Morphological Evolution of an Intertidal Mudflat in Relation to Mangrove Growth: Implications for Future Erosion Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
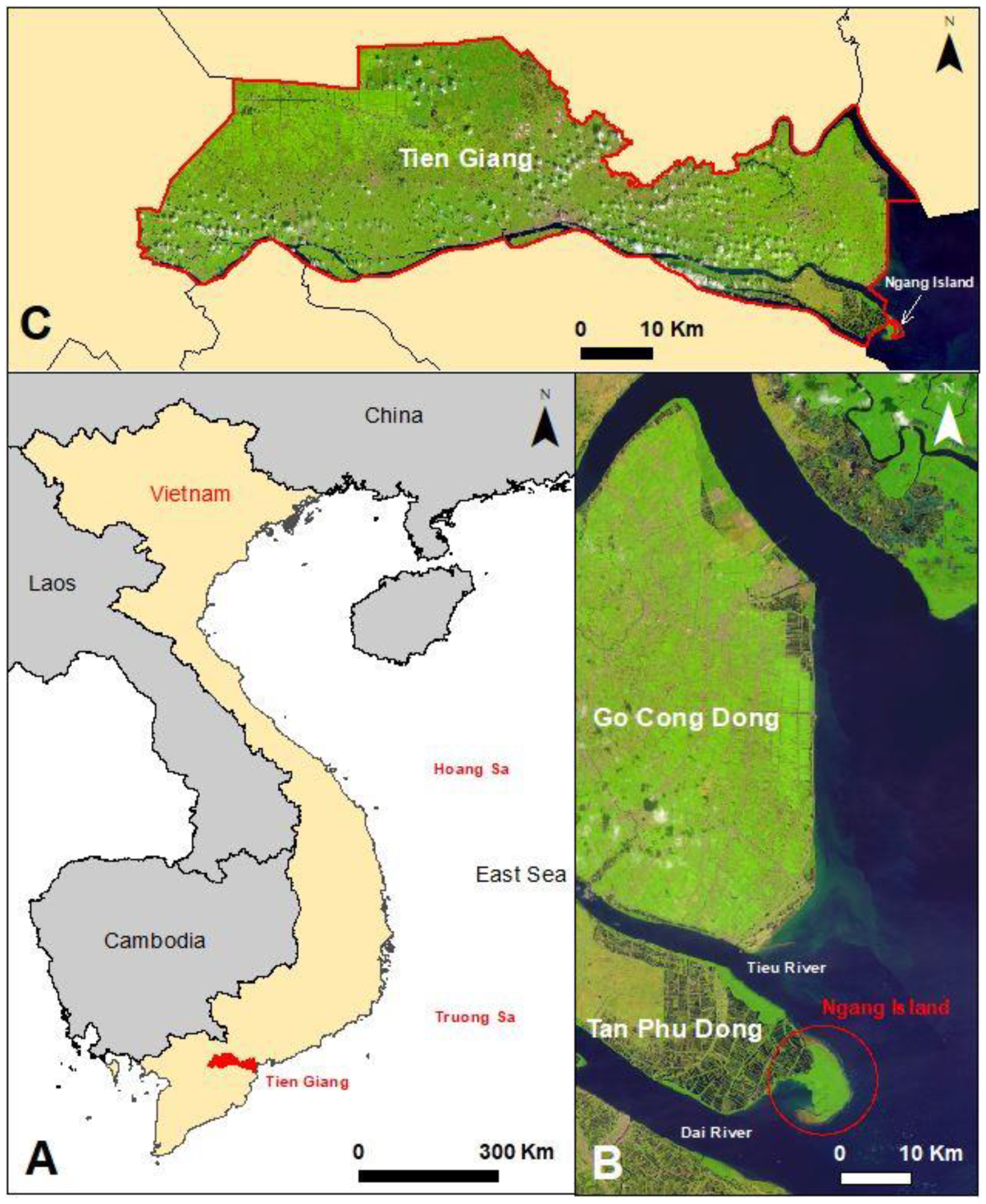
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Methods
- (1)
- The mNDWI formula is as follows:
- (2)
- The WFI formula is as follows:
- (3)
- Because the island is ecologically and hydrologically linked to the Tan Phu Dong coast of Tien Giang Province, the authors decided to extract satellite images from multiple dates (1995, 1997, 2000, 2004, 2005, 2008, 2010, 2013, 2015, 2018, 2020, and 2022) as vector ‘shapefiles’ for both the Tan Phu Dong coast and the island.
