The Justification of Open Surgical Repair for an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Retrospective Comparison of Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair and a Brief Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants and Data Collection
2.3. Interventions and Outcomes
2.4. Follow-Up
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
2.6. EVAR Technique
2.7. Open Surgical Repair Technique
2.8. Treatment Selection
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion with a Brief Review of the Literature
5.1. Failure of EVAR
5.2. Conversion to Open Surgery
6. Limitation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAA | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| OSR | Open surgical repair |
| COS | Conversion to open surgery |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| IFU | Instructions for use |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
References
- Summers, K.L.; Kerut, E.K.; Sheahan, C.M.; Sheahan, M.G., 3rd. Evaluating the prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms in the United States through a national screening database. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 73, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.L.; Applewhite, B.; Reddy, N.K.; Matiuto, N.; Dang, C.; Jiang, B. Advances and challenges in regenerative therapies for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1369785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirinen, R.; Laine, M.T.; Mani, K.; Gunnarsson, K.; Wanhainen, A.; Sund, R.; Venermo, M. The Outcome after Endovascular and Open Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms—A Binational Study Conducted between 1998 and 2017. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanhainen, A.; Van Herzeele, I.; Bastos Goncalves, F.; Bellmunt Montoya, S.; Berard, X.; Boyle, J.R.; D’Oria, M.; Prendes, C.F.; Karkos, C.D.; Kazimierczak, A.; et al. European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2024 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-Iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024, 67, 192–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansal, V.; Nagpal, S.; Jetty, P. Late open surgical conversion after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzetto, L.; D’Oria, M.; Lepidi, S.; Mastrorilli, D.; Calvagna, C.; Bassini, S.; Taglialavoro, J.; Bruno, S.; Veraldi, G. A Scoping Review on the Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Proximal Neck Dilatation after Standard and Complex Endovascular Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, U.; Borulu, F.; Tüydeş, O.; Ozmen, S.; Erkut, B. Surgical appearance of aortic involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: A report of two cases. Cor Vasa 2022, 64, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, J.; Levy, P.J.; Tabares, A.H.; Gottlieb, A.; Schoenwald, P.K.; Olin, J.W. Ischemic liver dysfunction after elective repair of infrarenal aortic aneurysm: Incidence and outcome. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1998, 12, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, A.O.; Gherasim, L. Ischemic hepatitis-intercorrelated pathology. Maedica 2018, 13, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyrønning, L.Å.; Skoog, P.; Videm, V.; Mattsson, E. Is the aortic size index relevant as a predictor of abdominal aortic aneurysm? A population-based prospective study: The Tromsø study. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2020, 54, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asenbaum, U.; Schoder, M.; Schwartz, E.; Langs, G.; Baltzer, P.; Wolf, F.; Prusa, A.M.; Loewe, C.; Nolz, R. Stent-graft surface movement after endovascular aneurysm repair: Baseline parameters for prediction, and association with migration and stent-graft-related endoleaks. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6385–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichlmaier, M.; Hoy, L.; Wilhelmi, M.; Khaladj, N.; Haverich, A.; Teebken, O.E. Renal perfusion with venous blood extends the permissible suprarenal clamp time in abdominal aortic surgery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.T.; Wanhainen, A. Analysis of the differences between the ESVS 2019 and NICE 2020 guidelines for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 60, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.; Gibelli, F.; Sirignano, A.; Taurino, M.; Sirignano, P. Physician-modified endografts for repair of complex abdominal aortic aneurysms: Clinical perspectives and medico-legal profiles. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendes, C.F.; Gouveia, E.; Melo, R.; Caldeira, D.; D’Oria, M.; Tsilimparis, N.; Koelemay, M.; Van Herzeele, I.; Wanhainen, A. Editor’s choice-systematic review and meta-analysis of contemporary abdominal aortic aneurysm growth rates. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024, 67, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomelli, J.; Summers, L.; Stevenson, A.; Lees, T.; Earnshaw, J.J. Update on the prevention of death from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Med. Screen. 2017, 24, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, U.K.; Norman, P.E.; Fowkes, F.G.; Aboyans, V.; Song, Y.; Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Naghavi, M.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; et al. Estimation of global and regional incidence and prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms 1990 to 2010. Glob. Heart 2014, 9, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, V.; Klopf, J.; Eilenberg, W.; Neumayer, C.; Brostjan, C. AAA revisited: A comprehensive review of risk factors, management, and hallmarks of pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Granville, D.J.; Golledge, J.; Kassiri, Z. Pathogenic mechanisms and the potential of drug therapies for aortic aneurysm. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H652–H670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokje, V.B.; Hamming, J.F.; Lindeman, J.H. Editor’s choice—Pharmaceutical management of small abdominal aortic aneurysms: A systematic review of the clinical evidence. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubost, C.; Allary, M.; Oeconomos, N. Resection of an aneurysm of the abdominal aorta: Reestablishment of the continuity by a preserved human arterial graft, with result after five months. AMA Arch. Surg. 1952, 64, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volodos, N.L.; Karpovich, I.P.; Troyan, V.I.; Kalashnikova, Y.V.; Shekhanin, V.E.; Ternyuk, N.E.; Neoneta, A.S.; Ustinov, N.I.; Yakovenko, L.F. Clinical experience of the use of self-fixing synthetic prostheses for remote endoprosthetics of the thoracic and the abdominal aorta and iliac arteries through the femoral artery and as intraoperative endoprosthesis for aorta reconstruction. VASA. Suppl. 1991, 33, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parodi, J.C.; Palmaz, J.C.; Barone, H.D. Transfemoral intraluminal graft implantation for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 5, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.L.; Arons, R.R.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Gelijns, A.; Magnell, C.; Faries, P.L.; Clair, D.; Nowygrod, R.; Kent, K.C. A statewide experience with endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: Rapid diffusion with excellent early results. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, B.F.; Scali, S.T.; D’Oria, M.; Neal, D.; Schermerhorn, M.L.; Huber, T.S.; Columbo, J.A.; Stone, D.H. Temporal trends and outcomes of abdominal aortic aneurysm care in the United States. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2024, 17, e010374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.W.; Sedrakyan, A.; Mao, J.; Venermo, M.; Faizer, R.; Debus, S.; Behrendt, C.A.; Scali, S.; Altreuther, M.; Schermerhorn, M.; et al. Variations in abdominal aortic aneurysm care: A report from the International Consortium of Vascular Registries. Circulation 2016, 134, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettex, D.A.; Lachat, M.; Pfammatter, T.; Schmidlin, D.; Turina, M.I.; Schmid, E.R. To compare general, epidural and local anaesthesia for endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2001, 21, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhaneni, S.R.; Harris, P.L. Lessons learnt from the EUROSTAR registry on endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur. J. Radiol. 2001, 39, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, R.M.; Brown, L.C.; Kwong, G.P.; Powell, J.T.; Thompson, S.G.; EVAR Trial Participants. Comparison of endovascular aneurysm repair with open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 1), 30-day operative mortality results: Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinssen, M.; Verhoeven, E.L.; Buth, J.; Cuypers, P.W.; van Sambeek, M.R.; Balm, R.; Buskens, E.; Grobbee, D.E.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Dutch Randomized Endovascular Aneurysm Management (DREAM) Trial Group. A randomized trial comparing conventional and endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.; White, G.H.; Yu, W.; Ly, C.N.; Waugh, R.; Stephen, M.S.; Arulchelvam, M.; Harris, J.P. Concurrent comparison of endoluminal versus open repair in the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: Analysis of 303 patients by life table method. J. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 27, 213–220; discussion 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostakos, J.; Lal, B.K. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 65, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siribumrungwong, B.; Kurita, J.; Ueda, T.; Yasui, D.; Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Miyagi, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Ishii, Y.; Morota, T.; et al. Outcomes of abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs: Endovascular aneurysm vs. open surgical repairs. Asian J. Surg. 2021, 45, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovic, L.B.; Maksic, M.; Koncar, I.; Ilic, N.; Dragas, M.; Fatic, N.; Markovic, M.; Banzic, I.; Mutavdzic, P. Open repair of AAA in a high volume center. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twine, C.P.; Von-Oppell, U.; Williams, I.M. Left retroperitoneal aortic aneurysm repair in patients unsuitable for endovascular treatment. ANZ J. Surg. 2014, 84, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.; Arnautovic, A.; Kilic, C.; Rembe, J.D.; Mulorz, J.; Schelzig, H.; Wagenhäuser, M.U.; Garabet, W. The comparison of endovascular and open surgical treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm in terms of safety and efficacy on the basis of a single-center 30-year experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Jing, Z. Open surgery (OS) versus endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) for hemodynamically stable and unstable ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (rAAA). Heart Vessel. 