Deep Learning Based Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection from Blood Smear and Its Smartphone Based Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- While doing experiments on the malaria dataset, we found that certain samples were mislabeled. These mislabeled samples were corrected and the corrections can be found in [41] for future research.
- Unlike previous works carried out for malaria parasite detection, our trained models are not only highly accurate (99.23%) but also the order of magnitude is more computationally efficient (4600 flops only) compared to previously published work [40].
- For better understand the performance of the model in low resources settings, it was deployed for inference in multiple mobile devices as well as a web application. We find that in such situation the model can be used to find accurate per cell classification prediction within 1 s.
2. Relevant Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Data-Set
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Proposed Model Architecture
3.4. Training Details
3.4.1. General Training
3.4.2. Distillation Training
3.4.3. Autoencoder Training
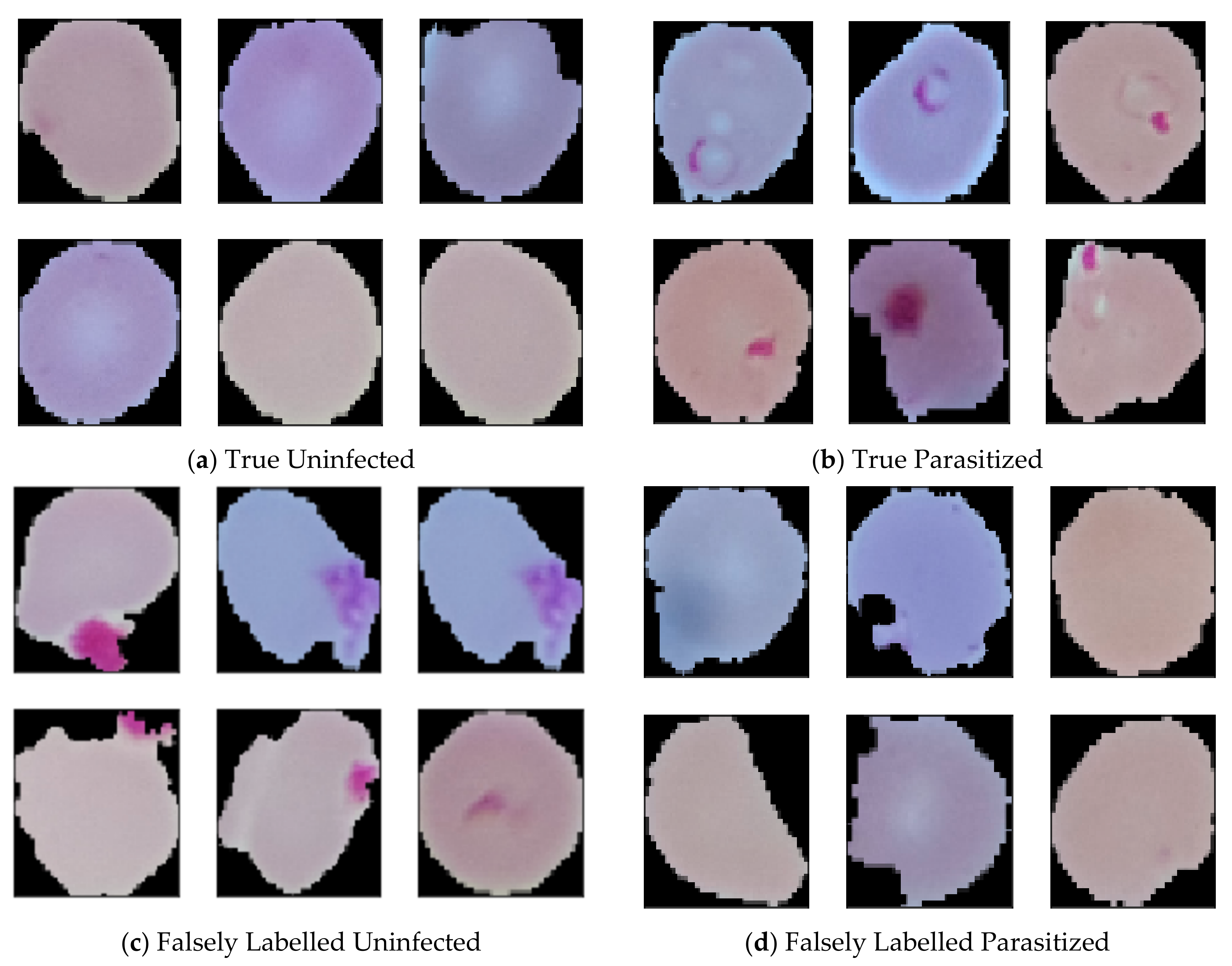
4. Result Analysis
5. Model Deployment
5.1. Mobile Based Application
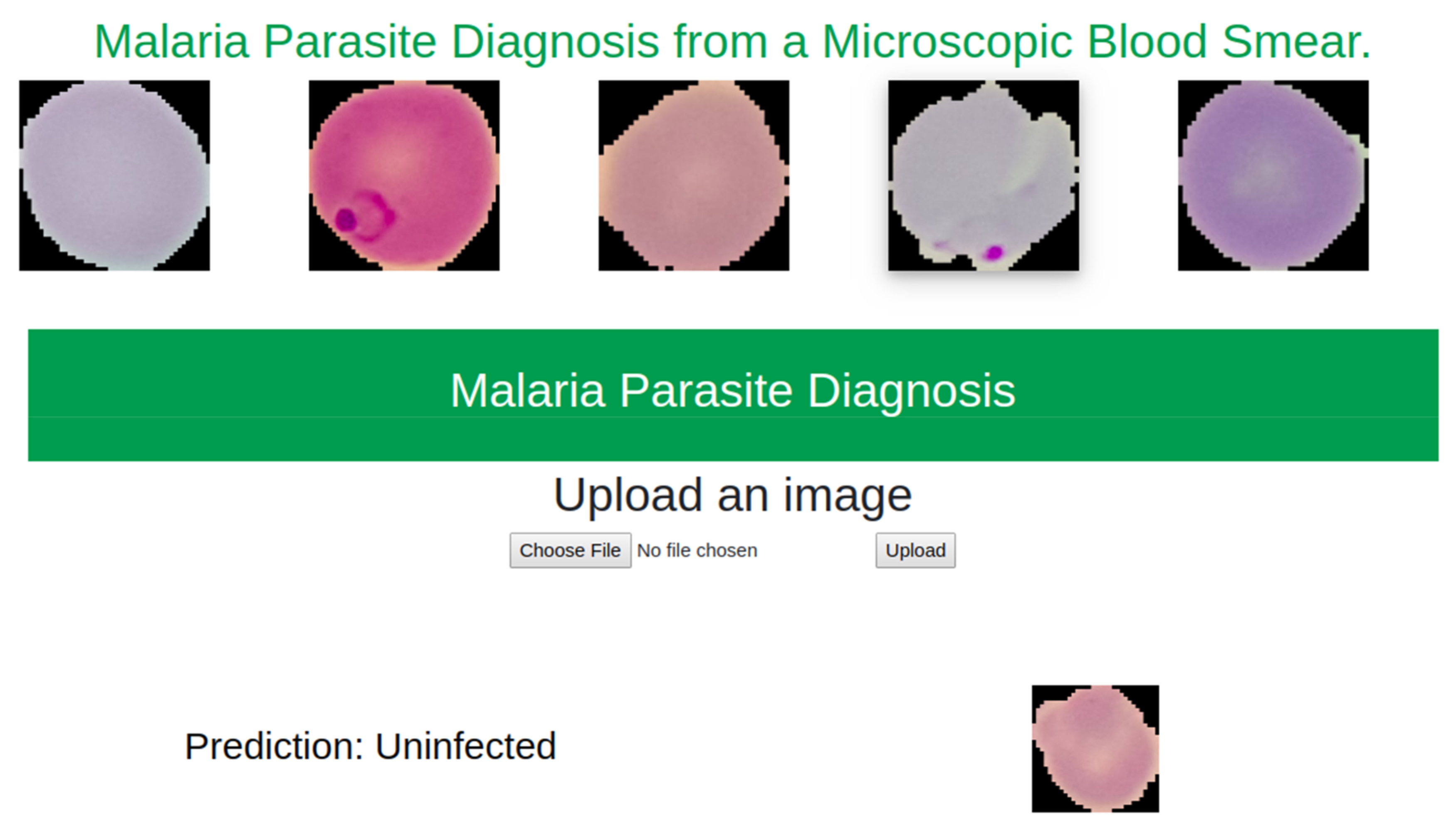
5.2. Web Based Application
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. (Additional Result)
Appendix A.1. Dataset

Appendix A.2. Experimental Details
| Process | Manual | Automatic |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Blood smears | 109 | 109 |
| Background change | Black | - |
| Average segmentation on per cell | 3 | 96 |
| Finally Annotate cells | 392 | 582 |
| Number of Parasitized cells | 196 | 291 |
| Number of Uninfected cells | 196 | 291 |
Appendix A.3. Result Analysis

| Method | Test Accuracy | Test Loss | F1 Score | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | 0.9974 | 0.0087 | 0.9974 | 1.00 | 0.9948 | 1.00 |
| Automatic | 0.9879 | 0.1183 | 0.9980 | 0.9797 | 0.9965 | 0.9793 |
References
- Fact Sheet about Malaria. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Fact Sheet about MALARIA. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Schellenberg, J.A.; Smith, T.; Alonso, P.; Hayes, R. What is clinical malaria? Finding case definitions for field research in highly endemic areas. Parasitol. Today 1994, 10, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarimo, D.; Minjas, J.; Bygbjerg, I. Malaria diagnosis and treatment under the strategy of the integrated management of childhood illness (imci): Relevance of laboratory support from the rapid immunochromatographic tests of ict malaria pf/pv and optimal. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2001, 95, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, G.; González, F.A.; Romero, E. A semi-automatic method for quantification and classification of erythrocytes infected with malaria parasites in microscopic images. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohrt, C.; Sutamihardja, M.A.; Tang, D.; Kain, K.C. Impact of microscopy error on estimates of protective efficacy in malaria-prevention trials. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggraini, D.; Nugroho, A.S.; Pratama, C.; Rozi, I.E.; Iskandar, A.A.; Hartono, R.N. Automated status identification of microscopic images obtained from malaria thin blood smears. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Bandung, Indonesia, 17–19 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Di Rubeto, C.; Dempster, A.; Khan, S.; Jarra, B. Segmentation of blood images using morphological operators. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR-2000, Barcelona, Spain, 3–7 September 2000; Volume 3, pp. 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Di Ruberto, C.; Dempster, A.; Khan, S.; Jarra, B. Morphological image processing for evaluating malaria disease. In International Workshop on Visual Form; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrjou, A.; Abbasian, T.; Izadi, M. Automatic malaria diagnosis system. In Proceedings of the 2013 First RSI/ISM International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 13–15 February 2013; pp. 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.S.; Mohon, A.N.; Mustafa, S.; Khan, W.A.; Islam, N.; Karim, M.J.; Khanum, H.; Sullivan, D.J.; Haque, R. Real-time pcr assay and rapid diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of clinically suspected malaria patients in bangladesh. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masanja, I.M.; McMorrow, M.L.; Maganga, M.B.; Sumari, D.; Udhayakumar, V.; McElroy, P.D.; Kachur, S.P.; Lucchi, N.W. Quality assurance of malaria rapid diagnostic tests used for routine patient care in rural tanzania: Microscopy versus real-time polymerase chain reaction. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wongsrichanalai, C.; Barcus, M.J.; Muth, S.; Sutamihardja, A.; Wernsdorfer, W.H. A review of malaria diagnostic tools: Microscopy and rapid diagnostic test (rdt). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77 (Suppl. 6), 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheirob, V.E.; Thaithongc, S.; Browna, K.N. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 61, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakers, C.; Ruijter, J.M.; Deprez, R.H.L.; Moorman, A.F. Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (pcr) data. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 339, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snounou, G.; Viriyakosol, S.; Jarra, W.; Thaithong, S.; Brown, K.N. Identification of the four human malaria parasite species in field samples by the polymerase chain reaction and detection of a high prevalence of mixed infections. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 58, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. New Perspectives: Malaria Diagnosis; Report of a jointwho/usaid informal consultation, 25–27 october 1999; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- How Malaria RDTs Work. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/areas/diagnosis/rapid-diagnostic-tests/about-rdt/en/ (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- WHO. New Perspectives: Malaria Diagnosis. Report of a Joint WHO/USAID Informal Consultation (Archived). 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/who_cds_rbm_2000_14/en/ (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Obeagu, E.I.; Chijioke, U.O.; Ekelozie, I.S. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDTs). Ann. Clin. Lab. Res. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/areas/diagnosis/rapid-diagnostic-tests/generic_PfPan_training_manual_web.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Microscopy. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/areas/diagnosis/microscopy/en/ (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Mathison, B.A.; Pritt, B.S. Update on malaria diagnostics and test utilization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajaraman, S.; Antani, S.K.; Poostchi, M.; Silamut, K.; Hossain, M.A.; Maude, R.J.; Jaeger, S.; Thoma, G.R. Pre-trained convolutional neural networks as feature extractors toward improved malaria parasite detection in thin blood smear images. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.A.; Nakasi, R.; Mugagga, P.K.; Byanyima, P.; Lubega, W.; Andama, A. Deep convolutional neural networks for microscopy-based point of care diagnostics. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 19–20 August 2016; pp. 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Poostchi, M.; Silamut, K.; Maude, R.J.; Jaeger, S.; Thoma, G. Image analysis and machine learning for detecting malaria. Transl. Res. 2018, 194, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anggraini, D.; Nugroho, A.S.; Pratama, C.; Rozi, I.E.; Pragesjvara, V.; Gunawan, M. Automated status identification of microscopic images obtained from malaria thin blood smears using Bayes decision: A study case in Plasmodium falciparum. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems, Jakarta, Indonesia, 17–18 December 2011; pp. 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Subramanian, G.; Duan, J.; Gao, S.; Bai, L.; Chandramohanadas, R.; Ai, Y. A portable image-based cytometer for rapid malaria detection and quantification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179161. [Google Scholar]
- Arco, J.E.; Górriz, J.M.; Ramírez, J.; Álvarez, I.; Puntonet, C.G. Digital image analysis for automatic enumeration of malaria parasites using morphological operations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 3041–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K.; Maiti, A.K.; Chakraborty, C. Automated system for characterization and classification of malaria-infected stages using light microscopic images of thin blood smears. J. Microsc. 2015, 257, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibin, D.; Nair, M.S.; Punitha, P. Malaria parasite detection from peripheral blood smear images using deep belief networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9099–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, I.; Pattanaik, P.; Swarnkar, T. Automatic detection of malaria parasites using unsupervised techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on ISMAC in Computational Vision and Bio-Engineering, Palladam, India, 16–17 May 2018; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yunda, L.; Ramirez, A.A.; Millán, J. Automated image analysis method for p-vivax malaria parasite detection in thick film blood images. Sist. Telemática 2012, 10, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, N.; Pattnaik, S.; Acharya, B. Advanced image analysis based system for automatic detection and classification of malarial parasite in blood images. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Knowl. Manag. 2012, 5, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, J.; Carpenter, A. Applying faster r-cnn for object detection on malaria images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tek, F.B.; Dempster, A.G.; Kale, I. Parasite detection and identification for automated thin blood film malaria diagnosis. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2010, 114, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, M.; Das, A.; Das, B.; Das, B.; Dash, B.; Chhotray, G. Distribution of plasmodium falciparum genotypes in clinically mild and severe malaria cases in orissa, india. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento, W.J.; Romero, E.; Restrepo, A.; y Electrónica, D.I. Colour estimation in images from thick blood films for the automatic detection of malaria. In: Memoriasdel IX Simposio de Tratamiento de Señales, Im ágenes y Visión artificial. Manizales 2004, 15, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, E.; Sarmiento, W.; Lozano, A. Automatic detection of malaria parasites in thick blood films stained with haematoxylin-eosin. In Proceedings of the III Iberian Latin American and Caribbean Congress of Medical Physics, ALFIM2004, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaraman, S.; Jaeger, S.; Antani, S.K. Performance evaluation of deep neural ensembles toward malaria parasite detection in thin-blood smear images. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6977. [Google Scholar]
- Corrected Malaria Data—Google Drive. 2019. Available online: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/10TXXa6B_D4AKuBV085tX7UudH1hINBRJ?usp=sharing (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Linder, N.; Turkki, R.; Walliander, M.; Mårtensson, A.; Diwan, V.; Rahtu, E.; Pietikäinen, M.; Lundin, M.; Lundin, J. A malaria diagnostic tool based on computer vision screening and visualization of plasmodium falciparum candidate areas in digitized blood smears. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104855. [Google Scholar]
- Opoku-Ansah, J.; Eghan, M.J.; Anderson, B.; Boampong, J.N. Wavelength markers for malaria (plasmodium falciparum) infected and uninfected red blood cells for ring and trophozoite stages. Appl. Phys. Res. 2014, 6, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Esbensen, K.; Geladi, P. Principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1987, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. Handb. Brain Theory Neural Netw. 1995, 3361, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, H.; Pan, W.D.; Williams, L.A.; Reddy, V.V.; Benjamin, W.H.; Bryan, A.W. Evaluations of deep convolutional neural networks for automatic identification of malaria infected cells. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics (BHI), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 February 2017; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y. Lenet-5, Convolutional Neural Networks. URL. Available online: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/lenet (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv Prepr. 