3. Results
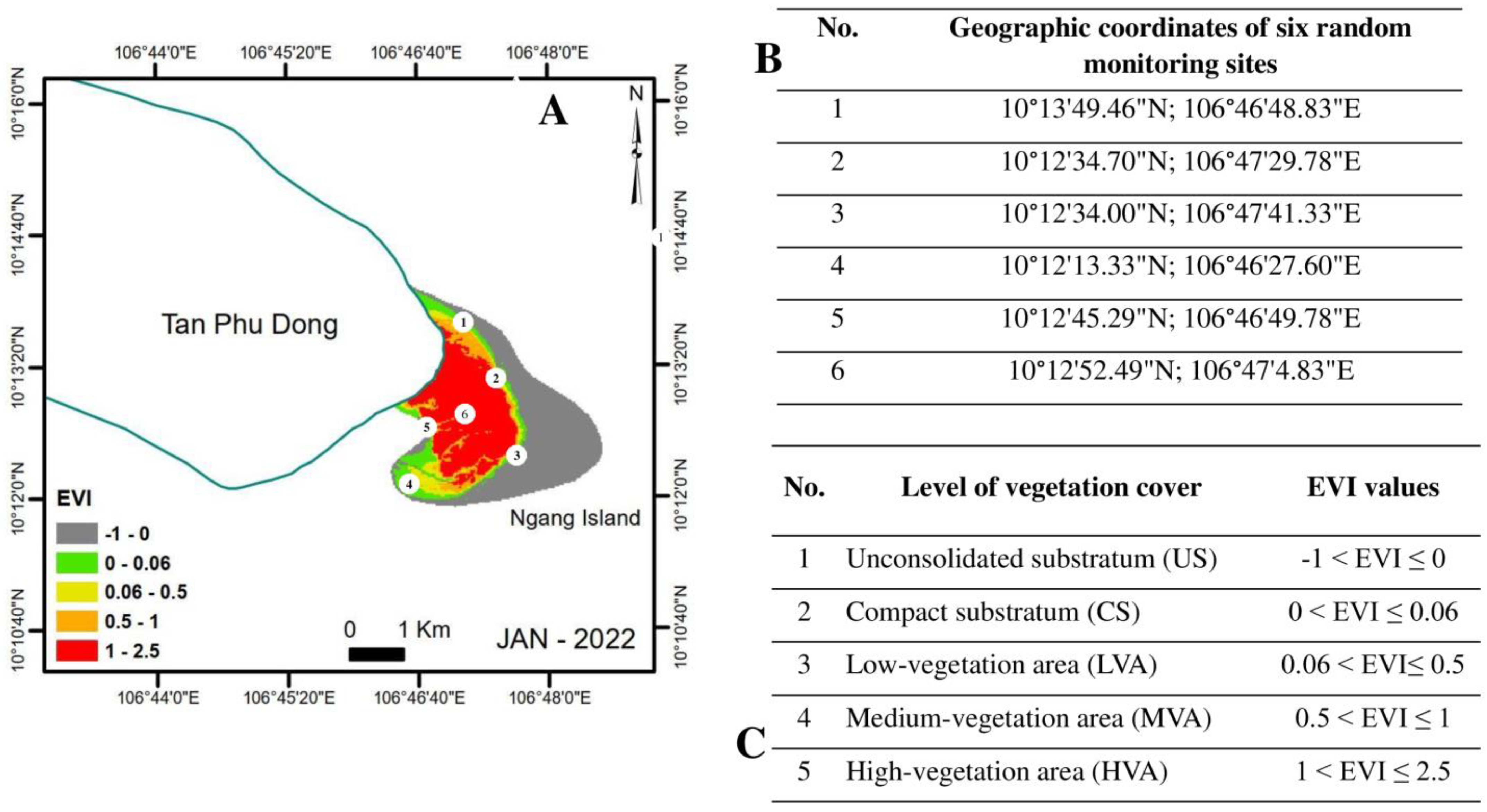
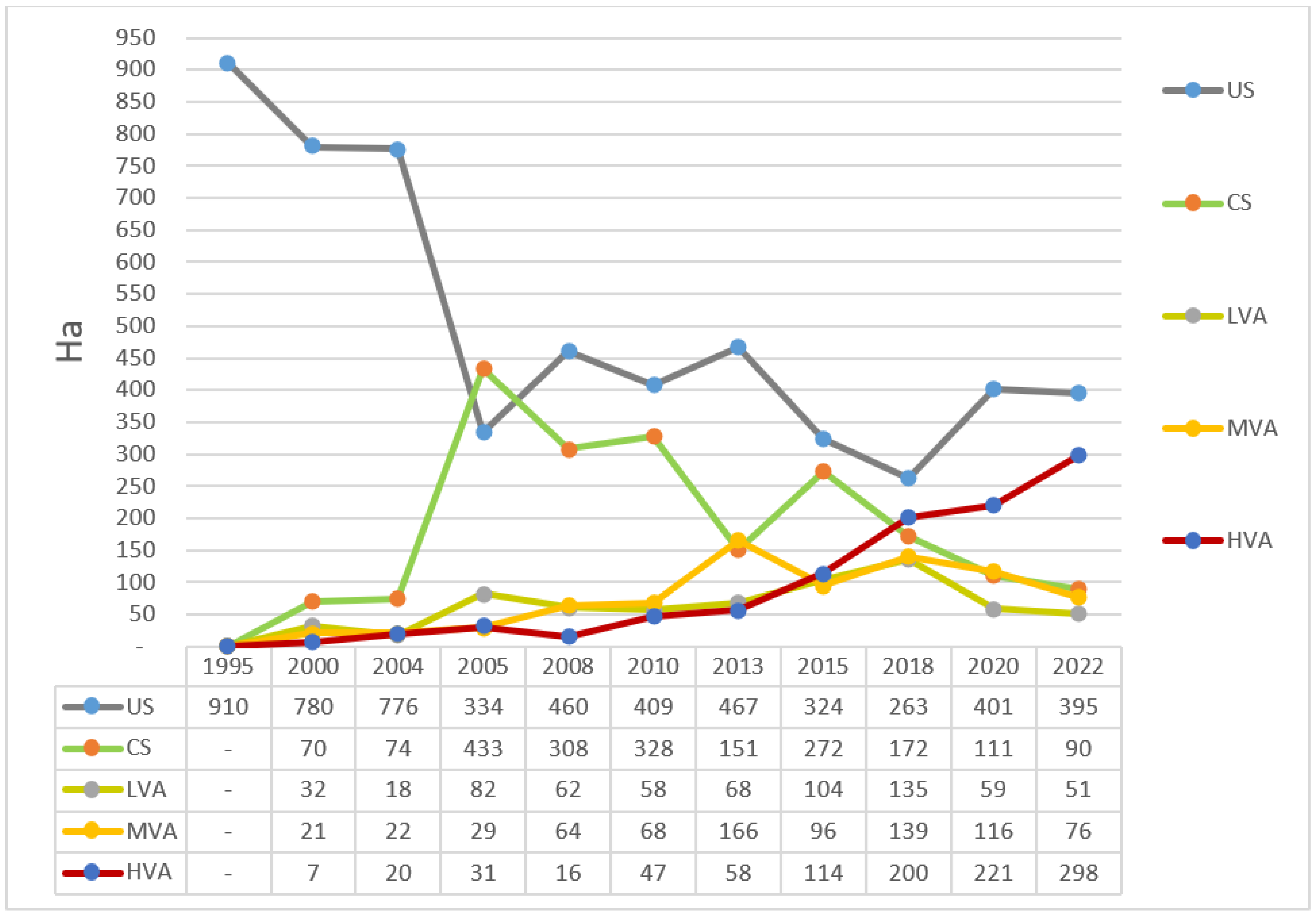
3.1. Morphological Evolution of Ngang Island between 1995 and 2022
3.2. Mangrove Growth between 1995 and 2022
4. Discussion
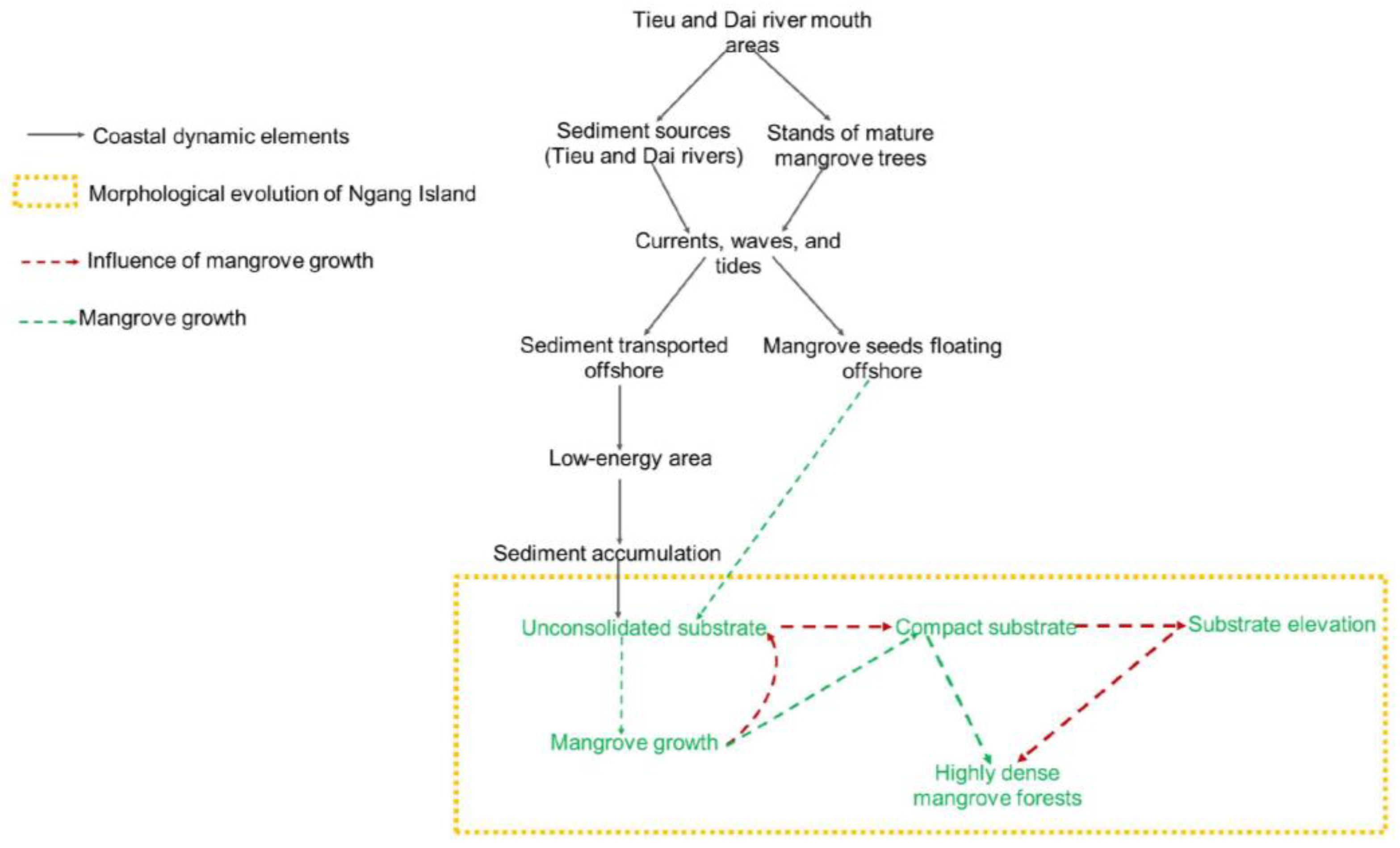
4.1. Morphological Evolution of Ngang Island and Mangrove Growth
4.2. Sand Accumulation and Mangrove Death
4.3. Implications of the Findings across a Wider Region
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodroffe, C.D. Coasts: Form, Process, Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, N.M.; Huson, M.D.; Bray, S.; Nicholls, R.J. Intertidal mudflats and saltmarsh conservation and sustainable use in the UK: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 126, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, K.R.; Christie, M.C.; Wright, E.W. Classification of intertidal mudflats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1039–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, C.; Hill, P. Wave Attenuation across an Intertidal Sand Flat: Implications for Mudflat Development. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 403–411. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40605468 (accessed on 25 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Möller, I.; Spencer, T. Wave dissipation over macro-tidal saltmarshes: Effects of marsh edge typology and vegetation change. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 36, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ysebaert, T.; Yang, S.L.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Bouma, T.J.; Herman, P.M.J. Wave Attenuation by Two Contrasting Ecosystem Engineering Salt Marsh Macrophytes in the Intertidal Pioneer Zone. Wetlands 2011, 31, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Shi, B.W.; Bouma, T.J.; Ysebaert, T.; Luo, X.X. Wave Attenuation at a Salt Marsh Margin: A Case Study of an Exposed Coast on the Yangtze Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, I.; Kudella, M.; Rupprecht, F.; Spencer, T.; Paul, M.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Wolters, G.; Jensen, K.; Bouma, T.J.; Miranda-Lange, M.; et al. Wave attenuation over coastal salt marshes under storm surge conditions. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster-Martinez, M.R.; Lacy, J.R.; Ferner, M.C.; Variano, E.A. Wave Attenuation Across a Tidal Marsh in San Francisco Bay. Coast. Eng. 2018, 136, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.J. Wave Dissipation Across Intertidal Surfaces in the Wash Tidal Inlet, Eastern England. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 21, 28–40. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4299388 (accessed on 27 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- De Vriend, H.J.; Wang, Z.B.; Ysebaert, T.; Herman, P.M.J.; Ding, P. Eco-morphological problems in the Yangtze estuary and the western Scheldt. Wetlands 2011, 31, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsje, B.W.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Dekker, F.; Paalvast, P.; Bouma, T.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; de Vries, M.B. How ecological engineering can serve in coastal protection. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vet, P.L.M.; van Prooijen, B.C.; Wang, Z.B. The differences in morphological development between the intertidal flats of the Eastern and Western Scheldt. Geomorphology 2017, 281, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Valuing ecosystem services for coastal wetland protection and restoration: Progress and challenges. Resources 2013, 2, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; van Belzen, J.; Balke, T.; van Dalen, J.; Klaassen, P.; Hartog, A.M.; Herman, P.M.J. Short-term mudflat dynamics drive long-term cyclic salt marsh dynamics. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziane, T.; Tsuchiya, M. Fatty acids as tracers of organic matter in the sediment and food web of a mangrove/intertidal flat ecosystem, Okinawa, Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.H.; Qin, W.H.; Wu, C.S. Spatial, temporal, and human-induced variations in suspended sediment concentration in the surface waters of the Yangtze Estuary and adjacent coastal areas. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deloffre, J.; Verney, R.; Lafite, R.; Lesueur, P.; Lesourd, S.; Cundy, A.B. Sedimentation on intertidal mudflats in the lower part of macrotidal estuaries: Sedimentation rhythms and their preservation. Mar. Geol. 2010, 241, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, V.; Bastos, A.C.; Amos, C.L. Sedimentary processes over an intertidal mudflat: A field investigation at Hythe flats, Southampton water (UK). Mar. Geol. 2007, 241, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuerch, M.; Spencer, T.; Evans, B. Coupling between tidal mudflats and salt marshes affects marsh morphology. Mar. Geol. 2019, 412, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Coco, G.; van der Wegen, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Townsend, I. Modelling sorting dynamics of cohesive and non-cohesive sediment on intertidal flats under the effect of tides and wind waves. Cont. Shelf Sci. 2015, 105, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marren, D.S.; Winterwerp, J.C. The role of flow asymmetry and mud properties on tidal flat sedimentation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 60, S71–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draut, A.E.; Kineke, G.C.; Huh, O.K.; Grymes, J.M., III; Westphal, K.A.; Moeller, C.C. Coastal mudflat accretion under energic conditions, Louisiana chenier-plain coast, USA. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.; Hogg, A.J.; Roberts, W. Morphological modelling of intertidal mudflats: The role of cross-shore tidal currents. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.S.; Kobayashi, N. Numerical modeling of intertidal mudflat profile evolution under waves and currents. Coast. Eng. J. 2022, 64, 406–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmilady, H.; van der Wegen, M.; Roelvink, D.; van der Spek, A. Modeling the Morphodynamic Response of Estuarine Intertidal Shoals to Sea-Level Rise. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2021JF006152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Cooper, J.R.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.L.; Luo, F.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.B. Hydrodynamics, erosion and accretion of intertidal mudflats in extremely shallow waters. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Townend, I.; Jin, C.; Li, H. Velocity and sediment surge: What do we see at times of very shallow water on intertidal mudflats? Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 113, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.P. Modeling shape evolution of accreting tidal flats composed of mud and sand: A case study of the central Jiangsu coast, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensac, E.; Gardel, A.; Lesourd, S.; Brutier, L. Morphodynamic evolution of an intertidal mudflat under the influence of Amazon sediment supply e Kourou mud bank, French Guiana, South America. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 158, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Thomaskutty, A.V.; Agraval, R.; Rajawat, A.S.; Solankim, H. Topography and morphodynamic study of intertidal mudflats along the eastern coast of the Gulf of Khambhat, India using remote sensing techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 27, 100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vet, P.L.M.; van Prooijen, B.C.; Colosino, I.; Steiner, N.; Ysebaert, T.; Herman, P.M.J.; Wang, Z.B. Variations in storm-induced bed level dynamics across intertidal flats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, G.; Fagherazzi, S. Wind waves on a mudflat: The influence of fetch and depth on bed shear stresses. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 60, S99–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, J.A.; Friedrichs, C.T.; Jaffe, B.E.; Foxgrover, A.C. Spatial trends in tidal flat shape and associated environmental parameters in South San Francisco Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 262, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wegen, M.; Roelvink, J.A.; Jaffe, B.E. Morphodynamic resilience of intertidal mudflats on a seasonal time scale. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 8290–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappucci, S.; Amos, C.L.; Hosoe, T.; Umgiesser, G. SLIM: A numerical model to evaluate factors controlling evolution of intertidal mudflats in Venice Lagoon, Italy. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chi, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Ly, K.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z. Spatial-temporal evolution of the eastern Nanhui mudflat in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary under intensified human activities. Geomorphology 2018, 309, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerman, E.J.; van de Koppel, J.; Eppinga, M.B.; Montserrat, F.; Liu, Q.X.; Herman, M.J. Spatial Self-Organization on Intertidal Mudflats through Biophysical Stress Divergence. Am. Nat. 2010, 176, E15–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galois, R.; Blanchard, G.; Seguignes, M.; Huet, V.; Joassard, L. Spatial distribution of sediment particulate organic matter on two estuarine intertidal mudflats: A comparison between Marennes-OleH ron Bay (France) and the Humber Estuary (UK). Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, N.C.; Meynecke, J.