Acute Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with High-Load Resistance Exercises on Repetitive Vertical Jump Performance and EEG Characteristics in Healthy Men
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Human Ethics and Consent to Participate Declarations
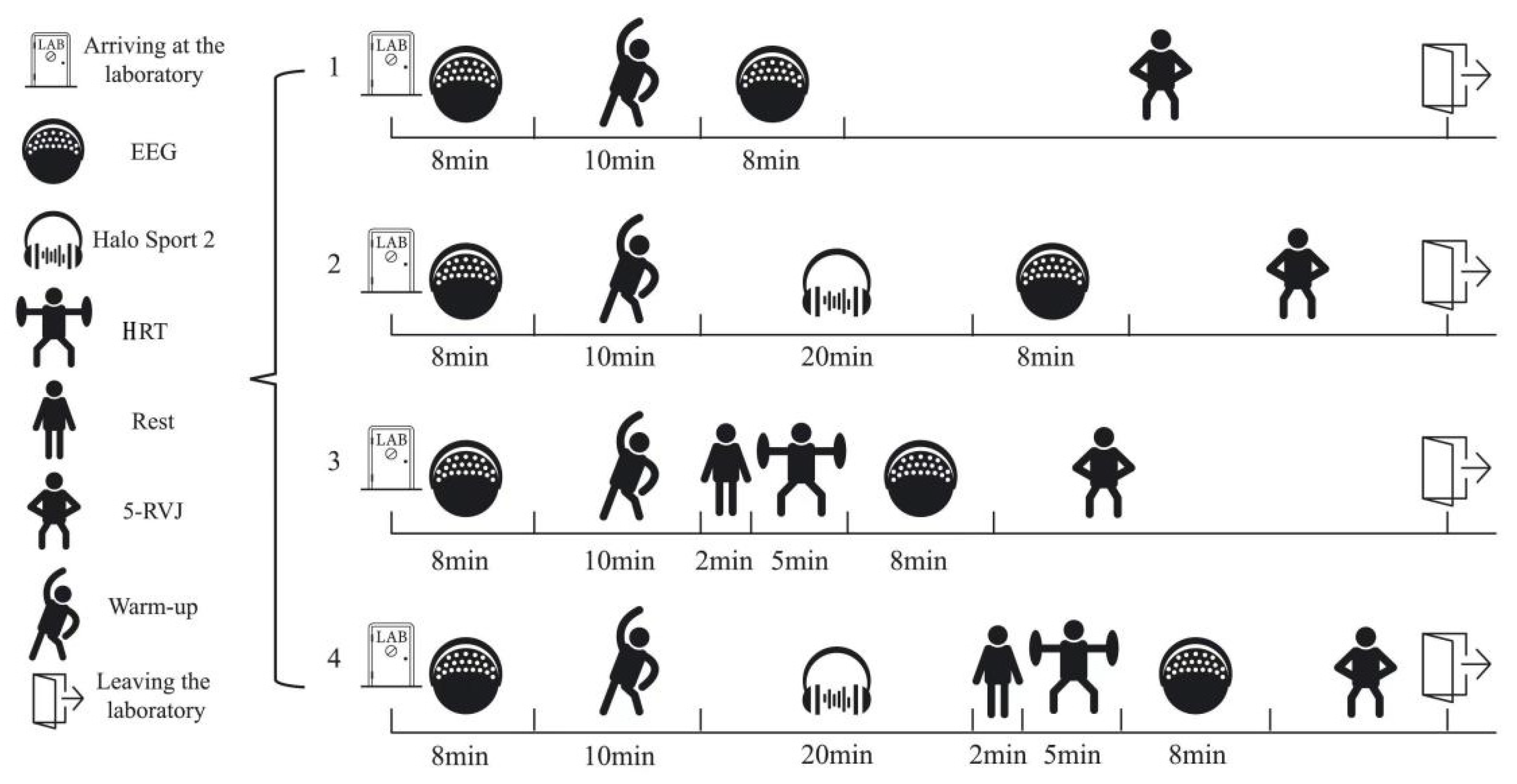
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Intervention
2.4.1. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
2.4.2. Lower Extremity High-Load Resistance Training
2.4.3. Outcome Measurement Tools
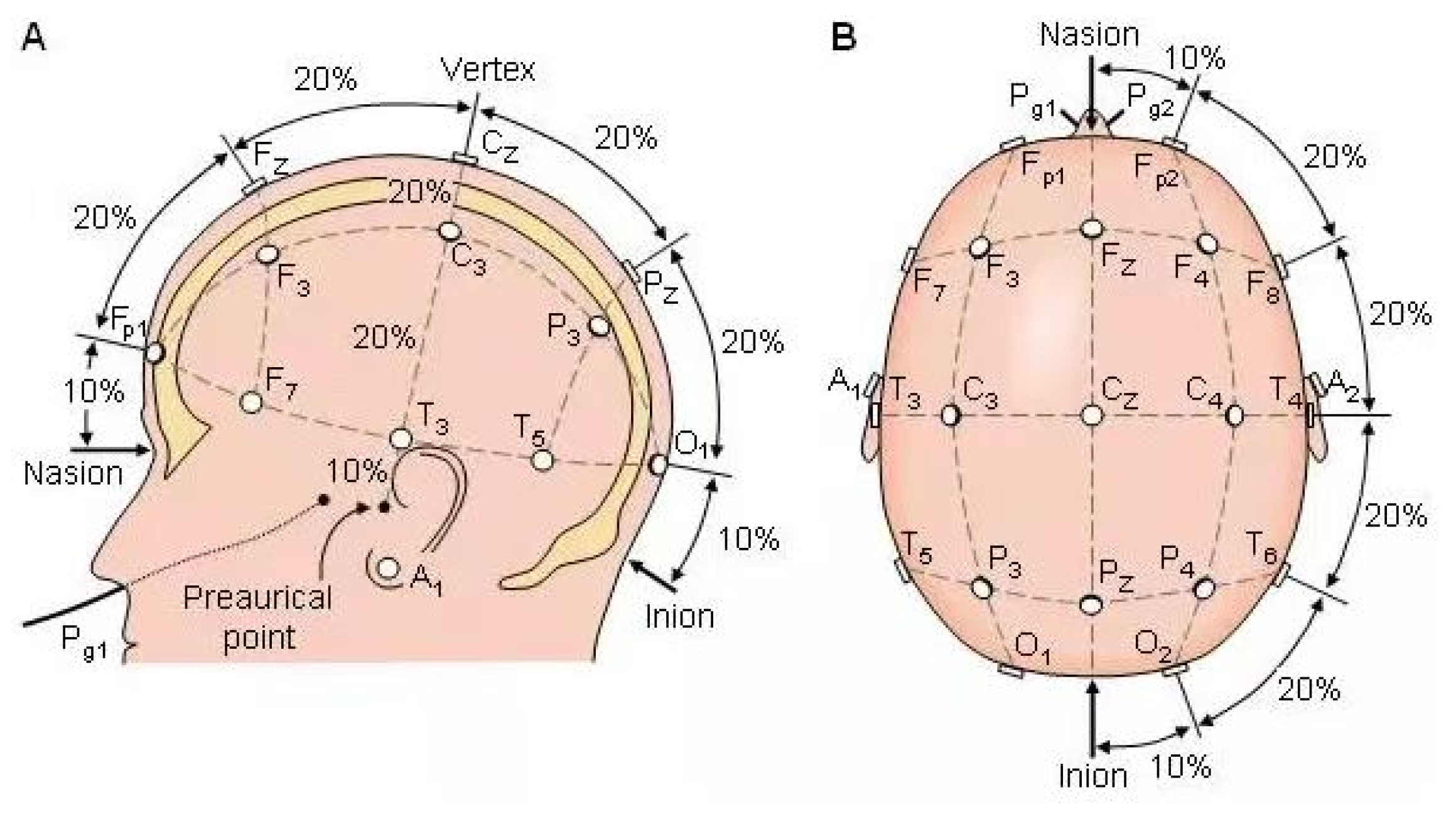
2.4.4. Electroencephalography
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Outcome Measures
3.1.1. Repeat Vertical Jumps
Contact Time (CT)
Flight Time (FT)
Jump Height (JH)
Reactive Strength Index (RSI)
Peak Power Output (PPO)
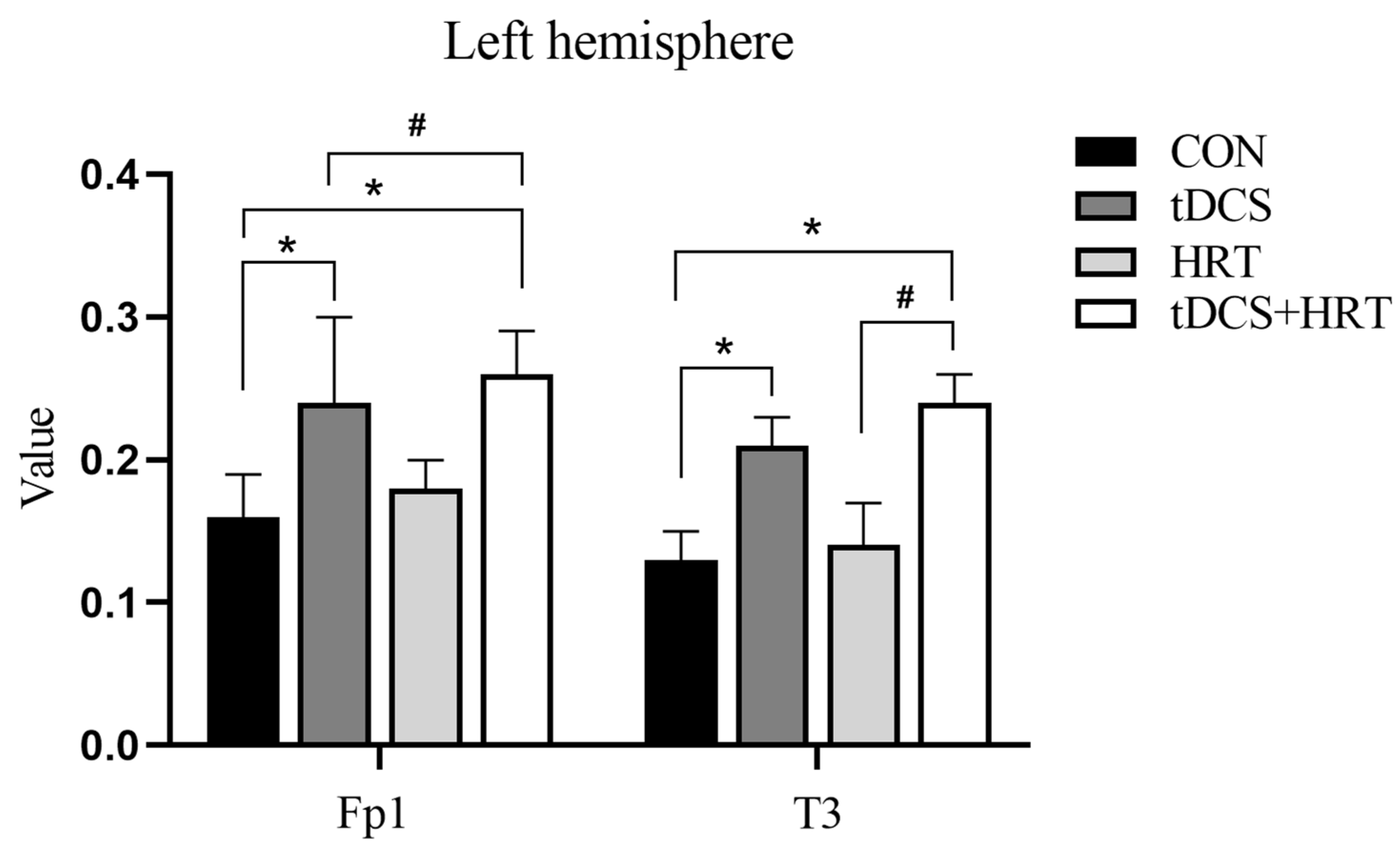
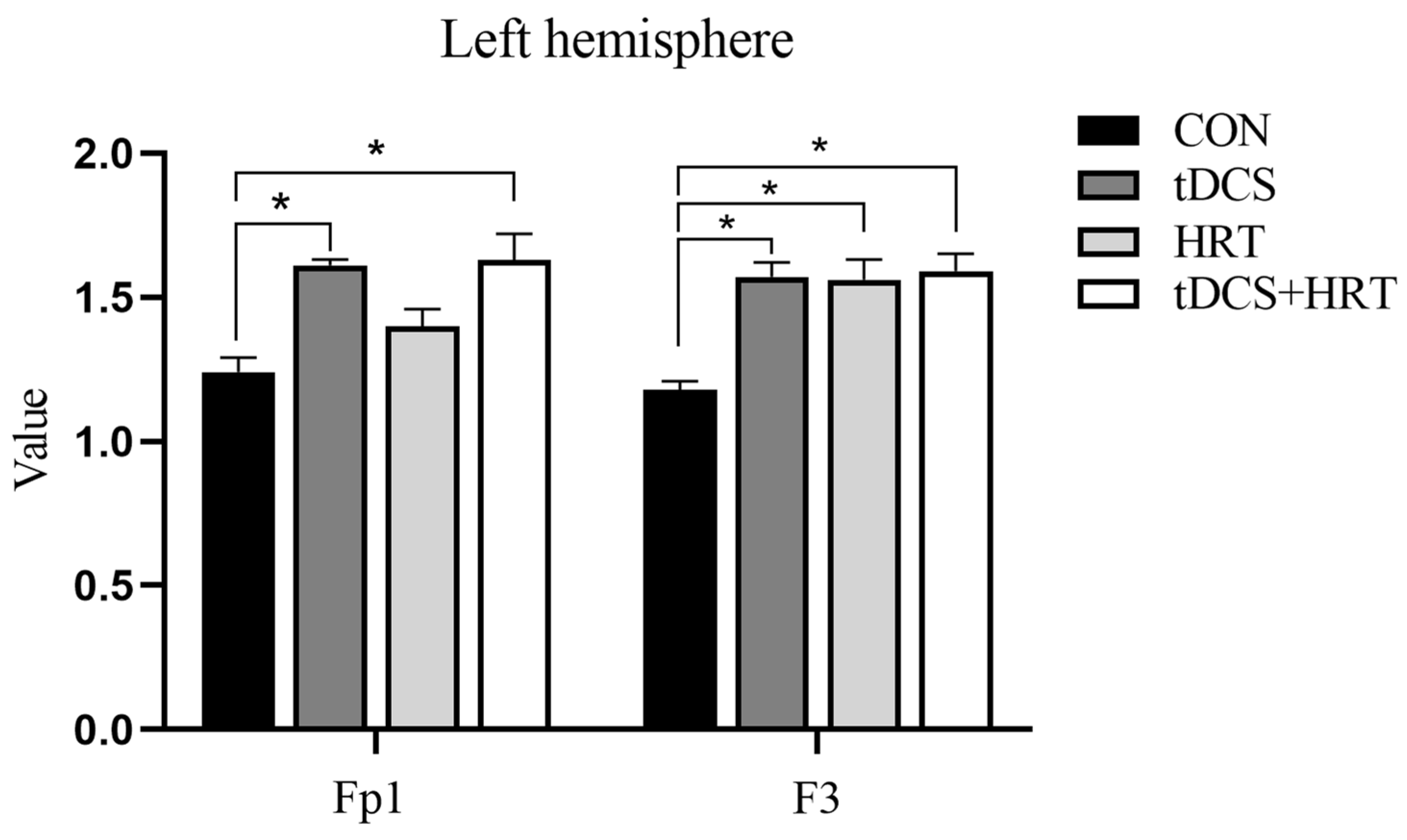
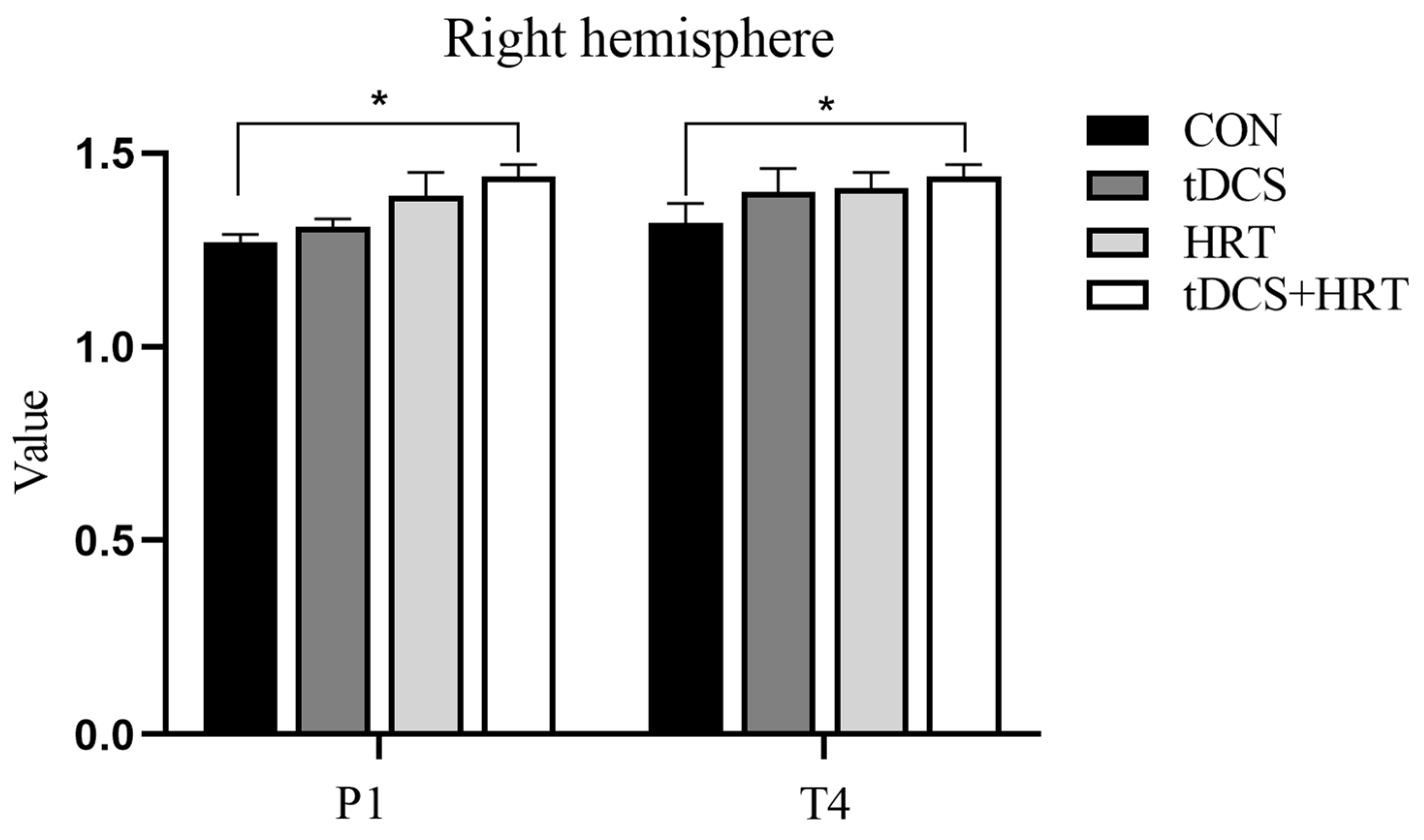
3.1.2. Electroencephalogram Characteristics Percentage of α-Wave EEG Power
3.1.3. Percentage of β-Wave EEG Power
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Interventions on Repetition Vertical Jump
4.2. Physiological Rationale behind Improved Performance
4.3. Cognitive Functions and Brain Synergy
5. Conclusions
5.1. Limitations and Future Directions
5.2. Future Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1RM | One Repetition Maximum |
| 5-RVT | Repeat the Vertical Jump 5 Times |
| C3,4 | Central Region 3,4 |
| CON | Control Condition |
| CT | Contact Time |
| EEG | Electroencephalographic |
| F7,8 | Frontal Electrode 7,8 |
| Fp1,2 | Frontal Lobe 1,2 |
| FT | Flight Time |
| H | Height |
| NSCA | National Strength and Conditioning Association |
| O1,2 | Occipital Lobe Region 1,2 |
| P3,4 | Parietal Region 3,4 |
| PPO | Peak Power Output |
| RSI | Reaction Force Index |
| HRT | High-load Resistance Training |
| T4,7 | Temporal Lobe Region 4,7 |
| tDCS | Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation |
References
- Schubert, M.M.; Astorino, T.A. A systematic review of the efficacy of ergogenic aids for improving running performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noakes, D.T. Fatigue is a brain-derived emotion that regulates the exercise behavior to ensure the protection of whole body homeostasis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, T.N. Time to move beyond a brainless exercise physiology: The evidence for complex regulation of human exercise performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab.=Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Et. Metab. 2011, 36, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.J.; Toth, A.J.; Moran, A.P.; Kowal, M.; Exton, C. eSports: A new window on neurocognitive expertise? Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 240, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, S.; Travassos, B.; Teixeira, D.S.; Rodrigues, F.; Cid, L.; Monteiro, D. Could tDCS Be a Potential Performance-Enhancing Tool for Acute Neurocognitive Modulation in eSports? A Perspective Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation With Halo Sport Enhances Repeated Sprint Cycling and Cognitive Performance. Front. Physiol. 2019, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitka, V.; Alireza, G. Non-invasive brain stimulation for improving gait, balance, and lower limbs motor function in stroke. J. Neuro Eng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwigsen, G. Adaptive Plasticity in the Healthy Language Network: Implications for Language Recovery after Stroke. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 9674790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelin, J.; Mondino, M.; Bation, R.; Palm, U.; Saoud, M.; Poulet, E. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, U.; Hasan, A.; Strube, W.; Padberg, F. tDCS for the treatment of depression: A comprehensive review. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 266, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, E.R.; Santarnecchi, E.; Antal, A.; Born, J.; Celnik, P.A.; Classen, J.; Gerloff, C.; Hallett, M.; Hummel, F.C.; Nitsche, M.A.; et al. Effects of tDCS on motor learning and memory formation: A consensus and critical position paper. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolin, S.; Loo, C.K.; Bai, S.; Dokos, S.; Martin, D.M. Focalised stimulation using high definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) to investigate declarative verbal learning and memory functioning. NeuroImage 2015, 117, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Qian, L.; Zorowitz, R.D.; Zhang, L.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Effects on Decreasing Upper-limb Poststroke Muscle Tone Using Transcranial Directcurrent Stimulation: A Randomized Sham-Controlled Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kähkönen, S.; Kesäniemi, M.; Nikouline, V.V.; Karhu, J.; Ollikainen, M.; Holi, M.; Ilmoniemi, R.J. Ethanol Modulates Cortical Activity: Direct Evidence With Combined TMS and EEG. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, F.; Vecchio, F.; Guerra, A.; Miraglia, F.; Ponzo, D.; Vollero, L.; Iannello, G.; Maatta, S.; Mervaala, E.; Rossini, P.M.; et al. Age Related Differences In Functional Synchronization of EEG Activity as Evaluated by Means of TMS-EEG Coregistrations. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 647, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Sansone, P.; Mitter, B.; Makivic, B.; Seitz, L.B.; Tschan, H. Acute Effects of Back Squats on Countermovement Jump Performance Across Multiple Sets of a Contrast Training Protocol in Resistance-Trained Men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, H.R.; Tate, R.J.; Conway, B.A. Transcutaneous Spinal Direct Current Stimulation Induces Lasting Fatigue Resistance and Enhances Explosive Vertical Jump Performance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Uhm, Y. The Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined Lumbar Stability Exercise on the Muscle Activity and Jump Performance of the Soccer Player. Arch. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.K. Examining the Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Sstimulation on the Dominant Motor Cortex in the Indirect Measurement of Physical Ability. J. Men’s Health 2022, 18, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinzara, T.T.; Buckingham, G.; Harris, D.J. Transcranial direct current stimulation and sporting performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis of transcranial direct current stimulation effects on physical endurance, muscular strength and visuomotor skills. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 55, 468–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, V.Z.; Baptista, A.F.; Pereira, G.O.C.; Pochini, A.C.; Ejnisman, B.; Santos, M.B.; João, S.M.A.; Hazime, F.A. Modulation of Isometric Quadriceps Strength in Soccer Players With Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: A Crossover Study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazime, F.A.; da Cunha, R.A.; Soliaman, R.R.; Romancini, A.C.B.; Pochini, A.C.; Ejnisman, B.; Baptista, A.F. anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) increases isometric strength of shoulder rotators muscles in handball players. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 12, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frazer, A.; Williams, J.; Spittles, M.; Rantalainen, T.; Kidgell, D. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex increases cortical voluntary activation and neural plasticity. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Hanakawa, T.; Honda, M.; Watanabe, K. Enhancement of pinch force in the lower leg by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 196, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, A.; Waddington, G.; Keegan, R.J.; Thompson, K.G.; Cathcart, S. The effects of elevated pain inhibition on endurance exercise performance. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthalib, M.; Kan, B.; Nosaka, K.; Perrey, S. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex on prefrontal cortex activation during a neuromuscular fatigue task: An fNIRS study. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 789, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, B.; Dundas, J.E.; Nosaka, K. Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on elbow flexor maximal voluntary isometric strength and endurance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Fages, C.; Romero-Arenas, S.; Castro-Alonso, M.; Colomer-Poveda, D.; Río-Rodriguez, D.; Jerez-Martínez, A.; Fernandez-Del-Olmo, M.; Márquez, G. Short-Term Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Endurance and Maximal Force Production: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Strength and Conditioning Association. Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning, 4th ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tillin, N.A.; Bishop, D. Factors modulating post-activation potentiation and its effect on performance of subsequent explosive activities. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, M.; Docherty, D.; Robbins, D. Post-activation potentiation: Underlying physiology and implications for motor performance. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.B.; Junqué, C.; Bartrés-Faz, D.; Martí, M.J.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Compta, Y.; Falcón, C.; Vendrell, P.