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Powell, A.; Ersoy, I.; Poostchi, M.; Silamut, K.; Palaniappan, K.; Guo, P.; Hossain, M.A.; Sameer, A.; Maude, R.J.; et al. Cnn-based image analysis for malaria diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, L.; Da Costa, J.M.C.; Elias, D.; Cardoso, J.S. Automated detection of malaria parasites on thick blood smears via mobile devices. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 90, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, G.P.; Swetha, M.; Sai Siva, G.; SaiSubrahmanyam, G.R.K. Convolutional neural network-based malaria diagnosis from focus stack of blood smear images acquired using custom-built slide scanner. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation; Tech. rep.; California Univ San Diego La Jolla Inst for Cognitive Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada, M.; Yairi, T. Anomaly detection using autoencoders with nonlinear dimensionality reduction. In Proceedings of the MLSDA 2014 2nd Workshop on Machine Learning for Sensory Data Analysis ACM, Gold Coast, Australia, 2 December 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Chen, F. High-resolution sar image classification via deep convolutional autoencoders. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2351–2355. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Shao, S.; Zhao, R.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. A sparse auto-encoder-based deep neural network approach for induction motor faults classification. Measurement 2016, 89, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gemulla, R.; Nijkamp, E.; Haas, P.J.; Sismanis, Y. Large-scale matrix factorization with distributed stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2011; pp. 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Denoeux, T. A k-nearest neighbor classification rule based on dempster-shafer theory. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1995, 25, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarap, A.F. An architecture combining convolutional neural network (cnn) and support vector machine (svm) for image classification. arXiv Prepr. 2017, arXiv:1712.03541. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.X.; Suen, C.Y. A novel hybrid cnn–svm classifier for recognizing handwritten digits. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y. Feature extraction from histopathological images based on nucleus-guided convolutional neural network for breast lesion classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 71, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Buciluă, C.; Caruana, R.; Niculescu-Mizil, A. Model compression. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining ACM, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 20–23 August 2006; pp. 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv Prepr. 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Gracelynxs/Malaria-Detection-Model. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/gracelynxs/malaria-detection-model (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Bengio, Y. Rmsprop and equilibrated adaptive learning rates for nonconvex optimization. arXiv Prepr. 2015, arXiv:1502.04390. [Google Scholar]
