Effect of Propolis Extracts on OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels in ApoE Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Diets and ELISA Kits
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Preparation of Water and Ethanolic Extracts of Propolis
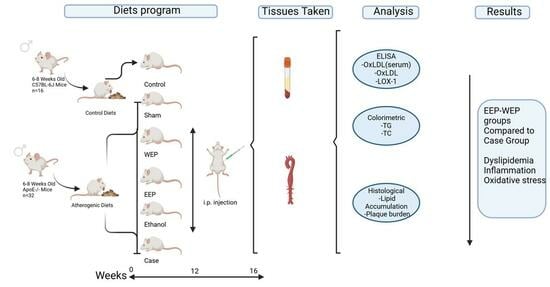
2.4. Study Groups, Treatment Administration, and Sample Collection Procedures
2.5. Serum Lipid Profile Analysis
2.6. Quantification of Serum OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels
2.7. Preparation and Processing of Aortic Arch Tissue for Protein Analysis
2.8. Quantification of OxLDL Levels in Aortic Arch Tissue
2.9. Histological Examination of Aortic Root Tissue
2.10. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
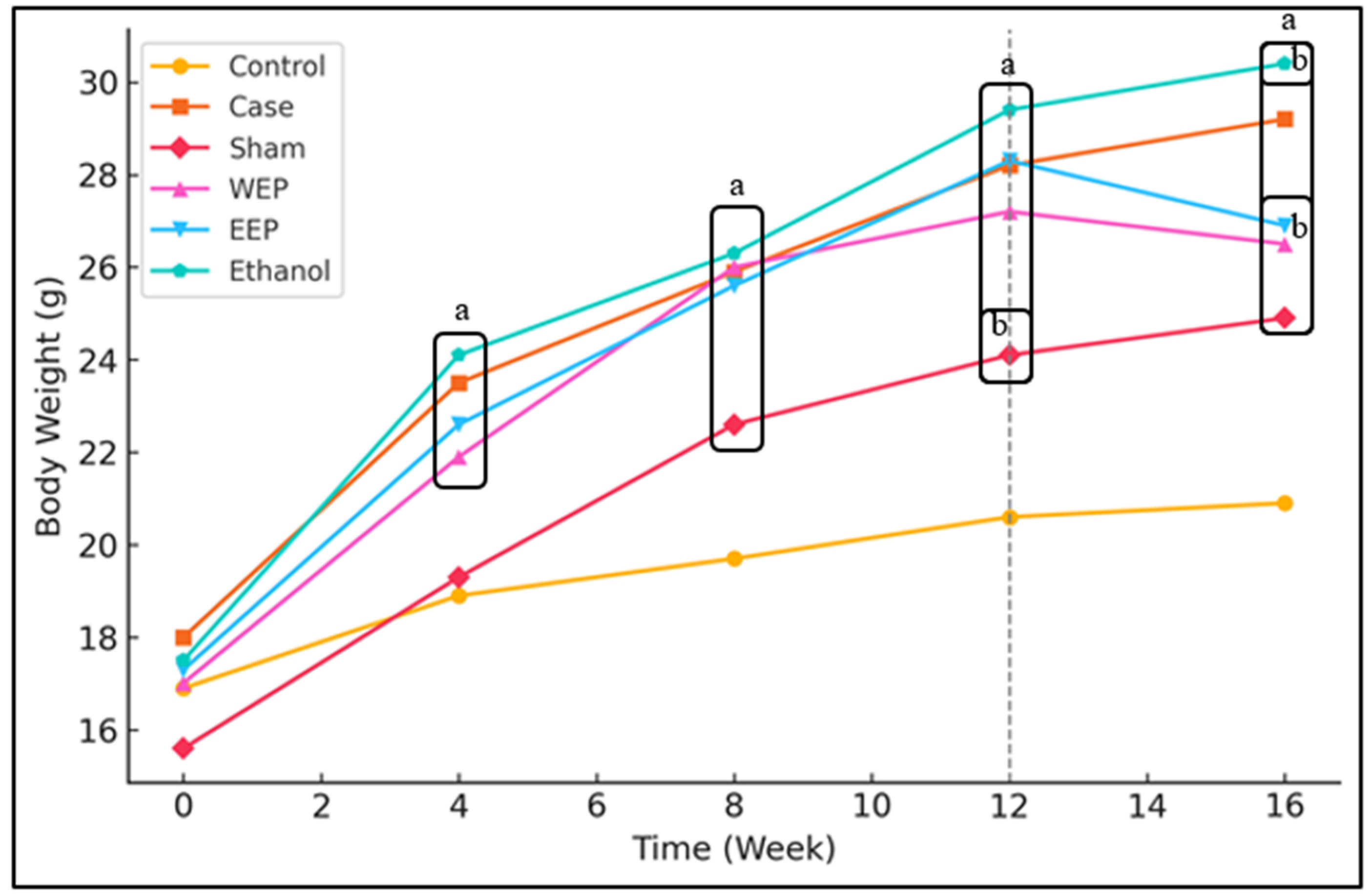
3.1. Extracts of Propolis Reduce Weight Gain of Mice
3.2. Extracts of Propolis Reduce HFD-Induced Dyslipidaemia
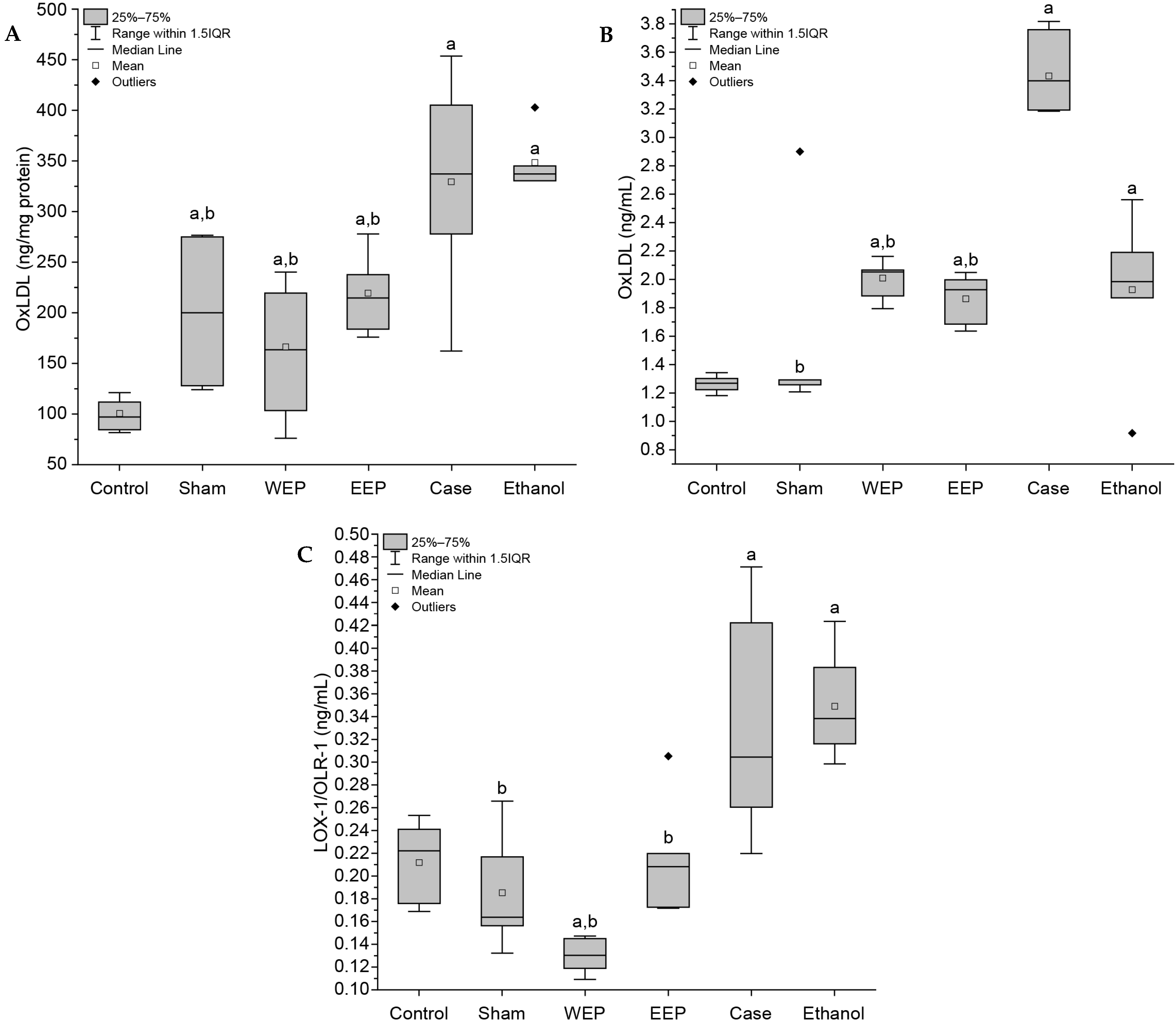
3.3. Extracts of Propolis Reduce Oxidative Stress Markers
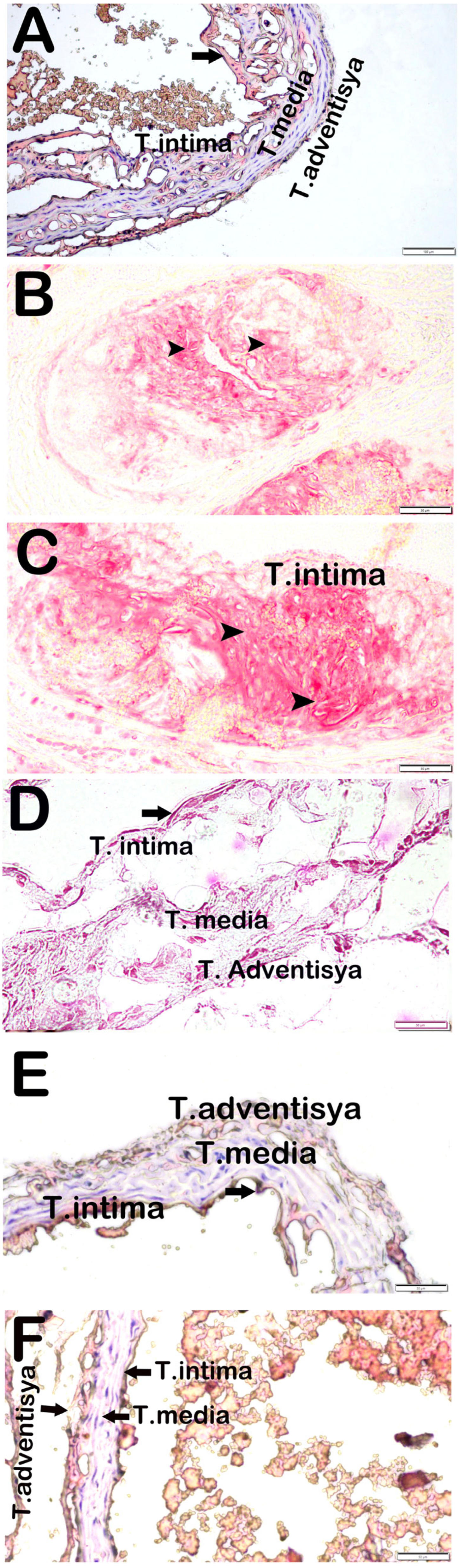
3.4. Attenuation of Aortic Root Plaque Formation and Lipid Deposition by Propolis Extracts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallucci, G.; Turazza, F.M.; Inno, A.; Canale, M.L.; Silvestris, N.; Farì, R.; Tarantini, L. Atherosclerosis and the Bidirectional Relationship between Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease: From Bench to Bedside—Part 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, P.P. Atherogenesis and Vascular Biology. In Therapeutic Lipidology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 11–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y.; Ali, F. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kowara, M.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A. Pathophysiology of atherosclerotic plaque development-contemporary experience and new directions in research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Patra, D.; Sinha, A.; Chakrabarty, D.; Patra, A.; Sarmah, R.; Dasgupta, S. Macrophage foam cell-derived mediator promotes spontaneous fat lipolysis in atherosclerosis models. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 117, qiae210. [Google Scholar]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Apoprotein E as a lipid transport and signaling protein in the blood, liver, and artery wall. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plump, A.S.; Smith, J.D.; Hayek, T.; Aalto-Setälä, K.; Walsh, A.; Verstuyft, J.G.; Rubin, E.M.; Breslow, J.L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipopro-tein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell 1992, 71, 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhong, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.Z. Functional role of Ash2l in oxLDL induced endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Mosalmanzadeh, N.; Pence, B.D. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein and Its Role in Immunometabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, R.; Shashidhar, K.N.; Soumya, N. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein and its Atherogenic Potential. Int. J. Biomed. 2022, 12, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munno, M.; Mallia, A.; Greco, A.; Modafferi, G.; Banfi, C.; Eligini, S. Radical Oxygen WEPcies, Oxidized Low-Density Lipoproteins, and Lectin-like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor 1: A Vicious Circle in Atherosclerotic Process. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 583. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrpyris, N.; Dimitriadis, K.; Beneki, E.; Iliakis, P.; Soulaidopoulos, S.; Tsioufis, P.; Tsioufis, K. LOX-1 Receptor: A Diagnostic Tool and Therapeutic Target in Atherogenesis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Orekhova, V.A.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Alexandra, A.; Melnichenko, M.; Popov, A.; Alexander, N.O. Overview of Atherosclerotic Plaque: From Formation to Complication. Online J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 24, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakov, A.; Berdalin, A.; Beregov, M.; Lelyuk, V. Emerging nuclear medicine imaging of atherosclerotic plaque formation. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becheva, M.S.V.; Kirkova-Bogdanova, A.G.; Ivanova, S.A.; Atanasov, P.J.; Chaneva, M.S.; Petkova, V.B. Prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacia 2023, 70, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsen, L. Cardiovascular disease prevention. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, D.; Kumbhakar, S.K.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, D.D. Natural product-based treatment potential for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P.G.; Gardana, C.; Pietta, A.M. Analytical methods for quality control of propolis. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezmirean, D.S.; Paşca, C.; Moise, A.R.; Bobiş, O. Plant sources responsible for the chemical composition and main bioactive properties of poplar-type propolis. Plants 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, J.; Miśkiewicz, M.; Noga, R.; Marcinkowska, J.; Herc, A.; Koczkodon, K.; Krompiewski, M. Propolis in Human Health: Unraveling Chemistry, Applications, and