The Behaviour of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Complex during Different Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Biological Samples
2.3. Quantitative Determination of IL-6, sIL-6R and sgp130
2.3.1. Variables
2.3.2. cDNA Synthesis and Amplicon Libraries
2.3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
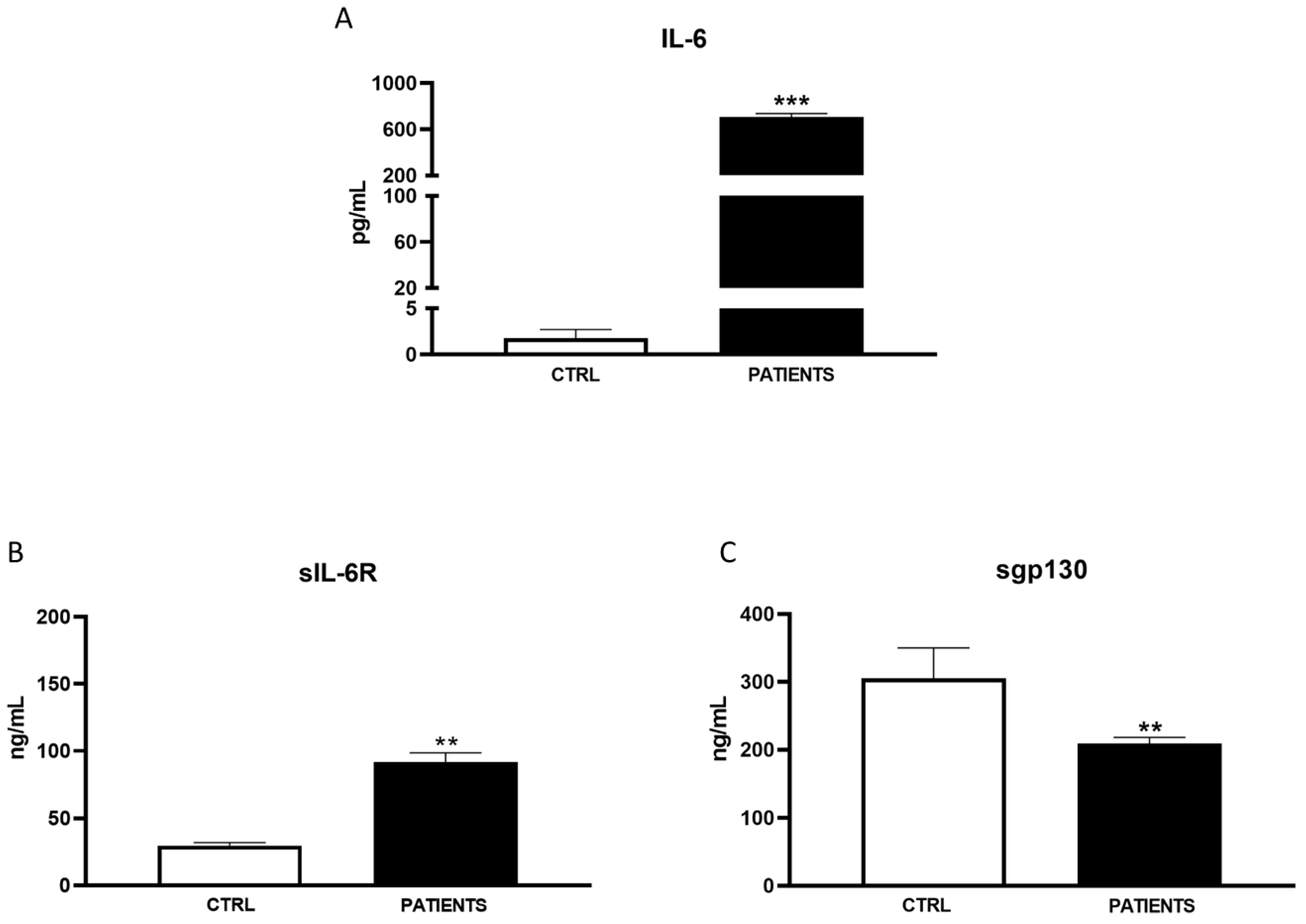
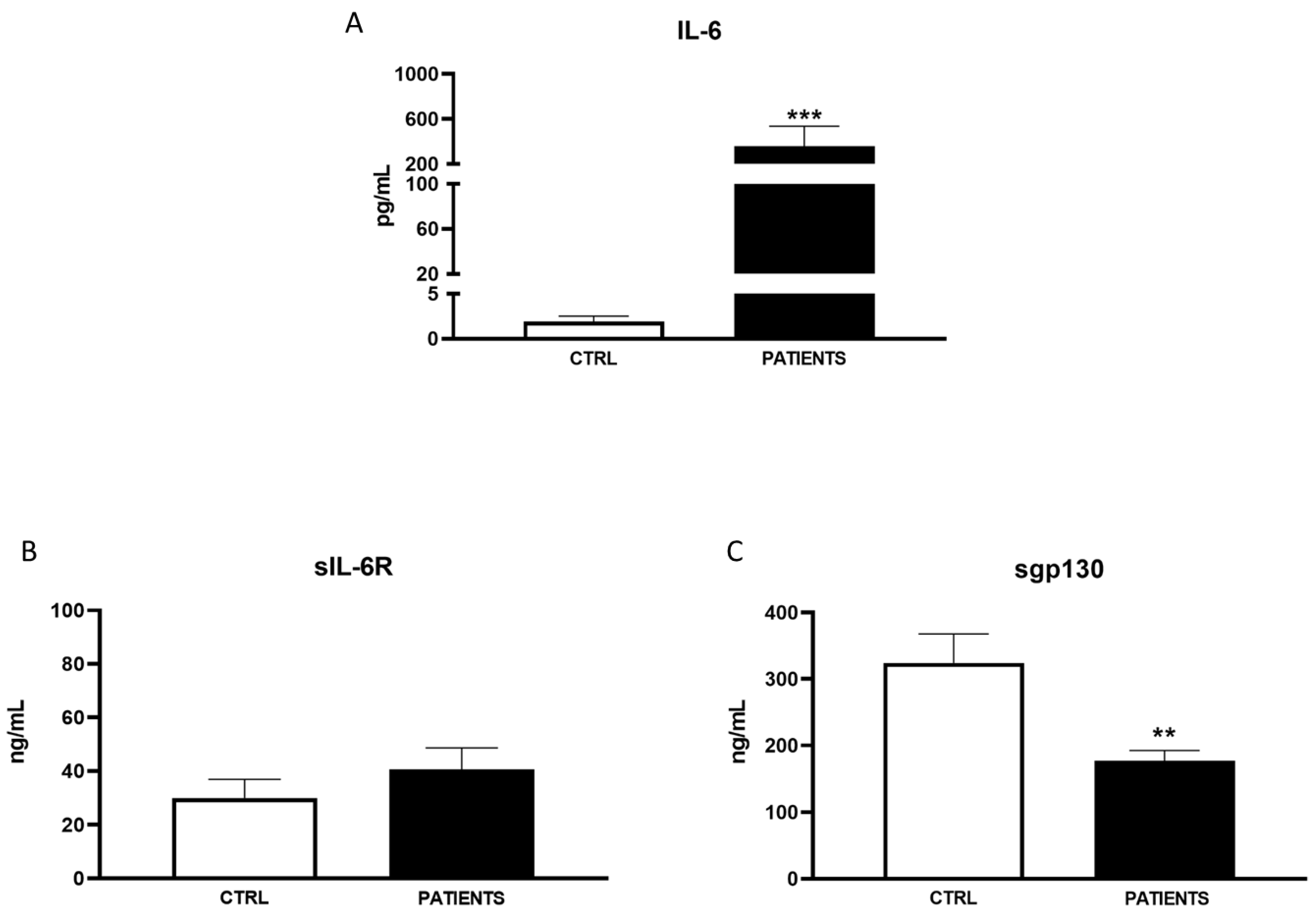
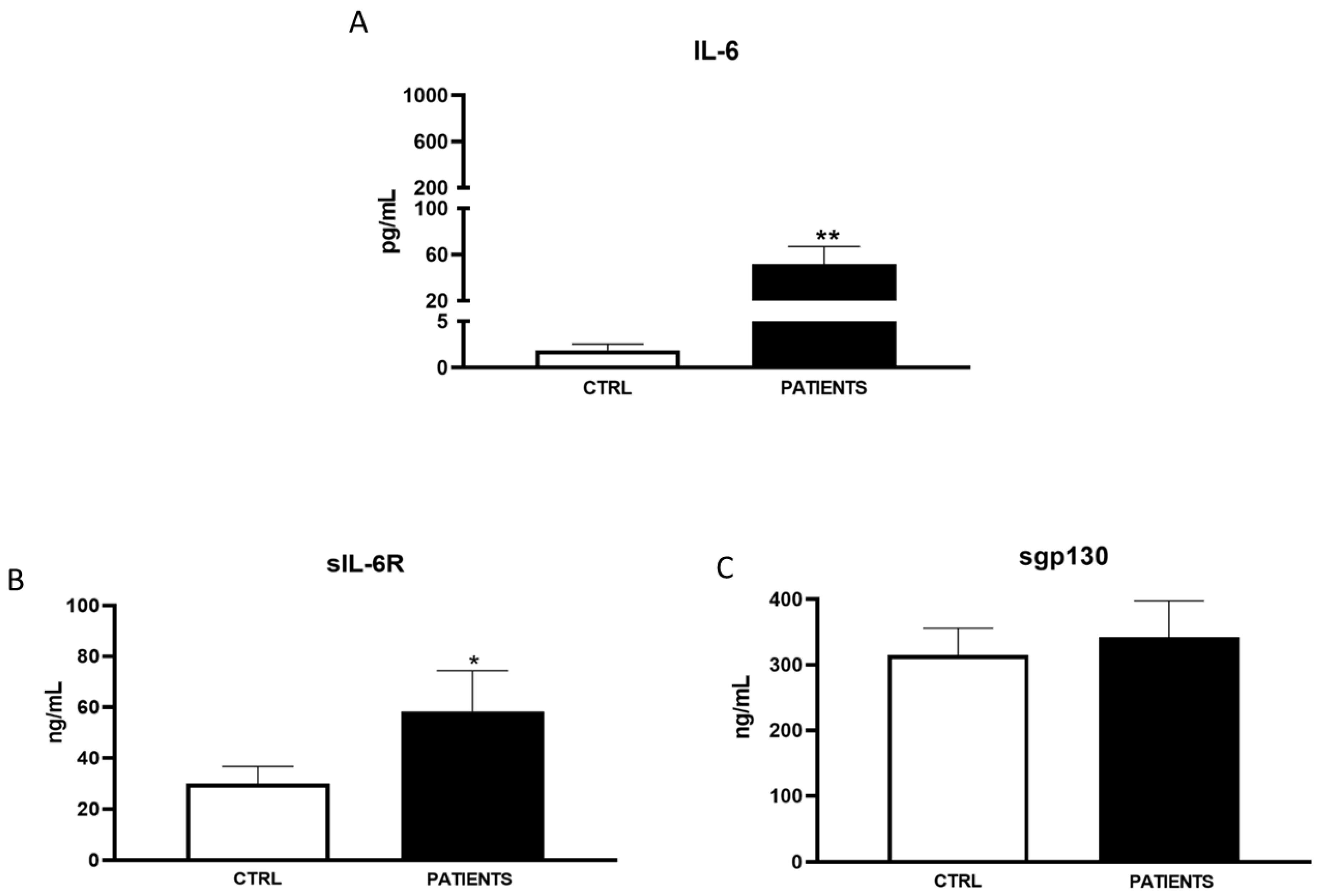
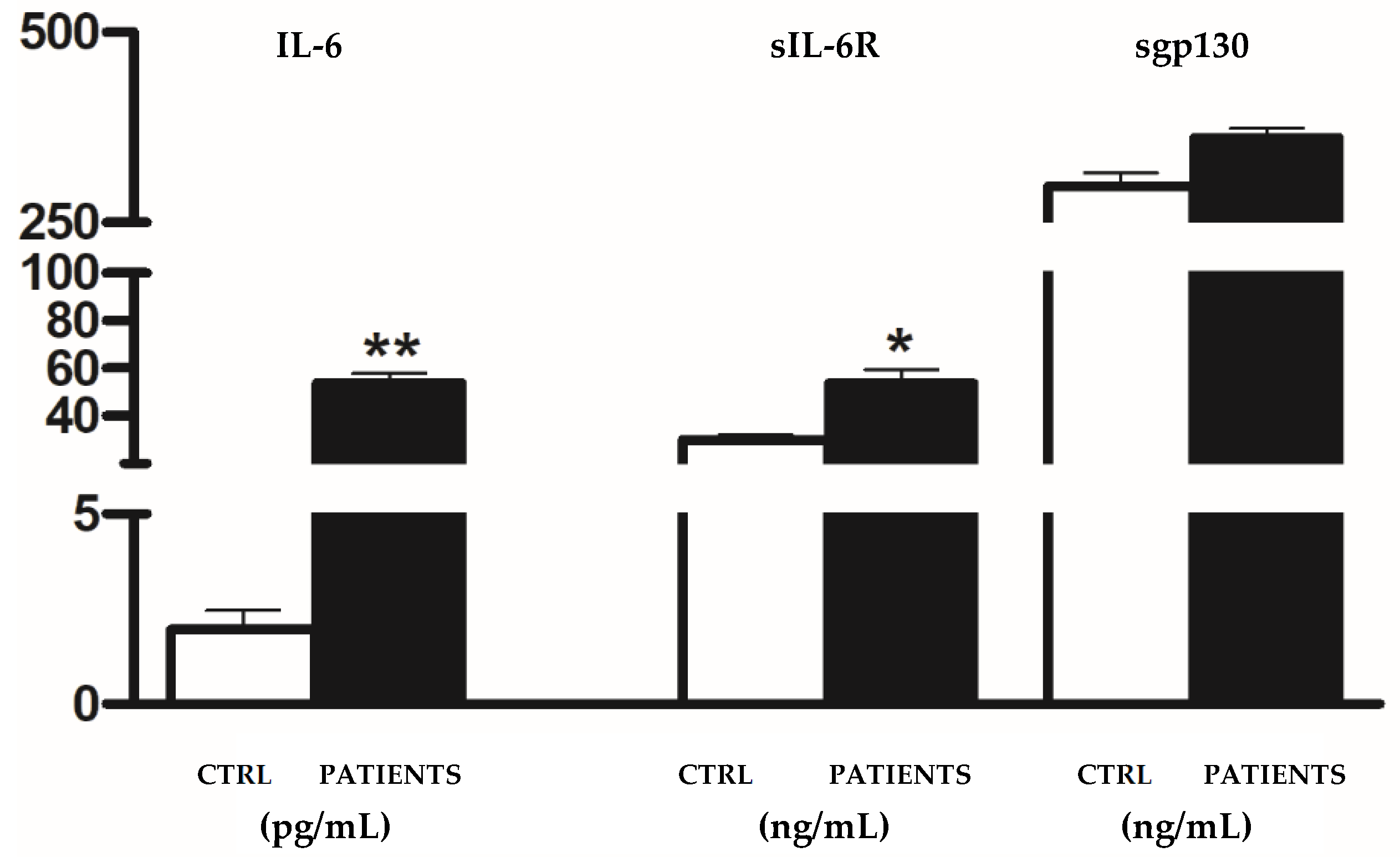
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s’ Characteristics
3.2. Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagbule, O.F. 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 17, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.D.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Azkur, A.K.; Azkur, D.; Gan, H.; Sun, Y.-L.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialo, F.; Daniele, A.; Amato, F.; Pastore, L.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Castaldo, G.; Bianco, A. ACE2: The Major Cell Entry Receptor for SARS- CoV-2. Lung 2020, 198, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Smith, D.M. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utrero-Rico, A.; Ruiz-Hornillos, J.; González-Cuadrado, C.; Rita, C.G.; Almoguera, B.; Minguez, P.; Herrero-González, A.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Carretero, O.; Taracido-Fernández, J.C.; et al. IL-6-based mortality prediction model for COVID-19: Validation and update in multicenter and second wave cohorts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta- analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.-W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.Q. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: From bench to bedside. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 195, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciapaglia, G.; Cot, C.; Sannino, F. Multiwave pandemic dynamics explained: How to tame the next wave of infectious diseases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisayo, T.; Tsukagoshi, S. Three waves of the COVID-19 pandemic. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, V.G.; Saivish, M.V.; Santos, D.E.R.; de Lima Silva, R.F.; Moreli, M.L. Comparative epidemiology between the 2009 H1N1 influenza and COVID-19 pandemics. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, V.; Gadi, N.; Spihlman, A.P.; Wu, S.C.; Choi, C.H.; Moulton, V.R. Aging, Immunity, and COVID-19: How Age Influences the Host Immune Response to Coronavirus Infections? Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 571416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinakis, I.; Selby, K.; Favrat, B.; Genton, B.; Cornuz, J. COVID-19 diagnosis: Clinical recommendations and performance of nasopharyngeal swab-PCR. Rev. Med. Suisse 2020, 16, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuccaro, V.; Colaneri, M.; Asperges, E.; Valsecchi, P.; Sambo, M.; Maiocchi, L.; Sacchi, P.; Muzzi, A.; Musella, V.; Cutti, S.; et al. Mortality due to COVID-19 during the pandemic: A comparison of first, second and third SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE). Heliyon 2022, 8, e08895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spigna, G.; Cernia, D.S.; Vargas, M.; Buonavolontà, L.; Servillo, G.; Postiglione, L. Drastically elevated levels of Interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor complex in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress. Clin. Med. Investig. 2020, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.C.; Biggs, C.M.; Jamal, S.; Stukas, S.; Wellington, C.L.; Sekhon, M.S. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor in the COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Román, J.M.; Rodríguez-García, S.C.; Roy-Vallejo, E.; Marcos-Jiménez, A.; Sánchez-Alonso, S.; Fernández-Díaz, C.; Alcaraz-Serna, A.; Mateu-Albero, T.; Rodríguez-Cortes, P.; Sánchez-Cerrillo, I.; et al. IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 72–80.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, T.; Meyer, K.; Geerling, L.; Isbell, T.S.; Hoft, D.F.; Brien, J.; Pinto, A.K.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans- signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Hunter, C.A. Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Xi, D.; Chen, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhu, L.; et al. The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorham, J.; Moreau, A.; Corazza, F.; Peluso, L.; Ponthieux, F.; Talamonti, M.; Izzi, A.; Nagant, C.; Djangang, N.N.; Garufi, A.; et al. Interleukine-6 in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.Y.; Goodman, R.B.; Steinberg, K.P.; Ruzinski, J.T.; Radella, F.; Park, D.R.; Pugin, J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Hudson, L.D.; Martin, T.R. Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164 Pt 1, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Fu, B.; Wei, H. IL-6 modulation for COVID-19: The right patients at the right time? J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabaro, S.; D‘Esposito, V.; Di Matola, T.; Sale, S.; Cennamo, M.; Terracciano, D.; Parisi, V.; Oriente, F.; Portella, G.; Beguinot, F.; et al. Cytokine signature and COVID-19 prediction models in the two waves of pandemics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horby, P.W.; Pessoa-Amorim, G.; Peto, L.; Brightling, C.E.; Sarkar, R.; Thomas, K.; Jeebun, V.; Ashish, A.; Tully, R.; Chadwick, D.; et al. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (recovery): Preliminary results of a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. MedRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mikulska, M.; Nicolini, L.A.; Signori, A.; Di Biagio, A.; Sepulcri, C.; Russo, C.; Dettori, S.; Berruti, M.; Sormani, M.P.; Giacobbe, D.R.; et al. Tocilizumab and steroid treatment in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Rothman, K.J.; Di Federico, S.; Orsini, N. The association between first and second wave COVID-19 mortality in Italy. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Asai, Y.; Tsuzuki, S.; Terada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Ohtsu, H.; Kitajima, K.; Toyoda, A.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Clinical characteristics of the first three waves of hospitalised patients with COVID-19 in Japan prior to the widespread use of vaccination: A nationwide observational study. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2022, 22, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, V.; Foulkes, S.; Insalata, F.; Kirwan, P.; Saei, A.; Atti, A.; Wellington, E.; Khawam, J.; Munro, K.; Cole, M.; et al. Protection against SARS-CoV-2 after COVID-19 Vaccination and Previous Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, C.; Malani, P.N.; Omer, S.B. Confronting the Delta Variant of SARS-CoV-2, Summer 2021. JAMA 2021, 326, 1001–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| WAVE I | WAVE II | WAVE III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | (N = 23) | (N = 104) | (N = 30) |
| Age | 66.88 ± 14.48 | 68.72 ± 18.32 | 67.42 ± 14.86 |
| Male (%) | 18 (78.26%) | 68 (65.38%) | 23 (76.67%) |
