Mental Manifestations and Biomarkers of Alcohol Consumption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
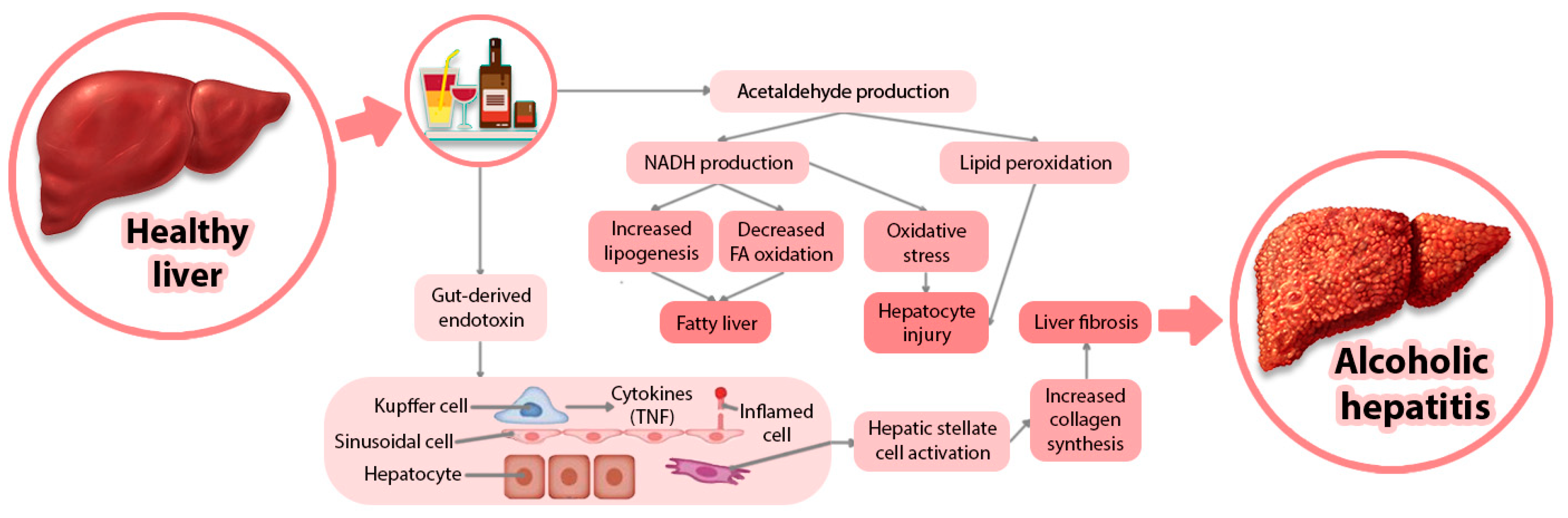
3. Alcohol-Related Disorders and Health Complications
4. Biomarkers
5. Mental Manifestations
6. Discussions
7. Future Research Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Settertobulte, W.; Jensen, B.; Hurrelmann, K. Drinking among young Europeans. In Proceedings of the WHO European Ministerial Conference on Young People and Alcohol Stockholm, Stockholm, Sweden, 19–21 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hannuksela, M.L.; Liisanantti, M.K.; Nissinen, A.E.; Savolainen, M.J. Biochemical markers of alcoholism. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, A. Biological markers in alcoholism. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2003, 66, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Javors, M.A.; Johnson, B.A. Current status of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin, total serum sialic acid, sialic acid index of apolipoprotein J, and serum beta-hexosaminidase as markers for alcohol consumption. Addiction 2003, 98, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orley, J.; Logan, D. Perspectives on Partnerships for corporate social responsibility in the beverage alcohol industry. In Cor-porate Social Responsibility and Alcohol; Marcus, G., O’Connor, J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Babor, T.F.; Higgins-Biddle, J.C.; Saunders, J.B.; Monteiro, M.G. Audit the alcohol use disorder identification test. In Guidelines for Use in Primary Care, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sheron, N.; Moore, M.; O’Brien, W.; Harris, S.; Roderick, P. Feasibility of detection and intervention for alcohol-related liver disease in the community: The alcohol and liver disease detection study (alddes). Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2013, 63, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westwood, G.; Meredith, P.; Atkins, S.; Greengross, P.; Schmidt, P.E.; Aspinall, R.J. Universal screening for alcohol misuse in acute medical admissions is feasible and identifies patients at high risk of liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.S.; Nielsen, B.; Søgaard, J.; Søgaard, N.A. Making a bridge between general hospital and specialised community-based treatment for alcohol use disorder—A pragmatic randomized controlled trial. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 196, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Taylor, B.; Mohapatra, S.; Irving, H.; Baliunas, D.; Patra, J.; Roerecke, M. Alcohol as a risk factor for liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2010, 29, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelbach, W.K. Liver damage in chronic alcoholism. Results of a clinical, clinical-chemical and bioptic-histological study in 526 alcoholic patients during a low-calorie diet in an open drinking sanatorium. Acta Hepatosplenol. 1966, 13, 321–349. [Google Scholar]
- Lelbach, W.K. Cirrhosis in the alcoholic and its relation to the volume of alcohol abuse. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1975, 252, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, U. Epidemiology and risk factors in alcohol liver disease. In Comprehensive Handbook of Alcohol-Related Pathology; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2005; pp. 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Askgaard, G.; Kjaer, M.S.; Tolstrup, J.S. Opportunities to Prevent Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis in High risk Populations: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 114, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askgaard, G.; Tolstrup, J.; Leon, D. A measure of alcohol consumption in late adolescence associated with liver disease after 39 years of follow-up is insufficient to guide alcohol safe limits. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrom, H.; Hemmingsson, T.; Discacciati, A.; Andreasson, A. Reply to: “A measure of alcohol consumption in late adolescence associated with liver disease after 39 years of follow-up is insufficient to guide alcohol safe limits”. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Hemmingsson, T.; Andreasson, A. Overweight in late adolescence predicts development of severe liver disease later in life: A 39 years follow-up study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Askgaard, G.; Gronbaek, M.; Kjaer, M.S.; Tjønneland, A.; Tolstrup, J.S. Alcohol drinking pattern and risk of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Balkwill, A.; Roddam, A.; Brown, A.; Beral, V.; on behalf of the million women study Collaborators. Separate and joint effects of alcohol and smoking on the risks of cirrhosis and gallbladder disease in middle-aged women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 169, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Sherliker, P.; Cai, Y.; Peto, R.; Wang, L.; Millwood, I.; Smith, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; et al. Alcohol drinking and overall and cause-specific mortality in China: Nationally representative prospective study of 220,000 men with 15 years of follow-up. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plourde, G. Biomarkers in health product development: Commentary. Int. J. Drug Saf. 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sillanaukee, P.; Massot, N.; Jousilahti, P.; Vartiainen, E.; Sundvall, J.; Olsson, U.; Poikolainen, K.; Pönniö, M.; Allen, J.P.; Alho, H. Dose response of laboratory markers to alcohol consumption in a general population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conigrave, K.M.; Davies, P.; Haber, P.; Whitfield, J.B. Traditional markers of excessive alcohol use. Addiction 2003, 98, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litten, R.Z.; Allen, J.P. Measuring Alcohol Consumption; Totowa, N.J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rosman, A.S.; Lieber, C.S. Biochemical markers of alcohol consumption. Alcohol Res. Health 1990, 14, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, P.C. Biochemical detection and monitoring of alcohol abuse and abstinence. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Biochem. Lab. Med. 2001, 38, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibler, H. Carbohydrate-deficient transferrin in serum: A new marker of potentially harmful alcohol consumption reviewed. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemela, O. Biomarkers in alcoholism. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.; Spies, C. Use of biomarkers for alcohol use disorders in clinical practice. Addiction 2003, 98, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borucki, K.; Schreiner, R.; Dierkes, J.; Jachau, K.; Krause, D.; Westphal, S.; Wurst, F.M.; Luley, C.; Schmidt-Gayk, H. Detection of recent ethanol intake with new markers: Comparison of fatty acid ethyl esters in serum and of ethyl glucuronide and the Ratio of 5-hydroxytryptophol to 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid in urine. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cylwik, B.; Chrostek, L.; Szmitkowski, M. New methods for the determination of transferrin isoforms in the diagnostics of alcohol abuse. Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej 2006, 60, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savola, O.; Niemelä, O.; Hillbom, M. Blood alcohol is the best indicator of hazardous alcohol drinking in young adults and working-age patients with trauma. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszkiewicz, N.; Pawłowicz, K.; Okuniewska, N.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Zalewski, D.; Wilczyńska, K.; Szulc, A.; Galińska-Skok, B.; Konarzewska, B.; Maciejczyk, M.; et al. Salivary Carbohydrate-Deficient Transferrin in Alcohol- and Nicotine-Dependent Males. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K. Biomarkers for alcohol use and abuse—A summary. Alcohol. Res. Health 2004, 28, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wurst, F.M.; Alexson, S.; Wolfersdorf, M.; Bechtel, G.; Forster, S.; Alling, C.; Aradóttir, S.; Jachau, K.; Huber, P.; Allen, J.P.; et al. Concentration of fatty acid ethyl esters in hair of al-coholics: Comparison to other biological state markers and self-reported-ethanol intake. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, K.M.; Cluette-Brown, J.E.; Dube, D.M.; Bernhardt, T.G.; Morse, C.R.; Laposata, M. Fatty acid ethyl esters in the blood as markers for ethanol intake. JAMA 1996, 276, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borucki, K.; Dierkes, J.; Wartberg, J.; Westphal, S.; Genz, A.; Luley, C. In heavy drinkers, fatty acid ethyl esters remain elevated for up to 99 hours. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borucki, K.; Kunstmann, S.; Dierkes, J.; Westphal, S.; Diekmann, S.; Bogerts, B.; Luley, C. In heavy drinkers fatty acid ethyl esters in the serum are increased for 44 hr after ethanol consumption. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragst, F.; Yegles, M. Determination of fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) and ethyl glucuronide (EtG) in hair: A promising way for retrospective detection of alcohol abuse during pregnancy? Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurst, F.M.; Metzger, J.; Marques, P.; Wiesbeck, A.G. On sensitivity, specificity, and the influence of various parameters on ethyl glucuronide levels in urine- results from the WHO/ISBRA study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 34A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M.; Roache, J.D.; Karns-Wright, T.E.; Lopez-Cruzan, M.; Javors, M.A. Chapter 58—Phosphatidylethanol homologs in blood as biomarkers for the time frame and amount of recent alcohol consumption. In Neuroscience of Alcohol; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 567–576. ISBN 9780128131251. [Google Scholar]
- Viel, G.; Boscolo-Berto, R.; Cecchetto, G.; Fais, P.; Nalesso, A.; Ferrara, S.D. Phosphatidylethanol in blood as a marker of chronic alcohol use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14788–14812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawiah, K.D.; Riley, S.B.; Budelier, M.M. Biomarkers and clinical laboratory detection of acute and chronic ethanol use. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnann, H.; Weinmann, W.; Thierauf, A. Formation of phosphatidylethanol and its subsequent elimination during an extensive drinking experiment over 5 days. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröck, A.; Thierauf-Emberger, A.; Schürch, S.; Weinmann, W. Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) detected in blood for 3 to 12 days after single consumption of alcohol—A drinking study with 16 volunteers. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2016, 131, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javors, M.A.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Roache, J.D.; Karns-Wright, T.E.; Dougherty, D.M. Characterization of the pharmacokinetics of phosphatidylethanol 16:0/18:1 and 16:0/18:2 in human whole blood after alcohol consumption in a clinical laboratory study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisfield, G.M.; Teitelbaum, S.A.; Large, S.O.; Jones, J.; Morrison, D.G.; Lewis, B. The roles of phosphatidylethanol (PEth), ethyl glucuronide (EtG), and ethyl sulfate (EtS) in identifying alcohol consumption among participants in professionals’ health programs. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhireva, L.N.; Savich, R.D.; Raisch, D.W.; Cano, S.; Annett, R.D.; Leeman, L.; Garg, M.; Goff, C.; Savage, D.D. The feasibility and cost of neonatal screening for prenatal alcohol exposure by measuring phosphatidylethanol in dried blood spots. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M.; Roache, J.D.; Karns-Wright, T.E.; Javors, M.A. Differences in the synthesis and elimination of phosphatidylethanol 16:0/18:1 and 16:0/18:2 after acute doses of alcohol. Acoholism Clin. Land Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, A.; Böttcher, M.; Dahmen, N.; Beck, O. Elimination Characteristics of the alcohol biomarker phosphatidylethanol (PEth) in blood during alcohol detoxification. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, N.; Strnad, P.; Bantel, H.; Omary, M.B. Keratins: Biomarkers and modulators of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in the liver. Hepatology 2016, 64, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Bridges, B.W.; Dunn, W.; Olson, J.C.; Weinman, S.A.; Jaeschke, H. Cell death and prognosis of mortality in alcoholic hepatitis patients using plasma Keratin-18. Gene Expr. 2017, 17, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuckit, M.A. Treatment of anxiety in patients who abuse alcohol and drugs. In Handbook of Anxiety; Noyes, R., Roth, M., Burros, G.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette, J.; Altamirano, J.; Devue, C.; Roux, O.; Payancé, A.; Lebrec, D.; Bedossa, P.; Valla, D.; Durand, F.; Ait-Oufella, H.; et al. A prospective study of the utility of plasma biomarkers to diagnose alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszkiewicz, N.; Popławska, R.; Konarzewska, B.; Szajda, S.D.; Galińska, B.; Rutkowski, P.; Leśniak, R.; Szulc, A. Biomarkers of alcohol abuse. Part II. New biomarkers and their interpretation. Psychiatr. Pol. 2010, 44, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Waszkiewicz, N.; Szajda, S.D.; Jankowska, A.; Kępka, A.; Dobryniewski, J.; Szulc, A.; Zwierz, K. The Effect of the Binge Drinking Session on the Activity of Salivary, Serum and Urinary -Hexosaminidase: Preliminary Data. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008, 43, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, J.; Room, R.; Monteiro, M. Alcohol use. In Comparative Quantification of Health Risks; Ezzati, M., Lopez, A., Rodgers, A., Murray, C., Eds.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 959–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Soyka, M.; Helten, B.; Cleves, M.; Schmidt, P. High rehospitalization rate in alcohol-induced psychotic disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 263, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jesse, S.; Bråthen, G.; Ferrara, M.; Keindl, M.; Ben-Menachem, E.; Tanasescu, R.; Brodtkorb, E.; Hillbom, M.; Leone, M.; Ludolph, A. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome: Mechanisms, manifestations, and management. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2016, 135, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasser, C.; Geller, A.; Howell, E.; Wartenberg, A. Detoxification: Principles and Protocols. American Society of Addiction Medicine. Available online: http://www.asam.org/pub1/detoxification.htm (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Tsuang, J.W.; Irwin, M.R.; Smith, T.L.; Schuckit, M.A. Characteristics of men with alcoholic hallucinosis. Addiction 1994, 89, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyka, M. Prevalence of alcohol-induced psychotic disorders. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 258, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perälä, J.; Kuoppasalmi, K.; Pirkola, S.; Härkänen, T.; Saarni, S.; Tuulio-Henriksson, A.; Viertiö, S.; Latvala, A.; Koskinen, S.; Lönnqvist, J.; et al. Alcohol-induced psychotic disorder and delirium in the general population. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 197, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, C.P.; Touquet, G.; Tansens, A.; De Fruyt, J. Alcohol-induced psychotic disorder: A systematic literature review. Tijdschr. Voor Psychiatr. 2015, 57, 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Irwin, M.; Brown, S. The history of anxiety symptoms among 171 primary alcoholics. J. Stud. Alcohol 1990, 51, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Sayette, M.A. Anxiety and the development of alcoholism. Am. J. Addict. 1993, 2, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.; Irwin, M.; Schuckit, M. Changes in anxiety among abstinent male alcoholics. J. Stud. Alcohol 1991, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karounos, M. Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome in the Elderly; University of North Carolina-Rex Hospital: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Winkleby, M.A. Sociodemographic, psychiatric and somatic risk factors for suicide: A Swedish national cohort study. Psychol. Med. 2013, 44, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2014; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, H.S.; Fenger-Gron, M.; Bech, B.H.; Erlangsen, A.; Vestergaard, M. Frequency of health care utilization in the year before completed suicide: A Danish nationwide matched comparative study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214605. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmedani, B.K.; Simon, G.E.; Stewart, C.; Beck, A.; Waitzfelder, B.E.; Rossom, R.; Lynch, F.; Owen-Smith, A.; Hunkeler, E.M.; Whiteside, U.; et al. Health care contacts in the year before suicide death. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kang, D.R.; Moon, K.T.; Suh, M.; Ha, K.H.; Kim, C.; Suh, I.; Shin, D.C.; Jung, S.H. Age and gender differences in medical care utilization prior to suicide. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 146, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.; Saini, P.; Da Cruz, D.; Miles, C.; While, D.; Swinson, N.; Williams, A.; Shaw, J.; Appleby, L.; Kapur, N. Primary care contact prior to suicide in individuals with mental illness. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2009, 59, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, U.A.; Andersen, M.; Rosholm, J.U.; Gram, L.F. Contacts to the health care system prior to suicide: A comprehensive analysis using registers for general and psychiatric hospital admissions, contacts to general practitioners and practising specialists and drug prescriptions. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2000, 102, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, E.; Shelef, L.; Mann, J.; Portugese, S.; Krivoy, A.; Shoval, G.; Weiser, M.; Fruchter, E. EPA-0233—Primary health care utilization prior to suicide: A retrospective case-control study among active-duty military personnel. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgen, M.A.; Conner, K.R.; Roeder, K.M.; Blow, F.C.; Austin, K.; Valenstein, M. Patterns of treatment utilization before suicide among male veterans with substance use disorders. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, S88–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.; Cruz-Lemini, M.; Altamirano, J.; Ndugga, N.; Couper, D.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bataller, R. Heavy daily alcohol intake at the population level predicts the weight of alcohol in cirrhosis burden worldwide. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, H.; Morling, J.; Aspinall, E.; Goldberg, D.; Hutchinson, S.; Guha, I. Late diagnosis of chronic liver disease in a community cohort (UK biobank): Determinants and impact on subsequent survival. Public Health 2020, 187, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, A.; Gheorge, C.; Dumitrascu, D.; Diculescu, M.; Gheorghe, I.; Sporea, I.; Tantau, M.; Ciurea, T. Gastroenterologie si Hepatologie Clinica; Altex Edition: Kreuzlingen, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 973-39-0943-9. [Google Scholar]
- Udell, J.A.; Wang, C.S.; Tinmouth, J.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ayas, N.T.; Simel, D.L.; Schulzer, M.; Mak, E.; Yoshida, E.M. Does this patient with liver disease have cirrhosis? JAMA 2012, 307, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silczuk, A.; Habrat, B. Alcohol-induced thrombocytopenia: Current review. Alcohol 2020, 86, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaspuro, M. Biological State Markers of Alcohol Abuse. Alcohol. Health Res. World 1994, 18, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, J.; Magnusson, P.H. Comparison between different methods of detecting patients with excesiv consumption of alcohol. Acta Medica Scand. 