Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment of Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Features of Included Studies
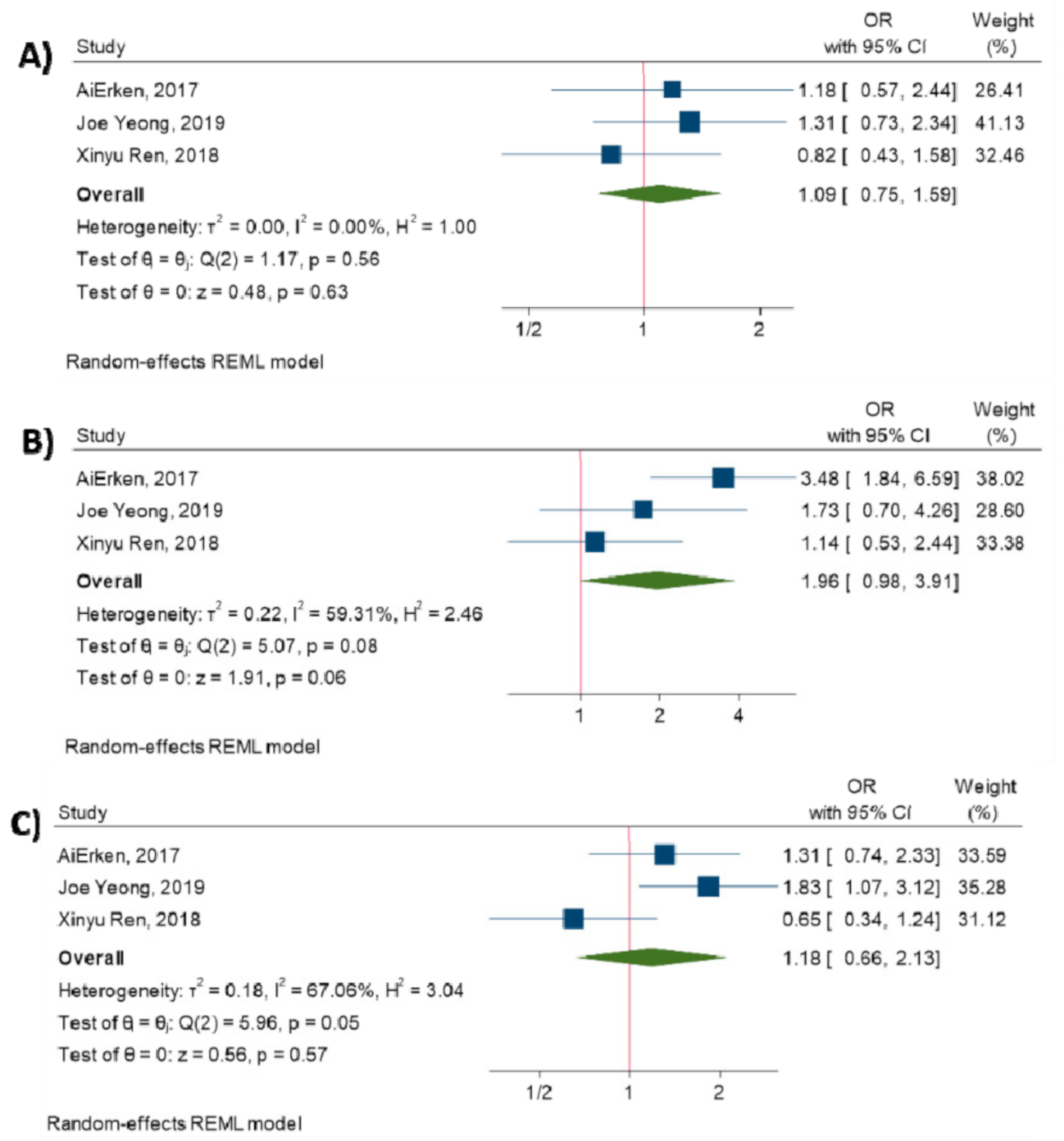
3.3. Expression of PD-L1 and Clinicopathological Features
3.4. TILs and Clinicopathological Features
3.5. Relationship between PD-L1 Expression and Survival
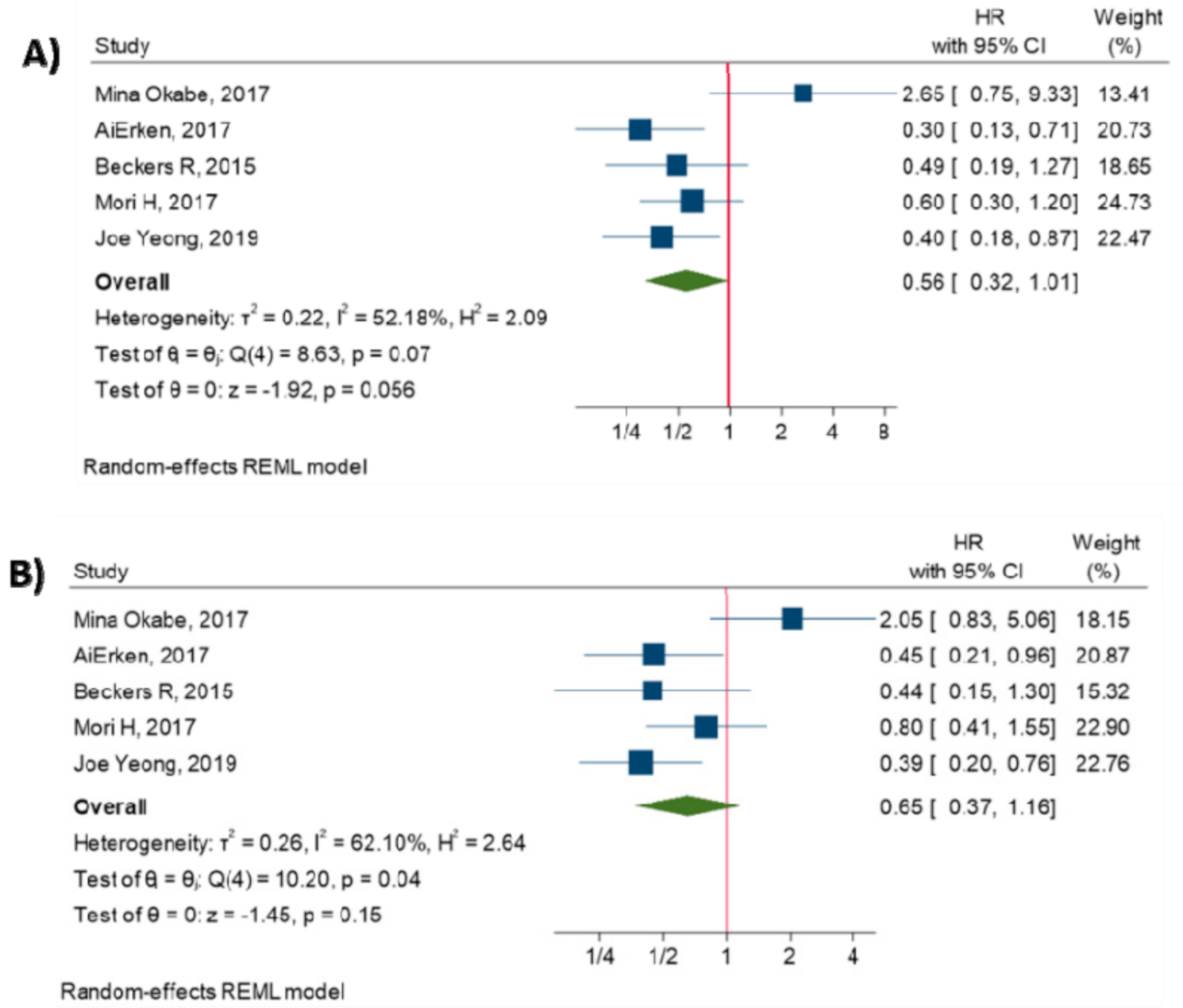
3.6. Relationship between TILs and Survival
3.7. Relationship between PD-L1 Expression and TILs
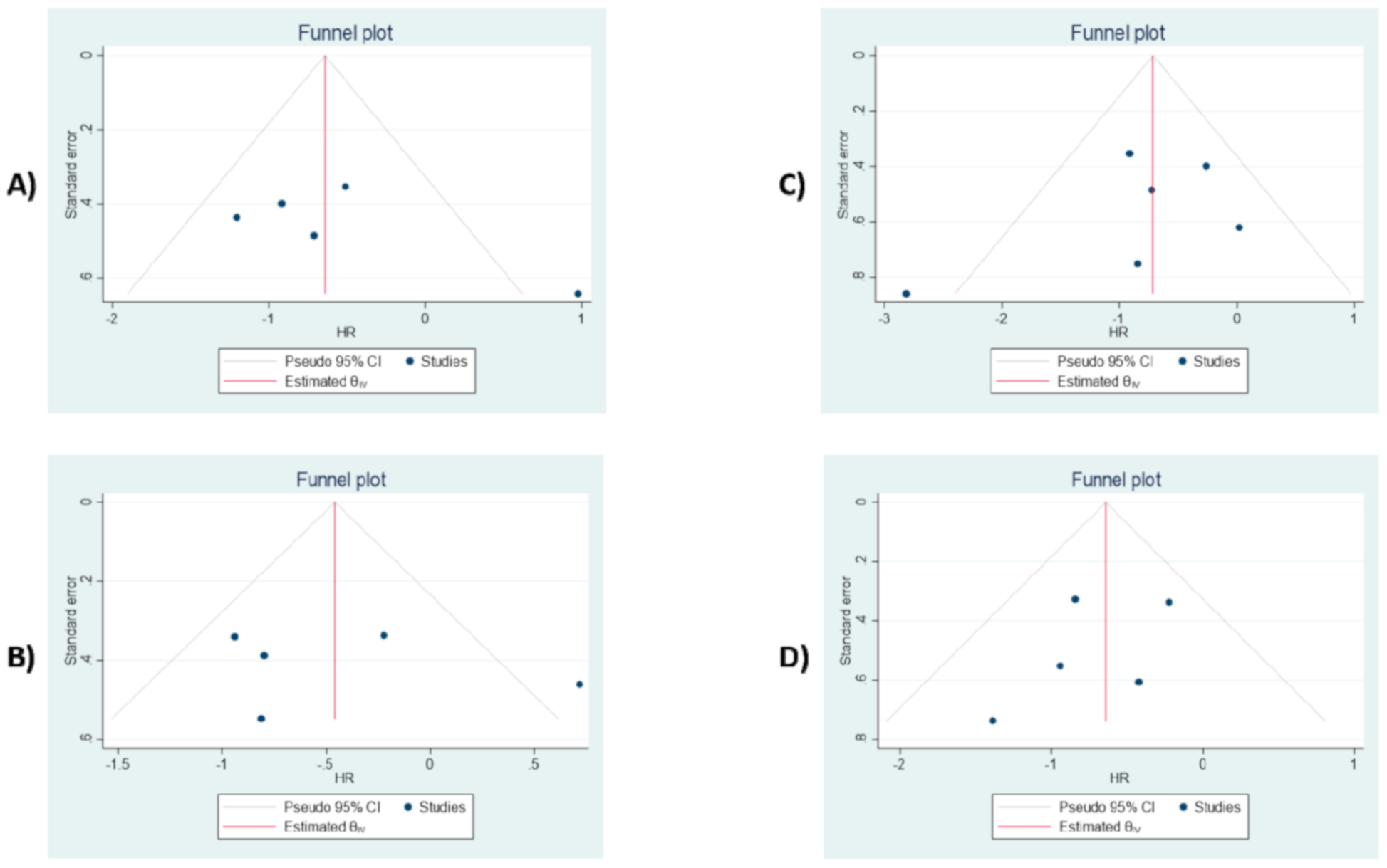
3.8. Publication Bias
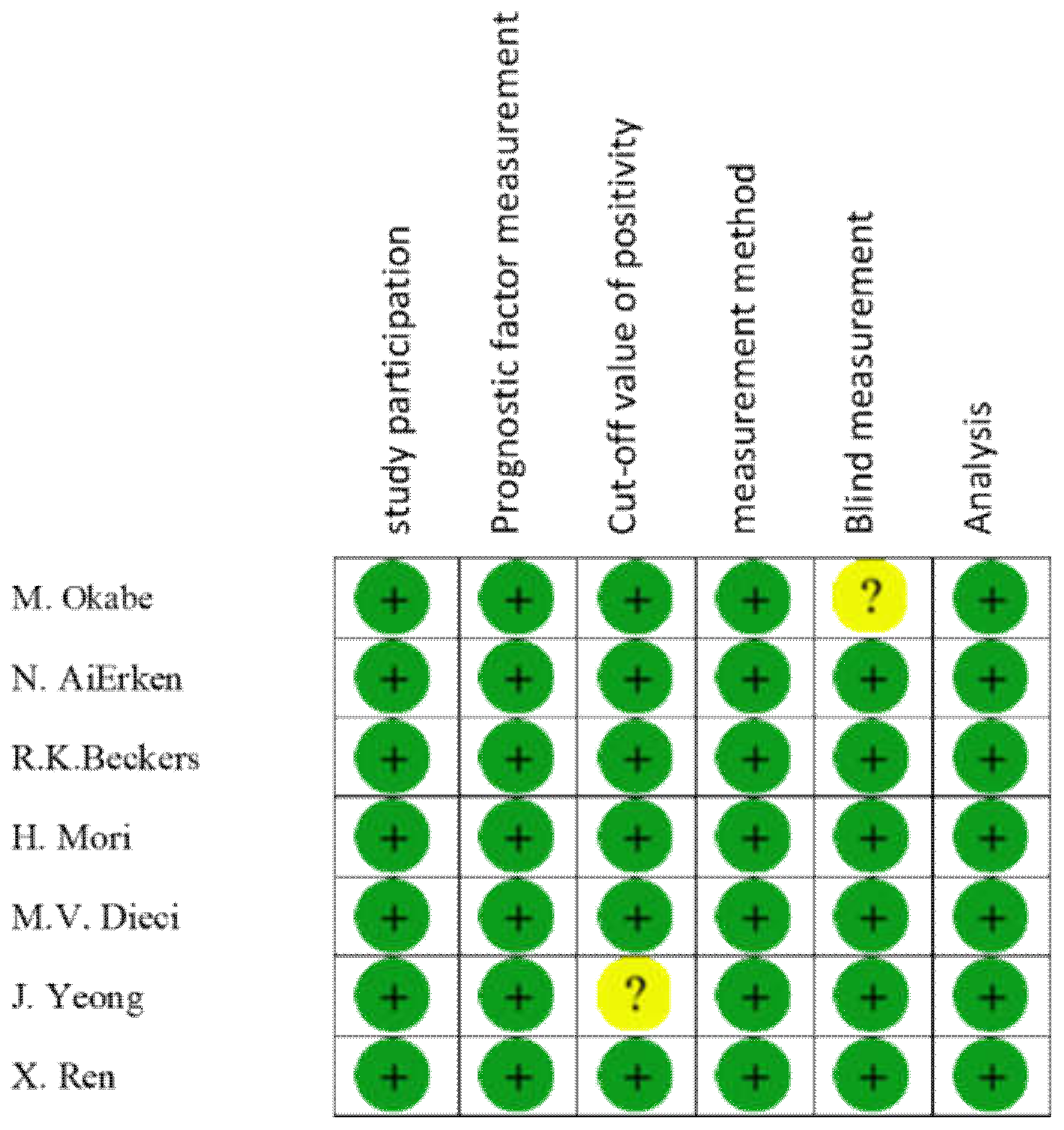
3.9. Bias Assessment in Included Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.-M.; Lee, A. Prognostic Role and Clinical Association of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte, Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression with Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Locally Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 51, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudis, C.A.; Gianni, L. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: An Unmet Medical Need. Oncologist 2011, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Sahin, A.A.; Huo, L.; Ward, K.C.; O’Regan, R.; Torres, M.A.; Meisel, J.L. Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 161, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; Dranoff, G. The biologic importance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labani-Motlagh, A.; Ashja-Mahdavi, M.; Loskog, A. The Tumor Microenvironment: A Milieu Hindering and Obstructing Antitumor Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormoen, G.W.; Crittenden, M.R.; Gough, M.J. Role of the immunosuppressive microenvironment in immunotherapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1 (PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, L.B.; Devaud, C.; Duong, C.P.M.; Yong, C.S.; Beavis, P.A.; Haynes, N.M.; Chow, M.T.; Smyth, M.J.; Kershaw, M.H.; Darcy, P. Anti-PD-1 Antibody Therapy Potently Enhances the Eradication of Established Tumors By Gene-Modified T Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5636–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagg, J.; Allard, B. Immunotherapeutic approaches in triple-negative breast cancer: Latest research and clinical prospects. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2013, 5, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.M. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, breast cancer subtypes and therapeutic efficacy. OncoImmunology 2013, 2, e24720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieci, M.V.; Tsvetkova, V.; Orvieto, E.; Piacentini, F.; Ficarra, G.; Griguolo, G.; Miglietta, F.; Giarratano, T.; Omarini, C.; Bonaguro, S.; et al. Immune characterization of breast cancer metastases: Prognostic implications. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, J.; Lim, J.C.T.; Lee, B.; Li, H.; Ong, C.C.H.; Thike, A.A.; Yeap, W.H.; Yang, Y.; Lim, A.Y.H.; Tay, T.K.Y.; et al. Prognostic value of CD8 + PD-1+ immune infiltrates and PDCD1 gene expression in triple negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Kubo, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nishimura, R.; Osako, T.; Arima, N.; Okumura, Y.; Okido, M.; Yamada, M.; Kai, M.; et al. The combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15584–15592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, R.K.; Selinger, C.I.; Vilain, R.; Madore, J.; Wilmott, J.; Harvey, K.; Holliday, A.; Cooper, C.L.; Robbins, E.; Gillett, D.; et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and