Expression of Transcript Variants of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes among Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Groups
2.2. Blood and Tissue Samples
2.3. Bioinformatical Analysis
2.4. Analysis of the Coding Region of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes by Direct cDNA Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Study Population Analysis
3.2. Analysis of the Expression Level of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes Isoforms
3.3. Expression Level of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes Transcript Variants and Aspirin Hypersensitivity
3.4. Analysis of Expression Levels of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes Transcript Variants in the Context of Clinical Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | acetylsalicylic acid |
| COX-1 | cyclooxygenase-1 (constitutive COX, prostaglandin G/H synthase1, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1, prostaglandin H2 synthase-1) |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 (inducible COX, prostaglandin G/H synthase-2, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase-2, prostaglandin H2 synthase-2) |
| CRSsNP | chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polys |
| CRSwNP | chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps |
| CT | computed tomography |
| FESS | functional endoscopic sinus surgery |
| NSAIDs | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| N-ERD | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs)-exacerbated respiratory disease |
| PTGS1 gene | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 gene |
| PTGS2 gene | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 gene |
| VAS | visual analogue scale |
References
- Kitzler, J.; Hill, E.; Hardman, R.; Reddy, N.; Philpot, R.; Eling, T.E. Analysis and quantification of splicing variants of the TPA-inducible PGHS-1 mRNA in tracheal epithelial cells. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 316, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-salmi, S.; Bernal-sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastan, D.; Fokkens, W.J.; Bachert, C.; Newson, R.B.; Bislimovska, J.; Bockelbrink, A.; Bousquet, P.J.; Brozek, G.; Bruno, A.; Dahlén, S.E.; et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe—An underestimated disease. A GA2LEN study. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 66, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Åkerlund, A.; Holmberg, K.; Melén, I.; Bende, M. Prevalence of nasal polyps in adults: The Skövde population-based study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2003, 112, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, J.; Seys, S.F.; Timmermans, M.; Levie, P.; Jorissen, M.; Fokkens, W.J.; Hellings, P.W. Real-life study showing uncontrolled rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery in a tertiary referral centre. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 72, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.M. Update on the molecular biology of nasal polyposis. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2005, 38, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, I.W.; Patel, N.N.; Cohen, N.A. Understanding the Role of Biofilms and Superantigens in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2018, 6, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Hirsch, A.G.; Nordberg, C.M.; Schwartz, B.S.; Mercer, D.G.; Mahdavinia, M.; Grammer, L.C.; Hulse, K.E.; Kern, R.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps, Asthma, and Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1061–1070.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.L. Rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis in aspirin sensitive and aspirin tolerant patients: Are they different? Thorax 2000, 55, S84–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makowska, J.S.; Burney, P.; Jarvis, D.; Keil, T.; Tomassen, P.; Bislimovska, J.; Brozek, G.; Bachert, C.; Baelum, J.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; et al. Respiratory hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs in Europe: The global allergy and asthma network (GA2LEN) survey. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 71, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.L.; Agache, I.; Bavbek, S.; Bakirtas, A.; Blanca, M.; Bochenek, G.; Bonini, M.; Heffler, E.; Klimek, L.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of NSAID-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease (N-ERD)—A EAACI position paper. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 74, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevens, W.W.; Schleimer, R.P. Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease as an Endotype of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2016, 36, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mastalerz, L.; Tyrak, K.E.; Ignacak, M.; Konduracka, E.; Mejza, F.; Ćmiel, A.; Buczek, M.; Kot, A.; Oleś, K.; Sanak, M. Prostaglandin E2 decrease in induced sputum of hypersensitive asthmatics during oral challenge with aspirin. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 74, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podwysocka, M.; Dąbrowska-Monti, K.; Fendler, W.; Pagacz, K.; Pietruszewska, W. Analysis of the impact of bronchial asthma and hypersensitivity to aspirin on the clinical course of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2019, 73, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaseki, D.; Potts, J.; Joos, G.; Baelum, J.; Haahtela, T.; Ahlström, M.; Matricardi, P.; Kramer, U.; Gjomarkaj, M.; Fokkens, W.; et al. The relation of airway obstruction to asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis and age: Results from a population survey of adults. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 69, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philpott, C.M.; Smith, R.; Davies-Husband, C.R.; Erskine, S.; Clark, A.; Welch, A.; Hopkins, C.; Carrie, S.; Ray, J.; Sunkaraneni, V.; et al. Exploring the association between ingestion of foods with higher potential salicylate content and symptom exacerbation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Data from the national chronic rhinosinusitis epidemiology study. Rhinology 2019, 57, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, I. Distinct functions of COX-1 and COX-2. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68–69, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Meade, E.A.; DeWitt, D.L. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase gene structure: Identification of the transcriptional start site and 5′-flanking regulatory sequences. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 293, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.T.; Hasstedt, S.J.; Bovill, E.G.; Callas, P.W.; Valliere, J.E.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.K.; Long, G.L. Characterization of the human prostaglandin H synthase 1 gene (PTGS1): Exclusion by genetic linkage analysis as a second modifier gene in familial thrombosis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2002, 13, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowski, M.G.; Thuresson, E.D.; Lakkides, K.M.; Rieke, C.J.; Micielli, R.; Smith, W.L.; Garavito, R.M. Structure of Eicosapentaenoic and Linoleic Acids in the Cyclooxygenase Site of Prostaglandin Endoperoxide H Synthase-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37547–37555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thuresson, E.D.; Lakkides, K.M.; Rieke, C.J.; Sun, Y.; Wingerd, B.A.; Micielli, R.; Mulichak, A.M.; Malkowski, M.G.; Garavito, R.M.; Smith, W.L. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-1: The functions of cyclooxygenase active site residues in the binding, positioning, and oxygenation of arachidonic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10347–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maekawa, M.; Sugano, K. Quantification of relative expression of genes with homologous sequences using fluorescence-based single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis—Application to lactate dehydrogenase and cyclooxygenase isozymes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1998, 36, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.L.; Botting, R.M.; Hla, T. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: The biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 387–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gyllfors, P.; Bochenek, G.; Overholt, J.; Drupka, D.; Kumlin, M.; Sheller, J.; Nizankowska, E.; Isakson, P.C.; Mejza, F.; Lefkowith, J.B.; et al. Biochemical and clinical evidence that aspirin-intolerant asthmatic subjects tolerate the cyclooxygenase 2-selective analgetic drug celecoxib. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halushka, M.K.; Walker, L.P.; Halushka, P.V. Genetic variation in cyclooxygenase 1: Effects on response to aspirin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.; Xu, Y.-M.; Li, J.; Huang, L.-F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Min, Q.-H.; Yang, W.-M.; et al. Mechanism of alternative splicing and its regulation. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddel, H.K.; Bateman, E.D.; Becker, A.; Boulet, L.P.; Cruz, A.A.; Drazen, J.M.; Haahtela, T.; Hurd, S.S.; Inoue, H.; De Jongste, J.C.; et al. A summary of the new GINA strategy: A roadmap to asthma control. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nizankowska-Mogilnicka, E.; Bochenek, G.; Mastalerz, L.; Świerczyńska, M.; Picado, C.; Scadding, G.; Kowalski, M.L.; Setkowicz, M.; Ring, J.; Brockow, K.; et al. EAACI/GA2LEN guideline: Aspirin provocation tests for diagnosis of aspirin hypersensitivity. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 62, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Browne, J.P.; Slack, R.; Lund, V.; Brown, P. The Lund-Mackay staging system for chronic rhinosinusitis: How is it used and what does it predict? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, V.J.; Kennedy, D.W. Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 117, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Mackey, K. Short technical reports. Modification of the TRI reagent procedure for isolation of RNA from polysaccharide- and proteoglycan-rich sources. Biotechniques 1995, 19, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chomczyński, P.; Sacchi, N. Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biolchem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Human Genome Project Website, University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser GRCh38/hg38. Available online: www.genome.ucsc.edu (accessed on 31 December 2013).
