Abstract
Obesity is an important condition affecting the quality of life of numerous patients and increasing their associated risk for multiple diseases, including tumors and immune-mediated disorders. Inflammation appears to play a major role in the development of obesity and represents a central point for the activity of cellular and humoral components in the adipose tissue. Macrophages play a key role as the main cellular component of the adipose tissue regulating the chronic inflammation and modulating the secretion and differentiation of various pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation also involves a series of signaling pathways that might represent the focus for new therapies and interventions. Weight loss is essential in decreasing cardiometabolic risks and the degree of associated inflammation; however, the latter can persist for long after the excess weight is lost, and can involve changes in macrophage phenotypes that can ensure the metabolic adjustment. A clear understanding of the pathophysiological processes in the adipose tissue and the interplay between obesity and chronic inflammation can lead to a better understanding of the development of comorbidities and may ensure future targets for the treatment of obesity.
Keywords:
obesity; inflammation; adipocytes; adipose tissue; cytokines; adipokines; macrophages; weight loss 1. Introduction
Obesity is defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat and is caused by the disparity between energy intake and consumption, facilitated mainly by excessive caloric intake, sedentarism, mental disorders, or genetic factors [1]
Obesity increases the risk for metabolic disease, atherosclerosis, various malignant tumors, and a host of immune-mediated disorders due to a chronic, systemic, inflammatory response [2,3,4]. The inflammation is directly correlated with exceeding weight and is dominated by clear hallmarks such as an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory processes, abnormal cytokine (CK) levels, and exaggerated production of acute-phase reactants, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) [5]. Numerous CKs, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL (interleukin)-6, CRP, and IL-1β, are studied in the interplay between metabolic disease, inflammation, and carcinogenesis, but mediators of innate immunity, namely inflammasomes, are also regarded with increasing interest [6,7,8,9].
Chronic over-nutrition leads to systemic toxicity exerted by glucose and unoxidized long-chain fatty acids and can stimulate the synthesis of pro-inflammatory adipokines [10]. High-fat diet (HFD) feeding can cause imbalances in the adipose tissue (AT) environment and alter its anti-inflammatory state by recruiting pro-inflammatory immune cells; a chronic inflammatory state may be achieved, both local and systemic [11,12].
The inflammation induced by obesity is triggered in the white adipose tissue (WAT) and spreads to various other tissues [13]. The obesity-associated chronic inflammation of the AT ultimately leads to its dysfunction and involves fibrosis, reorganization of the extracellular matrix (ECM), hypoxia, and altered angiogenesis, among other mechanisms [14].
There is a causal relationship between excessive caloric intake and inflammation. Weight gain leads to an increased amount or volume of adipocytes and subsequent changes in the phenotype of WAT [7]. This phenotype shift is characterized by the development of inflamed adipocytes with altered function as well as the recruitment of immune cells that release pro-inflammatory CKs [11,15,16,17,18,19].
However, the exact trigger of chronic inflammation in obesity, as well as the pathways of CKs released from the AT leading to systemic inflammation, is not well understood.
Some important differences between classical and obesity-related inflammation are worth highlighting. In various experimental models and human trials, it was shown that chronic inflammation develops in obese individuals; however, the level of circulating CKs is unable to generate, by itself, a sufficient chemotactic force to draw in monocytes [20]. Moreover, AT inflammation induced by overnutrition is not associated with a significant increase in energy expenditure, compared to the traditional inflammation model, thereby explaining the coexistence of inflammation and weight gain [21].
The innate and adaptive immune systems play a significant role in sustaining the metabolic activity of the WAT [12]. A causative relationship between excessive feeding and the activation of the immune system in organs regulating energy metabolism was demonstrated in both human and animal studies [22,23].
This paper aims to highlight the interplay between obesity and chronic inflammation by focusing on the cellular and humoral components, allowing for a more precise and complete image on the inflammatory mechanisms at play in obesity. Moreover, we will present the comprehensive role of macrophages in the propagation and regulation of inflammation within the adipose tissue and present the signaling pathways that can be targeted in the treatment of high-risk obese individuals. Persistent inflammation after weight loss is a topic that is often overlooked in other studies and is explored in the current paper, focusing on the management of weight loss in obesity-associated inflammation.
2. Methodology
For documenting this review paper, we performed a search in electronic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and Embase utilizing relevant search words including “obesity”, “inflammation”, “adipose”, “markers”, “immune”, “cytokines”, “signaling”, and “mechanism” in order to identify adequate papers on the topic. The grey literature was also screened, in order to obtain a comprehensive view of the topic and to ensure the inclusion of all relevant studies. Studies that were not in English or were not available in full-text were not included in this study.
3. Features of the Adipose Tissue
The AT is the largest fat-storing depot, an active immune and metabolic organ, and also the largest endocrine organ that secretes and releases adipokines, cytokines, and chemokines into the adjacent vascular network [24,25,26].
The AT comprises adipocytes, which make up less than 50% of the total cells, and the stromal vascular fraction [27]. The latter includes adipocytes not yet loaded with lipids (i.e., pre-adipocytes), cells belonging to the innate immune system (macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells), immune cells of the adaptive immune system (B cells, NKT, CD4, CD8 cells), vascular cells, and fibroblasts. Macrophages represent around 10% of a lean person’s AT but may increase up to 40% in obesity [28,29]. The innate response, mediated by neutrophils and macrophages, is rapid but non-specific. On the other hand, the adaptive response is mediated by T and B cells and is directed against a specific aggressor. The innate and adaptive responses reinforce each other; therefore, macrophages act as antigen-presenting cells for T cells, and, in turn, T cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ), which further activates macrophages [30,31].
Adipocytes are important energy storages, that take up and release lipids within the adipose tissue, according to the signaled needs. Their number is determined during childhood and adolescence and remains relatively stable throughout an individual’s lifetime [32].
Adipocytes modulate the inflammatory response by secreting TNF-α and IL-6, adipokines with opposite effects on inflammation, acting as signaling molecules [33,34,35]. Also, a number of adipocyte-produced lipids such as palmitate and other unsaturated fatty acids interfere with inflammation, augmenting the pro-inflammatory signaling [36]. Adipocytes also secrete branched-chain fatty acid esters of hydroxyl fatty acids that inhibit inflammation and improve insulin secretion and sensitivity [37,38].
Adipose tissue (AT) can be classified through morphological considerations into brown adipose tissue (BAT) and WAT. AT mostly comprises WAT which is deposited mainly subcutaneously and periviscerally and represents a major factor in the development of cardiovascular conditions and complications [39]. BAT represents only a minor proportion of AT, is distributed in the cervical, thoracal, mediastinal, and abdominal areas, exerts anti-obesity and anti-diabetes roles, and is involved in thermogenesis [39,40,41,42,43].
The main feature of BAT is the inclusion of numerous lipid droplets and mitochondria, necessary for thermogenesis. Conversely, WAT includes larger adipocytes that contain fewer mitochondria and only one fat droplet, thus enabling the cells to store energy rather than expend it in exchange for heat [44,45].
According to its distribution, white adipose tissue can be classified into two main compartments: subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and visceral adipose tissue (VAT), the latter comprising the adipose tissue deposited in the abdominal cavity, i.e., within the omentum, the mesentery, in the retroperitoneal space, and around the organs. There are several differences between SAT and VAT in terms of structure but also function [46]; furthermore, differences in lean and obese persons between these tissues are also noted. The volume of VAT is positively correlated with cardiovascular events and is a more significant risk factor than the BMI [47,48]. Perivascular adipose tissue surrounds blood vessels and hosts a variety of immune cells such as eosinophils and B cells, which were shown to be reduced in high-fat diets [49], and appear to be involved in vascular relaxation and atheroprotection [50].
As opposed to SAT, VAT has direct liver access, via the portal venous system [51], and is therefore involved in the hepatic production of C reactive protein [52]. VAT is richer in large adipocytes [53] and inflammatory cells [54]. VAT is the largest source of adiponectin [55], while SAT is the largest source of leptin [56].
Regarding the tissue structure, SAT includes small-size adipocytes with high avidity for FFA and triglyceride [57]. However, there are differences in the WAT structure in normal-weight and obese subjects. In lean persons, WAT contains mostly cells with regulatory and immunosuppressive actions: M2 macrophages, eosinophils, NKT, Th2 cells, and regulatory T cells. The macrophages are uniformly distributed within the AT in order to release anti-inflammatory CKs, assure the clearance of apoptotic adipocytes, and inhibit pre-adipocyte differentiation [29]. On the contrary, in the obese, the lipid storages of the WAT are increased and macrophages are increased in number and are inhomogeneously distributed, in clusters around apoptotic adipocytes, forming crown-like structures (CLSs) [36,58,59].
The VAT in obese persons contains more macrophages as compared to the SAT [60,61,62]. Moreover, VAT releases more inflammatory cells and does so more easily [54]. In obese persons, VAT inflammation is associated with hepatic and skeletal muscle ectopic lipoid deposits which may trigger insulin resistance [63]. The reported response to inflammation and apoptosis is more intense in VAT compared to SAT [64].
The capabilities of pre-adipocytes to differentiate into adipocytes are different between VAT and SAT, i.e., VAT expands via hypertrophy while SAT scales up mainly by hyperplasia [65]. The sensitivity to apoptosis is weaker in adipocytes from the SAT compared to the VAT [66]. Additionally, the uptake of FFA after meals is greater in VAT than in SAT [67,68].
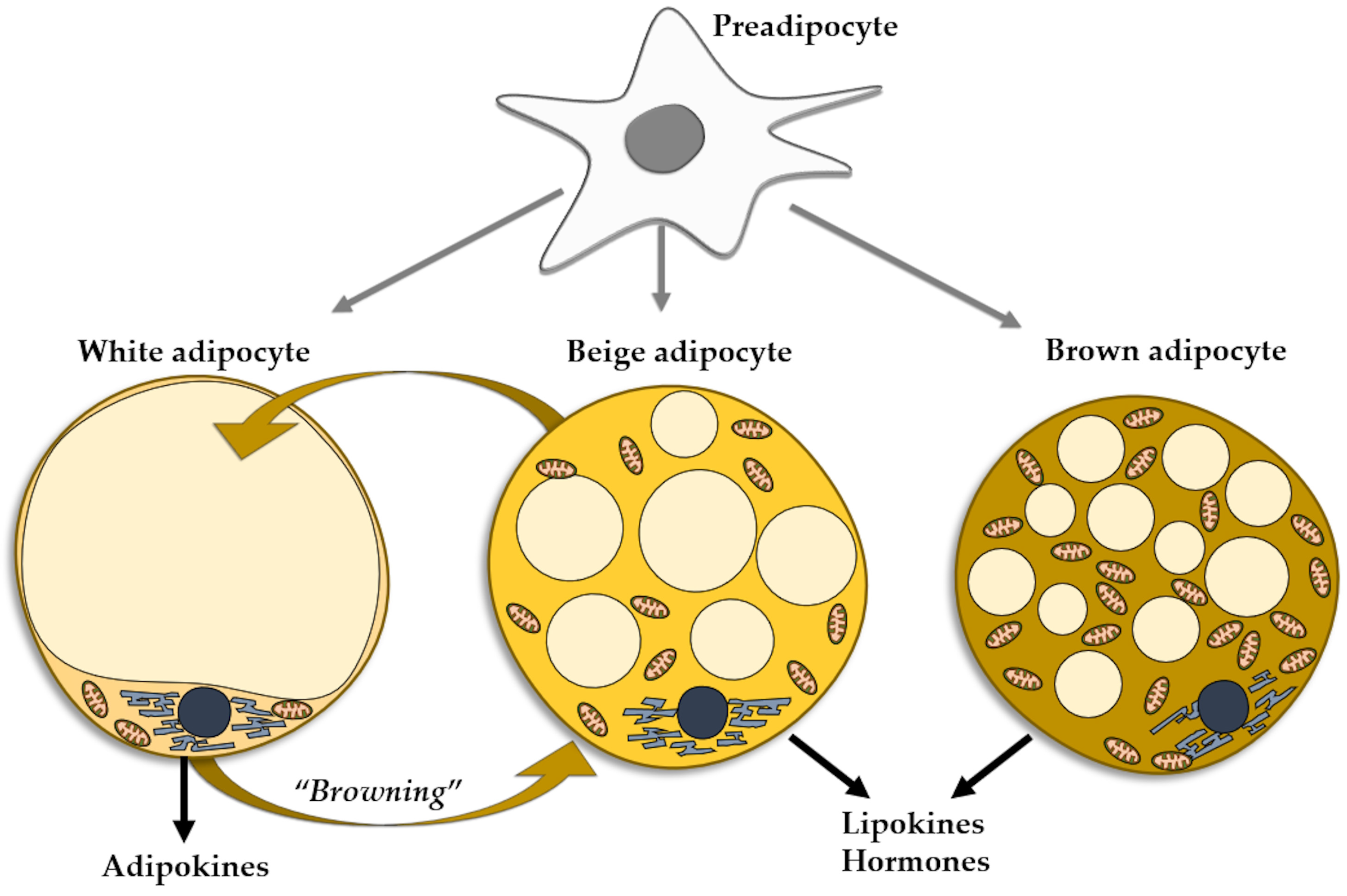
The adipocytes found in the WAT can be mainly regarded as energy accumulators. However, the brown adipocytes of the BAT act as a heat source. A third type of adipocytes, named beige adipocytes, have the same origin as white adipocytes, but present the functional phenotype of brown cells [69]. Under certain conditions, mature white fat cells trans-differentiate into beige adipocytes, a process referred to as WAT browning, which entails the appearance of beige cells in WAT depots, more so in subcutaneous than in visceral WAT [6] (Figure 1). As mentioned, the phenomenon of WAT browning may occur in various conditions, including exercise [70], prolonged cold exposure [71], and exposure to capsaicin, resveratrol, fish oil, cinnamon, short fatty acids [72], and PPAR gamma agonists [73]. The browning of WAT may be considered as an environmental adaptation mechanism in adult life, similarly to the presence of brown adipocytes produced during intrauterine life [74]. Resembling brown adipocytes, beige adipocytes contain multilocular lipid droplets [75] and are rich in mitochondria, expressing uncoupling protein-1, a thermogenic protein [76]. Beige adipocytes secrete minute amounts of leptin and adiponectin, pertaining to the overall small mass of cells [77]. They are mainly heat producers, but also contribute to the improvement of glucose and lipid metabolisms and mounting evidence supports the thesis of beige adipocytes as protectors against obesity and insulin resistance. Similarly to BAT, beige tissue is considered as a therapeutic target for metabolic diseases, including obesity [77]. The reverse is also true, as in aging, obesity, and metabolic disorders the capacity of the WAT cells to induce browning of WAT is decreased [78] (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Types of adipocytes in the adipose tissue evolved from the common progenitor. Trans-differentiation between white and beige adipocytes.