improved outcome. Histopathology 2016, 69, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aierken, N.; Shi, H.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, N.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Lin, Y. High PD-L1 Expression Is Closely Associated With Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Leads to Good Clinical Outcomes in Chinese Triple Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, M.; Toh, U.; Iwakuma, N.; Saku, S.; Akashi, M.; Kimitsuki, Y.; Seki, N.; Kawahara, A.; Ogo, E.; Itoh, K.; et al. Predictive factors of the tumor immunological microenvironment for long-term follow-up in early stage breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.M.; Al-Foheidi, M.E.; Al-Mansour, M.M.; Kazkaz, G.A. The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 148, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Pu, H.; Zhang, Q. Expression of PD-L1 and prognosis in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31347–31354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, J.A.; Côté, P.; Bombardier, C. Evaluation of the Quality of Prognosis Studies in Systematic Reviews. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.J.; Thompson, S.G. A Likelihood Approach to Meta—Analysis with Random Effects. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating Characteristics of a Rank Correlation Test for Publication Bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Liang, Z. PD1 protein expression in tumor infiltrated lymphocytes rather than PDL1 in tumor cells predicts survival in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikas, A.; Zerdes, I.; Lövrot, J.; Richard, F.; Sotiriou, C.; Bergh, J.; Valachis, A.; Foukakis, T. Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Immunohistochemistry and Pooled Analysis of Transcriptomic Data. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Teng, F.; Kong, L. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 5023–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.B.; Cho, H.D.; Oh, M.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, S.-H.; Hong, S.A.; Cho, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Expression of Programmed Death Receptor Ligand 1 with High Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Is Associated with Better Prognosis in Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2016, 19, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikas, P.; Borcherding, N.; Zhang, W. The clinical promise of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Author | Year | Country | Number of Patients | Cut-Off for PD-L1 (Positive/High Expression) | Cut-Off for TIL (Positive/High Expression) | PD-L1 Evaluation Method | TILs Evaluation Method | Follow-Up Time | Endpoint | Number of Patients with Experience of ICIs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M. Okabe [18] | 2017 | Japan | 21 | H-score > 3 | ≥50% | IHC | IHC | 127.3 | OS/DFS | 0 |
| 2 | N. AiErken [17] | 2017 | China | 215 | positive (>1) | (41% to 100%) | IHC | IHC | 67.7 (7–159) | OS/DFS | N/a |
| 3 | R. K. Beckers [16] | 2015 | Australia | 161 | H-score >100 | (score 3) > 60% | IHC | H&E | 55 (0–213) | OS/DFS | N/a |
| 4 | H. Mori [15] | 2017 | Japan | 248 | ≥50% | ≥50% | IHC | H&E | 68 (2–150) | OS/DFS | N/a |
