PIC-GAN: A Parallel Imaging Coupled Generative Adversarial Network for Accelerated Multi-Channel MRI Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
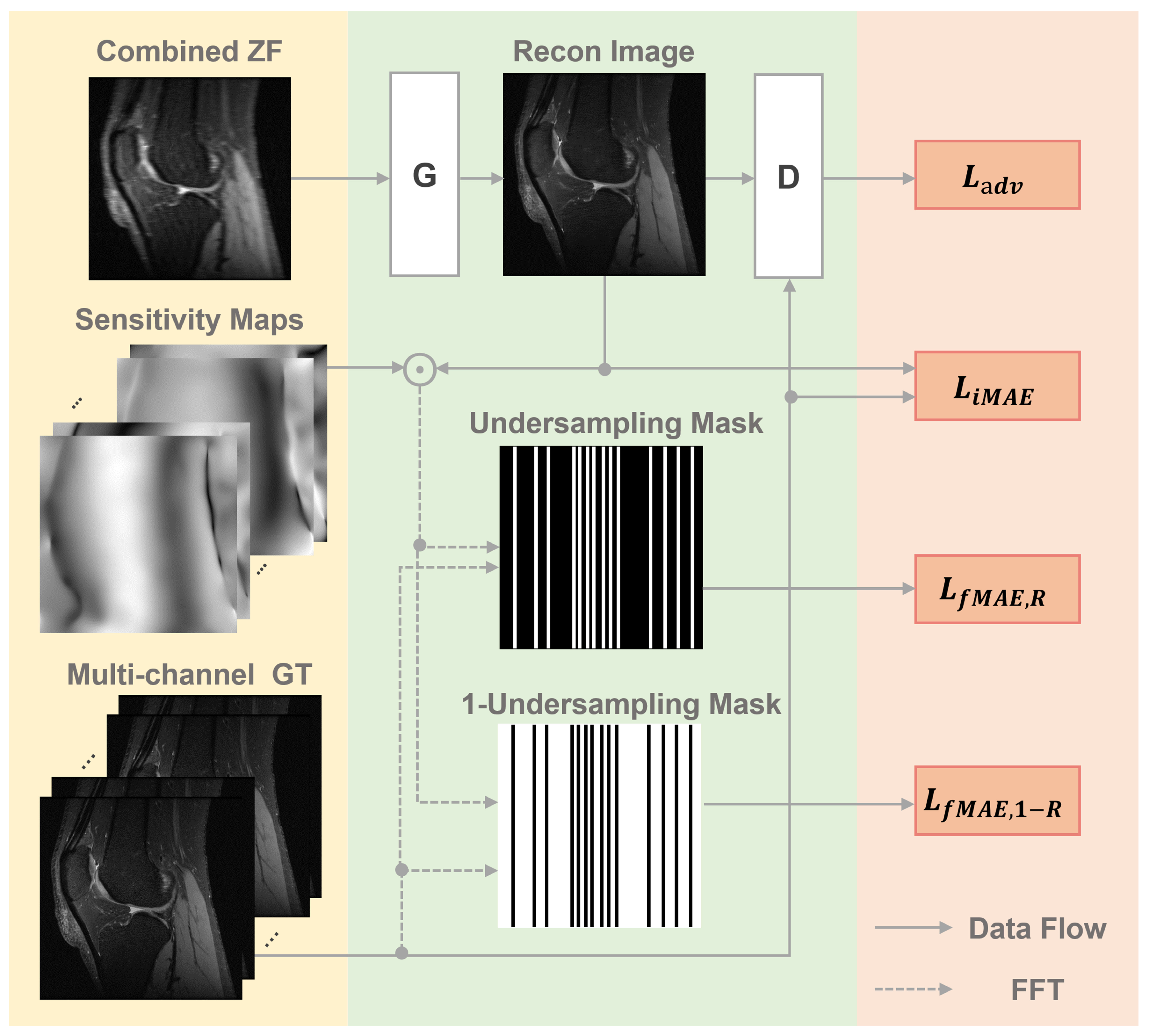
2.2. The Proposed PIC-GAN Reconstruction Framework
2.2.1. Datasets
2.2.2. Comparison Studies, Experimental Settings and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Reconstruction Results: Abdominal MRI Data
3.2. Reconstruction Results: Knee MRI Data
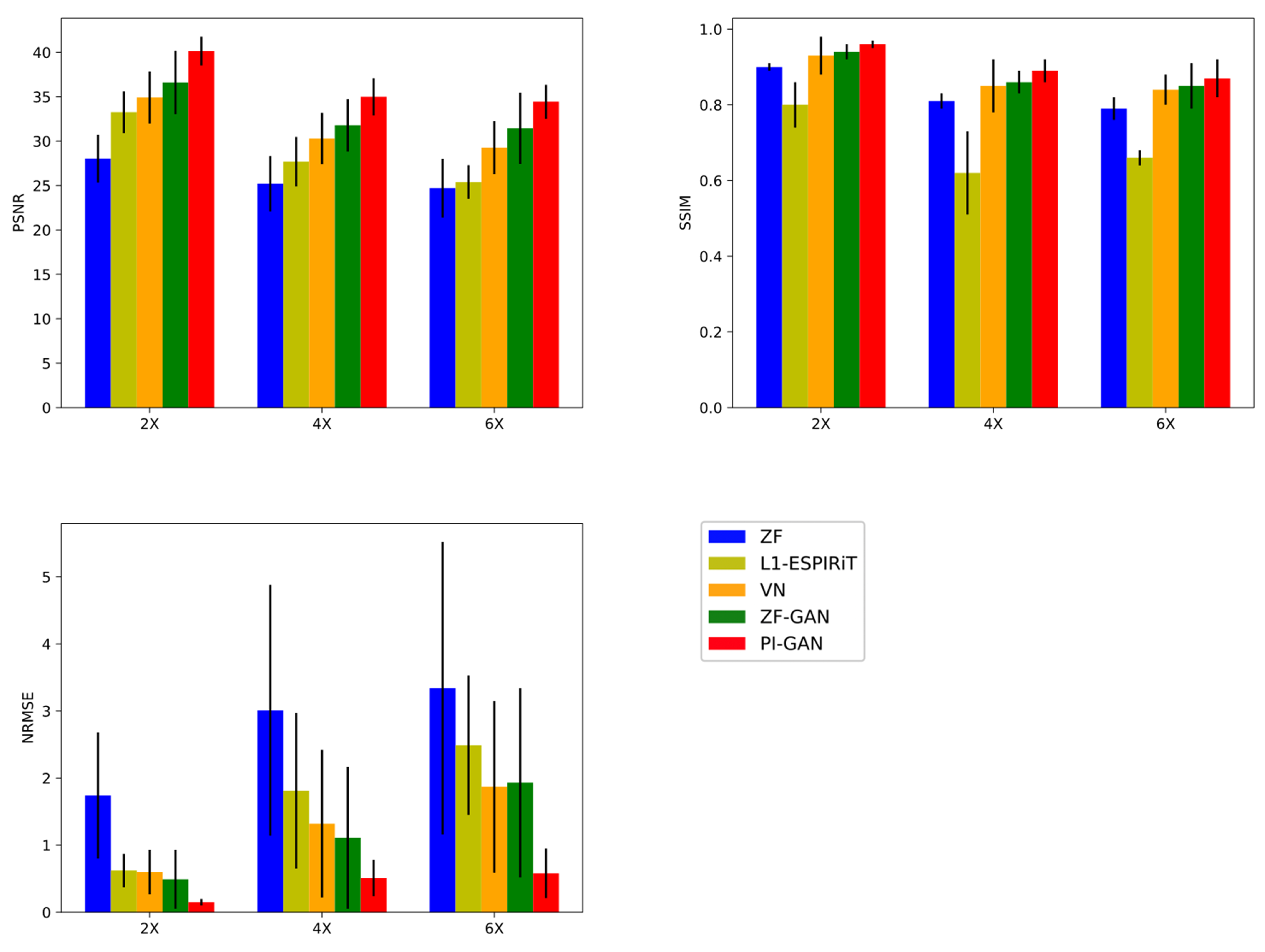
3.3. Quantitative Evaluations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sodickson, D.K.; Manning, W.J. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): Fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruessmann, K.P.; Weiger, M.; Scheidegger, M.B.; Boesiger, P. SENSE: Sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, M.A.; Jakob, P.M.; Heidemann, R.M.; Nittka, M.; Jellus, V.; Wang, J.; Kiefer, B.; Haase, A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deshmane, A.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A.; Seiberlich, N. Parallel MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robson, P.M.; Grant, A.K.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Lattanzi, R.; Sodickson, D.K.; McKenzie, C.A. Comprehensive quantification of signal-to-noise ratio and g-factor for image-based and k-space-based parallel imaging reconstructions. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, J.; Franson, D.; Seiberlich, N. Recent advances in parallel imaging for MRI. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 101, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Pauly, J.M. SPIRiT: Iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.; Sung, K.; Nayak, K.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Ye, J.C. k-t FOCUSS: A general compressed sensing framework for high resolution dynamic MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, J.P.; Zhuo, J. P-LORAKS: Low-rank modeling of local k-space neighborhoods with parallel imaging data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingala, S.G.; Hu, Y.; Dibella, E.; Jacob, M. Accelerated Dynamic MRI Exploiting Sparsity and Low-Rank Structure: K-t SLR. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sumbul, U.; Santos, J.M.; Pauly, J.M. A Practical Acceleration Algorithm for Real-Time Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 2042–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravishankar, S.; Bresler, Y. MR Image Reconstruction From Highly Undersampled k-Space Data by Dictionary Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Su, Z.; Ying, L.; Peng, X.; Zhu, S.; Liang, F.; Feng, D.; Liang, D. Accelerating magnetic resonance imaging via deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Prague, Czech Republic, 13–16 April 2016; pp. 514–517. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Deep ADMM-Net for compressive sensing MRI. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper, J.; Caballero, J.; Hajnal, J.V.; Price, A.N.; Rueckert, D. A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 37, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Yoo, J.; Ye, J.C. Deep artifact learning for compressed sensing and parallel MRI. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01120. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Reconstruction of undersampled radial free-breathing 3D abdominal MRI using stacked convolutional auto-encoders. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, J.; Xing, L. Self-attention convolutional neural network for improved MR image reconstruction. Inf. Sci. 2019, 490, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G. Deep Attentive Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks for MRI Reconstruction with Recurrent Context-Awareness. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Shitrit, O.; Raviv, T.R. Accelerated magnetic resonance imaging by adversarial neural network. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yu, S.; Dong, H.; Slabaugh, G.; Dragotti, P.L.; Ye, X.; Liu, F.; Arridge, S.; Keegan, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. DAGAN: Deep de-aliasing generative adversarial networks for fast compressed sensing MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 37, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, T.M.; Nguyen-Duc, T.; Jeong, W.K. Compressed sensing MRI reconstruction using a generative adversarial network with a cyclic loss. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Xia, L.; Li, T. Accelerating CS-MRI reconstruction with fine-tuning Wasserstein generative adversarial network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 152347–152357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, E.K.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S.; Ong, F. Unsupervised MRI Reconstruction with Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.13065. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Menpes-Smith, W.; Niu, Z.; Yang, G. SARA-GAN: Self-Attention and Relative Average Discriminator Based Generative Adversarial Networks for Fast Compressed Sensing MRI Reconstruction. Front. Neuroinform. 2020, 14, 611666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammernik, K.; Klatzer, T.; Kobler, E.; Recht, M.P.; Sodickson, D.K.; Pock, T.; Knoll, F. Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Han, F.; Ghodrati, V.; Gao, Y.; Yin, W.; Yang, Y.; Hu, P. Parallel imaging and convolutional neural network combined fast MR image reconstruction: Applications in low-latency accelerated real-time imaging. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 3399–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, H.; Ying, L.; Xiao, T.; Ke, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Liang, D. DeepcomplexMRI: Exploiting deep residual network for fast parallel MR imaging with complex convolution. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 68, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eksioglu, E.M. Decoupled algorithm for MRI reconstruction using nonlocal block matching model: BM3D-MRI. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2016, 56, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçakaya, M.; Basha, T.A.; Chan, R.H.