4. Molecular Mechanisms in Adipocyte Inflammation
Recent studies have shown that inflammation within the adipose tissue plays a paramount role in the development of metabolic syndrome and related complications. Moreover, chronic inflammation represents an intersection point of various molecular pathways impacting the immune system and potentially affecting the function of distant organs via cytokines [79]. Several signaling pathways may interfere with the expression of proteins regulating the cell cycle, apoptosis, or oxidative stress, leading to a higher risk of developing a subset of cancers [80,81,82].
Murine studies showed that FFA-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress [83]. Obese patients show a correspondence between the BMI and the level of ER markers, as well as between ROS generation and FFA levels [84,85]. FFAs directly stimulate toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), promoting the inflammatory cascade [86]. It was also observed that tenascin C, an endogenous TLR4 activator, shows increased levels in the WAT of obese subjects [87]. Interestingly, the expression of anti-inflammatory counterregulatory TLR types such as TLR9 is also increased in obesity [88].
Elevated FFAs and ROS in the AT induce the release of pro-inflammatory adipokines, favor immune activation, and lead to chronic inflammation [89]. Increased oxidative stress was identified in obesity and its complications and it is triggered by the dysregulation of mitochondrial function [10]. The subsequent accumulation of ROS leads to nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)-mediated apoptosis with associated inflammation due to increased production of inflammatory adipokines [90].
The senescence markers are elevated in hypertrophic VAT, and the secretion of senescent proinflammatory CKs from cells maintains and stimulates the inflammation within the adipose tissue and favors adipocyte apoptosis in obese persons [91,92,93].
Various signaling pathways may be activated or modulated by inflammation, and therefore represent potential new targets in the treatment of obesity-related metabolic dysfunctions.
The NF-κB signaling pathway plays a major role in the local and systemic inflammation induced by obesity [94,95,96]. The activation of the NF-kB inflammatory pathway leads to subsequent stimulated expression of pro-inflammatory CKs, which intensify the inflammatory processes [97,98].
In a second signaling pathway, the inflammasome multiprotein complexes that regulate the immune response following activation by myeloid cells are involved [99]. NLRP3 (NLR family pyrin domain containing 3) is a major representative of the immune metabolic response and is present in various tissues, including the CLSs of the AT [100,101]. The NLRP3 inflammasome requires pro-caspase 1 for activation and is associated with the release of IL-1β and IL-18 by AT macrophages [102,103,104,105]. Therefore, the NLRP3-IL-1β pathway is essential in the development of obesity-related complications and its downregulation was demonstrated to decrease the expression of pro-inflammatory CKs, inflammatory processes, and fibrosis within the AT [106,107]. Also, inhibition of NLRP3 in HFD showed a protective effect against liver steatosis and cardiovascular complications in murine studies [108]. On the other hand, blocking IL-1β via antagonists in type 2 DM or obesity showed a significant reduction in systemic inflammation [109,110,111].
Various proteins may be involved in the signaling processes regulating inflammation in obesity. Among these, galectin-3 is produced by macrophages, is upregulated in obesity, and shows a direct correlation with insulin resistance [112]. ATM-derived exosomes are also important factors in obesity-related insulin resistance and can shift their phenotype in lean versus obese individuals [113].
5. Obesity and Inflammation
The inflammatory response in inflammation includes cellular and humoral components. Early upstream markers for inflammation can be used in the detection and prevention of metabolic syndrome, in targeted therapies and anti-inflammatory treatments, in superior disease monitoring, as well as in public health programs that can identify at-risk obese individuals and facilitate early intervention [114,115]. Moreover, measuring certain adipokines can provide insight into the inflammatory status and can guide personalized interventions while some cytokines can be targeted in managing obesity-related metabolic disturbances [116].
5.1. Obesity and the Cellular Component of the Inflammatory Response
The inflammatory response in obesity is complex and features immune cells involved in both cellular and humoral immunity, to various degrees, and acting in different phases.
5.1.1. Macrophages
Macrophages are the main cellular component involved in the chronic inflammation of the AT in obese humans and animals [117,118].
Macrophages are responsible for clearing cellular waste originating from dead cells but they also contribute to angiogenesis as well as the remodeling of the ECM [119]. Macrophages are also essential in the expansion and remodeling of the AT during impaired adipogenesis [66].
The crosstalk between adipocytes and the AT macrophages triggers the process of systemic metabolic inflammation in obesity [120,121]. It was also shown that there is a relationship between adipose tissue macrophage (ATM) infiltration and resistance to insulin.
The central role that macrophages play in obesity is defined by their increase in number as well as the phenotype shift leading to several functional responses [122]. The number of macrophages can increase in obesity in various manners, e.g., through chemotaxis by capturing monocytes from the circulation, by increasing the proliferation of local macrophages, as well as through the stimulation of macrophage retention [23,29,123,124].
Monocytosis occurs during the migration of monocytes into the AT while the VAT releases monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and leukotriene B4 [20,125,126]. Osteopontin is also an important adipokine that attracts monocytes to the AT and contributes to macrophage proliferation and infiltration [127,128,129]. Additionally, calprotectin can contribute to the accumulation of monocytes within the inflammatory milieu following its release from the mature macrophages [129,130,131]. Hypoxia and adipocyte necrosis also contribute to macrophage recruitment [128].
In obese persons, a specific population of macrophages is encountered, comprising Ly6C+ monocyte-derived macrophages undergoing differentiation [132]. ATMs expressing the Ly6C monocyte marker were identified outside the CLSs and were shown to increase adipocyte differentiation [133].
In obesity, monocyte and macrophage infiltration enter a positive feedback, increasing their expression and ultimately leading to chronic inflammation within the WAT [7]. The proliferation of macrophages in the WAT occurs mainly within the CLSs and, under the stimulation of IL-4, leads to an increased selective expression of M2 macrophages [134,135].
The cellular features and tissue distribution of macrophages are distinct in obese compared to lean individuals. Obese mice have increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and inducible NO synthase (iNOs) while non-obese mice show increased expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and arginase-1 [58]. The infiltration of ATM is further stimulated by the increase in NF-κB levels that extend the lifespan of macrophages, which subsequently contribute to maintaining the local inflammation [136].
After the death of adipocytes within the CLSs, macrophages accumulate in the periphery, a process mediated by the adipocytes releasing MCP-1 [137]. The accumulated macrophages then release TNF-α, stimulating a subsequent release of FFAs from the adipocytes [138]. FFAs will then bind to TLR4 on adipocytes and macrophages, resulting in the activation of NF-kB signaling and the release of IL-1β by the macrophages [139].
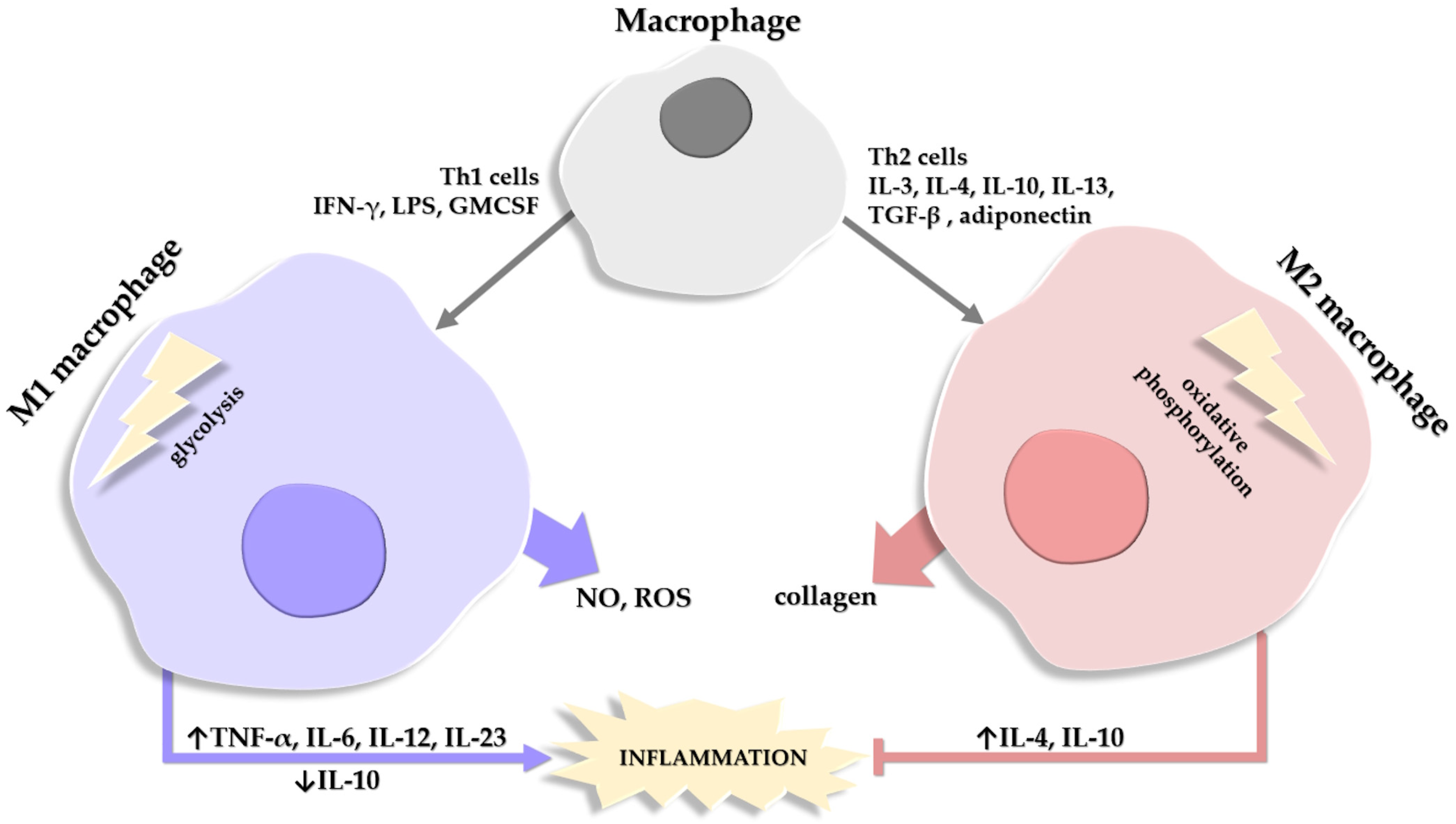
The population of macrophages in the AT comprises two main categories, M1 ATM which show pro-inflammatory features and are the majority in obese AT, and M2 ATM which exhibit anti-inflammatory effects and represent the main type in lean persons [58,140]. A third population of macrophages is described in obesity, with hybrid M1 and M2 characteristics, and plays a role in mitigating excessive lipids within the AT [141,142,143].
The M1 and M2 macrophages differ in two essential enzymes. M1 macrophages generate NO and ROS with the help of iNOS, while M2 macrophages use arginase to promote collagen production and deposition [144,145].
Another distinction between the two main types of macrophages is in ATP generation; M1 macrophages generate ATP quickly via the glycolysis pathway, while M2 macrophages use oxidative phosphorylation (OX PHOX) to obtain energy [146]. In lean mice, macrophages have low OX PHOX expression and a limited capacity for glycolysis; conversely, in obese mice, both types of pathways are overexpressed and highly effective [147]. Moreover, M1 macrophages produce lipids and pro-inflammatory lipid mediators while M2 macrophages contribute to lipid oxidation [148]. In activated M1 macrophages, eicosanoids are not the only pro-inflammatory components released; the synthesis of pro-inflammatory CKs such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-23 is also increased, with a concomitant decrease in the anti-inflammatory CKs, such as IL-10 [149].
An important mention is that the pro-inflammatory phenotype M1 in obesity is different from the phenotype of M1 macrophages in acute inflammatory reactions, in that M1 ATMs express lower levels of pro-inflammatory CKs like TNF-α and IL-6 compared to the classical acute inflammatory M1 response [143,150]. Additionally, a synchronous activation of the endogenous anti-inflammatory cascade is observed in obesity, with increased levels of IL-10, for example, which leads to the inhibition of macrophage activation [151]. Also, in obese persons, the distinct M1-like types of macrophages upregulate the expression of genes that encode proteins involved in lipid metabolism [150,152,153] (Figure 2).