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Valls-Solé, J.; et al. Modulation of Verbal Fluency Networks by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Kuo, M.F.; Karrasch, R.; Wächter, B.; Liebetanz, D.; Paulus, W. Serotonin Affects Transcranial Direct Current-induced Neuroplasticity in Humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordacre, B.; Moezzi, B.; Ridding, M.C. Neuroplasticity and Network Connectivity of the Motor Cortex Following Stroke:A Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 3326–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyor, J.M.; Martín-Fuentes, I.; Rodríguez-Ridao, D.; Antequera-Vique, J.A. Electromyographic activity in the gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and rectus femoris during the Monopodal Squat, Forward Lunge and Lateral Step-Up exercises. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natera, A.O.; Chapman, D.W.; Chapman, N.D.; Keogh, J.W.L. The reliability and validity of repeat power ability assessments and measurement indices in loaded vertical jumps. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogataj, Š.; Pajek, M.; Hadžić, V.; Andrašić, S.; Padulo, J.; Trajković, N. Validity, Reliability, and Usefulness of My Jump 2 App for Measuring Vertical Jump in Primary School Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeck, M.; Koessler, L.; Bast, T.; Leijten, F.; Michel, C.; Baumgartner, C.; He, B.; Beniczky, S. The standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattari, E.; Campos, C.; Lamego, M.K.; Legey, S.; Neto, G.M.; Rocha, N.B.; Oliveira, A.J.; Carpenter, C.S.; Machado, S. Can Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Improve Muscle Power in Individuals with Advanced Weight-Training Experience? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosprêtre, S.; Grandperrin, Y.; Nicolier, M.; Gimenez, P.; Vidal, C.; Tio, G.; Haffen, E.; Bennabi, D. Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on the psychomotor, cognitive, and motor performances of power athletes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Arenas, S.; Calderón-Nadal, G.; Alix-Fages, C.; Jerez-Martínez, A.; Colomer-Poveda, D.; Márquez, G. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Does Not Improve Countermovement Jump Performance in Young Healthy Men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 2918–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Han, D.H.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.W. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of Motor Cortex Enhances Spike Performances of Professional Female Volleyball Players. J. Mot. Behav. 