Combined Neurotoxic Effects of Commercial Formulations of Pyrethroid (Deltamethrin) and Neonicotinoid (Imidacloprid) Pesticides on Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral, Molecular, and Histopathological Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioral Evaluation
2.4.1. Behavioral Observation and Data Collection
2.4.2. Behavioral Parameters and Severity Scoring
2.5. Assessment of NTs and Their Receptors Gene Expression
2.5.1. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
2.5.2. cDNA Synthesis and Quantification
2.5.3. Primer Validation and Standard Curve Generation
2.5.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.5.5. Data Normalization and Expression Calculation
2.6. Assessment of Histopathological Changes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zebrafish Behavior Assessment
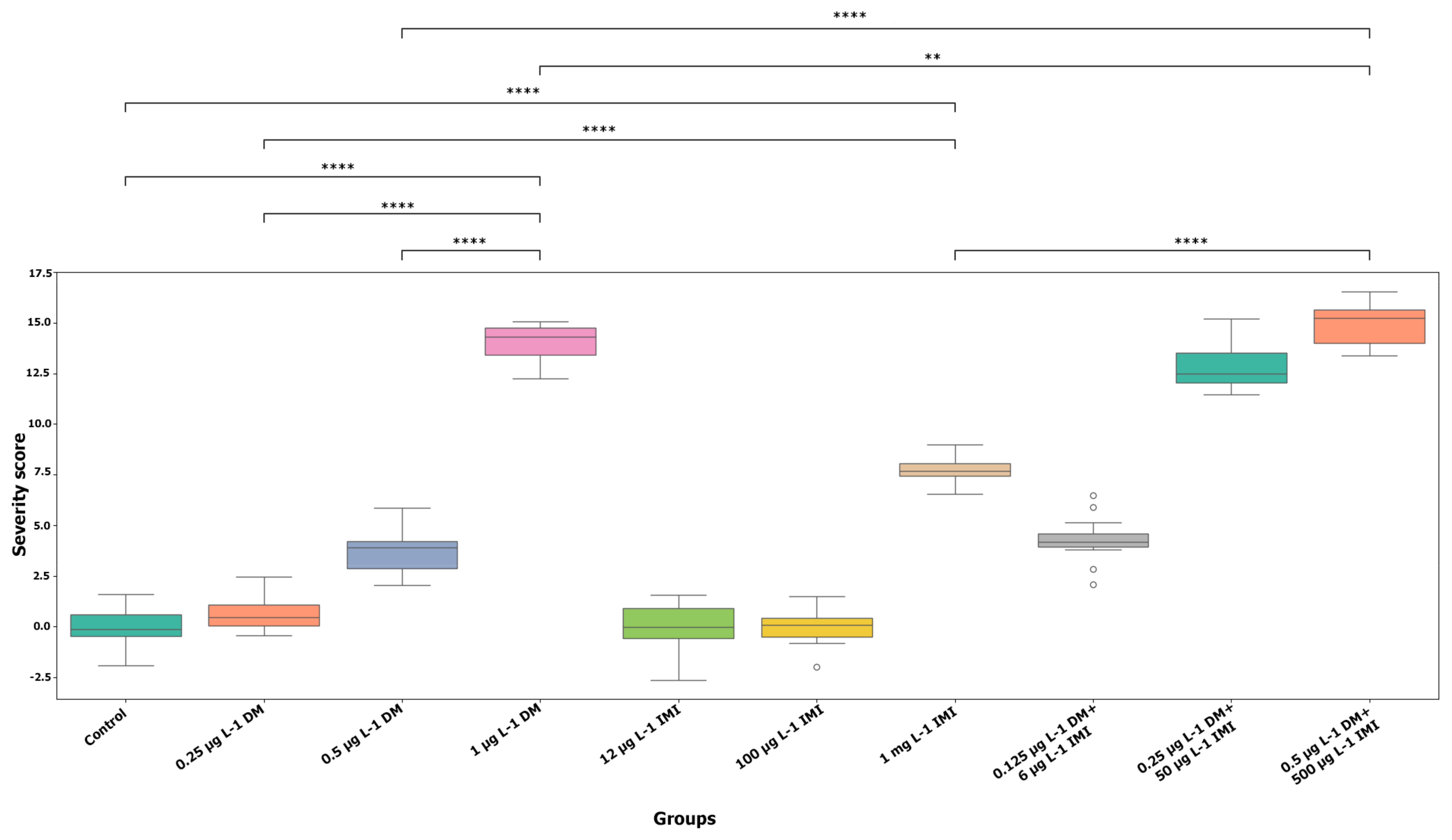
3.1.1. Behavioral Severity Analysis
3.1.2. Statistical Analysis of Behavioral Alterations
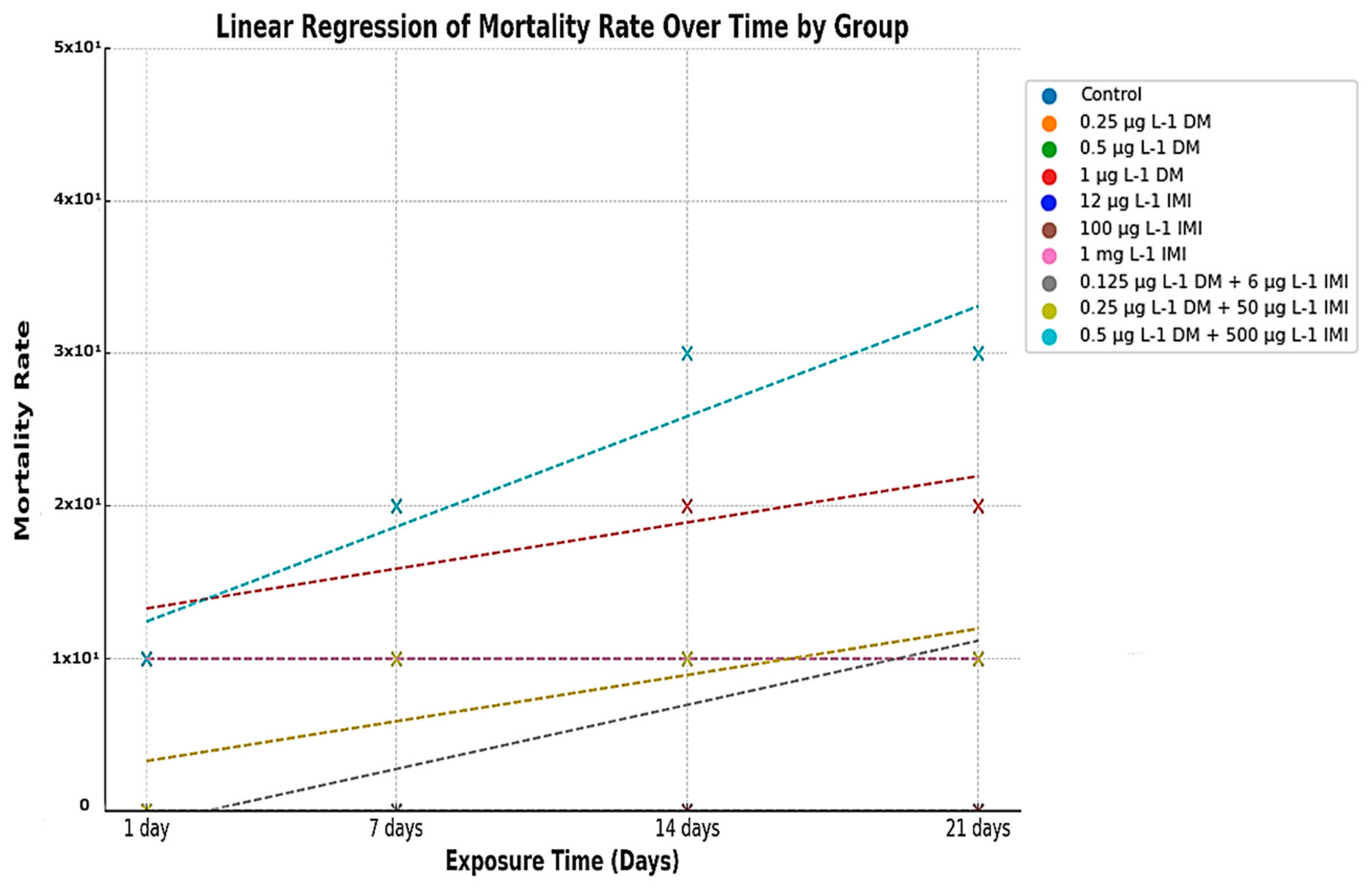
3.2. Mortality Assessment
Mortality Trends and Statistical Analysis
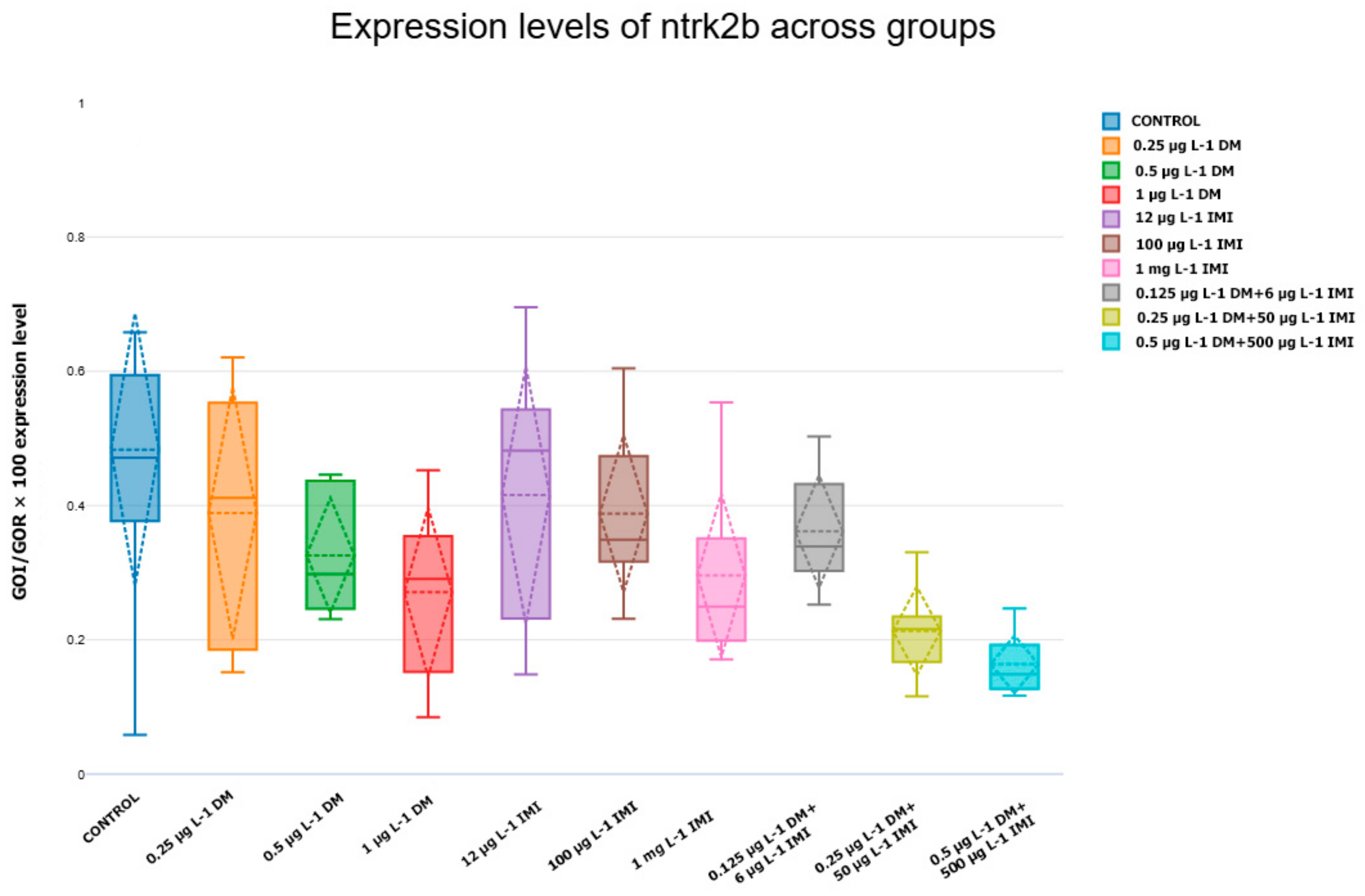
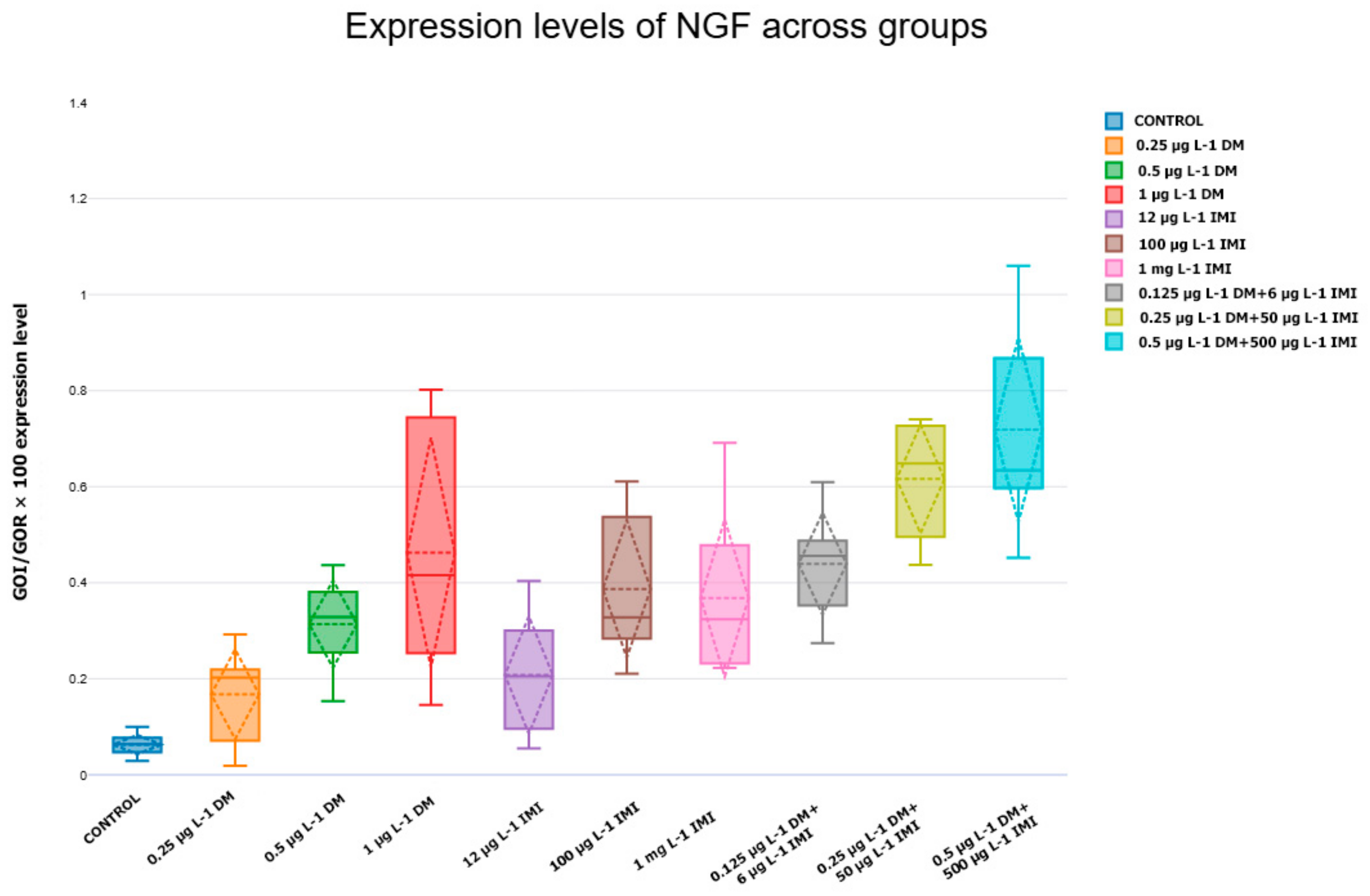
3.3. NTs and Their Receptors Upregulated/Downregulated Gene Expression
3.3.1. BDNF and TrkB Expression
3.3.2. NGF and TrkA Expression
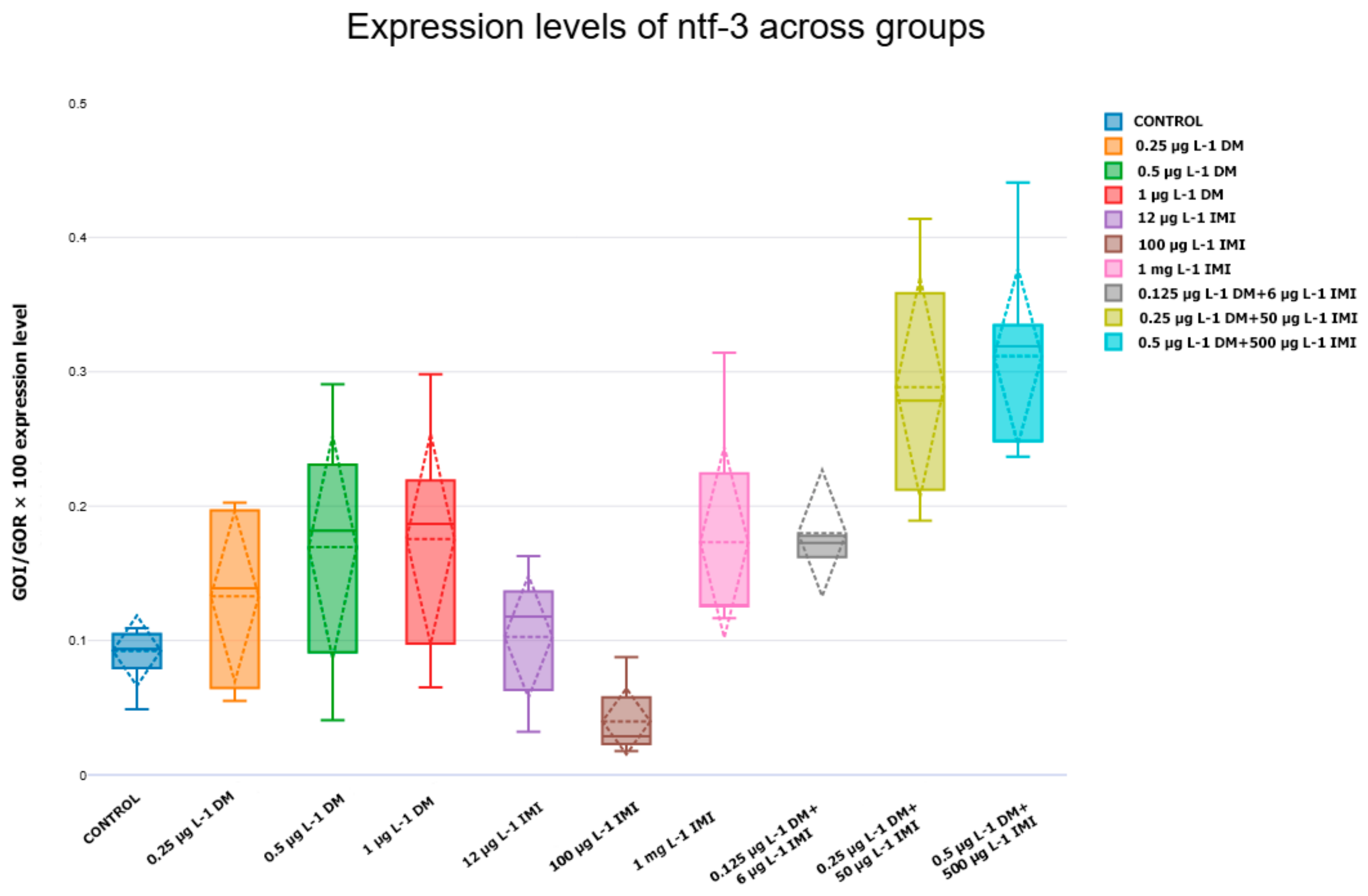
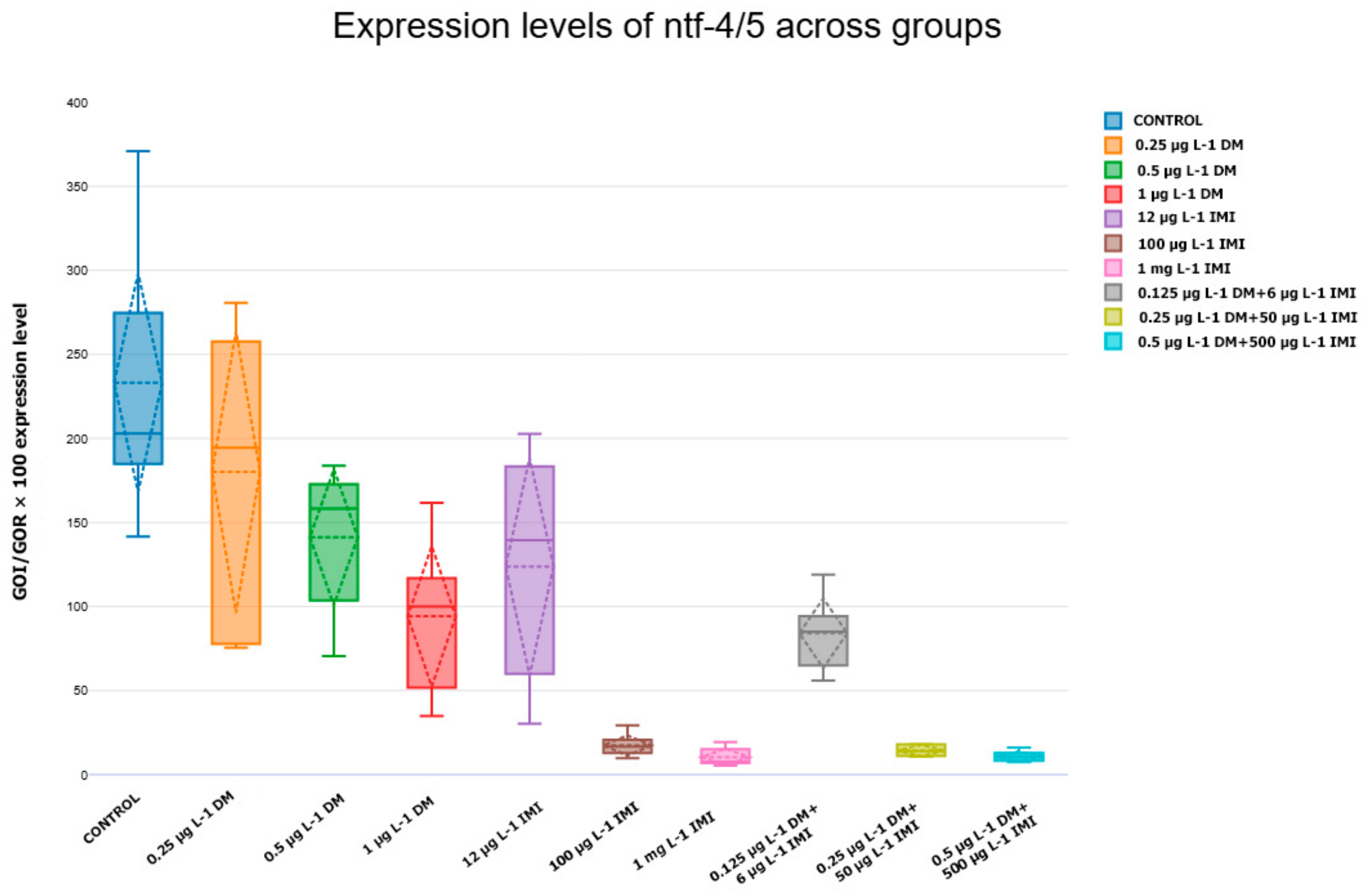
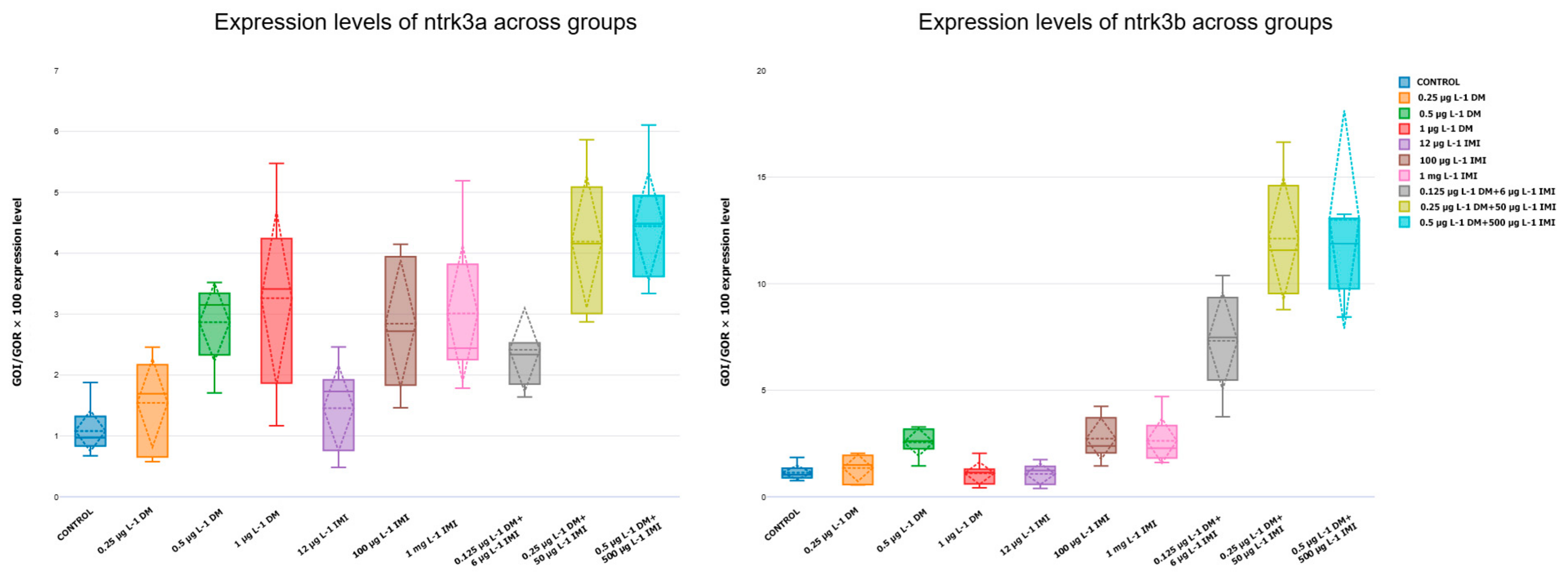
3.3.3. Expression Levels of ntf-3, ntf-4/5, ntrk3a, and ntrk3b
3.4. Histopathological Changes
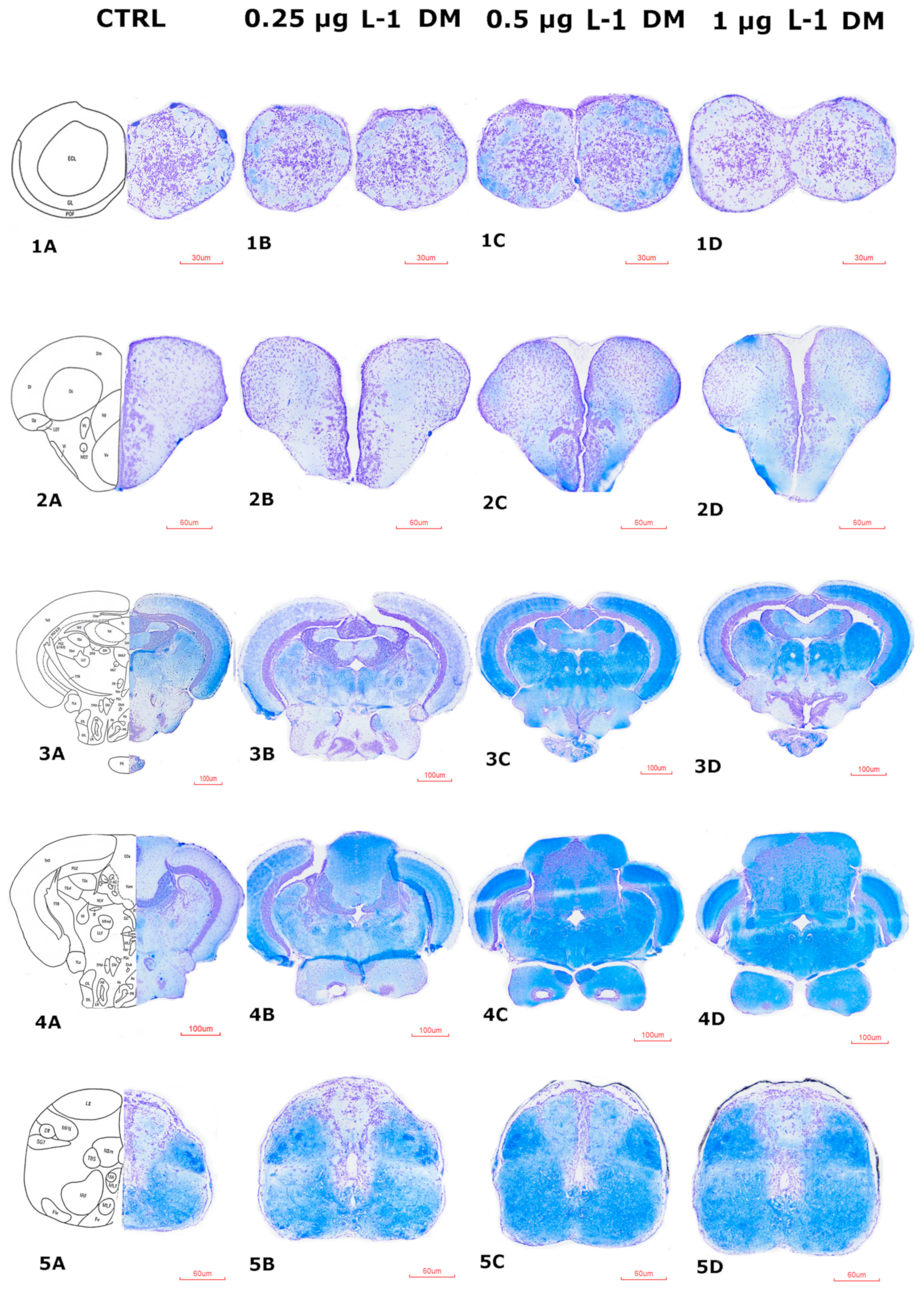
3.4.1. Histological Impairments of the Zebrafish Brain After DM Exposure
3.4.2. Histological Impairments of the Zebrafish Brain After IMI Exposure
3.4.3. Histological Impairments of the Zebrafish Brain After DM-IMI Exposure
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.K. Mode of action of pesticides and the novel trends—A critical review. Int. Res. J. Agric. Soil Sci. 2013, 3, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunast, C.; de Graeff, R.; Whitmore, G. Pesticides and Biodiversity Agricultural Productivity and Biodiversity Conservation. ELO (European Landowners’ Organization), ECPA (European Crop Protection Association). 2013. Available online: www.ecpa.eu (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- WHO. The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification, 2019th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. How Pesticides are Regulated in the EU—EFSA and the Assessment of Active Substances; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Craig, P.S.; Dujardin, B.; Hart, A.; Hernández-Jerez, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Kneuer, C.; Ossendorp, B.; Pedersen, R.; Wolterink, G.; et al. Cumulative dietary risk characterisation of pesticides that have acute effects on the nervous system. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, B.; Bocca, V. Cumulative dietary exposure assessment of pesticides that have acute effects on the nervous system using SAS® software. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, L.C.; Pastor, P.M. The 2020 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Goulson, D.; Pennacchio, F.; Nazzi, F.; Goka, K.; Desneux, N. Are bee diseases linked to pesticides?—A brief review. Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Troxler, A.; Retschnig, G.; Roth, K.; Yañez, O.; Shutler, D.; Neumann, P.; Gauthier, L. Neonicotinoid pesticides severely affect honey bee queens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Falquet, L.; Fragnière, A.L.; Brown, A.; Bacher, S. Effects of pesticides on soil bacterial, fungal and protist communities, soil functions and grape quality in vineyards. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2024, 5, e12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Van Den Brink, P.J.; Mann, R.M.; Schäfer, R.B.; Liess, M. Impacts of Pesticides on Freshwater Ecosystems. In Ecological Impacts of Toxic Chemicals; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2011; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bragança, I.A.G. Pyrethroid Pesticides in Soils: Assessment and Environmental Impact; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, D. Environmental and economic costs of the application of pesticides primarily in the United States. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2005, 7, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, F.; Bengtsson, J.; Berendse, F.; Weisser, W.W.; Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.B.; Ceryngier, P.; Liira, J.; Tscharntke, T.; Winqvist, C.; et al. Persistent negative effects of pesticides on biodiversity and biological control potential on European farmland. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Choudhary, D.; Bali, S.; Bandral, S.S.; Singh, V.; Ahmad, A.; Rani, N.; Singh, T.G.; Chandrasekaran, B. Pesticides: An alarming detrimental to health and environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 915, 170113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Sinha, A.K. Pesticides in Agricultural Run Offs Affecting Water Resources: A Study of Punjab (India). Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, M.; Henz, S.; Shahid, N. Modeling the synergistic effects of toxicant mixtures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Liess, M.; Knillmann, S. Environmental Stress Increases Synergistic Effects of Pesticide Mixtures on Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12586–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetz, C.A.; Baldwin, D.H.; Collier, T.K.; Hebert, V.; Stark, J.D.; Scholz, N.L. The synergistic toxicity of pesticide mixtures: Implications for risk assessment and the conservation of endangered Pacific salmon. Environ. Health Perspect 2009, 117, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Shen, W.; Xu, C.; Di, S.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Synergistic effect of fenpropathrin and paclobutrazol on early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Jia, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, S.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y. Individual and synergistic toxic effects of carbendazim and chlorpyrifos on zebrafish embryonic development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pesticide Programs. Organophosphorus Cumulative Risk Assessment. 2006. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=P1010KM6.TXT (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- FAO; WHO. Manual on development and use of FAO and WHO specifications for pesticides. In FAO/WHO Joint Meeting on Pesticide Specifications (JMPS); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Guidelines on Good Labelling Practice for Pesticides Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- EC. Farm to Fork: New Rules to Reduce the Risk and Use of Pesticides in the EU; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kortenkamp, A.; Backhaus, T.; Faust, M. State of the Art Report on Mixture Toxicity; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Wrzecińska, M.; Czerniawska-Piątkowska, E.; Araújo, J.P.; Cwynar, P. Molecular consequences of the exposure to toxic substances for the endocrine system of females. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-M.; Cheong, A.; Adgent, M.A.; Veevers, J.; Suen, A.A.; Tam, N.N.C.; Leung, Y.-K.; Jefferson, W.N.; Williams, C.J. Environmental factors, epigenetics, and developmental origin of reproductive disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.M.; Eugster, E.A. What is in our environment that effects puberty? Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloizou, A.-M.; Siokas, V.; Vogiatzi, C.; Peristeri, E.; Docea, A.O.; Petrakis, D.; Provatas, A.; Folia, V.; Chalkia, C.; Vinceti, M.; et al. Pesticides, cognitive functions and dementia: A review. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 326, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Feng, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Yao, P.; Liu, X.; et al. Pesticides, cancer, and oxidative stress: An application of machine learning to NHANES data. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammachai, A.; Sapbamrer, R. Effects of Organophosphate Pesticides on Neurological Impairment. Naresuan Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.L. Neuropathological mechanisms associated with pesticides in Alzheimer’s disease. Toxics 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, S.; Koehn, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Pfeil, R.; Kneuer, C.; Marx-Stoelting, P. Combination effects of (Tri)azole fungicides on hormone production and xenobiotic metabolism in a human placental cell line. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9660–9679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluth, T.B.; Zanini, L.A.G.; Battisti, I.D.E. Pesticide exposure and cancer: An integrative literature review. Saúde Debate 2019, 43, 906–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellingiri, B.; Chandrasekhar, M.; Sabari, S.S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Narayanasamy, A.; Venkatesan, D.; Iyer, M.; Kesari, K.; Dey, A. Neurotoxicity of pesticides—A link to neurodegeneration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhish, M.; Manjubala, I. Effectiveness of zebrafish models in understanding human diseases—A review of models. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.L.; Adeniyi, A.; Banerjee, R.; Dallaire, S.; Maguire, S.F.; Chi, J.; Ng, B.L.; Zepeda, C.; E Scott, C.; Humphray, S.; et al. Definition of the zebrafish genome using flow cytometry and cytogenetic mapping. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, J.S. History of zebrafish research. In The Zebrafish in Biomedical Research: Biology, Husbandry, Diseases, and Research Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The behaviour and ecology of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, Í.F.S.; Souza, T.M.; Vieira, L.R.; Marchi, F.C.; Nascimento, A.P.; Farias, D.F. Toxicity testing of pesticides in zebrafish—A systematic review on chemicals and associated toxicological endpoints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10185–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detrich, H.W., III; Westerfield, M.; Zon, L.I. Methods in Cell Biology The Zebrafish: Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, J.R. Zebrafish: Development of a Vertebrate Model Organism. Curr. Protoc. Essent. Lab. Tech. 2018, 16, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’agostino, Y.; Frigato, E.; Noviello, T.M.; Toni, M.; Frabetti, F.; Cigliano, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Sordino, P.; Cerulo, L.; Bertolucci, C.; et al. Loss of circadian rhythmicity in bdnf knockout zebrafish larvae. iScience 2022, 25, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Huang, L.; Li, C.; Nie, D.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, N.; Li, X.; Pang, S. Exposure to fenvalerate and tebuconazole exhibits combined acute toxicity in zebrafish and behavioral abnormalities in larvae. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 975634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xu, T.; Yin, D.; Gu, W.; Bai, J. Developmental exposure to lead at environmentally relevant concentrations impaired neurobehavior and NMDAR-dependent BDNF signaling in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlayanti, A.; Wijayanti, A.R.; Khotimah, H.; Ali, M. Protection of Centella asiatica Extract Through BDNF Expression on Stunting Model Zebrafish Larvae (Danio rerio) by Rotenone Induced. In Proceedings of the 1st Paris. Van. Java International Seminar on Health, Economics, Social. Science and Humanities (PVJ-ISHESSH 2020), Kota Bandung, Indonesia, 15 April 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.K.; Nazar, F.H.; Makpol, S.; Teoh, S.L. Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules 2022, 27, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CropLife International aisbl. Pesticides: Assessing Risk and Evaluating Epidemiological Studies—A guide for Journalists. 2011. Available online: https://croplife.org/wp-content/uploads/pdf_files/5849_MISC_2011_02_15_Assessing_Risk_and_Evaluating_Epidemiological_Studies_-_A_Guide_for_Journalists-2.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- FAO. Pesticides use, pesticides trade and pesticides indicators—Global, regional and country trends, 1990–2020. In FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; Volume 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, G.; Curmei, M.-M. Chemicals and pesticides. Fact. Sheets on the European Union. 2024. Available online: www.europarl.europa.eu/factsheets/en (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Wood, T.J.; Goulson, D. The environmental risks of neonicotinoid pesticides: A review of the evidence post 2013. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17285–17325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, A.; Kumar, J. Pyrethroid pesticides: An overview on classification, toxicological assessment and monitoring. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Definitions and Classifications of Pesticides; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; Available online: www.fao.org (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Forfert, N.; Troxler, A.; Retschnig, G.; Gauthier, L.; Straub, L.; Moritz, R.F.A.; Neumann, P.; Williams, G.R. Neonicotinoid pesticides can reduce honeybee colony genetic diversity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E. Potential Health Effects of Pesticides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Keifer, M.C.; Firestone, J. Neurotoxicity of pesticides. J. Agromed. 2007, 12, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hock, W.; Lorenz, E. Toxicity of Pesticides. 2006. Available online: www.cas.psu.edu (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Moffat, C.; Buckland, S.T.; Samson, A.J.; McArthur, R.; Pino, V.C.; Bollan, K.A.; Huang, J.T.-J.; Connolly, C.N. Neonicotinoids target distinct nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and neurons, leading to differential risks to bumblebees. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Bukowska, M.; Ligor, M.; Staneczko-Baranowska, I. A holistic study of neonicotinoids neuroactive insecticides—Properties, applications, occurrence, and analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34723–34740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective Toxicity of Neonicotinoids Attributable to Specificity of Insect and Mammalian Nicotinic Receptors. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2003, 48, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, J.; Lilliston, B. Unknown Benefits, Hidden Costs Neonicotinoid Seed Coatings, Crop Yields and Pollinators; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cowles, R.S.; Eitzer, B.D. Residues of neonicotinoid insecticides in pollen and nectar from model plants. J. Environ. Hort. 2017, 35, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Nault, B.A.; Taylor, A.G.; Urwiler, M.; Rabaey, T.; Hutchison, W.D. Neonicotinoid seed treatments for managing potato leafhopper infestations in snap bean. Crop Prot. 2004, 23, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sluijs, J.P.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; van Lexmond, M.F.I.J.B.; Bonmatin, J.