From Joints to the Heart: An Integrated Perspective on Systemic Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Systemic Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis
1.2. The Correlation of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Cardiovascular Risks
1.3. Scientific Background, Research Gap, and Hypothesis
2. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cardiovascular Disease
2.1. Chronic Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction
2.2. The Association Between Chronic Inflammation and CVD
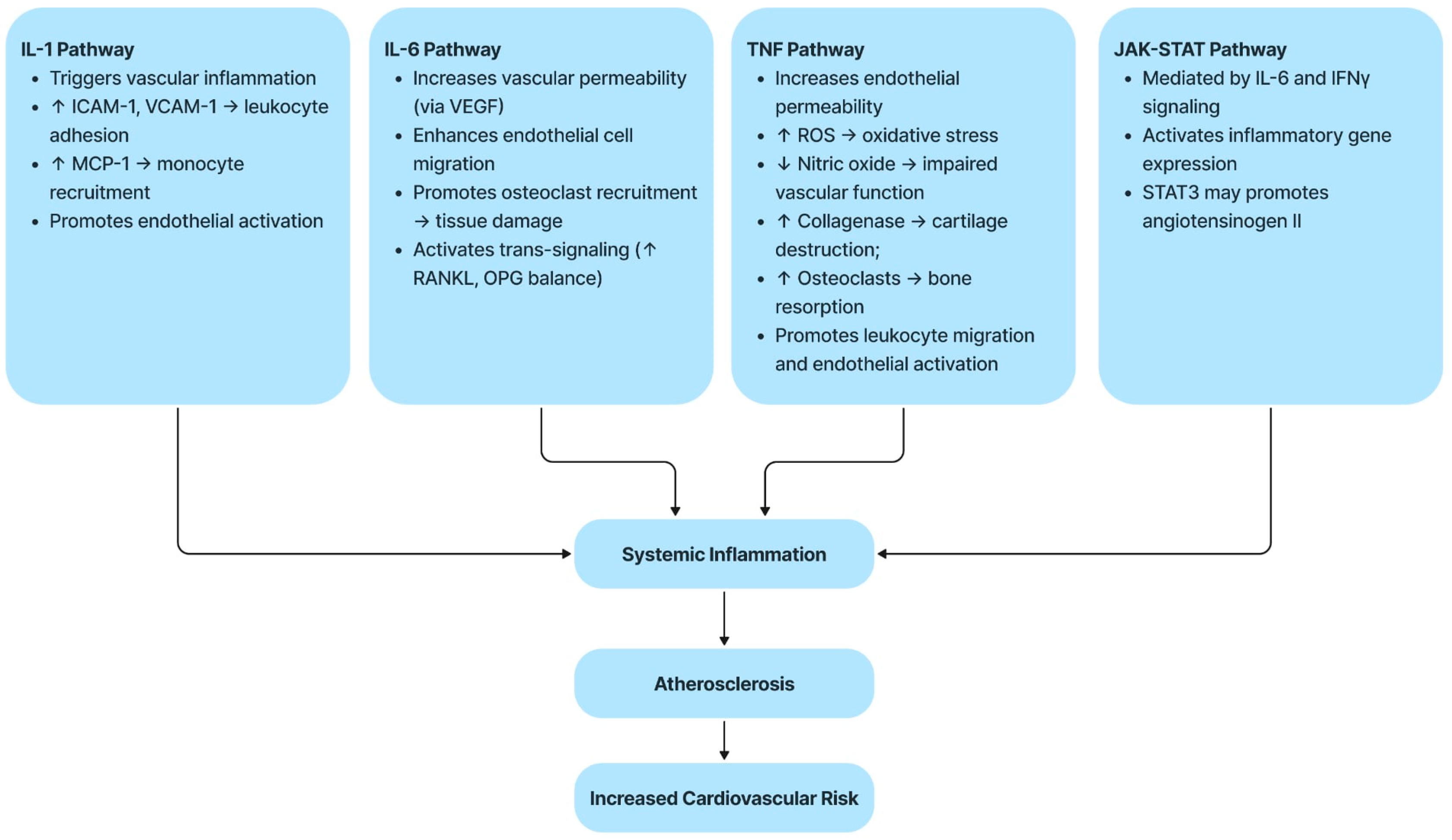
2.3. Molecular and Inflammatory Mechanisms
2.4. Brief Description of Each Pathway
2.4.1. The IL-1 Pathway
2.4.2. The IL-6 Pathway
2.4.3. The TNF Pathway
2.4.4. The JAK–STAT Pathway
3. Clinical Cardiovascular Manifestations in RA
3.1. Pericarditis
3.2. Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
These insights emphasize the importance of early detection of subclinical conduction abnormalities—preferably via ambulatory ECG monitoring—and tight control of RA disease activity. Anti-inflammatory therapies such as DMARDs and biologics have shown potential not only in improving joint-related symptoms but also in normalizing electrophysiological parameters and reducing cardiovascular mortality. Randomized trials are warranted to confirm their effectiveness in lowering SCD risk in this vulnerable population [4,78].