2016, 31, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopodis, N.; Galanakis, N.; Ioannou, C.V.; Tsetis, D.; Becquemin, J.P.; Antoniou, G.A. Time-to-event data meta-analysis of late outcomes of endovascular versus open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 628–638.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimerink, J.J.; Hoornweg, L.L.; Vahl, A.C.; Wisselink, W.; van den Broek, T.A.; Legemate, D.A.; Reekers, J.A.; Balm, R.; Amsterdam Acute Aneurysm Trial Collaborators. Endovascular repair versus open repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMPROVE Trial Investigators; Powell, J.T.; Sweeting, M.J.; Thompson, M.M.; Ashleigh, R.; Bell, R.; Gomes, M.; Greenhalgh, R.M.; Grieve, R.; Heatley, F.; et al. Endovascular or open repair strategy for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: 30-day outcomes from IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ 2014, 348, f7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviú-Molinari, T.; Chin-Bong Choi, J.; Roberts, M.C.; Faridmoayer, E.; Sharath, S.E.; Kougias, P. In-hospital mortality risk after endovascular and open aortic aneurysm repairs for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 80, 1448–1454.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Li, C.C.Y.; Cheng, M. Should open repair be the choice in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm instead of endovascular aortic repair—Experience in a tertiary referral vascular centre. Surg. Pr. 2022, 26, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Yordanov, M.D.; Hasso, M.; Heine, B.; Oberhuber, A. Open treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the endovascular era. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scali, S.T.; Stone, D.H. Modern management of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1323465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, P.; Oliveira-Pinto, J.; Mansilha, A. Abdominal compartment syndrome after r-EVAR: A systematic review with meta-analysis on incidence and mortality. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 1500–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A.M.; Venu, R.; Raja, P.I.; Saravanan, S.; Khan, U.; Kantawala, R.; Tasnim, S.; Bose, N.J.; Kumar, R.; Clementina, R.; et al. Outcomes of endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) compared to open repair in abdominal aortic aneurysm: An umbrella meta-analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e63183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulder, R.M.A.; Bastiaannet, E.; Hamming, J.F.; Lindeman, J.H.N. Meta-analysis of long-term survival after elective endovascular or open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L.; et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Böckler, D.; Vogl, T.J.; Grundmann, R.T. Endovascular and open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargul, M.; Skórka, P.; Gutowski, P.; Kazimierczak, A.; Rynio, P. Empowering EVAR: Revolutionizing patient understanding and qualification with 3D printing. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Columbo, J.A.; Kang, R.; Spangler, E.L.; Newhall, K.; Brooke, B.S.; Dosluoglu, H.; Lee, E.S.; Raffetto, J.D.; Henke, P.K.; Tang, G.S.; et al. Design of the PReferences for Open Versus Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (PROVE-AAA) Trial. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 65, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, N.; Giacovelli, J.K.; Gelijns, A.; Greco, G.; Moskowitz, A.; McKinsey, J.; Kent, K.C. Defining high-risk patients for endovascular aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 1271–1279.