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Accelerated isotropic sub-millimeter whole-heart coronary MRI: Compressed sensing versus parallel imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akçakaya, M.; Basha, T.A.; Goddu, B.; Goepfert, L.A.; Kissinger, K.V.; Tarokh, V.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Low-dimensional-structure self-learning and thresholding: Regularization beyond compressed sensing for MRI reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Grimm, R.; Block, K.T.; Chandarana, H.; Kim, S.; Xu, J.; Axel, L.; Sodickson, D.K.; Otazo, R. Golden-angle radial sparse parallel MRI: Combination of compressed sensing, parallel imaging, and golden-angle radial sampling for fast and flexible dynamic volumetric MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: http://old.mridata.org/undersampled/abdomens (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Available online: http://mridata.org/fullysampled/knees (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Tamir, J.I.; Ong, F.; Cheng, J.Y.; Uecker, M.; Lustig, M. Generalized Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction Using the Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox; ISMRM Workshop on Data Sampling & Image Reconstruction: Sedona, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Uecker, M.; Lai, P.; Murphy, M.J.; Virtue, P.; Elad, M.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S.; Lustig, M. ESPIRiT—An eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: Where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tensorpack. 2016. Available online: https://githubcom/tensorpack/ (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Tensorflow. Available online: http://www.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Wang, C.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Du, Y.P. Correction of out-of-FOV motion artifacts using convolutional neural network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 71, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, P.J.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Ohliger, M.A.; Elad, M.; Pauly, J.M.; Vigneron, D.B.; Lustig, M. Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on structured low-rank matrix completion. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlemper, J.; Duan, J.; Ouyang, C.; Qin, C.; Caballero, J.; Hajnal, J.V.; Rueckert, D. Data consistency networks for (calibration-less) accelerated parallel MR image reconstruction. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11795. [Google Scholar]





| R | METHOD | REGULAR | RANDOM | TIME (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | |||
| 2-FOLD | ZF | 28.03 ± 2.68 | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 1.74 ± 0.94 | 34.66 ± 2.98 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.33 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 33.25 ± 2.34 | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 0.62 ± 0.25 | 33.69 ± 1.48 | 0.81 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 143.71 ± 1.20 | |