3.3. Cardiomyopathy
3.4. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Data from a large population-based cohort in Sweden showed a reduction in mortality among patients with RA; however, the risk of death remains significantly increased in people with CAD and RA, which supports the findings of this review. Furthermore, a meta-analysis of 24 observational studies with a total of 111,758 subjects reported 22,927 deaths from cardiovascular causes, showing a 50% increase in mortality risk in patients diagnosed with RA [91].
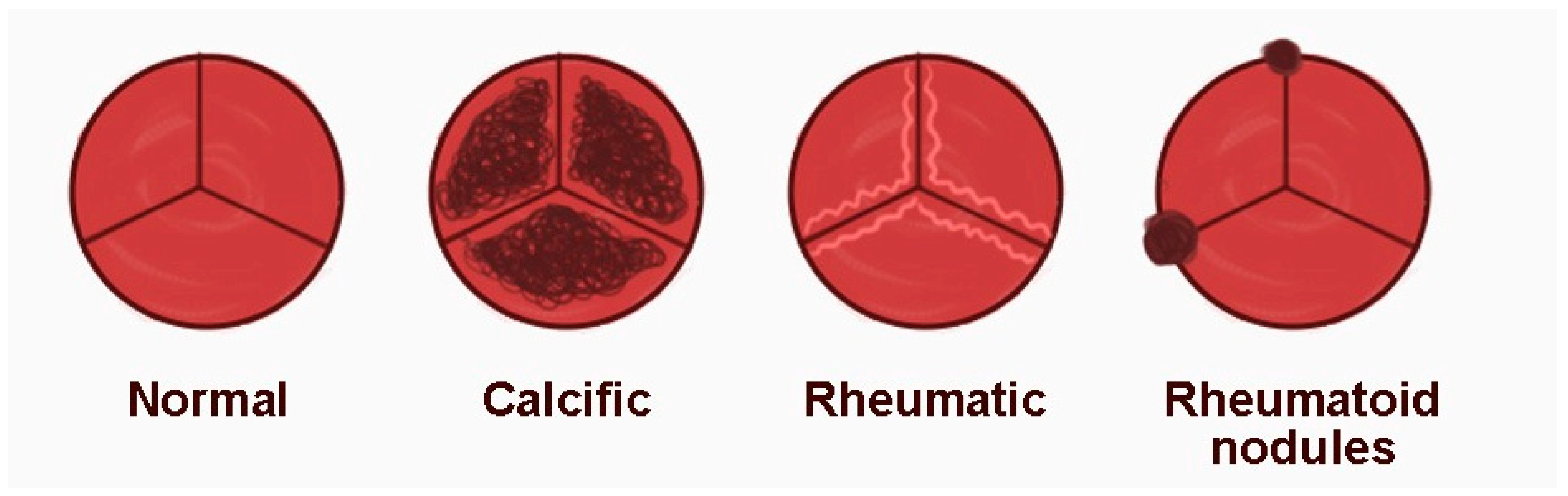
3.5. Rheumatoid Nodules
3.6. Arrhythmias
3.7. Valvular Diseases
3.8. The Role of Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP) in Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathogenesis
4. Diagnosis and Monitoring
4.1. Inflammatory and Metabolic Markers
4.1.1. Classic Inflammatory Markers
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Specific Markers in RA and CVD
Interleukin-6
4.1.2. Vascular Biomarkers (Leptin, Adiponectin)
Leptin
Adiponectin
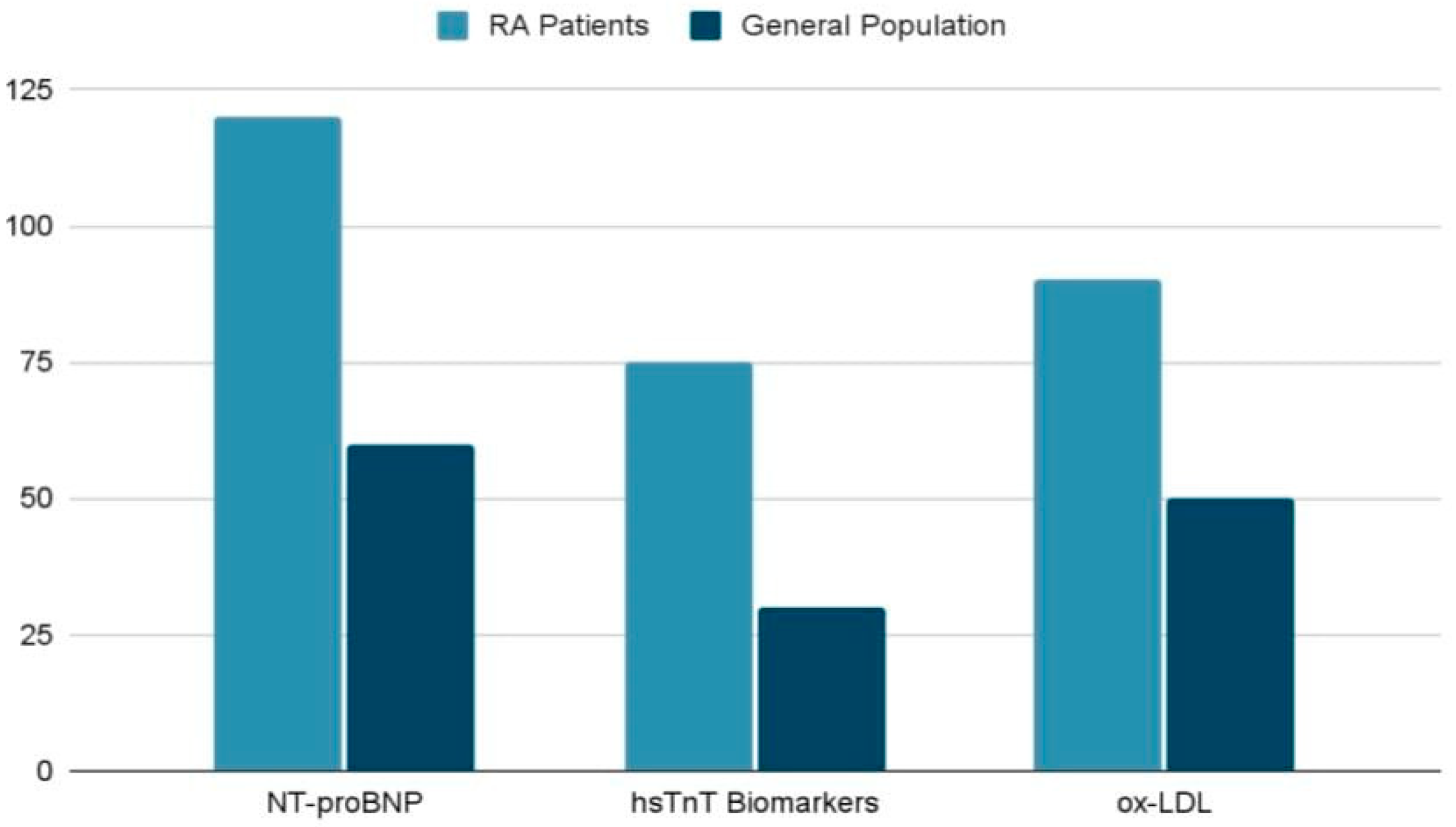
4.2. Cardiac Specific Biomarkers
4.3. Emerging Biomarkers and Future Directions
4.3.1. Ischemia Modified Albumin (IMA)
4.3.2. Catestatin (CST)
4.3.3. Fetuin-A
4.4. Practical Limitations and Specificity Issues in Biomarker Interpretation
4.5. Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Patients with RA
4.6. Integrated Strategies: Collaboration Between Rheumatologists and Cardiologists
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACCA | American College of Cardiology |
| ACPA | Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibody |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| ATACC-RA | Transatlantic Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CANTOS | Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcome Study |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CHD | coronary heart disease |
| CICs | Circulating immune complexes |
| CIMT | Carotid intima–media thickness |
| COMP | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| DAS-28 | Disease activity score-28 |
| DMARDs | Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DRB1 | DR Beta 1 |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ED | Endothelial dysfunction |
| EMs | Extra-articular manifestations |
| ERS-RA | Expanded Risk Score for RA |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| FRS | The Framingham Risk Score |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| Gp130 | Glycoprotein 130 |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| hsCRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein test |
| hsTnI | High-sensitivity troponin I |
| hsTnT | High-sensitivity troponin T |
| ICAM | Intercellular adhesion molecule |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IHD | ischemic heart disease |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IMA | Ischemia-modified albumin |
| JAK/STAT | Janus tyrosine kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiovascular events |
| MCP | Monocyte chemoattractant protein |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NSAIDs | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| ox-LDL | Oxidized LDL |
| PCE | Pooled Cohort Equation |
| QTc | Corrected QT interval |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RANKL | Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| RRS | Reynolds Risk Score |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SCD | Sudden Cardiac Death |
| SCORE | Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation |
| sIL-6R | Soluble IL-6 receptor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TNFR1 | TNF receptor 1 |
| TNFR2 | TNF receptor 2 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
References