- Borkowska, E.M.; Konecki, T.; Pietrusiński, M.; Borowiec, M.; Jabłonowski, Z. MicroRNAs Which Can Prognosticate Agressiveness of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansorge, W.; Sproat, B.; Stegemann, J.; Schwager, C.; Zenke, M. Automated DNA sequencing: Ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 4593–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosner, B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics, 5th ed.; Duxbury Press: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, A.; Reginato, A.M.; Jimenez, S.A. Alternative splicing of human prostaglandin G/H synthase mRNA and evidence of differential regulation of the resulting transcripts by transforming growth factorbeta 1, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10816–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiagis, D. Rat colorectal tumours treated with a range of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs show altered cyclooxygenase-2 and cyclooxygenase-1 splice variant mRNA expression levels. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogiagis, D.; Glare, E.M.; Misajon, A.; Brown, W.; O’Brien, P.E. Cyclooxygenase-1 and an alternatively spliced mRNA in the rat stomach: Effects of aging and ulcers. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2017, 278, G820–G827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, N.V.; Dai, H.; Roos, K.L.T.; Evanson, N.K.; Tomsik, J.; Elton, T.S.; Simmons, D.L. COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: Cloning, structure, and expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13926–13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hla, T. Molecular characterization of the 5.2 KB isoform of the human cyclooxygenase-1 transcript. Prostaglandins 1996, 51, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinauer, C.; Censarek, P.; Kaber, G.; Weber, A.A.; Steger, G.; Klamp, T.; Schrör, K. Expression and translation of the COX-1b gene in human cells—No evidence of generation of COX-1b protein. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N. Cloning, Expression, and Functional Characterization of Human Cyclooxygenase-1 Splicing Variants: Evidence for Intron 1 Retention. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.G.; Kuroda, H.; Chandrasekharan, N.V.; Pelaez, R.P.; Simmons, D.L.; Bazan, N.G.; Lukiw, W.J. Cyclooxygenase-3 gene expression in alzheimer hippocampus and in stressed human neural cells. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanson, N. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Chicken and Mammalian Cyclooxygenase-2. Ph.D. Thesis, Brigham Young Univerity, Provo, UT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

