Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of an Acellular Product
Abstract
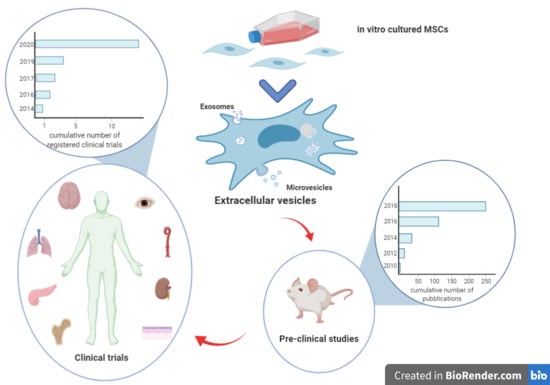
:1. Introduction
2. EV Applications in Prevention or Treatment of Acute and Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease
3. EV Applications in Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
4. EV Applications in Lung Injury
5. EV Applications in Skin Wound Repair
6. MSC-EV Possible New Tools in Advanced Clinical Approaches
6.1. Organ Pretreatment before Transplant
6.2. Engineered MSC-EVs
7. Clinical Trials
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aGVHD | acute GVHD |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| ALI | acute lung injury |
| APCs | antigen presenting cells |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| AT | Adipose Tissue |
| AT-MSCs | Adipose tissue-MSCs |
| BAFF | B-Cell Activating Factor |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| BM-MSCs | Bone marrow-MSCs |
| BPD | bronchopulmonary dysplasia |
| cGVHD | chronic GVHD |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| DCD | donation after circulatory death |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| Exos | exosomes |
| GVHD | Graft versus host disease |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase |
| IR | ischemia-reperfusion |
| miRNAs | micro-RNAs |
| m/lEVs | medium/large sized enriched in microvesicles |
| MSC-EVs | MSC-derived extracellular vesicles |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal cell |
| MVs | microvesicles |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| SCID | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
| sEVs | small EVs |
| Treg | regulatory T cells |
| UC-MSC-EVs | umbilical cord-MSCs derived EVs |
| UC-MSCs | umbilical cord-MSCs |
| VILI | ventilator-induced lung injury |
References
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Extracell Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kao, C.Y.; Papoutsakis, E.T. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microparticles, their parts, and their targets to enable their biomanufacturing and clinical applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Girolamo, L.; Lucarelli, E.; Alessandri, G.; Avanzini, M.A.; Bernardo, M.E.; Biagi, E.; Brini, A.T.; D’Amico, G.; Fagioli, F.; Ferrero, I.; et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new “cells as drugs” paradigm. Efficacy and critical aspects in cell therapy. Curr. Pharm Des. 2013, 19, 2459–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, S.; Shi, Y.; Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M.; Leblanc, K.; Martin, I.; Nolta, J.; Phinney, D.G.; Sensebe, L. Mesenchymal stem versus stromal cells: International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT®) Mesenchymal Stromal Cell committee position statement on nomenclature. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Rasmusson, I.; Sundberg, B.; Götherström, C.; Hassan, M.; Uzunel, M.; Ringdén, O. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 2004, 363, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Götherström, C.; Ringdén, O.; Hassan, M.; McMahon, R.; Horwitz, E.; Anneren, G.; Axelsson, O.; Nunn, J.; Ewald, U. Fetal mesenchymal stem-cell engraftment in bone after in utero transplantation in a patient with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; Bernardo, M.E.; Sgarella, A.; Maccario, R.; Avanzini, M.A.; Ubezio, C.; Minelli, A.; Alvisi, C.; Vanoli, A.; Calliada, F.; et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in the treatment of fistulising Crohn’s disease. Gut 2011, 60, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassberg, M.K.; Minkiewicz, J.; Toonkel, R.L.; Simonet, E.S.; Rubio, G.A.; DiFede, D.; Shafazand, S.; Khan, A.; Pujol, M.V.; LaRussa, V.F.; et al. Allogeneic Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Intravenous Delivery (AETHER): A Phase I Safety Clinical Trial. Chest 2017, 151, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.O.; Allez, M.; Clark, M.; Labopin, M.; Ricart, E.; Rogler, G.; Rovira, M.; Satsangi, J.; Farge, D.; Hawkey, C.J. ASTIC Trial Group. European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Autoimmune Disease Working Party. European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation Autologous stem-cell transplantation in treatment-refractory Crohn’s disease: An analysis of pooled data from the ASTIC trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meier, R.P.; Müller, Y.D.; More, P.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Bühler, L.H. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of liver diseases, is there enough evidence? Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 1348–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, M.E.; Ball, L.M.; Cometa, A.M.; Roelofs, H.; Zecca, M.; Avanzini, M.A.; Bertaina, A.; Vinti, L.; Lankester, A.; Maccario, R.; et al. Co-infusion of ex vivo-expanded, parental MSCs prevents life-threatening acute GVHD, but does not reduce the risk of graft failure in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic umbilical cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 46, 200–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gnecchi, M.; Danieli, P.; Malpassa, G.; Ciuffreda, M.C. Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1416, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.A.; Naik, C.; Cahill, P.A.; Bhonde, R.R. Placental mesenchymal stromal cells as an alternative tool for therapeutic angiogenesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyan, A.E.; Albini, T.A.; Townsend, J.H.; Rodriguez, M.; Pandya, H.K.; Leonard, R.E.; Parrott, M.B.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Flynn, H.W.; Goldberg, J.L. Vision Loss after Intravitreal Injection of Autologous “Stem Cells” for AMD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: a friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Dennis, J.E.; Muzic, R.F.; Lundberg, M.; Caplan, A.I. The dynamic in vivo distribution of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after infusion. Cells Tissues Organs 2001, 169, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgovan, T.; Crawford, L.; Nwizu, C.; Quesenberry, P. Stem cells and extracellular vesicles: biological regulators of physiology and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 317, C155–C166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, G. Stem cell therapy without the cells. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2013, 6, e26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, R.; Stroemer, P.; Hicks, C.; Stevanato, L.; Patel, S.; Corteling, R.; Miljan, E.; Vishnubhatla, I.; Sinden, J.; Madeddu, P. Clinical-grade human neural stem cells promote reparative neovascularization in mouse models of hindlimb ischemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardo, M.E.; Fibbe, W.E. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dokic, J.M.; Tomić, S.Z.; Čolić, M.J. Cross-Talk between Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Dendritic Cells. Curr. Stem. Cell. Res. Ther. 2016, 11, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.I. Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.D.; de Castro, L.L.; Braga, C.L.; Oliveira, G.P.; Trivelin, S.A.; Barbosa-Junior, C.M.; Morales, M.M.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Weiss, D.J.; Lopes-Pacheco, M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are More Effective Than Their Extracellular Vesicles at Reducing Lung Injury Regardless of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Etiology. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 8262849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Taghavi-Farahabadi, M.; Rezaei, N.; Hashemi, S.M. Comparison of the effects of adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes with conditioned media on neutrophil function and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Treatment of Eye Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1089, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, L.A.; Dutreil, M.; Fattman, C.; Pandey, A.C.; Torres, G.; Go, K.; Phinney, D.G. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11002–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouveia de Andrade, A.V.; Bertolino, G.; Riewaldt, J.; Bieback, K.; Karbanovà, J.; Odendahl, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Schmitz, M.; Corbeil, D.; Tonn, T. Extracellular vesicles secreted by bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells fail to suppress lymphocyte proliferation. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 1374–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, A.; Scarsella, M.; Starc, N.; Giorda, E.; Biagini, S.; Proia, A.; Carsetti, R.; Locatelli, F.; Bernardo, M.E. Microvescicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells are not as effective as their cellular counterpart in the ability to modulate immune responses in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kordelas, L.; Schwich, E.; Dittrich, R.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Börger, V.; Giebel, B.; Rebmann, V. Individual Immune-Modulatory Capabilities of MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Preparations and Recipient-Dependent Responsiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabrowska, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Neuroinflammation as a target for treatment of stroke using mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghimire, S.; Weber, D.; Mavin, E.; Wang, X.N.; Dickinson, A.M.; Holler, E. Pathophysiology of GvHD and Other HSCT-Related Major Complications. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Börger, V.; Bremer, M.; Ferrer-Tur, R.; Gockeln, L.; Stambouli, O.; Becic, A.; Giebel, B. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Potential as Novel Immunomodulatory Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.-K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, F.; Deng, A.; Zhao, S.; Luo, L.; Wei, H.; Guan, L.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Life-Threatening Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1874–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Miura, Y.; Fujishiro, A.; Shindo, T.; Shimazu, Y.; Hirai, H.; Tahara, H.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Ichinohe, T.; Maekawa, T. Graft-Versus-Host Disease Amelioration by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with Peripheral Preservation of Naive T Cell Populations. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Yeo, R.W.Y.; Lai, R.C.; Sim, E.W.K.; Chin, K.C.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosome-enhanced regulatory T-cell production through an antigen-presenting cell-mediated pathway. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Huang, T.; Geng, S.; Luo, C.; et al. A potent immunomodulatory role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells in preventing cGVHD. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Lai, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Chen, X.; Geng, S.; Huang, X.; Luo, C.; Wu, S.; Ling, W.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells prevent skin fibrosis in the cGVHD mouse model by suppressing the activation of macrophages and B cells immune response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzoli, S.; Simonini, M.; Manunta, P. Predicting acute kidney injury: current status and future challenges. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rewa, O.; Bagshaw, S.M. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Tritta, S.; Tapparo, M.; Cedrino, M.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G.; Brizzi, M.F. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit and revert fibrosis progression in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaishi, K.; Mizue, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Otani, M.; Nakano, M.; Konari, N.; Fujimiya, M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Wu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Yin, D.; Du, T.; Ju, G.; Miao, S.; Liu, G.; Lu, M.; Zhu, Y. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, D.; Zou, X.; Ju, G.; Zhang, G.; Bao, E.; Zhu, Y. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorate Acute Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibition of Mitochondrial Fission through miR-30. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2093940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.Y.; Moon, S.J.; Ratliff, B.B.; Ahn, S.H.; Jung, A.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.; Lim, B.J.; Kim, B.S.; Plotkin, M.D.; et al. Microparticles from kidney-derived mesenchymal stem cells act as carriers of proangiogenic signals and contribute to recovery from acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranghino, A.; Bruno, S.; Bussolati, B.; Moggio, A.; Dimuccio, V.; Tapparo, M.; Biancone, L.; Gontero, P.; Frea, B.; Camussi, G. The effects of glomerular and tubular renal progenitors and derived extracellular vesicles on recovery from acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Brubo, S.; Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Human liver stem cells and derived extracellular vesicles improve recovery in a murine model of acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kholia, S.; Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Cedrino, M.; Papadimitriou, E.; Tapparo, N.; Deregibus, M.C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent Aristolochic Acid-Induced Kidney Fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.-Z.; Liu, Y.-M.; Niu, X.; Yin, J.Y.; Hu, B.; Guo, S.-C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.-S. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Calogero, R.A.; Saviozzi, S.; Collino, F.; Morando, L.; Busca, A.; Falda, M.; Bussolati, B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindoso, R.S.; Collino, F.; Bruno, S.; Araujo, D.S.; Sant’Anna, J.F.; Tetta, C.; Provero, P.; Quesenberry, P.J.; Vieyra, A.; Einicker-Lamas, M.; et al. Extracellular vesicles released from mesenchymal stromal cells modulate miRNA in renal tubular cells and inhibit ATP depletion injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eirin, A.; Zhu, X.Y.; Puranik, A.S.; Tang, H.; McGurren, K.A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate kidney inflammation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Miao, S.; Liu, G.