Abstract
Radiomics, also known as quantitative imaging or texture analysis, involves extracting a large number of features traditionally unmeasured in conventional radiological cross-sectional images and converting them into mathematical models. This review describes this approach and its use in the evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs). This discipline has the potential of more accurately assessing, classifying, risk stratifying, and guiding the management of PCLs. Existing studies have provided important insight into the role of radiomics in managing PCLs. Although these studies are limited by the use of retrospective design, single center data, and small sample sizes, radiomic features in combination with clinical data appear to be superior to the current standard of care in differentiating cyst type and in identifying mucinous PCLs with high-grade dysplasia. Combining radiomic features with other novel endoscopic diagnostics, including cyst fluid molecular analysis and confocal endomicroscopy, can potentially optimize the predictive accuracy of these models. There is a need for multicenter prospective studies to elucidate the role of radiomics in the management of PCLs.
1. Introduction
The widespread use of high-resolution cross-sectional abdominal imaging has increased the incidental detection of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) on imaging studies performed for unrelated reasons [1]. In a recent systematic review, the pooled global prevalence of asymptomatic PCLs was 8% (95% confidence interval, 4–14%), being higher in older subjects and when employing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI, 25%) compared to computed tomography (CT, 3%) [2]. Although the majority of PCLs are asymptomatic, mucinous PCLs (intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms [IPMNs] and mucinous cystic neoplasms [MCNs]) are precursors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). PDACs have a dismal survival rate, and are on the rise to become the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States [3]. Since up to 15% of PDACs arise from a mucinous cyst, their identification offers an opportunity for early detection of PDAC [4].
The diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management of PCLs have relied heavily on qualitative imaging characteristics and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with cyst fluid analysis (cytology, carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA], and amylase level) as a standard of care [5,6,7]. However, these diagnostic tools are suboptimal in the accurate differentiation of premalignant or malignant cysts, and hence there are multiple somewhat diverging expert guidelines from various international societies [5,7,8,9]. As evidenced in large surgical databases, 17–25% of patients who undergo surgical resection for a presumed mucinous lesion ultimately have a benign cyst [10,11]. The current standard of care is further inadequate at discriminating patients with mucinous PCLs that harbor advanced neoplasia (high-grade dysplasia [HGD] or PDAC) from those with low- or intermediate-grade dysplasia. Hence, the surgical decision is challenging and generally favors resection due to the mortality risk of PDACs, resulting in more than 60% of patients with mucinous PCLs who undergo resection and are found to have low or intermediate dysplasia on surgical pathology [11,12]. This overdiagnosis is problematic [13], because surgical resection for what are considered benign pathologies (e.g., low or intermediate grade dysplasia) can have dire consequences, with attendant risks of mortality (2%) and higher risks of morbidity (20–30%) that include exocrine and endocrine pancreatic insufficiencies [6].
In the last decade, significant progress in diagnostic tools has been made towards preoperative differentiation of PCLs and identifying mucinous cysts with advanced neoplasia. New endoscopic-based technologies, such as contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS (CH-EUS), through-the-needle microforceps biopsy, needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE), and cyst fluid molecular biomarkers, have shown promising results but require future validation in large prospective multicenter studies [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The field of radiology has also transformed to minimize the issues inherent to qualitative imaging interpretation, including high intra- and inter-observer variability, and limited utilization of all the imaging data. Cross-sectional CT scans and MRIs are integral in the management of PCLs. Radiomics, which involves extraction of high-dimensional data from cross-sectional imaging studies, is an evolving field in radiology that could potentially improve differentiation and risk stratification of PCLs. This review aims to depict this novel technology and its application in the management of PCLs, including assessing the current limitations and discussing future directions.
2. Definition of Radiomics
Radiomics, sometimes referred to as quantitative imaging, implies the extraction of a vast number of features from medical images, and its conversion to high-dimensional data [21]. Imaging features such as size, shape, physical transport properties, and texture are extracted from conventional CT, MRI, or positron emission tomography (PET) images into a database, and are then used to create statistical models that can improve diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive accuracy [22]. The principle of radiomics is that the gray-scale values of an image (i.e., pixels), and their spatial and temporal relationships, contain information on phenotype, pathophysiology, and biology (e.g., genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) [23,24,25]. In addition, by using a quantitative, objective method and extracting large amounts of otherwise hidden imaging data, this technology offers an opportunity to circumvent some of the issues related to the traditional qualitative approach. Radiomics has been used to discern benign from malignant disease, and to prognosticate the clinical course of patients with lesions in a variety of organs (e.g., brain, pancreas, prostate, lung, liver, and kidneys) [22,26,27,28,29,30,31].