| Phenotypic Trait | Study Group | Control Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All CRSwNP | Aspirin Tolerance | Aspirin Intolerance | |||||
| Number (%) | 206 (100) | 162 (78.64) | 44 (21.36) | 203 (100) | |||
| Females N (%) | 85 (41.26) | 62 (38.27) | 23 (52.27) | 71 (34.98) | |||
| Males N (%) | 121 (58.74) | 100 (61.73) | 21 (47.73) | 132 (65.02) | |||
| Mean age (range) | 46.1 (18–79) | 46.29 (18–79) | 45.20 (20–71) | 41.72 (18–65) | |||
| Mean age of CRSwNP diagnosis (range) | 39.79 (9–75) | 40.47 (9–75) | 36.49 (12–66) | ||||
| Bronchial asthma N (%) | 57 (27.67) | 22 (10.68) | 35 (16.99) | ||||
| Mean number of surgeries (range) | 1.40 (1–10) | 1.18 (1–7) | 2.89 (1–10) | ||||
| Mean preoperative VAS scale (SD) | 4.4 (2.2) | 4.5 (2.4) | 4.2 (2.0) | ||||
| Endoscopical extent of polyposis N (%): | R | L | R | L | R | L | |
| No polyps | 45 (21.84) | 54 (26.21) | 42 (25.93) | 50 (30.86) | 3(6.82) | 4 (9.10) | |
| 1 | 25 (12.14) | 24 (11.70) | 22 (13.58) | 20 (12.35) | 3 (6.82) | 4 (9.10) | |
| 2 | 113 (54.85) | 89 (43.20) | 81 (50.00) | 66 (40.74) | 32 (72.73) | 23 (52.27) | |
| 3 | 23 (11.17) | 39 (18.93) | 17 (10.49 | 26 (16.05) | 6 (13.63) | 13 (29.54) | |
| Mean Lund-Mackay CT score (SD) | 16.5 (6.5) | 14.9 (4.7) | 19.8 (6.2) | ||||
| Type of Variant | Group | Mean rank of Expression (Range, std.) | Median | Modal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COX1.1 | Study group | 4.48 (1.00–5.00; 1.09) | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| COX1.2 | 2.88 (1.00–5.00; 0.98) | 3.00 | 3.00 | |
| COX1.3 | 1.85 (1.00–5.00; 0.87) | 2.00 | 1.00 | |
| COX1.4 | 2.25 (1.00–5.00; 1.27) | 2.00 | 1.00 | |
| COX1.5 | 3.45 (1.00–5.00; 1.05) | 4.00 | 4.00 | |
| COX 2.1 | 2.23 (1.00–3.00; 0.67) | 2.00 | 2.00 | |
| COX 2.2 | 2.38 (1.00–3.00; 0.65) | 2.00 | 3.00 | |
| COX 2.3 | 1.27 (1.00–3.00; 0.59) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| COX1.1 | Control group | 3.78 (1.00–5.00; 0.95) | 4.00 | 3.00 |
| COX1.2 | 1.82 (1.00–4.00; 0.58) | 2.00 | 2.00 | |
| COX1.3 | 4.16 (2.00–5.00; 0.87) | 4.00 | 5.00 | |
| COX1.4 | 1.41 (1.00–5.00; 0.83) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| COX1.5 | 3.78 (1.00–5.00; 0.87) | 4.00 | 4.00 | |
| COX 2.1 | 2.54 (1.00–3.00; 0.54) | 3.00 | 3.00 | |
| COX 2.2 | 2.39 (1.00–3.00; 0.54) | 2.00 | 2.00 | |
| COX 2.3 | 1.07 (1.00–3.00; 0.34) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Type of Variant | Aspirin Tolerance Mean dCT (Range, std.) | Aspirin Intolerance Mean dCT (range, std.) | FC | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COX1.1 | 5.81 (0.98–9.07; 5.52) | 4.88 (0.13–10.58; 5.81) | 1.91 | 0.318 |