-M.; Chagnon, M.; Downs, C.A.; Furlan, L.; Gibbons, D.W.; Giorio, C.; et al. Conclusions of the worldwide integrated assessment on the risks of neonicotinoids and fipronil to biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuah, J.F.; Messer, T.L.; Snow, D.D.; Comfort, S.D.; Mittelstet, A.R. Literature review: Global neonicotinoid insecticide occurrence in aquatic environments. Water 2020, 12, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schläppi, D.; Kettler, N.; Straub, L.; Glauser, G.; Neumann, P. Long-term effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on ants. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcherine, P.; Kelaher, B.P.; Taylor, M.D.; Lawson, C.; Benkendorff, K. Acute toxicity, accumulation and sublethal effects of four neonicotinoids on juvenile Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, D.; Morrissey, C.; Mineau, P. A review of the direct and indirect effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on vertebrate wildlife. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Lu, C.W.; Hsu, T.H.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, S.E. Neurotoxicity of fipronil affects sensory and motor systems in zebrafish. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Martínez, M.A. Neurotoxicity of Neonicotinoids. In Advances in Neurotoxicology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 167–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensley, S. Veterinary Toxicology—Chapter 39: Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hodoșan, C.; Gîrd, C.E.; Ghica, M.V.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E.; Nistor, L.; Bărbuică, I.S.; Marin, Ș.-C.; Mihalache, A.; Popa, L. Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids: A Comprehensive Review of Natural Occurring Compounds and Their Synthetic Derivatives. Plants 2023, 12, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderlund, D.M. Molecular mechanisms of pyrethroid insecticide neurotoxicity: Recent advances. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.R.H.; Jørs, E.; Lander, F.; Condarco, G.; Debes, F.; Bustillos, N.T.; Schlünssen, V. Neurological Deficits After Long-term Pyrethroid Exposure. Environ. Health Insights 2017, 11, 1178630217700628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranatunga, M.; Kellar, C.; Pettigrove, V. Toxicological impacts of synthetic pyrethroids on non-target aquatic organisms: A review. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, M.; Xu, S.; Yan, D. Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, S. Photodegradation kinetics, mechanism and aquatic toxicity of deltamethrin, permethrin and dihaloacetylated heterocyclic pyrethroids. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Horng, J.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Chou, M.Y. Fenpropathrin causes alterations in locomotion and social behaviors in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzer, E.M.; Williams, M.T.; Vorhees, C.V. Effects of pyrethroids on brain development and behavior: Deltamethrin. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2021, 87, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdesh, A.; Chen, M.; Martin-Iverson, M.T.; Mondal, A.; Ong, D.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Taddei, K.; Lardelli, M.; Groth, D.M.; Verdile, G.; et al. Regular care and maintenance of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) laboratory: An introduction. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 69, e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleström, P.; D’angelo, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Schorderet, D.F.