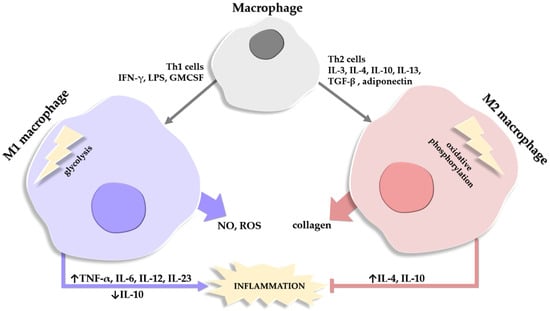
Figure 2.
Schematic depiction of the factors involved in the differentiation of a macrophage into a type M1 or M2 macrophage. Macrophages release substances that degrade (NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species) or help repair (collagen) the extracellular matrix. Roles of M1 and M2 macrophages in the balance of stimulating (→)/inhibiting (˫) inflammation are also depicted, alongside the cytokines involved in the process, where their expression/release is either stimulated (↑) or inhibited (↓).
CD9 is a cell surface marker expressed by various cells, including macrophages, and its expression can be regulated in inflammation and macrophage activation [154].
According to the CD9 expression, we can differentiate CD9+ ATMs, which are increased in obesity and are mostly derived from the bone marrow, and CD9- ATMs, which are responsible for angiogenesis [133,141]. CD9+ ATMs found within the CLSs show increased expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and CKs, as well as genes related to lipid metabolism and lysosomal pathways [20].
Macrophage polarization is one of the steps of the inflammatory reaction in obesity and is crucial for the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1 [155,156].
The expression of M1 and M2 markers can influence the activation and phenotype expression of the ATM [141]. The variability of phenotype expression is also known as phenotypic plasticity and allows for the adaptation to changes in the microenvironment (i.e., polarization); polarization towards the M1 type occurs through CKs produced by Th1 cells, while polarization towards the M2 type occurs via Th2 cells [128]. Most M1-like polarized ATMs derive from circulating monocytes and the transition is regulated by dietary or hydrolyzed bisaturated fatty acids via a TLR4-dependent mechanism [22,157,158,159,160]. The triglyceride-containing obese adipocytes are responsible for inducing an oxidative environment by stimulating ATMs to produce TNF-α, which subsequently increases the fatty acid release [10,136]. M1 macrophages resulting from the conversion of anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages further amplify the plethora of molecular events observed in obesity [161].
5.1.2. Other Cellular Components
Neutrophils represent the largest fraction of the circulating leukocytes and their infiltration and subsequent activation within the adipose tissue has recently been linked to obesity-associated inflammation [162]. Murine models have been used to study the interaction between neutrophils, cytokines, and other cells, including macrophages, in the development of obesity-related complications in HFD [163]. Neutrophils are infrequent cells in the AT of lean mice [164,165]. However, in obesity, neutrophils are the first immune cells in the AT recruited from peripheral circulation [128]. The migration and activation of neutrophils are stimulated by the lipids accumulated within adipocytes, as well as leptin and various pro-inflammatory factors including TNF-α [128,166,167,168].
Murine studies showed that macrophage recruitment is decreased in neutrophil activity impairment demonstrated by the decreased expression of neutrophil enzymes [164,169]. Moreover, in obesity, neutrophil dysfunction leads to resistance to insulin and inflammation within the AT [170].
The infiltration of the VAT by neutrophils after HFD occurs well before the onset of insulin resistance or even weight gain resulting in macrophage recruitment [171]. Murine studies show that neutrophil infiltration occurs at 3 days after the HFD initiation and disappears after one month [171]. In humans suffering from obesity, however, the definitive role of neutrophils in AT inflammation is uncertain.
Eosinophils are key factors in obesity-associated inflammation; they play a physiological role in the regulation of metabolic hemostasis [172]. Eosinophils release high levels of IL-3, IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β, leading to M2 polarization of ATMs, favoring the anti-inflammatory effects [173].
B cells are upregulated in obesity [174]. In murine studies on obesity, B cells accumulate in the AT and increase the recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes through the chemokines released within the microenvironment [165]. Furthermore, B cells promote the AT inflammation and the recruitment and activation of T cells [165,174,175], while also presenting antigens to T cells, releasing pro-inflammatory CKs and therefore contributing to the development of the inflammatory process [176,177,178].
T cells represent the second most common immune cell type after macrophages and are a population of cells significantly increased in obese mice undergoing HFD [152,175]. In particular, CD3+ T cells stimulate macrophage chemotaxis and differentiation [179]. The levels of CD3+CD4+ Th1 cells are higher in obese individuals and they release IFN-γ, stimulating inflammation, while the levels of CD3+CD4+ Th2 cells are lower, and they release IL-4 with anti-inflammatory effects [175,180,181].
Mast cells are found in increased numbers in the WAT of obese individuals [182]. Through degranulation, they release pro-inflammatory substances and facilitate the macrophage infiltration of the AT [182,183,184]. Within the WAT, the activity of mast cells is influenced by IFN-γ and IL-6 [182].
Regarding the cellular component, the WAT tends to have a higher concentration of pro-inflammatory immune cells such as M1 macrophages, neutrophils, and mast cells, as well as B and T cells, modulating metabolic inflammation and IR, while BAT presents more anti-inflammatory immune cells such as M2 macrophages, eosinophils, and innate lymphoid cells pertaining to its thermogenic and anti-inflammatory roles [7,163,185,186,187].
5.2. Obesity and Cytokines in the AT Inflammation
The CKs released in the AT have various effects, mainly pro-inflammatory ones. The amount of anti-inflammatory CKs appears to decrease with weight gain; therefore, the pro-inflammatory CKs become dominant.
The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 are elevated in obesity. However, their concentrations are far below the limits for exhibiting their biological effects, with the exception of IL-6 [188,189,190,191,192]. Therefore, a deeper and more complex analysis of the processes and interactions of the CKs is required for a better understanding of the inflammatory balance in obesity.
TNF-α plays a major role in adipocyte apoptosis as well as in cellular signaling in obesity-induced inflammation. The production of TNF-α occurs mainly in macrophages, as well as adipocytes, neutrophils, and other immune and supportive cells. After its release, TNF-α subsequently favors the production of IL-6 and IL-1β via the MAPK and the NF-κB signaling pathways [128]. After binding to its receptor, TNFR1, TNF-α creates a receptor signaling complex named complex I [193]. Complex I favors the activation of genes for TNF-α and IL-6 [194,195]. TNF-α can also create complex II (also named “cell death complex”) that can induce apoptosis through the activation of caspase-3 [194,196,197].
In obesity, IL-1β is produced mainly after TLR4-mediated FFA activation of canonical inflammasomes, which is associated with increased expression of inflammation [194,198]. The adipocyte and macrophage production of IL-1β within the WAT contributes to the inflammation process and plays a role in the adipocyte–neutrophil interplay [199]. After its release, IL-1β contributes to vascular endothelial cell damage and other cardiovascular complications of diabetes [200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207]. The endothelial dysfunction may be modulated by local factors, vascular morphometry, diet, exercise, and other patient-related factors [208,209,210,211].
IL-6 is released by adipocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells and stimulates the production of CRP in the liver [168]. The plasmatic concentrations correlate with patient body weight (i.e., waist size, BMI) but also with FFA levels [212,213].
CRP acts as a marker of systemic inflammation and its levels show high sensitivity in obesity [128].
As previously mentioned, MCP-1 is responsible for macrophage recruitment and proliferation in obese AT [214,215]. MCP-1 is released by macrophages and endothelial cells and shows increased levels in obesity [216].
Another pro-inflammatory CK, IL-18, is activated through the NLRP1 inflammasome, increases the expression of additional pro-inflammatory CKs, and, overall, amplifies the inflammation associated with obesity [29,217].
5.3. Obesity and Adipokines
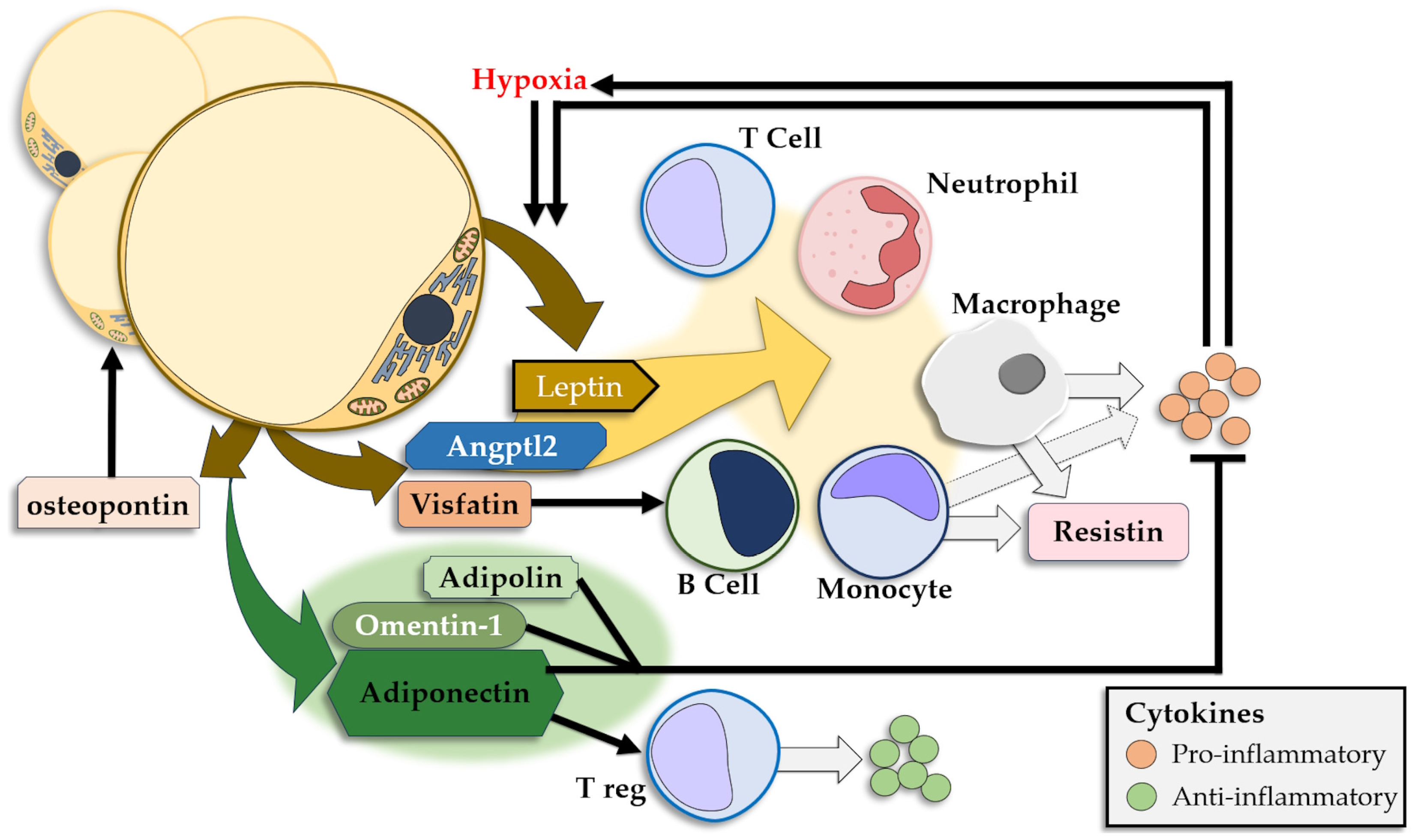
The WAT releases a large number of adipokines that either show anti-inflammatory effects or promote inflammation, and releases insulin resistance-inducing CKs [218,219] (Figure 3). Leptin and adiponectin are the most prominent adipokines and show significantly different plasmatic concentrations in obese individuals, with high levels of leptin and low levels of adiponectin [176,220]. Other adipokines modulate the signaling pathways in the AT as well as the cellular and CK interplay in local and systemic inflammation.
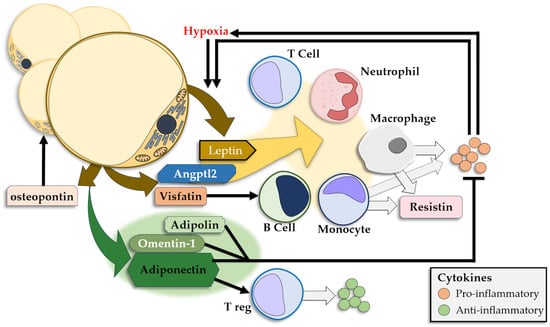
Figure 3.
Adipokines released by the adipose tissue and their pro-/anti-inflammatory effects.
Leptin regulates food intake and energy consumption, therefore playing a major role in the management of body weight [221,222]. With the development of fatty tissue, circulating levels of leptin increase [128]. Moreover, leptin is produced in significantly higher quantities in the SAT compared to the VAT due to a direct correlation with adipocyte size [223,224,225]. When circulating levels of leptin are reduced, the hypothalamus regains its sensitivity to leptin and subsequent limitation of weight gain ensues, alongside an increase in the sensitivity to insulin [226]. Leptin is part of a positive feedback loop, where, acting as a pro-inflammatory molecule, adipokine leads to increased expression of inflammatory mediators and hypoxia, leading to subsequent leptin expression in the AT [227,228,229,230].
Through its receptors, leptin modulates the activity of monocytes, macrophages, T and B cells, and neutrophils [231,232]. Following leptin stimulation, B cells stimulate monocyte proliferation, while T cells will show decreased apoptosis and increased proliferation and activity with polarization toward Th1 cells [215,233,234,235,236]. A concurrent increase in levels of pro-inflammatory CKs such as TNFα, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-12 and a corresponding decrease in levels of IL-4 and IL-10 is observed [234,237]. Furthermore, in neutrophils, leptin leads to enhanced ROS production, proliferation, and migration [238,239,240].