| Diabetes (%) | 9 (39.13%) | 24 (23.12%) | 4 (13.31%) |
| Hypertension (%) | 18 (78.26%) | 66 (63.46%) | 13 (43.32%) |
| Chronic kidney disease (%) | 8 (34.78%) | 22 (21.15%) | 7 (23.11%) |
| Died (%) | 12 (52.17%) | 48 (46.15%) | 3 (10%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Spigna, G.; Covelli, B.; Vargas, M.; Di Caprio, R.; Rubino, V.; Iacovazzo, C.; Napolitano, F.; Servillo, G.; Postiglione, L. The Behaviour of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Complex during Different Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Life 2024, 14, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070814
Di Spigna G, Covelli B, Vargas M, Di Caprio R, Rubino V, Iacovazzo C, Napolitano F, Servillo G, Postiglione L. The Behaviour of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Complex during Different Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Life. 2024; 14(7):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070814
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Spigna, Gaetano, Bianca Covelli, Maria Vargas, Roberta Di Caprio, Valentina Rubino, Carmine Iacovazzo, Filomena Napolitano, Giuseppe Servillo, and Loredana Postiglione. 2024. "The Behaviour of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Complex during Different Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic" Life 14, no. 7: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070814
APA StyleDi Spigna, G., Covelli, B., Vargas, M., Di Caprio, R., Rubino, V., Iacovazzo, C., Napolitano, F., Servillo, G., & Postiglione, L. (2024). The Behaviour of IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Complex during Different Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Life, 14(7), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070814