| COX1.2 | 10.43 (8.87–12.17; 4.45) | 9.37 (8.03–10.91; 4.30) | 2.08 | 0.034 |
| COX1.3 | 11.57 (9.66–13.41; 4.63) | 9.90 (7.12–12.07; 4.30) | 3.18 | 0.003 |
| COX1.4 | 11.31 (7.76–14.99; 5.62) | 9.59 (6.74–12.28; 5.14) | 3.29 | 0.049 |
| COX1.5 | 8.81 (6.83–11.04; 4.20) | 7.70 (5.71–9.69; 3.66) | 2.16 | 0.021 |
| COX2.1 | 6.54 (3.96–8.38; 4.33) | 5.32 (1.94–7.90; 3.56) | 2.33 | 0.124 |
| COX2.2 | 6.50 (4.10–8.04; 4.90) | 5.45 (2.52–7.82; 3.82) | 2.07 | 0.294 |
| COX2.3 | 10.66 (6.16–15.07; 6.46) | 9.64 (5.20–13.66; 6.00) | 2.03 | 0.348 |
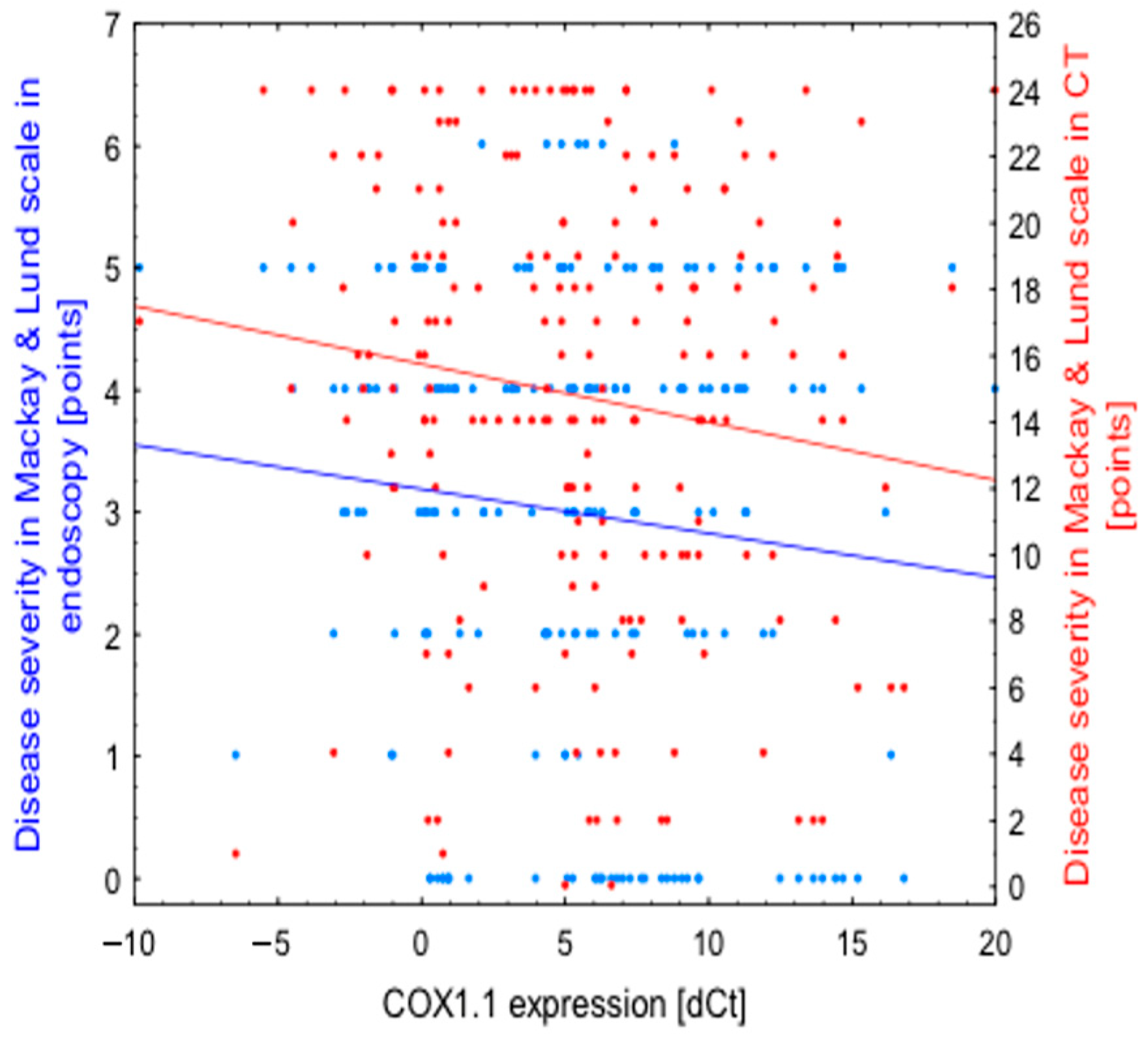
| Expression (in dCt) | Disease Severity in Endoscopic Evaluation | Disease Severity in Lund-Mackay CT Scale |
|---|---|---|
| COX1.1 | r = −0.1103 | r = -0.1462 |
| p = 0.118 | p = 0.038 | |
| COX1.2 | r = −0.0194 | r = −0.0552 |
| p = 0.785 | p = 0.436 | |
| COX1.3 | r = −0.0196 | r = −0.0009 |
| p = 0.781 | p = 0.990 | |
| COX1.4 | r = −0.0016 | r = −0.0887 |
| p = 0.982 | p = 0.210 | |
| COX1.5 | r = −0.0839 | r = −0.0579 |
| p = 0.234 | p = 0.412 | |
| COX2.1 | r = −0.0612 | r = −0.1065 |
| p = 0.385 | p = 0.130 | |
| COX2.2 | r = −0.0376 | r = −0.0458 |
| p = 0.613 | p = 0.537 | |
| COX2.3 | r = −0.0863 | r = −0.1063 |
| p = 0.227 | p = 0.136 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietruszewska, W.; Fendler, W.; Podwysocka, M.; Białas, A.J.; Kuna, P.; Kupryś-Lipińska, I.; Borowiec, M. Expression of Transcript Variants of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes among Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010135
Pietruszewska W, Fendler W, Podwysocka M, Białas AJ, Kuna P, Kupryś-Lipińska I, Borowiec M. Expression of Transcript Variants of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes among Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010135
Chicago/Turabian StylePietruszewska, Wioletta, Wojciech Fendler, Marta Podwysocka, Adam J. Białas, Piotr Kuna, Izabela Kupryś-Lipińska, and Maciej Borowiec. 2021. "Expression of Transcript Variants of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes among Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010135
APA StylePietruszewska, W., Fendler, W., Podwysocka, M., Białas, A. J., Kuna, P., Kupryś-Lipińska, I., & Borowiec, M. (2021). Expression of Transcript Variants of PTGS1 and PTGS2 Genes among Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Diagnostics, 11(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010135





