Endarachne binghamiae Extract Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Through Regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT Pathways, and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of EB-WE
2.2. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. Determination of NO, Cytokines, and Chemokines
2.4. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.5. Western Blot for Signal Transduction Assay
2.6. Animal Experiment for ALI
2.7. Body Temperature and Lung Edema Measurement
2.8. Histology
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
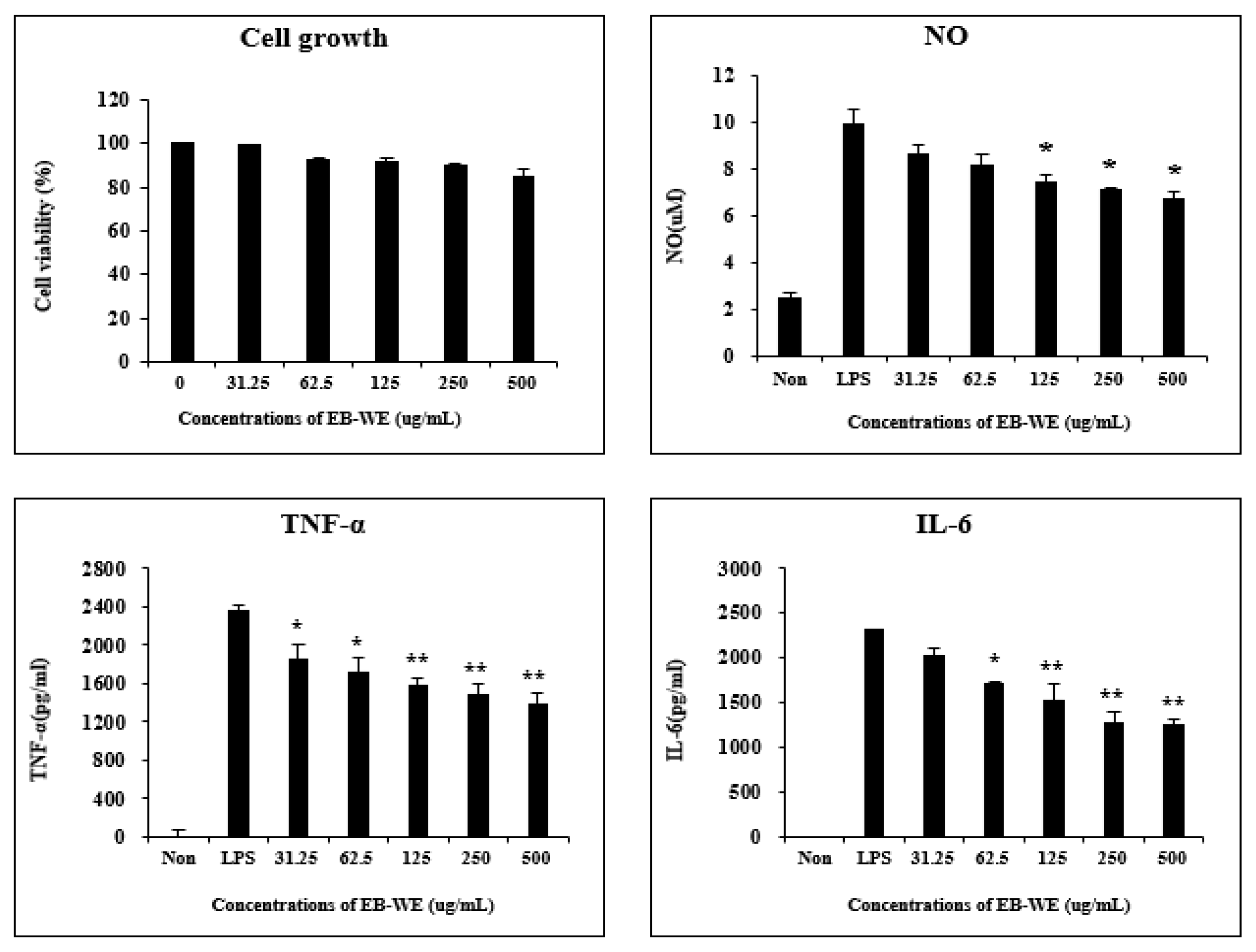
3.1. EB-WE Inhibits Production of Inflammatory Mediators in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
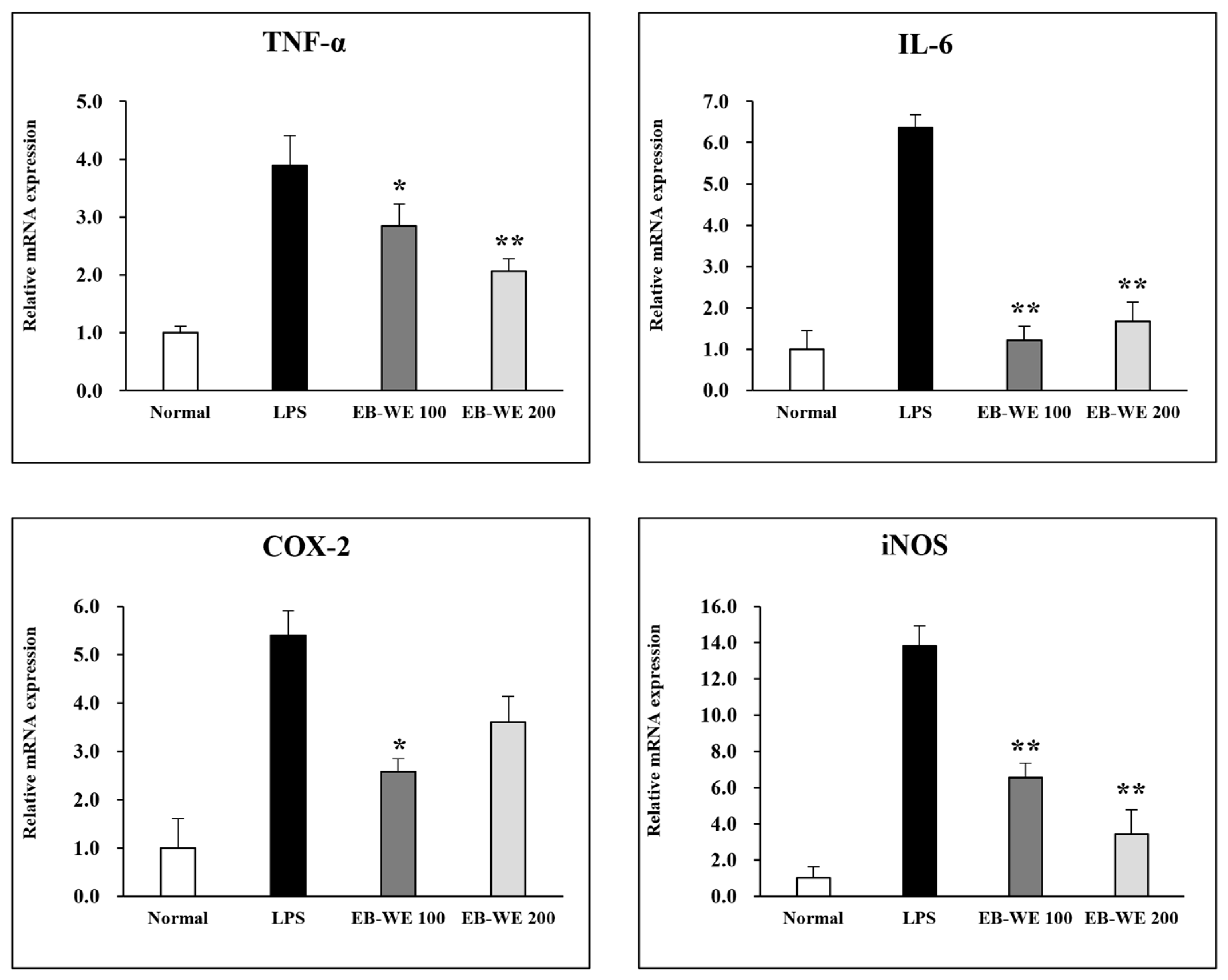
3.2. Inhibition of mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Mediators by EB-WE
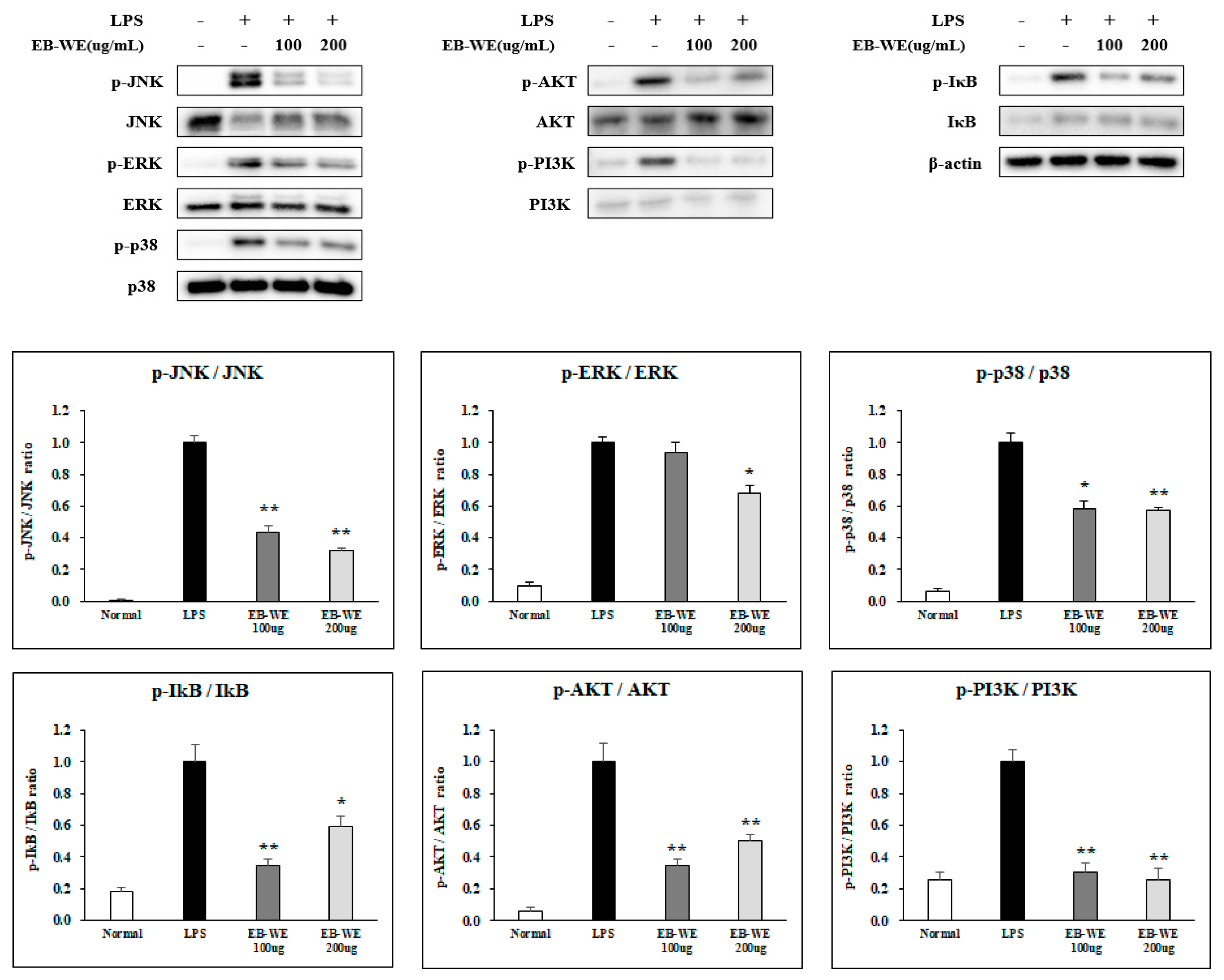
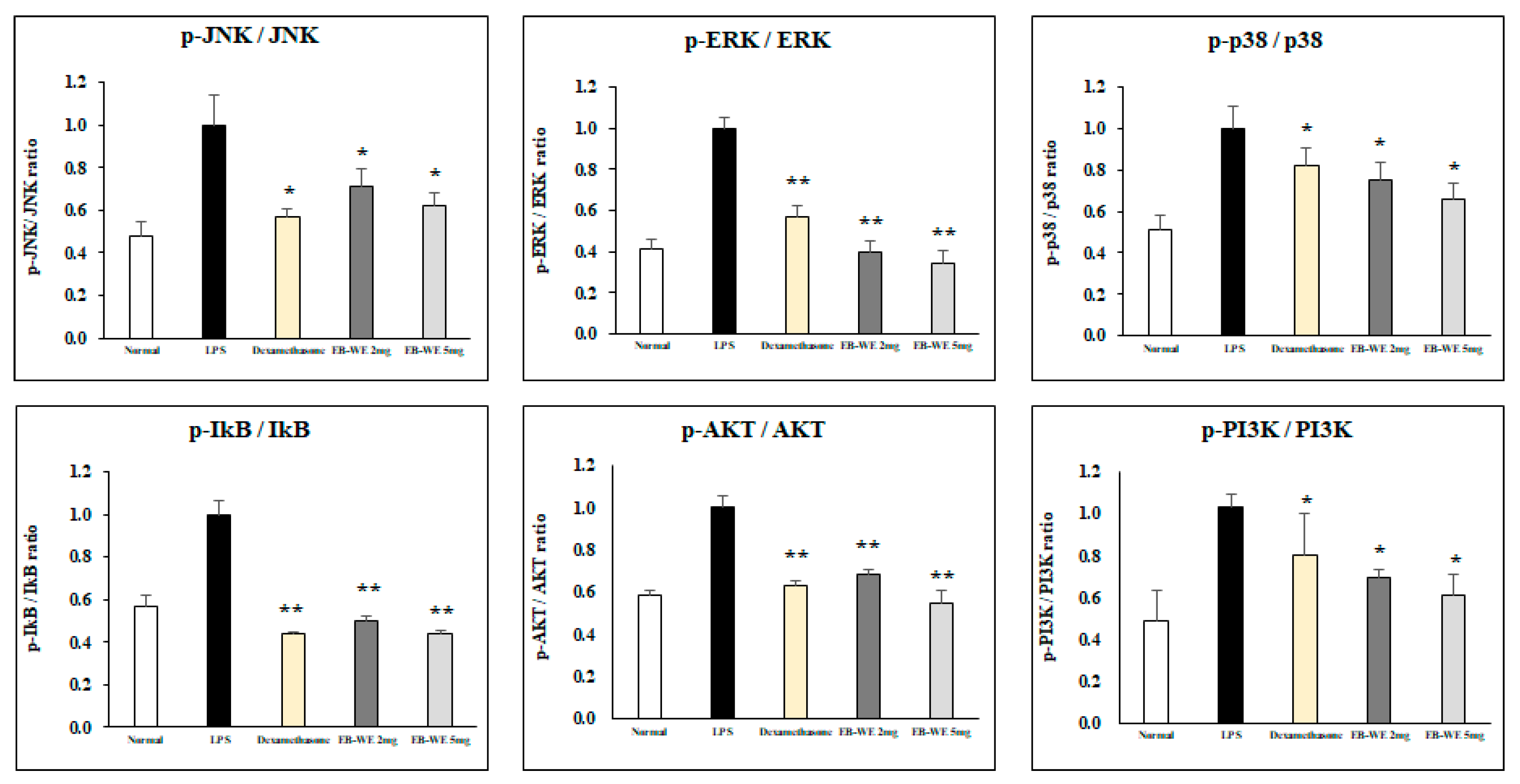
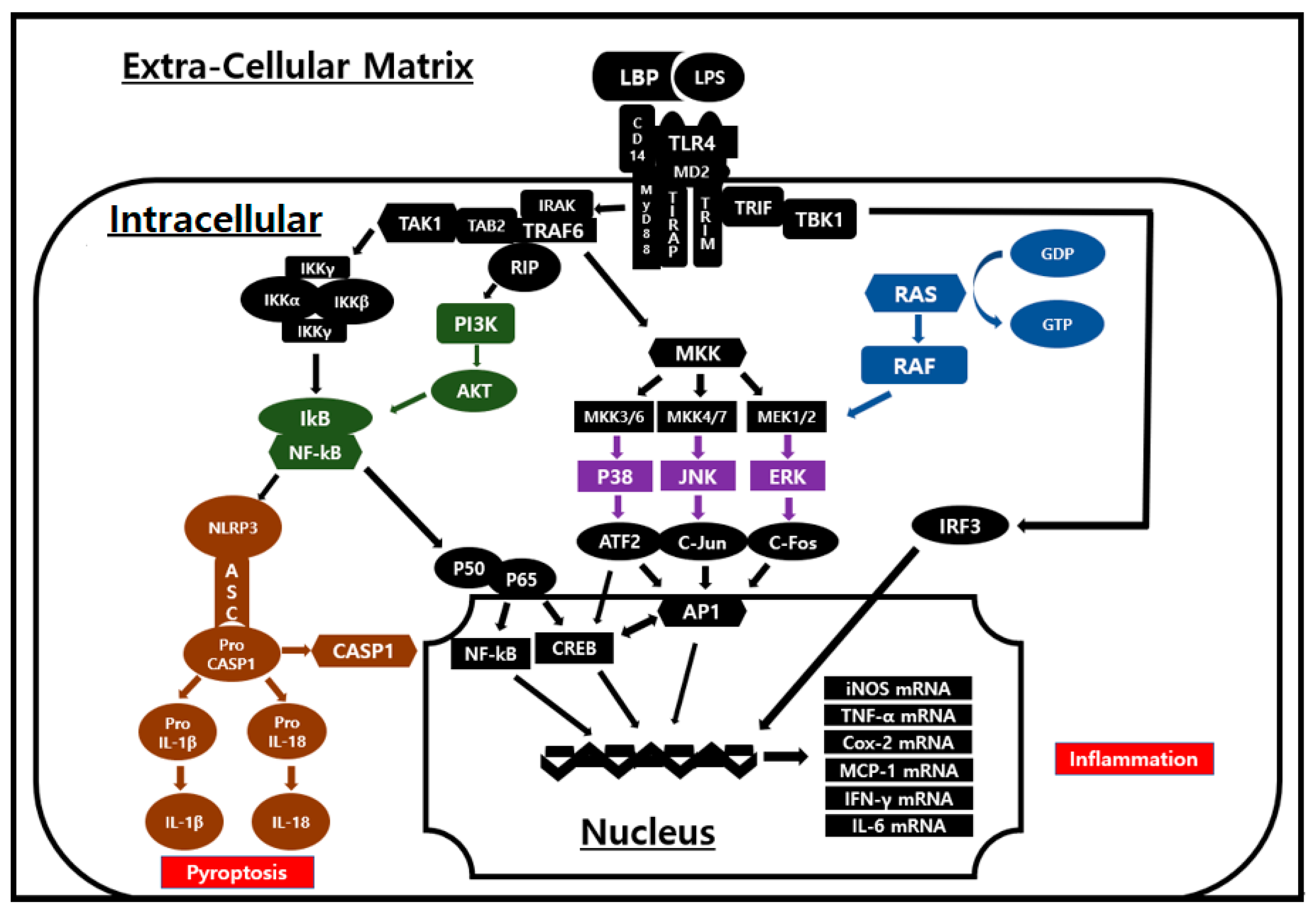
3.3. Signal Transduction Inhibition of EB-WE in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
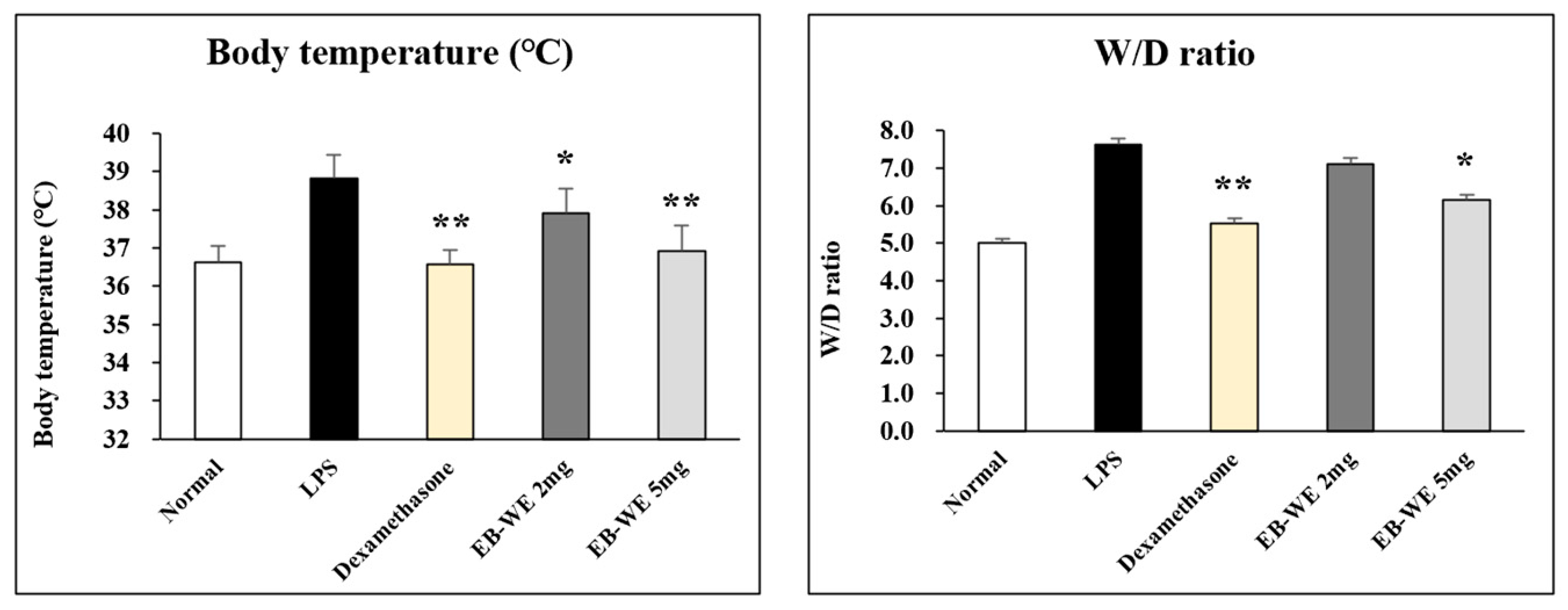
3.4. EB-WE Suppresses Body Temperature and Lung Edema in ALI In Vivo Model
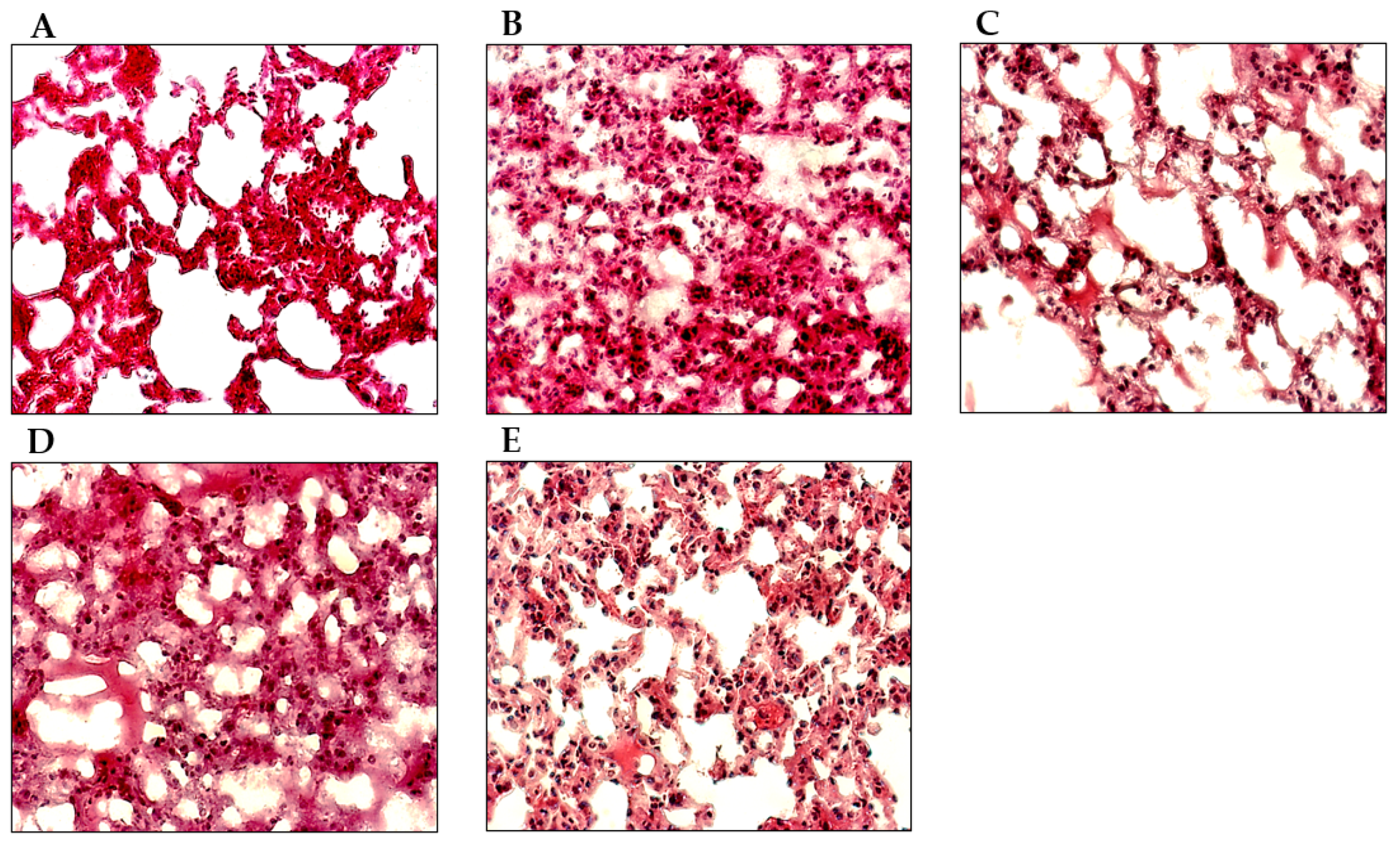
3.5. EB-WE Ameliorates Histopathological Changes in ALI Model Lungs
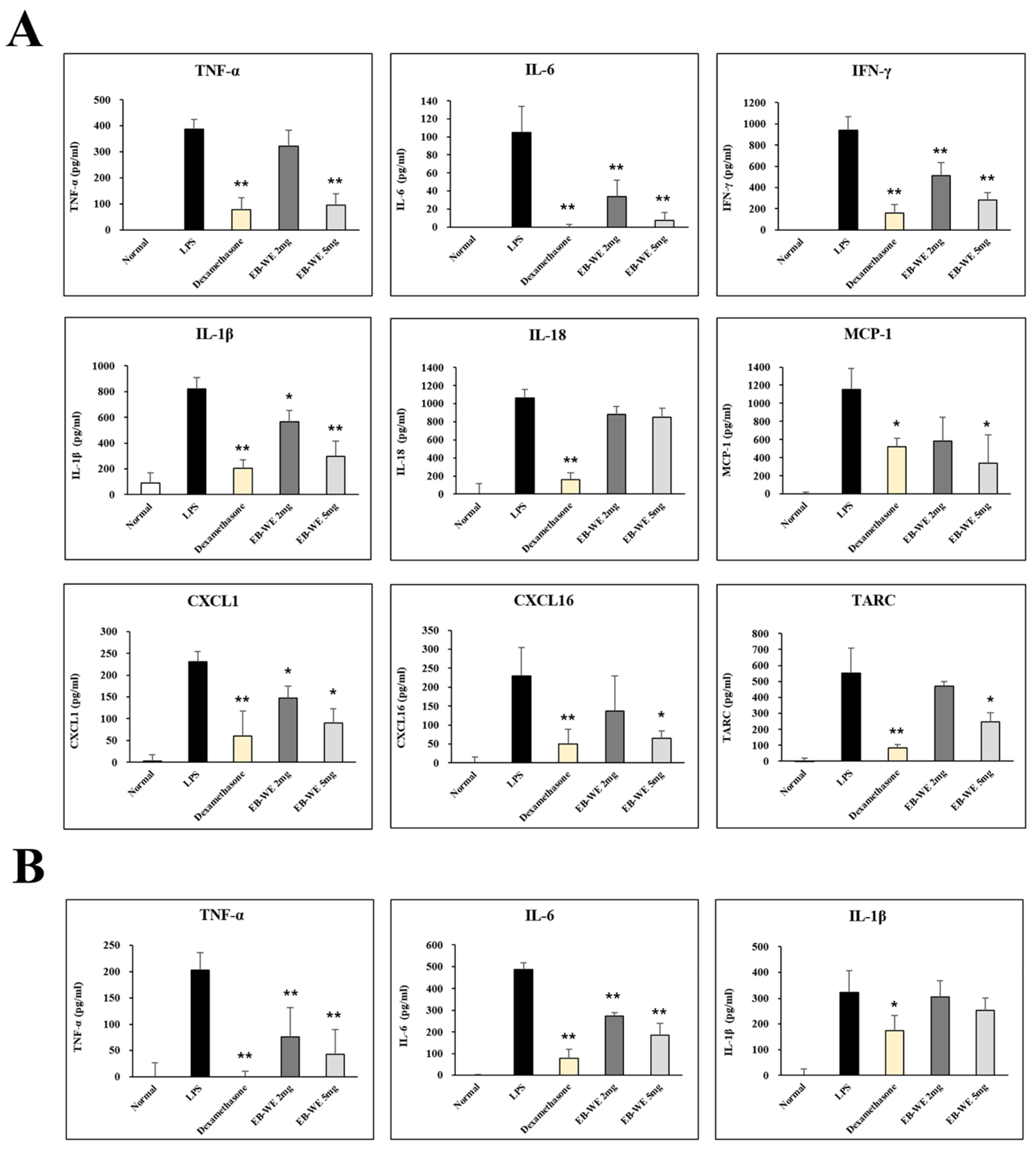
3.6. EB-WE Inhibits Level of Cytokines and Chemokines in BALF and Serum
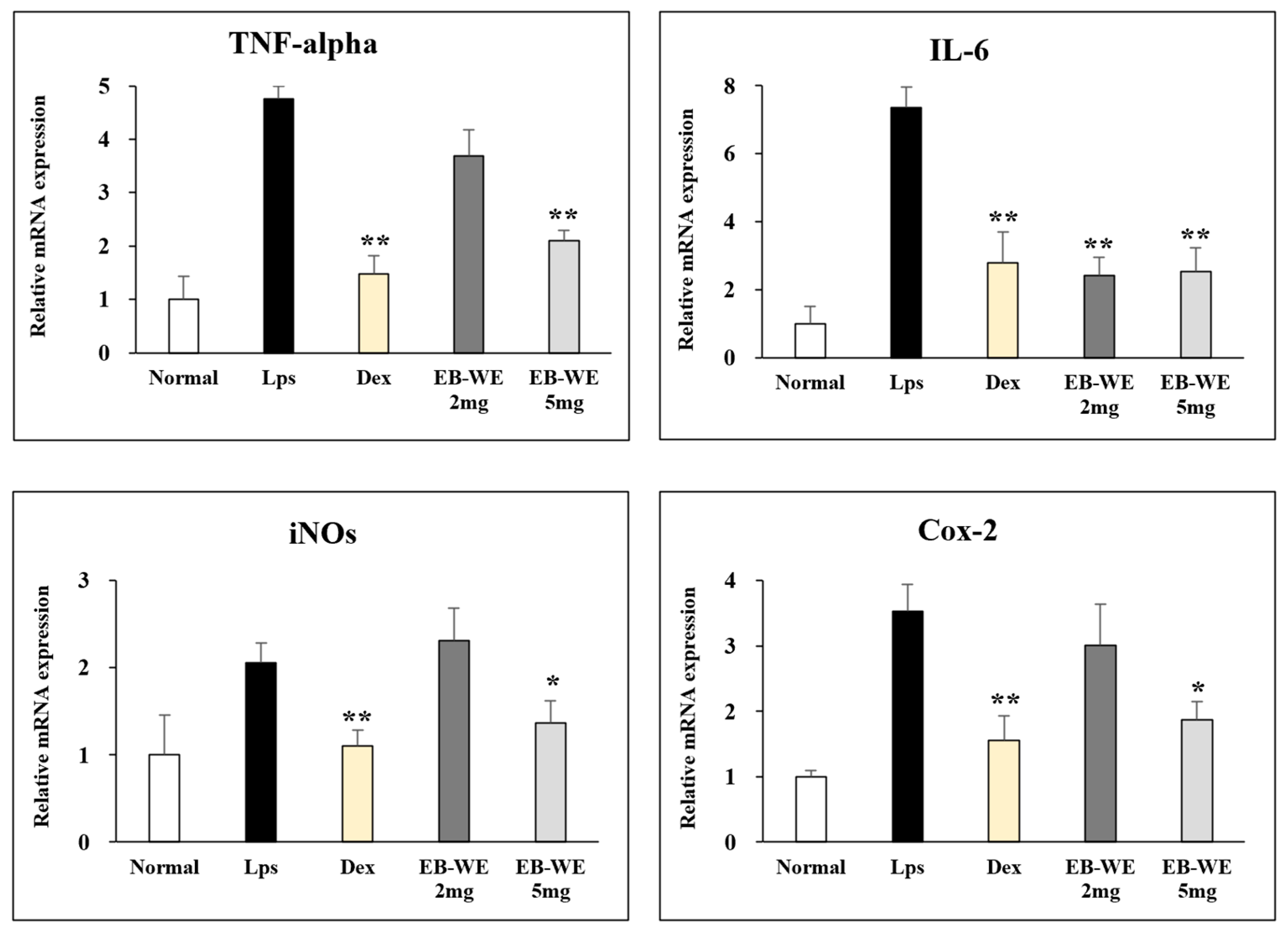
3.7. Regulation of mRNA Expression by EB-WE in Lung Tissues
