, resulting in a median progression-free survival of 4.0 months, a 26% overall response rate, and a progression-free survival at 6 months at 36.5%, demonstrating no superiority to isolated bevacizumab usage [83].
3.4. TGF-β Inhibitors
Tumor growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a multifaceted cytokine, whose signaling pathway contributes to cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis in plenty of cell series, including GB cells [84]. It activates plenty of intracellular pathways and is associated with the knockdown of the SUMO gene, which seems to contribute to the development of TMZ resistance in gliomas. Concomitant treatment with TMZ and OKN-007, a TGF-β inhibitor, was found to be superior to monotherapy with TMZ in preclinical series [85]. Bogdan et al. designed a phase IIb clinical trial, evaluating the effectiveness and safety of trabedersen (AP 12009), a TGF-β2 inhibitor, compared with standard chemotherapy for high-grade gliomas; median survival was 39.1 months for 10 µM trabedersen, 35.2 months for 80 µM, and 21.7 months for standard chemotherapy group. The results remain not statistically significant [86].
3.5. Antibody Drug Conjugates
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) consist of a monoclonal antibody specific for a certain cell surface antigen attached to a cytotoxic agent. Their efficacy in plenty of cancer types is undebatable, as possessing lower possibility of complications and a tumor-specific anti-oncogenic effect; however, their efficiency and safety in advanced, TMZ-resistant GBs remains controversial [16,87]. A large number of ADCs has been tested; 131I radio-conjugated antibodies [88], 131I-labeled murine antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81C6 (131I-81C)] [89], 125I-labeled anti-epidermal growth factor receptor 425 murine monoclonal antibody (125I-mAb 425) [90], ligand-targeted toxin conjugate Transferrin-CRM107 (Tf-CRM107) [91], EGFR targeting recombinant toxin (TP-38) [92], convection-enhanced delivery of IL13-PE38QQR versus Gliadel [93], and IL-4 Pseudomonas exotoxin (NBI-3001) [94]. Contrarily, the usage of more recent ADCs is remarkably promising; ABT-414, depatuxizumab mafodotin, an EGFR targeting ADC [95,96] (p4) and AMG 595 [97], an anti-EGFRvIII ADC, remain the most promising potential therapeutic approaches.
3.6. NTRK Inhibitors
Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) fusion mutations are detected in approximately <2% of GBs; however, it is known that these mutations lead to Tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk) activation and tumorigenesis, possessing the possible role of a drive mutation in some types of GBs [98]. The role of repotrectinib (NCT04094610), like the role of larotrectinib (NCT02637687, NCT02576431) is being studied in phase I/II trials at the moment. Entrectinib, an NTRK/ROS1 (c-ros oncogene 1)/ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) pathway inhibitor, was tested, with promising results, in a case of a radiation recurrent GB [99].
3.7. BRAF Inhibitors
V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF) is a serine/threonine kinase protein that signals the Ras-Raf-MEK pathway and is mutated in 1–8% cases of GBs [100]. Dabrafenib alone [101] or combined with trametinib in patients with BRAF V600E-mutant low-grade and high-grade glioma showed beneficial results in a ROAR study [102], while vemurafenib had mixed results that varied according to the histological subtype of the tumor [103]. Clinical trials are running at the moment to test the efficacy of dabrafenib and trametinib co-administration in high-grade brain tumors, including GBs (NCT03593993, NCT03919071), while one study examines the use of binimetinib with encorafenib (NCT03973918).
3.8. Bevacizumab-Modified Docetaxel-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
Docetaxel is a chemotherapeutic agent with significant anti-tumor legacies; however, its clinical usage in GB is limited due to its sparing brain distribution through BBB. Di Filippo et al. (2022) manufactured an agent that could cross BBB and precisely release docetaxel only at GB cells, via docetaxel-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers attached to bevacizumab (BVZ-NLC-DTX). They managed to prove that BVZ-NLC-DTX led to malignant cells’ apoptosis, via targeting specifically VEGF overexpressing cells, and leaving intact the surrounding, healthy brain parenchyma. Its efficacy in vitro and in vivo remains to be reproduced in future clinical trials [104].
3.9. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy retains a critical position in therapeutic novelties of plenty of cancer types. Its clinical usage in GBs is, nonetheless, not thoroughly examined [105].
3.10. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICPIs)
ICPIs on GB, such as Nivolumab (an anti-Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 PD-1 inhibitor/anti-PD 1 inhibitor) with or without Ipilimumab (an anti- cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 inhibitor/an anti-CTLA-4 inhibitor) or TMZ plus radiotherapy, is tested in current clinical trials (NCT02017717, NCT02667587). Uprising ICPIs, like magrolimab, an anti-CD47, and other anti-CD73 monoclonal antibodies, are investigated in phase II (NCT02953509, for hematological malignancies) and phase I clinical trials, respectively (NCT02503774 for a variety of solid tumors).
3.11. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T (CAR-T)
CAR-T cell therapy has been examined in a first-in-human administration study with 10 recurrent GB patients enrolled; nevertheless, heterogeneity and TME’s vital contribution to malignant cell survival are yet to be overcome [106].
3.12. The Role of Sorafenib
Sorafenib is a versatile kinase inhibitor capable of blocking multiple kinases, such as VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3 (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor), c-RAF (proto-oncogene Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma), RET (Rearranged during transfection), wildtype and V599E mutant B-Raf (V-Raf Murine Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog B), fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, p38α, platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ), c-KIT and Flt3, resulting in both tumor cell suppression and inhibition of GB’s neovascularization [107]. Sorafenib’s usage as first-line therapy ended up disappointing [108], like its coordinating administration with erlotinib, an EGFR inhibitor [109].