- Lin, Y.J.; Anzaghe, M.; Schülke, S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2020, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Luo, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, X.; Lv, T.; Fang, G.; Ou, P.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Huang, A.; et al. Systemic complications of rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on pathogenesis and treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1051082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Davis, J.; Matteson, E.L.; Crowson, C.S. Is the epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis changing? Results from a population-based incidence study, 1985–2014. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figus, F.A.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.; Ganeshalingam, K.; Semb, A.G.; Szekanecz, Z.; Nurmohamed, M. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: Recent advances in the understanding of the pivotal role of inflammation, risk predictors and the impact of treatment. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Rimm, E.B.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Mandl, L.A.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Curhan, G.C. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation 2003, 107, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.; van Halm, V.P.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Smulders, Y.M.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; Visser, M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; et al. Does rheumatoid arthritis equal diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhardsen, J.; Ahlehoff, O.; Gislason, G.H.; Madsen, O.R.; Olesen, J.B.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Hansen, P.R. The risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus: A Danish nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.E. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessein, P.H.; Joffe, B.I.; Veller, M.G.; Stevens, B.A.; Tobias, M.; Reddi, K.; Stanwix, A.E. Traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors are associated with atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.F.; Gourraud, P.A.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.L.; Constantin, A. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.; Symmons, D.P.; McCarey, D.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Nicola, P.; Kvien, T.K.; McInnes, I.B.; Haentzschel, H.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Provan, S.; et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, I.A.; Imboden, J.B.; Hsue, P.Y.; Ganz, P. Rheumatoid arthritis: Model of systemic inflammation driving atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinblatt, M.E.; Kuritzky, L. RAPID: Rheumatoid arthritis. J. Fam. Pract. 2007, 56, S1–S7. quiz S8. [Google Scholar]
- Situnayake, R.D.; Kitas, G. Dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rincón, I.D.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Freeman, G.L.; Escalante, A. High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; McInnes, I.B. Vascular comorbidity in rheumatoid arthritis: Potential mechanisms and solutions. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2005, 17, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Roger, V.L.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: The impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Yang, K.; Han, T.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Protocol for rheumatoid arthritis complicated with cardiovascular damage treated with Guanxining tablet with a randomized controlled trial. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semb, A.G.; Ikdahl, E.; Wibetoe, G.; Crowson, C.; Rollefstad, S. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, S.R.; Panjiyar, B.K.; Panicker, S.S.; Danduboyina, A. Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in the Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e47416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Chessa, I.; Bassu, S.; Cavagna, L.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G.; Giordo, R.; Mangoni, A.A.; Damiano Sanna, G.; Zinellu, A. Association between ischemia-modified albumin (IMA) and peripheral endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Piga, M.; Fedele, A.L.; Mura, S.; Piras, A.; Cadoni, M.L.; Cangemi, I.; Dessi, M.; Di Sante, G.; Tolusso, B.; et al. Prevalence and Determinants of Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 6548715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Lopez-Diaz, M.J.; Piñeiro, A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Ollier, W.E.; Martin, J.; Llorca, J. HLA-DRB1 and persistent chronic inflammation contribute to cardiovascular events and cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 57, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Morales, R.