The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Imaging
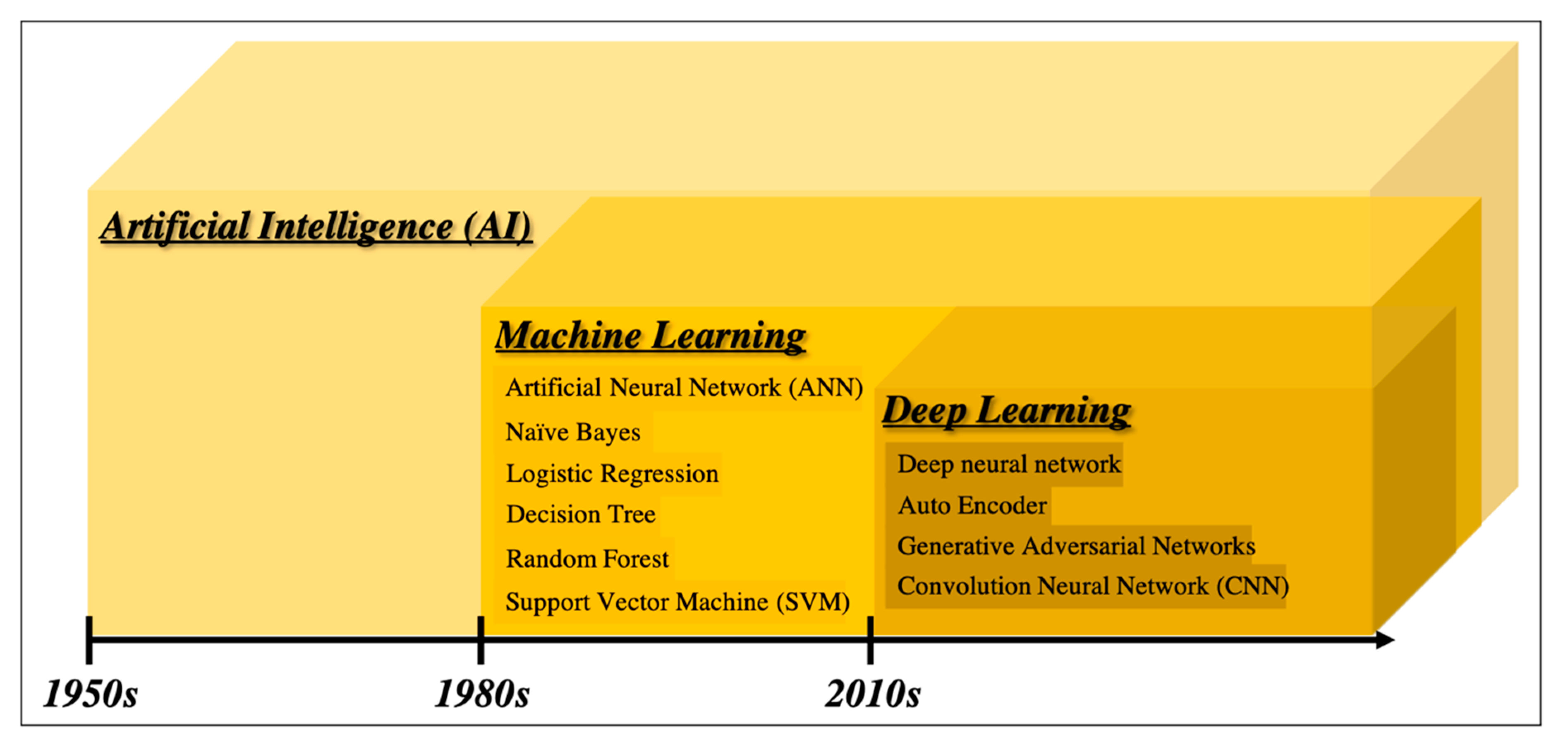
2.1. From Artificial Intelligence to Deep Learning
2.2. Computer-Aided Diagnosis
2.3. Support Vector Machine
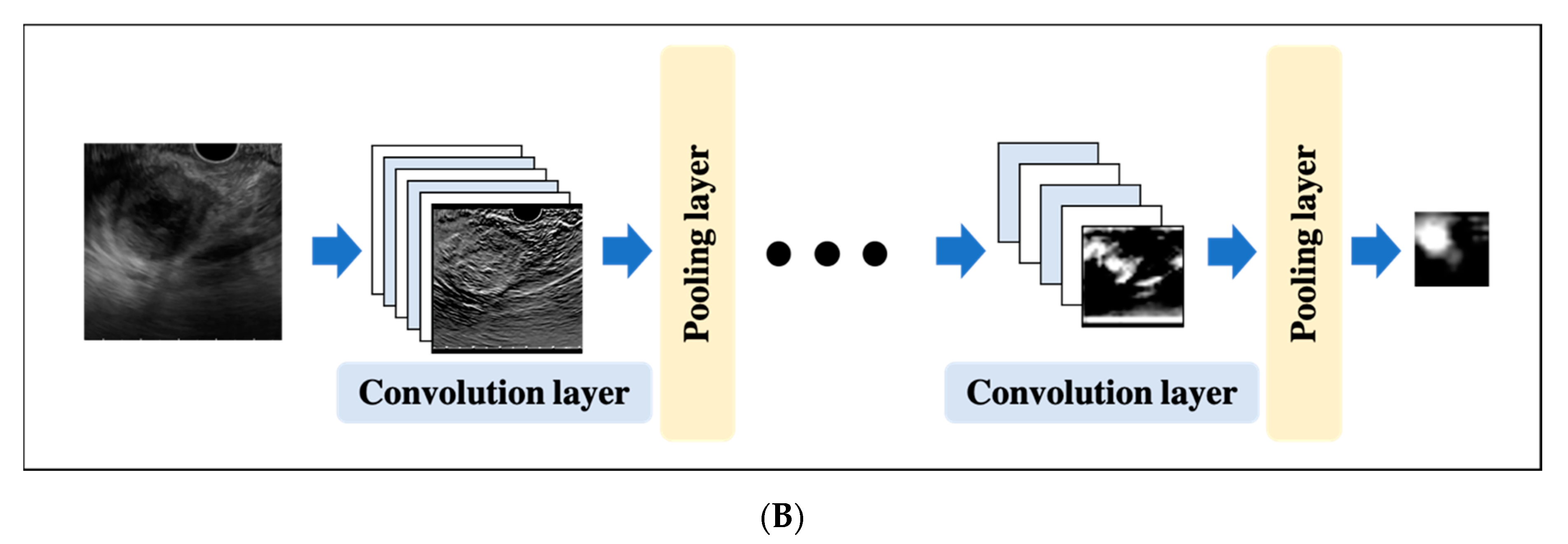
2.4. Convolutional Neural Network
2.5. Validating Methods in Machine Learning
2.5.1. Hold out Validation
2.5.2. K-Fold Cross-Validation
2.5.3. Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation
3. Literature Search
4. Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Pancreatic Endoscopic Ultrasound
4.1. Conventional Computer-Aided Diagnosis
4.2. Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egawa, S.; Toma, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Okusaka, T.; Nakao, A.; Hatori, T.; Maguchi, H.; Yanagisawa, A.; Tanaka, M. Japan Pancreatic Cancer Registry; 30th year anniversary: Japan Pancreas Society. Pancreas 2012, 41, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, M.; Yoshida, T.; Itonaga, M.; Tamura, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Yamashita, Y. Impact of endoscopic ultrasonography on diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, J.; Brady, P.G.; Freeman, M.; Gress, F.; Gross, G.W.; Hassall, E.; Hawes, R.; Jacobsen, N.A.; Liddle, R.A.; Ligresti, R.J.; et al. Guidelines for training in electronic ultrasound: Guidelines for clinical application. From the ASGE. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999, 49, 829–833. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Inciardi, M.F.; Edwards, A.V.; Papaioannou, J. Interpretation Time Using a Concurrent‒Read Computer‒Aided Detection System for Automated Breast Ultrasound in Breast Cancer Screening of Women With Dense Breast Tissue. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Lavin, P.T.; Birch, M.; Shah, N.; Folk, J.C. Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI‒based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices. Digit. Med. 2018, 39, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kudo, S.-E.; Misawa, M.; Saito, Y.; Ikematsu, H.; Hotta, K.; Ohtsuka, K.; Urushibara, F.; Kataoka, S.; Ogawa, Y. Real-Time Use of Artificial Intelligence in Identification of Diminutive Polyps During Colonoscopy: A Prospective Study. Ann Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, H.; Mann, R.; Gandhi, Z.; Perisetti, A.; Ali, A.; Aman Ali, K.; Sharma, N.; Saligram, S.; Tharian, B.; Inamdar, S. Scope of Artificial Intelligence in Screening and Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanesaka, T.; Lee, T.-C.; Uedo, N.; Lin, K.-P.; Chen, H.-Z.; Lee, J.-Y.; Wang, H.-P.; Chang, H.T. Computer-aided diagnosis for identifying and delineating early gastric cancers in magnifying narrow-band imaging. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-I.; Matsuda, T. Estimation of Invasion Depth: The First Key to Successful Colorectal ESD. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The perceptron: A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 2006, 65, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Schuurmans, D.; Wang, S. Augmenting naive bayes classifiers with statistical language models. Inf. Retr. 2004, 7, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.H.; Duncan, D.B. Estimation of the probability of an event as a function of several independent variables. Biometrika 1967, 54, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, J. Ross. Simplifying decision trees. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1987, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 1, p. 624. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved Techniques for Training GANs. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03498. [Google Scholar]