3.13. IDH Mutations
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations are most common in grade 2 and 3 gliomas but can also be seen in tumors with grade 4 histology; the latter are no longer referred to as IDH-mutated glioblastoma according to the 2021 WHO classification of CNS tumors and are now called “astrocytoma, IDH mutated, WHO grade 4”. Regardless of grade, IDH mutations in glioma are associated with younger age and comparatively favorable prognosis [2], while olutasidenib (FT-2102), an IDH1 inhibitor, was examined in a phase Ib/II clinical trial, giving a 12-month PFS rate of 20.8% in patients with relapsing glioma [110]. Vorasidenib (AG-881) has shown preliminary antitumor activity in patients with recurrent or progressive nonenhancing mIDH lower-grade gliomas (NCT02481154) [111], whereas in patients with mIDH1 advanced glioma, ivosidenib (AG-120) was associated with a favorable safety profile, prolonged disease control, and reduced growth of nonenhancing tumor (NCT02073994). The dual IDH1/IDH2 inhibitor vorasidenib exhibited better brain permeability and target engagement than ivosidenib in a pilot perioperative randomized clinical trial in patients with IDH1-mutant glioma (NCT03343197) [112]. Other agents such as BAY1436032 are also under investigation at the moment (NCT02746081).
3.14. Other Therapies
p53 is a protein produced by a tumor suppressor gene, TP53, while Mdm2 gene overexpression leads to p53 suppression. Nutlin-3 is a molecule that inhibits p53-Mdm2 binding, with interesting results in the preclinical stage [1,113]. Adenoviral-associated gene therapy for p53 has shown improvement in quality of life and optimization of prognosis in patients with recurrent GBs in some clinical trials [1]. Moreover, Heimberger et al. are running a clinical trial, which started back in 2013 and is at phase I at the moment with a STAT3 inhibitor, WP1066, for newly diagnosed or recurrent GB (NCT01904123). An interventional, non-randomized clinical trial (phase Ib/II) with napabucasin (BBI608), a STAT3 inhibitor, is being conducted comparing the use of napabucasin with TMZ versus standard therapy for recurrent or progressed glioma (NCT02315534). Sotelo et al. are investigating the use of chloroquine as adjuvant therapy to GB in an interventional, double-blinded, phase III clinical trial (NCT00224978). Additionally, a phase II trial tested the use of regorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor (VEGFR1-3, KIT, RET, BRAF, and others), resulting in an increase in OS rate in recurrent GBs. Its promising results indicate that its administration should be examined in a phase II clinical trial [114]. Furthermore, gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs) inhibit the Notch pathway and have been tested in clinical trials in concomitant use with TMZ, giving fruitful results [115].
3.15. Neuronavigation-Guided Focused Ultrasound
The BBB, the basal vascular structure of the brain, is composed of endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocytes’ end-feet, restricting more than 95% of drug’s supply to the brain parenchyma. Chen et al. planned a phase I clinical trial, testing the use of neuronavigation-guided focused ultrasound (NaviFUS) to modify the BBB and potentially improve drug delivery in recurrent GBs, with less significant adverse effects. A phase II clinical trial is under construction [116].
3.16. Tumor-Treating Fields/Synergy with Temozolamide
A promising therapy in the field of oncology is tumor-treating field therapy (TTF-T), with increasing usage in a variety of tumor types. TTF-T, via impeding the transition from metaphase to anaphase, has gained popularity among novel therapeutic treatments in variable malignancies, including GBs, demonstrating their effectiveness in preclinical stages [117]. Stupp et al. (2012) carried out a phase III clinical trial comparing TTF-T to standard chemotherapy; this study did not reach its primary end-points, but displayed similar efficacy between TTF-T and chemotherapy, along with more favorable toxicity and quality of life for the TTF group [118]. Five years later, Stupp et al. (2017) managed to demonstrate that patients who received TTF-T combined with TMZ, versus TMZ monotherapy, achieved statistically significant although modest prolongation in progression-free survival and overall survival [119].
3.17. Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy is an emerging therapy for plenty of cancer types, including glioblastomas. It is a light-based therapy which delivers the drug specifically to the tumor site, reducing drug toxicity to normal, healthy surrounding tissues [120]. In the past, phototherapy was mainly linked to the administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA), which leads to the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer cell apoptosis. Nowadays, the use of plenty of molecules along with photodynamic therapy is tested; nanoparticle-linked microRNAs as photosensitizers, near-infrared light delivery, nanoparticle-like photosensitizers, phytocompounds, etc., are the main examples [121]. Clinical trials are running at the present time, including NCT04469699, NCT03897491, and NCT04391062.
- Nanoparticle (NP)-Based Combinational Strategies for Overcoming the BBB
Ongoing research is increasingly directed towards exploring diverse mechanisms to achieve targeted drug delivery into the brain. The use of genetically modified cells or the engineering of living cells with functionalized NP provides exciting avenues for tailored and targeted therapies. Combining nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems with cell-based carriers not only enhances the delivery of therapeutic agents but also presents additional benefits such as immunomodulation, tumor targeting, and the prospect of personalized medicine [122].