3. Process of Radiomics
The workflow processes in radiomics involve the following steps (Figure 1): (a) preprocessing, (b) segmentation, (c) feature extraction, and (d) data handling and analysis. Most of these processes are accomplished with computer software programs. Preprocessing follows imaging acquisition, and involves standardizing several parameters such as size of the pixel or voxels, number of the gray levels, range of gray level values, and signal intensity.
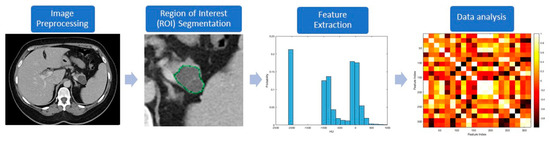
Figure 1.
Diagnostic steps used in radiomics to evaluate a representative pancreatic cystic lesion (PCL).
The process of segmentation consists of contouring the regions of interest (ROI), and represents a critical step because radiomic features will be extracted from these segmented volumes. Segmentation can be challenging due to the unclear margins of some lesions and lack of consensus about what to include—for example, the inclusion of normal pancreatic parenchyma in the analysis of PCLs. While this process can be conducted manually or automatically, both methods are subject to imprecision and reproducibility issues. Manual segmentation, usually conducted by experts, is tedious, time-consuming, and prone to inter-observer variability. In contrast, computer-aided methods may not reliably differentiate artifact and noise from the lesion itself. A combination of both approaches, in which automatic segmentation is performed first, followed by manual verification, might provide a more robust, reproducible, and consistent delineation of the ROI [32].
The next step, feature extraction, has the purpose of finding previously unseen patterns using computed automatic algorithms. Traditional nontexture features, which were created by human image processing experts, include size, shape, and location of a lesion. The texture analysis looks for the frequency distribution of pixels in a ROI (first-order features) and the relationship between pixels (second- or higher-order features), to evaluate properties such as smoothness, coarseness, and regularity (Table 1) [25,33].

Table 1.
Summary of most frequently used radiomic features.
Statistical analysis is performed after feature extraction. The initial step is changing the numeric values to a common scale and randomization of the data set. The number of variables (features) is then reduced to the lowest possible quantity to avoid over-fitting of the model by removing features with poor reproducibility and high correlation (“redundant” features) [21,34]. Statistical models can then be built using different algorithms (e.g., logistic regression, decision tree, k-nearest neighbors, neural networks, and deep learning) that include radiomic features with or without other predicting parameters. Model performance is measured using the area under the receiver-operating curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). Finally, these models can be internally validated during preliminary/single center studies but should ideally be externally validated in independent multicenter data sets [22].
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) offers a very powerful set of analytic tools to the massive amount of data extracted and used in radiomics [22]. Deep learning algorithms can be constructed to perform segmentation tasks, to extract hundreds of imaging features, and to directly analyze the imaging features using an automatic process without human intervention [35,36]. Consequently, the fields of radiomics and AI are being coupled to segment, extract, and analyze quantitative imaging data.
4. Literature Search
One of the authors (J.M.) conducted the electronic search. We searched MEDLINE via PubMed from inception through May 2020 to identify relevant studies. The search was limited to studies published using English language. The electronic search strategy was conducted on 25 June 2020 using a combination of phrases indicating the diseases of interest [“pancreatic cyst”, “pancreatic cystic lesion(s)”, “intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm”, “mucinous cyst”, “serous cystadenoma”, “pancreatic cancer”] and imaging technology [“radiomic(s)”, “texture analysis”, “quantitative imaging”]. To identify additional potential studies, we reviewed the reference lists of the eligible primary studies and reviews.
