Detecting Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Emptying by Submental Ultrasonography and High-Resolution Impedance Manometry: Intubated vs. Non-Intubated Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Equipment
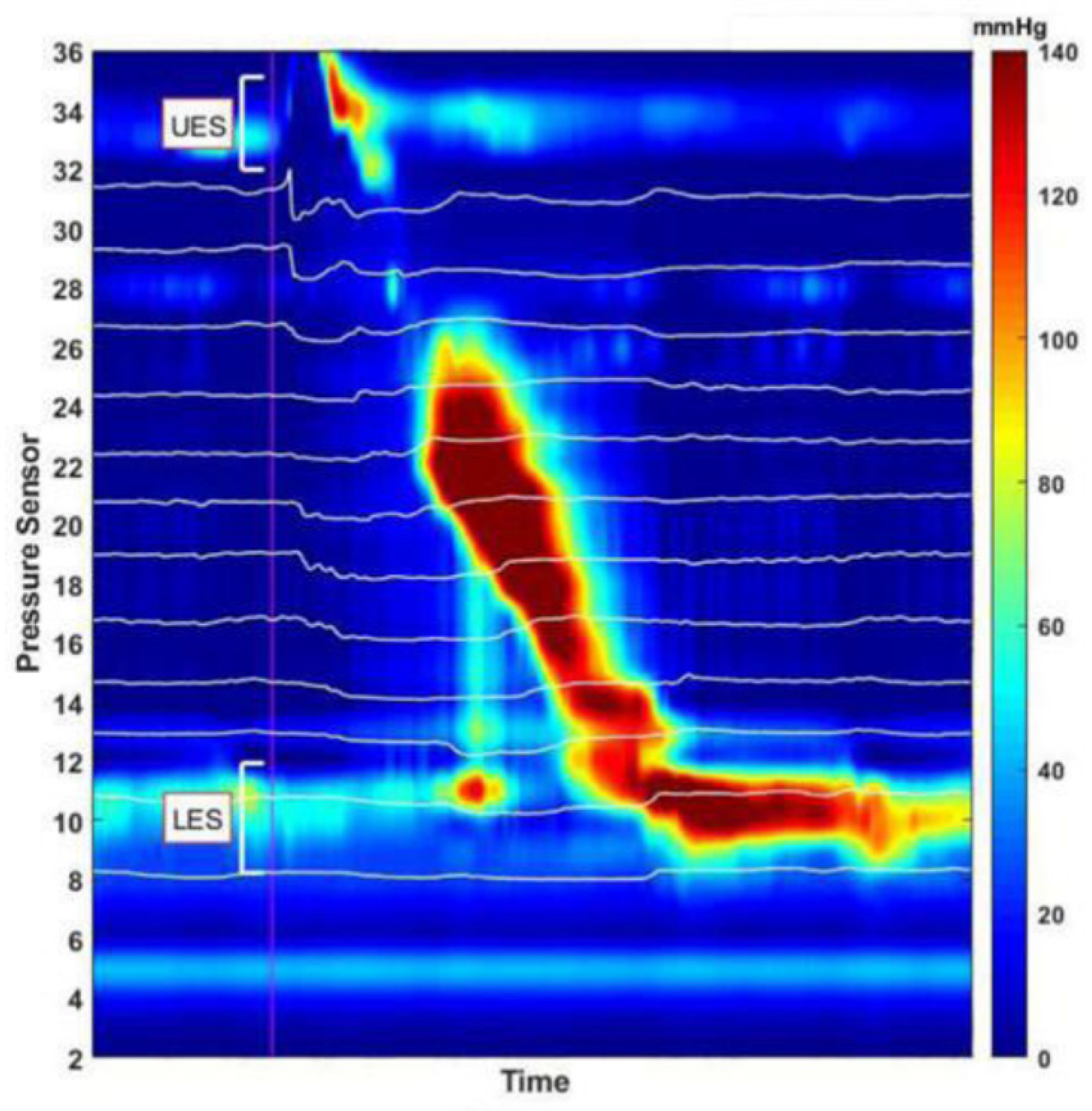
2.3.1. High-Resolution Impedance Manometry
2.3.2. Measurements
- Assessing successful oropharyngeal emptying using hyoid bone displacement measured by submental ultrasonography
- Assessing successful oropharyngeal and esophageal emptying using HRIM data
- (1)
- Bolus transmission through the esophagus:
- (2)
- Successful bolus transmission through the LES into the stomach
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
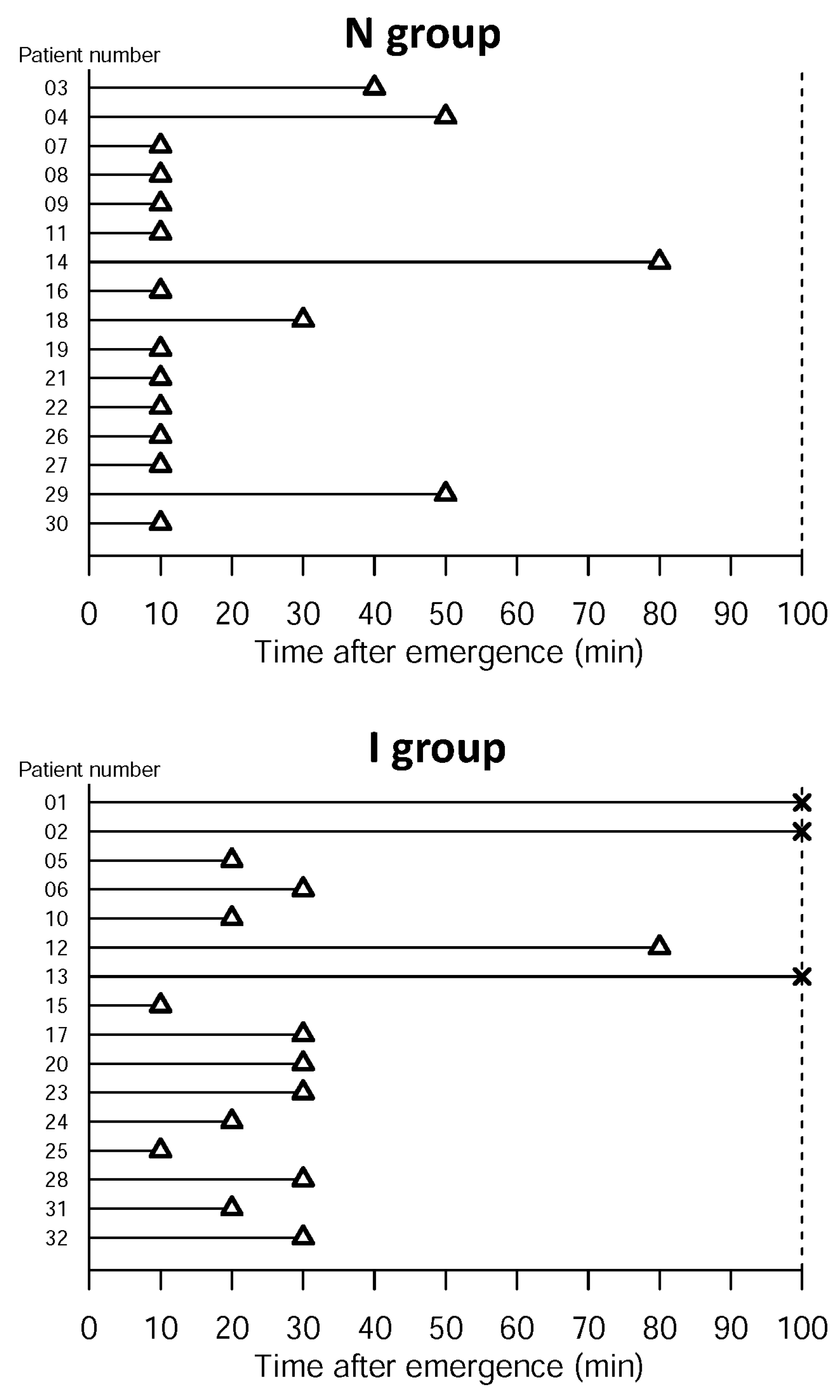
- Successful oropharyngeal emptying assessed via HBD submental ultrasonography after complete emergence
- Success of oropharyngeal emptying and esophageal emptying assessed based on bolus transmission through the esophagus, LES and into the stomach, measured with HRIM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Triadafilopoulos, G.; Hallstone, A.; Nelson-Abbott, H.; Bedinger, K. Oropharyngeal and esophageal interrelationships in patients with nonobstructive dysphagia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.L.; Dantas, R.O. Esophageal contractions and oropharyngeal and esophageal transits in patients with iron deficiency anemia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Palmer, J.B. Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing: Normal and abnormal. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.S.; Ryu, J.H. Aspiration Pneumonia and Related Syndromes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.A.; Harkin, C.P.; Bailey, P.L. Postoperative Tracheal Extubation. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 80, 149–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, A.M.; Davis, J.W.; Cagle, K.M.; Sue, L.P.; Kaups, K.L. Post-extubation dysphagia in trauma patients: it’s hard to swallow. Am. J. Surg. 2013, 206, 924–927; discussion 927–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macht, M.; Wimbish, T.; Bodine, C.; Moss, M. ICU-acquired swallowing disorders. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheel, R.; Pisegna, J.M.; McNally, E.; Noordzij, J.P.; Langmore, S.E. Endoscopic Assessment of Swallowing After Prolonged Intubation in the ICU Setting. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2016, 125, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoretz, S.A.; Flowers, H.L.; Martino, R. The incidence of dysphagia following endotracheal intubation: A systematic review. Chest 2010, 137, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, M.B.; Nollet, J.L.; Spronk, P.E.; González-Fernández, M. Prevalence, Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Modalities and Treatment Options for Dysphagia in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, N.; Hamdy, S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Manifestations and diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, R.J.; Kendall, K.A.; McKenzie, S.; Gonçalves, M.I.; Walker, A. Structural displacements in normal swallowing: A videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia 2000, 15, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, A.L.; VanDaele, D.J.; Otterbacher, M.S. Quantitative assessment of hyoid bone displacement from video images during swallowing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1995, 38, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Hsiao, M.