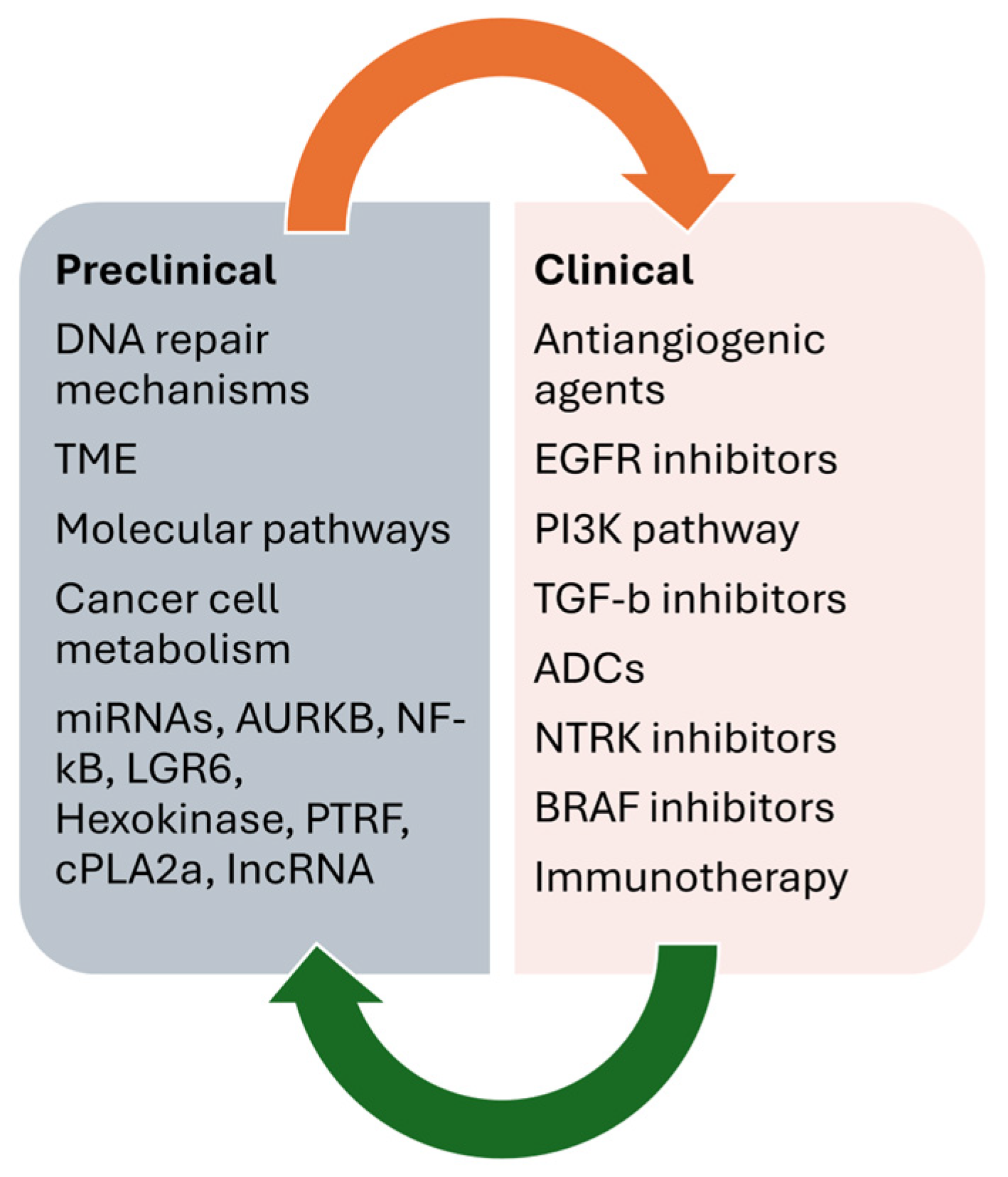
Figure 3 summarizes the main preclinical and clinical data on overcoming resistance to temozolomide in GB.
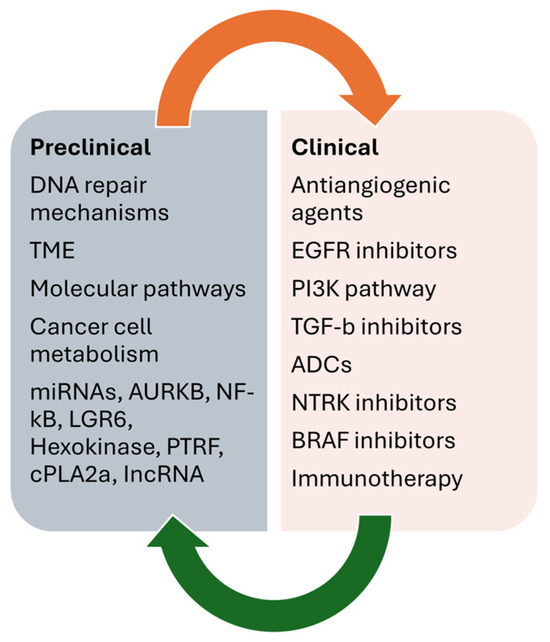
Figure 3.
Main preclinical and clinical data on overcoming resistance to temozolomide in GB.
4. Future Approaches
Currently, preclinical and clinical research investigates potential mechanisms to overcome TMZ resistance in GBs.
Despite multimodal treatment including surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy, GB IDH wild-type has a real-world median overall survival of approximately 12 to 15 months, although recent phase 3 clinical trials have suggested that the median overall survival may be closer to 18 to 20 months in selected populations with good performance status [123]. No uniform standard of care exists for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. Treatment options are tailored to the individual patient. A second resection may be a reasonable option for selected patients [124]. Although bevacizumab remains the only FDA-approved systemic therapy for recurrent glioblastoma, current data show that it does not improve overall survival.
TMZ resistance remains a major limitation in the treatment of GB and contributes to the dismal prognosis. Dissecting the mechanisms of TMZ resistance might impact the subsequent treatment options and guide clinical decisions. In this review, we tried to explore potential strategies to maximize therapeutic potential of novel targets, achieve better patient selection, and identify novel methods of GB management.
Regarding the underlying resistance mechanisms of TMZ, rationales have been proposed to combine TMZ with another reagent to seek for opportunity to enhance the drug efficacy or to develop novel targeted therapies by modulating selective factors related to cancer pathways, energy metabolism, and adaptation in the microenvironment. Though the inhibition may not be straightforward, the rationale suggests a potential framework to benefit cancer treatment.
