The Suitability of FGF21 and FGF23 as New Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients
Abstract
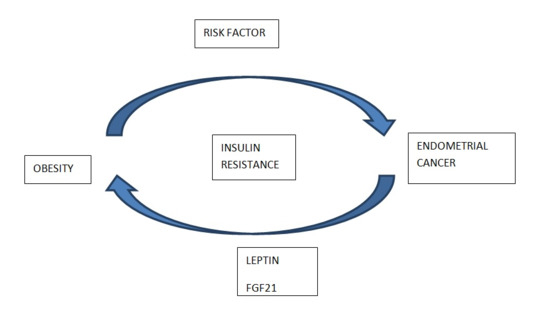
1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Material and Methods
- 22 < BMI < 25, n = 36
- BMI 25–30, n = 77
- BMI > 30, n = 69
- WC < 100 cm, n = 42
- WC > 100 cm, n = 140
- Fasting glucose intolerance, No, n = 161
- Fasting glucose intolerance, Yes, n = 21
- DM type 2, yes, n = 101
- DM type 2, no, n = 81
- Endometrial cancer patient, n = 98
- Patients with normal endometrium, n = 51
- Patients with endometrial polyps, n = 33
- Group A—Endometrial cancer patient, n = 98,
- Group B—Patients with benign endometrium changes, n = 84
- Subgroups B1—Patients with normal endometrium, n = 51
- Subgroups B2—Patients with endometrial polyps, n = 33
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Protein Analysis
3.2. Comparative Analysis Based on the Presence of Risk Factors
3.3. ROC Curve Analysis and Test Sensitivity/Specificity Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Compliance with ethical Standards
- Ethics approval and informed consent:
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Gong, T.T.; Liu, F.H.; Jiang, Y.T.; Sun, H.; Ma, X.X.; Zhao, Y.H.; Wu, Q.J. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Endometrial Cancer, 1990–2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study, 2017. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 291546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurin, S.; Yang, C.H.; Reyes, M.; Cho, S.; Coombs, D.M.; Jarboe, E.A.; Werner, T.L.; Peterson, C.M.; Janát-Amsbury, M.M. Endometrial cancers harboring mutated fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 protein are successfully treated with a new small tyrosine kinase inhibitor in an orthotopic mouse model. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosu, H.; Kuro-o, M. The Klotho gene family as a regulator of endocrine fibroblast growth factors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 299, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziczak, M.; Holbro, T.; Hynes, N.E. Blocking of FGFR signaling inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation through downregulation of D-type cyclins. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.E.; Kim, J.T.; Lim, M.; Oh, C.; Liu, L.; Jung, S.N.; Won, H.R.; Lee, K.; Chang, J.W.; Yi, H.S.; et al. Association between circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and aggressiveness in thyroid cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnedos, M.; Andre, F.; Soria, J.C.; Dieci, M.V. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors as a cancer treatment: From a biologic rationale to medical perspectives. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 264–279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ibrahimi, O.A.; Olsen, S.K.; Umemori, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Ornitz, D.M. Receptor Specificity of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15694–15700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF family: Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, M.; Janus, D.; Dolezal-Oltarzewska, K.; Drozdz, D.; Sztefko, K.; Starzyk, J.B. The association of FGF23 levels in obese adolescents with insulin sensitivity. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Mima, T.; Yashiro, M.; Sonou, T.; Ohya, M.; Masumoto, A.; Yamanaka, S.; Koreeda, D.; Tatsuta, K.; Hanba, Y.; et al. Expression and localization of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)23 and Klotho in the spleen: Its physiological and functional implications. Growth Factors 2016, 34, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.R.; Chiu, K.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Wang, S.S.; Chen, C.S.; Yang, C.K.; Ho, H.C.; Cheng, C.L.; Yang, C.R.