| 5 | M. V. Dieci [13] | 2018 | Italy | 43 | ≥5% | ≥10% | IHC | H&E | unclear | OS | N/a |
| 6 | J. Yeong [14] | 2019 | Singapore | 269 | unclear | unclear | IHC | IHC | 97 (1–213) | OS/DFS | N/a |
| 7 | X. Ren [27] | 2018 | China | 195 | >25% | (score 3) > 60% | IHC | H&E | unclear | OS/DFS | N/a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lotfinejad, P.; Asghari Jafarabadi, M.; Abdoli Shadbad, M.; Kazemi, T.; Pashazadeh, F.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Jadidi Niaragh, F.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Vahed, N.; Silvestris, N.; et al. Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090704
Lotfinejad P, Asghari Jafarabadi M, Abdoli Shadbad M, Kazemi T, Pashazadeh F, Sandoghchian Shotorbani S, Jadidi Niaragh F, Baghbanzadeh A, Vahed N, Silvestris N, et al. Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(9):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090704
Chicago/Turabian StyleLotfinejad, Parisa, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Mahdi Abdoli Shadbad, Tohid Kazemi, Fariba Pashazadeh, Siamak Sandoghchian Shotorbani, Farhad Jadidi Niaragh, Amir Baghbanzadeh, Nafiseh Vahed, Nicola Silvestris, and et al. 2020. "Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study" Diagnostics 10, no. 9: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090704
APA StyleLotfinejad, P., Asghari Jafarabadi, M., Abdoli Shadbad, M., Kazemi, T., Pashazadeh, F., Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S., Jadidi Niaragh, F., Baghbanzadeh, A., Vahed, N., Silvestris, N., & Baradaran, B. (2020). Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Diagnostics, 10(9), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090704







