Ultrasound Assessment of Autonomous Thyroid Nodules before and after Radioiodine Therapy Using Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
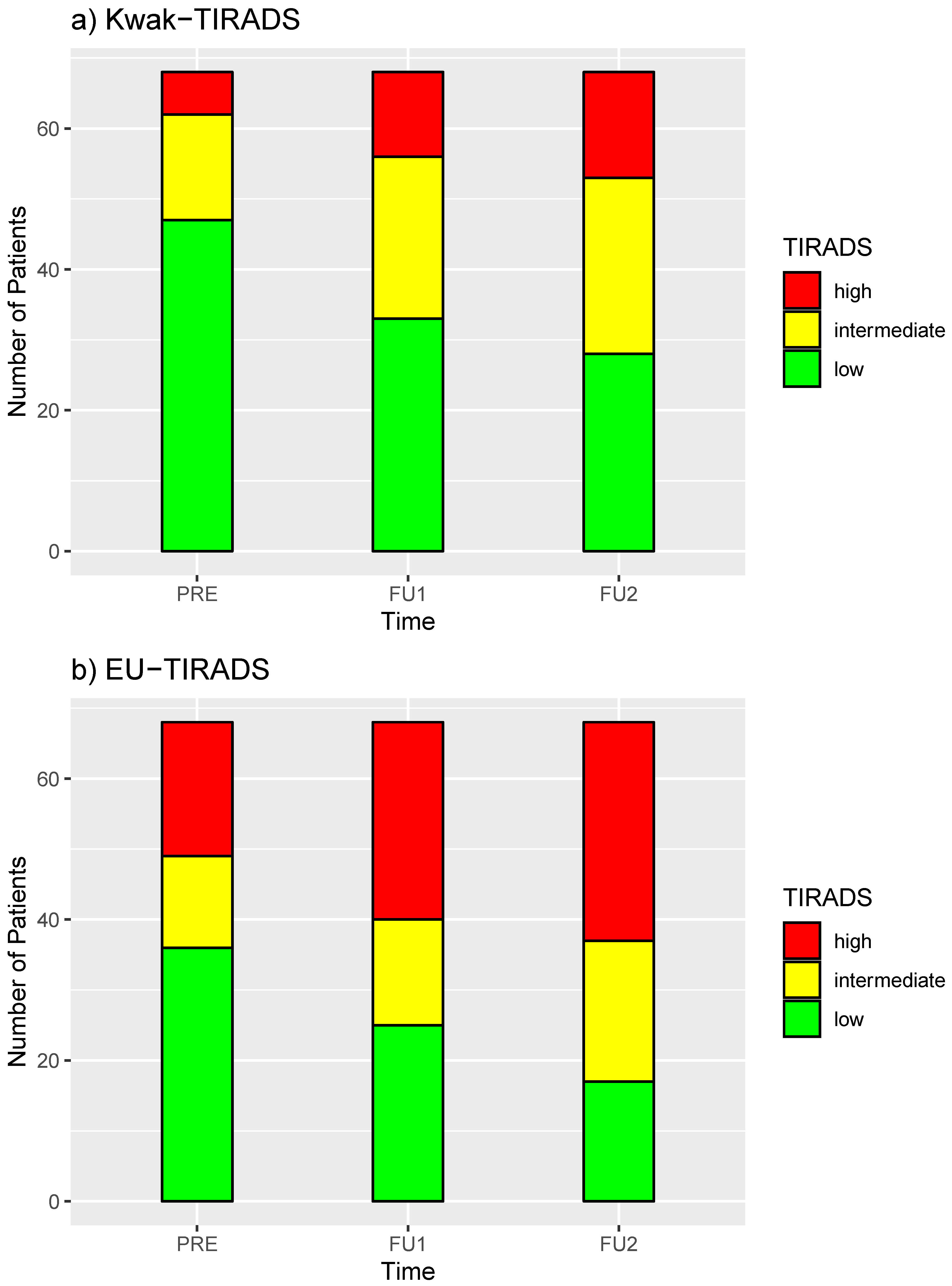
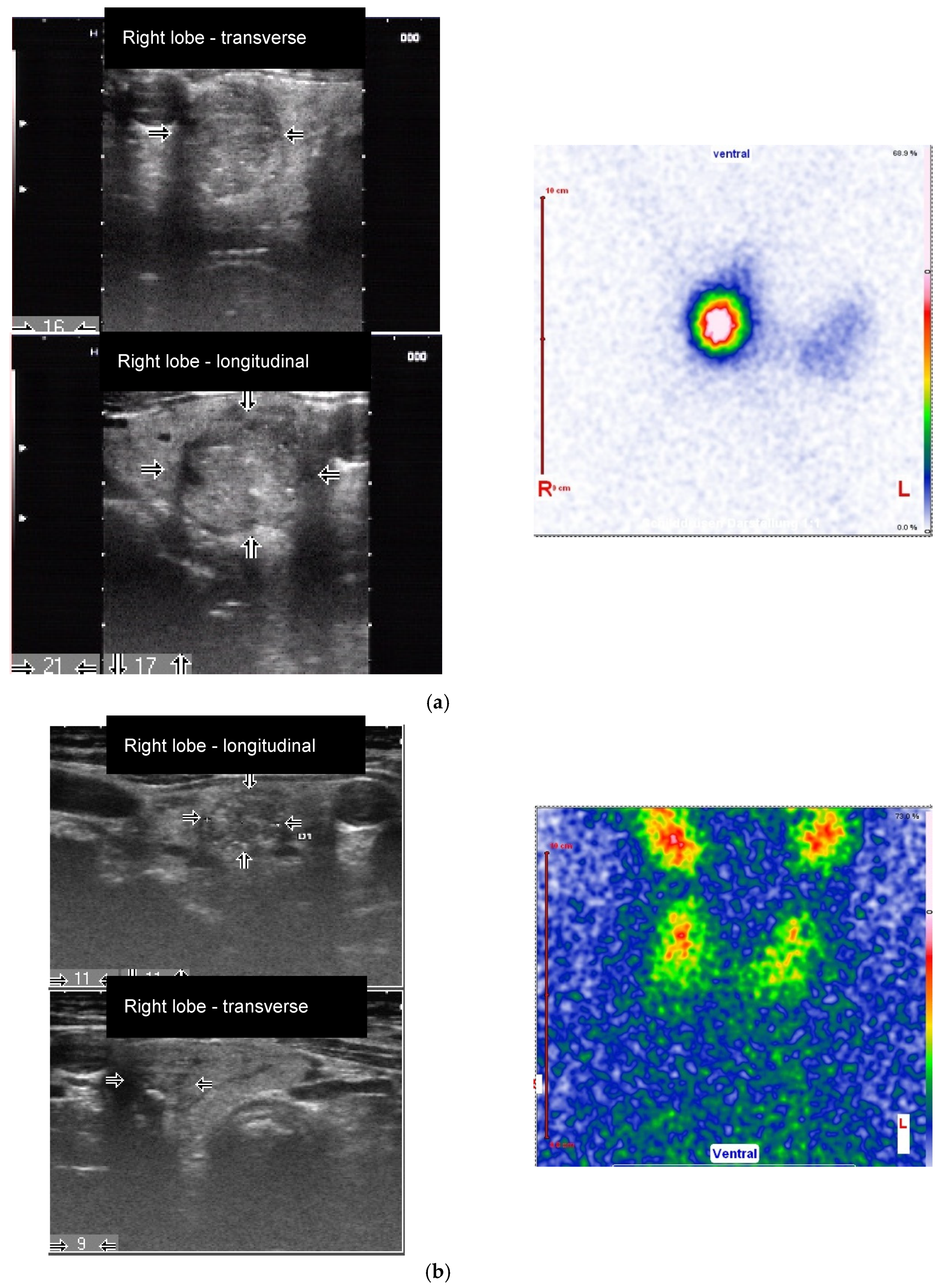
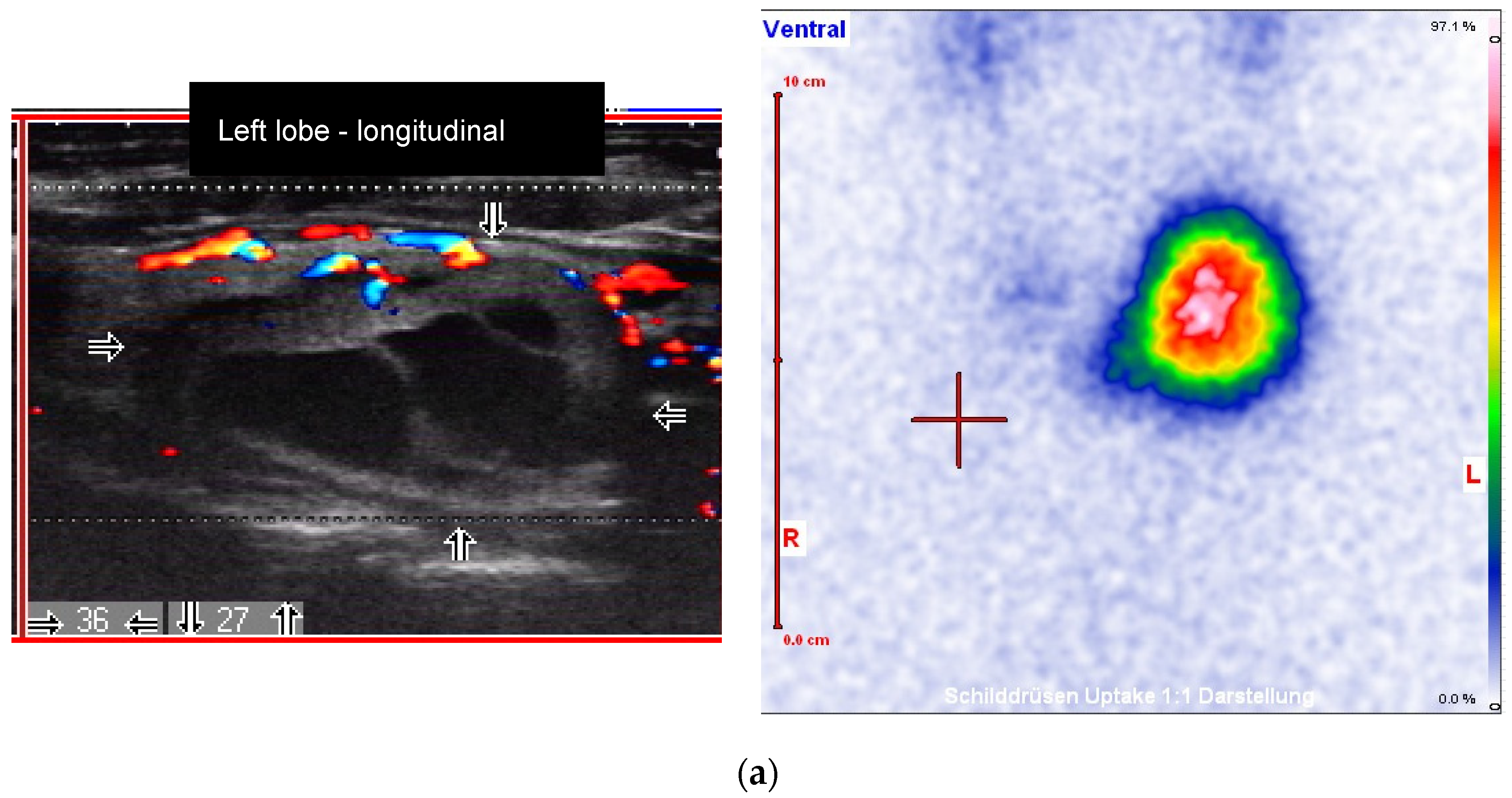
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giovanella, L.; Avram, A.M.; Iakovou, I.; Kwak, J.; Lawson, S.A.; Lulaj, E.; Luster, M.; Piccardo, A.; Schmidt, M.; Tulchinsky, M.; et al. EANM practice guideline/SNMMI procedure standard for RAIU and thyroid scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reschini, E.; Ferrari, C.; Castellani, M.; Matheoud, R.; Paracchi, A.; Marotta, G.; Gerundini, P. The trapping-only nodules of the thyroid gland: Prevalence study. Thyroid 2006, 16, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenke, S.; Seifert, P.; Zimny, M.; Winkens, T.; Binse, I.; Goerges, R. Risk stratification of thyroid nodules using Thyroid Imaging Reporting And Data System (TIRADS): The omission of thyroid scintigraphy increases the rate of falsely suspected lesions. J. Nucl. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruhlmann, M.; Stebner, V.; Görges, R.; Farahati, J.; Simon, D.; Bockisch, A.; Rosenbaum-Krumme, S.; Nagarajah, J. Diagnosis of hyperfunctional thyroid nodules: Impact of US-elastography. Nuklearmedizin 2014, 53, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanella, L.; Piccardo, A.; Pezzoli, C.; Bini, F.; Ricci, R.; Ruberto, T.; Trimboli, P. Comparison of high intensity focused ultrasound and radioiodine for treating toxic thyroid nodules. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, G.; Filesi, M.; D’Apollo, R.; Toteda, M.; Di Nicola, A.D.; Colandrea, M.; Travascio, L.; Vestri, A.R.; Montesano, T. Autonomous functioning thyroid nodules and 131I in diagnosis and therapy after 50 years of experience: What is still open to debate? Clin. Nucl. Med. 2013, 38, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietlein, M.; Grünwald, F.; Schmidt, M.; Schneider, P.; Verburg, F.A.; Luster, M. Radioiodine therapy for benign thyroid diseases (version 5). German Guideline. Nuklearmedizin 2016, 55, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokkel, M.; Handkiewicz Junak, D.; Lassmann, M.; Dietlein, M.; Luster, M. EANM procedure guidelines for therapy of benign thyroid disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelli, R.; Mazzeo, S.; Boni, G.; Boccuzzi, A.; Bianchi, F.; Brozzi, F.; Santini, P.; Vitti, P.; Cioni, R.; Caramella, D. Comparison between radioiodine therapy and single-session radiofrequency ablation of autonomously functioning thyroid nodules: A retrospective study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 90, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratini, B.; Ciuoli, C.; Di Cairano, D.; Guarino, E.; Mazzucato, P.; Montanaro, A.; Burroni, L.; Vattimo, A.; Pacini, F. Effectiveness of radioiodine (131-I) as definitive therapy in patients with autoimmune and non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, M.F.; Küçük, N.O.; Anil, C.; Aras, S.; Ozer, D.; Aras, G.; Kamel, N. Effect of radioiodine therapy on thyroid nodule size and function in patients with toxic adenomas. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2004, 25, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, V.; Eterovic, D. Thyroid echogenicity predicts outcome of radioiodine therapy in patients with Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- English, C.; Casey, R.; Bell, M.; Bergin, D.; Murphy, J. The Sonographic Features of the Thyroid Gland After Treatment with Radioiodine Therapy in Patients with Graves’ Disease. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, E.; Majlis, S.; Rossi, R.; Franco, C.; Niedmann, J.P.; Castro, A.; Dominguez, M. An ultrasonogram reporting system for thyroid nodules stratifying cancer risk for clinical management. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1748–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Han, K.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Moon, H.J.; Son, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Jung, H.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, E.-K. Thyroid imaging reporting and data system for US features of nodules: A step in establishing better stratification of cancer risk. Radiology 2011, 260, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russ, G.; Bonnema, S.J.; Erdogan, M.F.; Durante, C.; Ngu, R.; Leenhardt, L. European Thyroid Association Guidelines for Ultrasound Malignancy Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules in Adults: The EU-TIRADS. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tessler, F.N.; Middleton, W.D.; Grant, E.G.; Hoang, J.K.; Berland, L.L.; Teefey, S.A.; Cronan, J.J.; Beland, M.D.; Desser, T.S.; Frates, M.C.; et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenke, S.; Rink, T.; Zimny, M. TIRADS for sonographic assessment of hypofunctioning and indifferent thyroid nodules. Nuklearmedizin 2015, 54, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, S.; Zimny, M. Combination of Sonoelastography and TIRADS for the Diagnostic Assessment of Thyroid Nodules. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remonti, L.R.; Kramer, C.K.; Leitão, C.B.; Pinto, L.C.F.; Gross, J.L. Thyroid ultrasound features and risk of carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Thyroid 2015, 25, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Tae, K.; Park, D.W.; Kim, S.T. Radiofrequency ablation of benign cold thyroid nodules: Initial clinical experience. Thyroid 2006, 16, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, E.J.