2022, 55, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinus, N.; Van Hoornweder, S.; Aarts, M.; Vanbilsen, J.; Hansen, D.; Meesen, R. The influence of a single transcranial direct current stimulation session on physical fitness in healthy subjects: A systematic review. Exp. Brain Res. 2023, 241, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, X. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on upper limb muscle strength and endurance in healthy individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 834397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoury, R.; Kibele, A.; Behm, D.G. Methodological issues with transcranial direct current stimulation for enhancing muscle strength and endurance: A narrative review. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2022, 6, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Mustafaoglu, R.; Rossi, S.; Cavdar, F.A.; Agyenkwa, S.K.; Pang, M.Y.C.; Straudi, S. Non-invasive Brain Stimulation Techniques for the Improvement of Upper Limb Motor Function and Performance in Activities of Daily Living After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med Rehabil. 2023, 104, 1683–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, N.; Bono, D.; Dedic, N.; Kodandaramaiah, S.B.; Rudenko, A.; Suk, H.J.; Cassara, A.M.; Neufeld, E.; Kuster, N.; Tsai, L.H.; et al. Noninvasive Deep Brain Stimulation via Temporally Interfering Electric Fields. Cell 2017, 169, 1029–1041.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, L.S.; Mazini-Filho, M.; Lima-Júnior, D.; Machado, D.G.S.; Albuquerque, M.R.; Fonseca, F.S.; Ferreira, M.E.C. Transcranial Stimulation Improves Volume and Perceived Exertion but does not Change Power. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, H.; Amiri, E.; Tahmasebi, W.; Hoseini, R.; Grospretre, S.; Machado, D.G.D.S. Effect of tDCS targeting the M1 or left DLPFC on physical performance, psychophysiological responses, and cognitive function in repeated all-out cycling: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, O.; Friedman, J.; Frenkel-Toledo, S. The effect of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation intensity on motor performance in healthy adults: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagg, C.J.; Antal, A.; Nitsche, M.A. Physiology of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. J. ECT 2018, 34, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrac, C.; Benoit-Marand, M. Monoaminergic Modulation of Motor Cortex Function. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapeton, J.I.; Haque, R.; Wittig JHJr Inati, S.K.; Zaghloul, K.A. Large-Scale Communication in the Human Brain Is Rhythmically Modulated through Alpha Coherence. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2801–2811.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, B.C.; Beek, P.J.; Daffertshofer, A. Neural synchrony within the motor system: What have we learned so far? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacca, V.; Maleki, N.; Wen, Y.; Hodges, S.; Kong, J. Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipski, W.J.; Wozny, T.A.; Alhourani, A.; Kondylis, E.D.; Turner, R.S.; Crammond, D.J.; Richardson, R.M. Dynamics of human subthalamic neuron phase-locking to motor and sensory cortical oscillations during movement. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 118, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engchuan, P.; Wongsuphasawat, K.; Sittiprapaporn, P. Brain electrical activity during bench press weight training exercise. Asian J. Med. Sci. 2019, 10, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Graff-Radford, J. Executive Dysfunction and the Prefrontal Cortex. Continuum 2021, 27, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.P.; Robbins, T.W. The role of prefrontal cortex in cognitive control and executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Shin, S.H.; Ryu, J.K.; Jung, K.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.H. Commercial video games and cognitive functions: Video game genres and modulating factors of cognitive enhancement. Behav. Brain Funct. 2020, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigas, A.; Karyotaki, M. Executive Functioning and Problem Solving: A Bidirectional Relation. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2019, 9, 76–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Lei, M.; Tao, S.; Jie, L.T.; Qian, L.; Lin, F.Q.; Ping, W.X. Effects of combined intervention of physical exercise and cognitive training on cognitive function in stroke survivors with vascular cognitive impairment: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil 2019, 33, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatelli, F.; Messina, A.; Valenzano, A.; Monda, V.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F.; La Torre, E.; Tafuri, D.; Scarinci, A.; Perrella, M.; et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation as a tool to investigate motor cortex excitability in sport. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, J. Physical activity, motor performance and skill learning: A focus on primary motor cortex in healthy aging. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 3431–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyng, C.M.; Amin, H.U.; Saad, M.N.M.; Malik, A.S. The Influences of Emotion on Learning and Memory. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Number of Participants (n) | Age (yr) | Height (cm) | Body Weight (kg) | 1RM Back squat/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | 21.8 ± 2.13 | 178.1 ± 6.15 | 77.1 ± 7.70 | 2.15 ± 0.20 |
| CON | tDCS | HRT | tDCS + HRT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT (s) | 0.5 ± 0.03 ▲ | 0.4 ± 0.13 *▲ | 0.4 ± 0.32 ▲ | 0.3 ± 0.24 * |
| FT (s) | 0.5 ± 0.04 | 0.5 ± 0.02 | 0.5 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.05 |
| JH (cm) | 36.5 ± 3.04 ▲ | 39.6 ± 3.19 *▲ | 40.1 ± 3.03 *▲ | 42.7 ± 3.01 * |
| RSI | 2.0 ± 0.07 | 2.2 ± 0.07 | 2.3 ± 0.05 | 2.4 ± 0.03 |
| PPO (w/kg) | 41.5 ± 4.01 | 45.0 ± 3.36 * | 41.6 ± 3.57 | 45.8 ± 3.53 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Zhai, H.; Wei, H. Acute Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with High-Load Resistance Exercises on Repetitive Vertical Jump Performance and EEG Characteristics in Healthy Men. Life 2024, 14, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091106
Zhou Y, Zhai H, Wei H. Acute Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with High-Load Resistance Exercises on Repetitive Vertical Jump Performance and EEG Characteristics in Healthy Men. Life. 2024; 14(9):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091106
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuping, Haiting Zhai, and Hongwen Wei. 2024. "Acute Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with High-Load Resistance Exercises on Repetitive Vertical Jump Performance and EEG Characteristics in Healthy Men" Life 14, no. 9: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091106
APA StyleZhou, Y., Zhai, H., & Wei, H. (2024). Acute Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with High-Load Resistance Exercises on Repetitive Vertical Jump Performance and EEG Characteristics in Healthy Men. Life, 14(9), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091106