-O.; Dittmann, S.; Ellison, A.M.; Anger, K.; Berger, U.; Cannicci, S.; Diele, K.; Ewel, K.C.; Field, C.D.; et al. A world without mangrove? Science 2007, 317, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, J.P.; Dolique, F.; Gratiot, N. Geomorphic evolution of a coastal mudflat under oceanic influences: An example from the dynamic shoreline of French Guiana. Mar. Geol. 2004, 208, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, G.N. Processes and factors regulating the growth of an intertidal mudflat within a middle estuarine region of Zuari tropical estuary, west coast of India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis III, R.R. Ecological engineering for successful management and restoration of mangrove forests. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; Borst, W.G.; de Vries, M.B. Pilot study on the erosion and rehabilitation of a mangrove mud coast. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 21, 223–230. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4299409 (accessed on 14 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Suryadiputra, N.; Van Eijk, P.; Zhang, L. Defining Eco-Morphodynamic Requirements for Rehabilitating Eroding Mangrove-Mud Coasts. Wetlands 2013, 33, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, B.; Hashim, R. Mangrove restoration without planting. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Parnell, K.E. Gradual expansion of mangrove areas as an ecological solution for stabilizing a severely eroded mangrove dominated muddy coast. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 107, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luom, T.T.; Nguyen, T.P.; Anh, N.T.; Tung, N.T.; Tu, L.X.; Duong, T.A. Using Fine-Grained Sediment and Wave Attenuation as a New Measure for Evaluating the Efficacy of Offshore Breakwaters in Stabilizing an Eroded Muddy Coast: Insights from Ca Mau, the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swales, A.; Bentley, S.J.; Lovelock, C.E. Mangrove-forest evolution in a sediment-rich estuarine system: Opportunists or agents of geomorphic change? Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1672–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.F.A.; Gunasiri, C.W.D. Impact of Coastal Land Use Change on Shoreline Dynamics in Yunlin County, Taiwan. Environments 2014, 1, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichsen, D. The Atlas of Coasts and Oceans: Mapping Ecosystems, Threatened Resources and Marine Conservation; Earthscan: Brighton, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Balke, T.; Eijk, P.; Tonneijck, F.; Siry, H.Y.; Rudianto, M.E.; Winterwerp, J.C. Aquaculture induced erosion of tropical coastlines throws coastal communities back into poverty. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 116, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Duan, X.; Gao, F.; Li, M.; Lü, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, L. Coastal erosion in Shandong of China: Status and protection challenges. China Geol. 2018, 1, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, K.; DhivyaSri, M.; Bhaskar, A.S.; Jayappa, K.S. Long-term coastal erosion assessment along the coast of Karnataka, west coast of India. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, K.; Albers, T. Area coastal protection and the use of bamboo breakwaters in the Mekong Delta. In Coastal Disasters and Climate Change in Vietnam: Engineering and Planning Perspectives; Danh Thao, N., Takagi, H., Esteban, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 107–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hjalager, A.M. Land-use conflicts in coastal tourism and the quest for governance innovations. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.X.; Ba, H.T.; Le Manh, H.; Van, D.D.; Nguyen, N.M.; Wright, D.P.; Bui, V.H.; Mai, S.T.; Anh, D.T. Hydraulic performance and wave transmission through pile-rock breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2020, 218, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P. Offshore structures, sea mud accumulation and mangrove regeneration: Insights from the Vietnamese Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 225, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.; Anfuso, G. Hard protection structures as a principal coastal erosion management strategy along the Caribbean coast of Colombia. A chronicle of pitfalls. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, H.V.; Anh, N.T.; Nguyen, T.P.; Nhut, M.L.M. Ecological Engineering and Restoration of Eroded Muddy Coasts in South East Asia: Knowledge Gaps and Recommendations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, M.P.; Jayatissa, L.P.; Krauss, K.W.; Phillips, D.H.; Huxham, M. High mangrove density enhances surface accretion, surface elevation change, and tree survival in coastal areas susceptible to sea-level rise. Oecologia 2010, 164, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullarney, J.C.; Henderson, S.M.; Norris, B.K.; Bryan, K.R.; Fricke, A.T.; Sandwell, D.R.; Culling, D.P. A question of scale: How turbulence around aerial roots shapes the seabed morphology in mangrove forests of the Mekong Delta. Oceanography 2017, 30, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Kamali, B.; Tamin, N.M.; Zakaria, R.M. An integrated approach to coastal rehabilitation: Mangrove restoration in Sungai Haji Dorani, Malaysia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, O.D.; Lewis, R.R., III. Strategies for mangrove rehabilitation in an eroded coastline of Selangor, peninsular Malaysia. J. Coast. Dev. 2009, 12, 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Saengsupavanich, C. Erosion protection options of a muddy coastline in Thailand: Stakeholders’ shared responsibilities. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 83, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.X.; Manh, L.H.; Ba, H.T.; Duong, D.V.; Vu, H.T.D.; Wright, D.; Bui, V.H.; Anh, D.T. Wave energy dissipation through a hollow triangle breakwater on the coastal Mekong Delta. Ocean Eng. 2022, 245, 110419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.X.; Phong, N.C.; Thanh, V.Q.; Quan, T.Q.; Wright, D.P.; Anh, D.T. Multi-scale modelling for hydrodynamic and morphological changes of breakwater in coastal Mekong Delta in Vietnam. J. Coast. Conserv. 2022, 26, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, D.C.; Duong, N.B.; Phong, N.C.; Tu, L.X.; Damien, P.V.B.; Guillou, S.; Dan, N.K. Numerical Study on Measures for Protecting the Go-Cong Coastlines (Vietnam) from Erosion. Water 2022, 14, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.N.; Duong, D.V.; Tu, L.D.; San, D.C.; Chuong, L.T.; Hai, T.D.; Cong, T.N.; Wright, D.P.; Tamin, A.H.; Truong, P.N.; et al. Experimental and numerical modeling of pile-rock breakwater gap arrangement for optimal coastal erosion protection in deltaic coasts. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VPM. Program to Upgrading and Reinforcing the Sea Dyke System from Quang Ngai to Kien Giang Provinces; VPM: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, N.B.; Phong, N.T.; Thuan, N.B.; Quang, C.N.X.; Loi, L.T.; Quoc, H.V. Hollow Triangular Offshore Breakwaters and Sediment Accumulation: Lessons Learnt and Recommendations; Ton Duc Thang University: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2024; (manuscript submitted for publication). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Batistella, M.; Moran, E. Integration of Landsat TM and SPOT HRG Images for Vegetation Change Detection in the Brazilian Amazon. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Singh, A. Identification of flooded area from satellite images using Hybrid Kohonen Fuzzy C-Means sigma classifier. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 20, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.J. Shoreline mapping techniques. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 111–124. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4300016 (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N. Detecting coastline change with all available Landsat data over 1986–2015: A case study for the State of Texas, USA. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberg, A.J.; Park, J.W.; Hager, B.W.; Brock, M.V.; Diener-West, M. The use of ‘Overall Accuracy’ to evaluate the validity of screening or diagnostic tests. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2004, 19, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.D.; Walter, S.D. A reappraisal of the Kappa Coeficient. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.A.; Phinn, S.; Dargusch, P. Investigating the decline of ecosystem services in a production mangrove forest using Landsat and object-based image analysis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.; Wilson, N.; Tung, H.T.; Quisthoudt, K.; Minh, V.Q.; Tuan, L.X.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Koedam, N. Changes in mangrove vegetation area and character in a war and land use change affected region of Vietnam (Mui Ca Mau) over six decades. Acta Oecologica 2015, 63, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatorre, L.C.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Miramontes-Beltrán, S.; Medina, R.L.; Torres-Olave, M.E.; Bravo, L.C.; Wiebe, L.C.; Granados, A.; Adams, D.K.; Sánchez, E.; et al. Temporal changes of NDVI for qualitative environmental assessment of mangroves: Shrimp farming impact on the health decline of the arid mangroves in the Gulf of California (1990–2010). J. Arid. Environ. 2016, 125, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.S.; Yang, H. Spatial-temporal NDVI pattern of global mangroves: A growing trend during 2000–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Landsat Enhanced Vegetation Index. 2023. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-enhanced-vegetation-index#:~:text=Landsat%20Enhanced%20Vegetation%20Index%20(EVI,in%20areas%20with%20dense%20vegetation (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Nguyen, T.P.; Tam, N.V.; Quoi, L.P.; Parnell, K.E. Community perspectives on an internationally funded mangrove restoration project: Kien Giang province, Vietnam. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