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Fu, C.P.; Wang, T.G. Reliability of Ultrasonography in Evaluating Hyoid Bone Movement. J. Med. Ultrasound 2017, 25, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfino, J.E.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ghosh, S.; Brasseur, J.G.; Kahrilas, P.J. Measuring EGJ opening patterns using high resolution intraluminal impedance. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Imam, H.; Nicodeme, F.; Carlson, D.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Yim, B.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Flow time through esophagogastric junction derived during high-resolution impedance-manometry studies: A novel parameter for assessing esophageal bolus transit. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G158–G163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sifrim, D.; Castell, D.; Dent, J.; Kahrilas, P.J. Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring: Review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 2004, 53, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckxstaens, G.E.; Zaninotto, G.; Richter, J.E. Achalasia. Lancet 2014, 383, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Rhee, P.-L.; Son, H.J.; Song, K.J.; Kim, J.J.; Rhee, J.C. Is all ineffective esophageal motility the same? A clinical and high-frequency intraluminal US study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, C.; Backholer, K.; Gearon, E.; Stevenson, C.; Swinburn, B.; Moodie, M.; Carter, R.; Peeters, A. Prevalence of class-I, class-II and class-III obesity in Australian adults between 1995 and 2011–12. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, T.J.P.; Rasburn, N.J.; Abdelnour-Berchtold, E.; Brunelli, A.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Gonzalez, M.; Ljungqvist, O.; Petersen, R.H.; Popescu, W.M.; Slinger, P.D.; et al. Guidelines for enhanced recovery after lung surgery: Recommendations of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS). Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.E.; Winkelman, C.J.; Huckabee, M.L. Variability in Ultrasound Measurement of Hyoid Bone Displacement and Submental Muscle Size Using 2 Methods of Data Acquisition. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2016, 68, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, M.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, W.S.; Chang, H.Y.; Wang, T.G. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, P.J.; Newell, S.; Strickland, P.A.; Barry, J.J. Response of bispectral index to neuromuscular block in awake volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, i95–i103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.J.; Yeh, K.C.; Wang, M.L.; Tai, W.H.; Cheng, Y.J. Heated humidified high-flow nasal oxygen prevents intraoperative body temperature decrease in non-intubated thoracoscopy. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Hung, M.H.; Chen, J.S.; Hsu, H.H.; Cheng, Y.J. Nasal high-flow oxygen therapy improves arterial oxygenation during one-lung ventilation in non-intubated thoracoscopic surgery. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.H.; Hsu, H.H.; Chan, K.C.; Chen, K.C.; Yie, J.C.; Cheng, Y.J.; Chen, J.S. Non-intubated thoracoscopic surgery using internal intercostal nerve block, vagal block and targeted sedation. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2014, 46, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.-J.; Liu, C.-M.; Wu, C.-Y.; Tsai, F.-F.; Tseng, P.-H.; Fan, S.-Z. I-Gel is a suitable alternative to endotracheal tubes in the laparoscopic pneumoperitoneum and trendelenburg position. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussières, J.S.; Somma, J.; Del Castillo, J.L.; Lemieux, J.; Conti, M.; Ugalde, P.A.; Gagné, N.; Lacasse, Y. Bronchial blocker versus left double-lumen endotracheal tube in video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A randomized-controlled trial examining time and quality of lung deflation. Can. J. Anaesth. 2016, 63, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; Eriksson, L.I.; Miller, R.D. Reversal (antagonism) of neuromuscular blockade. In Miller’s Anesthesia, 9th ed.; Gropper, M., Eriksson, L., Fleisher, L., Wiener-Kronish, J., Cohen, N., Leslie, K., Eds.; Elsevier Health Science: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 853–854. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Fukano, N.; Kitajima, O.; Saeki, S.; Ogawa, S. Normalization of acceleromyographic train-of-four ratio by baseline value for detecting residual neuromuscular block. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 96, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, J.W. Update on Bispectral Index monitoring. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2006, 20, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutuian, R.; Vela, M.F.; Shay, S.S.; Castell, D.O. Multichannel intraluminal impedance in esophageal function testing and gastroesophageal reflux monitoring. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 37, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.J.; Cheng, Y.J. Postoperative Recovery of Esophageal Function Measured by High Resolution Impedance Manometry. Jpn. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, D.A.; Omari, T.; Lin, Z.; Rommel, N.; Starkey, K.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Tack, J.; Pandolfino, J.E. High-resolution impedance manometry parameters enhance the esophageal motility evaluation in non-obstructive dysphagia patients without a major Chicago Classification motility disorder. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, W.T.; Hung, M.H.; Wang, M.L.; Cheng, Y.J.; Hsu, H.H.; Chen, J.S. Nonintubated Thoracoscopic Surgery for Lung Tumor: Seven Years’ Experience With 1025 Patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, L.; Wiechmann, R.J.; Magovern, J.A.; Szydlowski, G.W.; Mack, M.J.; Naunheim, K.S.; Landreneau, R.J. Early chest tube removal after video-assisted thoracoscopic wedge resection of the lung. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 66, 1751–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Hsieh, S.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, T.G. Ultrasonographic evaluation of hyoid-larynx approximation in dysphagic stroke patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, M.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Fu, C.-P.; Wang, T.