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Baek, J.H. Radiofrequency ablation of benign non-functioning thyroid nodules: 4-year follow-up results for 111 patients. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aysan, E.; Idiz, U.O.; Akbulut, H.; Elmas, L. Single-session radiofrequency ablation on benign thyroid nodules: A prospective single center study: Radiofrequency ablation on thyroid. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2016, 401, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All | Study Site 1 Hanau | Study Site 2 Magdeburg | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 68 | 34 | 34 | |
| Age (years) mean ± SD | 60.6 ± 13.0 | 58.8 ± 14.3 | 62.5 ± 11.4 | 0.228 * |
| Sex Female Male | 39 29 | 21 13 | 18 16 | 0.624 † |
| Location AFTN Right lobe Left lobe Isthmus | 35 28 5 | 14 16 4 | 21 12 1 | 0.167 † |
| Max. size AFTN (mm) median (25/75th-P) | 33 (27/36) | 32 (24.8/35) | 33 (27/38.3) | 0.144 ‡ |
| Activity (MBq) median (25/75th-P) | 539 (347/787.5) | 534.5 (403.5/743.8) | 539 (320.8/807.5) | 0.806 ‡ |
| Dose AFTN (Gy) median (25/75th-P) | 361.5 (202.3/422) | 398.5 (277.8/521.8) | 241.5 (151.3/392) | 0.0004 ‡ |
| Ultrasound Features | Before RIT | FU1 5 months | FU2 16 months | p-Value * (pre-RIT to FU1) | p-Value * (pre-RIT to FU2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition, n (%) | 0.09 | 0.28 | |||
| solid/<10% cystic | 32 (47.06) | 38 (55.88) | 41 (60.29) | ||
| 10–50% cystic | 32 (47.06) | 21 (30.88) | 23 (33.82) | ||
| >50% cystic | 4 (5.88) | 9 (13.24) | 4 (5.88) | ||
| Calcifications, n (%) | 0.23 | 0.37 | |||
| none | 53 (77.94) | 49 (72.06) | 44 (64.71) | ||
| macrocalcifications | 7 (10.29) | 3 (4.41) | 9 (13.24) | ||
| microcalcifications | 5 (7.35) | 11 (16.18) | 9 (13.24) | ||