| VN | 34.99 ± 2.09 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.27 | 33.20 ± 2.82 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.63 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | |
| ZF-GAN | 34.91 ± 2.92 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 0.60 ± 0.33 | 37.22 ± 1.77 | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.00 | |
| PIC-GAN | 36.60 ± 3.57 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.44 | 39.59 ± 2.64 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.13 | 0.69 ± 0.00 | |
| 4-FOLD | ZF | 25.21 ± 3.13 | 0.81 ± 0.02 | 3.01 ± 1.87 | 27.31 ± 3.23 | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.15 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 27.69 ± 2.79 | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 1.81 ± 1.16 | 27.87 ± 0.78 | 0.70 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 0.46 | 143.01 ± 1.13 | |
| VN | 30.30 ± 2.88 | 0.85 ± 0.07 | 1.32 ± 1.10 | 30.72 ± 2.31 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 1.12 ± 0.51 | 0.38 ± 0.00 | |
| ZF-GAN | 31.79 ± 2.95 | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 1.11 ± 1.06 | 32.95 ± 2.57 | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.64 | 0.36 ± 0.00 | |
| PIC-GAN | 34.99 ± 2.09 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.27 | 33.20 ± 2.82 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.63 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | |
| 6-FOLD | ZF | 24.71 ± 3.31 | 0.79 ± 0.03 | 3.34 ± 2.18 | 25.15 ± 3.37 | 0.79 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.21 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 25.40 ± 1.88 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 2.49 ± 1.04 | 25.71 ± 2.94 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 2.49 ± 1.30 | 143.43 ± 2.18 | |
| VN | 29.26 ± 2.98 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 1.87 ± 1.28 | 20.76 ± 2.64 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 1.54 ± 0.97 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | |
| ZF-GAN | 31.45 ± 4.00 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | 1.93 ± 1.41 | 30.91 ± 2.72 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 1.42 ± 1.01 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | |
| PIC-GAN | 34.43 ± 1.92 | 0.87 ± 0.05 | 0.58 ± 0.37 | 31.76 ± 3.04 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 1.22 ± 0.97 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | |
| R | METHOD | REGULAR | RANDOM | TIME (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | |||
| 2-FOLD | ZF | 25.95 ± 1.42 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 5.25 ± 1.21 | 25.94 ± 1.19 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 5.28 ± 1.13 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 31.60 ± 1.27 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 0.89 ± 0.55 | 30.07 ± 1.00 | 0.73 ± 0.02 | 1.01 ± 0.61 | 67.18 ± 1.10 | |
| VN | 32.79 ± 1.42 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.60 ± 0.12 | 32.54 ± 1.43 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 0.57 ± 0.12 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | |
| ZF-GAN | 34.71 ± 1.31 | 0.86 ± 0.00 | 0.44 ± 0.08 | 34.45 ± 1.60 | 0.87 ± 0.00 | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | |
| PIC-GAN | 37.80 ± 1.02 | 0.91 ± 0.00 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 37.98 ± 1.02 | 0.91 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | |
| 4-FOLD | ZF | 24.27 ± 1.41 | 0.78 ± 0.03 | 8.05 ± 1.89 | 24.21 ± 1.23 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 8.04 ± 1.89 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 30.67 ± 1.38 | 0.59 ± 0.07 | 1.12 ± 0.57 | 28.98 ± 1.27 | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.22 | 66.12 ± 1.13 | |
| VN | 31.65 ± 1.31 | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 0.82 ± 0.21 | 31.23 ± 1.26 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.20 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | |
| ZF-GAN | 33.28 ± 1.27 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.19 | 33.10 ± 1.26 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.17 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | |
| PIC-GAN | 36.49 ± 1.30 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 36.17 ± 0.94 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.12 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | |
| 6-FOLD | ZF | 23.18 ± 1.45 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | 8.09 ± 1.91 | 22.44 ± 1.46 | 0.76 ± 0.04 | 8.98 ± 2.31 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| L1-ESPIRiT | 28.01 ± 0.98 | 0.55 ± 0.00 | 1.28 ± 0.24 | 27.52 ± 1.09 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 1.59 ± 0.10 | 66.02 ± 1.76 | |
| VN | 30.01 ± 1.01 | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.31 | 28.54 ± 1.22 | 0.80 ± 0.00 | 0.98 ± 0.10 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | |
| ZF-GAN | 31.47 ± 1.05 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.29 | 30.48 ± 1.24 | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.11 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | |
| PIC-GAN | 34.10 ± 1.09 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 0.80 ± 0.26 | 33.85 ± 1.11 | 0.85 ± 0.00 | 0.81 ± 0.10 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, G. PIC-GAN: A Parallel Imaging Coupled Generative Adversarial Network for Accelerated Multi-Channel MRI Reconstruction. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010061
Lv J, Wang C, Yang G. PIC-GAN: A Parallel Imaging Coupled Generative Adversarial Network for Accelerated Multi-Channel MRI Reconstruction. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Jun, Chengyan Wang, and Guang Yang. 2021. "PIC-GAN: A Parallel Imaging Coupled Generative Adversarial Network for Accelerated Multi-Channel MRI Reconstruction" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010061
APA StyleLv, J., Wang, C., & Yang, G. (2021). PIC-GAN: A Parallel Imaging Coupled Generative Adversarial Network for Accelerated Multi-Channel MRI Reconstruction. Diagnostics, 11(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010061