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, T.R.; Rodriguez, L.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; Llorca, J.; Martin, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A. A1298C polymorphism in the MTHFR gene predisposes to cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; González-Juanatey, C.; García-Bermúdez, M.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, T.R.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, B.; Llorca, J.; Martin, J.; González-Gay, M.A. CCR5Δ32 variant and cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoloni, E.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Gerli, R. Inflammatory and autoimmune mechanisms in the induction of atherosclerotic damage in systemic rheumatic diseases: Two faces of the same coin. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reriani, M.K.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Endothelial function as a functional expression of cardiovascular risk factors. Biomark. Med. 2010, 4, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoloni, E.; Alunno, A.; Valentini, V.; Luccioli, F.; Valentini, E.; La Paglia, G.M.C.; Leone, M.C.; Cafaro, G.; Marcucci, E.; Gerli, R. Targeting Inflammation to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Rheumatic Diseases: Myth or Reality. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goëb, V.; Aegerter, P.; Parmar, R.; Fardellone, P.; Vittecoq, O.; Conaghan, P.G.; Emery, P.; Le Loët, X.; Ponchel, F. Progression to rheumatoid arthritis in early inflammatory arthritis is associated with low IL-7 serum levels. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; Toldo, S.; Marchetti, C.; Kron, J.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1260–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.N.; Giles, J.T.; Liao, K.P. Shared inflammatory pathways of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Collagenases and cracks in the plaque. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3201–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vromman, A.; Ruvkun, V.; Shvartz, E.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Santos Masson, G.; Tesmenitsky, Y.; Folco, E.; Gram, H.; Nahrendorf, M.; Swirski, F.K.; et al. Stage-dependent differential effects of interleukin-1 isoforms on experimental atherosclerosis. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2482–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangan, S.; Choy, E.H. The role of interleukin 6 in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2010, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K.; Libby, P. The immune response in atherosclerosis: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Rose-John, S. The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: Recent advances towards specific inhibition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 34, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Rajasingh, J.; Lambers, E.; Qin, G.; Losordo, D.W.; Kishore, R. IL-10 inhibits inflammation and attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via activation of STAT3 and suppression of HuR. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, e9–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plens-Galaska, M.; Szelag, M.; Collado, A.; Marques, P.; Vallejo, S.; Ramos-González, M.; Wesoly, J.; Sanz, M.J.; Peiró, C.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. Genome-Wide Inhibition of Pro-atherogenic Gene Expression by Multi-STAT Targeting Compounds as a Novel Treatment Strategy of CVDs. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNγ: Signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, R.R.; Olsen, N.J. Room for more IL-6 blockade? Sarilumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, R.Q.; Li, L.; Yuan, W.; Shord, S.S.; Nie, L.; Habtemariam, B.A.; Przepiorka, D.; Farrell, A.T.