The leptin/adiponectin (L/A) ratio was proposed as a predictor of cardiometabolic events due to its identified correlation with metabolic syndrome, IR, and also with carotid intima media thickness [241,242,243,244]. A study on adolescents concluded that the L/A ratio is more accurate than adiponectin alone in identifying the risk of IR [244]. Moreover, the adiponectin/leptin (A/L) ratio is inversely related to the BMI [245] and to serum inflammatory markers such as CRP and serum amyloid A. An A/L ratio over 1 is considered normal, between 0.5 and 1 it indicates a moderate cardiovascular risk, and below 0.5 it is linked to a severe cardiovascular risk [246,247]. The A/L ratio increases with exercise due to the increase in adiponectin and concurrent decrease in leptin levels [248], and increases in diets associated with decreasing leptin levels such as fish or omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplements, or by fiber ingestion, accompanied by increases in adiponectin levels in all above-mentioned cases [249,250]. Statins also increase the A/L ratio, as shown in experimental studies [251]. The L/R ratio positively correlates with PCR levels and HOMA-IR, regardless of the presence of obesity or other metabolic risk factors in non-diabetic patients [252]. However, in obese patients, an inverse correlation between the L/A values and serum levels of soluble P-selectin was found [253,254]. Some authors consider that adiponectin and leptin, and consequently the L/A ratio, represent more accurate biomarkers for atherosclerosis than the traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, diabetes, or arterial hypertension [255,256].
Resistin is another adipokine with increased levels in obesity, albeit with a low correlation between plasma levels and the BMI or insulin resistance [168,257,258]. While mainly produced in monocytes and macrophages, resistin can also be produced in adipocytes, but only in mice [259]. The effects of resistin are an increase in the pro-inflammatory response in adipocytes and a TLR4-mediated release of pro-inflammatory CKs such as IL-1β, IL-2, and IL-6 from white blood cells [260].
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is produced by adipocytes, with higher levels in obesity, and regulates the cellular inflammatory response in the AT, mainly acting on monocytes and macrophages [261].
Visfatin is an adipocyte-produced growth factor for B-cell precursors and presents effects similar to insulin [262]. Its values increase in obesity, apparently reflecting the regulatory response to increased glycemia; however, highly increased levels reflect an increase in inflammation that may correlate with the development of type 2 diabetes, IR, and other metabolic dysfunctions [263].
Calprotectin also presents increased expression in obesity and regulates WAT inflammation by contributing to macrophage recruitment and monocyte infiltration [129,264].
Chemerin is another adipokine involved in inflammation and also plays a role in angiogenesis and adipogenesis [265]. The levels of chemerin correlate with the BMI, insulin resistance, and the risk of developing type 2 DM, as well as with liver markers of inflammation [265,266,267,268].
A pro-inflammatory adipokine, osteopontin, is expressed in adipocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, and other cells, and contributes to adipogenesis [222].
Released mainly by adipocytes, adiponectin shows decreased levels in obesity and AT inflammation [128,269]. With the most potent anti-inflammatory effect, adiponectin inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory CKs, like TNF-α and IL-6, while stimulating IL-10 release [128,270]. Adiponectin polarizes macrophages towards the M2 type, and decreases ROS production, monocyte adhesion, and endothelial cell activation [271,272,273,274].
Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 correlates inversely with pro-inflammatory CK production and macrophage expression in the AT [128].
While produced specifically by adipocytes, adipolin is downregulated in obesity and promotes anti-inflammatory CKs while inhibiting the pro-inflammatory response and macrophage accumulation [128,275].
Omentin-1 is a strong anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative adipokine produced in the stromal cells of the VAT [276]. It shows decreased expression and inverse correlation to the BMI and the waist size in obesity [222].
6. Regulation of AT Expansion and Interplay with Inflammation
The expansion of the AT during excessive caloric intake occurs either through the accumulation of triglycerides in adipocytes leading to hypertrophy or through the increase in differentiation of PAs into adipocytes, leading to hyperplasia. Apoptosis and autophagy regulate and limit the adipocyte expansion; however, when adipocytes are saturated with lipids, ectopic storage of fat can occur, with deposition of lipids in various regions outside the AT [277].
As previously mentioned, adipocyte hypertrophy is accompanied by an increased expression of MCP-1 leading to amplified macrophage recruitment and clustering in CLSs [235,278]. As a result, an NF-κB-mediated TNF-α secretion occurs alongside a release of macrophage-activating triglycerides [105,278,279]. Subsequently, insulin resistance develops via the downregulation of the IRS-1 pathway, leading to impaired glucose absorption into the AT [45,97,280,281,282].
With hypertrophy, an important adipocyte organoid and cell membrane dysfunction occurs, leading to an increased predisposition to apoptosis, inflammation, and hypoxia [283].
The hypertrophic adipocytes are skewed towards pro-inflammatory effects, with increased expression of CKs such as TNF-α and IL-6, while anti-inflammatory CKs and adipokines are downregulated [33,34,35]. Conversely, during hyperplasia, the smaller adipocytes contribute to a smaller degree to inflammation [284].
Furthermore, there is a fundamental relationship between inflammation and cardiometabolic obesity-related complications. Metabolically healthy obesity (MHO) is described in obese people who do not exhibit cardiometabolic abnormalities [285]. Interestingly, MHO is characterized by lower adipocyte size and lower infiltration of immune cells into fat deposits, as well as altered dynamics of adipokine secretion with lower levels of CRP but higher levels of neuroregulin and adiponectin [35,99,169].
One of the hallmarks of AT expansion is angiogenesis and both processes seem to negatively correlate with inflammation in MHO [11,286,287,288]. However, the development of hypoxia modulates the secretion of adipokines and increases the hypoxia-inducible factor 1a (HIF-1a) expression and, subsequently, the recruitment of monocytes into the AT [20,289,290,291]. The interplay between angiogenesis and hypoxia is extremely relevant due to the fact that the AT expansion limits vascular supply while increasing oxygen consumption, leading to hypoxia [99,289,290,292].
AT expansion is opposed by apoptosis and autophagy. Apoptosis in the WAT is mediated by caspase 8 and is a crucial part of the inflammatory cascade and development of insulin resistance in obesity [121,293]. Adipocyte apoptosis contributes to macrophage recruitment and infiltration in the AT and favors polarization towards type 2 macrophages which carry anti-inflammatory effects [194,294]. On the other hand, autophagy acts as a physiological limitation to exaggerated hyperplasia/hypertrophy and restricts the development of inflammatory processes [295].
7. Managing Weight Loss in Obesity-Associated Inflammation
The development of adipose tissue inflammation triggers subsequent cardiovascular events and therefore represents a major reason for the treatment of obesity. In this regard, with weight loss, fewer cardiovascular events and less inflammation are to be expected. However, an experimental study showed controversial results, i.e., a phasic response to weight loss; in the beginning, lipolysis led to an increase in ATMs with sustained inflammation, and only in the later stages did the number of ATMs decrease, with gradual extinguishing of the inflammatory processes [296]. Some studies on formerly obese people showed that inflammation in the AT may persist long after weight loss, which is in contrast to the inflammatory processes in the liver, for instance, where the inflammation and lipid storage decline immediately after weight loss [141].
Weight loss triggers early changes to the macrophage phenotypes, with a shift from the lipid-binding population that is prevalent in the obese AT to the phagocytosis-type population [297].
As mentioned above, attenuation of the WAT inflammation in obese individuals was expected to lead to corresponding decreases in cardiovascular risks and complications. However, recent research has reported mixed results.
A moderate weight loss, of 3 to 10% of body weight showed some health improvements; however, at least 10% is required for sustained clinically meaningful effects [298,299,300]. The arsenal for weight loss relies on a combination of caloric deficit nutrition and physical exercises; failure to attain optimal weight may be followed by pharmaceutical treatment, which can include one of the approved medications for clinical use [300,301,302]. Surgical interventions for weight loss are another viable option, especially considering that a significant proportion of individuals who have achieved the ideal weight through a diet and physical activity, alone or in combination, are unable to sustain their weight loss [303].
7.1. Dietary Interventions
The weight loss through diet is accompanied by an increased expression of genes stimulating adipogenesis, demonstrating that PA signaling and secretion are modulated by weight loss [304]. In dietary interventions applied to obese subjects, an evident decrease in obesity-related inflammatory markers (ORIMs) occurs when patients lose over 10% of their body mass, regardless of the type of diet [305,306,307,308].
7.2. Physical Activity
Physical activity contributes to a smaller extent to weight loss compared with dietary interventions; this phenomenon occurs due to the increase in fat-free mass [309]. Additionally, the impact on the ORIMs is lower in physical activity alone.
7.3. Combination of Diet and Physical Activity
Similarly to dietary interventions alone, at least a 10% body weight decrease is needed to observe significant decreases in the levels of ORIM [310,311,312]. Physical exercise with high intensity appears to favor macrophage polarization towards type 2, therefore leading to an anti-inflammatory dominance within the AT [270,313]. As the reduction in inflammation occurs with latency after weight loss, a sustained decrease in body mass is essential to obtain a favorable decrease in ORIM levels [314,315,316].
7.4. Surgical Interventions
In obesity, a variety of bariatric surgical procedures are available, such as fat removal, gastric restrictive surgery, gastric reduction, or gastric bypass. While the adipocyte number and mass are reduced through bariatric surgery, inflammation attenuation does not always occur. This is demonstrated by abdominal liposuction, a procedure that eliminates high quantities of SAT but is not accompanied by corresponding decreases in the levels of ORIMs [317]. Various procedures and techniques have been employed in bariatric surgery, involving robotic, needlescopic, and laparoscopic approaches, some adapted and extended from other fields [318,319,320,321,322,323]. Most surgical procedures are followed by a reduction in CRP and leptin, with increases in adiponectin levels. While decreases in CRP levels are reported after 3 months by numerous studies, TNF-α and IL-6 do not exhibit similar tendencies [324,325].
Bariatric surgery leads to a decrease in both pro-inflammatory macrophages and total macrophages and can also polarize the macrophage phenotype towards anti-inflammatory [326,327,328].
Neutrophil levels are also decreased after bariatric surgery-associated weight loss [329]. Moreover, decreases in CD4+ and CD8+ circulating T-cell levels are recorded after gastric sleeve in morbidly obese patients [330]. In patients with DM, gastric banding leads to a decrease in Th1 levels with no effects on the Th2 population [331,332]. ROS generation also diminishes after bariatric surgery-induced weight loss [328]. Additionally, gastric bypass leads to a decreased expression of pro-inflammatory genes [333].
Bariatric surgery also influences the ECM composition of the AT. Obesity is associated with increased collagen gene expression in the WAT which leads to high ORIM levels, increased inflammation, and insulin resistance [173,334,335,336,337]. The evaluation of genetic markers of the AT in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery showed that lytic enzymes are expressed in larger quantities in obesity, leading to the breakdown of the ECM, a phenomenon that may be alleviated several months after bariatric surgery [45,338].
Blocking or antagonizing the effects of pro-inflammatory CKs does not seem to be an effective way to counter the inflammation in obesity. Drugs inhibiting TNF-α do not seem effective, most likely due to low penetrance into the AT [20]. Conversely, anti-IL-1β antibodies show anti-inflammatory effects and can lead to a decrease in cardiovascular events, showing good promise in the management of atherosclerotic disease [339].
Nuclear factor erythroid2 p45-related factor 2 has a significant anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative role, however, attempts to increase its activation did not yield the expected results [10,340,341,342,343].
In some cases, rapid weight loss via bariatric surgery or extreme caloric restriction may have detrimental effects, such as the paradoxical increase in pro-inflammatory CKs [344,345]. However, among all the therapeutic methods described here, low-calorie dieting and gastric bypass surgery led to the most effective weight loss with the highest drops in ORIM levels [308].