- Tek, F.B.; Dempster, A.G.; Kale, I. Computer vision for microscopy diagnosis of malaria. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, N.E.; Pritchard, C.J.; Rubin, D.M.; Duse, A.G. Automated image processing method for the diagnosis and classification of malaria on thin blood smears. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.K.; Ghosh, M.; Pal, M.; Maiti, A.K.; Chakraborty, C. Machine learning approach for automated screening of malaria parasite using light microscopic images. Micron 2013, 45, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.S.; Sheikh, S.A.; Talukdar, A.; Laskar, R.H. Malaria infected erythrocyte classification based on the histogram features using microscopic images of thin blood smear. Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najman, L.; Schmitt, M. Watershed of a continuous function. Signal Process. 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Update Your Browser to Use Google Drive—Google Drive Help. 2020. Available online: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1etEDs71yLqoL9XpsHEDrSpUGwqtrBihZ?usp=sharing (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Preim, B.; Botha, C. Visual Computing for Medicine, 2nd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parvati, K.; Rao, P.; Mariya Das, M. Image segmentation using gray-scale morphology and marker-controlled watershed transformation. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2008, 2008, 384346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, B.B.; Vass, J.; Zhuang, X. Significance-linked connected component analysis for wavelet image coding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1999, 8, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Update Your Browser to Use Google Drive—Google Drive Help. 2020. Available online: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/17YnJIMJIzOga5sC6jUEsexqZACs2n0Nw?usp=sharing (accessed on 3 May 2020).














| Augmentation Type | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Random Rotation | 20 Degree |
| Random Zoom | 0.05 |
| Width Shift | (0.05, −0.05) |
| Height Shift | (0.05, −0.05) |
| Shear Intensity | 0.05 |
| Horizontal Flip | True |
| Image Size | Augmentation | Epochs | Validation Accuracy | Validation Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (32,32) | No | 300 | 0.9982 | 0.06 |
| (64,64) | No | 300 | 0.9748 | 0.16 |
| (32,32) | Yes | 300 | 0.9920 | 0.02 |
| (64,64) | Yes | 300 | 0.9813 | 0.08 |
| Image Size | Augmentation | Epochs | Validation Accuracy | Validation Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (32,32) | Yes | 500 | 0.9897 | 0.04 |
| (64,64) | Yes | 500 | 0.9859 | 0.05 |
| Image Size | Training Accuracy | Training Loss | Validation Accuracy | Validation Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (28,28) | 0.9943 | 0.018 | 0.9924 | 0.025 |
| (32,32) | 0.9941 | 0.019 | 0.9900 | 0.032 |
| Image Size | Aug | Method | Test Acc | Test Loss | F1 Score | Precs. | Sens. | Spec. | Size (KB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (32,32) | Yes | - | 0.9915 | 0.03 | 0.9914 | 0.9861 | 0.9960 | 0.9865 | 233.60 |
| (32,32) | No | - | 0.9877 | 0.05 | 0.9876 | 0.9892 | 0.9861 | 0.9893 | 233.60 |
| (64,64) | Yes | - | 0.9843 | 0.07 | 0.9839 | 0.9836 | 0.9840 | 0.9842 | 954.50 |
| (64,64) | No | - | 0.9755 | 0.15 | 0.9751 | 0.9851 | 0.9650 | 0.9855 | 954.60 |
| (32,32) | Yes | Distillation | 0.9900 | 0.04 | 0.9900 | 0.9877 | 0.9920 | 0.9878 | 233.60 |
| (64,64) | Yes | Distillation | 0.9885 | 0.04 | 0.9882 | 0.9929 | 0.9836 | 0.9932 | 954.60 |