1988, 223, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, B.; Shaw, S.; Cleary, P.; Delbanco, T.L.; Aronson, M.D. Screening for alcohol abuse using the cage questionnaire. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, R.K.; Lee, K.K.; Gordis, E. Validity of Self-Report in Alcoholism Research: Results of a Veterans Administration Cooperative Study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1988, 12, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanopol, I.A.; Baroiu, L.; Neagu, A.I.; Danila, D.M.; Nechifor, A.; Miulescu, M.; Balan, G.; Vasile, C.I.; Niculet, E.; Tatu, A.L. Aspecte clinice, imagistice, histologice și chirurgicale privind chisturile paraovariene gigantice: O revizuire sistematică. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemel, O. Biomarker-based approaches for assessing alcohol use disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbrock, M.N.; Meyer, R.E.; Keener, J.J. Psychopathology in hospitalized alcoholics. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1985, 42, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helzer, J.E.; Pryzbeck, T.R. The co-occurrence of alcoholism with other psychiatric disorders in the general population and its impact on treatment. J. Stud. Alcohol 1988, 49, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, M.M.; Myers, J.K.; Harding, P.S. Prevalence and psychiatric heterogeneity of alcoholism in an urban community in the United States. J. Stud. Alcohol 1980, 41, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudose, F.; Tudose, C.; Dobranici, L. Tratat de Psihopatologie si Psihiatrie Pentru Psihologi; Editura Trei: Bucharest, Romania, 2011; Volume 3, ISBN 978-973-707. [Google Scholar]
| CRITERIA | SIGNIFICANCE |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | or validity; the correlation between the cases distinguished of the marker and the truly positive cases |
| Precision | or confidence; the ability of the marker to identify the cases that are truly positive in a heterogeneous population |
| Sensitivity | the proportion of patients without alcoholism that come out positive |
| Specificity | the proportion of patients without alcoholism that come out positive |
| Stability | the marker must persist at least a few days after stopping drinking and return to normal after a reasonable period |
| Practicability | the ease of obtaining biological evidence from which to check the presence of the marker |
| Disponibility | the ease with which the identifying of the marker can be performed |
| Low cost | the cost of the materials, the method and techniques, and the lab |
| Transportability | the ease of implementing of the technique in different, appropriate places |
| Non-invasive | the sampling of the biological evidence in which you can detect the marker must be as least invasive as possible for the organism |
| Acceptability | the desire of the patients to use this technique, and the desire to submit themselves to this test |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarpe, A.-M.; Dodul, C.; Vlase, E.-A.; Onișor, C.; Niculet, E.; Ciobotaru, O.C.; Drima, E.P. Mental Manifestations and Biomarkers of Alcohol Consumption. Life 2024, 14, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070873
Sarpe A-M, Dodul C, Vlase E-A, Onișor C, Niculet E, Ciobotaru OC, Drima EP. Mental Manifestations and Biomarkers of Alcohol Consumption. Life. 2024; 14(7):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070873
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarpe (Paduraru), Ana-Maria, Cristina Dodul, Emil-Andrei Vlase, Cristian Onișor, Elena Niculet, Octavian Catalin Ciobotaru, and Eduard Polea Drima. 2024. "Mental Manifestations and Biomarkers of Alcohol Consumption" Life 14, no. 7: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070873
APA StyleSarpe, A.-M., Dodul, C., Vlase, E.-A., Onișor, C., Niculet, E., Ciobotaru, O. C., & Drima, E. P. (2024). Mental Manifestations and Biomarkers of Alcohol Consumption. Life, 14(7), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070873







