Cerebral Microbleeds in a Stroke Prevention Clinic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients
2.2. Stroke Outcome at Follow-Up
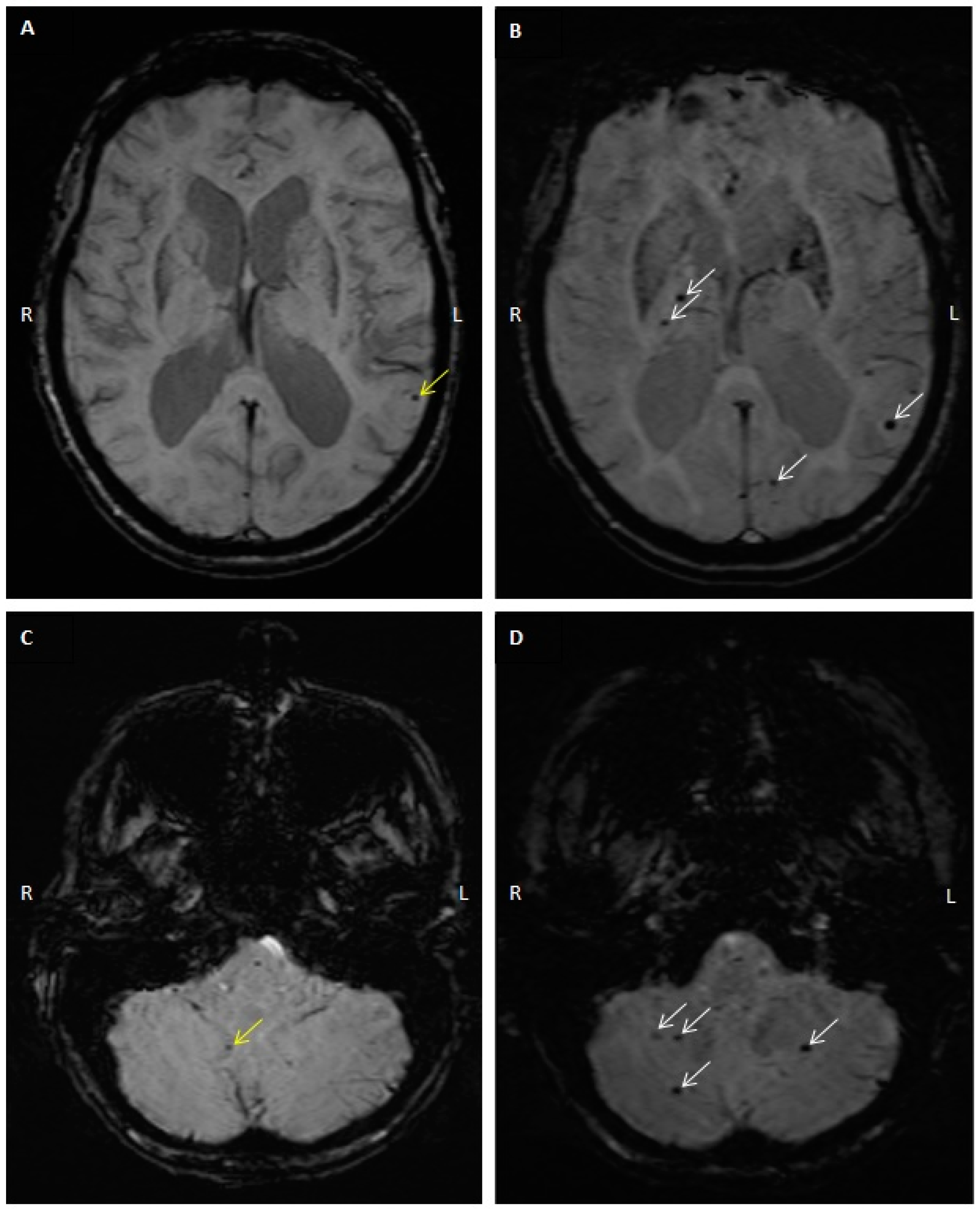
2.3. CMB Progression on Follow-Up MRI Studies
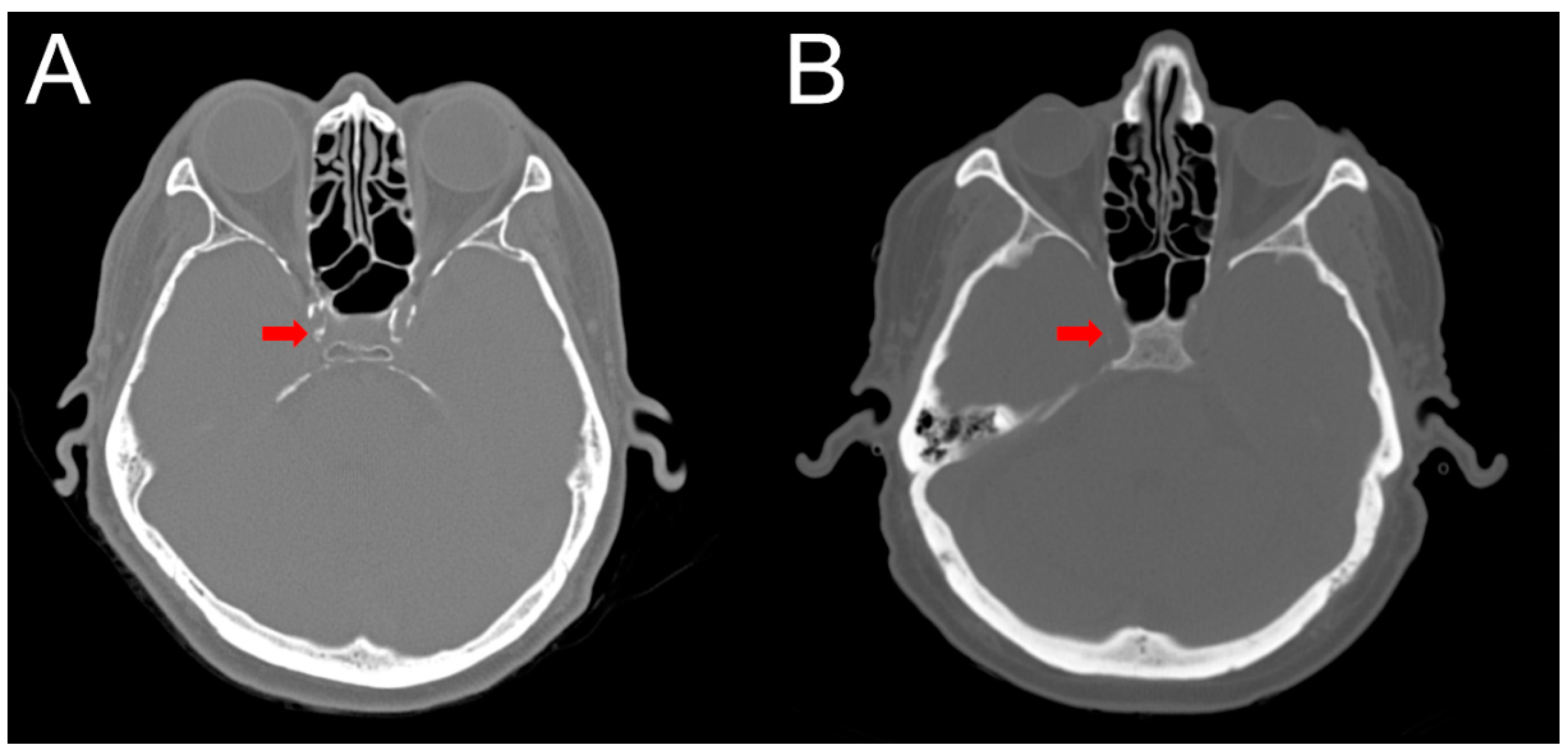
2.4. Intracranial Calcification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Standard Protocol Approvals, Registrations, and Patient Consents
4.2. Patient Selection
4.3. MRI and CMB Identification
4.4. Computed Tomography (CT) Interpretation and Cerebral Arterial Calcification Score
4.5. Clinical Outcomes
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Viswanathan, A.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Warach, S.; Launer, L.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Breteler, M.M.; Microbleed Study Group. Cerebral microbleeds: A guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokura, H.; Saika, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nagai, A.; Oguro, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, S. Microbleeds are associated with subsequent hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke in healthy elderly individuals. Stroke 2011, 42, 1867–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M. The challenge of mixed cerebrovascular disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2010, 1207, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M.; Vasilevko, V.; Cribbs, D.H. Mixed cerebrovascular disease and the future of stroke prevention. Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Li, C. Antiplatelet Drug Use and Cerebral Microbleeds: A Meta-analysis of Published Studies. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wei, C.; Hu, M.; Xu, J.; Niu, K.; Zhang, C.; Lv, P.; Li, L.; Dong, Y. Correlation between antiplatelet therapy in secondary prevention of acute cerebral infarction and cerebral microbleeds: A susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) study. J. Xray Sci. Technol. 2018, 26, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, A.; Shoamanesh, A.; International, M.-M.I. Clinical relevance of microbleeds in acute stroke thrombolysis: Comprehensive meta-analysis. Neurology 2016, 87, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Song, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Lin, J.; Qu, H.; Zhao, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, M. Cerebral Microbleeds and the Safety of Anticoagulation in Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 41, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M. Cerebral Microbleeds and Thrombolysis: Clinical Consequences and Mechanistic Implications. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Sato, N.; Sugiyama, E.; Okada, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Akasaka, K.; Hasebe, N. Cerebral Microbleeds Remain for Nine Years: A Prospective Study with Yearly Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, A.M.; Raz, N. Incident risk and progression of cerebral microbleeds in healthy adults: A multi-occasion longitudinal study. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoudad, S.; Wolters, F.J.; Viswanathan, A.; de Bruijn, R.F.; van der Lugt, A.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W. Association of Cerebral Microbleeds With Cognitive Decline and Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.R.; Beiser, A.; Himali, J.J.; Shoamanesh, A.; DeCarli, C.; Seshadri, S. Cerebral microbleeds and risk of incident dementia: The Framingham Heart Study. Neurobiol Aging 2017, 54, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soros, P.; Whitehead, S.; Spence, J.D.; Hachinski, V. Antihypertensive treatment can prevent stroke and cognitive decline. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.W.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, D.W.; Ha, S.Y. Carotid artery calcification is associated with deep cerebral microbleeds. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.S.; Sigurdsson, S.; Jonsdottir, M.K.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Kjartansson, O.; Garcia, M.E.; van Buchem, M.A.; Harris, T.B.; Gudnason, V.; et al. Coronary artery calcium, brain function and structure: The AGES-Reykjavik Study. Stroke 2010, 41, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, D.; Ikram, M.A.; Elias-Smale, S.E.; Krestin, G.P.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.; van der Lugt, A.; Vernooij, M.W. Calcification in major vessel beds relates to vascular brain disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, P.W.; Park, K.Y.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Youn, Y.C.; Byun, J.S.; Kwon, O.S. Intracranial internal carotid artery calcification: A representative for cerebral artery calcification and association with white matter hyperintensities. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 30, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Sun, W.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xu, E.; Cheng, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, Y.; Hong, Z.; et al. Different impacts of blood pressure variability on the progression of cerebral microbleeds and white matter lesions. Stroke 2012, 43, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramadan, M.M.; Mahfouz, E.M.; Gomaa, G.F.; El-Diasty, T.A.; Alldawi, L.; Ikrar, T.; Limin, D.; Kodama, M.; Aizawa, Y. Evaluation of coronary calcium score by multidetector computed tomography in relation to endothelial function and inflammatory markers in asymptomatic individuals. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M. Cerebral microbleeds: Where are we now? Neurology 2014, 83, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoire, S.M.; Chaudhary, U.J.; Brown, M.M.; Yousry, T.A.; Kallis, C.; Jager, H.R.; Werring, D.J. The Microbleed Anatomical Rating Scale (MARS): Reliability of a tool to map brain microbleeds. Neurology 2009, 73, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| CMB No Progression (n = 21) | CMB Progression (n = 25) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |||
| Age | 73.3 ± 12.1 | 73.7 ± 10.4 | 0.90 | |
| Clinical follow-up interval (months) | 24.2 ± 23.3 | 29.1 ± 22.1 | 0.46 | |
| MRI follow-up interval (months) | 18.6 ± 12.1 | 33.1 ± 18.8 | 0.003 | |
| N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Male | 12 (57) | 14 (56) | 1.00 | |
| Race | White | 6 (29) | 14 (56) | 0.08 (White vs. Other) |
| Asian | 8 (38) | 9 (36) | ||
| Hispanic | 5 (24) | 2 (8) | ||
| Black | 2 (10) | 0 (0) | ||
| Hypertension | 14 (67) | 22 (88) | 0.15 | |
| Diabetes | 5 (24) | 7 (28) | 1.00 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 13 (62) | 15 (60) | 1.00 | |
| Smoking | 3 (14) | 4 (16) | 1.00 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 5 (24) | 8 (32) | 0.22 | |
| Cerebral amyloid angiopathy | 3 (14) | 6 (24) | 0.48 | |
| Use of antithrombotics | 13 (62) | 15 (60) | 1.00 | |
| Stroke event at follow-up | 1 (5) | 3 (12) | 0.61 | |
| Calcification Score (cm3) | Number of CMB at Initial Scan | Number of CMB at Follow-Up Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD Range No. of Subjects | Mean ± SD Range No. of Subjects | |
| <300 Range 32–286 | 4.9 ± 2.2 1–7 (n = 8) | 5.6 ± 2.4 3–8 (n = 5) |
| 300–1000 Range 309–770 | 12.3. ± 12.4 0–32 (n = 9) † | 13.7 ± 13.5 0–32 (n = 9) † |
| >1000 Range 1159–4021 | 13.0 ± 11.7 3–37 (n = 8) | 15.0 ± 8.6 7–27 (n = 4) |
| p-value for difference in low vs. intermediate and high groups | 0.02 | 0.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, A.-H.; Wadi, L.; Chow, D.; Chang, P.; Floriolli, D.; Shah, K.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Fisher, M. Cerebral Microbleeds in a Stroke Prevention Clinic. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010018
Cho A-H, Wadi L, Chow D, Chang P, Floriolli D, Shah K, Paganini-Hill A, Fisher M. Cerebral Microbleeds in a Stroke Prevention Clinic. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, A-Hyun, Lara Wadi, Daniel Chow, Peter Chang, David Floriolli, Krunal Shah, Annlia Paganini-Hill, and Mark Fisher. 2020. "Cerebral Microbleeds in a Stroke Prevention Clinic" Diagnostics 10, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010018
APA StyleCho, A.-H., Wadi, L., Chow, D., Chang, P., Floriolli, D., Shah, K., Paganini-Hill, A., & Fisher, M. (2020). Cerebral Microbleeds in a Stroke Prevention Clinic. Diagnostics, 10(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010018