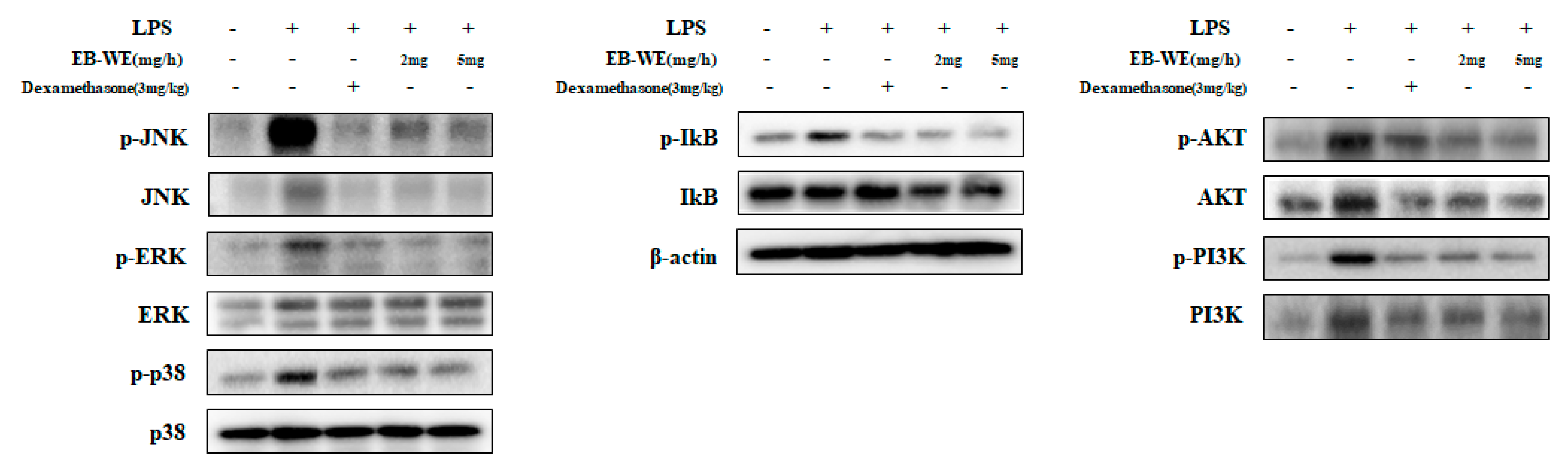
3.8. Inhibition of Signal Transduction by EB-WE in Lung Tissues
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozzi-Silva, S.C.; Teixeira, F.M.E.; Duarte, A.; Sato, M.N.; Oliveira, L.M. Immunomodulatory Role of Nutrients: How Can Pulmonary Dysfunctions Improve? Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 674258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettelman, R.C.; Allen, E.K.; Thomas, P.G. Mucosal immune responses to infection and vaccination in the respiratory tract. Immunity 2022, 55, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htoutou Sedlakova, M.; Pudova, V.; Kolar, M. Bacterial pathogens causing hospital-acquired pneumonia—A multicenter study in the Czech Republic. Klin. Mikrobiol. Infekc. Lek. 2015, 21, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Long, M.E.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Horowitz, J.C. Pathogenesis of pneumonia and acute lung injury. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 747–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.M.; Tsai, F.J.; Lee, Y.L.; Chang, J.H.; Chang, L.T.; Chang, T.Y.; Chung, K.F.; Kuo, H.P.; Lee, K.Y.; Chuang, K.J.; et al. The impact of air pollution on respiratory diseases in an era of climate change: A review of the current evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 166340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiz-Vesper, B.; Schmetzer, H.M. Antigen-Presenting Cells: Potential of Proven und New Players in Immune Therapies. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2020, 47, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Lee, J.O. Recognition of lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V. Toll-like receptors in sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative regulators as future immunomodulatory targets. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Kang, H. Immunotherapy in the context of sepsis-induced immunological dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1391395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral lead compounds from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, J. The Crustose Brown Algae of New Zealand: A Taxonomic Study. Master’s Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.C. Extraction and chacterization of fucoidan from six brown macroalgae. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.H.; Hong, G.L.; Kang, H.B.; Lee, N.S.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kim, C.S.; Yoo, Y.C.; Lee, B.H.; Jung, J.Y.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Water Extract from Brown Algae Petalonia binghamiae in an Experimental Model of Focal Cerebral Ischemia In Vitro and In Vivo. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8427–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.I.; Jin, Y.J.; Ko, H.C.; Choi, S.-Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Whang, I.; Kim, M.H.; Shin, H.S.; Jeong, H.B.; Kim, S.J. Petalonia improves glucose homeostasis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Petalonia binghamiae in LPS- Induced Macrophages is Mediated by Suppression of iNOS and COX-2. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 754–758. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.S.; Choi, I.W.; Han, M.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, G.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, C.M.; Yoo, Y.H.; Choi, Y.H. The Cytoprotective Effect of Petalonia binghamiae Methanol Extract against Oxidative Stress in C2C12 Myoblasts: Mediation by Upregulation of Heme Oxygenase-1 and Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2 Related Factor 2. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniandy, K.; Gothai, S.; Badran, K.M.H.; Suresh Kumar, S.; Esa, N.M.; Arulselvan, P. Suppression of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Mediators in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Stem Extract of Alternanthera sessilis via the Inhibition of the NF-kappaB Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3430684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pei, S.; Wang, Y. Ethnopharmacological study on Adenosma buchneroides Bonati inhibiting inflammation via the regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2024, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-kappaB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Ding, M.; Fan, L.; Yu, X.; Liang, Z.; Wu, L.; Gao, Z.