The Impact of Exercise Training in a Hypobaric/Normobaric Hypoxic Environment on Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Literature Search
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
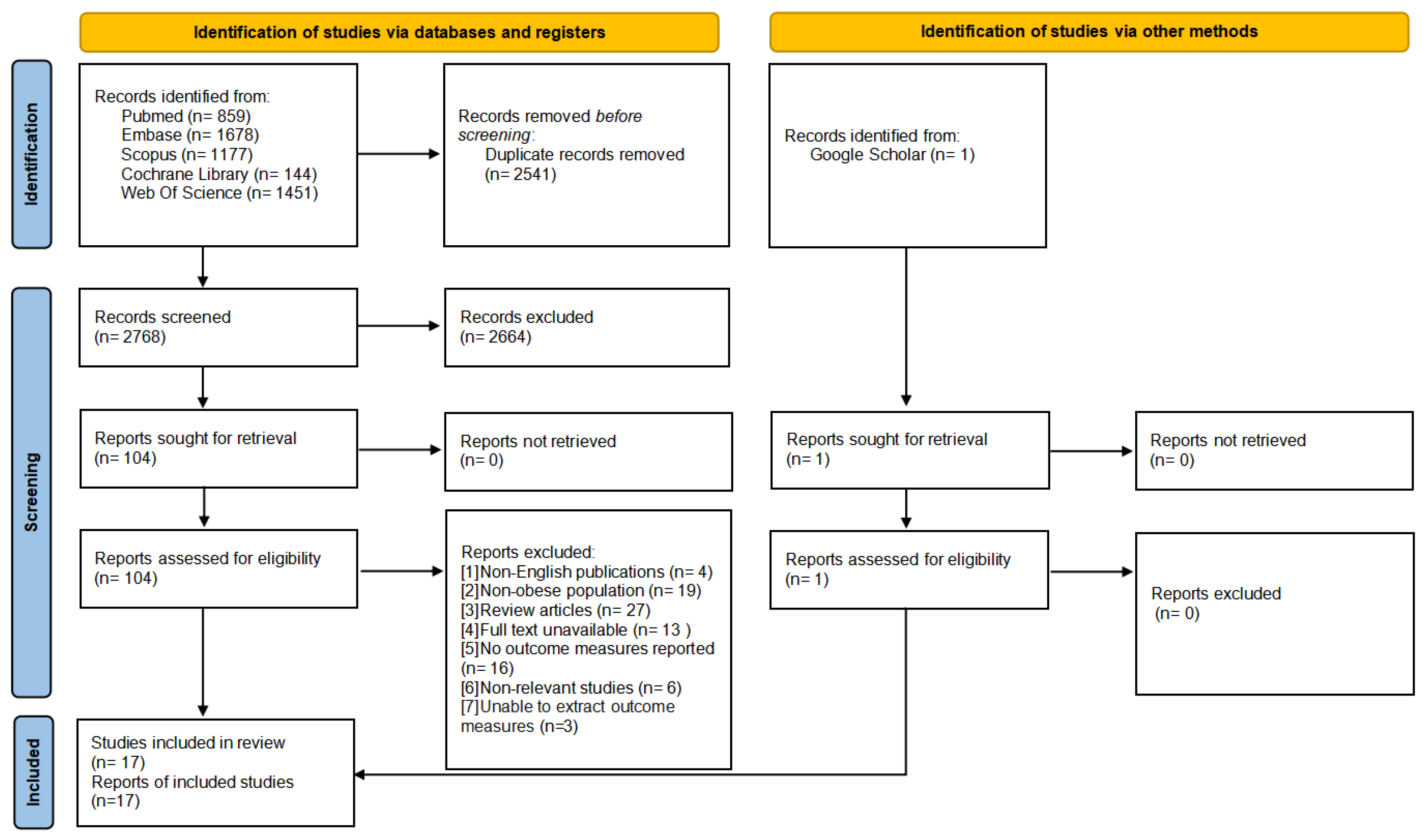
2.4. Literature Screening and Data Extraction
2.5. Risk-of-Bias Assessment for Included Studies
2.6. Certainty of Evidence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subsection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment Results
3.4. Certainty of Evidence
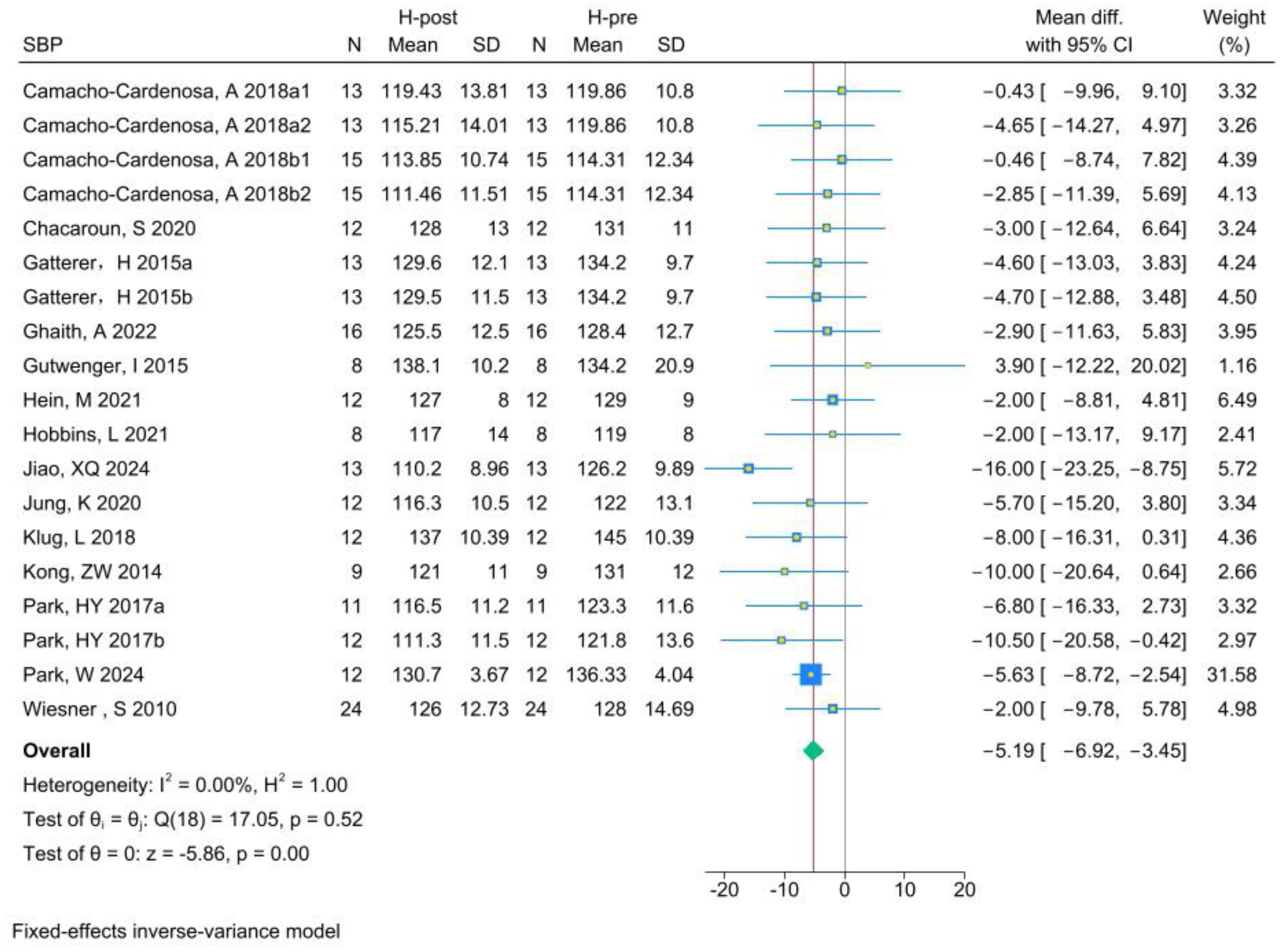
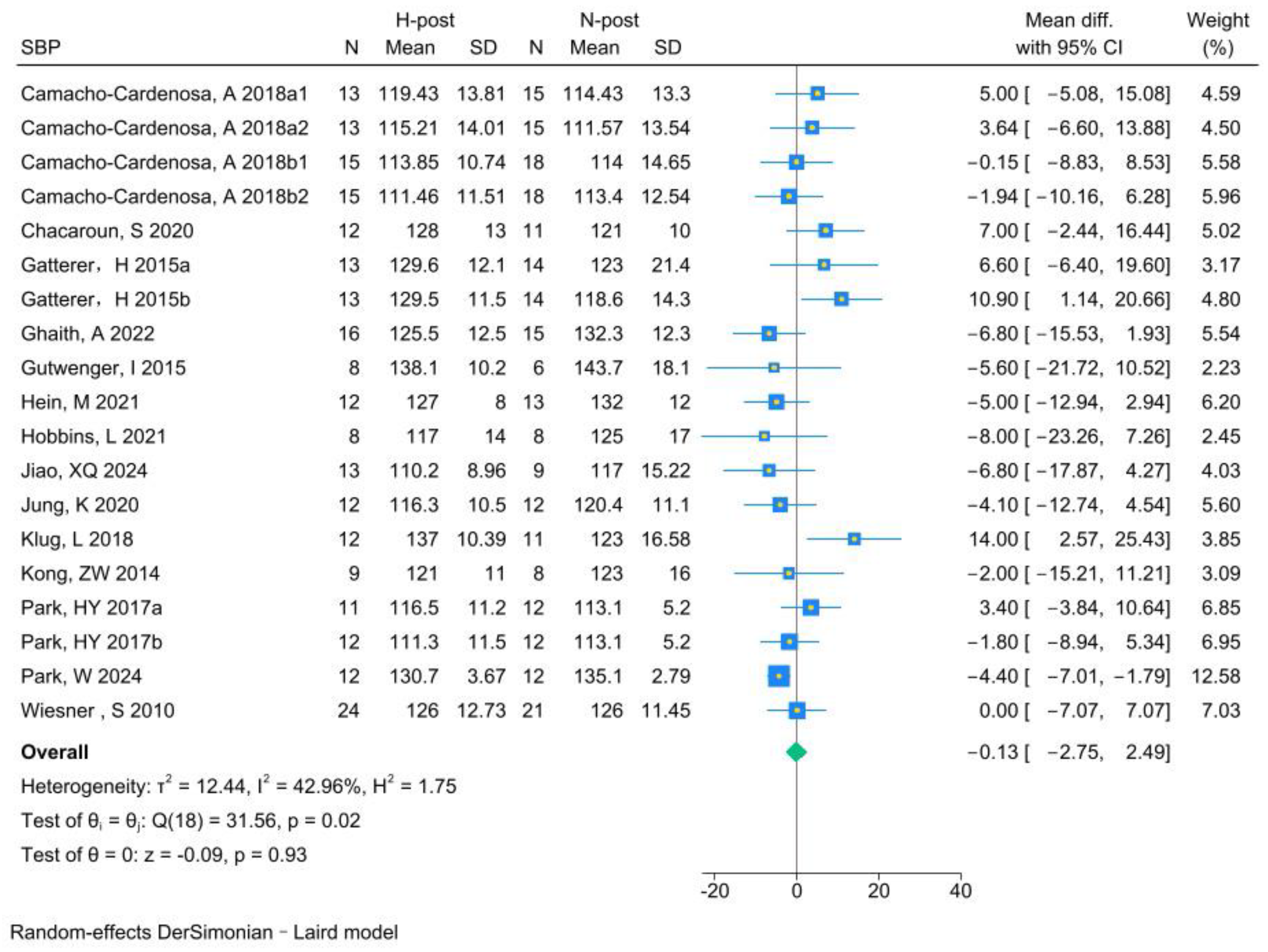
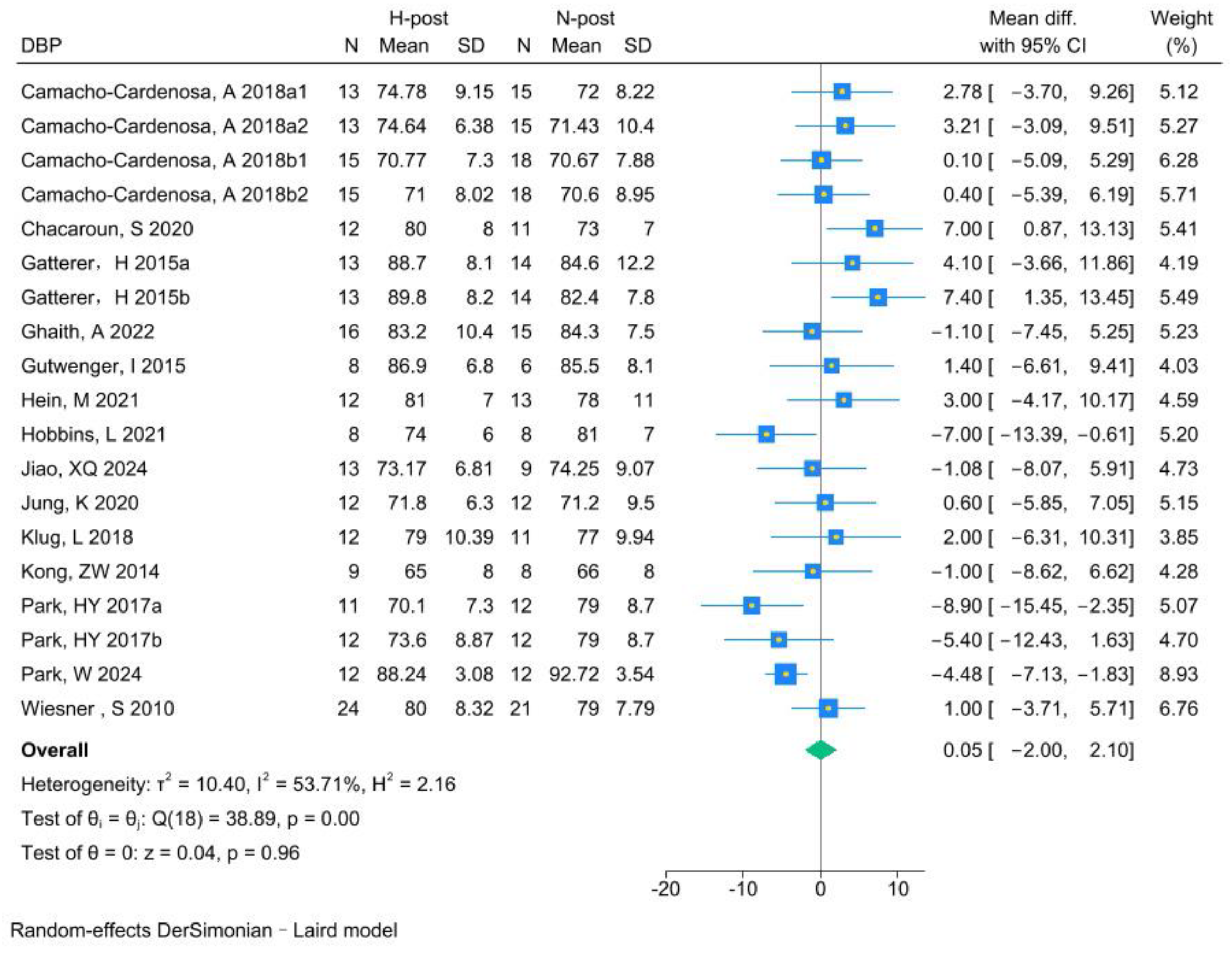
3.5. Meta-Analysis
3.5.1. CRF
3.5.2. SBP
3.5.3. DBP
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3.7. Subgroup Analysis
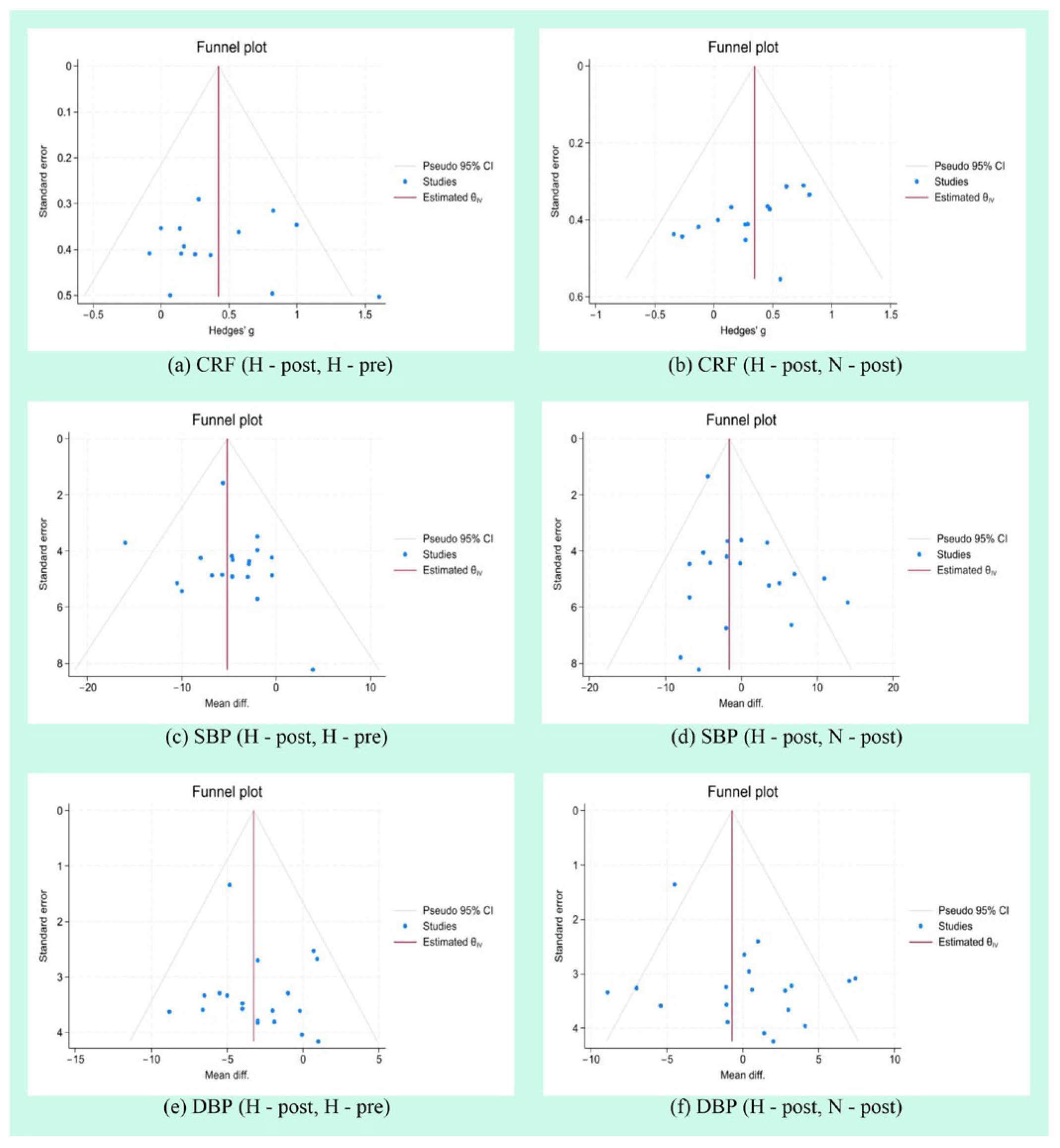
3.8. Publication Bias Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breen, C.; O’Connell, J.; Geoghegan, J.; O’Shea, D.; Birney, S.; Tully, L.; Gaynor, K.; O’Kelly, M.; O’Malley, G.; O’Donovan, C.; et al. Obesity in Adults: A 2022 Adapted Clinical Practice Guideline for Ireland. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.A.B. Global, regional, and national prevalence of adult overweight and obesity, 1990-2021, with forecasts to 2050: A forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, L.; Bugiardini, R.; Cenko, E.; Cubedo, J.; Dorobantu, M.; Duncker, D.J.; Estruch, R.; Milicic, D.; Tousoulis, D.; Vasiljevic, Z.; et al. Position paper of the European Society of Cardiology-working group of coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation: Obesity and heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.; McAuley, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Despres, J.P.; Arena, R.; Kokkinos, P. Physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness as major markers of cardiovascular risk: Their independent and interwoven importance to health status. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaith, A.; Chacaroun, S.; Borowik, A.; Chatel, L.; Doutreleau, S.; Wuyam, B.; Tamisier, R.; Pépin, J.L.; Flore, P.; Verges, S. Hypoxic high-intensity interval training in individuals with overweight and obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 323, R700–R709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspersen, C.J.; Powell, K.E.; Christenson, G.M. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: Definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep. 1985, 100, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Harber, M.P.; Kaminsky, L.A.; Arena, R.; Blair, S.N.; Franklin, B.A.; Myers, J.; Ross, R. Impact of Cardiorespiratory Fitness on All-Cause and Disease-Specific Mortality: Advances Since 2009. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 60, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, S.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, S.; Maki, M.; Yachi, Y.; Asumi, M.; Sugawara, A.; Totsuka, K.; Shimano, H.; Ohashi, Y.; et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a quantitative predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in healthy men and women: A meta-analysis. Jama 2009, 301, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Bakken, K.; D’Elia, E.; Lewis, G.D. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Heart Failure. JACC. Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbadj, K.; Taiek, N.; El Hjouji, W.; El Karrouti, O.; El Hangouche, A.J. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: Methodology, Interpretation, and Role in Exercise Prescription for Cardiac Rehabilitation. US Cardiol. 2024, 18, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblom-Bak, E.; Ekblom, B.; Söderling, J.; Börjesson, M.; Blom, V.; Kallings, L.V.; Hemmingsson, E.; Andersson, G.; Wallin, P.; Ekblom, Ö. Sex- and age-specific associations between cardiorespiratory fitness, CVD morbidity and all-cause mortality in 266.109 adults. Prev. Med. 2019, 127, 105799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuki, T.; Kotato, T.; Zempo-Miyaki, A. Habitual exercise decreases systolic blood pressure during low-intensity resistance exercise in healthy middle-aged and older individuals. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H1024–H1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Vithran, D.T.A.; Li, Y.; Kazemi, A.; Boyer, L.; Fond, G.; Smith, L.; et al. Associations Between Exercise Training, Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Mortality: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2025, 16, e13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atakan, M.M.; Türkel, İ.; Özerkliğ, B.; Koşar, Ş.N.; Taylor, D.F.; Yan, X.; Bishop, D.J. Small peptides: Could they have a big role in metabolism and the response to exercise? J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, M.M.; Koşar, Ş.N.; Güzel, Y.; Tin, H.T.; Yan, X. The Role of Exercise, Diet, and Cytokines in Preventing Obesity and Improving Adipose Tissue. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, R.B.; Baggish, A.L. Exercise-induced cardiac remodeling. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 54, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Blood Lipids in People with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Life 2025, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, M.J.; Parr, E.B.; Hawley, J.A.; Camera, D.M. Can High-Intensity Interval Training Promote Skeletal Muscle Anabolism? Sports Med. 2021, 51, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, M.J.; McGee, S.L. Metabolic adaptations to short-term high-intensity interval training: A little pain for a lot of gain? Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2008, 36, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnis, M.J.; Gibala, M.J. Physiological adaptations to interval training and the role of exercise intensity. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2915–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdampilleta, A.; González-Muniesa, P.; Portillo, M.P.; Martínez, J.A. Usefulness of combining intermittent hypoxia and physical exercise in the treatment of obesity. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 68, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppert, J.M.; Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Carraça, E.V.