-G. Effects of Bolus Consistency and Volume on Hyoid Bone Displacement during Swallowing. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassameehiran, S.; Klomjit, S.; Mankongpaisarnrung, C.; Rakvit, A. Postextubation Dysphagia. Proceedings (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2015, 28, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.H.; Sohn, H.M.; Choi, E.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Oh, A.Y.; Jeon, Y.T.; Ryu, J.H. The Effect of Adjustment of Endotracheal Tube Cuff Pressure during Scarless Remote Access Endoscopic and Robotic Thyroidectomy on Laryngo-Pharyngeal Complications: Prospective Randomized and Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorelli, A.; Vicidomini, G.; Milione, R.; Grassi, R.; Rotondo, A.; Santini, M. The effects of lung resection on physiological motor activity of the oesophagus. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2013, 44, 250–256; discussion 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lipowska, A.M.; Nicodème, F.; Teitelbaum, E.N.; Hungness, E.S.; Johnston, E.R.; Gawron, A.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Assessing bolus retention in achalasia using high-resolution manometry with impedance: A comparator study with timed barium esophagram. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinucci, I.; de Bortoli, N.; Giacchino, M.; Bodini, G.; Marabotto, E.; Marchi, S.; Savarino, V.; Savarino, E. Esophageal motility abnormalities in gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tibbling, L.; Gezelius, P.; Franzén, T. Factors influencing lower esophageal sphincter relaxation after deglutition. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2844–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Fox, M.; Gyawali, C.P.; Roman, S.; Smout, A.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cohen, S. Disorders of the lower esophageal sphincter. Annu. Rev. Med. 1975, 26, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, F.; Pompeo, E.; Gonzalez-Rivas, D.; Chen, H.; Yin, W.; Shao, W.; Li, S.; Pan, H.; Shen, J.; et al. The impact of non-intubated versus intubated anaesthesia on early outcomes of video-assisted thoracoscopic anatomical resection in non-small-cell lung cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaud, B.; Debaene, B.; Donati, F.; Marty, J. Residual paralysis after emergence from anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2010, 112, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, W.T.; Sprung, J.; Jankowski, C.J. Sugammadex: A novel agent for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Meyer, M.J.; Malviya, S.A.; Stanislaus, A.B.; MacDonald, T.; Doran, M.E.; Igumenshcheva, A.; Hoang, A.H.; Eikermann, M. Effects of Neostigmine Reversal of Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agents on Postoperative Respiratory Outcomes: A Prospective Study. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Koh, J.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Hong, J.H.; Nam, H.J.; Bai, S.J. Influence of reversal of neuromuscular blockade with sugammadex or neostigmine on postoperative quality of recovery following a single bolus dose of rocuronium: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded, controlled study. J. Clin. Anesth. 2019, 57, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.D.; Richter, J.E.; Anderson, K.O.; Bradley, L.A.; Katz, P.O.; McElveen, L.; Obrecht, W.F.; Dalton, C.; Snyder, R.M. The effects of psychological and environmental stressors on peristaltic esophageal contractions in healthy volunteers. Psychophysiology 1987, 24, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | N Group (n = 16) | I Group (n = 16) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 11(68.75) | 10 (67.50) | 0.71 |