5. Radiomics to Identify Cyst Type
A summary of the studies that have evaluated radiomic features in discriminating PCL type is presented in Table 2. Three recent studies have used radiomics with CT scans to differentiate serous cystadenomas (SCNs) from other types of PCLs. In a retrospective study of 260 patients who underwent pancreatic resection for a PCL between 2007–2017 in a single center from China, 409 radiomic features were evaluated to differentiate SCNs from other PCLs [37]. The use of 22 radiomic features (AUC 0.77) outperformed five clinical and standard imaging characteristics (AUC 0.71) to accurately diagnose SCNs preoperatively. In the independent validation cohort, the radiomic model yielded an AUC of 0.84, sensitivity of 67%, and specificity of 82%. In another study of patients with macrocystic SCNs (n = 26) and MCNs (n = 31) in surgical histopathology, 1,942 radiomic features were extracted [38]. A model with 18 high-order radiomic features (AUC 0.99) was far superior to using standard radiologic characteristics (AUC 0.77) in preoperatively differentiating macrocystic SCNs and MCNs. The third study including surgically resected patients with SCNs (n = 52) and MCNs (n = 25) also revealed that CT textural features are helpful in noninvasive differentiation of SCNs from MCNs (AUC from 0.66 to 0.77) [39].

Table 2.
Summary of studies evaluating the diagnostic role of radiomics on discrimination of PCL type.
The use of radiomics also appears to outperform conventional clinical and radiologic methods in discriminating between cyst types. In a study of 134 patients with a variety of histologically-confirmed PCLs, Dmitriev et al. found that manually selected quantitative features (location, intensity, and shape) in preoperative CTs more accurately classified cystic lesions than conventional clinical criteria (accuracy 80% vs. 62%) [40]. This study also found that the use of convolutional neural network features performed similarly to manual quantitative features, but the combination of both reached the highest accuracy (84%). Another study of 164 patients with postoperative pathological diagnosis of SCNs (n = 76), IPMNs (n = 48), and MCNs (n = 40) found that a model including 5 of 547 evaluated CT radiomic features with 4 clinical parameters achieved the highest accuracy to distinguish cyst types (84% in the training cohort and 80% in the validation cohort) [41]. None of the published studies evaluating the role of radiomics in discriminating cyst type has yet used MRI images.
6. Radiomics to Advanced Neoplasia in IPMNs
Only a few studies have evaluated the role of radiomics in differentiating IPMNs with advanced neoplasia from indolent lesions with low-grade or intermediate dysplasia (Table 3). All these studies were retrospective; they had small sample sizes, were conducted at single centers, and only included patients with IPMNs confirmed in surgical pathology and with available preoperative images.

Table 3.
Summary of studies evaluating the role of radiomics on differentiating IPMNs with and without advanced neoplasia.
6.1. Role of CT
Most of the studies evaluating radiomics in IPMNs have used CT scans. The first study by Hanania et al. evaluated the performance of 360 imaging features using pancreas protocol CTs (arterial phase) of 53 patients with IPMNs who underwent surgical resection between 2003 and 2011 at MD Anderson Cancer Center (Texas, US) [42]. A total of 14 second-order texture features accurately distinguished IPMNs with low- from high-grade dysplasia on univariate analysis, with individual AUCs ranging from 0.64 to 0.82. The final panel consisted of 10 highest-performing features, which resulted in an AUC of 0.96, sensitivity of 97%, and specificity of 88%. Using this radiomic panel would have resulted in fewer patients with low-grade IPMNs who underwent an unnecessary surgery (12%), compared to the 2012 Fukuoka guidelines (36%).
In another study by Permuth et al. of 38 patients with IPMNs resected between 2006 and 2011 at the Moffit Cancer Center (Florida, US), a total of 112 features were extracted from portal-venous phase CT images [43]. Univariate analysis revealed 14 features that detected IPMNs with high-grade dysplasia with an AUC that ranged from 0.69 to 0.79. The diagnostic performance of the 14 features when combined (AUC 0.77) was better than using worrisome features as defined by the 2012 Fukuoka guidelines (AUC 0.54) and clinical parameters alone (AUC 0.73), but was lower than using Fukuoka guidelines specified high-risk PCL features (AUC 0.84) and blood expression of 5 mi-RNAs (AUC 0.83). Integration of radiomic features with mi-RNA improved the model performance to AUC of 0.92, and the addition of worrisome PCL features further improved the AUC to 0.93.