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; Pramono, A.; et al. Exercise training in the management of overweight and obesity in adults: Synthesis of the evidence and recommendations from the European Association for the Study of Obesity Physical Activity Working Group. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S4), e13273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Girard, O.; Pérez, A.; Rubio-Arias, J. Additive stress of normobaric hypoxic conditioning to improve body mass loss and cardiometabolic markers in individuals with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 207, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, C.C.L.; Cooke, M.B.; Chong, M.C.; Yeo, W.K.; Camera, D.M. Mechanisms for Combined Hypoxic Conditioning and Divergent Exercise Modes to Regulate Inflammation, Body Composition, Appetite, and Blood Glucose Homeostasis in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Li, H.; Bai, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Deng, J.; Deng, S.; Meng, C.; Vollaard, N.B.J.; Little, J.P.; et al. Is low-volume high-intensity interval training a time-efficient strategy to improve cardiometabolic health and body composition? A meta-analysis. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 49, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharhag-Rosenberger, F.; Meyer, T.; Gässler, N.; Faude, O.; Kindermann, W. Exercise at given percentages of VO2max: Heterogeneous metabolic responses between individuals. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Zang, Y.; Hu, Y. Normobaric hypoxia training causes more weight loss than normoxia training after a 4-week residential camp for obese young adults. Sleep Breath. Schlaf Atm. 2014, 18, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; Burtscher, M.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Timon, R.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Olcina, G. High-Intensity Interval Training in Normobaric Hypoxia Leads to Greater Body Fat Loss in Overweight/Obese Women than High-Intensity Interval Training in Normoxia. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Xu, K.; Deng, J.; Deng, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Toledo, M.J.L.; et al. Optimal Frequency of Interrupting Prolonged Sitting for Cardiometabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Crossover Trials. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2024, 34, e14769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakoulis, A.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Metsios, G.S.; Perivoliotis, K.; Liguori, G.; Feito, Y.; Riebe, D.; Thompson, W.R.; Angelopoulos, T.J.; Krustrup, P.; et al. Comparative Efficacy of 5 Exercise Types on Cardiometabolic Health in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of 81 Randomized Controlled Trials. Circulation. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2022, 15, e008243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.E.; Tew, G.A.; Aning, J.J.; Gilbert, S.E.; Lewis, L.; Saxton, J.M. Effects of short-term, medium-term and long-term resistance exercise training on cardiometabolic health outcomes in adults: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, I.H.; Boushel, R.; Kalliokoski, K.K. The Circulatory and Metabolic Responses to Hypoxia in Humans—With Special Reference to Adipose Tissue Physiology and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, O.; Duan, R.; Suzuki, K.; Yan, X. Editorial: Hypoxia and exercise: Tissue specific and systemic adaptive responses. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1095416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippl, F.J.; Neubauer, S.; Schipfer, S.; Lichter, N.; Tufman, A.; Otto, B.; Fischer, R. Hypobaric hypoxia causes body weight reduction in obese subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Diaz-Cidoncha Garcia, J. Impact of exercise training in a hypobaric/normobaric hypoxic environment on body composition and glycolipid metabolism in individuals with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1571730. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwar, A.; Paul, S.; Ahmad, Y.; Bhargava, K. Intermittent hypoxia modulates redox homeostasis, lipid metabolism associated inflammatory processes and redox post-translational modifications: Benefits at high altitude. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, O.; Malatesta, D.; Millet, G.P. Walking in Hypoxia: An Efficient Treatment to Lessen Mechanical Constraints and Improve Health in Obese Individuals? Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roels, B.; Thomas, C.; Bentley, D.J.; Mercier, J.; Hayot, M.; Millet, G. Effects of intermittent hypoxic training on amino and fatty acid oxidative combustion in human permeabilized muscle fibers. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefferts, W.K.; Babcock, M.C.; Tiss, M.J.; Ives, S.J.; White, C.N.; Brutsaert, T.D.; Heffernan, K.S. Effect of hypoxia on cerebrovascular and cognitive function during moderate intensity exercise. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 165, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schega, L.; Peter, B.; Brigadski, T.; Leßmann, V.; Isermann, B.; Hamacher, D.; Törpel, A. Effect of intermittent normobaric hypoxia on aerobic capacity and cognitive function in older people. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocherie, F.; Girard, O.; Faiss, R.; Millet, G.P. Effects of Repeated-Sprint Training in Hypoxia on Sea-Level Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, E.Y.; Saunders, P.U.; Pyne, D.B.; Gore, C.J.; Anson, J.M. Effectiveness of intermittent training in hypoxia combined with live high/train low. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Timón, R.; González-Custodio, A.; Olcina, G. Repeated sprint in hypoxia as a time-metabolic efficient strategy to improve physical fitness of obese women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Vist, G.E.; Glasziou, P.P.; Akl, E.A.; Skoetz, N.; Guyatt, G.H. Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 375–402. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner, S.; Haufe, S.; Engeli, S.; Mutschler, H.; Haas, U.; Luft, F.C.; Jordan, J. Influences of normobaric hypoxia training on physical fitness and metabolic risk markers in overweight to obese subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, T.; Kurihara, T.; Hamaoka, T.; Goto, K. Whole body, regional fat accumulation, and appetite-related hormonal response after hypoxic training. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Shi, Q.; Nie, J.; Tong, T.K.; Song, L.; Yi, L.; Hu, Y. High-Intensity Interval Training in Normobaric Hypoxia Improves Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Overweight Chinese Young Women. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, L.; Mähler, A.; Rakova, N.; Mai, K.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Rahn, G.; Busjahn, A.; Jordan, J.; Boschmann, M.; Luft, F.C. Normobaric hypoxic conditioning in men with metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Kim, J.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, W.S.; Lim, K. Hypoxic Pilates Intervention for Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Niu, G.; Wang, L.; Ji, X.; Lv, C.; Guo, X. Helpful to Live Healthier? Intermittent Hypoxic/Ischemic Training Benefits Vascular Homeostasis and Lipid Metabolism with Activating SIRT1 Pathways in Overweight/Obese Individuals. Obes. Facts 2024, 17, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, M.; Chobanyan-Jürgens, K.; Tegtbur, U.; Engeli, S.; Jordan, J.; Haufe, S. Effect of normobaric hypoxic exercise on blood pressure in old individuals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutwenger, I.; Hofer, G.; Gutwenger, A.K.; Sandri, M.; Wiedermann, C.J. Pilot study on the effects of a 2-week hiking vacation at moderate versus low altitude on plasma parameters of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatterer, H.; Haacke, S.; Burtscher, M.; Faulhaber, M.; Melmer, A.; Ebenbichler, C.; Strohl, K.P.; Högel, J.; Netzer, N.C. Normobaric Intermittent Hypoxia over 8 Months Does Not Reduce Body Weight and Metabolic Risk Factors--a Randomized, Single Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study in Normobaric Hypoxia and Normobaric Sham Hypoxia. Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacaroun, S.; Borowik, A.; Vega-Escamilla, Y.G.I.; Doutreleau, S.; Wuyam, B.; Belaidi, E.; Tamisier, R.; Pepin, J.L.; Flore, P.; Verges, S. Hypoxic Exercise Training to Improve Exercise Capacity in Obese Individuals. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, S.W. Effects of 12 Weeks of Combined Exercise Training in Normobaric Hypoxia on Arterial Stiffness, Inflammatory Biomarkers, and Red Blood Cell Hemorheological Function in Obese Older Women. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.; Lim, K. The Effects of Aerobic Exercise at Hypoxic Condition during 6 Weeks on Body Composition, Blood Pressure, Arterial Stiffness, and Blood Lipid Level in Obese Women. Int. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbins, L.; Hunter, S.; Gaoua, N.; Girard, O. Short-Term Perceptually Regulated Interval-Walk Training in Hypoxia and Normoxia in Overweight-to-Obese Adults. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2021, 20, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Burtscher, M.; Timón, R.; Olcina, G. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Under Normobaric Hypoxia on Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Overweight/Obese Women. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2018, 19, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Kong, Z.; Zou, L.; Chapman, R.; Shi, Q.; Nie, J. Comparative efficacy of various hypoxic training paradigms on maximal oxygen consumption: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2023, 21, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Hou, J.; Liu, A.; Yuan, X. Impact of Altitude Training on Athletes’ Aerobic Capacity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmacott, A.; Sanal-Hayes, N.E.M.; McLaughlin, M.; Mair, J.L.; Hayes, L.D. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) in Hypoxia Improves Maximal Aerobic Capacity More Than HIIT in Normoxia: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y. A Meta-Analysis on Influence of Intermittent Hypoxia Training on Athlete’s Aerobic Endurance. J. Shanghai Univ. Sport 2012, 36, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X. Effects of Altitude Training on Middle-and-Long Distance Runners’ Oxygen-Carrying Ability of Blood. J. Beijing Sport Univ. 2008, 1223–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.P.; Ponsot, E.; Zoll, J.; Doutreleau, S.; Lonsdorfer-Wolf, E.; Geny, B.; Lampert, E.; Flück, M.; Hoppeler, H.; Billat, V.; et al. Exercise training in normobaric hypoxia in endurance runners. I. Improvement in aerobic performance capacity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Morais Fernandes, T.; Argolo, J.G.M.; Morais Fernandes, A.P.; Sorgi, C.A.; Lizzi, E.A.d.S.; Trapé, Á.A. Effects of Moderate-Intensity Cyclic Normobaric Hypoxic Training on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors of Patients Recovered from COVID-19: The AEROBICOVID Randomized Controlled Trial. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2025. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, L.; Harrison, S.W.D.; Rice, C.L.; McNeil, C.J. Neuromuscular fatigability at high altitude: Lowlanders with acute and chronic exposure, and native highlanders. Acta Physiol. 2022, 234, e13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, J.S.; Silveira, A.C.; Azevedo, R.A.; Schamne, J.C.; Rondon, M.; Papoti, M.; Lima-Silva, A.E.; Koehle, M.S.; Bertuzzi, R. No sex differences in performance and perceived fatigability during a self-paced endurance exercise performed under moderate hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2025, 328, R352–R363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S.; Wiesner, S.; Engeli, S.; Luft, F.C.; Jordan, J. Influences of normobaric hypoxia training on metabolic risk markers in human subjects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Lopez-Pascual, A.; de Andrés, J.; Lasa, A.; Portillo, M.P.; Arós, F.; Durán, J.; Egea, C.J.; Martinez, J.A. Impact of intermittent hypoxia and exercise on blood pressure and metabolic features from obese subjects suffering sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, R.H. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002, 16, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudder, M.R.; Lambourne, K.; Drollette, E.S.; Herrmann, S.D.; Washburn, R.A.; Donnelly, J.E.; Hillman, C.H. Aerobic capacity and cognitive control in elementary school-age children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; Olcina, G.; Timón, R.; Brazo-Sayavera, J. Detraining effect on overweight/obese women after high-intensity interval training in hypoxia. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, R.; Xie, L.; Hu, F. Comparative efficacy of exercise training modes on systemic metabolic health in adults with overweight and obesity: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1294362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Atakan, M.M.; Kuang, J.; Hu, Y.; Bishop, D.J.; Yan, X. The Molecular Adaptive Responses of Skeletal Muscle to High-Intensity Exercise/Training and Hypoxia. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Gurd, B.J.; Bonafiglia, J.T.; Voisin, S.; Li, Z.; Harvey, N.; Croci, I.; Taylor, J.L.; Gajanand, T.; Ramos, J.S.; et al. A Multi-Center Comparison of O(2peak) Trainability Between Interval Training and Moderate Intensity Continuous Training. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, M.J.; Little, J.P.; Macdonald, M.J.; Hawley, J.A. Physiological adaptations to low-volume, high-intensity interval training in health and disease. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabag, A.; Little, J.P.; Johnson, N.A. Low-volume high-intensity interval training for cardiometabolic health. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tong, T.K.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Y. Comparable Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training and Prolonged Continuous Exercise Training on Abdominal Visceral Fat Reduction in Obese Young Women. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 5071740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewege, M.; van den Berg, R.; Ward, R.E.; Keech, A. The effects of high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition in overweight and obese adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2017, 18, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreato, L.V.; Esteves, J.V.; Coimbra, D.R.; Moraes, A.J.P.; de Carvalho, T. The influence of high-intensity interval training on anthropometric variables of adults with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2019, 20, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wong, S.H.; Chen, Y.; Siu, P.M.; Baker, J.S.; Sun, F. Effects and dose-response relationship of high-intensity interval training on cardiorespiratory fitness in overweight and obese adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 2829–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugbeer, N.; Constantinou, D.; Torres, G. Comparison of High-Intensity Training Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Fat Percentage in Persons With Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 18, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mhanna, S.B.; Batrakoulis, A.; Wan Ghazali, W.S.; Mohamed, M.; Aldayel, A.; Alhussain, M.H.; Afolabi, H.A.; Wada, Y.; Gülü, M.; Elkholi, S.; et al. Effects of combined aerobic and resistance training on glycemic control, blood pressure, inflammation, cardiorespiratory fitness and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes and overweight/obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saco-Ledo, G.