Endoscopic Management of Malignant Biliary Stricture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Endoscopic Management of Resectable Malignant Biliary Stricture
3. Endoscopic Management of Unresectable Malignant Biliary Stricture
3.1. Plastic vs. Metal Stents
3.2. Unresectable Distal Malignant Biliary Stricture
3.3. Unresectable Hilar Malignant Biliary Stricture (HMBS)
3.4. Endobiliary Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
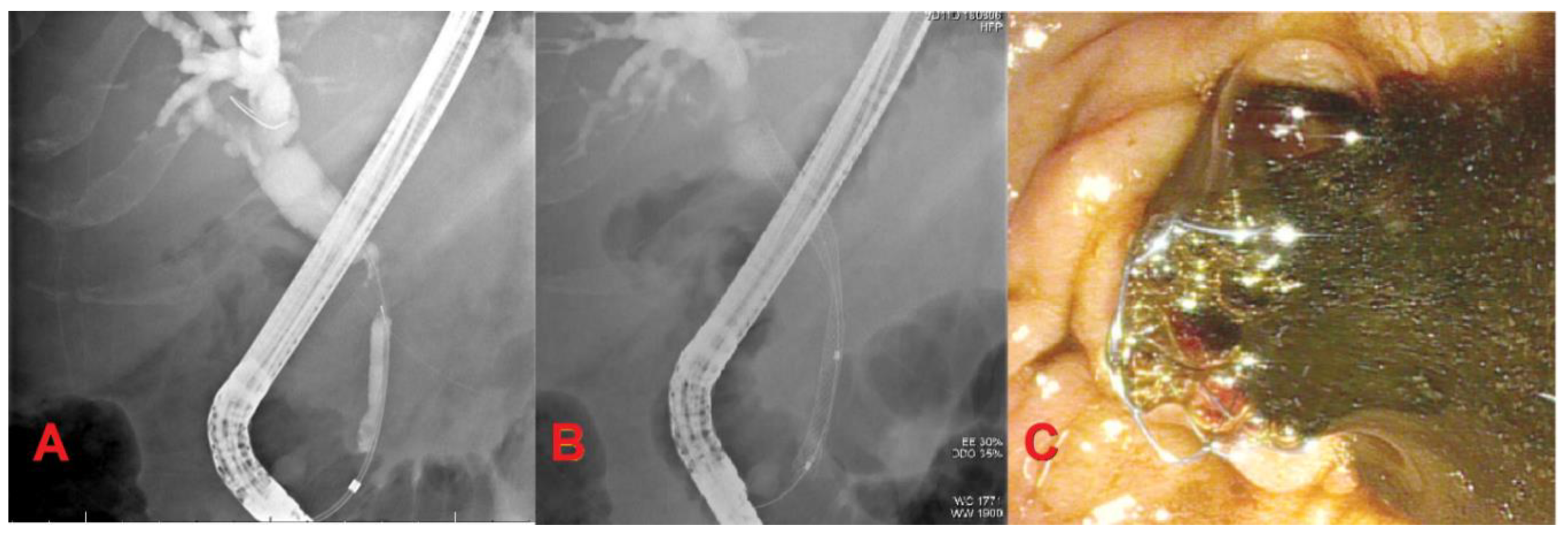
4. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, A.; Gelrud, A.; Agarwal, B. Biliary strictures: Diagnostic considerations and approach. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2014, 3, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DaVee, T.; Lee, J.H. Biliary obstruction: Endoscopic approaches. In Seminars in Interventional Radiology; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Gaag, N.A.; Rauws, E.A.J.; Van Eijck, C.H.; Bruno, M.J.; Van Der Harst, E.; Kubben, F.J.G.M.; Gerritsen, J.J.; Greve, J.W.; Gerhards, M.F.; De Hingh, I.; et al. Preoperative biliary drainage for cancer of the head of the pancreas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Gurusamy, K.S.; Wang, Q.; Davidson, B.R.; Lin, H.; Xie, X.; Wang, C. Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials on safety and efficacy of biliary drainage before surgery for obstructive jaundice. BJS 2013, 100, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelen, R.; Roos, E.; Wiggers, J.K.; Besselink, M.G.; Buis, C.I.; Busch, O.R.; DeJong, C.H.; Van Delden, O.M.; Van Eijck, C.H.; Fockens, P.; et al. Endoscopic versus percutaneous biliary drainage in patients with resectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinel, J.; Adham, M. Preoperative biliary drainage for resectable or borderline resectable periampullary tumor: What is the best management? HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2019, 8, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, A.B.; McHugh, M.; Catnach, S.M.; Alstead, E.M.; Clark, M.L. Symptom relief and quality of life after stenting for malignant bile duct obstruction. Gut 1994, 35, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lima, S.L.A.; Bustamante, F.A.C.; De Moura, E.G.H.; Bernardo, W.M.; Artifon, E.L.D.A.; Chaves, D.M.; Franzini, T.A.P.; Junior, C.K.F.; Marques, W.B. Endoscopic palliative treatment versus surgical bypass in malignant low bile duct obstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. 2015, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viesca, M.F.Y.; Arvanitakis, M. Early diagnosis and management of malignant distal biliary obstruction: A Review on current recommendations and guidelines. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arshad, S.A.; Phuoc, V.H. Surgical palliation of biliary obstruction: Bypass in the era of drainage. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 120, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.Z.; Moura, E.G.H.d.; Bernardo, W.M.; Baracat, F.L.; Mendonça, E.Q.; Kondo, A.; Luz, G.O.; Júnior, C.K.F.; Artifon, E.L.d.A. Endoscopic stenting for inoperable malignant biliary obstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13374–13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moole, H.V.; Jaeger, A.; Cashman, M.; Volmar, F.H.; Dhillon, S.; Bechtold, M.L.; Puli, S.R. Are self-expandable metal stents superior to plastic stents in palliating malignant distal biliary strictures? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Med. J. Armed. Forces India 2016, 73, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, W.J.; Ryu, J.K.; Yang, K.Y.; Paik, W.H.; Lee, J.K.; Woo, S.M.; Park, J.K.; Kim, Y.