- Kido, S.; Hirano, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Computer-aided classification of pulmonary diseases: Feature extraction based method versus non-feature extraction based method. In Proceedings of the IWAIT2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Penang, Malaysia, 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 198–21111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Kim, K.; Dong, B.; El Fakhri, G.; Li, Q. End‒to‒End Lung Nodule Detection in Computed Tomography. In International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, W.S. What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasaka, K.; Akai, H.; Kunimatsu, A.; Kiryu, S.; Abe, O. Deep learning with convolutional neural network in radiology. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2018, 36, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Net Works. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv Preprint 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; REN, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, I.D.; Zheng, Y.; Wiersema, M.S.; Greenleaf, J.; Clain, J.E.; Dimagno, E.P. Neural network analysis of EUS images to differentiate between pancreatic malignancy and pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001, 54, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Nguyen, C.C.; Li, F.; Li, B. Digital image analysis of EUS images accurately differentiates pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis and normal tissue. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Yang, H.; Jin, Z.D.; Yu, J.G.; Cai, Z.Y.; Li, Z.S. Differential diagnosis of pancreatic cancer from normal tissue with digital imaging processing and pattern recognition based on a support vector machine of EUS images. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Janssen, J.; Hocke, M.; Larsen, M.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Arcidiacono, P.; Will, U.; Giovannini, M.; et al. European EUS Elastography Multicentric Study Group. Efficacy of an artificial neural network-based approach to endoscopic ultrasound elastography in diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 84–90.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. Differentiation of pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis using computer-aided diagnosis of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) images: A diagnostic test. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Dietrich, C.F.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Hocke, M.; Seicean, A.; Ignee, A.; Hassan, H.; Streba, C.T.; Ioncică, A.M.; et al. Quantitative contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS in differential diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, M.; Ozkan, M.; Cakiroglu, M.; Kocaman, O.; Yilmaz, B.; Can, G.; Korkmaz, U.; Dandil, E.; Eksi, Z. Age-based computer-aided diagnosis approach for pancreatic cancer on endoscopic ultrasound images. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Okuno, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Obata, M.; Kurita, Y.; Koda, H.; Toriyama, K.; Onishi, S.; et al. Usefulness of Deep Learning Analysis for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, L.; Ding, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; An, P.; et al. Deep learning-based pancreas segmentation and station recognition system in EUS: Development and validation of a useful training tool (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 874–885.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonozuka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Nagata, N.; Kojima, H.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Mukai, S. Deep learning analysis for the detection of pancreatic cancer on endosonographic images: A pilot study. J. Hepato-Biliary Pancreat. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]





| Author | Year | Objective | Case Number | Analysis Target | Type of CAD | Algorithm of AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norton ID [31] | 2001 | Classification (PC vs. CP) | 35 | Grayscale pixels from B-mode image | Conventional CAD | Basic neural network |
| Das A [32] | 2008 | Classification (PC vs. CP and NP) | 56 | Texture features from B-mode image | Conventional CAD | ANN (multilayered perceptron) |
| Zhang MM [33] | 2010 | Classification (PC vs. CP and NP) | 216 | Texture features from B-mode image | Conventional CAD | SVM |
| Saftoiu A [34] | 2012 | Classification (PC vs. CP) | 258 | Hue histogram from EUS-elastgraphy | Conventional CAD | ANN (multilayered perceptron) |
| Zhu M [35] | 2013 | Classification (PC vs. CP) | 388 | Texture features from B-mode image | Conventional CAD | SVM |
| Saftoiu A [36] | 2015 | Classification (PC vs. CP) | 167 | Parameters of time-intensity curve from contrast-enhanced EUS | Conventional CAD | ANN |
| Ozkan M [37] | 2016 | Classification (PC vs. NP) | 172 | Digital features from B-mode image | Conventional CAD | ANN |
| Kuwahara T [38] | 2019 | Classification (malignant IPMN vs. benign IPMN) | 50 | B-mode image | Deep Learning based CAD | CNN |
| Zhang J [39] | 2020 | EUS station recognition and pancreas segmentation | 480 | B-mode image | Deep Learning based CAD | CNN |
| Tonozuka R [40] | 2020 | Detection of PC | 139 | B-mode image | Deep Learning based CAD | CNN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonozuka, R.; Mukai, S.; Itoi, T. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Disorders. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010018
Tonozuka R, Mukai S, Itoi T. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Disorders. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonozuka, Ryosuke, Shuntaro Mukai, and Takao Itoi. 2021. "The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Disorders" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010018
APA StyleTonozuka, R., Mukai, S., & Itoi, T. (2021). The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Disorders. Diagnostics, 11(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010018