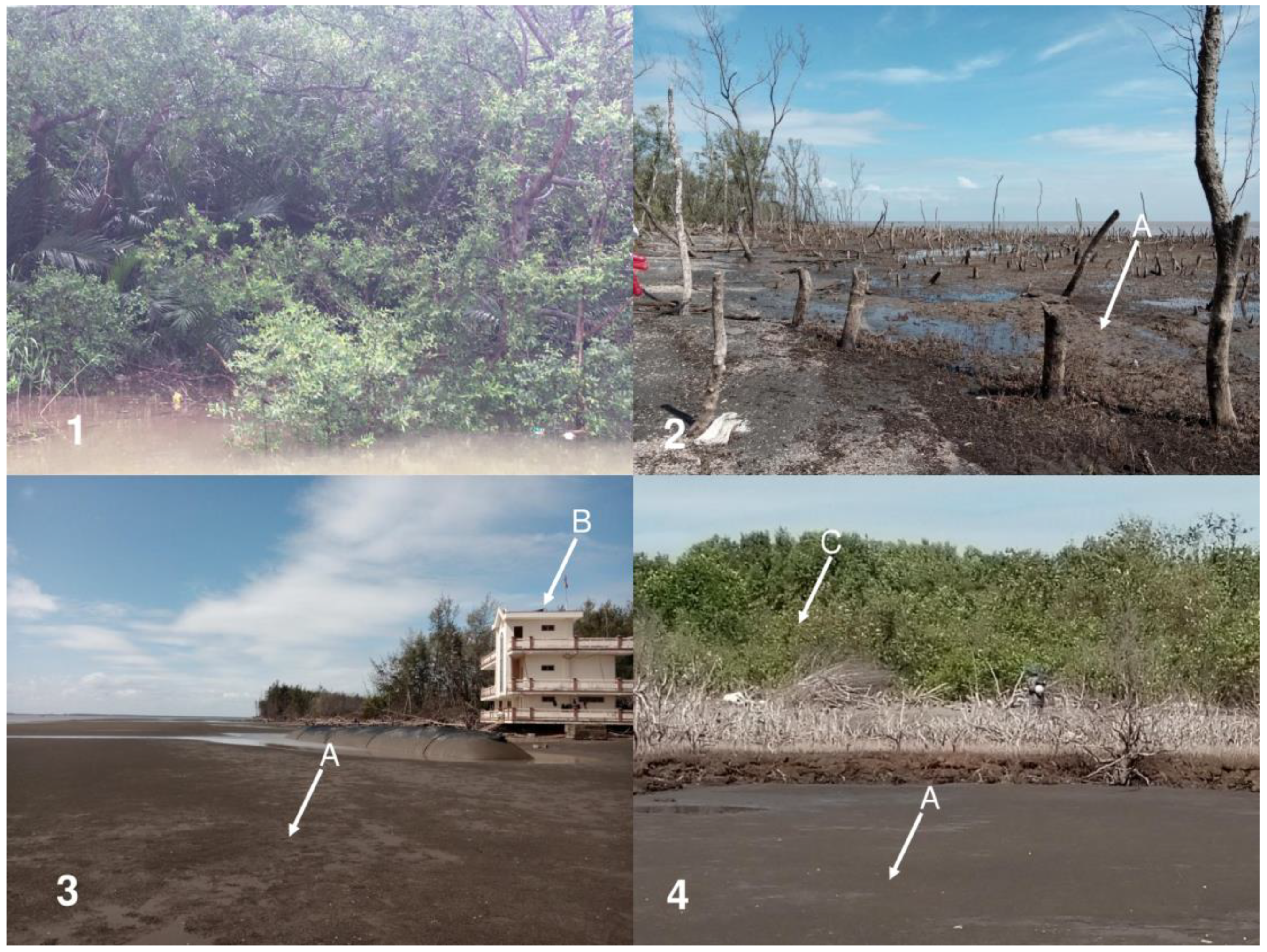



| Year | Path | Row | Acquisition Date | Satellite Image | Cloud Cover | Cloud Cover Land | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 125 | 053 | 14 February 1995 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 15 | 13 | 30 |
| 1997 | 125 | 053 | 18 March 1997 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 15 | 13 | |
| 2000 | 125 | 053 | 27 September 2000 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 15 | 13 | |
| 2004 | 125 | 053 | 11 February 2004 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 13 | 15 | |
| 2005 | 125 | 053 | 13 February 2005 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 12 | 12 | |
| 2008 | 125 | 053 | 9 March 2008 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 12 | 13 | |
| 2010 | 125 | 053 | 27 February 2010 | Landsat-5 (TM) | 20 | 23 | |
| 2013 | 125 | 053 | 18 November 2013 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 18.34 | 17.63 | |
| 2015 | 125 | 053 | 9 February 2015 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 2.86 | 3.37 | |
| 2018 | 125 | 053 | 31 October 2018 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 6.80 | 6.42 | |
| 2020 | 125 | 053 | 6 January 2020 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 2.28 | 2.18 | |
| 2022 | 125 | 053 | 28 January 2022 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 2.28 | 2.18 |
| Levels of Vegetation Cover | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| US | Liquid sediment condition and seasonally inundated by local tidal regimes |
| CS | Compact substrate with scattered juvenile Avicennia trees growing |
| LVA | Scattered juvenile mangrove trees (Avicennia alba, Bruiguiera gymnorhyza, Sonneratia alba, and Sonneratia caseolaris) or areas with mangrove trees with roots buried in sand (dried mangrove trees) |
| MVA | Stands of growing Avicennia alba, Bruiguiera gymnorhyza, Sonneratia alba, and Sonneratia caseolaris |
| HVA | Stands of fully grown Avicennia alba and Sonneratia alba |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phong, N.T.; Thuan, N.B.; Loi, L.T.; Quoc, H.V. Morphological Evolution of an Intertidal Mudflat in Relation to Mangrove Growth: Implications for Future Erosion Control. Life 2024, 14, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060711
Phong NT, Thuan NB, Loi LT, Quoc HV. Morphological Evolution of an Intertidal Mudflat in Relation to Mangrove Growth: Implications for Future Erosion Control. Life. 2024; 14(6):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060711
Chicago/Turabian StylePhong, Nguyen Tan, Nguyen Bao Thuan, Le Tan Loi, and Huynh Van Quoc. 2024. "Morphological Evolution of an Intertidal Mudflat in Relation to Mangrove Growth: Implications for Future Erosion Control" Life 14, no. 6: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060711
APA StylePhong, N. T., Thuan, N. B., Loi, L. T., & Quoc, H. V. (2024). Morphological Evolution of an Intertidal Mudflat in Relation to Mangrove Growth: Implications for Future Erosion Control. Life, 14(6), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060711