More recently, a study of 103 patients with branch-duct IPMNs operated between 2005 and 2015 at Memorial Sloan Kettering Center (New York, US) assessed 255 radiomic features using portal-venous phase CTs [44]. Prediction of high-grade dysplasia in IPMNs was suboptimal with clinical and standard radiologic parameters (AUC 0.67); however, application of radiomic features, either alone (AUC 0.76) or in combination with clinical data (AUC 0.79), increased the diagnostic accuracy. In a separate study, the investigators used the same patient cohort to evaluate the predictive performance of 4 novel radiographic features (enhanced boundary fraction, enhanced inside fraction, filled largest connected component fraction, and average-weighted eccentricity) and compared them with texture features [45]. The model performed best when combining the novel features with clinical covariates (AUC 0.81) or with texture features (AUC 0.78), rather than using the novel features (AUC 0.77) or texture features alone (AUC 0.74). The same research group recently compared the combination of 13 texture features, with cyst fluid protein markers predictive of high-grade dysplasia [46] in 33 patients with IPMN [47]. Radiomic features (AUC 0.83) outperformed proteomic analysis (AUC 0.74); however, the combination of both methods predicted high-grade lesions better (AUC 0.88).
6.2. Role of MRI
There is paucity of information regarding the use of radiomics with MRIs in PCLs including IPMNs. Some investigators have attempted to discriminate high-grade from low-grade dysplasia in IPMNs using apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) calculated with diffusion-weight images (DWI). These studies used a modified process of radiomics, in which only ADC summary metrics are extracted, rather than including the full array of potential radiomic features. Most of these studies used a single-slice ROI and found that lower ADC values were associated with high-grade dysplasia in IPMNs [48,49,50,51]. Hoffman et al. evaluated the utility of whole lesion ADC metrics among 18 patients with pathologically proven branch-duct IPMNs diagnosed between 2006 and 2015 in New York University [52]. Quantitative ADC metrics such as entropy (AUC 0.86), mean of the bottom 10th percentile (AUC 0.81), and mean of the 10–25th percentile (AUC 0.79) outperformed other ADC characteristics and standard radiologic findings. In a multivariate analysis with all ADC and standard features, entropy was the only significant predictor of high-grade dysplasia in IPMN.
7. Limitations of Radiomics
Radiomics is still an early discipline. While radiomic analysis is a tool that uses big data to identify correlations, it does not to provide a definitive diagnosis or establish malignant potential through imaging alone. Some of the challenges that have hindered translation of this approach into clinical practice include technical complexity; clinical research limited to expert institutions; and lack of standardization for segmentation, feature extraction, and reported metrics [21,23]. One of the biggest problems precluding multicenter collaborations has been that the acquisition techniques and processing methods used to generate the images vary significantly across institutions. Changes in parameters such as current, voltage, slice thickness, and reconstruction algorithms can impact image noise, pixel intensity, and relationship between pixels, and therefore might impair the reliability and reproducibility of radiomic models [53,54,55]. Although challenging, one possible solution to this problem is using uniform imaging acquisition protocols across institutions. An alternative would be applying harmonization corrections and generating stable models that account for imaging protocol peculiarities [56]. Overcoming these limitations will be of paramount importance to allow data sharing across multiple sites and to conduct large external validation studies.
Specifically in the field of PCLs and IPMNs, previous studies used heterogeneous imaging modalities, different inclusion/exclusion criteria, and variable radiomic features, which makes it difficult to combine and compare results in a meta-analysis. The retrospective and single-center nature of these studies also increases the risk of biased results and internal validity. Most studies had small sample sizes, raising concern for low power and over-fitted predictive models. This is despite the fact that most studies were conducted in large referral centers and participants were enrolled over long periods (~10 years). An explanation for this is that that reference histologic standard is surgical pathology, and only a limited number of patients with PCLs need resection. Adding autopsy data or using other endpoints for nonsurgical patients might enrich the sample sizes and increase the power of future studies. Another limitation of prior research is the lack of validation of the proposed models in independent datasets, so external validity and generalizability of their results are not ensured. In addition, to the best of our knowledge, the field of radiomics has not been applied to ultrasonographic or endonosonographic images of pancreatic cysts. Finally, the vast majority of previous studies used CT imaging, which cannot be extrapolated to other imaging modalities such as MRI.