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Tocilizumab for Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Severe or Life-Threatening Cytokine Release Syndrome. Oncologist 2018, 23, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Weisenfeld, D.; Seyok, T.; Huang, S.; Massarotti, E.; Barrett, L.; Bibbo, C.; Solomon, D.H.; Plutzky, J.; Bolster, M.; et al. Relationship Between Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, Inflammation, and Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e025467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.; Williams, J.; Sime, K.; Jin, H.S.; Thompson, C.; Jordan, L.; Lang, D.; Halcox, J.P.; Ellins, E.; Jones, G.W.; et al. The role of interleukin-6 trans-signalling on cardiovascular dysfunction in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Libby, P.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Koenig, W.; Shimokawa, H.; Everett, B.M.; Glynn, R.J. Modulation of the interleukin-6 signalling pathway and incidence rates of atherosclerotic events and all-cause mortality: Analyses from the Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, P.; Myles, I.A. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors: Pleiotropic Signaling Complexes and Their Differential Effects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Brand, D.D.; Zheng, S.G. Role of TNF-TNF Receptor 2 Signal in Regulatory T Cells and Its Therapeutic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1108–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Schwarz, E.M. The TNF-alpha transgenic mouse model of inflammatory arthritis. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2003, 25, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keffer, J.; Probert, L.; Cazlaris, H.; Georgopoulos, S.; Kaslaris, E.; Kioussis, D.; Kollias, G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: A predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 4025–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, F.M.; McInnes, I.B. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayer, J.M.; Beutler, B.; Cerami, A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 162, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, D.R.; Nedwin, G.E.; Bringman, T.S.; Smith, D.D.; Mundy, G.R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature 1986, 319, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, S.; Mauri, C.; Ehrenstein, M.R. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy induces a distinct regulatory T cell population in patients with rheumatoid arthritis via TGF-beta. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenstein, M.R.; Evans, J.G.; Singh, A.; Moore, S.; Warnes, G.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. Compromised function of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by anti-TNFalpha therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Park, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.p.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Dellsperger, K.C.; Zhang, C. Role of TNF-alpha in vascular dysfunction. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegewisch, S.; Weh, H.J.; Hossfeld, D.K. TNF-induced cardiomyopathy. Lancet 1990, 335, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canault, M.; Peiretti, F.; Mueller, C.; Kopp, F.; Morange, P.; Rihs, S.; Portugal, H.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Nalbone, G. Exclusive expression of transmembrane TNF-alpha in mice reduces the inflammatory response in early lipid lesions of aortic sinus. Atherosclerosis 2004, 172, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Wada, H.; Niwa, T.; Kirii, H.; Iwamoto, N.; Fujii, H.; Saito, K.; Sekikawa, K.; Seishima, M. Disruption of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene diminishes the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 2005, 180, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.S.; Packer, M.; Lo, K.H.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Willerson, J.T. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in patients with moderate-to-severe heart failure: Results of the anti-TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) trial. Circulation 2003, 107, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.L.; McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Swedberg, K.; Borer, J.S.; Colucci, W.S.; Djian, J.; Drexler, H.; Feldman, A.; Kober, L.; et al. Targeted anticytokine therapy in patients with chronic heart failure: Results of the Randomized Etanercept Worldwide Evaluation (RENEWAL). Circulation 2004, 109, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.L.; Bozkurt, B.; Torre-Amione, G.; Soran, O.Z.; Sivasubramanian, N. Effect of the soluble TNF-antagonist etanercept on tumor necrosis factor bioactivity and stability. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2008, 1, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and Cancer Risk with Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, F.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Aazami, H.; Mohsenzadegan, M.; Sedighi, G.; Bahar, M. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Tai, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhou, W.; Han, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Q. Triggers of Cardiovascular Diseases in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, B.; Gür, G.; Artüz, F.; Allı, N. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Behçet disease: A case-control study in Turkey. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 14, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskuyl, A.E. The heart and cardiovascular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2006, 45 (Suppl. S4), iv4–iv7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviña-Zubieta, J.A.; Choi, H.K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Etminan, M.; Esdaile, J.M.; Lacaille, D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Capecchi, P.L.; Guidelli, G.M.; Selvi, E.; Acampa, M.; Laghi-Pasini, F. Spotlight on sirukumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: The evidence to date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3083–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, S.; Lim, P.B.; Kitas, G.D.; Panoulas, V. Sudden cardiac death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. World J. Cardiol. 2017, 9, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrengül, H.; Dursunoglu, D.; Cobankara, V.; Polat, B.; Seleci, D.; Kabukçu, S.; Kaftan, A.; Semiz, E.; Kilic, M. Heart rate variability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2004, 24, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Buono, M.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. Interplay of inflammation, oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Heart 2018, 104, 1991–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsson, P.M.; Eberhardt, K. Hand deformities are important signs of disease severity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L. Association of congestive heart failure with mortality in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis: A cohort study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, E.R. Extraarticular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1979, 8, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Griffin, J.; Bathon, J.M. Myocardial Dysfunction and Heart Failure in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Koutsogeorgopoulou, L.; Dimitroulas, T.; Katsifis, G.; Vartela, V.; Mitsikostas, D.; Kolovou, G.; Voulgari, P.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Kitas, G.D.; et al. Is There a Brain/Heart Interaction in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Seronegative Spondyloartropathies? A Combined Brain/Heart Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals the Answer. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutaleb, A.R.A.; McNally, E.M.; Khan, S.S.; Anderson, A.S.; Carr, J.C.; Wilcox, J.E. Myocarditis in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy After Changing Steroids. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Cardiomyopathies: An Overview. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.C.; Libby, P. Cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic inflammation: Mechanisms underlying premature cardiovascular events in rheumatologic conditions. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 482-9c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Gong, G. Cardiovascular outcomes in patients with co-existing coronary artery disease and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hundelshausen, P.; Weber, C. Chronic inflammation and atherosclerosis. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2013, 138, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Segami, N.; Fukuda, H.; Minato, H. Rheumatoid nodule in the lower lip of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: A novel case report and review of literature. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawałko, M.; Balsam, P.; Lodziński, P.; Grabowski, M.; Krzowski, B.; Opolski, G.; Kosiuk, J. Cardiac Arrhythmias in Autoimmune Diseases. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Piras, A.; Piga, M.; Fedele, A.L.; Mangoni, A.A.; Lazzerini, P.E.; Gremese, E.; Mathieu, A.; Ferraccioli, G.; Passiu, G.; et al. QT and QT dispersion intervals in long-standing and moderately active rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a multicentre cross-sectional study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selinski, C.; Addetia, K. Aortic Regurgitation and Rheumatoid Arthritis. JACC Case Rep. 2024, 29, 102671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydell, E.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Saxne, T.; Turesson, C. Cardiovascular disease risk in early rheumatoid arthritis: The impact of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and disease activity. BMC Rheumatol. 2023, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Choy, E.H. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batún-Garrido, J.A.J.; Salas-Magaña, M.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E. Association between leptin and IL-6 concentrations with cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.E.; Johnson, T.M.; England, B.R.; Wysham, K.D.; George, M.D.; Sauer, B.; Hamilton, B.C.; Hunter, C.D.; Duryee, M.J.; Thiele, G.M.; et al. Circulating Adipokines and Associations With Incident Cardiovascular Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pàmies, A.; Llop, D.; Ibarretxe, D.; Rosales, R.; Girona, J.; Masana, L.; Vallvé, J.C.; Paredes, S. Enhanced Association of Novel Cardiovascular Biomarkers Fetuin-A and Catestatin with Serological and Inflammatory Markers in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankad, R.; Gabriel, S.E. Rheumatoid arthritis: Treating cardiovascular risk in RA requires multidisciplinary care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Specific Risk Factors | Key Points | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Risk Factors | Yu et al., 2023 [21] | ||
| Smoking | Doubles CVD risk in RA. | Encourages smoking cessation interventions. | |
| Hypertension | Affects ~70% of RA patients; often underdiagnosed. | Screening every 5 years recommended. | |
| Diabetes | Correlated with a twofold increase in CVD risk in RA. | Anti-diabetic therapies that minimize inflammation. | |
| Dyslipidemia | Paradoxical ↓ low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels ↑ CV risk. | Lipid-monitoring statins. | |
| RA-Specific Risk Factors | |||
| Chronic inflammation | High sensitivity C-reactive protein test (hsCRP) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) highlight systemic inflammation. | Methotrexate, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors ↓ CVD risk. | |
| Disease activity and duration | Longer disease activity ↑ CVD risk. | Aggressive RA control is vital. | |
| Use of glucocorticoids | Prolonged use risk ↑ risk of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia. | Dose minimization recommended. | |
| Autoantibodies-Rheumatoid factor (RF), Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibody (ACPA) | RF-positive are 2.5 times more at risk of HF. | Requires tailored monitoring and therapy. | |