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Alteration in serum concentrations of FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23 in patients with urothelial carcinoma. BioFactors 2019, 45, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaess, B.M.; Barnes, T.A.; Stark, K.; Charchar, F.J.; Waterworth, D.; Song, K.; Wang, W.Y.; Vollenweider, P.; Waeber, G.; Mooser, V.; et al. FGF21 signalling pathway and metabolic traits- genetic association analysis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presta, M.; Chiodelli, P.; Giacomini, A.; Rusnati, M.; Ronca, R. Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in cancer: FGF traps as a new therapeutic approach. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin-induced JAK/STAT signaling and cancer growth. Vaccines 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchelek-Myśliwiec, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Wiśniewska, M.; Safranow, K.; Pawlik, A.; Domański, L.; Dołęgowska, K.; Dołęgowska, B.; Stępniewska, J.; et al. Bone Metabolism Parameters in Hemodialysis Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and in Patients After Kidney Transplantation. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Wisniewska, M.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Safranow, K.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Banach, B.; Dołegowska, B.; Dołegowska, K.; Stepniewska, J.; Domanski, L.; et al. Association between Plasma Concentration of Klotho Protein, Osteocalcin, Leptin, Adiponectin, and Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, P.C.; Antonellis, P.J.; Bina, H.A.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Obesity is a fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21)-resistant state. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar]
- Daley-Brown, D.; Oprea-Ilies, G.M.; Lee, R.; Pattillo, R.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Molecular cues on obesity signals, tumor markers and endometrial cancer HHS Public Access Author manuscript. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 21, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cymbaluk-Płoska, A.; Chudecka-Głaz, A.; Jagodzińska, A.; Pius-Sadowska, E.; Sompolska-Rzechuła, A.; Machaliński, B.; Menkiszak, J. Evaluation of biologically active substances promoting the development of or protecting against endometrial cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Ai, H. Correlation analysis between the expressions of leptin and its receptor (ObR) and clinicopathology in endometrial cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2014, 14, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tian, J.; Lv, Y.; Shi, F.; Kong, F.; Shi, H.; Zhao, L. Leptin induces functional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 through JAK2/ STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in human endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundåsen, T.; Hunt, M.C.; Nilsson, L.M.; Sanyal, S.; Angelin, B.; Alexson, S.E.; Rudling, M. PPARα is a key regulator of hepatic FGF21. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, C.; Sánchez-Garrido, M.A.; Tschöp, M.H.; Clemmensen, C. Renaissance of leptin for obesity therapy. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funcke, J.B.; Scherer, P.E. Beyond adiponectin and leptin: Adipose tissue-derived mediators of inter-organ communication. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1648–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muise, E.S.; Azzolina, B.; Kuo, D.W.; El-Sherbeini, M.; Tan, Y.; Yuan, X.; Mu, J.; Thompson, J.R.; Berger, J.P.; Wong, K.K. Adipose fibroblast growth factor 21 is up-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and altered metabolic states. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badman, M.K.; Pissios, P.; Kennedy, A.R.; Koukos, G.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Hepatic Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is Regulated by PPARα and Is a Key Mediator of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Ketotic States. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, M.; Jin, C.; He, W.; Wang, F.; McKeehan, W.L.; Luo, Y. Control of lipid metabolism by adipocyte FGFR1-mediated adipohepatic communication during hepatic stress. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, A.; Yokoyama, K.; Kawanami, D.; Ohkido, I.; Urashima, M.; Utsunomiya, K.; Yokoo, T. Association between resistin and fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Herman, Y.; Ayers, C.; Beg, M.S.; Lakoski, S.G.; Abdullah, S.M.; Johnson, D.H.; Neeland, I.J. Plasma leptin levels and risk of incident cancer: Results from the dallas heart study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozgit, J.M.; Squillace, R.M.; Wongchenko, M.J.; Miller, D.; Wardwell, S.; Mohemmad, Q.; Narasimhan, N.I.; Wang, F.; Clackson, T.; Rivera, V.M. Combined targeting of FGFR2 and mTOR by ponatinib and ridaforolimus results in synergistic antitumor activity in FGFR2 mutant endometrial cancer models. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kwak, Y.; Kim, N.D.; Sim, T. Antitumor effects and molecular mechanisms of ponatinib on endometrial cancer cells harboring activating FGFR2 mutations. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Creighton, C.J.; Ittmann, M. FGF23 promotes prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17291–17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, J.H.; Bianchi, F.; Voshol, J.; Bonenfant, D.; Oakeley, E.J.; Hynes, N.E. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors blocks PI3K/AKT signaling, induces apoptosis, and impairs mammary tumor outgrowth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4151–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, R.S.; Zheng, L.; Liu, W.; Winer, D.; Asa, S.L.; Ezzat, S. Fibroblast growth factor receptors as molecular targets in thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lu, W.; Lin, T.; You, P.; Ye, M.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Lee, M.H.; et al. Activation of Liver FGF21 in hepatocarcinogenesis and during hepatic stress. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Kumar, G.; Chan, S.; Ma, Y.; Vardeh, H.G.; Nasser, I.A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Deficiency of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in mice on a long term obesogenic diet. Mol. Metab. 2018, 13, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Tikk, K.; Weigl, K.; Balavarca, Y.; Brenner, H. Fibroblast growth factor 21 as a circulating biomarker at various stages of colorectal carcinogenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Risk Factor | Patients (n) | Leptin (ng/mL) Median (95%CI) | FGF 21 (pg/mL) Median (95%CI) | FGF-23 (pg/mL) Median (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI 22–25 | 48 | 6.9 (3.6–8.8) | 134.2 (116.4–149.7) | 56.7 (50.5–68.8) |
| BMI 25–30 | 76 | 18.2 (15.4–22.3) | 120.8 (126.1–143.8) | 74.5 (63.3–78.8) |
| BMI > 30 | 58 | 25.9 (19.1–26.8) | 230.1 (136.8–221.4) | 87.7 (69.4–91.1) |
| DM type 2—yes | 105 | 21.6 (4.9–26.8) | 241.5 (155.5–267.1) | 83.4 (67.6–88.6) |
| DM type 2—no | 77 | 17.4 (15.1–23.4) | 143.8 (133.7–167.7) | 72.8 (69.5–91.3) |
| WC < 100 cm | 67 | 14.8 (11.3–19.0) | 118.8 (121.1–148.8) | 62.3 (51.5–69.9) |
| WC > 100 cm | 115 | 21.8 (14.9–29.8) | 187.8 (145.6–206.5) | 69.1 (65.8–83.2) |
| PM | 68 | 15.0 (14.6–22.6) | 117.4 (131.8–182.2) | 66.2 (65.6–73.4) |
| M | 114 | 12.0 (13.7–24.8) | 111.7 (108.6–144.9) | 71.3 (65.6–78.7) |
| Fasting glucose intolerance, yes | 21 | 13.4 (8.8–19.2) | 149.6 (136.9–182.1) | 79.7 (64.4–79.9) |
| Fasting glucose intolerance, no | 161 | 14.6 (12.3–18.8) | 141.4 (140.7–170.4) | 70.7 (63.681.2) |
| Study Group | Median Age (Years) | n |
|---|---|---|
| All patients | 54.43 | 182 |
| Premenopausal | 42.63 | 68 |
| Postmenopausal | 66.68 | 114 |
| Endometrial cancer | 54.36 | 98 |
| Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma | 55.71 | 82 |