8. Conclusions
The interplay between obesity and inflammation is complex and involves a variety of cellular and humoral factors. Macrophages are the main cellular component involved in the chronic inflammation of the obese adipose tissue and their modulation is instrumental in the interaction between the inflammatory and immune responses and can be a key factor in the medical intervention in obese patients. The development of adipose tissue inflammation triggers subsequent cardiovascular events and therefore represents a major reason for the treatment of obesity. There are a variety of options in the management of weight loss; however, it should be noted that due to the complexity and particular features of the adipose tissue, the inflammation within may persist for long periods of time, compared to the inflammatory processes in the liver, for instance, where the inflammation and lipid storage decline immediately after weight loss. Understanding the pathophysiological changes in the adipose tissue and the interplay with chronic inflammation can assist in the design of future studies and reveal opportunities for the development of more efficient therapies for obesity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.S.-F., C.C. and S.N.B.; formal analysis, R.M., S.D., C.S., A.C. and C.C.; resources, R.O.B., A.-E.S. and S.N.B.; data curation, I.S.-F., R.O.B., A.C., A.-E.S. and C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, I.S.-F., R.M., S.D., C.S., R.O.B., A.C., A.-E.S., C.C. and S.N.B.; writing—review and editing, I.S.-F., C.S., C.C. and S.N.B.; supervision, I.S.-F., C.S. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CCCDI—UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2021-2243, within PNCDI III.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Poirier, P.; Després, J.P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity: Clinical Challenges and Implications for Management. Circulation 2018, 137, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Draghici, C.; Ilie, M.A.; Lupu, M.; Solomon, I.; Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Caruntu, A.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; et al. Neuroendocrine Factors in Melanoma Pathogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.H.; Park, H.T.; Jeon, B.H.; Ha, M.S. Moderate intensity walking exercises reduce the body mass index and vascular inflammatory factors in postmenopausal women with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Inflammation of brown/beige adipose tissues in obesity and metabolic disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Mihai, L.G.; Bădărău, I.A.; Caruntu, C. Emerging applications of some important natural compounds in the field of oncology. Farmacia 2020, 68, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyala, S.; Neff, L.M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Holt, P.R. Diet-induced weight loss reduces colorectal inflammation: Implications for colorectal carcinogenesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, L.V.; Savova, M.S.; Amirova, K.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Georgiev, M.I. Obesity and NRF2-mediated cytoprotection: Where is the missing link? Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, P.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—A growing challenge. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pararasa, C.; Bailey, C.J.; Griffiths, H.R. Ageing, adipose tissue, fatty acids and inflammation. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, E.; Somers, V.K.; Sochor, O.; Goel, K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. The concept of normal weight obesity. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.M.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Emanuele, E.; Lucia, A.; Gálvez, B.G. ‘Adipaging’: Ageing and obesity share biological hallmarks related to a dysfunctional adipose tissue. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3187–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruntu, A.; Moraru, L.; Surcel, M.; Munteanu, A.; Costache, D.O.; Tanase, C.; Constantin, C.; Scheau, C.; Neagu, M.; Caruntu, C. Persistent Changes of Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Healthcare 2022, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Olefsky, J. Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.P.; Elliott, S.A.; Siervo, M.; Padwal, R.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A.; Prado, C.M. Is Obesity Associated with Altered Energy Expenditure? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Deyoung, S.M.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackey, D.E.; Olefsky, J.M. Regulation of metabolism by the innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G. Overview of adipose tissue and its role in obesity and metabolic disorders. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 456, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. Adipokines and the peripheral and neural control of energy balance. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvera, S. Cellular Heterogeneity in Adipose Tissues. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.R.; Côrtes, I.; Liechocki, S.; Carneiro, J.R.; Souza, A.A.; Borojevic, R.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Baptista, L.S. Characterization of stromal vascular fraction and adipose stem cells from subcutaneous, preperitoneal and visceral morbidly obese human adipose tissue depots. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G. Role of Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 7457269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronkite, D.A.; Strutt, T.M. The Regulation of Inflammation by Innate and Adaptive Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1467538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalding, K.L.; Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Bernard, S.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bergmann, O.; Blomqvist, L.; Hoffstedt, J.; Näslund, E.; Britton, T.; et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008, 453, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carobbio, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose Tissue Function and Expandability as Determinants of Lipotoxicity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 161–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caër, C.; Rouault, C.; Le Roy, T.; Poitou, C.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Torcivia, A.; Bichet, J.C.; Clément, K.; Guerre-Millo, M.; André, S. Immune cell-derived cytokines contribute to obesity-related inflammation, fibrogenesis and metabolic deregulation in human adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöting, N.; Blüher, M. Adipocyte dysfunction, inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, J.D.; Machkovech, H.M.; He, L.; Sidhu, R.; Fujiwara, H.; Weber, K.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Palmitate and lipopolysaccharide trigger synergistic ceramide production in primary macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yore, M.M.; Syed, I.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Zhang, T.; Herman, M.A.; Homan, E.A.; Patel, R.T.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; Peroni, O.D.; et al. Discovery of a class of endogenous mammalian lipids with anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. Cell 2014, 159, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, P.; Syed, I.; Lee, J.; Patel, R.; Nelson, A.T.; Siegel, D.; Saghatelian, A.; Kahn, B.B. Distinct biological activities of isomers from several families of branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs). J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, M.; Hill, M.A.; Cohen, P.; Sowers, J.R. Obesity, Adipose Tissue and Vascular Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lidell, M.E.; Orava, J.; Heglind, M.; Westergren, R.; Niemi, T.; Taittonen, M.; Laine, J.; Savisto, N.J.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, B.P.; Huang, S.; Brychta, R.J.; Duckworth, C.J.; Baskin, A.S.; McGehee, S.; Tal, I.; Dieckmann, W.; Gupta, G.; Kolodny, G.M.; et al. Mapping of human brown adipose tissue in lean and obese young men. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8649–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Hao, G.; Shao, M.; Nham, K.; An, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Kusminski, C.M.; Hassan, G.; Gupta, R.K.; et al. An Adipose Tissue Atlas: An Image-Guided Identification of Human-like BAT and Beige Depots in Rodents. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 252–262.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, T.; Palanisamy, S.; Kramer, D.J.; Eljalby, M.; Marx, S.J.; Wibmer, A.G.; Butler, S.D.; Jiang, C.S.; Vaughan, R.; Schöder, H.; et al. Brown adipose tissue is associated with cardiometabolic health. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Marken Lichtenbelt, W. Brown adipose tissue and the regulation of nonshivering thermogenesis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Farias, M.; Fos-Domenech, J.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L.; Sánchez-Infantes, D. White adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity and aging. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macotela, Y.; Emanuelli, B.; Mori, M.A.; Gesta, S.; Schulz, T.J.; Tseng, Y.H.; Kahn, C.R. Intrinsic differences in adipocyte precursor cells from different white fat depots. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A. Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: Emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 24, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, G. Leptin signalling. Cell. Signal. 2002, 14, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, S.N.; Heagerty, A.M.; Withers, S.B. Perivascular adipose tissue: An immune cell metropolis. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikakulapu, P.; Upadhye, A.; Rosenfeld, S.M.; Marshall, M.A.; McSkimming, C.; Hickman, A.W.; Mauldin, I.S.; Ailawadi, G.; Lopes, M.B.S.; Taylor, A.M.; et al. Perivascular Adipose Tissue Harbors Atheroprotective IgM-Producing B Cells. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikuni, N.; Lam, Q.L.; Lu, L.; Matarese, G.; La Cava, A. Leptin and Inflammation. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 4, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Structural and functional differences. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, V.A.; Carvalho, D.; Freitas, P. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Inflammation Answered in Questions. J. Obes. 2022, 2022, 2252516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.M.; Lihn, A.S.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release is higher in visceral than subcutaneous human adipose tissue (AT): Implication of macrophages resident in the AT. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedland, E.S. Role of a critical visceral adipose tissue threshold (CVATT) in metabolic syndrome: Implications for controlling dietary carbohydrates: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2004, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, P. Regional adipocity in man. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 155, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.; Azzimato, V.; Choudhury, R.P.; Aouadi, M. Extracellular vesicles in metabolic disease. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancello, R.; Tordjman, J.; Poitou, C.; Guilhem, G.; Bouillot, J.L.; Hugol, D.; Coussieu, C.; Basdevant, A.; Bar Hen, A.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Increased infiltration of macrophages in omental adipose tissue is associated with marked hepatic lesions in morbid human obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlev, A.; Aricha-Tamir, B.; Shaco-Levy, R.; Tarnovscki, T.; Bashan, N.; Rudich, A.; Sheiner, E.; Press, F.; Wiznitzer, A. Macrophage infiltration and stress-signaling in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue in diabetic pregnancies. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman-Boehm, I.; Blüher, M.; Redel, H.; Sion-Vardy, N.; Ovadia, S.; Avinoach, E.; Shai, I.; Klöting, N.; Stumvoll, M.; Bashan, N.; et al. Macrophage infiltration into omental versus subcutaneous fat across different populations: Effect of regional adiposity and the comorbidities of obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain-Godefroy, O.; Lecoeur, C.; Pattou, F.; Frühbeck, G.; Froguel, P. Inflammation is associated with a decrease of lipogenic factors in omental fat in women. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1–R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, C.; Foley, J.E.; Bogardus, C.; Tataranni, P.A.; Pratley, R.E. Enlarged subcutaneous abdominal adipocyte size, but not obesity itself, predicts type II diabetes independent of insulin resistance. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, A.W.; Yi, L.; Even, Y.; Vogl, A.W.; Rossi, F.M. Depot-specific differences in adipogenic progenitor abundance and proliferative response to high-fat diet. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrinelli, V.; Carobbio, S.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose tissue plasticity: How fat depots respond differently to pathophysiological cues. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mårin, P.; Lönn, L.; Andersson, B.; Odén, B.; Olbe, L.; Bengtsson, B.A.; Björntorp, P. Assimilation of triglycerides in subcutaneous and intraabdominal adipose tissues in vivo in men: Effects of testosterone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Dumesic, D.A.; Southorn, P.A.; Levine, J.A. Regional uptake of meal fatty acids in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E1282–E1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.Y.; Kady, J.; Nam, M.; Rojas-Rodriguez, R.; Berkenwald, A.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, H.L.; Kim, J.K.; Cooper, M.P.; Fitzgibbons, T.; et al. Human ‘brite/beige’ adipocytes develop from capillary networks, and their implantation improves metabolic homeostasis in mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollisch, K.S.; Brandauer, J.; Jessen, N.; Toyoda, T.; Nayer, A.; Hirshman, M.F.; Goodyear, L.J. Effects of exercise training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal- and high-fat diet-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E495–E504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.; Arch, J.R.; Ashwell, M. Brown adipose tissue in the parametrial fat pad of the mouse. FEBS Lett. 1984, 167, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.V.; Frassetto, A.; Kowalik, E.J., Jr.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Lu, M.M.; Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.A.; Szeto, D.; Yao, X.; Forrest, G.; et al. Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesmati, Z.; Rashid, M.; Fayezi, S.; Gieseler, F.; Alizadeh, E.; Darabi, M. An update on the secretory functions of brown, white, and beige adipose tissue: Towards therapeutic applications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, N.; Walden, T.B.; Shabalina, I.G.; Timmons, J.A.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Chronic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) activation of epididymally derived white adipocyte cultures reveals a population of thermogenically competent, UCP1-containing adipocytes molecularly distinct from classic brown adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7153–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adaptive thermogenesis in adipocytes: Is beige the new brown? Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown adipose tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L. Brown and Beige Adipose Tissues in Health and Disease. Compr Physiol 2017, 7, 1281–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, R.; Tanaka, M.; Itoh, M.; Suganami, T. Molecular mechanism of crosstalk between immune and metabolic systems in metabolic syndrome. Inflamm. Regen. 2022, 42, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzschaschel, M.; Friedl, T.W.P.; Schochter, F.; Schütze, S.; Polasik, A.; Fehm, T.; Pantel, K.; Schindlbeck, C.; Schneeweiss, A.; Schreier, J.; et al. Association Between Obesity and Circulating Tumor Cells in Early Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2023, 23, e345–e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, L.W.; Doerstling, S.S.; Shamsunder, M.G.; Lineberger, C.G.; Rossi, E.L.; Montgomery, S.A.; Coleman, M.F.; Gong, W.; Parker, J.S.; Howell, A.; et al. Reversing the Genomic, Epigenetic, and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-Enhancing Effects of Obesity. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila. Pa.) 2022, 15, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Matei, C.; Scheau, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Recent Advances in Signaling Pathways Comprehension as Carcinogenesis Triggers in Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, N.; Asada, R.; Saito, A.; Kanemoto, S.; Imaizumi, K. Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K.; Das, S.K.; Mondal, A.K.; Hackney, O.G.; Chu, W.S.; Kern, P.A.; Rasouli, N.; Spencer, H.J.; Yao-Borengasser, A.; Elbein, S.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers are associated with obesity in nondiabetic subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4532–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, M.E.; Weisberg, S.; Vardhana, P.; Tortoriello, D.V. Obesity in C57BL/6J mice is characterized by adipose tissue hypoxia and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, G.I.; Langley, K.G.; Berglund, N.A.; Kammoun, H.L.; Reibe, S.; Estevez, E.; Weir, J.; Mellett, N.A.; Pernes, G.; Conway, J.R.W.; et al. Evidence that TLR4 Is Not a Receptor for Saturated Fatty Acids but Mediates Lipid-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming Macrophage Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1096–1110.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Rotellar, F.; Valentí, V.; Silva, C.; Gil, M.J.