Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography: Comparison of Radiation Exposure and Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. CT Myelography and CT Scanners
2.3. Dose Assessment
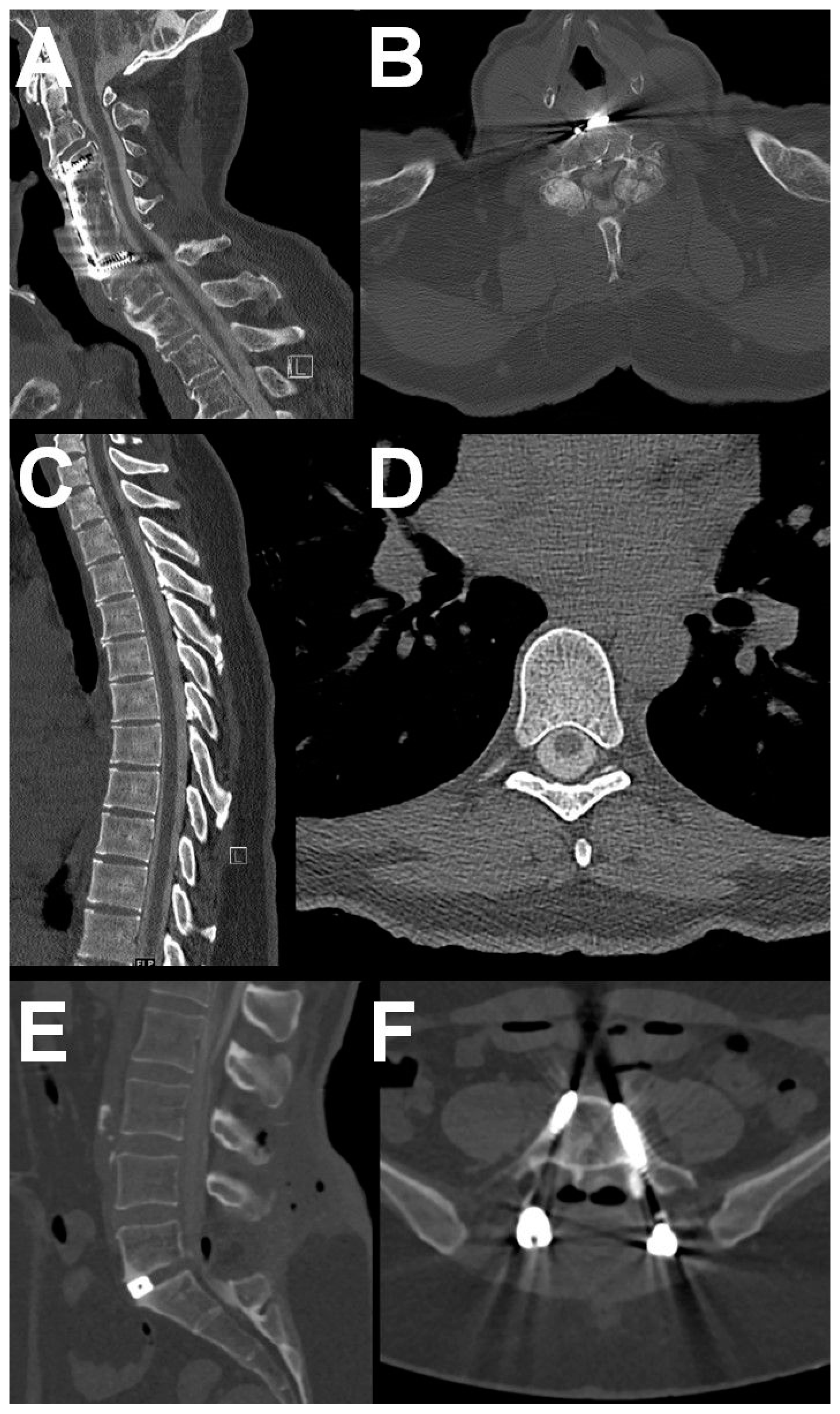
2.4. Image Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort
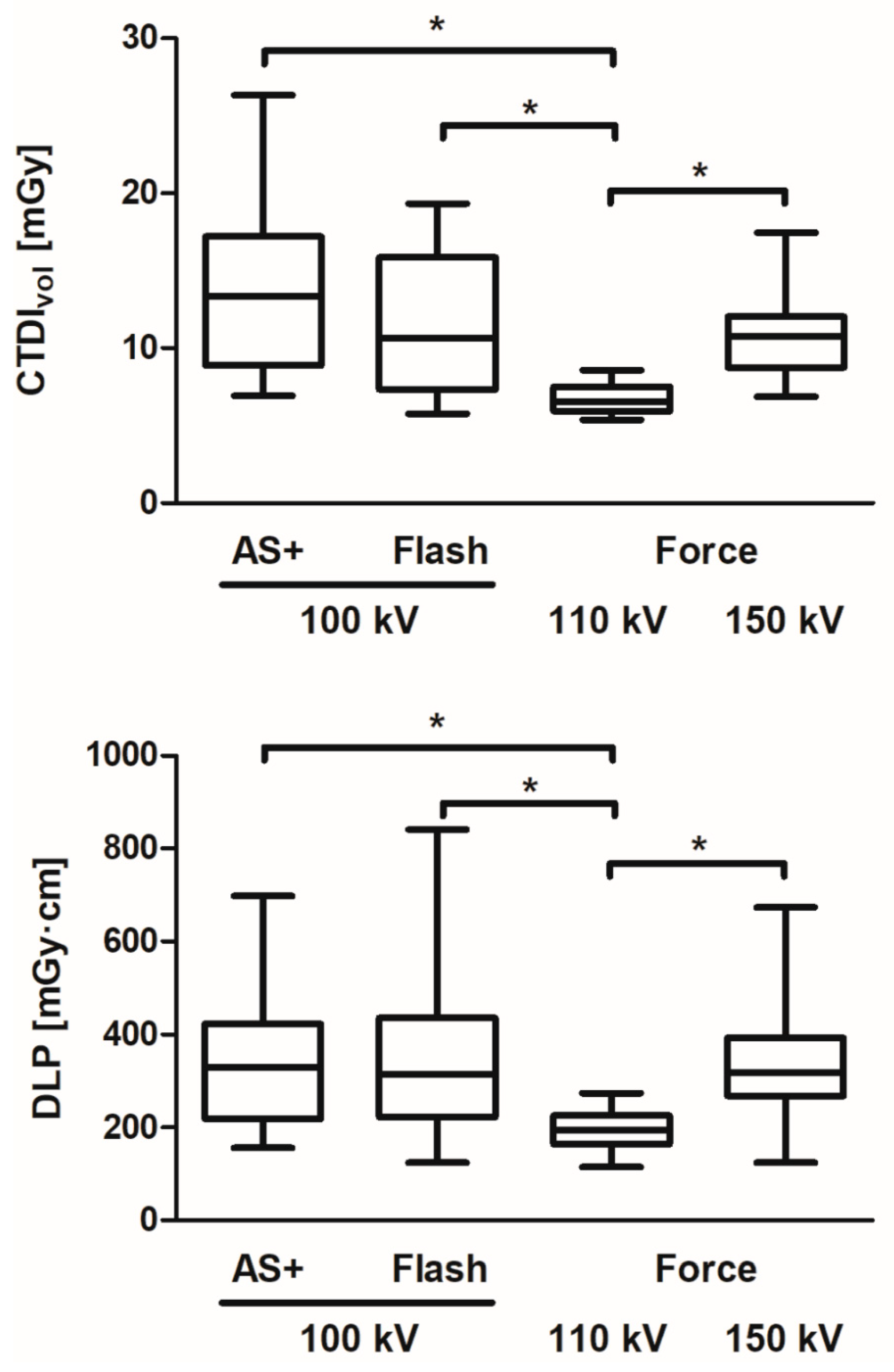
3.2. Radiation Exposure and DRLs
3.3. Comparison of Radiation Exposure of Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography
3.4. Dose Differences of CT Myelography Protocols for the Lumbar Spine
3.5. Image Quality of CT Myelography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harreld, J.H.; McMenamy, J.M.; Toomay, S.M.; Chason, D.P. Myelography: A primer. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2011, 40, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.M.; Weinberg, B.D.; Hoch, M.J. CT Myelography: Clinical Indications and Imaging Findings. Radiographics 2020, 40, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, S.R. Myelography: Modern technique and indications. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 135, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, A.A.; Das, M.; Stadler, A.A.R.; Wildberger, J.E. Dual-Energy CT: What the Neuroradiologist Should Know. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menon, S.K.; Onyia, C.U. A short review on a complication of lumbar spine surgery: CSF leak. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 139, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grams, A.; Sender, J.; Möritz, R.; Obert, M.; Stein, M.; Oertel, M.; Krombach, G.; Gizewski, E.; Schmidt, T. Dual Energy CT Myelography after Lumbar Osteosynthesis. Rofo 2014, 186, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deak, P.D.; Smal, Y.; Kalender, W.A.; Multisection, C.T. Protocols: Sex- and Age-specific Conversion Factors Used to Determine Effective Dose from Dose-Length Product. Radiology 2010, 257, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrimpton, P.; Wall, B. The Increasing Importance of X ray Computed Tomography as a Source of Medical Exposure. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1995, 57, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, P.J.; Guest, W.C.; Van Prooijen, M.; Farb, R.I. Digital Subtraction Myelography is Associated with Less Radiation Dose than CT-based Techniques. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2021, 31, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrocky, T.; Mosimann, P.J.; Zibold, F.; Mordasini, P.; Raabe, A.; Ulrich, C.T.; Gralla, J.; Beck, J.; Piechowiak, E.I. Cryptogenic Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Role of Dynamic CT Myelography. Radiology 2018, 289, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thielen, K.R.; Sillery, J.C.; Morris, J.M.; Hoxworth, J.; Diehn, F.E.; Wald, J.T.; Rosebrock, R.E.; Yu, L.; Luetmer, P.H. Ultrafast dynamic computed tomography myelography for the precise identification of high-flow cerebrospinal fluid leaks caused by spiculated spinal osteophytes. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 22, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. European Guidelines on Quality Criteria for Computed Tomography; EUR; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1999; Volume 16262. [Google Scholar]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements. Reference levels and achievable doses in medical and dental imaging: Recommendations for the United States. In NCRP Report; National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012; Volume 172. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz. Bekanntmachung der aktualisierten diagnostischen Referenzwerte für diagnostische und interventionelle Röntgenanwendungen. Bundesanzeiger, 15 July 2016.
- McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S.; Yu, L.; Cody, D.D.; Boone, J.M.; McNItt-Gray, M. CT Dose Index and Patient Dose: They AreNotthe Same Thing. Radiology 2011, 259, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Task Group on Control of Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Managing patient dose in computed tomography. Ann. ICRP 2000, 30, 7. [CrossRef]