| (28,28) | Yes | Autoencoder | 0.9950 | 0.01 | 0.9951 | 0.9929 | 0.9880 | 0.9917 | 73.70 |
| (32,3) | Yes | Autoencoder | 0.9923 | 0.02 | 0.9922 | 0.9892 | 0.9952 | 0.9917 | 73.70 |
| (32,32) | Yes | CNN-SVM | 0.9893 | - | 0.9918 | 0.9921 | 0.9916 | - | - |
| (32,32) | Yes | CNN-KNN | 0.9912 | - | 0.9928 | 0.9911 | 0.9923 | - | - |
| Version | Codename | API | Distribution | Device | Model | Ram | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.3.3–2.3.7 | Gingerbread | 10 | 0.30% | - | - | - | Almost obsolete OS |
| 4.0.3–4.0.4 | Ice Cream Sandwich | 15 | 0.30% | - | - | - | Almost obsolete OS |
| 4.1.X | Jelly Bean | 16 | 1.20% | - | - | - | Almost obsolete OS |
| 4.4 | Kitkat | 19 | 6.90% | Samsung | GT-190601 | 2 GB | Work Perfectly |
| 5 | Lollipop | 21 | 3.00% | Nexus 4 (Emulator) | 2 GB | Work Perfectly | |
| 6 | Marshmallow | 23 | 16.90% | Nexus 5 (Emulator) | 1 GB | Work Perfectly | |
| 7 | Nougat | 24 | 11.40% | Xiaomi | Readmi Note 4 | 3 GB | Work Perfectly |
| 8 | Oreo | 26 | 12.90% | Samsung | S8 (Emulator) | 2 GB | Work Perfectly |
| 8.1 | - | 27 | 15.40% | LG | LM-X415L | 2 GB | Work Perfectly but latency is higher compared to other devices. |
| 9 | Pie | 28 | 10.40% | Xiaomi | A2 Lite | 4 GB | Work Perfectly |
| Method | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1 Score | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ross et al., (2006) [73] | 0.730 | 0.850 | - | - | - |
| Das et al., (2013) [74] | 0.840 | 0.981 | 0.689 | - | - |
| SS. Devi et al., (2016) [75] | 0.9632 | 0.9287 | 0.9679 | 0.8531 | - |
| Zhaohuiet al., (2016) [54] | 0.9737 | 0.9699 | 0.9775 | 0.9736 | 0.9736 |
| Bibin et al., (2017) [31] | 0.963 | 0.976 | 0.959 | - | - |
| Gopakumar et al., (2018) [58] | 0.977 | 0.971 | 0.985 | - | - |
| S. Rajaraman et al., (2019) [40] | 0.995 | 0.971 | 0.985 | - | - |
| Proposed Model | 0.9923 | 0.9952 | 0.9917 | 0.9922 | 0.9892 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuhad, K.M.F.; Tuba, J.F.; Sarker, M.R.A.; Momen, S.; Mohammed, N.; Rahman, T. Deep Learning Based Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection from Blood Smear and Its Smartphone Based Application. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050329
Fuhad KMF, Tuba JF, Sarker MRA, Momen S, Mohammed N, Rahman T. Deep Learning Based Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection from Blood Smear and Its Smartphone Based Application. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(5):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050329
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuhad, K. M. Faizullah, Jannat Ferdousey Tuba, Md. Rabiul Ali Sarker, Sifat Momen, Nabeel Mohammed, and Tanzilur Rahman. 2020. "Deep Learning Based Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection from Blood Smear and Its Smartphone Based Application" Diagnostics 10, no. 5: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050329
APA StyleFuhad, K. M. F., Tuba, J. F., Sarker, M. R. A., Momen, S., Mohammed, N., & Rahman, T. (2020). Deep Learning Based Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection from Blood Smear and Its Smartphone Based Application. Diagnostics, 10(5), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050329