| Age, y | 56.00 (4.71) | 56.38 (6.13) | 0.85 |
| Body weight, kg | 57.09 (8.30) | 62.24 (10.81) | 0.14 |
| Body height, cm | 161.17 (8.20) | 161.63 (9.64) | 0.89 |
| ASA I/II/III, n | 7/9/0 | 3/12/1 | 0.25 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n | 2/14 | 2/14 | 1 |
| Pulmonary function test, % of prediction | |||
| FVC | 111.99 (13.95) | 107.62 (16.43) | 0.42 |
| FEV1 | 108.75 (16.79) | 106.82 (16.50) | 0.75 |
| Comorbidity, n | |||
| COPD | 0 | 0 | |
| Asthma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cardiac disease | 0 | 0 | |
| Hypertension | 1 | 2 | 0.6 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Surgical Method | N Group (n = 16) | I Group (n = 16) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wedge resection, n (%) | 9 (76.62) | 9 (70.35) | 1 |
| Segmentectomy, n (%) | 2 (5.95) | 2 (6.98) | 1 |
| Lobectomy, n (%) | 5 (19.05) | 5 (19.19) | 1 |
| Operation time, min | 70.50 (60.00–95.50) | 72.00 (49.50–134.50) | 0.85 |
| Anesthetic time, min | 106.00 (86.00–145.00) | 120.00 (77.00–164.00) | 0.95 |
| Blood loss | 0.6 | ||
| <50 c.c., n (%) | 14 (87.50) | 13 (81.25) | |
| 50 to 150 c.c., n (%) | 1 (6.25) | 3 (18.75) | |
| >150 c.c., n (%) | 1 (6.25) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Blood transfusion | 0 | 0 | |
| Intraoperative SpO2 < 90 | 0 | 0 | |
| Postoperative time to oral intake, hours | 4.11 (3.25–4.95) | 3.35 (2.95–7.29) | 0.49 |
| Hospital stay, day | 4 (4–6.5) | 4.5 (4–5.5) | 0.95 |
| Tumor size, mm | 10.50 (7.50–17.50) | 12.50(5.50–21.50) | 0.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-J.; Chen, J.-S.; Ho, S.-I.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Huang, Y.-J.; Cheng, Y.-J. Detecting Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Emptying by Submental Ultrasonography and High-Resolution Impedance Manometry: Intubated vs. Non-Intubated Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121079
Lai C-J, Chen J-S, Ho S-I, Lu Z-Y, Huang Y-J, Cheng Y-J. Detecting Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Emptying by Submental Ultrasonography and High-Resolution Impedance Manometry: Intubated vs. Non-Intubated Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121079
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chih-Jun, Jin-Shing Chen, Shih-I Ho, Zhi-Yin Lu, Yi-Ju Huang, and Ya-Jung Cheng. 2020. "Detecting Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Emptying by Submental Ultrasonography and High-Resolution Impedance Manometry: Intubated vs. Non-Intubated Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121079
APA StyleLai, C.-J., Chen, J.-S., Ho, S.-I., Lu, Z.-Y., Huang, Y.-J., & Cheng, Y.-J. (2020). Detecting Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Emptying by Submental Ultrasonography and High-Resolution Impedance Manometry: Intubated vs. Non-Intubated Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121079