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Sohm, F.; Warner, S. Zebrafish: Housing and husbandry recommendations. Lab Anim. 2020, 54, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadón, A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Martínez, M.A. Use and abuse of pyrethrins and synthetic pyrethroids in veterinary medicine. Vet. J. 2009, 182, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méjanelle, L.; Jara, B.; Dachs, J. Fate of pyrethroids in freshwater and marine environments. In Pyrethroid Insecticides; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balen, E.; Wolansky, M.; Kosatsky, T. Increasing Use of Pyrethroids in Canadian Households: Should We Be Concerned? Can. J. Public Health 2012, 103, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, D.; Braun, M.; Brüggmann, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Neonicotinoids: A critical assessment of the global research landscape of the most extensively used insecticide. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.-M.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; Long, E.; Marzaro, M.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; et al. Environmental fate and exposure; neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouhova, A.; Velisek, J.; Stara, A. Selected neonicotinoids and associated risk for aquatic organisms. Veterinární Medicína 2023, 68, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Liu, J.; Richardson, J.R. Pyrethroid insecticides directly activate microglia through interaction with voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 155, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, S.; Altun, S.; Özkaraca, M.; Ghosi, A.; Toraman, E.; Arslan, H. Cypermethrin, chlorpyrifos, deltamethrin, and imidacloprid exposure up-regulates the mRNA and protein levels of bdnf and c-fos in the brain of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 203, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proca, T.M.B.; Solcan, C.; Solcan, G. Neurotoxicity of Some Environmental Pollutants to Zebrafish. Life 2024, 14, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Richardson, J.R. Mechanism of pyrethroid pesticide-induced apoptosis: Role of calpain and the ER stress pathway. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 122, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Mustieles, V.; Suárez, B.; Smagulova, F.; David, A.; Peinado, F.; Artacho-Cordón, F.; López, L.C.; Arrebola, J.P.; et al. Exposure to non-persistent pesticides, BDNF, and behavioral function in adolescent males: Exploring a novel effect biomarker approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, A.M.; Boyles, A.L.; Thayer, K.A.; Perry, M.J. Effects of neonicotinoid pesticide exposure on human health: A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H. The Role of Neurotrophin Signaling in Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Cognitive Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. Neurotrophins and Other Growth Factors in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Life 2023, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Palacio-Schjetnan, A.; Escobar, M.L. Neurotrophins and synaptic plasticity. Neurogenesis Neural Plast. 2013, 15, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rando, M.; Castillo-Gomez, E. Editorial: Neurotrophins and their importance on neural plasticity: New insights and potential therapeutic effects on brain pathology. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1082116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Massa, S.M.; Tran, K.C.; Simmons, D.A.; Rajadas, J.; Zeng, A.Y.; Jang, T.; Carsanaro, S.; Longo, F.M. A small molecule TrkB/TrkC neurotrophin receptor co-activator with distinctive effects on neuronal survival and process outgrowth. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; You, Y.; Gupta, V.B.; Klistorner, A.; Graham, S.L. TrkB receptor signalling: Implications in neurodegenerative, psychiatric and proliferative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10122–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Triaca, V.; Besusso, D.; Costanzi, M.; Horn, J.M.; Koudelka, J.; Geibel, M.; Cestari, V.; Minichiello, L. Loss of NGF-TrkA signaling from the CNS is not sufficient to induce cognitive impairments in young adult or intermediate-aged mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14885–14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canu, N.; Amadoro, G.; Triaca, V.; Latina, V.; Sposato, V.; Corsetti, V.; Severini, C.; Ciotti, M.T.; Calissano, P. The intersection of NGF/TrkA signaling and amyloid precursor protein processing in Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, A.A.; Pinto, M.T.C.; Andrade, J.C.; de Jesus, L.P.; de Medeiros, M.W.; Haddad, N.M.; van de Bilt, M.T.; Talib, L.L.; Gattaz, W.F. Plasma levels of neurotrophin 4/5, NGF and pro-BDNF influence transition to mental disorders in a sample of individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 327, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, N.A.; Kumar, J.; Teoh, S.L. Neuroprotective effects of Neurotrophin-3 in MPTP-induced zebrafish Parkinson’s disease model. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1307447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yan, Y.-S.; Hu, H.-Y.; Xiong, M.-F.; Bai, C.-B.; et al. NTRK1 knockdown induces mouse cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal damage through mitophagy suppression via inactivating the AMPK/ULK1/FUNDC1 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Sun, D.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Pang, K.; Guo, W.; Lu, B. Extracellular juxtamembrane motif critical for TrkB preformed dimer and activation. Cells 2019, 8, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, K.F.; Zakaria, R. Recent Advances on the Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhlmann, L.; Linz, R.; Valk, S.; Vrticka, P.; de Wael, R.V.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Caldairou, B.; Papassotiriou, I.; Chrousos, G.; et al. Association between hippocampal structure and serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in healthy adults: A registered report. Neuroimage 2021, 236, 118011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, F.; Oltramari, A.R.; Kuhn, K.Z.; Schneider, S.E.; Mazon, S.C.; Garbinato, C.L.L.; Aguiar, G.P.S.; Kreutz, L.C.; Oliveira, J.V.; Siebel, A.M.; et al. Fluoxetine and Curcumin Prevent the Alterations in Locomotor and Exploratory Activities and Social Interaction Elicited by Immunoinflammatory Activation in Zebrafish: Involvement of BDNF and Proinflammatory Cytokines. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, T.; Cakir, M. Assessment of deltamethrin-induced DNA damage, neurotoxic and neuroimmune effects in the brain tissue of brown trout (Salmo trutta fario). Veter. Med. 2024, 69, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.I.; Awad, T.I.; Mohamed, E.H. Deltamethrin-induced oxidative damage and biochemical alterations in rat and its attenuation by Vitamin E. Toxicology 2006, 227, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strungaru, S.-A.; Plavan, G.; Ciobica, A.; Nicoara, M.; Robea, M.A.; Solcan, C.; Petrovici, A. Toxicity and chronic effects of deltamethrin exposure on zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a reference model for freshwater fish community. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Narasimhamurthy, R.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Dsouza, H.S.; Mumbrekar, K.D. Pesticides Exposure-Induced Changes in Brain Metabolome: Implications in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.J.; McIntosh, L.J.; Mink, P.J.; Jurek, A.M.; Li, A.A. Pesticide exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes: Review of the epidemiologic and animal studies. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2013, 16, 127–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokanović, M.; Oleksak, P.; Kuca, K. Multiple neurological effects associated with exposure to organophosphorus pesticides in man. Toxicology 2022, 484, 153407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, R.K.; Singh, M.K.; Jain, A.K.; Yadav, R.S. Neurochemical and Behavioral Dysfunctions in Pesticide Exposed Farm Workers: A Clinical Outcome. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 33, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavanja, M.C.R.; Hoppin, J.A.; Kamel, F. Health effects of chronic pesticide exposure: Cancer and neurotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2004, 25, 155–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xing, Y.; Yang, G.; You, M. Impact of pesticides exposure during neurodevelopmental period on autism spectrum disorders—A focus on gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 260, 115079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, F.; Umbach, D.M.; Bedlack, R.S.; Richards, M.; Watson, M.; Alavanja, M.C.; Blair, A.; Hoppin, J.A.; Schmidt, S.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide exposure and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Type of Tank | Temperature (°C) | pH | Salinity | Conductivity (μS/cm−1) | Ammonia (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Housing tank | 25 ± 0.5 | 7.5 | 0.27 | 556 | 0.04 |
| Control aquariums | 26 ± 0.5 | 7.4 | 0.26 | 554 | 0.02 |
| Experimental aquariums | 26 ± 0.5 | 7.4 | 0.25 | 553 | 0.03 |
| Gene Name | NCBI Reference Sequence | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELFA | BC064291.1 | CTTCTCAGGCTGACTGTGC | CCGCTAGCATTACCCTCC | 358 |
| BDNF | NM_001308649.1 | CTTGAGGTGGAAGGGGAAGCG | GTAACGGCGGCTCCAAAGGC | 157 |
| NGF | NM_199210.2 | AGATGCCACGCTGGTCGATAC | ACCACCGCATGGGCTCAAC | 121 |
| ntf-3 | NM_001327813.1 | TTACCTTCATGTCGGCTCTGCTG | CGCGAGGAACATCACGTACAG | 115 |
| ntf-4/5 | XM_005163972.4 | CACGGAGGTGACAAAGAGGC | GGCGGGCTCTAGGAACGTG | 79 |
| ntf-6/7 | NM_131064.3 | CATTGAGAAGGCGGCGAAAT | CAACGACCTCATGGGCACTA | 208 |
| ntrk1 | NM_001301356.1 | GCTGCTCCTTCGCTATGCTA | TGGCGAGGTCTACATCTGTG | 147 |
| ntrk2a | NM_001366554.1 | GTACATGATGCACGGCG | GAGATTTTCTCCGACTAGGC | 217 |
| ntrk2b | NM_001197161.2 | CCAGAGATGTGTACAGCACC | CATTGTTTGAGAGCTGATACC | 189 |
| ntrk3a | NM_001256664 | TCCCGAAATCAGCGTCAGTC | GGAGTGGACATTCGGTGGAT | 169 |
| ntrk3b | XM_002662753.6 | |||
| ngfra | XM_003198085 | TACAGGACAGTAGGCTACAGGA | TCACACTCCTCTTCCACCGC | 292 |
| ngfrb | NM_001198660.1 | TTAAACGGTGGAACAGTTGTAA | CTCCACTACAGTGGTCAAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrovici, A.; Savuța, G.; Lucini, C.; Robea, M.-A.; Solcan, C. Combined Neurotoxic Effects of Commercial Formulations of Pyrethroid (Deltamethrin) and Neonicotinoid (Imidacloprid) Pesticides on Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral, Molecular, and Histopathological Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040538
Petrovici A, Savuța G, Lucini C, Robea M-A, Solcan C. Combined Neurotoxic Effects of Commercial Formulations of Pyrethroid (Deltamethrin) and Neonicotinoid (Imidacloprid) Pesticides on Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral, Molecular, and Histopathological Analysis. Life. 2025; 15(4):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040538
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrovici, Adriana, Gheorghe Savuța, Carla Lucini, Madalina-Andreea Robea, and Carmen Solcan. 2025. "Combined Neurotoxic Effects of Commercial Formulations of Pyrethroid (Deltamethrin) and Neonicotinoid (Imidacloprid) Pesticides on Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral, Molecular, and Histopathological Analysis" Life 15, no. 4: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040538
APA StylePetrovici, A., Savuța, G., Lucini, C., Robea, M.-A., & Solcan, C. (2025). Combined Neurotoxic Effects of Commercial Formulations of Pyrethroid (Deltamethrin) and Neonicotinoid (Imidacloprid) Pesticides on Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral, Molecular, and Histopathological Analysis. Life, 15(4), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040538






