Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Autoimmune Diseases: How to Recognize Them?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Signs
2.1. Arthritis, Arthralgia, and Morning Stiffness
2.2. Sicca Syndrome and Glandular Swelling
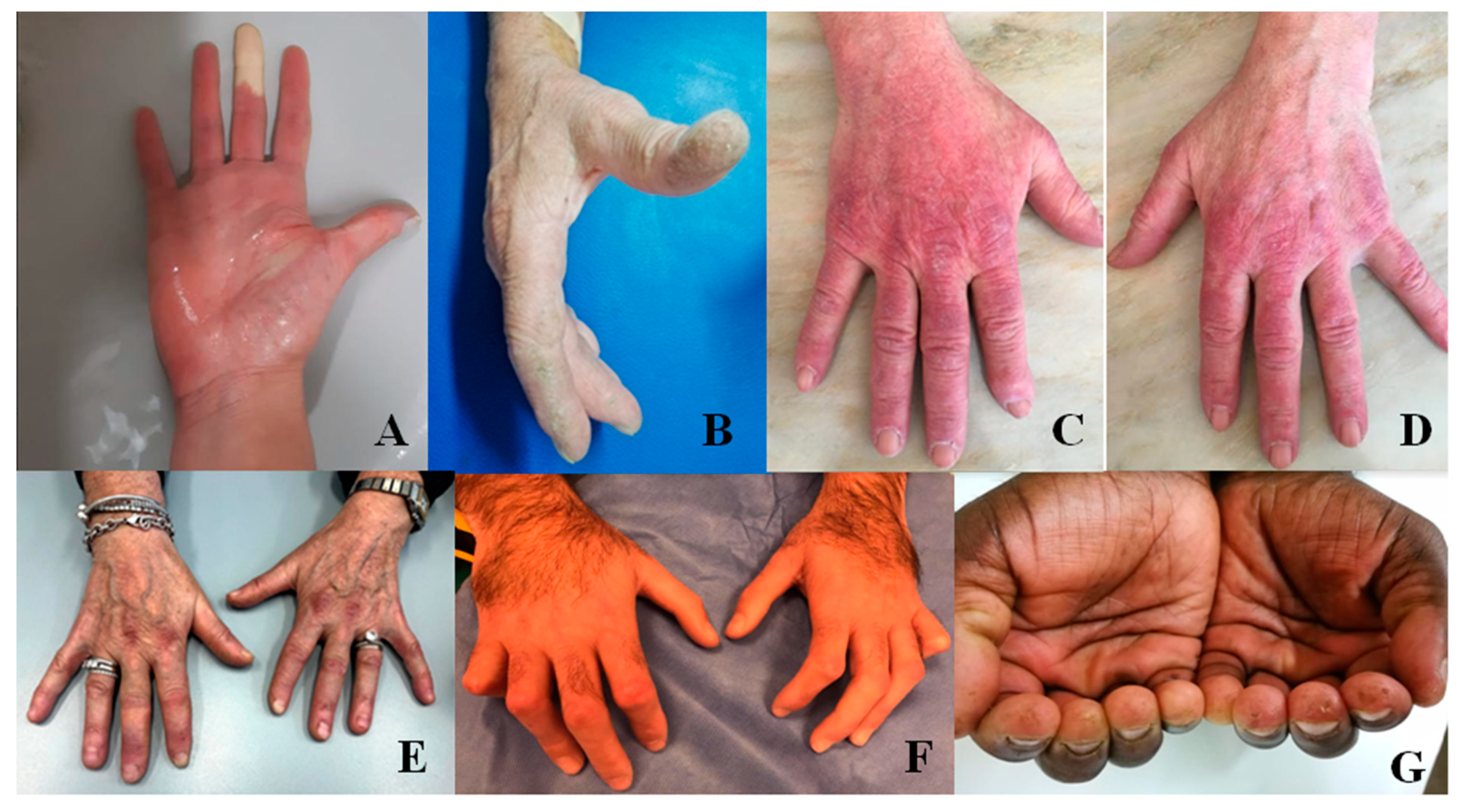
2.3. Raynaud’s Phenomenon, Digital Ulcers, and Pitting Scars
2.4. Puffy Hands and Skin Sclerosis
2.5. Gottron’s Papules and Gottron’s Sign
2.6. Mechanic’s Hands and Hiker’s Feet
2.7. Heliotrope Rash
2.8. Shawl Sign, V-Sign, and Holster Sign
2.9. Telangiectasias
2.10. Calcinosis
2.11. Muscle Weakness
2.12. Dysphagia
2.13. Fever of Unknown Origin
3. Laboratory Exams
4. General Laboratory Exams
5. Autoantibodies
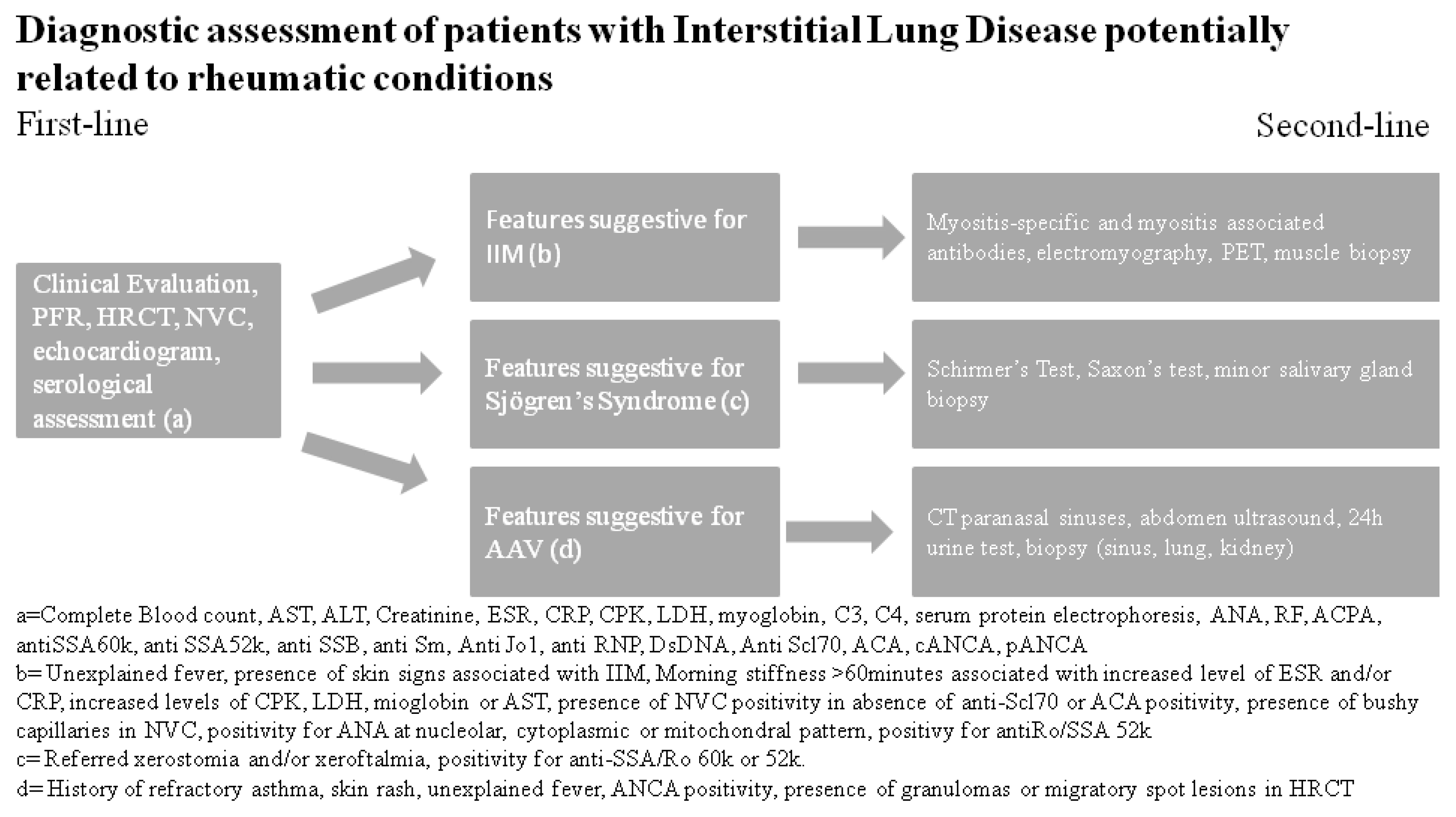
6. First-Line Autoimmunity Exams
7. Second-Line Autoimmunity Exams
8. Instrumental Evaluation
9. First-Line Instrumental Exams
10. Second-Line Instrumental Exams
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Alanine Aminotransferase | ALT |
| ANCA-Associated Vasculitis | AAV |
| Anti-3-hydroxy-3methyl-glutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase | Anti-HMGCR |
| Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody | ACPA |
| Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasm Antibody | ANCA |
| Anti-Small ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme | Anti SAE |
| Anti-Topoisomerase I | Scl70 |
| Anticentromere Antibody | ACA |
| Anti-Mitochondrial Antibody | AMA |
| Antinuclear Antibody | ANA |
| Antiphospholipid Syndrome | APS |
| Antiphospholipid Antibody | APLA |
| Antisynthetase Antibody | ATSA |
| Antisynthetase Syndrome | ASS |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase | AST |
| Autoimmune Disorders | ADs |
| Avascular Areas | AAs |
| CENtromere Protein B | CENP-B |
| Clinically Suspect Arthralgia | CSA |
| Connective Tissue Diseases | CTDs |
| C-Reactive Protein | CRP |
| Creatinine Phosphokinase | CPK |
| Dermatomyositis | DM |
| Diffusion Lung Capacity for Carbon Monoxide | DLCO |
| Digital Pitting Scars | DPSs |
| Digital Ulcer | DU |
| Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs | DMARDs |
| Double-Stranded DNA | DsDNA |
| Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis | EGPA |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate | ESR |
| Extractable Nuclear Antigen | ENA |
| Forced Vital Capacity | FVC |
| Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis | GPA |
| High-Resolution Computed Tomography | HRCT |
| Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies | IIMs |
| Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis | IPF |
| Interstitial Lung Disease | ILD |
| Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features | IPAF |
| Lactic Dehydrogenase | LDH |
| Lupus Anticoagulant | LAC |
| Mechanic’s Hands | MH |
| Melanoma Differentiation-Associated 5 gene | MDA5 |
| Microscopic Polyangiitis | MPA |
| Mixed Connective Tissue Disease | MCTD |
| Multidisciplinary Team | MDT |
| Myeloperoxidase | MPO |
| Myositis-Associated Antibodies | MAAs |
| Myositis-Specific Antibodies | MSAs |
| Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy | NVC |
| Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia | NSIP |
| Number of microhEMOrrages | NEMO |
| Polymyalgia Rheumatica | PMR |
| Polymyositis | PM |
| Proteinase-3 | PR3 |
| Puffy Hands | PH |
| Pulmonary Function Tests | PET |
| Raynaud’s Phenomenon | RP |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | RA |
| Rheumatoid Factor | RF |
| Ribonucleoprotein | RNP |
| Schirmer’s Test | ST |
| Serum Protein Electrophoresis | SPEP |
| Sjögren’s Syndrome | SjS |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | SLE |
| Systemic Sclerosis | SSc |
| Unstimulated Salivary Flow Rate Test | USFRT |
| Usual Interstitial Pneumonia | UIP |
| Very Early Diagnosis of SSc | VEDOSS |
| White Blood Cell | WBC |
References
- Antoniou, K.M.; Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Tomassetti, S.; Bonella, F.; Costabel, U.; Poletti, V. Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cottin, V. Lung biopsy in interstitial lung disease: Balancing the risk of surgery and diagnostic uncertainty. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furini, F.; Carnevale, A.; Casoni, G.; Guerrini, G.; Cavagna, L.; Govoni, M.; Scirè, C.A. The role of the Multidisciplinary evaluation of interstitial lung diseases: Systematic literature review of the current evidence and future perspectives. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levi, Y.; Israeli-Shani, L.; Kuchuk, M.; Epstein Shochet, G.; Koslow, M.; Shitrit, D. Rheumatological assessment is important for interstitial lung disease diagnosis. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casal, M.; Brito-Zeror, P.; Seror, R.; Bootsma, H.; Bowman, S.J.; Doner, T.; Gottemberg, J.E.; Mariette, X.; Theander, E.; On behalf of the EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Task Force; et al. Characterization of systemic disease in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: EULAR-SS Task Force recommendations for articular, cutaneous, pulmonary and renal involvements. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorand, V.; Czirjak, L.; Minier, T. Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2014, 43, e315–e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, A.; Marasco, E.; Cometi, L.; De Stefano, L.; Marcucci, E.; Furini, F.; Barsotti, S.; Cavagna, L. One year in review 2019: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Van Steenbergen, H.W.; van Nies, J.A.B.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Bloem, J.L.; Reijnierse, M.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Characterising arthralgia in the preclinical phase of rheumatoid arthritis using MRI. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Steenbergen, H.W.; Mangnus, L.; Reijnierse, M.; Huizinga, T.W.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H. Clinical factors, anticitrullinated peptide antibodies and MRI-detected subclinical inflammation in relation to progression from clinically suspect arthralgia to arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenbergen, H.W.; Aletaha, D.; Beaart-van de Voorde, L.J.J.; Brouwer, E.; Codreanu, C.; Combe, B.; Fonseca, J.E.; Hetland, M.L.; Humby, F.; Kvien, T.K.; et al. EULAR definition of arthralgia suspicious for progression to rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Salvarani, C.; Olivieri, I.; Hunder, G.G. Polymyalgia manifestation in different conditions mimicking polymyalgia rheumatica. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000, 18, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sambataro, G.; Sambataro, D.; Pignataro, F.; Torrisi, S.E.; Vancheri, A.; Pavone, M.; Palmucci, S.; Del Papa, N.; Vancheri, C. Interstitial Lung Disease in patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A case series. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 26, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadatare, S.P.; Momin, M.; Nighojkar, P.; Askarkar, S.; Singh, K.K. A comprehensive review on dry eye disease: Diagnosis, medical management, recent developments, and future challenges. Adv. Pharm. 2015, 2015, 704946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, B.A.; Cericato, G.O.; da Silveira, E.R.; Giacomelli Nascimento, G.; dos Santos Costa, F.; Thomson, W.M.; Demarco, F.F. How common is dry mouth? Systematic review and meta-regression analysis of prevalence estimates. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Dal Bosco, Y.; Polosa, R. Present and future of biologic drugs in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamideh, F.; Prete, P.E. Ophthalmologic manifestations of rheumatic disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 30, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobak, S.; Oksel, F.; Aksu, K.; Kabasakal, Y. The frequency of sicca symptoms and Sjögren’s syndrome in patients with systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 16, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanski, A.L.; Tomiak, C.; Pleyer, U.; Dietrich, T.; Rudiger Burmester, G.; Dorner, T. The diagnosis and treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome. Dtsch Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Zou, Z.J.; Yu, S.F.; Zhu, J.R. Recurrent swelling of parotid glands and Sjögren’s syndrome. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 22, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z. Interstitial ling disease in non-sicca onset primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A large-scale case-control study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, R.; Bowman, S.J.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Theander, E.; Bootsma, H.; Tzioufas, A.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Dorner, T.; Ravaud, P.; et al. EULAR Sjögren’s syndrome disease activity index (ESSDAI): A user guide. RMD Open 2015, 1, e000022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alunno, A.; Leone, M.C.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R.; Carubbi, F. Lymphoma and lymphomagenesis in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maverakis, E.; Patel, F.; Kronenberg, D.; Chung, L.; Fiorentino, D.; Allanore, Y.; Guiducci, S.; Hesselstrand, R.; Hummers, L.; Duong, C.; et al. International consensus criteria for the diagnosis of Raynaud’s phenomenon. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 48–49, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Block, J.A.; Sequeira, W. Raynaud’s phenomenon. Lancet 2001, 357, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, F.M.; Flavahan, N.A. Raynaud’s phenomenon. N. Eng. J. Med. 2016, 375, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pope, J.E. Raynaud’s phenomenon (primary). BMJ Clin. Evid. 2013, 2013, 1119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.; Riemekasten, G.; Carreira, P.; et al. Classification criteria of Systemic Sclerosis: An ACR-EULAR collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witt, L.J.; Curran, J.J.; Strek, M.E. The diagnosis and treatment of antisynthetase syndrome. Clin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 23, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer-Green, G. Outcomes in primary Raynaud phenomenon: A meta-analysis of the frequency, rates, and predictors of transition to secondary disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 58, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khimdas, S.; Harding, S.; Bonner, A.; Zummer, B.; Baron, M.; Pope, J.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Association with digital ulcers in a large cohort of systemic sclerosis: Results from the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group registry. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthon, L.; Mestre-Stanislas, C.; Berezné, A.; Rannou, F.; Guilpain, P.; Revel, M.; Pagnoux, C.; Guillevin, L.; Fermanian, J.; Poideraudeau, S. Impact of digital ulcers on disability and health-related quality of life in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuggioli, D.; Manfredi, A.; Colaci, M.; Lumetti, F.; Ferri, C. Osteomyelitis complicating scleroderma digital ulcers. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzi, L.; Braschi, F.; Fiori, G.; Galluccio, F.; Miniati, I.; Guiducci, S.; Conforti, M.L.; Kaloudi, O.; Nacci, F.; Sacu, O.; et al. Digital ulcers in scleroderma: Staging, characteristics and sub-setting through observation of 1614 digital ulcers. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, M.; Matubara, K.; Hirano, H.; Watabe, H.; Ichiki, Y.; Mori, S. Pitting scars in progressive systemic sclerosis. Dermatology 1993, 187, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddali Bongi, S.; Del Rosso, A.; Passalacqua, M.; Miccio, S.; Matucci Cerinic, M. Manual lymph drainage improving upper extremity edema and hand function in patients with systemic sclerosis in edematous phase. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matucci Cerinic, M.; Allanore, Y.; Czirjak, L.; Tyndall, A.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Denton, C.; Valentini, G.; Distler, O.; Fligelstone, K.; Tyrrel-Kennedy, A.; et al. The challenge of early systemic sclerosis of the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research group (EUSTAR) community. It is time to cut the Gordian knot and develop a prevention or rescue strategy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.; Avvedimento, E.V.; Krieg, T. Scleroderma. N. Eng. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.; Walker, U.; Tyndall, A.; Kahan, A.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Allanore, Y.; EUSTAR group. Characteristics of joint involvement and relationships with systemic inflammation in systemic sclerosis: Results from the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR) database. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, E.C.; Black, C.; Fleischmajer, R.; Jablonska, S.; Krieg, T.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Rowwell, N.; Wollheim, F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): Classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Allanore, Y.; Baron, M.; Czirjak, L.; Distler, O.; Foeldvari, I.; Kuwana, M.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; et al. Standardization of the modified Rodnan skin score for use in clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottron, H. Hautveranderungen bei Dermatomyositis. In VIII Congress Intern Dermatol et Syphilogr; Lomholt: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1931; pp. 826–830. [Google Scholar]
- Callen, J.P. Dermatomyositis. Lancet 2000, 355, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.L.; Lokke, A.; Hilberg, O.; Hyldgaaed, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Tran, D. Clinical characteristics and outcome in patients with antisynthetase syndrome associated interstitial lung disease: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2019, 6, 1583516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, M.A.; Donmez, S.; Saritas, F.; Bas, V.; Pamuk, O.N. The epidemiology of dermatomyositis in northwestern Thrace region in Turkey: Epidemiology of Dermatomyositis in Turkey. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euwer, R.L.; Sontheimer, R.D. Dermatologic aspects of myositis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 1994, 6, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Brown, K.K.; Cadranel, J.; Corte, T.J.; du Bois, R.M.; Lee, J.S.; Leslie, K.O.; Lynch, D.A.; Matteson, E.L.; et al. An official European Respiratory Society / American Thoracic Society research statement: Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambataro, G.; Sambataro, D.; Torrisi, S.E.; Vancheri, A.; Colaci, M.; Pavone, M.; Pignataro, F.; Del Papa, N.; Palmucci, S.; Vancheri, C. Clinical, serological and radiological features of a prospective cohort of Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features (IPAF) patients. Respir. Med. 2019, 150, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, N.I.; Klippel, J.H.; Decker, J.L. A cutaneous lesion associated with myositis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohara, E.; Saraya, T.; Sato, S.; Tsujimoto, N.; Watanabe, T.; Takata, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishii, H.; Takizawa, H.; Goto, H. Mechanic’s hands revisited: Is this sign still useful for diagnosis in patients with lung involvement of collagen vascular disease? BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gusdorf, L.; Moruzzi, C.; Goetz, J.; Lipsker, D.; Sibilia, J.; Cribier, B. Mechanics hands in patients with antisynthetase syndrome: 25 cases. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 146, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.T.; Gullotti, G.M.; Mecoli, C.A.; Lahouti, A.H.; Albayda, J.; Paik, J.; Danoff, S.K.; Mammen, A.L.; Christopher-Stine, L. “Hiker’s feet”: A novel cutaneous finding in the inflammatory myopathies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, E.; Uruha, A.; Suzuki, S.; Hamanaka, K.; Ohnuki, Y.; Tsugawa, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakahara, J.; Shiina, T.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Skeletal muscle involvement in antisynthetase syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvi, U.; Chung, L.; Fiorentino, D.F. Clinical presentation and evaluation of dermatomyositis. Indian J. Dermatol. 2012, 57, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Wigley, F.M.; Hummers, L.K. Telangiectases in scleroderma: A potential clinical marker of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuillard, C.; Pineton de Chambrun, M.; de Prost, N.; Guerin, C.; Schmidt, M.; Dargent, A.; Quenot, J.P.; Preau, S.; Ledoux, G.; Neuville, M.; et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with acute respiratory failure revealing anti-synthetase or anti-MDA-5 dermato-pulmonary syndrome: A French multicenter retrospective study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulman, N.; Slobodin, G.; Rozenbaum, M.; Rosner, I. Calcinosis in rheumatic disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, A.; Chung, L. Management of calcinosis associated with systemic sclerosis. Curr. Treat. Options Rheum. 2016, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuyuki Shinjo, S.; de Souza, F.H.C. Update on the treatment of calcinosis in dermatomyositis. Rev. Bras. Rheumatol. 2013, 53, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzuela, A.; Chung, L. Calcinosis: Pathophysiology and management. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Atwal, S.S.; Mndal, D.; Garga, U.C. Radiographic patterns of soft tissue calcinosis in juvenile dermatomyositis and its clinical implications. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, RD08–RD11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Zaccara, E.; Maglione, W.; Vitali, C.; Del Papa, N. Tumoral calcinosis of the spine in the course of systemic sclerosis: Report of a new case and review of the literature. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli, F.; Fiori, G.; Braschi, F.; Amanzi, L.; Bruni, C.; Blagojevic, J.; Bellando Randone, S.; Cometi, L.; de Souza Muller, C.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Subsets, distribution and complication. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barohn, R.J.; Dimanchkie, M.M.; Jackson, E.C. A pattern recognition approach to the patient with a suspected myopathy. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, M. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein. Aust. Prescr. 2015, 38, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N. Complement diagnostics: Concepts, indications, and practical guidelines. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 962702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Augusto, J.F.; Langs, V.; Demiselle, J.; Lavigne, C.; Brilland, B.; Duveau, A.; Poli, C.; Chevailler, A.; Croue, A.; Tollis, F.; et al. Low Serum Complement C3 Levels at diagnosis of renal ANCA-Associated vasculitis is associated with poor prognosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambataro, G.; Ferro, F.; Orlandi, M.; Sambataro, D.; Torrisi, S.E.; Quartuccio, L.; Vancheri, C.; Baldini, C.