-T.; Yoon, Y.B. A comparison of metal and plastic stents for the relief of jaundice in unresectable malignant biliary obstruction in Korea: An emphasis on cost-effectiveness in a country with a low ERCP cost. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawas, T.; Al Halabi, S.; Parsi, M.A.; Vargo, J. Self-expandable metal stents versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: A meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayama, H.; Komatsu, Y.; Tsujino, T.; Sasahira, N.; Hirano, K.; Toda, N.; Nakai, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Tada, M.; Yoshida, H.; et al. A prospective randomised study of “covered” versus “uncovered” diamond stents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gut 2004, 53, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aljahdli, E.S. Management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, A.; Leggett, C.L.; Murad, M.H.; Baron, T.H. Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing the patency of covered and uncovered self-expandable metal stents for palliation of distal malignant bile duct obstruction. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 321–327.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conio, M.; Mangiavillano, B.; Caruso, A.; Filiberti, R.A.; Baron, T.H.; De Luca, L.; Signorelli, S.; Crespi, M.; Marini, M.; Ravelli, P.; et al. Covered versus uncovered self-expandable metal stent for palliation of primary malignant extrahepatic biliary strictures: A randomized multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majmudar, K.; Murad, F. Fully-covered self-expandable metal stents may increase the risk of cholecystitis in patients with intact gallbladders compared to uncovered self-expandable metal stents when placed for malignant biliary obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayama, H.; Kawabe, T.; Nakai, Y.; Tsujino, T.; Sasahira, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Arizumi, T.; Togawa, O.; Matsubara, S.; Ito, Y.; et al. Cholecystitis after metallic stent placement in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tringali, A.; Hassan, C.; Rota, M.; Rossi, M.; Mutignani, M.; Aabakken, L. Covered vs. uncovered self-expandable metal stents for malignant distal biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bismuth, H.; Majno, P.E. Biliary strictures: Classification based on the principles of surgical treatment. World J. Surg. 2001, 25, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meybodi, M.A.; Shakoor, D.; Nanavati, J.; Ichkhanian, Y.; Vosoughi, K.; Gutierrez, O.I.B.; Kalloo, A.N.; Singh, V.; Kumbhari, V.; Ngamruengphong, S.; et al. Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic stenting in patients with unresectable malignant hilar obstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E281–E290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienne, A.; Hobeika, E.; Gouya, H.; Lapidus, N.; Fritsch, J.; Choury, A.D.; Chryssostalis, A.; Gaudric, M.; Pelletier, G.; Buffet, C.; et al. Prediction of drainage effectiveness during endoscopic stenting of malignant hilar strictures: The role of liver volume assessment. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowsett, J.; Vaira, D.; Hatfield, A.; Cairns, S.; Polydorou, A.; Frost, R.; Croker, J.; Cotton, P.; Russell, R.; Mason, R.; et al. Endoscopic biliary therapy using the combined percutaneous and endoscopic technique. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.; Ayaru, L.; Rogowska, A.; Mosse, A.; Hatfield, A.R.; Bown, S.G. Photodynamic therapy of malignant biliary strictures using meso-tetrahydroxyphenylchlorin. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolak, W.; Austrian Biliary RFA Study Group; Schreiber, F.; Schwaighofer, H.; Gschwantler, M.; Plieschnegger, W.; Ziachehabi, A.; Mayer, A.; Kramer, L.; Kopecky, A.; et al. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for malignant biliary obstruction: A nationwide retrospective study of 84 consecutive applications. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 28, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallis, Y.; Phillips, N.; Steel, A.; Kaltsidis, H.; Vlavianos, P.; Habib, N.; Westaby, D. Analysis of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of biliary malignant strictures in pancreatic cancer suggests potential survival benefit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 3449–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sofi, A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Das, A.; Sachdev, M.; Khuder, S.; Nawras, A.; Lee-Smith, W. Radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement versus stent placement alone for malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Ito, K.; Yoneda, M. Novel balloon catheter-based endobiliary radiofrequency ablation system: An ex-vivo experimental study. Dig. Endosc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, R.; Davies, S.E.C.; Mezzina, N.; Ardizzone, S. Comprehensive review on EUS-guided biliary drainage. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 11, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashita, T.; Doi, S.; Yasuda, I. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage: A review. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, P.; Baars, J.E.; Kaffes, A.J. EUS-guided biliary drainage: A comprehensive review of the literature. Endosc. Ultrasound 2018, 7, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Meta-Analysis by Moole et al. Comparing PS vs. SEMS [12] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | SEMS | Complication | Odds Ratio SEMS vs. PS | |
| Stent patency (days) | 73.3 | 167.7 | Cholangitis | 0.46 |
| Reintervention rate | 1.7 | 1.1 | Stent migration | 0.45 |
| Patient survival (days) | 120.6 | 157.3 | Cholecystitis | 1.85 |
| Pancreatitis | 0.80 | |||
| Occlusion rate | 0.48 | |||
| Meta-Analysis by Saleem et al. Comparing FCSEMS and USEMS for Distal MBS [17] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Mean Difference (Days) of FCSEMS vs. UCSEMS | Relative Risk (RR) of FCSEMS vs. UCSEMS | ||
| Patient survival | +51.2 | Migration | 8.11 |
| Stent patency | +60.6 | Overgrowth | 2.03 |
| Stent survival | +68.9 | Sludge | 2.89 |
| Ingrowth | 0.23 | ||
| Type | Distinction |
|---|---|
| I | Limited to the common hepatic duct |
| II | Involving the confluence of the left and right hepatic ducts |
| IIIa | Involving the main hepatic confluence and extending to the bifurcation of the right hepatic duct |
| IIIb | Involving the main hepatic confluence and extending to the bifurcation of the left hepatic duct |
| IV | Involving the main, right, and left hepatic confluence |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorrell, R.; Pawa, S.; Pawa, R. Endoscopic Management of Malignant Biliary Stricture. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060390
Dorrell R, Pawa S, Pawa R. Endoscopic Management of Malignant Biliary Stricture. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(6):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060390
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorrell, Robert, Swati Pawa, and Rishi Pawa. 2020. "Endoscopic Management of Malignant Biliary Stricture" Diagnostics 10, no. 6: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060390
APA StyleDorrell, R., Pawa, S., & Pawa, R. (2020). Endoscopic Management of Malignant Biliary Stricture. Diagnostics, 10(6), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060390