Efficacy. Qual. Sport 2024, 21, 54248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids from propolis via Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Foods 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deger, O.; Yigit, E.; Korkmaz, K.; Aygün, P.; Asghari, A.; Çakıroglu, K.A.; Demir, S. Protective Effect of Bee Products Against Oxidative Damage in Erythrocytes. Gümüşhane Univ. J. Health Sci. 2023, 12, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sforcin, J.M.; Bankova, V. Propolis: Is there a potential for the development of new drugs? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, V.R.; Sammugam, L.; Ramesh, N.; Gan, S.H. Honey, propolis, and royal jelly: A comprehensive review of their biological actions and health benefits. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1259510. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, V.S.; Santamarina-Fojo, S.; Brown, D.R.; Parrott, C.L.; Applebaum-Bowden, D.; Meyn, S.; Brewer, H.B. Apolipoprotein E deficiency in mice: Gene replacement and prevention of atherosclerosis using adenovirus vectors. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozkus, T.N.; Deger, O.; Yasar, A. Chemical characterization of water and ethanolic extracts of Turkish propolis by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yigit, E.; Deger, O.; Korkmaz, K.; Huner Yigit, M.; Uydu, H.A.; Mercantepe, T.; Demir, S. Propolis Reduces Inflammation and Dyslipidemia Caused by High-Cholesterol Diet in Mice by Lowering ADAM10/17 Activities. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Sang, H.; Yuan, N.; Sun, H.; Yao, S.; Wang, J.; Qin, S. Ethanolic extract of propolis inhibits atherosclerosis in ApoE-knockout mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sahebkar, A.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Weng, J.; Ge, J. Mechanisms of Oxidized LDL-Mediated Endothelial Dysfunction and Its Consequences for the Development of Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 925923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Du, G.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y. The LOX-1 receptor ectopically expressed in the liver alleviates atherosclerosis by clearing Ox-LDL from the circulation. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oršolić, N.; Landeka Jurčević, I.; Đikić, D.; Rogić, D.; Odeh, D.; Balta, V.; Perak Junaković, E.; Terzić, S.; Jutrić, D. Effect of Propolis on Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia and Atherogenic Indices in Mice. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.; Francisco, R.; Saraiva, A.; Francisco, S.; Carrascosa, C.; Raposo, A. The cardiovascular therapeutic potential of propolis—A comprehensive review. Biology 2021, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Bamba, R.; Nakajima, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Kimura, T.; Fukui, M. Brazilian green propolis improves gut microbiota dysbiosis and protects against sarcopenic obesity. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 3028–3047. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T.; Ohhata, M.; Fujii, M.; Oda, S.; Kusaka, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Shuto, E. Brazilian green propolis promotes weight loss and reduces fat accumulation in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Koya-Miyata, S.; Arai, N.; Mizote, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Ushio, S.; Iwaki, K.; Fukuda, S. Propolis prevents diet-induced hyperlipidemia and mitigates weight gain in diet-induced obesity in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ge, S.; Li, S.; Lin, H.; Lin, S. Anti-obesity effect of trans-cinnamic acid on HepG2 cells and HFD-fed mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111148. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftel, S.; Klisic, A.; Ciftel, E.; Mercantepe, T.; Yilmaz, A.; Ciftel, S.; Mercantepe, F. Investigating the Hepatic Response to Orlistat and White Tea in Rats on a High-Fat Diet. Life 2024, 14, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.; Corstjens, I.; Sanchez, S.; Dooley, D.; Lemmens, S.; Van Broeckhoven, J.; Hendrix, S. ADAM17-deficiency on microglia but not on macrophages promotes phagocytosis and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bankova, V. Chemical diversity of propolis and the problem of standardiza-tion. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Washio, K.; Shimamoto, Y.; Kitamura, H. Brazilian propolis extract increases leptin expression in mouse adipocytes. Biomed. Res. 2015, 36, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; Tezuka, H.; Tsuji, N.M.; Ohteki, T.; Karasuyama, H.; Kumazawa, T. Propolis induces Ca2+ signaling in immune cells. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2019, 38, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Naoe, Y.; Kimura, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Okamoto, S.; Toda, C.; Miyoshi, I. Beneficial effects of Brazilian propolis on type 2 diabetes in ob/ob mice: Possible involvement of immune cells in mesenteric adipose tissue. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedov, A.; Rozenberg, I.; Paneni, F.; Camici, G.G.; Shi, Y.; Doerries, C.; Lüscher, T.F. Endothelial overexpression of LOX-1 increases plaque formation and promotes atherosclerosis in vivo. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Sun, H.W.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhao, L.; Guo, S.D.; Yao, S.T. Ethanol extract of propolis protects macrophages from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by inhibiting CD36 expression and endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous protein pathway. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, P.; Yao, S. Ethanol extract of propolis protects endothelial cells from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced injury by inhibiting lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1-mediated oxidative stress. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trpkovic, A.; Resanovic, I.; Stanimirovic, J.; Radak, D.; Mousa, S.A.; Cenic-Milosevic, D.; Isenovic, E.R. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Minami, M.; Yoshida, K.; Nagata, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takayama, N.; Miyamoto, S. Niclosamide downregulates LOX-1 expression in mouse vascular smooth muscle cells and changes the composition of atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE−/− mice. Heart Vessels 2022, 37, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Yuan, W.; Wu, H.; Yin, X.; Xuan, H. Bioactive components and mechanisms of Chinese poplar propolis alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cells injury. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Yao, P. Quercetin attenuates high fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice: A critical role of NADPH oxidase. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Gu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, R.; Yu, J. Inflammation inhibition and gut microbiota regulation by TSG to combat atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 247, 112232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roos, T.U.; Heiss, E.H.; Schwaiberger, A.V.; Schachner, D.; Sroka, I.M.; Oberan, T.; Dirsch, V.M. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of p38 MAPK, HIF-1α, and heme oxygenase-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghallab, D.; Shawky, E.; Mohyeldin, M.; Metwally, A.M.; Ibrahim, R.S. Propolis: An update on its chemical diversity, botanical origin and biological activities. J. Adv. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 2, 76–99. [Google Scholar]
| Group (n = 8) | Animal Type | Diet | Time | Injection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | C57BL-6J | Control Diet (CD) | 16 Weeks | |
| Case | ApoE−/− | HFD | 16 Weeks | |
| Sham | C57BL-6J | HFD | 16 Weeks | |