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EVAR Trial Participants. Endovascular aneurysm repair and outcome in patients unfit for open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR Trial 2): Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvroy, V.M.; Houben, I.B.; Trimarchi, S.; Patel, H.J.; Moll, F.L.; Van Herwaarden, J.A. Identifying and addressing the limitations of EVAR technology. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2018, 15, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitoulias, A.G.; Loutradis, C.N.; Chatzelas, D.A.; Pitoulias, M.G.; Politi, L.A.; Bontinis, V.; Pitoulias, G. Distal landing zone-related complications of conventional endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) in the long term: A comprehensive systematic review. Cureus 2025, 17, e77379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallitto, E.; Faggioli, G.; Mascoli, C.; Goretti, M.; Pini, R.; Logiacco, A.; Rocchi, C.; Feroldi, F.; Caputo, S.; Gargiulo, M. Morphological and clinical predictors of early/follow-up failure of the endovascular infrarenal abdominal aneurysm repair with currently available endografts. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2024, 31, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakalihasan, N.; Michel, J.B.; Katsargyris, A.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Defraigne, J.O.; Nchimi, A.; Powell, J.T.; Yoshimura, K.; Hultgren, R. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2018, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzelas, D.A.; Loutradis, C.N.; Pitoulias, A.G.; Kalogirou, T.E.; Pitoulias, G.A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of proximal aortic neck dilatation after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 77, 941–956.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EVAR Trial Participants. Endovascular aneurysm repair versus open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 1): Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Behrendt, C.A.; Falster, M.O.; Varcoe, R.L.; Zheng, X.; Peters, F.; Beiles, B.; Schermerhorn, M.L.; Jorm, L.; Beck, A.W.; et al. Long-term mortality and reintervention after endovascular and open abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs in Australia, Germany, and the United States. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, e626–e633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, G.A.; Antoniou, S.A.; Torella, F. Endovascular vs. open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm: Systematic review and meta-analysis of updated peri-operative and long-term data of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 59, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Powell, J.T.; Sweeting, M.J.; Epstein, D.M.; Barrett, J.K.; Greenhalgh, R.M. The UK EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) randomised controlled trials: Long-term follow-up and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2018, 22, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulakakis, K.G.; Dalainas, I.; Mylonas, S.; Giannakopoulos, T.G.; Avgerinos, E.D.; Liapis, C.D. Conversion to open repair after endografting for abdominal aortic aneurysm: A review of causes, incidence, results, and surgical techniques of reconstruction. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2010, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovic, L.B.; Palombo, D.; Treska, V.; Sladojevic, M.; Koncar, I.B.; Houdek, K.; Spinella, G.; Zlatanovic, P.; Pane, B. Late open conversion after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: Experience of three high-volume centers. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.; Riggi, M.; Wyss, T.R.; Jungi, S.; Weiss, S.; Kotelis, D.; Schmidli, J.; Bosiers, M.J.; Makaloski, V. Indication and outcome of late open conversion after abdominal endovascular aortic repair. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 106, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, A.; Robinson, D.; Malak, O.; Madigan, M.C.; Avgerinos, E.D.; Chaer, R.A.; Singh, M.J.; Makaroun, M.S. Increasing use of open conversion for late complications after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clagett, G.P. EVAR, TEVAR, FEVAR, too far? Perspect. Vasc. Surg. Endovasc. Ther. 2008, 20, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppelenbosch, N.; Buth, J.; Harris, P.L.; van Marrewijk, C.; Fransen, G.; EUROSTAR Collaborators. Diameter of abdominal aortic aneurysm and outcome of endovascular aneurysm repair: Does size matter? A report from EUROSTAR. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanzer, A.; Greenberg, R.K.; Hevelone, N.; Robinson, W.P.; Eslami, M.H.; Goldberg, R.J.; Messina, L. Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Sac Enlargement after Endovascular Repair. Circulation 2011, 123, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iner, H.; Yurekli, I.; Karaagac, E.; Peker, I.; Tunca, N.U.; Tellioglu, T.M.; Durmaz, H.; Selcuk, H.O.; Yilik, L. Expanding the EVAR pool with non-IFU patients: How important is subjective physician assessment? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; Allen, C.; Grima, M.J.; Brownrigg, J.R.W.; Patterson, B.O.; Holt, P.J.E.; Thompson, M.M.; Karthikesalingam, A. A systematic review of predictors of reintervention after EVAR: Guidance for risk-stratified surveillance. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 51, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouvelos, G.; Koutsoumpelis, A.; Lazaris, A.; Matsagkas, M. Late open conversion after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultee, K.H.; Soden, P.A.; Zettervall, S.L.; Darling, J.; Verhagen, H.J.; Schermerhorn, M.L. Conversion from endovascular to open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Byrne, W.J.; Robinson, H.; Roddy, S.P.; Paty, P.S.; Kreienberg, P.B.; Feustel, P.; Darling, R.C., III. Women derive less benefit from elective endovascular aneurysm repair than men. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 55, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.C.; Kan, C.D.; Hsieh, C.C.; Omara, M.; Henry, B.M.; Davidovic, L.B. Improved outcomes from endovascular aortic repair in younger patients: Towards improved risk stratification. Vascular 2019, 27, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Ricco, J.B. Part two: Against the motion. Young patients with good risk factors should not be treated with EVAR. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2013, 46, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuzawa, K.; Ohki, T.; Maeda, K.; Kanaoka, Y. Risk factors and treatment outcomes for stent graft infection after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunnerhagen, T.; Schwartz, F.; Christophersen, L.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Qvortrup, K.; Eldrup, N.; Vogt, K.; Moser, C. Biofilm formation on endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) grafts—A proof of concept in vitro model. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 1600.e1–1600.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berard, X.; Brizzi, V. Current management of aortic endograft infection: Prepare your team for this new challenge. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 58, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörelius, K.; Mani, K.; Björck, M.; Sedivy, P.; Wahlgren, C.M.; Taylor, P.; Clough, R.E.; Lyons, O.; Thompson, M.; Brownrigg, J.; et al. Endovascular treatment of mycotic aortic aneurysms: A European multicenter study. Circulation 2014, 130, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Silver, M.; Jacob, T.; Meghpara, M.; Almadani, M.; Shiferson, A.; Rhee, R.; Pu, Q. Open conversion after failed endovascular aneurysm repair is increasing and its 30-day mortality is higher than that after primary open repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 76, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin, B.; Akkaya, B.B.; Mavioğlu, H.L.; İşcan, H.Z. A retrospective analysis of late open conversions following failed endovascular aneurysm repair. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
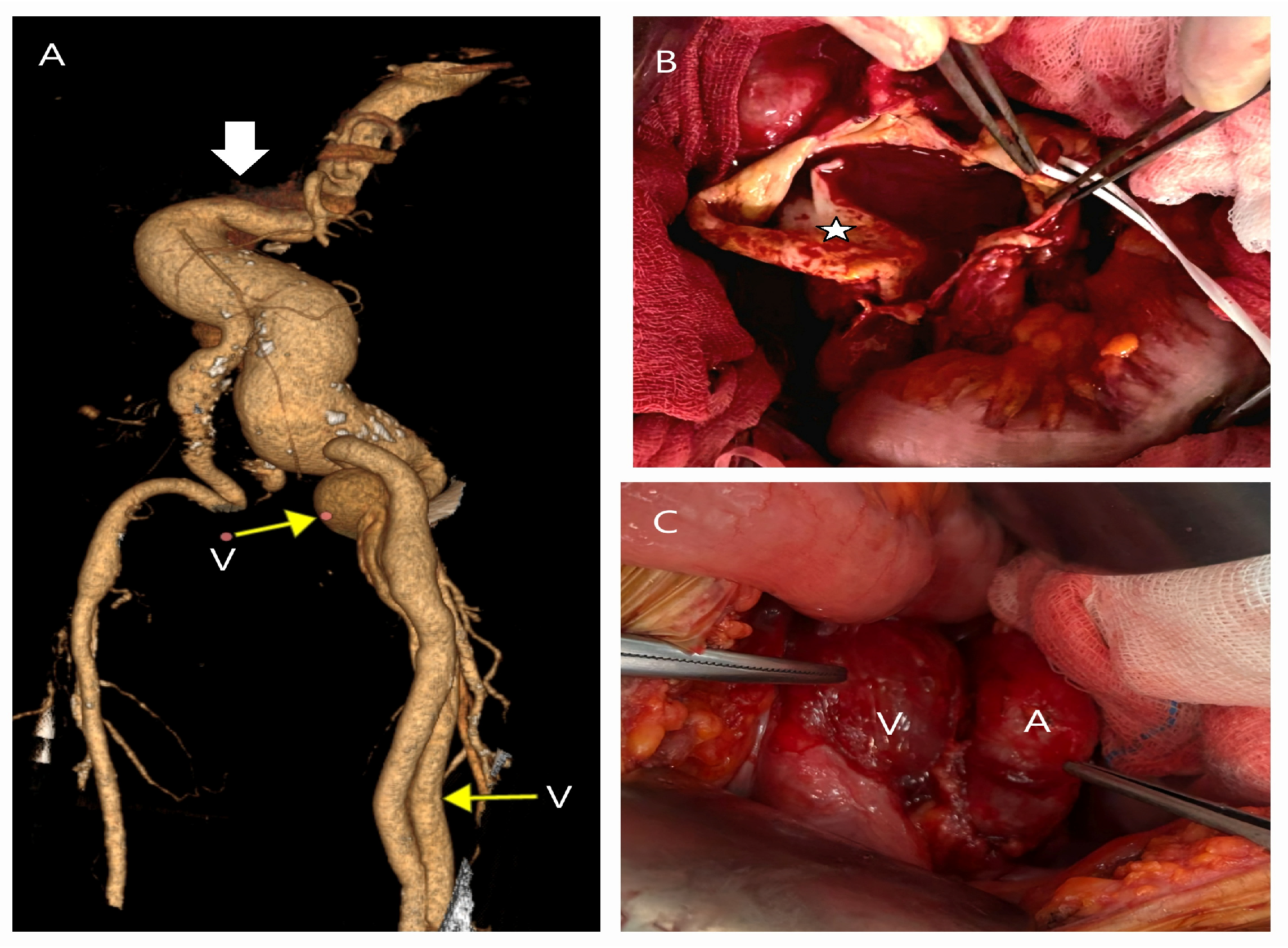
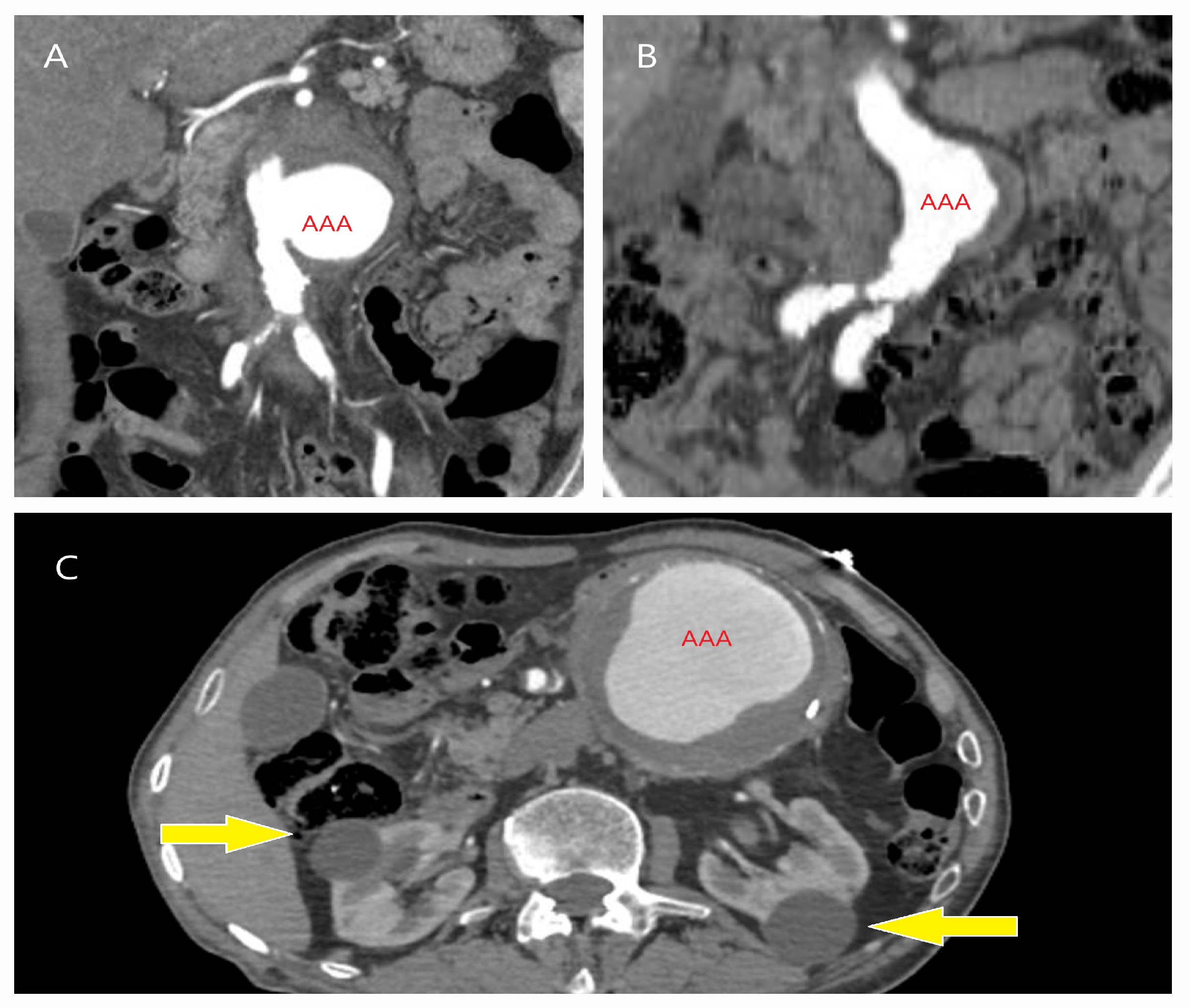
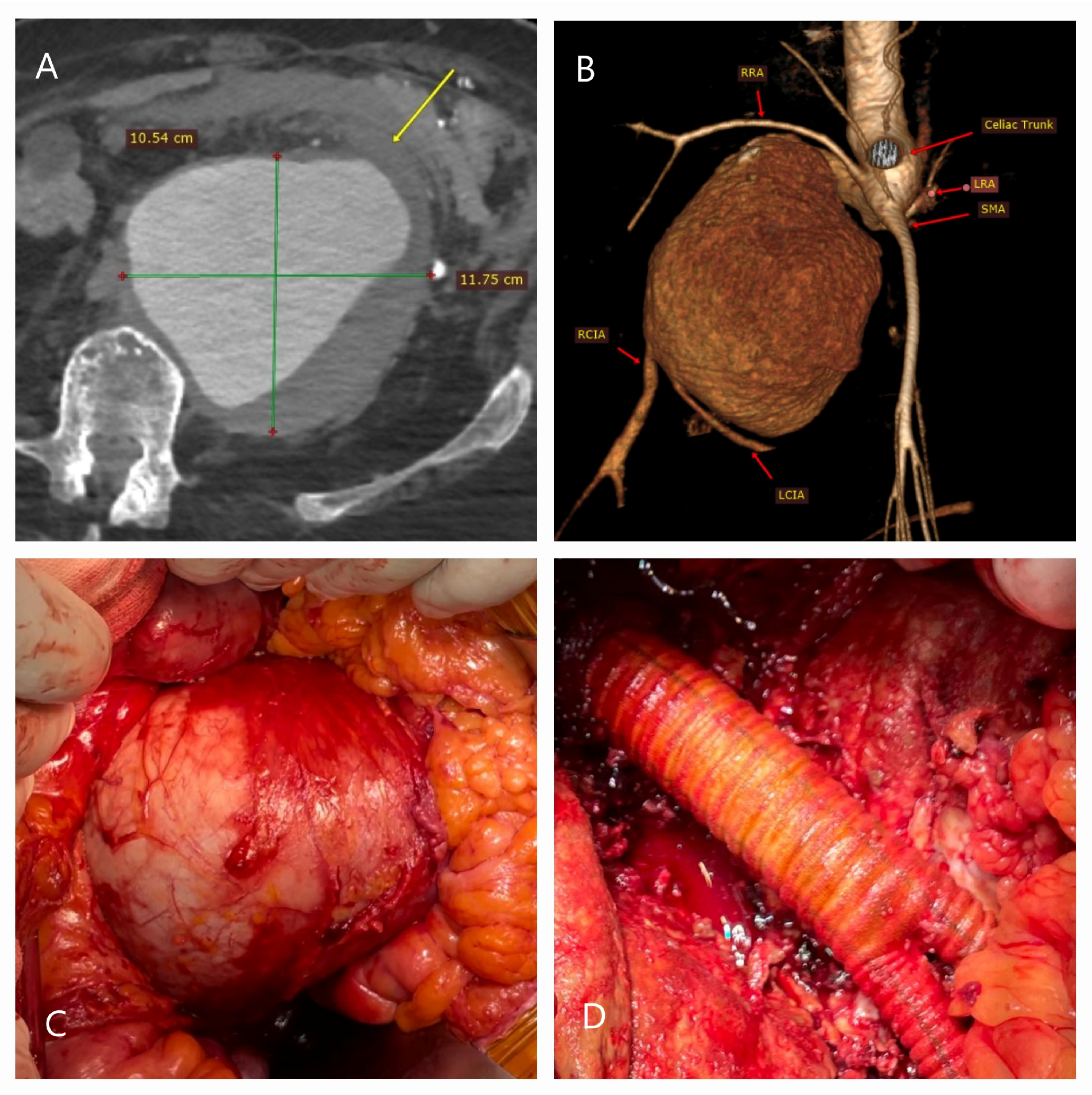
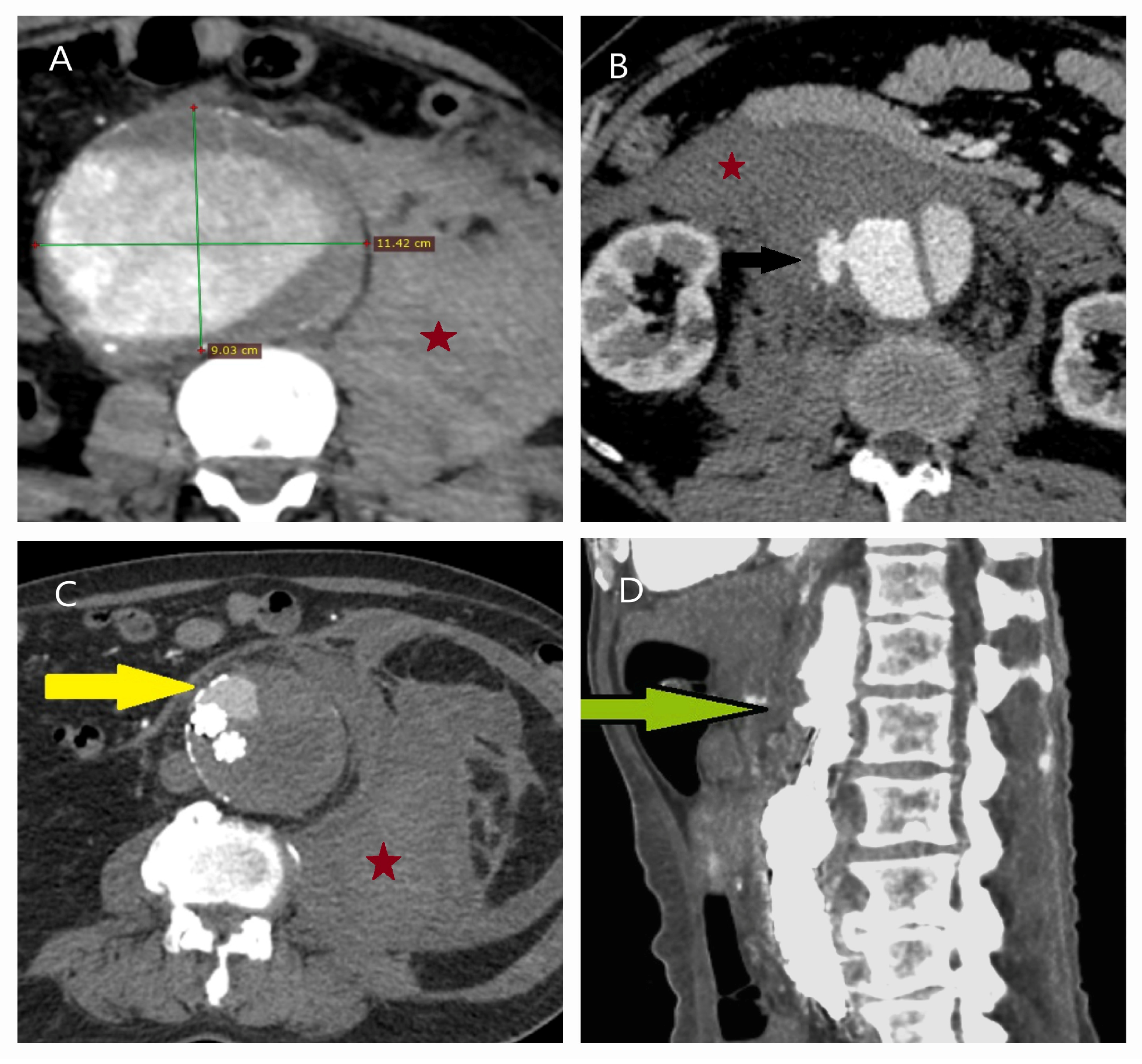
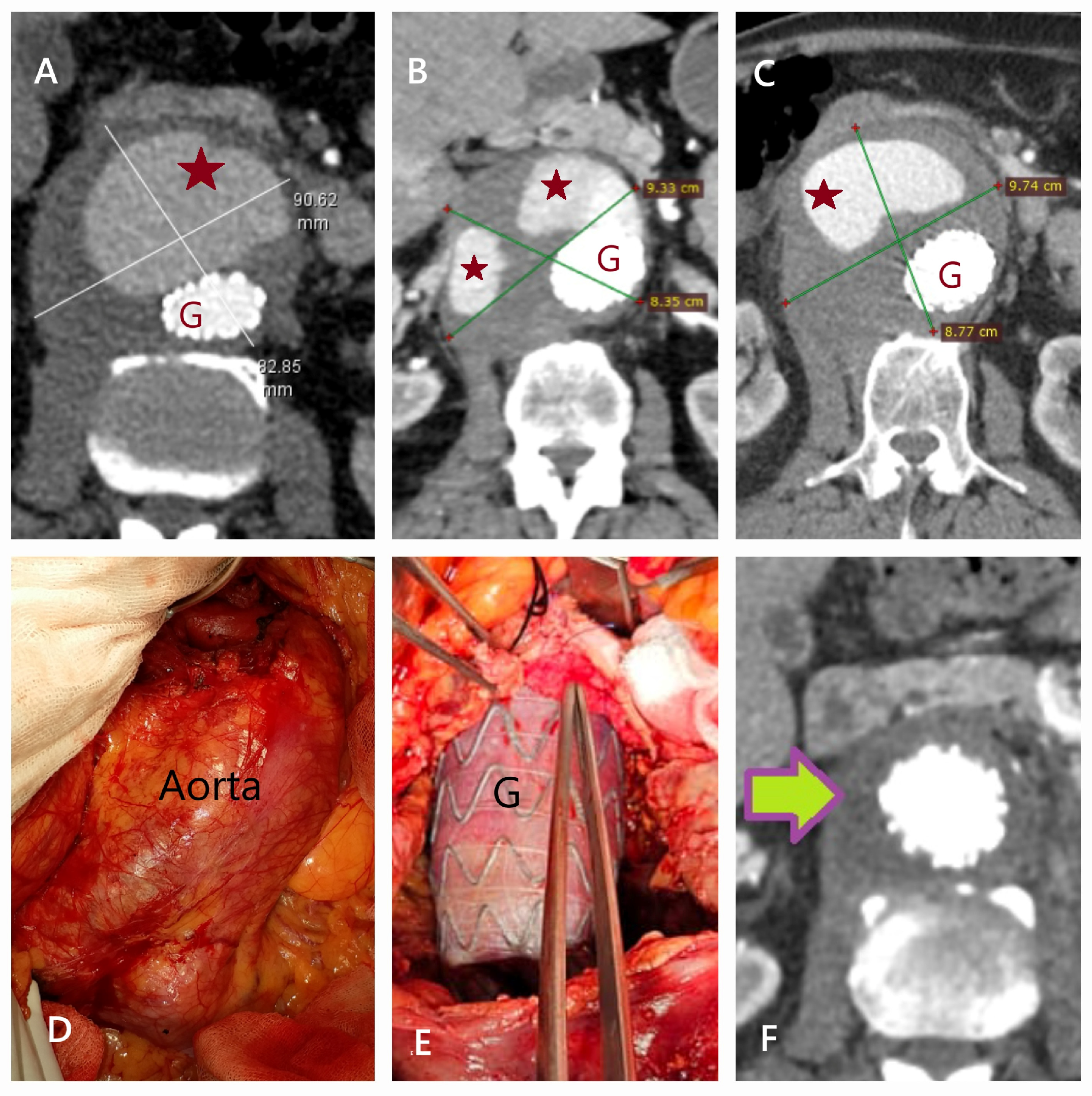
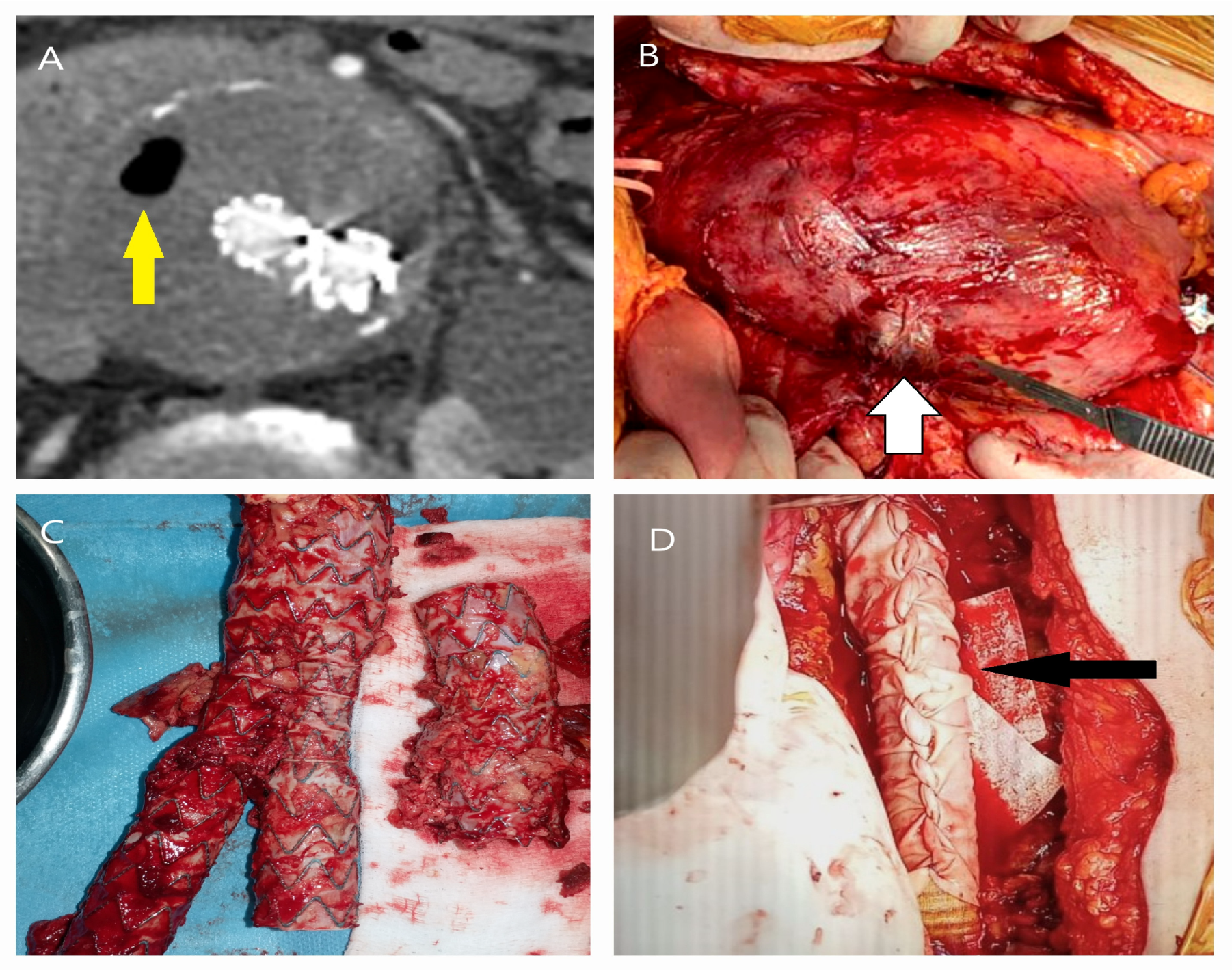

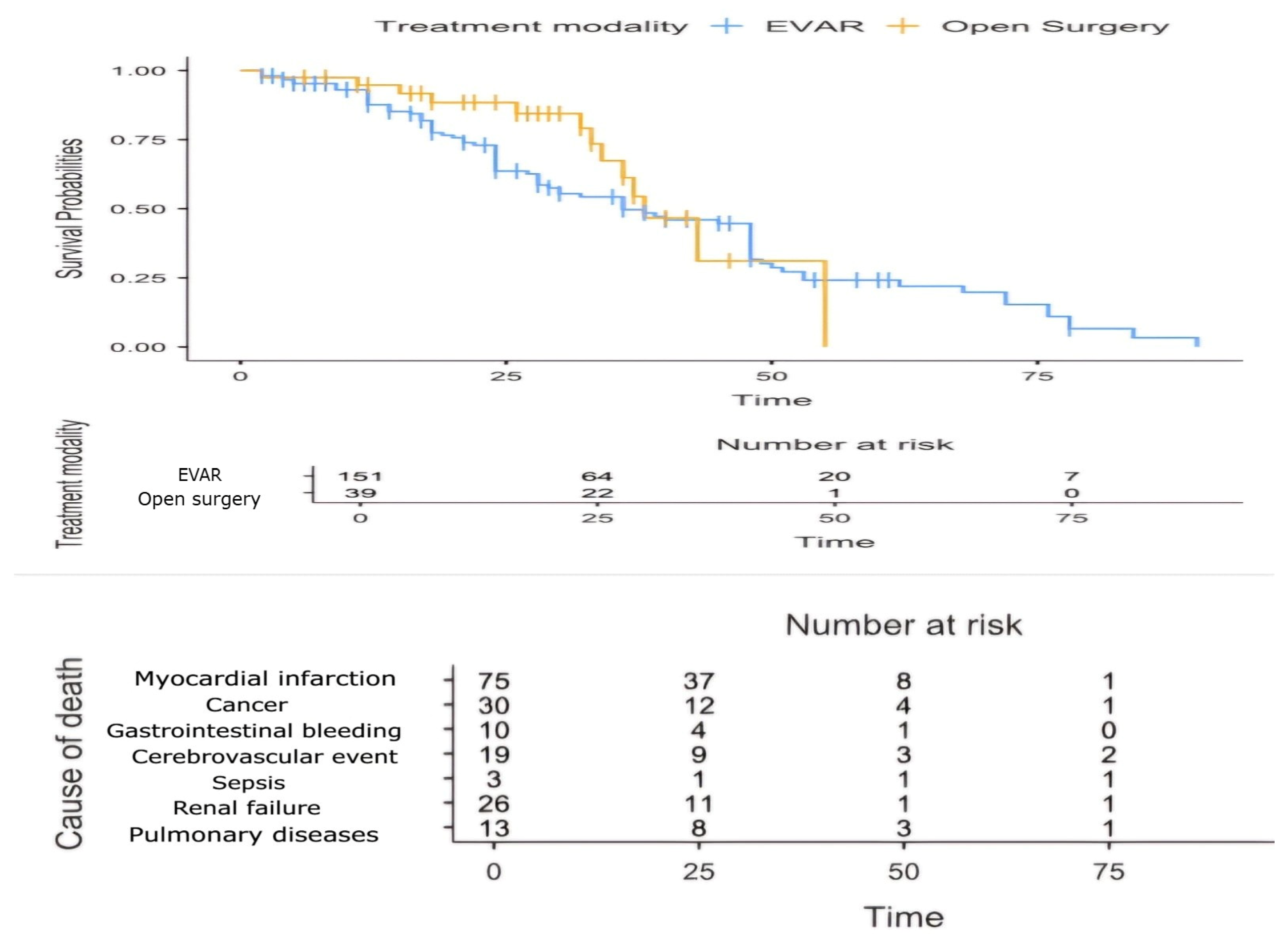


| Patient Demographics | Treatment Modality | Patients with Rupture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVAR (n =163) | OSR (n = 47) | p | EVAR (n = 19) | OSR (n = 15) | p | ||
| Female/Male | 21/142 | 6/41 | 0.983 | 5/14 | 0/15 | 0.042 | |
| Age (years) | 73.5 ± 8.7 | 68.7 ± 8.7 | 0.001 | 72.3 ± 12.9 | 71.4 ± 6.0 | 0.790 | |
| Smoker | 148 (90.8%) | 40 (85.1%) | 0.263 | 17 | 13 | 0.603 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 45 (27.6%) | 11 (23.4%) | 0.566 | 5 | 5 | 0.978 | |
| Hypertension | 152 (93.3%) | 38 (80.9%) | 0.011 | 18 | 13 | 0.409 | |
| COPD | 124 (76.1%) | 29 (61.7%) | 0.051 | 13 | 11 | 0.755 | |
| * Cardiac disease | 113 (69.3%) | 28 (59.6%) | 0.210 | 16 | 9 | 0.112 | |
| ** Renal disease | 53 (32.5%) | 19 (40.4%) | 0.327 | 12 | 12 | 0.285 | |
| *** Extracoronary arteriopathy | 28 (17.2%) | 9 (19.1%) | 0.755 | 1 | 4 | 0.080 | |
| Cancer | 20 (12.3%) | 5 (10.6%) | 0.761 | 3 | 1 | 0.397 | |
| Saccular aneurysm | 9 (5.5%) (Tube graft no iliac limbs) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.103 | - | - | - | |
| Mycotic aneurysm | 0 | 2 (4%) | NA | - | - | - | |
| Incidental diagnosis | 57 (35%) | 9 (19.1%) | <0.05 | - | - | - | |
| Diameter (mm) | Anteroposterior | 66.9 ± 12.9 | 68.8 ± 17.5 | 0.567 | 81.0 ± 14.4 | 81.0 ± 21.7 | 1 |
| Transvers | 67.5 ± 12.9 | 71.5 ± 16.1 | 0.042 | 82.7 ± 12.0 | 83.8 ± 19.5 | 0.478 | |
| Level of the renal artery | 21.9 ± 3.6 | 22.8 ± 6.3 | 0.148 | 22.5 ± 4.5 | 23.8 ± 5.2 | 0.455 | |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 124 ± 40 | 129 ±42 | 0.483 | 144 ± 56 | 147 ± 53 | 0.880 | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.4 ± 2.8 | 13.3 ± 2.3 | 0.697 | 10.6 ± 2.4 | 10.8 ±2.5 | 0.812 | |
| Hematocrit, % | 42.5 ± 27.3 | 40.0 ± 8.3 | 0.538 | 32.1 ± 7.0 | 32.7 ± 7.7 | 0.818 | |
| WBC, 103/µL | 9.4 ± 3.4 | 10.4 ± 4.7 | 0.423 | 12.1 ± 4.7 | 14.8 ± 5.2 | 0.123 | |
| ALT, U/L | 22.2 ± 17.9 | 29.7 ± 24.9 | 0.078 | 24.8 ± 18.7 | 46.2 ± 36.8 | 0.089 | |
| AST, U/L | 27.0 ± 20.0 | 40.2 ± 35.4 | 0.091 | 37.5 ± 23.9 | 61.2 ± 55.2 | 0.286 | |
| BUN, mg/dL | 23.5 ± 11.7 | 29.6 ± 15.6 | 0.054 | 32.5 ± 17.5 | 42.3 ± 15.1 | 0.096 | |
| Cr, mg/dL | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 0.168 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 1.0 | 0.280 | |
| LDL, mg/dL | 113 ± 32 | 117 ± 31 | 0.381 | 88 ± 34 | 111 ± 36 | 0.068 | |
| D-dimer, mg/L | 5.4 ± 4.7 | 5.9 ± 6.1 | 0.213 | 15.2 ± 4.4 | 12.5 ± 4.7 | 0.104 | |
| CRP, mg/L | 33.6 ± 37.2 | 47.4 ± 58.5 | 0.653 | 100.3 ± 33.5 | 106.0 ± 55.3 | 0.918 | |
| HbA1c, % | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 0.546 | 6.1 ± 1.0 | 6.6 ± 1.3 | 0.238 | |
| Anatomical Challenges | EVAR | OSR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Female | Male | |
| Neck diameter of <17 mm or >32 mm | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Neck length of <15 mm | 2 | 12 | 3 | 8 |