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; On behalf of the Italian Study group on Lung iNvolvement in rheumatic Disease (ISLaND). Clinical, morphological features and prognostic factors associated with Interstitial Lung Disease in primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A systematic review from the Italian Society of Rheumatology. Autoimmun Rev. 2020, 18, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, T.J.; Richards, J.C.; Olson, A.L.; Groshong, S.D.; Gelfand, E.W.; Lynch, D.A. Pulmonary manifestations of Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J. Thorac. Imaging 2018, 33, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagna, L.; Nuno, L.; Scirè, C.A.; Govoni, M.; Longo, F.J.; Franceschin, I.F.; Neri, R.; Castañeda, S.; Sifuentes Giraldo, W.A.; Caporali, R.; et al. Clinical spectrum time course in anti Jo-1 positive Antisynthetase Syndrome: Results from an International retrospective Multicenter study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancio, N.; Pavone, M.; Torrisi, S.E.; Vancheri, A.; Sambataro, D.; Palmucci, S.; Vancheri, C.; Di Marco, F.; Sambataro, G. Contribution of pulmonary function tests (PFTs) to the diagnosis and follow up of connective tissue diseases. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2019, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Kouliatsis, G.; Anevlavis, S.; Bouros, D. Serum biomarkers in interstitial lung diseases. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavagna, L.; Castaneda, S.; Scirè, C.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; AENEAS Collaborative Group Members. Antisynthetase syndrome or what else? Different perspectives indicate the need for new classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbuckle, M.R.; McClain, M.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Scofield, R.H.; Dennis, G.J.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner-Weiner, L. Laboratory evaluation of children with rheumatic disease. Pediat. Ann. 2002, 31, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M.; Feltkamp, T.E.; Smolen, J.S.; Butcher, B.; Dawkins, R.; Fritzler, M.J.; Gordon, T.; Hardin, J.A.; Kalden, J.R.; Lahita, R.G.; et al. Range of antinuclear antibodies in “healthy” individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, A.E. Recent Approaches to optimize laboratory assessment of antinuclear antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00270-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielen, M.M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Reesink, H.W.; van de Stadt, R.J.; van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; de Koning, M.H.; Habibuw, M.R.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Dijkmans, B.A. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: A study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, O.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Hay, F.C. Rheumatoid factors: What’s new? Rheumatology 2006, 45, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambataro, G.; Sambataro, D.; Torrisi, S.E.; Vancheri, A.; Pavone, M.; Rosso, R.; Schisano, M.; Crimi, C.; Pignataro, F.; Fischer, A.; et al. State of the art in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features: A systematic review on retrospective studies and suggestions for further advances. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensvold, A.H.; Frisell, T.; Magnusson, P.K.; Holmdahl, R.; Askling, J.; Catrina, A.I. How well do ACPA discriminate and predict RA in the general population: A study based on 12 590 population-representative Swedish twins. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.; Kelly, C.; Eggleton, P.; De Soyza, A.; Hutchinson, D. The lug in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis: An initiating site of injury? Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azizah, M.R.; Azila, M.N.; Zulkifli, M.N.; Norita, T.Y. The prevalence of antinuclear, anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies in a group of healty blood donors. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 1996, 14, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; De Pasquale, L.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Vacchi, C.; Luppi, F.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features: A signle center prospective follow-up study. Autoimmun Rev. 2020, 19, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambataro, G.; Vancheri, A.; Torrisi, S.E.; Colaci, M.; Pavone, M.; Libra, A.; Martorana, E.; Rosso, R.; Pignataro, F.; Del Papa, N.; et al. The morphological domain does not affect the rate of progression to defined autoimmune diseases in Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features (IPAF) patients. Chest 2020, 157, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radice, A.; Sinico, R.A. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, E.; Bax, W.A.; van Dam, B.; Slieker, W.A.T.; Verhave, G.; Frerichs, F.C.P.; van Eijk, I.C.; Boersma, W.G.; de Kuyper, G.T.M.; Penne, E.L. Diagnosing ANCA-associated vasculitis in ANCA positive patients. Medicine 2016, 95, e5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnoux, C. Updates in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Ventura, I.B.; Achtar-Zadeh, N.; Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; Wolters, P.J.; Collard, H.R.; Adegunsoye, A.; Strek, M.E.; Ley, B. Prevalence and clinical significance of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies in North American Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2019, 4, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Yamanaka, H. Interstitial Lung Disease with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarenza, A.; Esposto Ultimo, L.; Falsaperla, D.; Travali, M.; Foti, P.V.; Torrisi, S.E.; Schisano, M.; Mauro, L.A.; Sambataro, G.; Basile, A.; et al. Chest imaging using signs, symbols, and naturalistic images: A practical guide for radiologists and non-radiologists. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domsic, R.T.; Medsger, T.A. Autoantibodies and their role in scleroderma clinical care. Curr. Treat. Options Rheum. 2016, 2, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iniesta Arandia, N.; Simeon-Aznar, C.P.; Guillen Del Castillo, A.; Colunga Arguelles, D.; Rubio-Rivas, M.; Trapiella Martinez, L.; Garcia Hernandez, F.J.; Saez Comet, L.; Egurbide Arberas, M.V.; Ortego-Centeno, N.; et al. Influence of antibody profile in clinical features and prognosis in a cohort of Spanish patients with Systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. 106), 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Migliorini, P.; Baldini, C.; Rocchi, V.; Bombardieri, S. Anti-Sm and Anti-RNP antibodies. Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palterer, B.; Vitiello, G.; Carraresi, A.; Giudizi, M.G.; Cammelli, D.; Parronchi, P. Bench to bedside review of myositis autoantibodies. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification criteria or Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Consensus and data-Driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.N.; Mc Adams DeMarco, M.; Shiboski, S.C.; Lam, M.Y.; Challacombe, S.; Daniels, T.E.; Dong, Y.; Greenspan, J.S.; Kirkham, B.W.; Lanfranchi, H.E.; et al. The SSB-positive/SSA-negative antibody profile is not associated with key phenotypic features of Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, F.; Cavazzana, I. Anti-Ro/SSa and La/SSB antibodies. Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gay, M.A.; Montecucco, C.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Trallero-Araguas, E.; Molberg, O.; Andersson, H.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Perez-Roman, D.I.; Bauhammer, J.; Fiehn, C.; et al. Timing of onset affects arthritis presentation pattern in antisynthetase syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Cavagna, L.; Nuño, L.; Scirè, C.A.; Govoni, M.; Longo, F.J.; Franceschini, F.; Neri, R.; Castañeda, S.; Sifuentes Giraldo, W.A.; Caporali, R.; et al. Serum Jo-1 Autoantibody and isolated arthritis in the Antisynthetase Syndrome: Review of the literature and report of the experience of AENEAS Collaborative Group. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aoust, J.; Hudson, M.; Tatibouet, S.; Wick, J.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group; Mahler, M.; Baron, M.; Fritzler, M.J. Clinical and serologic correlates of anti-PM-Scl antibodies in systemic sclerosis: A multicenter study of 763 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillen-Del Castillo, A.; Pilar Simeòn-Aznar, C.; Fonollosa-Pla, V.; Alonso-Vila, S.; Reverte-Vinaixa, M.M.; Munoz, X.; Pallisa, E.; Selva-O’allaghan, A.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Vilardell-Tarrès, M. Good outcome of interstitial lung disease in patients with scleroderma associated to anti-PM/Scl antibody. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, Y.; Hosono, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Mimori, T.; Akiyama, M. Anti-PM/Scl antibodies are found in Japanese patients with various systemic autoimmune conditions besides myositis and scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rigolet, A.; Musset, L.; Dubourg, O.; Maisonobe, T.; Grenier, P.; Charuel, J.L.; Behin, A.; Herson, S.; Amoura, Z.; Benveniste, O. Inflammatory myopathies with anti-ku antibodies: A prognosis dependent on associated lung disease. Medicine 2012, 91, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayda, J.; Khan, A.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Corse, A.M.; Paik, J.J.; Cristopher-Stine, L. Inflammatory myopathy associated with anti-mitochondrial antibodies: A distinct phenotype with cardiac involvement. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagna, L.; Trallero Araguas, E.; Meloni, F.; Cavazzana, I.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Feist, E.; Zanframundo, G.; Morandi, V.; Meyer, A.; Pereira da Silva, J.A.; et al. Antisynthetase antibodies specificities: Impact on clinical spectrum time course of Antisynthetase syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, R. Clinical significance of myositis-specific autoantibodies. Immunol. Med. 2018, 41, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koga, T.; Fujikawa, K.; Horai, Y.; Okada, A.