Among the most promising therapeutic agents discussed, ADCs have shown to be effective and safe therapies transforming treatment paradigms in various solid tumors, including CNS. More sophisticated biomarkers to select patients are needed for these new agents, since their effectiveness is correlated with tumor target expression. Furthermore, emerging data suggest that selection based on payload sensitivity may add additional value above simple target expression. In addition, improving drug access to tumors across the BBB remains an unmet need.
5. Conclusions
Advanced TMZ-resistant GBs remain a challenging research domain for the scientific community, still possessing the role of the most lethal primary brain tumor, with devastating overall survival and prognosis. The mechanisms involved in the development of the TMZ resistance are steadily unraveling; however, more research needs to be performed in order to fully explain this immensely complicated phenomenon. Exploring preclinical and clinical data reveals promising avenues for future therapeutic strategies that not only target restoring sensitivity to temozolomide (TMZ), but also aim to achieve the ultimate primary endpoint: effective treatment of the disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/life14060673/s1. Table S1. Preclinical data/Targeting DNA repair mechanisms. Table S2. Preclinical data/Survival and metastasis regulation proteins (Galectin-1, ID1). Table S3. Preclinical data/TME. Table S4. Preclinical data/Key molecular pathways. Table S5. Preclinical data/Cancer cell metabolism and pH regulation. Table S6. Preclinical data/Molecules contributing to temozolomide resistance. Table S7. Clinical data.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Messaoudi, K.; Clavreul, A.; Lagarce, F. Toward an effective strategy in glioblastoma treatment. Part I: Resistance mechanisms and strategies to overcome resistance of glioblastoma to temozolomide. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbraith, K.; Snuderl, M. Molecular Pathology of Gliomas. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2021, 14, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Cohen, A.L.; Colman, H. Targeted Therapeutics in Patients With High-Grade Gliomas: Past, Present, and Future. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2016, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taal, W.; Bromberg, J.E.; van den Bent, M.J. Chemotherapy in glioma. CNS Oncol. 2015, 4, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015–2019. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24 (Suppl. S5), v1–v95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Miner, A.; Hennis, L.; Mittal, S. Mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma—A comprehensive review. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, F.; Turriziani, M.; Tortorelli, G.; Avvisati, G.; Torino, F.; De Vecchis, L. Triazene compounds: Mechanism of action and related DNA repair systems. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 56, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, J.L.; Seery, T.E.; Bressler, L.R. Temozolomide in malignant gliomas: Current use and future targets. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 64, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karve, A.S.; Desai, J.M.; Gadgil, S.N.; Dave, N.; Wise-Draper, T.M.; Gudelsky, G.A.; Phoenix, T.N.; DasGupta, B.; Yogendran, L.; Sengupta, S.; et al. A Review of Approaches to Potentiate the Activity of Temozolomide against Glioblastoma to Overcome Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.; Basu, M.; Karmakar, S.; Ghosh, M.K. MGMT in TMZ-based glioma therapy: Multifaceted insights and clinical trial perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, K.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, P. Chemoresistance caused by the microenvironment of glioblastoma and the corresponding solutions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Stevens, M.F.; Bradshaw, T.D. Temozolomide: Mechanisms of Action, Repair and Resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaina, B. Temozolomide, Procarbazine and Nitrosoureas in the Therapy of Malignant Gliomas: Update of Mechanisms, Drug Resistance and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parakh, S.; Nicolazzo, J.; Scott, A.M.; Gan, H.K. Antibody Drug Conjugates in Glioblastoma–Is There a Future for Them? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 718590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, J.; Martenhed, G.; Egyházi, S.; Tani, E.; Platz, A. Analysis of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase mRNA in fine needle biopsies from human melanoma metastases by reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster-Garcia, E.; Lorente Estellés, D.; del Mar Álvarez-Torres, M.; Juan-Albarracín, J.; Chelebian, E.; Rovira, A.; Acosta, C.A.; Pineda, J.; Oleaga, L.; Mollá-Olmos, E.; et al. MGMT methylation may benefit overall survival in patients with moderately vascularized glioblastomas. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzoli, G.; Prados, J.; Ortiz, R.; Caba, O.; Cabeza, L.; Berdasco, M.; Gónzalez, B.; Melguizo, C. Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma Cell Lines: Implication of MGMT, MMR, P-Glycoprotein and CD133 Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.; Smith, R.; Cahill, D.P.; Stephens, P.; Stevens, C.; Teague, J.; Greenman, C.; Edkins, S.; Bignell, G.; Davies, H.; et al. A Hypermutation Phenotype and Somatic MSH6 Mutations in Recurrent Human Malignant Gliomas after Alkylator Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3987–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Koczor, C.A.; Saville, K.M.; Hayat, F.; Beiser, A.; McClellan, S.; Migaud, M.E.; Sobol, R.W. Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma via Enhanced NAD+ Bioavailability and Inhibition of Poly-ADP-Ribose Glycohydrolase. Cancers 2022, 14, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.M.; Doukas, A.; Hugo, H.-H.; Hedderich, J.; Hattermann, K.; Maximilian Mehdorn, H.; Held-Feindt, J. Expression of DNA mismatch repair proteins MLH1, MSH2, and MSH6 in recurrent glioblastoma. Neurol. Res. 2015, 37, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, T.J. Coordination of DNA Mismatch Repair and Base Excision Repair Processing of Chemotherapy and Radiation Damage for Targeting Resistant Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.J.; Edelmann, W. Mismatch repair proteins as sensors of alkylation DNA damage. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; Hata, N.; Murata, H.; Hatae, R.; Amano, T.; Nakamizo, A.; Sasaki, T. Complex DNA repair pathways as possible therapeutic targets to overcome temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, L.X.; Sboarina, M.; Cacace, A.; Grasso, D.; Thabault, L.; Hamelin, L.; Vazeille, T.; Dumon, E.; Rossignol, R.; Frédérick, R.; et al. Olaparib Is a Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor That Kills Temozolomide-Resistant Human Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, R.N.; Almeida, K.H.; Fornsaglio, J.L.; Schamus, S.; Sobol, R.W. The Role of Base Excision Repair in the Sensitivity and Resistance to Temozolomide-Mediated Cell Death. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6394–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strik, H.M.; Schmidt, K.; Lingor, P.; Tönges, L.; Kugler, W.; Nitsche, M.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Bähr, M. Galectin-1 expression in human glioma cells: Modulation by ionizing radiation and effects on tumor cell proliferation and migration. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, R.; Wu, M.; Smiljanic, S.; Kaskun, O.; Ghannad-Zadeh, K.; Celebre, A.; Isaev, K.; Morrissy, A.S.; Guan, J.; Tong, J.; et al. ID1 Is Critical for Tumorigenesis and Regulates Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4057–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Kaushik, I.; Srivastava, S.K. Pimozide Suppresses the Growth of Brain Tumors by Targeting STAT3-Mediated Autophagy. Cells 2020, 9, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, L.; Hadamitzky, M.; Dammann, P.; Schedlowski, M.; Sure, U.; Thakur, B.K.; Hetze, S. Glioma: Molecular signature and crossroads with tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2022, 41, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, H.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chuang, J.-Y.; Su, C.-L.; Gean, P.-W. Inhibition of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Suppresses Glioma Stem-Like Cells Likely Through Inducing Autophagic Cell Death. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, N.; Aoki, K.; Hirai, N.; Fujita, S.; Iwama, J.; Hiramoto, Y.; Ishii, M.; Sato, K.; Nakayama, H.; Harashina, J.; et al. Effect of Notch expression in glioma stem cells on therapeutic response to chemo-radiotherapy in recurrent glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2015, 32, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Ping, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Liu, M.; Gong, W.; Chen, C.; Niu, Q.; Guo, D.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) Plays a Key Role in Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation, Neovascularization and Tumor Initiation by Glioma Stem-like Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameratunga, M.; Pavlakis, N.; Wheeler, H.; Grant, R.; Simes, J.; Khasraw, M. Anti-angiogenic therapy for high-grade glioma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 018, CD008218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. Tumor-associated microglia and macrophages in glioblastoma: From basic insights to therapeutic opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 964898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geribaldi-Doldán, N.; Fernández-Ponce, C.; Quiroz, R.N.; Sánchez-Gomar, I.; Escorcia, L.G.; Velásquez, E.P.; Quiroz, E.N. The Role of Microglia in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 603495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.L.; Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic targeting of tumor-associated macrophages and microglia in glioblastoma. Immunotherapy 2014, 6, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virga, J.; Szivos, L.; Hortobágyi, T.; Chalsaraei, M.K.; Zahuczky, G.; Steiner, L.; Tóth, J.; Reményi-Puskár, J.; Bognár, L.; Klekner, A. Extracellular matrix differences in glioblastoma patients with different prognoses. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, H.; Powathil, G.; Kim, H.; Trucu, D.; Lee, W.; Lawler, S.; Chaplain, M. Role of extracellular matrix and microenvironment in regulation of tumor growth and LAR-mediated invasion in glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Chekhonin, V.P. Extracellular vesicles shed by glioma cells: Pathogenic role and clinical value. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 8425–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Sui, R.; Piao, H. Tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles: Potential roles and mechanism in glioma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandhu, M.S.; Behera, P.; Bhaskaran, V.; Longo, S.L.; Barrera-Arenas, L.M.; Sengupta, S.; Rodriguez-Gil, D.J.; Chiocca, E.A.; Viapiano, M.S. Development of a Function-Blocking Antibody Against Fibulin-3 as a Targeted Reagent for Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaeth, N.; Wyss, M.T.; Pahnke, J.; Biollaz, G.; Trachsel, E.; Drandarov, K.; Treyer, V.; Weber, B.; Neri, D.; Buck, A. Radioimmunotherapy targeting the extra domain B of fibronectin in C6 rat gliomas: A preliminary study about the therapeutic efficacy of iodine-131-labeled SIP(L19). Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, S.S.; Silacci, M.; Birchler, M.; Neri, D. Tumor-Targeting Properties of Novel Antibodies Specific to the Large Isoform of Tenascin-C. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3200–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingasamy, P.; Tobi, A.; Haugas, M.; Hunt, H.; Paiste, P.; Asser, T.; Rätsep, T.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Bjerkvig, R.; Teesalu, T. Bi-specific tenascin-C and fibronectin targeted peptide for solid tumor delivery. Biomaterials 2019, 219, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zukiel, R.; Nowak, S.; Wyszko, E.; Rolle, K.; Gawronska, I.; Barciszewska, M.Z.; Barciszewski, J. Suppression of human brain tumor with interference RNA specific for tenascin-C. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sette, P.; Amankulor, N.; Li, A.; Marzulli, M.; Leronni, D.; Zhang, M.; Goins, W.F.; Kaur, B.; Bolyard, C.; Cripe, T.P.; et al. GBM-Targeted oHSV Armed with Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Enhances Anti-tumor Activity and Animal Survival. Mol. Ther. Oncolyt. 2019, 15, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Z.; Qi, B.; Xia, H. HSP47 Promotes Glioblastoma Stemlike Cell Survival by Modulating Tumor Microenvironment Extracellular Matrix through TGF-β Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Ramirez, A.C.; Dmitrieva, N.; Yoo, J.Y.; Banasavadi-Siddegowda, Y.; Zhang, J.; Relation, T.; Bolyard, C.; Wojton, J.; Kaur, B. Humanized chondroitinase ABC sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, e2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, Y.; Biswas, A.; Kumar, U.; Banerjee, I.; Das, S.; Maji, S.; Das, S.K.; Emdad, L.