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Protect Against Acute Kidney Injury Through Anti-Oxidation by Enhancing Nrf2/ARE Activation in Rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016, 41, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Sterpone, L.; Aghemo, G.; Viltono, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Kitamura, S.; Wada, J. Secretomes from Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Acute Kidney Injury: Possible Heterogeneity. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 8693137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avecillas, J.F.; Freire, A.X.; Arroliga, A.C. Clinical epidemiology of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: incidence, diagnosis, and outcomes. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.; Agarwal, S.; Clauss, M.; Britt, N.S.; Dhillon, N.K. Extracellular vesicles: novel communicators in lung diseases. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; Naito, Y.; Sugita, S.; Lee, J.W. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived secretome and vesicles for lung injury and disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Feng, X.M.; Abbott, J.; Fang, X.H.; Hao, Q.; Monsel, A.; Qu, J.M.; Matthay, M.A.; Lee, J.W. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monsel, A.; Zhu, Y.G.; Gennai, S.; Hao, Q.; Hu, S.; Rouby, J.J.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Matthay, M.A.; Lee, J.W. Therapeutic Effects of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Microvesicles in Severe Pneumonia in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 324–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsel, A.; Zhu, Y.G.; Gudapati, V.; Lim, H.; Lee, J.W. Mesenchymal stem cell derived secretome and extracellular vesicles for acute lung injury and other inflammatory lung diseases. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatri, M.; Richardson, L.A.; Meulia, T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate influenza virus-induced acute lung injury in a pig model. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worthington, E.N.; Hagood, J.S. Therapeutic Use of Extracellular Vesicles for Acute and Chronic Lung Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willis, G.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Reis, M.; Yeung, V.; Liu, X.; Ericsson, M.; Andrews, N.A.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived small extracellular vesicles restore lung architecture and improve exercise capacity in a model of neonatal hyperoxia-induced lung injury. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1790874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.F.; Borg, Z.D.; Goodwin, M.; Sokocevic, D.; Wagner, D.E.; Coffey, A.; Antunes, M.; Robinson, K.L.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S.; et al. Systemic Administration of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorates Aspergillus Hyphal Extract-Induced Allergic Airway Inflammation in Immunocompetent Mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, D.; Wen, X.; Tang, X.; Qi, D.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhu, T. Adipose-derived exosomes protect the pulmonary endothelial barrier in ventilator-induced lung injury by inhibiting the TRPV4/Ca2+ signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L723–L741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, V.; Sengupta, S.; Lazo, A.; Woods, P.; Nolan, A.; Bremer, N. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008, 15, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Grose, R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 835–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Díaz, A.; Quesada-Gómez, J.M.; Dorado, G. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Skin Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Chai, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Yin, H. Exosome Derived From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Mediates MiR-181c Attenuating Burn-induced Excessive Inflammation. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, A.D.F.; Cunha, P.D.S.; Carregal, V.M.; da Silva, P.C.; de Miranda, M.C.; Kunrath-Lima, M.; de Melo, M.I.A.; Faraco, C.C.F.; Barbosa, J.L.; Frezard, F.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Accelerate Migration and Activate AKT Pathway in Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Independently of miR-205 Activity. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 9841035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.W.; Seo, M.K.; Woo, E.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, S. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote proliferation and migration of skin fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 10, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelizzo, G.; Avanzini, M.A.; Icaro Cornaglia, A.; De Silvestri, A.; Mantelli, M.; Travaglino, P.; Croce, S.; Romano, P.; Avolio, L.; Iacob, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal cells: perspective treatment for cutaneous wound healing in pediatrics. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, E.; Di Silvestre, D.; Mastracci, L.; Grillo, F.; Grisoli, P.; Marrubini, G.; Nardini, M.; Mastrogiacomo, M.; Sorlini, M.; Rossi, R.; et al. GMP-compliant sponge-like dressing containing MSC lyo-secretome: Proteomic network of healing in a murine wound model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 155, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Xi, Z.; Chen, G.; Liu, K.; Ma, R.; Zhou, C. Extracellular vesicle-carried microRNA-27b derived from mesenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11254–11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Rega, F.; Devos, T.; Pirenne, J. Machine perfusion in organ transplantation: A tool for ex-vivo graft conditioning with mesenchymal stem cells? Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2013, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Fernández-Rivera, C.; Villaverde, P.; Oliver, J.; Cillero, S.; Lorenzo, D.; Valdés, F. Renal transplantation from non-heart-beating donors: a single-center 10-year experience. Transplant Proc. 2005, 37, 3658–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypel, M.; Keshavjee, S. Extracorporeal lung perfusion (ex-vivo lung perfusion). Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2016, 21, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, M.; Corradetti, V.; Pattonieri, E.F.; Rocca, C.; Milanesi, S.; Peloso, A.; Canevari, S.; De Cecco, L.; Dugo, M.; Avanzini, M.A.; et al. Perfusion of isolated rat kidney with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/Extracellular Vesicles prevents ischaemic injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3381–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.L.; Zhao, Y.; Robert Smith, J.; Weiss, M.L.; Kron, I.L.; Laubach, V.E.; Sharma, A.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and enhance. reconditioning of donor lungs after circulatory death. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, B.; Chlapanidas, T.; Perteghella, S.; Lucarelli, E.; Pascucci, L.; Brini, A.T.; Ferrero, I.; Marazzi, M.; Pessina, A.; Torre, M.L. Italian Mesenchymal Stem Cell Group (GISM). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell extracellular vesicles: From active principle to next generation drug delivery system. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, O.G.; Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Murphy, D.E.; Jiang, L.; Evers, M.W.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles: From Imagination to Innovation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.R.; Teixeira, G.Q.; Santos, S.G.; Barbosa, M.A.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Gonçalves, R.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome: Influencing Therapeutic Potential by Cellular Pre-conditioning. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, T.N.; Jeyaram, A.; Patel, D.B.; Parajuiku, B.; Livingston, N.K.; Arumugasaamy, N.; Schardt, J.S.; Jay, S.M. Oncogene Knockdown via Active Loading of Small RNAs into Extracellular Vesicles by Sonication. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, G.; Herrmann, I.K.; Stevens, M.M. Cell-derived vesicles for drug therapy and diagnostics: opportunities and challenges. Nano Today 2015, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, M.E.; Leonard, J.N. Stabilization of exosome-targeting peptides via engineered glycosylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8166–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Aleza, C.G.; Roffler, S.R.; van Solinge, W.W.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R. Display of GPI-anchored anti-EGFR nanobodies on extracellular vesicles promotes tumour cell targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L. Delivery of nanomedicines to extracellular and intracellular compartments of a solid tumor. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.K.; Stylianopoulos, T. Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irimie, A.I.; Sonea, L.; Jurj, A.; Mehterov, N.; Zimta, A.A.; Budisan, L.; Braicu, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Future trends and emerging issues for nanodelivery systems in oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4593–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascucci, L.; Coccè, V.; Bonomi, A.; Ami, D.; Ceccarelli, P.; Ciusani, E.; Viganò, L.; Locatelli, A.; Sisto, F.; Doglia, S.M.; et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: A new approach for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Bojar, D.; Rizzi, G.; Charpin-El Hamri, G.; El-Baba, M.D.; Saxena, P.; Ausländer, S.; Tan, K.R.; Fussenegger, M. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, S.C.; Kim, O.Y.; Yoon, C.M.; Choi, D.S.; Roh, T.Y.; Park, J.; Nilsson, J.; Lötvall, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S. Bioinspired exosome-mimetic nanovesicles for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics to malignant tumors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7698–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börger, V.; Weiss, D.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Borràs, F.E.; Bussolati, B.; Carter, D.R.F.; Dominici, M.; Fàlcon-Pèrez, J.M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; et al. International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy statement on extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells and other cells: considerations for potential therapeutic agents to suppress coronavirus disease-19. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Szabò, T.G.; Pàsztoi, M.; Pàl, Z.; Misjàk, P.; Aradi, B.; Làszlò, V.; Pàllinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiner, A.T.; Witwer, K.W.; van Balkom, B.W.M.; de Beer, J.; Brodie, C.; Corteling, R.L.; Gabrielsson, S.; Gimona, M.; Ibrahim, A.G.; de Kleijn, D.; et al. Concise Review: Developing Best-Practice Models for the Therapeutic Use of Extracellular Vesicles. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lener, T.; Gimona, M.; Aigner, L.; Börger, V.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Chaput, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Court, F.A.; del Portillo, H.A.; et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials-an ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Clinical Trial Number | MSC Origin | Title | Year of Registration |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02138331 | Cord blood | Effect of Microvesicles and Exosomes Therapy on β-cell Mass in Type I Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) | 2014 |
| Not found | Umbilical cord | Chronic kidney injury | 2016 |
| NCT03437759 | Human umbilical cord | MSC-Exos Promote Healing of Macular holes MHs | 2017 |
| NCT03857841 | Bone marrow | A Safety Study of IV Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles (UNEX-42) in Preterm Neonates at High Risk for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 2019 |
| NCT04173650 | Bone marrow | MSC EVs in Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa | 2020 |
| NCT04223622 | Adipose tissue | Effects of ASC Secretome on Human Osteochondral Explants (ASC-OA) | 2020 |
| NCT04313647 | Bone marrow | A Tolerance Clinical Study on Aerosol Inhalation of MSC-EXO in Healthy Volunteers | 2020 |
| NCT04276987 | Adipose Tissue | A Pilot Clinical Study on Inhalation of MSC-EXO Treating Severe Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia | 2020 |
| NCT04491240 | Adipose Tissue | Evaluation of Safety and Efficiency of Method of Exosome Inhalation in SARS-CoV-2 Associated PneumoniaSARS-Cov2 pneumonia | 2020 |
| NCT04213248 | Human umbilical cord | Effect of UMSCs Derived Exosomes on Dry Eye in Patients With cGVHD | 2020 |
| NCT04270006 | Adipose tissue | Evaluation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells Exo in Treatment of Periodontitis | 2020 |
| NCT04134676 | Wharton’s jelly | Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cell Conditioned Medium on Chronic Ulcer Wounds | 2020 |
| NCT04356300 | Bone marrow | MSC-EXO for Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome After Surgical Repair of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection | 2020 |
| NCT04544215 | Adipose tissue | A Clinical Study of MSC-EXO Nebulizer for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection | 2020 |
| NCT04388982 | Adipose tissue | Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of Allogenic Adipose MSC-Exos in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease | 2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massa, M.; Croce, S.; Campanelli, R.; Abbà, C.; Lenta, E.; Valsecchi, C.; Avanzini, M.A. Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of an Acellular Product. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10120999
Massa M, Croce S, Campanelli R, Abbà C, Lenta E, Valsecchi C, Avanzini MA. Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of an Acellular Product. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10120999
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassa, Margherita, Stefania Croce, Rita Campanelli, Carlotta Abbà, Elisa Lenta, Chiara Valsecchi, and Maria Antonietta Avanzini. 2020. "Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of an Acellular Product" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10120999
APA StyleMassa, M., Croce, S., Campanelli, R., Abbà, C., Lenta, E., Valsecchi, C., & Avanzini, M. A. (2020). Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of an Acellular Product. Diagnostics, 10(12), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10120999