| WEP | ApoE−/− | HFD | 16 Weeks | 16 Weeks 400 mg/kg WEP by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection every day for the last 4 weeks |
| EEP | ApoE−/− | HFD | 16 Weeks | 16 Weeks 200 mg/kg EEP by i.p. injection every day for the last 4 weeks |
| Ethanol | ApoE−/− | HFD | 16 Weeks | Ethanol 30% by i.p. injection every day for the last 4 weeks |
| Parameters | Control (C57BL/6J + CD) | Case (ApoE−/− + HFD) | Sham (ApoE−/− + HFD) | WEP (ApoE−/− + HFD) | EEP (ApoE−/− + HFD) | Ethanol (ApoE−/− + HFD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG (mg/dL) (Median-IQR) | 82 (72–82) | 144 a (110–117) | 99 b (70–79) | 64 a,b (52–58) | 67 a,b (54.5–62) | 137 a (92.3–1013) |
| TC (mg/dL) (Median-IQR) | 115 (128–154) | 1569 a (1355–1412) | 164 (129–138) | 1106 a,b (1212–1267) | 1148 a,b (1103–1259) | 1610 a (1327–1505) |
| Group | Adipocyte Subendothelial Involvement | Adipocyte Vascular Wall Involvement | Fibrosis Cap Formation | AHHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Case | 2 (2–2) a | 1.5 (1–1) a | 0 (0–0.5) | 3 (2–3) a |
| Sham | 2 (2–3) b | 1 (0–1) b | 1 (0–1) b | 3 (2–3) b |
| WEP | 1 (0.5–1) a,b | 0.5 (0–1) a,b | 0 (0–0) a,b | 1 (0.5–1) a,b |
| EEP | 1 (0–1) a,b | 0 (0–1) a,b | 0 (0–0) a,b | 0.5 (0–1) a,b |
| Ethanol | 0 (0–0) a,b | 1 (0–0) a,b | 0 (0–0) a,b | 0 (0–1) a,b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korkmaz, K.; Deger, O.; Yigit, E.; Uydu, H.A.; Mercantepe, T.; Demir, S. Effect of Propolis Extracts on OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels in ApoE Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat Diet. Life 2025, 15, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040565
Korkmaz K, Deger O, Yigit E, Uydu HA, Mercantepe T, Demir S. Effect of Propolis Extracts on OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels in ApoE Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat Diet. Life. 2025; 15(4):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040565
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorkmaz, Katip, Orhan Deger, Ertugrul Yigit, Hüseyin Avni Uydu, Tolga Mercantepe, and Selim Demir. 2025. "Effect of Propolis Extracts on OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels in ApoE Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat Diet" Life 15, no. 4: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040565
APA StyleKorkmaz, K., Deger, O., Yigit, E., Uydu, H. A., Mercantepe, T., & Demir, S. (2025). Effect of Propolis Extracts on OxLDL and LOX-1 Levels in ApoE Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat Diet. Life, 15(4), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040565