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mandal, M.; et al. Lumefantrine, an antimalarial drug, reverses radiation and temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12324–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, H.-S.; Park, M.-J.; Park, I.-C.; Woo, S.H.; Jin, H.-O.; Rhee, C.H.; Jung, H.-W. Tetraarsenic oxide–induced inhibition of malignant glioma cell invasion in vitro via a decrease in matrix metalloproteinase secretion and protein kinase B phosphorylation: Laboratory investigation. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2014, 121, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafate, W.; Wang, M.; Zuo, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Xie, W.; Wang, J. Targeting Aurora kinase B attenuates chemoresistance in glioblastoma via a synergistic manner with temozolomide. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.-J.; Kim, S.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Baek, S.T. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway induces autophagy-mediated temozolomide-resistance in human glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, A.; Ott, M.; Fang, D.; Heimberger, A.B. The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of JAK/STAT Signaling in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.R.; Hill, R.; Pilkington, G.J.; Madureira, P.A. The Role of Hypoxia in Glioblastoma Invasion. Cells 2017, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Current Understanding of Hypoxia in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Its Response to Immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.U.; Coman, D.; Walsh, J.J.; Ali, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Hyder, F. Temozolomide arrests glioma growth and normalizes intratumoral extracellular pH. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, M.; Hirano, M.; Aoki, K.; Okuno, Y.; Ohka, F.; Yamamichi, A.; Kato, A.; Maeda, S.; Motomura, K.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Aberrant Active cis-Regulatory Elements Associated with Downregulation of RET Finger Protein Overcome Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2274–2281.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Ranjit, M.; Yamamichi, A.; Aoki, K.; Ohka, F.; Kato, T.; Enomoto, A.; Takahashi, M.; Wakabayashi, T.; Natsume, A. GENE-49. Aberrant super-enhancers associated with downregulation of ret finger protein overcomes chemoresistance in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19 (Suppl. S6), vi103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, A.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Gao, L.; Qi, S.; Lu, Y. miR-519a enhances chemosensitivity and promotes autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting STAT3/Bcl2 signaling pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Morais, C.M.; Sousa, M.; Rebelo, O.; Tão, H.; Barbosa, M.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C.; Jurado, A.S. MiR-200c-based metabolic modulation in glioblastoma cells as a strategy to overcome tumor chemoresistance. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 2315–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Maly, D.J.; Chanthery, Y.H.; Sirkis, D.W.; Nakamura, J.L.; Berger, M.S.; James, C.D.; Shokat, K.M.; Weiss, W.A.; Persson, A.I. Radiotherapy Followed by Aurora Kinase Inhibition Targets Tumor-Propagating Cells in Human Glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Qiu, R.; He, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhi, F.; Long, W. The Aurora Kinase Inhibitor TAK901 Inhibits Glioblastoma Growth by Blocking SREBP1-Mediated Lipid Metabolism. Cancers 2022, 14, 5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shireman, J.M.; Atashi, F.; Lee, G.; Ali, E.S.; Saathoff, M.R.; Park, C.H.; Savchuk, S.; Baisiwala, S.; Miska, J.; Lesniak, M.S.; et al. De novo purine biosynthesis is a major driver of chemoresistance in glioblastoma. Brain 2021, 144, 1230–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Scott, A.J.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Dresser, J.J.; Werner, C.K.; Sun, H.; Pratt, D.; Sajjakulnukit, P.; Zhao, S.G.; et al. Purine metabolism regulates DNA repair and therapy resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Narasimamurthy, R.; Xia, Y.; Myskiw, C.; Soda, Y.; Verma, I.M. Targeting NF-κB in glioblastoma: A therapeutic approach. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, Y. Inhibition of NF-κB results in anti-glioma activity and reduces temozolomide-induced chemoresistance by down-regulating MGMT gene expression. Cancer Lett. 2018, 428, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, N.G.; Ebrahimzadeh-Pustchi, S.; Akay, Y.M.; Esquenazi, Y.; Tandon, N.; Zhu, J.-J.; Akay, M. NF-κB inhibitor with Temozolomide results in significant apoptosis in glioblastoma via the NF-κB(p65) and actin cytoskeleton regulatory pathways. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Song, S.X.; Yang, M.F.; Xie, F.M. LGR6 promotes glioblastoma malignancy and chemoresistance by activating the Akt signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Gao, Y.; Liang, H. HOTAIR/miR-125 axis-mediated Hexokinase 2 expression promotes chemoresistance in human glioblastoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5707–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, L.; Lyu, X.; Yin, J.; Shi, Z.; You, Y. EIF4A3-induced circular RNA ASAP1 promotes tumorigenesis and temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma via NRAS/MEK1/ERK1–2 signaling. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Bai, Y.; Liao, H.; Qiu, S.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X.; Guo, H. Polymerase I and Transcript Release Factor Acts As an Essential Modulator of Glioblastoma Chemoresistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. PTRF/Cavin-1 enhances chemo-resistance and promotes temozolomide efflux through extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4330–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H. Expression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Alpha in Glioblastoma Is Associated With Resistance to Chemotherapy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahinfar, P.; Baradaran, B.; Davoudian, S.; Vahidian, F.; Cho, W.C.; Mansoori, B. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Multidrug Resistance of Glioblastoma. Genes 2021, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Meng, X.; Wu, P.; Zha, C.; Han, B.; Li, L.; Sun, N.; Qi, T.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Glioblastoma Cell–Derived lncRNA-Containing Exosomes Induce Microglia to Produce Complement C5, Promoting Chemotherapy Resistance. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuaje, F.; Tiemann, K.; Niclou, S.P. Therapeutic control and resistance of the EGFR-driven signaling network in glioblastoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Maire, C.L.; Lamszus, K. EGFR as a Target for Glioblastoma Treatment: An Unfulfilled Promise. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.E.; Furnari, F.B.; Cavenee, W.K. Targeting EGFR for Treatment of Glioblastoma: Molecular Basis to Overcome Resistance. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2012, 12, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.Y.; Lee, E.Q.; Reardon, D.A.; Ligon, K.L.; Alfred Yung, W.K. Current clinical development of PI3K pathway inhibitors in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainsworth, J.D.; Becker, K.P.; Mekhail, T.; Chowdhary, S.A.; Eakle, J.F.; Wright, D.; Langdon, R.M.; Yost, K.J.; Padula, G.D.A.; West-Osterfield, K.; et al. Phase I/II study of bevacizumab with BKM120, an oral PI3K inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid tumors (phase I) and relapsed/refractory glioblastoma (phase II). J. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 144, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, B.; Cyranowski, S. Recent Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of TGF Beta Signaling and Its Role in Glioma Pathogenesis. In Glioma Signaling; Barańska, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 179–201. ISBN 978-3-030-30651-9. [Google Scholar]
- Towner, R.A.; Smith, N.; Saunders, D.; Brown, C.A.; Cai, X.; Ziegler, J.; Mallory, S.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Coutinho De Souza, P.; Wiley, G.; et al. OKN-007 Increases temozolomide (TMZ) Sensitivity and Suppresses TMZ-Resistant Glioblastoma (GBM) Tumor Growth. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdahn, U.; Hau, P.; Stockhammer, G.; Venkataramana, N.K.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Suri, A.; Balasubramaniam, A.; Nair, S.; Oliushine, V.; Parfenov, V.; et al. Targeted therapy for high-grade glioma with the TGF-β2 inhibitor trabedersen: Results of a randomized and controlled phase IIb study. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashima, T. Brain Cancer Chemotherapy through a Delivery System across the Blood-Brain Barrier into the Brain Based on Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis Using Monoclonal Antibody Conjugates. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, P.; Franceschi, G.; Frattarelli, M.; Riva, N.; Guiducci, G.; Cremonini, A.M.; Giuliani, G.; Casi, M.; Gentile, R.; Jekunen, A.A.; et al. 131I Radioconjugated Antibodies for the Locoregional Radioimmunotherapy of High-grade Malignant Glioma: Phase I and II Study. Acta Oncol. 1999, 38, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Zalutsky, M.R.; Akabani, G.; Coleman, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Herndon, J.E., II; McLendon, R.E.; Pegram, C.N.; Quinn, J.A.; Rich, J.N.; et al. A pilot study: 131I-Antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81c6 to deliver a 44-Gy resection cavity boost. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Quang, T.S.; Gracely, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Emrich, J.G.; Yaeger, T.E.; Jenrette, J.M.; Cohen, S.C.; Black, P.; Brady, L.W. A Phase II study of anti–epidermal growth factor receptor radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2010, 113, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.; Laske, D.W. Transferrin Receptor Ligand-Targeted Toxin Conjugate (Tf-CRM107) for Therapy of Malignant Gliomas. J. Neuro Oncol. 2003, 65, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Akabani, G.; Archer, G.E.; Berger, M.S.; Coleman, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Greer, K.; Herndon, J.E., II; Kunwar, S.; et al. Intracerebral infusion of an EGFR-targeted toxin in recurrent malignant brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, S.; Chang, S.; Westphal, M.; Vogelbaum, M.; Sampson, J.; Barnett, G.; Shaffrey, M.; Ram, Z.; Piepmeier, J.; Prados, M.; et al. Phase III randomized trial of CED of IL13-PE38QQR vs Gliadel wafers for recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, F.; Asher, A.; Bucholz, R.; Berger, M.; Prados, M.; Chang, S.; Bruce, J.; Hall, W.; Rainov, N.G.; Westphal, M.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and tumor response of IL4-Pseudomonas exotoxin (NBI-3001) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2003, 64, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Lassman, A.B.; van den Bent, M.; Kumthekar, P.; Merrell, R.; Scott, A.M.; Fichtel, L.; Sulman, E.P.; Gomez, E.; Fischer, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety results of ABT-414 in combination with radiation and temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Fichtel, L.; Lassman, A.B.; Merrell, R.; van den Bent, M.; Kumthekar, P.; Scott, A.M.; Pedersen, M.; Gomez, E.; Fischer, J.; et al. ET-19A phase 1 study evaluating ABT-414 with temozolomide (TMZ) or concurrent radiotherapy (RT) and TMZ in glioblastoma (GBM). Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16 (Suppl. S5), v83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, M.; Curry, R.; Reardon, D.A.; Rasmussen, E.; Upreti, V.V.; Damore, M.A.; Henary, H.A.; Hill, J.S.; Cloughesy, T. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of anti-EGFRvIII antibody–drug conjugate AMG 595 in patients with recurrent malignant glioma expressing EGFRvIII. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Long, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. NTRK Fusions and TRK Inhibitors: Potential Targeted Therapies for Adult Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 593578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, P.T.; Deming, D.A.; Helgager, J.; Ruszkiewicz, T.; Baskaya, M.K.; Howard, S.P.; Robins, H.I. Entrectinib demonstrates prolonged efficacy in an adult case of radiation-refractory NTRK fusion glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayi, A.; Alnahhas, I.; Ong, S.; Giglio, P.; Puduvalli, V.K. Targeted Therapy for BRAF Mutant Brain Tumors. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.C.; Ronellenfitsch, M.W.; Lorenz, N.I.; Wagner, M.; Voss, M.; Capper, D.; Tzaridis, T.; Herrlinger, U.; Steinbach, J.P.; Stoffels, G.