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
The field of radiomics has the significant potential to inform the appropriate management of PCLs using an objective, noninvasive, and low-cost platform. Early studies have consistently shown better performance of CT radiomic features in differentiating PCLs compared to clinical and qualitative imaging interpretation, but more validation will be needed to ensure broad applicability and reproducibility. Additionally, future studies need to directly compare radiomic features with more invasive novel techniques such as fluid molecular biomarkers and EUS-nCLE, which have been shown to improve the distinction between mucinous and nonmucinous PCLs. However, EUS is not always indicated or performed in all PCLs, so even if radiomic features are not superior to other endoscopic-based technologies, they may still be valuable to noninvasively differentiate PCLs.
More importantly, and despite the limitations of previous studies, radiomic models appear to outperform international consensus guidelines in accurately identifying IPMNs with advanced neoplasia. Furthermore, the integration of radiomic features with clinical variables and other diagnostic parameters (blood mi-RNA, cyst fluid protein markers) has demonstrated improved predictive accuracy of the models compared to using radiomics alone. While future multicenter prospective studies are needed to validate these findings with CT and MRI images, the impact of combining radiomic features with other novel methods such as cyst fluid molecular markers, EUS-nCLE, and CH-EUS should be tested as a possible multimodal approach that might increase the diagnostic accuracy of individual methods and might lead to the reduction of unnecessary pancreatic surgeries for PCLs. For this purpose, a multidisciplinary collaboration involving experts in radiology, gastroenterology, pathology, bioinformatics, and statistics is needed. Finally, local institutions need to envision dedicated teams with expertise in AI that might allow a transition from a qualitative radiologic assessment of PCLs into a new paradigm of quantitative imaging in clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization S.G.K.; methodology, J.D.M. and S.G.K.; investigation J.D.M., E.J.K., and S.G.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.D.M. and S.G.K.; writing—review and editing, J.D.M., E.J.K., and S.G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Eugene Koay was supported by the MD Anderson Cancer Center Support (Core) Grant CA016672 and U54CA210181-01, 5U01CA214263-02, 1P50CA221707-01A1, U01CA196403, 5R01CA218004-02, and 5U01CA200468-04.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Klibansky, D.A.; Reid-Lombardo, K.M.; Gordon, S.R.; Gardner, T.B. The clinical relevance of the increasing incidence of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerboni, G.; Signoretti, M.; Crippa, S.; Falconi, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Capurso, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Prevalence of incidentally detected pancreatic cystic lesions in asymptomatic individuals. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.P.; Oldfield, L.; Ney, A.; Hart, P.A.; Keane, M.G.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D.; Greenhalf, W.; Jeon, C.Y.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Early detection of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; Koay, E.J.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, J.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Moayyedi, P. American gastroenterological association technical review on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 824–848.e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elta, G.H.; Enestvedt, B.K.; Sauer, B.G.; Lennon, A.M. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vege, S.S.; Ziring, B.; Jain, R.; Moayyedi, P. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, B.; Rebours, V.; Malleo, G.; Salvia, R.; Fontana, M.; Maggino, L.; Bassi, C.; Manfredi, R.; Moran, R.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Serous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: A multinational study of 2622 patients under the auspices of the International Association of Pancreatology and European Pancreatic Club (European Study Group on Cystic Tumors of the Pancreas). Gut 2016, 65, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsangkar, N.P.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Wargo, J.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C. 851 resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: A 33-year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Surgery 2012, 152, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Masica, D.L.; Dal Molin, M.; Douville, C.; Thoburn, C.J.; Afsari, B.; Li, L.; Cohen, J.D.; Thompson, E.; Allen, P.J.; et al. A multimodality test to guide the management of patients with a pancreatic cyst. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahora, K.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Brugge, W.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Sahani, D.; Pitman, M.B.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.F. Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Does cyst size change the tip of the scale? A critical analysis of the revised international consensus guidelines in a large single-institutional series. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Koay, E.J.; Borowsky, A.D.; De Marzo, A.M.; Ghosh, S.; Wagner, P.D.; Kramer, B.S. Cancer overdiagnosis: A biological challenge and clinical dilemma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, K.; Kitano, M.; Omoto, S.; Kadosaka, K.; Miyata, T.; Yamao, K.; Imai, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Harwani, Y.; Chikugo, T.; et al. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for differential diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Endoscopy 2016, 48, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Itoi, T.; Ikeuchi, N.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Kamada, K.; Umeda, J.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; et al. Effectiveness of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound for detecting mural nodules in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas and for making therapeutic decisions. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerveld, D.R.; Ponniah, S.A.; Draganov, P.V.; Yang, D. Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy versus EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E656–E667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, C.; Krishna, S.G. Advanced diagnostics for pancreatic cysts: Confocal endomicroscopy and molecular analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2734–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.G.; Hart, P.A.; Malli, A.; Kruger, A.J.; McCarthy, S.T.; El-Dika, S.; Walker, J.P.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Manilchuk, A.; Schmidt, C.R.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Increases Accuracy of Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 432–440.e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; McGrath, K.; Brand, R.E.; Khalid, A.; Zeh, H.J.; Chennat, J.S.; Fasanella, K.E.; Papachristou, G.I.; Slivka, A.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. Preoperative next-generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid is highly accurate in cyst classification and detection of advanced neoplasia. Gut 2018, 67, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Wang, Y.; Dal Molin, M.; Masica, D.L.; Jiao, Y.; Kinde, I.; Blackford, A.; Raman, S.P.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Tomita, T.; et al. A combination of molecular markers and clinical features improve the classification of pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Ates, E.; Kilickesmez, O. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: A practical guide for beginners. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, B.A.; Cen, S.Y.; Hwang, D.H.; Duddalwar, V.A. Texture Analysis of Imaging: What Radiologists Need to Know. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanfardino, M.; Franzese, M.; Pane, K.; Cavaliere, C.; Monti, S.; Esposito, G.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Bringing radiomics into a multi-omics framework for a comprehensive genotype-phenotype characterization of oncological diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, D.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Wibmer, A.; Gondo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Vargas, H.A.; Sala, E.; Hricak, H.; Deasy, J.O. Automatic classification of prostate cancer Gleason scores from multiparametric magnetic resonance images. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6265–E6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehn, M.; Nardini, C.; Wang, D.S.; McGovern, S.; Jayaraman, M.; Liang, Y.; Aldape, K.; Cha, S.; Kuo, M.D. Identification of noninvasive imaging surrogates for brain tumor gene-expression modules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Wang, D.S.; Kim, H.J.; Sirlin, C.B.; Chan, M.G.; Korn, R.L.; Rutman, A.M.; Siripongsakun, S.; Lu, D.; Imanbayev, G.; et al. A computed tomography radiogenomic biomarker predicts microvascular invasion and clinical outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 62, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, O.; Berglund, A.E.; Schabath, M.B.; Aerts, H.J.; Dekker, A.; Wang, H.; Velazquez, E.R.; Lambin, P.; Gu, Y.; Balagurunathan, Y.; et al. Quantitative computed tomographic descriptors associate tumor shape complexity and intratumor heterogeneity with prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, A.M.; Rendell, V.R.; Lubner, M.G.; Winslow, E.R. Texture Analysis: An Emerging Clinical Tool for Pancreatic Lesions. Pancreas 2020, 49, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, V.; Carmicheal, J.; Dhaliwal, A.; Jain, M.; Kaur, S.; Batra, S.K. Radiomics in stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions: Machine learning in action. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagurunathan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Kumar, V.; Grove, O.; Hawkins, S.; Kim, J.; Goldgof, D.B.; Hall, L.O.; Gatenby, R.A.; et al. Reproducibility and Prognosis of Quantitative Features Extracted from CT Images. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, V.; Jacobs, M.A. Radiomics: A new application from established techniques. Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2016, 1, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeskops, P.; Viergever, M.A.; Mendrik, A.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Benders, M.J.; Isgum, I. Automatic Segmentation of MR Brain Images with a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Lin, K.; Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Pancreas Serous Cystic Neoplasms: A Radiomics Method on Preoperative MDCT Images. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ma, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Preoperative differentiation of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm from macrocystic serous cystic adenoma using radiomics: Preliminary findings and comparison with radiological model. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 122, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Ou, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X. Discrimination of Pancreatic Serous Cystadenomas From Mucinous Cystadenomas with CT Textural Features: Based on Machine Learning. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, K.; Kaufman, A.E.; Javed, A.A.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Lennon, A.M.; Saltz, J.H. Classification of Pancreatic Cysts in Computed Tomography Images Using a Random Forest and Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2017, 10435, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, F.; Yang, P.; Yang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhuo, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.S.; et al. A Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Based Radiomics Approach for Preoperative Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasm Subtypes: A Feasibility Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, A.N.; Bantis, L.E.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Tamm, E.P.; Katz, M.H.; Maitra, A.; Koay, E.J. Quantitative imaging to evaluate malignant potential of IPMNs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85776–85784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permuth, J.B.; Choi, J.; Balarunathan, Y.; Kim, J.; Chen, D.T.; Chen, L.; Orcutt, S.; Doepker, M.P.; Gage, K.; Zhang, G.; et al. Combining radiomic features with a miRNA classifier may improve prediction of malignant pathology for pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85785–85797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attiyeh, M.A.; Chakraborty, J.; Gazit, L.; Langdon-Embry, L.; Gonen, M.; Balachandran, V.P.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Kingham, T.P.; et al. Preoperative risk prediction for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms by quantitative CT image analysis. HPB 2019, 21, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, J.; Midya, A.; Gazit, L.; Attiyeh, M.; Langdon-Embry, L.; Allen, P.J.; Do, R.K.G.; Simpson, A.L. CT radiomics to predict high-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Efishat, M.A.; Attiyeh, M.A.; Eaton, A.A.; Gonen, M.; Prosser, D.; Lokshin, A.E.; Castillo, C.F.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Ferrone, C.R.; Pergolini, I.; et al. Multi-institutional Validation Study of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid Protein Analysis for Prediction of High-risk Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Ann. Surg. 2018, 268, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, K.A.; Williams, T.L.; Lawrence, S.A.; Chakraborty, J.; Al Efishat, M.A.; Attiyeh, M.A.; Askan, G.; Chou, Y.; Pulvirenti, A.; McIntyre, C.A.; et al. Multimodal radiomics and cyst fluid inflammatory markers model to predict preoperative risk in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. J. Med. Imaging 2020, 7, 031507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.M.; Lee, J.M.; Shin, C.I.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Added value of diffusion-weighted imaging to MR cholangiopancreatography with unenhanced mr imaging for predicting malignancy or invasiveness of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Horaguchi, J.; Fujita, N.; Noda, Y.; Kobayashi, G.; Ito, K.; Koshita, S.; Kanno, Y.; Masu, K.; Sugita, R. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating the histological degree of malignancy in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. J. Hepato-Biliary Pancreat. Sci. 2014, 21, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, Z.; Ichikawa, T.; Motosugi, U.; Muhi, A.; Sano, K.; Sou, H.; Haradome, H.; Kiryu, S.; Araki, T. Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging in the characterization of pancreatic mucinous cystic lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrasegaran, K.; Akisik, F.M.; Patel, A.A.; Rydberg, M.; Cramer, H.M.; Agaram, N.P.; Schmidt, C.M. Diffusion-weighted imaging in characterization of cystic pancreatic lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.H.; Ream, J.M.; Hajdu, C.H.; Rosenkrantz, A.B. Utility of whole-lesion ADC histogram metrics for assessing the malignant potential of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs). Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Dogan, N.; Stoyanova, R.; Ford, J.C. Evaluation of radiomic texture feature error due to MRI acquisition and reconstruction: A simulation study utilizing ground truth. Phys. Med. 2018, 50, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Tan, Y.; Tsai, W.Y.; Qi, J.; Xie, C.; Lu, L.; Schwartz, L.H. Reproducibility of radiomics for deciphering tumor phenotype with imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galavis, P.E.; Hollensen, C.; Jallow, N.; Paliwal, B.; Jeraj, R. Variability of textural features in FDG PET images due to different acquisition modes and reconstruction parameters. Acta Oncol. 2010, 49, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackin, D.; Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Jones, A.K.; Ng, C.S.; Court, L. Harmonizing the pixel size in retrospective computed tomography radiomics studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).