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G. Increased tenascin C and Toll-like receptor 4 levels in visceral adipose tissue as a link between inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1880–E1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomalla, M.; Schmid, A.; Neumann, E.; Pfefferle, P.I.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schäffler, A.; Karrasch, T. Evidence of an anti-inflammatory toll-like receptor 9 (TLR 9) pathway in adipocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 240, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.S.; Harrison, D.J.; Kisielewski, D.; Cassidy, D.M.; McNeilly, A.D.; Gallagher, J.R.; Walsh, S.V.; Honda, T.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; et al. Experimental Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis Are Ameliorated by Pharmacologic Activation of Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-Related Factor 2). Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 367–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawans, P.; Behl, T.; Bhardwaj, S. Angiogenesis in obesity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.J.; White, T.A.; Evans, G.; Tonne, J.M.; Verzosa, G.C.; Stout, M.B.; Mazula, D.L.; Palmer, A.K.; Baker, D.J.; Jensen, M.D.; et al. Exercise Prevents Diet-Induced Cellular Senescence in Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrysse, L.; van Loo, G. Inflammation and the Metabolic Syndrome: The Tissue-Specific Functions of NF-κB. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könner, A.C.; Brüning, J.C. Selective insulin and leptin resistance in metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanti, J.F.; Ceppo, F.; Jager, J.; Berthou, F. Implication of inflammatory signaling pathways in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, G.; Pasalar, P.; Zare, M.; Rizzuto, R.; Meshkani, R. High glucose induces inflammatory responses in HepG2 cells via the oxidative stress-mediated activation of NF-κB, and MAPK pathways in HepG2 cells. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Lee, J. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardo, D.; Latz, E. NLRP3 inflammasomes link inflammation and metabolic disease. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Zhou, R.; Tschopp, J. The NLRP3 inflammasome: A sensor for metabolic danger? Science 2010, 327, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.K.; Wen, H.; Ting, J.P. The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Han, B.Z.; Su, D.F.; Liu, C. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Yuan, M. Inflammation and the IKKβ/IκB/NF-κB axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, S49–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fang, Z.; Linghu, K.G.; Liu, J.; Gan, L.; Lin, L. Small molecule-driven SIRT3-autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition ameliorates inflammatory crosstalk between macrophages and adipocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4645–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Ramírez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces adipose tissue inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, M.; Yang, K.; Hansen, S.H.; Louwe, M.C.; Kummen, M.; Hov, J.E.R.; Sjaastad, I.; Berge, R.K.; Halvorsen, B.; Aukrust, P.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome deficiency attenuates metabolic disturbances involving alterations in the gut microbial profile in mice exposed to high fat diet. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.M.; Faulenbach, M.; Vaag, A.; Vølund, A.; Ehses, J.A.; Seifert, B.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Donath, M.Y. Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, O.; Brownell, S.E.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Salomon, D.; Gram, H.; Bartfai, T. Treatment with an Interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity. Cytokine 2008, 44, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, N.S.; Schulthess, F.T.; Galasso, R.; Castellani, L.W.; Maedler, K. The antiinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protects from high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Oh, D.; Imamura, T.; Johnson, A.M.F.; Sears, D.; Shen, Z.; Cui, B.; et al. Hematopoietic-Derived Galectin-3 Causes Cellular and Systemic Insulin Resistance. Cell 2016, 167, 973–984.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschuren, L.; Kooistra, T.; Bernhagen, J.; Voshol, P.J.; Ouwens, D.M.; van Erk, M.; de Vries-van der Weij, J.; Leng, L.; van Bockel, J.H.; van Dijk, K.W.; et al. MIF deficiency reduces chronic inflammation in white adipose tissue and impairs the development of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and associated atherosclerotic disease. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M.; Witte, D.R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Davey Smith, G.; Cooper, J.A.; Miller, M.; Lowe, G.D.; Rumley, A.; Casas, J.P.; et al. Inflammation, insulin resistance, and diabetes--Mendelian randomization using CRP haplotypes points upstream. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Tian, X.; Zhai, X.; Sun, C. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Obesity: A Link to Posttranslational Modification. Immunol. Investig. 2023, 52, 635–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.H.; Li, D.Y.; Liang, S.; Yang, C.; Tang, J.X.; Liu, H.F. Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 946832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Nguyen, K.D.; Goh, Y.P. Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorisky, A.; Magun, R.; Gagnon, A.M. Adipose cell apoptosis: Death in the energy depot. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24 (Suppl. 4), S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouri, N.; Gornicka, A.; Berk, M.P.; Thapaliya, S.; Dixon, L.J.; Kashyap, S.; Schauer, P.R.; Feldstein, A.E. Adipocyte apoptosis, a link between obesity, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3428–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Kim, M.S.; Pae, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Eberlé, D.; Shimada, T.; Kamei, N.; Park, H.S.; Sasorith, S.; Woo, J.R.; et al. Adipose Natural Killer Cells Regulate Adipose Tissue Macrophages to Promote Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkhelawon, B.; Hennessy, E.J.; Ménager, M.; Ray, T.D.; Sheedy, F.J.; Hutchison, S.; Wanschel, A.; Oldebeken, S.; Geoffrion, M.; Spiro, W.; et al. Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, S.U.; Cohen, J.L.; Vangala, P.; Tencerova, M.; Nicoloro, S.M.; Yawe, J.C.; Shen, Y.; Czech, M.P.; Aouadi, M. Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagareddy, P.R.; Kraakman, M.; Masters, S.L.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Gorman, D.J.; Grant, R.W.; Dragoljevic, D.; Hong, E.S.; Abdel-Latif, A.; Smyth, S.S.; et al. Adipose tissue macrophages promote myelopoiesis and monocytosis in obesity. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Oh, D.Y.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Lagakos, W.S.; Talukdar, S.; Osborn, O.; Johnson, A.; Chung, H.; Maris, M.; Ofrecio, J.M.; et al. LTB4 promotes insulin resistance in obese mice by acting on macrophages, hepatocytes and myocytes. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardelli, M.; Zeyda, K.; Moreno-Viedma, V.; Wanko, B.; Grün, N.G.; Staffler, G.; Zeyda, M.; Stulnig, T.M. Osteopontin is a key player for local adipose tissue macrophage proliferation in obesity. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemniak-Wojtowicz, D.; Kucharska, A.M.; Pyrżak, B. Obesity and chronic inflammation crosslinking. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 45, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Rotellar, F.; Valentí, V.; Silva, C.; Gil, M.J.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Salvador, J.; et al. Increased levels of calprotectin in obesity are related to macrophage content: Impact on inflammation and effect of weight loss. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrchen, J.M.; Sunderkötter, C.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J. The endogenous Toll-like receptor 4 agonist S100A8/S100A9 (calprotectin) as innate amplifier of infection, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manitz, M.P.; Horst, B.; Seeliger, S.; Strey, A.; Skryabin, B.V.; Gunzer, M.; Frings, W.; Schönlau, F.; Roth, J.; Sorg, C.; et al. Loss of S100A9 (MRP14) results in reduced interleukin-8-induced CD11b surface expression, a polarized microfilament system, and diminished responsiveness to chemoattractants in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubzick, C.V.; Randolph, G.J.; Henson, P.M. Monocyte differentiation and antigen-presenting functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.A.; Lim, H.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Ho, W.Y.; Foong, Y.H.; Nelson, V.L.; Nguyen, H.C.B.; Chegireddy, K.; Kim, J.; Habertheuer, A.; et al. Distinct macrophage populations direct inflammatory versus physiological changes in adipose tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5096–E5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, S.J.; Ruckerl, D.; Cook, P.C.; Jones, L.H.; Finkelman, F.D.; van Rooijen, N.; MacDonald, A.S.; Allen, J.E. Local macrophage proliferation, rather than recruitment from the blood, is a signature of TH2 inflammation. Science 2011, 332, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, J.; Weyer, U.; Immig, K.; Klöting, N.; Blüher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Local proliferation of macrophages in adipose tissue during obesity-induced inflammation. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kang, B.; Suh, H.J.; Choi, H.S. Parthenolide, a feverfew-derived phytochemical, ameliorates obesity and obesity-induced inflammatory responses via the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 145, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A.B. Adipocyte-Macrophage Cross-Talk in Obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganami, T.; Nishida, J.; Ogawa, Y. A paracrine loop between adipocytes and macrophages aggravates inflammatory changes: Role of free fatty acids and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganami, T.; Tanimoto-Koyama, K.; Nishida, J.; Itoh, M.; Yuan, X.; Mizuarai, S.; Kotani, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Miyake, K.; Aoe, S.; et al. Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goforth, M.H.; Morel, C.R.; Subramanian, V.; Mukundan, L.; Red Eagle, A.; Vats, D.; Brombacher, F.; Ferrante, A.W.; et al. Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature 2007, 447, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caslin, H.L.; Bhanot, M.; Bolus, W.R.; Hasty, A.H. Adipose tissue macrophages: Unique polarization and bioenergetics in obesity. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.; Lumeng, C.N. Properties and functions of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity. Immunology 2018, 155, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, M.; Coats, B.R.; Hisert, K.B.; Hagman, D.; Mutskov, V.; Peris, E.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Kuzma, J.N.; Larson, I.; Billing, P.S.; et al. Metabolic dysfunction drives a mechanistically distinct proinflammatory phenotype in adipose tissue macrophages. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.E.; Ko, M.S.; Yun, J.Y.; Kim, M.O.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.J.; Ahn, Y.E.; et al. Nitric Oxide Produced by Macrophages Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation and Promotes Profibrogenic Responses in Preadipocytes to Induce Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2516–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y. Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species on Insulin Resistance in Adipose Tissue. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Kishton, R.J.; Rathmell, J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadl, A.; Meher, A.K.; Sharma, P.R.; Lee, M.Y.; Doran, A.C.; Johnstone, S.R.; Elliott, M.R.; Gruber, F.; Han, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Identification of a novel macrophage phenotype that develops in response to atherogenic phospholipids via Nrf2. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmerie, A.; Scott, C.L. Macrophages and lipid metabolism. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 330, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Grijalva, A.; Skowronski, A.; van Eijk, M.; Serlie, M.J.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity activates a program of lysosomal-dependent lipid metabolism in adipose tissue macrophages independently of classic activation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Usui, I.; Bukhari, A.; Ikutani, M.; Oya, T.; Kanatani, Y.; Tsuneyama, K.; Nagai, Y.; Takatsu, K.; Urakaze, M.; et al. Regulatory mechanisms for adipose tissue M1 and M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2574–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Thaiss, C.A.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammasomes and metabolic disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Evans, G.F.; Alfaro, M.L.; Zuckerman, S.H. Down-regulation of macrophage CD9 expression by interferon-gamma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, M.; Woods, N.B.; de Luca, C.; Schenk, S.; Lu, J.C.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Verma, I.M.; Olefsky, J.M. Hematopoietic cell-specific deletion of toll-like receptor 4 ameliorates hepatic and adipose tissue insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Bikman, B.T.; Wang, L.P.; Yuguang, G.; Sargent, K.M.; Bulchand, S.; Knotts, T.A.; Shui, G.; Clegg, D.J.; Wenk, M.R.; et al. Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, J.S.; Puglisi, M.J.; Ellacott, K.L.; Lumeng, C.N.; Wasserman, D.H.; Hasty, A.H. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency promotes the alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Holland, W.L.; Wang, Q.A.; Shao, M.; Jia, L.; Sun, K.; Lin, X.; Kuo, Y.C.; Johnson, J.A.; Gordillo, R.; et al. Short-Term Versus Long-Term Effects of Adipocyte Toll-Like Receptor 4 Activation on Insulin Resistance in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils Actively Contribute to Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Pathological Complications. Cells 2022, 11, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, Z.; Gomez-Salazar, M.; Alexaki, V.I. Innate Immune Cells in the Adipose Tissue in Health and Metabolic Disease. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Oh, D.Y.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Li, D.; Xu, J.; McNelis, J.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, H.; Lynch, L. Innate Immune Control of Adipose Tissue Homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynan, G.A.; Hearnden, C.H.; Oleszycka, E.; Lyons, C.L.; Coutts, G.; O’Connell, J.; Corrigan, M.A.; Lynch, L.; Campbell, M.; Callanan, J.J.; et al. Endogenous oils derived from human adipocytes are potent adjuvants that promote IL-1α-dependent inflammation. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2037–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruun, J.M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Regulation of interleukin 8 production and gene expression in human adipose tissue in vitro. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, K.; Froguel, P.; Wolowczuk, I. Adipose tissue in obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance: Cells, cytokines, and chemokines. ISRN Inflamm 2013, 2013, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, J.W.; Goldberg, I.J. Myeloperoxidase: A therapeutic target for preventing insulin resistance and the metabolic sequelae of obesity? Diabetes 2014, 63, 4001–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, H.; Meng, Y.; He, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W. Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgazar-Carmon, V.; Rudich, A.; Hadad, N.; Levy, R. Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat early in the course of high-fat feeding. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.C.d.; Silveira, A.L.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.C.; Lana, J.P.; Costa, K.A.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Pinho, V.; Teixeira, M.M.; Merabtene, F.; Marcelin, G.; et al. Eosinophils protect from metabolic alterations triggered by obesity. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2023, 146, 155613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophils and Th2 immunity: Contemporary insights. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, D.A.; Winer, S.; Shen, L.; Wadia, P.P.; Yantha, J.; Paltser, G.; Tsui, H.; Wu, P.; Davidson, M.G.; Alonso, M.N.; et al. B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Wollam, J.; Olefsky, J.M. An Integrated View of Immunometabolism. Cell 2018, 172, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M.; Halaas, J.; Ravussin, E.; Pratley, R.E.; Lee, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, H.; Kim, S.; Lallone, R.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, G.; Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Horvath, T.L.; La Cava, A. Regulatory T cells in obesity: The leptin connection. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Romero, M.; Diaz, A.; Blomberg, B.B. Obesity accelerates age defects in B cells, and weight loss improves B cell function. Immun. Ageing 2023, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Nagasaki, M.; Eto, K.; Yamashita, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Otsu, M.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Sugiura, S.; et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, S.; Chan, Y.; Paltser, G.; Truong, D.; Tsui, H.; Bahrami, J.; Dorfman, R.; Wang, Y.; Zielenski, J.; Mastronardi, F.; et al. Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Divoux, A.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Clément, K.; Glickman, J.N.; Sukhova, G.K.; Wolters, P.J.; Du, J.; Gorgun, C.Z.; et al. Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Ji, Y.; Kersten, S.; Qi, L. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses in obese adipose tissue. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żelechowska, P.; Agier, J.; Kozłowska, E.; Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E. Mast cells participate in chronic low-grade inflammation within adipose tissue. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agueda-Oyarzabal, M.; Emanuelli, B. Immune Cells in Thermogenic Adipose Depots: The Essential but Complex Relationship. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 839360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhshandehroo, M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Boes, M. Invariant natural killer T cells in adipose tissue: Novel regulators of immune-mediated metabolic disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4711–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, J.M.; Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is accompanied by a loss of insulin receptor substrate-1 and GLUT4 expression without a loss of insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, S.; Zhou, Q.; Shaik-Dasthagirisaheb, Y.; Leeman, S. Diet-induced obesity in mice causes changes in immune responses and bone loss manifested by bacterial challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20466–20471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, F.C.; Harford, K.A.; Reynolds, C.M.; Oliver, E.; Claessens, M.; Mills, K.H.; Roche, H.M. Lack of interleukin-1 receptor I (IL-1RI) protects mice from high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation coincident with improved glucose homeostasis. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.L.; Steinberg, G.R.; Macaulay, S.L.; Thomas, W.G.; Holmes, A.G.; Ramm, G.; Prelovsek, O.; Hohnen-Behrens, C.; Watt, M.J.; James, D.E.; et al. Interleukin-6 increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckhauser, S.; Elias, I.; Rotter Sopasakis, V.; Ferré, T.; Nagaev, I.; Andersson, C.X.; Agudo, J.; Ruberte, J.; Bosch, F.; Smith, U. Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondelinger, Y.; Darding, M.; Bertrand, M.J.; Walczak, H. Poly-ubiquitination in TNFR1-mediated necroptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell death and inflammation during obesity: “Know my methods, WAT(son)”. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annibaldi, A.; Meier, P. Checkpoints in TNF-Induced Cell Death: Implications in Inflammation and Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, N.; Walczak, H. Cell Death and Inflammation—A Vital but Dangerous Liaison. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H. Death receptor-ligand systems in cancer, cell death, and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell 2014, 157, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Honda, H.; Okamoto, N.; Yanagibashi, T.; Ogasawara, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Imamura, R.; Takasaki, I.; Hara, H.; et al. Bidirectional crosstalk between neutrophils and adipocytes promotes adipose tissue inflammation. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11821–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Smith, D.E. The IL-1 family: Regulators of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Bongaerts, B.W.; Rathmann, W.; Heier, M.; Kowall, B.; Koenig, W.; Thorand, B.; Roden, M.; Meisinger, C.; Ziegler, D. Association of subclinical inflammation with polyneuropathy in the older population: KORA F4 study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herder, C.; Dalmas, E.; Böni-Schnetzler, M.; Donath, M.Y. The IL-1 Pathway in Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Complications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.K.; Kant, S. Targeting inflammation in diabetes: Newer therapeutic options. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahel, M.; Becker, M.; Graf, N.; Michels, S. Systemic Interleukin 1β Inhibition in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: A Prospective Open-Label Study Using Canakinumab. Retina 2016, 36, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Targeting innate immune mediators in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, E.; Salaices, M. Cytokines and vascular reactivity in resistance arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1016–H1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkin, P.N.; Jain, N.; Miller, Y.I.; Rissing, B.A.; Huo, Y.; Keller, S.R.; Vandenhoff, G.E.; Nadler, J.L.; McIntyre, T.M. Insulin and glucose play a role in foam cell formation and function. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2006, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woo, K.S.; Chook, P.; Yu, C.W.; Sung, R.Y.; Qiao, M.; Leung, S.S.; Lam, C.W.; Metreweli, C.; Celermajer, D.S. Effects of diet and exercise on obesity-related vascular dysfunction in children. Circulation 2004, 109, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, R.A.; Scheau, C.; Niscoveanu, C.; Bordei, P. Morphometry of the Entire Internal Carotid Artery on CT Angiography. Medicina 2021, 57, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Z.T.; Akins, J.D.; Merlau, E.R.; Kolade, J.O.; Al-Daas, I.O.; Cardenas, N.; Vu, J.K.; Brown, K.K.; Brothers, R.M. The acute effect of whole-body heat therapy on peripheral and cerebral vascular reactivity in Black and White females. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 148, 104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climie, R.E.; Alastruey, J.; Mayer, C.C.; Schwarz, A.; Laucyte-Cibulskiene, A.; Voicehovska, J.; Bianchini, E.; Bruno, R.M.; Charlton, P.H.; Grillo, A.; et al. Vascular ageing: Moving from bench towards bedside. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pou, K.M.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Vasan, R.S.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Larson, M.G.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Meigs, J.B.; Lipinska, I.; Kathiresan, S.; et al. Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes are cross-sectionally related to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopasakis, V.R.; Sandqvist, M.; Gustafson, B.; Hammarstedt, A.; Schmelz, M.; Yang, X.; Jansson, P.A.; Smith, U. High local concentrations and effects on differentiation implicate interleukin-6 as a paracrine regulator. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremer, A.A.; Devaraj, S.; Afify, A.; Jialal, I. Adipose tissue dysregulation in patients with metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1782–E1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.B. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Park, H.S.; Kawada, T.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, D.; Hubbard, N.E.; Kwon, B.S.; Erickson, K.L.; Yu, R. Circulating levels of MCP-1 and IL-8 are elevated in human obese subjects and associated with obesity-related parameters. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.J.; Kraakman, M.J.; Kammoun, H.L.; Dragoljevic, D.; Lee, M.K.; Lawlor, K.E.; Wentworth, J.M.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Gerlic, M.; Whitehead, L.W.; et al. IL-18 Production from the NLRP1 Inflammasome Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, F.; Dieguez, C.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as emerging mediators of immune response and inflammation. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Marino, M.W.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 1997, 389, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruzábal, F.J.; Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Archanco, M.; Burrell, M.A. Immunocytochemical detection of leptin in non-mammalian vertebrate stomach. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 128, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landecho, M.F.; Tuero, C.; Valentí, V.; Bilbao, I.; de la Higuera, M.; Frühbeck, G. Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Harmelen, V.; Reynisdottir, S.; Eriksson, P.; Thörne, A.; Hoffstedt, J.; Lönnqvist, F.; Arner, P. Leptin secretion from subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in women. Diabetes 1998, 47, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, E.; Stuppy, A.; Harig, F.; Carbon, R.; Horbach, T.; Stöhr, W.; Rascher, W.; Dötsch, J. Comparison of leptin gene expression in different adipose tissues in children and adults. Eur. J. Endocrinol. Eur. Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2004, 150, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Russell, C.D.; Petersen, R.N.; Rao, S.P.; Ricci, M.R.; Prasad, A.; Zhang, Y.; Brolin, R.E.; Fried, S.K. Leptin expression in adipose tissue from obese humans: Depot-specific regulation by insulin and dexamethasone. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, E507–E515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaszczak, A.M.; Jalilvand, A.; Hsueh, W.A. Adipocytes, Innate Immunity and Obesity: A Mini-Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 650768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; Campos-Cabaleiro, V.; Ruiz-Fernández, C.; Mera, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gómez, R.; Gualillo, O. Obesity, Fat Mass and Immune System: Role for Leptin. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunfeld, C.; Zhao, C.; Fuller, J.; Pollack, A.; Moser, A.; Friedman, J.; Feingold, K.R. Endotoxin and cytokines induce expression of leptin, the ob gene product, in hamsters. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2152–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosfeld, A.; Andre, J.; Hauguel-De Mouzon, S.; Berra, E.; Pouyssegur, J.; Guerre-Millo, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 transactivates the human leptin gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42953–42957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Guo, K.; Cremona, M.L.; McGraw, T.E.; Leibel, R.L.; Zhang, Y. TNF-α up-regulates protein level and cell surface expression of the leptin receptor by stimulating its export via a PKC-dependent mechanism. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5821–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Riejos, P.; Najib, S.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Martín-Romero, C.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; González-Yanes, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 568343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Osei, S.Y. Leptin signaling. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 81, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cava, A. Leptin in inflammation and autoimmunity. Cytokine 2017, 98, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoleone, E.A.D.I.S.; Amore, C.; Baccante, G.; di Febbo, C.; Porreca, E.; de Gaetano, G.; Donati, M.B.; Lorenzet, R. Leptin induces tissue factor expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: A possible link between obesity and cardiovascular risk? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Vilariño-García, T.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Inflammation and Vice Versa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, B.; Straface, E.; Quaranta, M.G.; Giordani, L.; Viora, M. Leptin promotes differentiation and survival of human dendritic cells and licenses them for Th1 priming. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6820–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin enhances activation and proliferation of human circulating T lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 199, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Poulin, A.; Tridon, A.; Sion, B.; Vasson, M.P. Leptin: A potential regulator of polymorphonuclear neutrophil bactericidal action? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, A.; Conus, S.b.; Schmid, I.s.; Simon, H.-U. Apoptotic pathways are inhibited by leptin receptor activation in neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 8090–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottonello, L.; Gnerre, P.; Bertolotto, M.; Mancini, M.; Dapino, P.; Russo, R.; Garibotto, G.; Barreca, T.; Dallegri, F. Leptin as a uremic toxin interferes with neutrophil chemotaxis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jaramillo, P.; Gómez-Arbeláez, D.; López-López, J.; López-López, C.; Martínez-Ortega, J.; Gómez-Rodríguez, A.; Triana-Cubillos, S. The role of leptin/adiponectin ratio in metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2014, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, N.; Imamura, S.; Fujita, T.; Uchida, Y.; Inagaki, K.; Kakizawa, H.; Hayakawa, N.; Suzuki, A.; Takeda, J.; Horikawa, Y.; et al. The ratio of leptin to adiponectin can be used as an index of insulin resistance. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2008, 57, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norata, G.D.; Raselli, S.; Grigore, L.; Garlaschelli, K.; Dozio, E.; Magni, P.; Catapano, A.L. Leptin:adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of intima media thickness of the common carotid artery. Stroke 2007, 38, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Vicente, S.; Norkiene, S.; Rauckienė-Michaelsson, A.; Kievisienė, J.; Dubey, V.P.; Razbadauskas, A.; Lopes, L.; Santos, R. Is the Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio a Better Diagnostic Biomarker for Insulin Resistance than Leptin or Adiponectin Alone in Adolescents? Children 2022, 9, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.R.; Yoo, S.J.; Hong, O.K.; Son, H.S.; Chang, S.A. The relationship between adipokines, metabolic parameters and insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, Leptin and Cardiovascular Disorders. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görgens, S.W.; Eckardt, K.; Jensen, J.; Drevon, C.A.; Eckel, J. Exercise and Regulation of Adipokine and Myokine Production. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 135, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Neilson, H.K.; Woolcott, C.G.; McTiernan, A.; Wang, Q.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Jones, C.A.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Brant, R.F.; Yasui, Y.; et al. Changes in insulin resistance indicators, IGFs, and adipokines in a year-long trial of aerobic exercise in postmenopausal women. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.M.; de Almeida, J.C.; Feoli, A.M. Effect of diet on adiponectin levels in blood. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Morimoto, N.; Kawai, H.; Ohta, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Abe, K. Atorvastatin and pitavastatin reduce oxidative stress and improve IR/LDL-R signals in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2013, 35, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.H.; Hsu, L.A.; Wu, S.; Teng, M.S.; Sun, Y.C.; Ko, Y.L. Leptin-to-Adiponectin Ratio is Related to Low Grade Inflammation and Insulin Resistance Independent of Obesity in Non-Diabetic Taiwanese: A Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. Acta Cardiol Sin 2014, 30, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salah, A.; Ragab, M.; Mansour, W.; Taher, M. Leptin and adiponectin are valuable serum markers explaining obesity/bronchial asthma interrelationship. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2015, 64, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pergola, G.; Pannacciulli, N.; Coviello, M.; Scarangella, A.; Di Roma, P.; Caringella, M.; Venneri, M.T.; Quaranta, M.; Giorgino, R. sP-selectin plasma levels in obesity: Association with insulin resistance and related metabolic and prothrombotic factors. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, F.M.; Luan, J.; Wareham, N.J.; Sharp, S.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Balkau, B.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Walker, M.; Højlund, K.; Nolan, J.J.; et al. Correlation of the leptin:adiponectin ratio with measures of insulin resistance in non-diabetic individuals. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 2345–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, K.; Sakane, N. Leptin:adiponectin ratio and metabolic syndrome in the general Japanese population. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2011, 31, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Tong, J.; Wallace, T.M.; Hull, R.L.; Zraika, S.; Xiao, Q.; Mistry, J.S.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; et al. Resistin is not associated with insulin sensitivity or the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2330–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vozarova de Courten, B.; Degawa-Yamauchi, M.; Considine, R.V.; Tataranni, P.A. High serum resistin is associated with an increase in adiposity but not a worsening of insulin resistance in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarese, G.; Moschos, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in immunology. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokarewa, M.; Nagaev, I.; Dahlberg, L.; Smith, U.; Tarkowski, A. Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5789–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Kadomatsu, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyata, K.; Ito, Y.; Endo, M.; Urano, T.; Zhu, H.J.; Tsukano, H.; Tazume, H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue inflammation and obesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.M.; Bochner, B.S. Eosinophil survival and apoptosis in health and disease. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.M.I. Role of visfatin in obesity-induced insulin resistance. World J Clin Cases 2022, 10, 10840–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, O.H.; Nielsen, A.R.; Erikstrup, C.; Plomgaard, P.; Fischer, C.P.; Krogh-Madsen, R.; Lindegaard, B.; Petersen, A.M.; Taudorf, S.; Pedersen, B.K. Calprotectin--a novel marker of obesity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, G.; Wu, Q.F. Chemerin: A multifaceted adipokine involved in metabolic disorders. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, R79–R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, K.B.; McCarthy, T.C.; Hanniman, E.A.; Zabel, B.A.; Butcher, E.C.; Parlee, S.D.; Muruganandan, S.; Sinal, C.J. Chemerin, a novel adipokine that regulates adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28175–28188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozaoglu, K.; Segal, D.; Shields, K.A.; Cummings, N.; Curran, J.E.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Mahaney, M.C.; Rainwater, D.L.; VandeBerg, J.L.; MacCluer, J.W.; et al. Chemerin is associated with metabolic syndrome phenotypes in a Mexican-American population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3085–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, H.; Divoux, A.; Poitou, C.; Basdevant, A.; Bouillot, J.L.; Bedossa, P.; Tordjman, J.; Eckel, J.; Clément, K. Chemerin correlates with markers for fatty liver in morbidly obese patients and strongly decreases after weight loss induced by bariatric surgery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2892–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Shibazaki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nagai, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T. Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, M. Adiponectin: A versatile player of innate immunity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikaris, K.A. The clinical biochemistry of obesity. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 25, 165–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, K.; Parker, J.L.; Ouchi, N.; Higuchi, A.; Vita, J.A.; Gokce, N.; Pedersen, A.A.; Kalthoff, C.; Tullin, S.; Sams, A.; et al. Adiponectin promotes macrophage polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6153–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastel, E.; Joshi, S.; Knight, B.; Liversedge, N.; Ward, R.; Kos, K. Effects of Exendin-4 on human adipose tissue inflammation and ECM remodelling. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ohlsson, C.; Hammarstedt, A.; Vandenput, L.; Saarinen, N.; Ryberg, H.; Windahl, S.H.; Farman, H.H.; Jansson, J.O.; Movérare-Skrtic, S.; Smith, U.; et al. Increased adipose tissue aromatase activity improves insulin sensitivity and reduces adipose tissue inflammation in male mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 313, E450–E462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Ohashi, K.; Shibata, R.; Murohara, T. Adipocytokines and obesity-linked disorders. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Ye, D.D. The potential of adipokines as biomarkers and therapeutic agents for vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 48, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J. Impaired adipose tissue expandability and lipogenic capacities as ones of the main causes of metabolic disorders. J Diabetes Res 2015, 2015, 970375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Suganami, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Takeya, M.; Kamei, Y.; Ogawa, Y. Role of MAPK phosphatase-1 in the induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 during the course of adipocyte hypertrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25445–25452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Krämer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin resistance associated to obesity: The link TNF-alpha. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verboven, K.; Wouters, K.; Gaens, K.; Hansen, D.; Bijnen, M.; Wetzels, S.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Goossens, G.H.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Blaak, E.E.; et al. Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipocyte size, lipolysis and inflammation relate to insulin resistance in male obese humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 461s–465s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, S.; Saarinen, L.; Naukkarinen, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Frühbeck, G.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E.; et al. Adipocyte morphology and implications for metabolic derangements in acquired obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, N.B.; Schneider, S.H.; Berchtold, P. The “metabolically-obese,” normal-weight individual. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, A.; Orjalo, A.V.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: Causes and consequences. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, S.; Queguiner, I.; Msika, S.; Calderari, S.; Rufat, P.; Gasc, J.M.; Corvol, P.; Larger, E. Angiogenesis associated with visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue in severe human obesity. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Khan, T.; Trujillo, M.E.; Wernstedt-Asterholm, I.; Attie, A.D.; Sherwani, S.; Wang, Z.V.; Landskroner-Eiger, S.; Dineen, S.; Magalang, U.J.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha induces fibrosis and insulin resistance in white adipose tissue. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4467–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, R.W.; White, A.E.; Metcalf, M.D.; Olivas, A.S.; Mitra, P.; Larison, W.G.; Cheang, E.C.; Varlamov, O.; Corless, C.L.; Roberts, C.T., Jr.; et al. Hypoxia-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion in human adipose tissue stromovascular cells. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Trujillo, M.E.; Combs, T.P.; Iyengar, P.; Jelicks, L.; Roth, K.A.; Kitsis, R.N.; Scherer, P.E. Fat apoptosis through targeted activation of caspase 8: A new mouse model of inducible and reversible lipoatrophy. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Wang, Q.A.; Asterholm, I.W.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Scherer, P.E. Targeted deletion of adipocytes by apoptosis leads to adipose tissue recruitment of alternatively activated M2 macrophages. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhat, M.; Funai, K.; Boudina, S. Autophagy in Adipose Tissue Physiology and Pathophysiology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosteli, A.; Sugaru, E.; Haemmerle, G.; Martin, J.F.; Lei, J.; Zechner, R.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Weight loss and lipolysis promote a dynamic immune response in murine adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3466–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitin, D.A.; Adlung, L.; Thaiss, C.A.; Weiner, A.; Li, B.; Descamps, H.; Lundgren, P.; Bleriot, C.; Liu, Z.; Deczkowska, A.; et al. Lipid-Associated Macrophages Control Metabolic Homeostasis in a Trem2-Dependent Manner. Cell 2019, 178, 686–698.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrani, A.A.; Morton, J. Benefits of weight loss of 10% or more in patients with overweight or obesity: A review. Obesity 2022, 30, 802–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Frühbeck, G.; Ryan, D.H.; Wilding, J.P. Management of obesity. Lancet 2016, 387, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Pandey, A.; Chandar, A.K.; Murad, M.H.; Prokop, L.J.; Neeland, I.J.; Berry, J.D.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S. Effects of Weight-Loss Medications on Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1309–1319.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, G.; Apovian, C. Future Pharmacotherapy for Obesity: New Anti-obesity Drugs on the Horizon. Curr Obes Rep 2018, 7, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look AHEAD Research Group. Eight-year weight losses with an intensive lifestyle intervention: The look AHEAD study. Obesity 2014, 22, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossmeislová, L.; Malisová, L.; Kracmerová, J.; Tencerová, M.; Kovácová, Z.; Koc, M.; Siklová-Vítková, M.; Viquerie, N.; Langin, D.; Stich, V. Weight loss improves the adipogenic capacity of human preadipocytes and modulates their secretory profile. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougoulia, M.; Triantos, A.; Koliakos, G. Effect of weight loss with or without orlistat treatment on adipocytokines, inflammation, and oxidative markers in obese women. Hormones 2006, 5, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raitakari, M.; Ilvonen, T.; Ahotupa, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Harmoinen, A.; Suominen, P.; Elo, J.; Hartiala, J.; Raitakari, O.T. Weight reduction with very-low-caloric diet and endothelial function in overweight adults: Role of plasma glucose. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.A.; Swain, J.; Goldfine, A.B.; Rifai, N.; Ludwig, D.S. Effects of a low-glycemic load diet on resting energy expenditure and heart disease risk factors during weight loss. JAMA 2004, 292, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, L.K.; Wallace, J.M.; Livingstone, M.B. Obesity and inflammation: The effects of weight loss. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2008, 21, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballor, D.L.; Poehlman, E.T. Exercise-training enhances fat-free mass preservation during diet-induced weight loss: A meta-analytical finding. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1994, 18, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Church, T.S.; Willis, M.S.; Priest, E.L.; Lamonte, M.J.; Earnest, C.P.; Wilkinson, W.J.; Wilson, D.A.; Giroir, B.P. Obesity, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, and weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, F.; Di Palo, C.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; D’Andrea, F.; D’Armiento, M.; Giugliano, D. Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004, 291, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Desmond, R.; Hunter, G.; Gower, B. Baseline inflammatory markers do not modulate the lipid response to weight loss. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2008, 57, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baek, K.-W.; Lee, D.-I.; Kang, S.A.; Yu, H.S. Differences in macrophage polarization in the adipose tissue of obese mice under various levels of exercise intensity. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 76, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, P.; Nordby, P.; Bendtsen, L.Q.; Mehlsen, J.L.; Basnet, S.K.; Vestergaard, H.; Ploug, T.; Stallknecht, B. Differential effects of endurance training and weight loss on plasma adiponectin multimers and adipose tissue macrophages in younger, moderately overweight men. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R490–R498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancello, R.; Henegar, C.; Viguerie, N.; Taleb, S.; Poitou, C.; Rouault, C.; Coupaye, M.; Pelloux, V.; Hugol, D.; Bouillot, J.L.; et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčiková, M.; Sengenes, C.; Kováčová, Z.; Šiklová-Vítková, M.; Klimčáková, E.; Polák, J.; Rossmeislová, L.; Bajzová, M.; Hejnová, J.; Hněvkovská, Z.; et al. Dietary intervention-induced weight loss decreases macrophage content in adipose tissue of obese women. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Fontana, L.; Young, V.L.; Coggan, A.R.; Kilo, C.; Patterson, B.W.; Mohammed, B.S. Absence of an effect of liposuction on insulin action and risk factors for coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvholm, K.; Janson, A.; Peltonen, M.; Neovius, M.; Gronowitz, E.; Engström, M.; Laurenius, A.; Beamish, A.J.; Dahlgren, J.; Sjögren, L.; et al. Metabolic and bariatric surgery versus intensive non-surgical treatment for adolescents with severe obesity (AMOS2): A multicentre, randomised, controlled trial in Sweden. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2023, 7, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juo, Y.Y.; Park, C.; Yoo, J.; Guerron, D.; Sudan, R.; Friedman, K.; Portenier, D.; Seymour, K.A. Technical Feasibility, Outcomes, and Patient Satisfaction After Needlescopic and Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery: A Randomized Study. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 5085–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, O.M.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, J.C.; Ser, K.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.C. Revisional Gastric Bypass for Failed Restrictive Procedures: Comparison of Single-Anastomosis (Mini-) and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holländer, S.W.; Klingen, H.J.; Hess, S.; Merscher, A.; Glanemann, M.; Birk, D. Benefits of Robotic Camera Assistance in Minimally Invasive Bariatric Procedures: Prospective Clinical Trial Using a Joystick-Guided Camera-Holder. Surg. Technol. Int. 2019, 34, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dragosloveanu, S.; Petre, M.-A.; Capitanu, B.S.; Dragosloveanu, C.D.M.; Cergan, R.; Scheau, C. Initial Learning Curve for Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Dedicated Orthopedics Center. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, B.R.; Mohr, C.J.; Morton, J.M.; Safadi, B.Y.; Alami, R.S.; Curet, M.J. Comparison of totally robotic laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and traditional laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2005, 1, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askarpour, M.; Khani, D.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Alizadeh, S. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Inflammatory Factors of Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2631–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, G.; Nicoletti, G.; Grella, E.; Giugliano, F.; Esposito, K.; Scuderi, N.; D’Andrea, F. Effect of liposuction on insulin resistance and vascular inflammatory markers in obese women. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2004, 57, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasselin, J.; Magne, E.; Beau, C.; Ledaguenel, P.; Dexpert, S.; Aubert, A.; Layé, S.; Capuron, L. Adipose inflammation in obesity: Relationship with circulating levels of inflammatory markers and association with surgery-induced weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E53–E61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, J.; Laforest, S.; Michaud, A.; Biertho, L.; Tchernof, A. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on White Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Calderón, J.R.; Cuéllar, R.X.; Ramos-González, M.R.; Rubio-Infante, N.; Castillo, E.C.; Elizondo-Montemayor, L.; García-Rivas, G. Interplay between the Adaptive Immune System and Insulin Resistance in Weight Loss Induced by Bariatric Surgery. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3940739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rubio, J.; León, J.; Redruello-Romero, A.; Pavón, E.; Cozar, A.; Tamayo, F.; Caba-Molina, M.; Salmerón, J.; Carazo, Á. Cytometric analysis of adipose tissue reveals increments of adipocyte progenitor cells after weight loss induced by bariatric surgery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathy, S.M.; Morshed, G. Peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets (CD4+, CD8+ T cells), leptin level and weight loss after laparoscopic greater curvature plication in morbidly obese patients. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viardot, A.; Lord, R.V.; Samaras, K. The effects of weight loss and gastric banding on the innate and adaptive immune system in type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaras, K.; Viardot, A.; Botelho, N.K.; Jenkins, A.; Lord, R.V. Immune cell-mediated inflammation and the early improvements in glucose metabolism after gastric banding surgery. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reggio, S.; Rouault, C.; Poitou, C.; Bichet, J.C.; Prifti, E.; Bouillot, J.L.; Rizkalla, S.; Lacasa, D.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K. Increased Basement Membrane Components in Adipose Tissue During Obesity: Links With TGFβ and Metabolic Phenotypes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasarica, M.; Gowronska-Kozak, B.; Burk, D.; Remedios, I.; Hymel, D.; Gimble, J.; Ravussin, E.; Bray, G.A.; Smith, S.R. Adipose tissue collagen VI in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5155–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankel, S.N.; Svärd, J.; Matthä, S.; Claussnitzer, M.; Klöting, N.; Glunk, V.; Fandalyuk, Z.; Grytten, E.; Solsvik, M.H.; Nielsen, H.J.; et al. COL6A3 expression in adipocytes associates with insulin resistance and depends on PPARγ and adipocyte size. Obesity 2014, 22, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Muise, E.S.; Iyengar, P.; Wang, Z.V.; Chandalia, M.; Abate, N.; Zhang, B.B.; Bonaldo, P.; Chua, S.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: Role of collagen VI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henegar, C.; Tordjman, J.; Achard, V.; Lacasa, D.; Cremer, I.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Poitou, C.; Basdevant, A.; Stich, V.; Viguerie, N.; et al. Adipose tissue transcriptomic signature highlights the pathological relevance of extracellular matrix in human obesity. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Rangasamy, T.; Reddy, S.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Biswal, S. Nrf2 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during experimental sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.H.; Suzuki, T.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sekine, H.; Tanaka, N.; Moriguchi, T.; Motohashi, H.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Surcel, M.; Munteanu, A.; Scheau, C.; Savulescu-Fiedler, I.; Caruntu, C. Diabetic neuropathy: A NRF2 disease? J. Diabetes 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capel, F.; Klimcáková, E.; Viguerie, N.; Roussel, B.; Vítková, M.; Kováciková, M.; Polák, J.; Kovácová, Z.; Galitzky, J.; Maoret, J.J.; et al. Macrophages and adipocytes in human obesity: Adipose tissue gene expression and insulin sensitivity during calorie restriction and weight stabilization. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, D.K.; Larson, I.; Kuzma, J.N.; Cromer, G.; Makar, K.; Rubinow, K.B.; Foster-Schubert, K.E.; van Yserloo, B.; Billing, P.S.; Landerholm, R.W.; et al. The short-term and long-term effects of bariatric/metabolic surgery on subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation in humans. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 70, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).