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with recurrent, BRAF V600E mutated malignant glioma and leptomeningeal disease. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3291–3296. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.Y.; Stein, A.; van den Bent, M.; De Greve, J.; Wick, A.; de Vos, F.Y.F.L.; von Bubnoff, N.; van Linde, M.E.; Lai, A.; Prager, G.W.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAFV600E-mutant low-grade and high-grade glioma (ROAR): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2, basket trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaley, T.; Touat, M.; Subbiah, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Rodon, J.; Lockhart, A.C.; Keedy, V.; Bielle, F.; Hofheinz, R.-D.; Joly, F.; et al. BRAF Inhibition in BRAFV600-Mutant Gliomas: Results From the VE-BASKET Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Filippo, L.D.; Lobato Duarte, J.; Hofstätter Azambuja, J.; Isler Mancuso, R.; Tavares Luiz, M.; Hugo Sousa Araújo, V.; Delbone Figueiredo, I.; Barretto-de-Souza, L.; Miguel Sábio, R.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; et al. Glioblastoma multiforme targeted delivery of docetaxel using bevacizumab-modified nanostructured lipid carriers impair in vitro cell growth and in vivo tumor progression. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma: Current state and future directions. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Wan, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, X. Oxidative Stress Activated by Sorafenib Alters the Temozolomide Sensitivity of Human Glioma Cells Through Autophagy and JAK2/STAT3-AIF Axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 660005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottinger, A.F.; Aissa, A.B.; Espeli, V.; Squiban, D.; Dunkel, N.; Vargas, M.I.; Hundsberger, T.; Mach, N.; Schaller, K.; Weber, D.C.; et al. Phase I study of sorafenib combined with radiation therapy and temozolomide as first-line treatment of high-grade glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Kuhn, J.; Lamborn, K.R.; Abrey, L.E.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Lieberman, F.; Robins, H.I.; Chang, S.M.; Yung, W.K.A.; Drappatz, J.; et al. Phase I/II study of sorafenib in combination with erlotinib for recurrent glioblastoma as part of a 3-arm sequential accrual clinical trial: NABTC 05-02. Neuro Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, M.I.; Colman, H.; Rosenthal, M.; Van Tine, B.A.; Levacic, D.; Walbert, T.; Gan, H.K.; Vieito, M.; Milhem, M.M.; Lipford, K.; et al. Olutasidenib (FT-2102) in patients with relapsed or refractory IDH1-mutant glioma: A multicenter, open-label, phase Ib/II trial. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Penas-Prado, M.; Peters, K.B.; Burris, H.A., III; Maher, E.A.; Janku, F.; Cote, G.M.; de la Fuente, M.I.; Clarke, J.L.; Ellingson, B.M.; et al. Vorasidenib, a Dual Inhibitor of Mutant IDH1/2, in Recurrent or Progressive Glioma; Results of a First-in-Human Phase I Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Lu, M.; Wen, P.Y.; Taylor, J.W.; Maher, E.A.; Arrillaga-Romany, I.; Peters, K.B.; Ellingson, B.M.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Chun, S.; et al. Vorasidenib and ivosidenib in IDH1-mutant low-grade glioma: A randomized, perioperative phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punganuru, S.R.; Arutla, V.; Zhao, W.; Rajaei, M.; Deokar, H.; Zhang, R.; Buolamwini, J.K.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wang, W. Targeted Brain Tumor Therapy by Inhibiting the MDM2 Oncogene: In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of Action. Cells 2020, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; De Salvo, G.L.; Brandes, A.A.; Eoli, M.; Rudà, R.; Faedi, M.; Lolli, I.; Pace, A.; Daniele, B.; Pasqualetti, F.; et al. Regorafenib compared with lomustine in patients with relapsed glioblastoma (REGOMA): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, C.A.; Daou, M.-C.; Moser, R.P.; Ross, A.H. γ-Secretase Inhibitors Enhance Temozolomide Treatment of Human Gliomas by Inhibiting Neurosphere Repopulation and Xenograft Recurrence. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6870–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chai, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, P.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, J.S.; Liu, H.-L.; Wei, K.-C. Neuronavigation-guided focused ultrasound (NaviFUS) for transcranial blood-brain barrier opening in recurrent glioblastoma patients: Clinical trial protocol. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 673. Available online: https://atm.amegroups.org/article/view/44421 (accessed on 1 January 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirson, E.D.; Dbalý, V.; Tovaryš, F.; Vymazal, J.; Soustiel, J.F.; Itzhaki, A.; Mordechovich, D.; Steinberg-Shapira, S.; Gurvich, Z.; Schneiderman, R.; et al. Alternating electric fields arrest cell proliferation in animal tumor models and human brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10152–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Wong, E.T.; Kanner, A.A.; Steinberg, D.; Engelhard, H.; Heidecke, V.; Kirson, E.D.; Taillibert, S.; Liebermann, F.; Dbalý, V.; et al. NovoTTF-100A versus physician’s choice chemotherapy in recurrent glioblastoma: A randomised phase III trial of a novel treatment modality. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretti, M.; González Graglia, M.A.; Suárez, A.I.; Prucca, C.G. Photodynamic therapy for glioblastoma: A light at the end of the tunnel. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2023, 13, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, D.; Wilding, H.; Baroz, A.; Trifoi, M.; Shenoy, G.; Slagle-Webb, B.; Hayes, D.; Soudagar, Y.; Connor, J.; Mansouri, A. Photodynamic Therapy for Glioblastoma: Illuminating the Path toward Clinical Applicability. Cancers 2023, 15, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Tonn, J.C.; Stupp, R.; Preusser, M.; Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal, E.; Henriksson, R.; Rhun, E.L.; Balana, C.; Chinot, O.; et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e315–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, O.; Han, S.J.; Cha, S.; Sun, M.Z.; Aghi, M.K.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; Parsa, A.T. Impact of extent of resection for recurrent glioblastoma on overall survival: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2012, 117, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).