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of Inflammation and Regulation of AQPs/ENaCs/Na+-K+-ATPase Mediated Alveolar Fluid Transport by Total Flavonoids Extracted From Nervilia fordii in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 603863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, N.O.; Imam, F.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Zoheir, K.M.; Korashy, H.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M.; Attia, S.M.; Shabanah, O.A.; Ahmad, S.F. Dexamethasone Attenuates LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibition of NF-kappaB, COX-2, and Pro-inflammatory Mediators. Immunol. Invest. 2016, 45, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Zemans, R.L.; Jeyaseelan, S. Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.B.; Pugin, J.; Lee, J.S.; Matthay, M.A. Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zou, K.; Diao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z. Liensinine alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by blocking autophagic flux via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anilkumar, S.; Wright-Jin, E. NF-kappaB as an Inducible Regulator of Inflammation in the Central Nervous System. Cells 2024, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.H.; Kim, D.; Park, S.J. Anti-inflammatory and immune enhancing activities of PB203 in mouse macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. J. Biomed. Transl. Res. 2023, 24, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hung, M.C. Beyond NF-kappaB activation: Nuclear functions of IkappaB kinase alpha. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Kostenko, S.; Sveinbjornsson, B. The Role of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKAPKs) in Inflammation. Genes 2013, 4, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, E.; Weis, M.C.; Avva, J.; Shukla, S.; Shukla, M.; Sreenath, S.N.; Gupta, S. Complex Systems Biology Approach in Connecting PI3K-Akt and NF-kappaB Pathways in Prostate Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; An, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, N.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X. Phenethylferulate as a natural inhibitor of inflammation in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages: Focus on NF-kappaB, Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Flores, Y.K.; Martinez-Galero, E.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Sixto-Lopez, Y.; Villegas, I.; Rosillo, M.A.; Cardeno, A.; Alarcon-de-la-Lastra, C. Daidzein and Equol: Ex Vivo and In Silico Approaches Targeting COX-2, iNOS, and the Canonical Inflammasome Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Meng, G.; Kan, X.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y. Oxypeucedanin relieves LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the lung air-blood barrier. Aging 2022, 14, 6626–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H. The role of alpha7-nAChR-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway in lung cancer induced by nicotine. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.C.; Chi, W.M.; Perng, W.C.; Huang, K.L. Body temperature control in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Chin. J. Physiol. 2003, 46, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Wang, H.S.; Lee, M.W. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fermented Bark of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and Its Isolated Compounds on Lipopolysaccharide-Treated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 6749425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Sun, Y.N.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.P. Inhibition of Lung Inflammation by Acanthopanax divaricatus var. Albeofructus and Its Constituents. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.; Evangelista, S.; Cirillo, R.; Terracciano, R.; Lippi, A.; Maggi, C.A.; Manzini, S. Antinociceptive activity of ricinoleic acid, a capsaicin-like compound devoid of pungent properties. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 407, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | AGC-CCC-CAG-TCT-GTA-TCC-TT | CTC-CCT-TTG-CAG-AAC-TCA-GG |
| IL-6 | CCA-CGG-CCT-TCC-CTA-CTT-C | TTG-GGA-GTG-GTA-TCC-TCT-GTG-A |
| COX-2 | CCA-CTT-CAA-GGG-AGT-CTG-GA | AGT-CAT-CTG-CTA-CGG-GAG-GA |
| iNOS | GTA-GTG-ACA-AGC-ACA-TTT-GG | GGC-TCC-ACT-TTT-CAC-TCT-GC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, G.-Y.; Han, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, B.-H.; Yoo, Y.-C. Endarachne binghamiae Extract Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Through Regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT Pathways, and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Life 2025, 15, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010088
Lee S-H, Lee S-S, Lee G-Y, Han S-Y, Kim D-S, Lee B-H, Yoo Y-C. Endarachne binghamiae Extract Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Through Regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT Pathways, and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Life. 2025; 15(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang-Hoon, Sang-Seop Lee, Ga-Young Lee, Seung-Yun Han, Dong-Sub Kim, Bong-Ho Lee, and Yung-Choon Yoo. 2025. "Endarachne binghamiae Extract Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Through Regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT Pathways, and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in Mice" Life 15, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010088
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Lee, S.-S., Lee, G.-Y., Han, S.-Y., Kim, D.-S., Lee, B.-H., & Yoo, Y.-C. (2025). Endarachne binghamiae Extract Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Through Regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT Pathways, and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Life, 15(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010088