| Neck angulation of > 600 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Neck thrombus > 50% | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Distal iliac artery diameter of <8 mm or >20 mm | 2 | 5 | 1 | 7 |
| Small common femoral artery (<6 mm) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Univariable | Multivariable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor | Estimate | p | OR (95% CI) | Estimate | p | OR (95% CI) |
| Open surgery | 0.9 | 0.053 | 2.5 (0.98–6.7) | 1.14 | 0.212 | 3.2 (0.5–18.8) |
| Rupture | 2.7 | <0.001 | 15.0 (5.3–41.6) | 1.7 | 0.045 | 5.8 (1.0–32.3) |
| Female | 1.24 | 0.022 | 3.4 (1.2–9.9) | 2.8 | 0.018 | 16.7 (1.7–88.0) |
| Age | 0.01 | 0.659 | 1.01 (0.96–1.07) | 0.05 | 0.398 | 1.04 (0.95–1.15) |
| Aortic size index (cm/m2) | 1.06 | <0.001 | 2.9 (1.6–5.0) | 1.3 | 0.019 | 3.7 (1.2–10.9) |
| BMI > 28 (kg/cm2) | 0.15 | 0.080 | 1.15 (0.98–1.36) | 0.81 | 0.003 | 2.2 (1.3–3.9) |
| Cardiac disease | 0.73 | 0.206 | 2.1 (0.67–6.5) | 2.1 | 0.064 | 8.4 (0.8–80.0) |
| Preoperative creatinin >1.8 mg/dL | 1.8 | <0.01 | 6.2 (2.3–16.3) | 0.3 | 0.718 | 1.5 (0.2–9.1) |
| Nephropathy with dialysis | 3.1 | <0.001 | 23.5 (8.0–69.0)) | 1.4 | 0.101 | 4.2 (0.7–24.0) |
| Presence of complication | 3.0 | <0.001 | 20.5 (5.7–67.0) | 3.0 | 0.003 | 20 (2.6–127.0) |
| Complications | EVAR | Treatment | OSR | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal tamponade | 4 | Open surgery | 3 | Re-exploration |
| Mesenteric ischemia/ileus | 1 | Open surgery | 1 | Re-exploration- |
| Paralytic ileus | - | - | 3 | Mobilization |
| Sepsis | 1 | Sepsis filter and antibiotics | 2 | Sepsis filter and antibiotics (One patient with stent graft infection) |
| Femoral bleeding or pseudoaneurysm | 3 | Revision/aneurysmectomy | 6 | Revision/aneurysmectomy |
| Graft limb thrombosis/kinked | 5 | Embolectomy/balloon Angioplasty/cross-femoral bypass | 2 | Embolectomy |
| Graft infection | 2 | Stent explantation | ||
| Graft migration | 1 | Stent explantation | ||
| Type Ia endoleak | 6 | Stent-sparing surgery (2 cases); Proximal stent extension (4 cases) | ||
| Type Ib endoleak | 10 | Stent extension and balloon angioplasty | ||
| Type II endoleak | 3 | Embolization | ||
| Type V endoleak | 1 | Stent-sparing surgery |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arslan, Ü.; Yıldız, Z.; Pir, İ.; Aykut, Ç. The Justification of Open Surgical Repair for an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Retrospective Comparison of Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair and a Brief Review of the Literature. Life 2025, 15, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030426
Arslan Ü, Yıldız Z, Pir İ, Aykut Ç. The Justification of Open Surgical Repair for an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Retrospective Comparison of Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair and a Brief Review of the Literature. Life. 2025; 15(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleArslan, Ümit, Ziya Yıldız, İbrahim Pir, and Çağrı Aykut. 2025. "The Justification of Open Surgical Repair for an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Retrospective Comparison of Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair and a Brief Review of the Literature" Life 15, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030426
APA StyleArslan, Ü., Yıldız, Z., Pir, İ., & Aykut, Ç. (2025). The Justification of Open Surgical Repair for an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Retrospective Comparison of Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair and a Brief Review of the Literature. Life, 15(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030426