| both | 3 (4.41) | 5 (7.35) | 6 (8.82) | ||
| Margin, n (%) | 0.08 | 0.002 | |||
| well-circumscribed | 61 (89.71) | 54 (79.41) | 45 (66.18) | ||
| irregular | 1 (1.47) | 7 (10.29) | 5 (7.35) | ||
| blurred | 6 (8.82) | 7 (10.29) | 18 (26.47) | ||
| Shape, n (%) | 0.45 | 0.45 | |||
| wider-than-tall | 57 (83.82) | 61 (89.71) | 61 (89.71) | ||
| taller-than-wide | 11 (16.18) | 7 (10.29) | 7 (10.29) | ||
| Echogenicity, n (%) | 0.05 | 0.003 | |||
| hypoechoic | 21 (30.88) | 30 (44.12) | 34 (50) | ||
| isoechoic | 47 (69.12) | 35 (51.47) | 30 (44.12) | ||
| hyperechoic | 0 (0) | 2 (2.94) | 0 (0) | ||
| marked-hypoechoic | 0 (0) | 1 (1.47) | 4 (5.88) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schenke, S.A.; Wuestemann, J.; Zimny, M.; Kreissl, M.C. Ultrasound Assessment of Autonomous Thyroid Nodules before and after Radioiodine Therapy Using Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS). Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121038
Schenke SA, Wuestemann J, Zimny M, Kreissl MC. Ultrasound Assessment of Autonomous Thyroid Nodules before and after Radioiodine Therapy Using Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS). Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchenke, Simone Agnes, Jan Wuestemann, Michael Zimny, and Michael Christoph Kreissl. 2020. "Ultrasound Assessment of Autonomous Thyroid Nodules before and after Radioiodine Therapy Using Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS)" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121038
APA StyleSchenke, S. A., Wuestemann, J., Zimny, M., & Kreissl, M. C. (2020). Ultrasound Assessment of Autonomous Thyroid Nodules before and after Radioiodine Therapy Using Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS). Diagnostics, 10(12), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121038