| Non-endometrial endometrioid carcinoma | 68.20 | 16 |
| FIGO I, II | 48.96 | 69 |
| FIGO III, IV | 68.95 | 29 |
| Grade 1 | 52.34 | 32 |
| Grade 2 | 61.08 | 41 |
| Grade 3 | 63.44 | 25 |
| Lymphonode metastasis, Yes | 67.81 | 33 |
| Lymphonode metastasis, No | 54.37 | 65 |
| Lymph vessel involvement, Yes | 61.67 | 52 |
| Lymph vessel involvement, No | 56.93 | 46 |
| Myometrial infiltration depth | 55.69 | 59 |
| Myometrial infiltration superficial | 55.04 | 29 |
| Benign changes endometrium | 53.22 | 84 |
| Normal endometrium | 60.04 | 51 |
| Endometrial polyp | 47.12 | 33 |
| Diabetes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A with diabetes | Group B with diabetes | p | |
| n | 64 | 41 | - |
| % | 65.3% | 48.9% | - |
| median leptin (ng/mL) | 24.2 | 19.9 | 0.01 |
| medianFGF21 (pg/mL) | 254.6 | 229.2 | 0.001 |
| Obesity | |||
| Group A with obesity | Group B with obesity | p | |
| n | 36 | 22 | - |
| % | 36.7% | 26.2% | - |
| median leptin (ng/mL) | 26.7 | 22.1 | 0.03 |
| median FGF21 (pg/mL) | 251.6 | 222.5 | 0.001 |
| Fasting Glucose Intolerance | |||
| Group A with FGI | Group B with FGI | p | |
| n | 11 | 10 | - |
| % | 11.2% | 11.9% | - |
| median leptin (ng/mL) | 16.1 | 12.2 | 0.001 |
| median FGF21 (pg/mL) | 154.8 | 147.2 | NS |
| Variable | Group A | Group B | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | Range | Median (95% CI) | Patients (n) | Range | Median (95% CI) | ||
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 98 | (0.11–117) | 16.9 (11–46.8) | 84 | (0.4–44.7) | 14.1 (12.6–17.0) | 0.0004 |
| FGF21 (pg/mL) | 98 | (144.8–217.7) | 181.8 (169.9–222.1) | 84 | (121.1–188.6) | 152.1 (146.3–168.3) | 0.003 |
| FGF23 (pg/mL) | 98 | (61.3–91.4) | 81.3 (77.2–86.3) | 84 | (53.0–71.4) | 70.5 (67.8–73.6) | NS |
| Variable | Group A | Group B2 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | Range | Median (95% CI) | Patients (n) | Range | Median(95% CI) | ||
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 98 | (0.11–117) | 16.9 (11–46.8) | 33 | (0.4–38.9) | 15.3 (12.7–16.4) | 0.01 |
| FGF21 (pg/mL) | 98 | (144.8–217.7) | 181.8 (169.9–222.1) | 33 | (108.1–161.3) | 140.7 (146.3–162.6) | 0.004 |
| FGF23 (pg/mL) | 98 | (61.3–91.4) | 81.3 (77.2–86.3) | 33 | (18.0–73.2) | 68.1 (65.9–72.6) | NS |
| Leptin Cut Off 17.2 ng/mL | FGF23 Cut Off 74.7 pg/mL | FGF21 Cut Off 176.5 pg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 82% | 60% | 86% |
| Specificity | 71% | 52% | 77% |
| OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.26 | 0.96–1.41 | 0.02 |
| WC | 0.98 | 0.79–1.06 | 0.54 |
| DM type 2 | 0.76 | 0.59–0.88 | 0.58 |
| Age | 0.92 | 0.78–1.02 | 0.02 |
| FGF21 | 1.21 | 0.96–1.31 | 0.03 |
| FGF23 | 0.66 | 0.59–0.79 | 0.48 |
| Leptin | 1.24 | 1.08–1.30 | 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cymbaluk-Płoska, A.; Gargulińska, P.; Chudecka-Głaz, A.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Pius-Sadowska, E.; Machaliński, B. The Suitability of FGF21 and FGF23 as New Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060414
Cymbaluk-Płoska A, Gargulińska P, Chudecka-Głaz A, Kwiatkowski S, Pius-Sadowska E, Machaliński B. The Suitability of FGF21 and FGF23 as New Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(6):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060414
Chicago/Turabian StyleCymbaluk-Płoska, Aneta, Paula Gargulińska, Anita Chudecka-Głaz, Sebastian Kwiatkowski, Ewa Pius-Sadowska, and Bogusław Machaliński. 2020. "The Suitability of FGF21 and FGF23 as New Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients" Diagnostics 10, no. 6: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060414
APA StyleCymbaluk-Płoska, A., Gargulińska, P., Chudecka-Głaz, A., Kwiatkowski, S., Pius-Sadowska, E., & Machaliński, B. (2020). The Suitability of FGF21 and FGF23 as New Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients. Diagnostics, 10(6), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060414