| Novel Risk Factors | |||
| Carotid intima–media thickness (CIMT) | Elevated in RA patients. | Non-invasive atherosclerosis marker for early CVD detection. | |
| Valvular disease | ↑ Prevalence; linked to systemic Inflammation. | Echocardiography for monitoring. |
| No. | Inflammatory Marker | Pathogenic Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IL-1β | Stimulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) activation | Weber et al., 2023 [35] |
| 2 | IL-6 | Promotes vascular inflammation, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated permeability | Libby et al., 2013 [37] Srirangan et al., 2010 [39] |
| 3 | TNF-α | Promotes endothelial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and increased permeability | Hansson et al., 2006 [40] |
| 4 | IFN-γ | Activates JAK-STAT pathway, enhances inflammatory response | Ivashkiv et al., 2018 [44] |
| 5 | STAT3 | Dual role: pro-cardiac hypertrophy (via angiotensinogen II)/cardioprotection (via IL-10) | Krishnamurthy et al., 2009 [42] Plens-Galaska et al., 2018 [43] |
| Biomarker | Association | Clinical Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NT-proBNP | Ventricular dysfunction | MACE | Borra et al., 2023 [23] |
| hsTnT | Myocardial injury | Detects subclinical cardiac damage | |
| Anti-Apo A-I IgG | Atherosclerotic plaque presence | FRS predictive accuracy | |
| ox-LDL | Atherogenesis, inflammation | Indicates disease activity |
| Risk Model | Target Population | Key Features | Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCORE (Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation) | General population (Europe) | 10-year CVD mortality risk. | Fatal events only; no RA-specific adjustments. | Semb et al., 2020 [22] |
| FRS | General population (USA) | Includes stroke, vascular events, HF. | Overestimates risk; based on predominantly white cohorts. | |
| American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE) | General population (USA) | Considers ethnicity, 10-year ASCVD risk. | Not RA-specific; traditional risk factors only. | |
| QRISK3 | General population (UK) | Includes RA (weight = 1.4); integrates multiple risk factors. | May overestimate risk; limited validation outside the UK. | |
| Reynolds Risk Score (RRS) | General population (USA) | Incorporates hsCRP for improved risk estimation. | Not validated for RA; may underestimate risk. | |
| ERS-RA (Expanded Risk Score for RA) | RA-specific | Combines traditional with RA-specific characteristics. | Limited validation: modest predictive accuracy. | |
| ATACC-RA (Transatlantic Cardiovascular Risk in RA) | RA-specific | Integrates RA-specific inflammation markers with traditional factors. | Requires further validation, inconsistent results. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosău, D.E.; Costache Enache, I.I.; Costache, A.D.; Tudorancea, I.; Ancuța, C.; Șerban, D.N.; Bădescu, C.M.; Loghin, C.; Șerban, I.L. From Joints to the Heart: An Integrated Perspective on Systemic Inflammation. Life 2025, 15, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040629
Cosău DE, Costache Enache II, Costache AD, Tudorancea I, Ancuța C, Șerban DN, Bădescu CM, Loghin C, Șerban IL. From Joints to the Heart: An Integrated Perspective on Systemic Inflammation. Life. 2025; 15(4):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040629
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosău, Diana Elena, Irina Iuliana Costache Enache, Alexandru Dan Costache, Ionuț Tudorancea, Codrina Ancuța, Dragomir Nicolae Șerban, Codruța Minerva Bădescu, Cătălin Loghin, and Ionela Lăcrămioara Șerban. 2025. "From Joints to the Heart: An Integrated Perspective on Systemic Inflammation" Life 15, no. 4: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040629
APA StyleCosău, D. E., Costache Enache, I. I., Costache, A. D., Tudorancea, I., Ancuța, C., Șerban, D. N., Bădescu, C. M., Loghin, C., & Șerban, I. L. (2025). From Joints to the Heart: An Integrated Perspective on Systemic Inflammation. Life, 15(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040629