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Iwamoto, N.; Suzuki, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Tamai, M.; Arima, K.; et al. The diagnostic utility of anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody testing for predicting the prognosis of Japanese patients with DM. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggioggero, M.; Meroni, P.L. The geoepidemiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A299–A304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, S.E.; Vancheri, A.; Pavone, M.; Sambataro, G.; Palmucci, S.; Vancheri, C. Comorbidities of IPF: How do they impact in prognosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 53, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Madioni, C.; Bianchi, N.; Refini, R.M.; Cappelli, R.; Rottoli, P. Serum analysis of coagulation factors in IPF and NSIP. Inflammation 2014, 37, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, K.S.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, J.M.; Han, J.Y.; Chung, W.T.; Kim, K.H. Prevalence and clinical associations of lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, anti beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2010, 30, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cutolo, M.; Sulli, A.; Smith, V. How to perform and interpret capillaroscopy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 27, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Zaccara, E.; Maglione, W.; Polosa, R.; Afeltra, A.M.; Vitali, C.; Del Papa, N. Nailfold videocapillaroscopy micro-haemorrhage and giant capillary counting a san accurate approach for a steady state definition of disease activity in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andracco, R.; Irace, R.; Zaccara, E.; vettori, S.; Maglione, W.; Riccardi, A.; pignataro, F.; Ferrara, R.; Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; et al. The cumulative number of micro-haemorrhages and micro-thromboses in nailfold videocapillaroscopy is a good indicator of disease severity in systemic sclerosis: A validation study of the NEMO score. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastiani, M.; Manfredi, A.; Vukatana, G.; Moscatelli, S.; Riato, L.; Bocci, M.; Iudici, M.; Principato, A.; Mazzuca, S.; Del Medico, P.; et al. Predictive role of capillaroscopic skin ulcer risk index in systemic sclerosis: A multicentre validation study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, F.; Maglione, W.; Minniti, A.; Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Campanaro, F.; Valentini, G.; Vitali, C.; Del Papa, N. NEMO score in nailfold videocapillaroscopy is a good tool to assess both steady state levels and overtime changes of disease activity in patients with systemic sclerosis: A comparison with the proposed composite indices for this disease status entity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastiani, M.; Triantafyllias, K.; Manfredi, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Palmou-Fontana, N.; Cassone, G.; Drott, U.; Delbruck, C.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Bertolazzi, C.; et al. Nailfold Capillaroscopy Characteristics of Antisynthetase Syndrome and possible clinical associations: Results of a multicenter International Study. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manfredi, A.; Sebastiani, M.; Campomori, F.; Pipitone, N.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Praino, E.; Ferri, C. Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy alterations in Dermatomyositis and Systemic Sclerosis: Toward identification of a specific pattern. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcher, J.P.; Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Heidenreich, A.M.; Kitagawa, K.; Zhang, S.; Hamann, S.; Larkin, G.; McNamara, N.A.; Greenspan, J.S.; et al. A simplified quantitative method for assessing keratoconjunctivitis sicca from the Sjögren’s Syndrome International Registry. Am. J. Ophtalmol. 2010, 149, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, S. Schirmer’s test. Community Eye Health 2011, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navazesh, M.; Kumar, S.K.; University of Southern California School of Dentistry. Measuring salivary flow: Challenges and opportunities. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2008, 139, 35S–40S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouros, D.; Wells, A.U.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Pantelidis, P.; Haslam, P.L.; Vassilakis, D.A.; Black, C.M.; du Bois, R.M. Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to outcome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhou, J.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y. A retrospective analysis of distinguishing features of chest HRCT and clinical manifestation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome-related interstitial lung disease in a Chinese population. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Kim, J.S.; Newell, J.D.; Brown, K.K.; Cool, C.D.; Meehan, R.; Emoto, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Lynch, D.A. Rheumatoid arthritis-related lung diseases: CT findings. Radiology 2004, 232, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lega, J.C.; Cottin, V.; Fabien, N.; Thivolet-Béjui, F.; Cordier, J.F. Interstitial lung disease associated with anti-PM/Scl or anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase autoantibodies: A similar condition? J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.H.; Lee, E.B.; Shin, K.C.; Im, C.H.; Chung, D.H.; Han, S.K.; Song, Y.W. Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cottin, V. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias with connective tissue diseases features: A review. Respirology 2016, 21, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, N.; Egashira, R.; Tabata, K.; Hashisako, M.; Kitani, M.; Waseda, Y.; Ishizuka, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kasahara, K.; Izumi, S.; et al. Analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus-related interstitial pneumonia: A retrospective multicentre study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, T.; Goletto, T.; Beltramo, G.; Dupuy, H.; Jouneau, S.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Cottin, V.; Blockmans, D.; Lazaro, E.; et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A poor prognostic factor. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 106, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisado Vasco, P.; Silva, M.; Duarte, M.A.; Sambataro, G.; Bertolazzi, C.; Pavone, M.; Martin-Garrido, I.; Martin-Segarra, O.; Luque-Pinilla, J.M.; Santilli, D.; et al. Quantitative assessment of interstitial lung disease in Sjögren’s syndrome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariani, A.; Silva, M.; Seletti, V.; Bravi, E.; Saracco, M.; Parisi, S.; De Gennaro, F.; Idolazzi, L.; Caramaschi, P.; Benini, C.; et al. Quantitative Chest computed tomography is associated with two prediction models of mortality in interstitial lung disease related to systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nurmi, H.M.; Kettunen, H.P.; Suoranta, S.K.; Purokivi, M.K.; Karkkainen, M.S.; Selander, T.A.; Kaarteenaho, R.L. Several high-resolution computed tomography findings associate with survival and clinical features in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 2018, 134, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.J.; Collard, H.R.; King, T.E., Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: The relevance of histopathologic and radiographic pattern. Chest 2009, 136, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohshimo, S.; Guzman, J.; Costabel, U.; Bonella, F. Differential diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: Clues and pitfalls: Number 4 in the series “pathology for the clinician” edited by Peter Dorfmuller and Alberto Cavazza. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.; Watts, R.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Cid, M.C.; Crestani, B.; Hauser, T.; Hellmich, B.; Holle, J.U.; Laudien, M.; Little, M.A.; et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenzel, W.; Goebel, H.H.; Aronica, E. Review: Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathies—A heterogeneous group of diseases with specific myopathological features. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, N.; Spencer, L.; Greaves, M.; Bishop, P.; Chaturvedi, A.; Leonard, C. A review of the multidisciplinary diagnosis if Interstitial Lung Diseases: A retrospective analysis in a single UK specialist centre. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Pignataro, F.; Zanframundo, G.; Codullo, V.; Fagone, E.; Martorana, E.; Ferro, F.; Orlandi, M.; Del Papa, N.; et al. Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Autoimmune Diseases: How to Recognize Them? Diagnostics 2020, 10, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040208
Sambataro D, Sambataro G, Pignataro F, Zanframundo G, Codullo V, Fagone E, Martorana E, Ferro F, Orlandi M, Del Papa N, et al. Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Autoimmune Diseases: How to Recognize Them? Diagnostics. 2020; 10(4):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040208
Chicago/Turabian StyleSambataro, Domenico, Gianluca Sambataro, Francesca Pignataro, Giovanni Zanframundo, Veronica Codullo, Evelina Fagone, Emanuele Martorana, Francesco Ferro, Martina Orlandi, Nicoletta Del Papa, and et al. 2020. "Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Autoimmune Diseases: How to Recognize Them?" Diagnostics 10, no. 4: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040208
APA StyleSambataro, D., Sambataro, G., Pignataro, F., Zanframundo, G., Codullo, V., Fagone, E., Martorana, E., Ferro, F., Orlandi, M., Del Papa, N., Cavagna, L., Malatino, L., Colaci, M., & Vancheri, C. (2020). Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Autoimmune Diseases: How to Recognize Them? Diagnostics, 10(4), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040208