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Ruilope, L.M.; Lucia, A. Exercise Reduces Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Patients With Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e018487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroll, B.; Beaglehole, R. Does physical activity lower blood pressure: A critical review of the clinical trials. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Mark, A.; Esler, M. The sympathetic nervous system alterations in human hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Radavelli-Bagatini, S.; Ho, S. Potential benefits of exercise on blood pressure and vascular function. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. JASH 2013, 7, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, S.P.; Chin, A.; Xin, X.; He, J. Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyall, D.M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Ward, J.; Iliodromiti, S.; Anderson, J.J.; Gill, J.M.R.; Smith, D.J.; Ntuk, U.E.; Mackay, D.F.; Holmes, M.V.; et al. Association of Body Mass Index With Cardiometabolic Disease in the UK Biobank: A Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Morey, R.; Jones, M.D.; Marcos, L.; Ristov, M.; Ram, A.; Hakansson, S.; Franklin, A.; McCarthy, C.; De Carli, L.; et al. High-intensity interval training for reducing blood pressure: A randomized trial vs. moderate-intensity continuous training in males with overweight or obesity. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2020, 43, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Atakan, M.M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Nazif, M.; Zarekookandeh, N.; Ye, H.Z.; Kuang, J.; Ferri, A.; et al. Methods to match high-intensity interval exercise intensity in hypoxia and normoxia—A pilot study. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2022, 20, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, X. The Impact of Exercise Training in a Hypobaric/Normobaric Hypoxic Environment on Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040566
Liu P, Chen H, Deng Y, Jiang X. The Impact of Exercise Training in a Hypobaric/Normobaric Hypoxic Environment on Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life. 2025; 15(4):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040566
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Hao Chen, Yidi Deng, and Xin Jiang. 2025. "The Impact of Exercise Training in a Hypobaric/Normobaric Hypoxic Environment on Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Life 15, no. 4: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040566
APA StyleLiu, P., Chen, H., Deng, Y., & Jiang, X. (2025). The Impact of Exercise Training in a Hypobaric/Normobaric Hypoxic Environment on Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life, 15(4), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040566