- Bauhs, J.A.; Vrieze, T.J.; Primak, A.N.; Bruesewitz, M.R.; McCollough, C.H. CT Dosimetry: Comparison of Measurement Techniques and Devices. Radiographics 2008, 28, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, W.; Ogden, K.M.; Khorasani, M.R. Converting Dose-Length Product to Effective Dose at CT. Radiology 2008, 248, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, K.; Li, I.; Dowdell, T.; Gray, B.G. Identifying Institutional Diagnostic Reference Levels for CT with Radiation Dose Index Monitoring Software. Radiology 2015, 276, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, R.; Winklhofer, S.; Osterhoff, G.; Wanner, G.A.; Fortunati, M.; Andreisek, G.; Alkadhi, H.; Stolzmann, P. Metallic artefact reduction with monoenergetic dual-energy CT: Systematic ex vivo evaluation of posterior spinal fusion implants from various vendors and different spine levels. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, A.; Hoeffner, E.; Ibrahim, M.; Shah, G.V.; Lamarca, F.; Mukherji, S.K. Utility of Dual-Energy CT Virtual keV Monochromatic Series for the Assessment of Spinal Transpedicular Hardware-Bone Interface. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, R.G.; Oladghaffari, M.; Sajjadian, F.; Ghaziyani, M.F. Image Quality and Dose Comparison of Single-Energy CT (SECT) and Dual-Energy CT (DECT). Radiol. Res. Pr. 2020, 2020, 1403957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.M.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Hurwitz, L.M.; Nelson, R.C.; Marin, D.; Toncheva, G.; Schindera, S.T. Dual Energy Versus Single Energy MDCT: Measurement of Radiation Dose Using Adult Abdominal Imaging Protocols. Acad. Radiol. 2009, 16, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, W.; Schwarzwaelder, C.; Sommer, C.; Veloza, S.; Radeleff, B.; Kauczor, H. Dual-energy, standard and low-kVp contrast-enhanced CT-cholangiography: A comparative analysis of image quality and radiation exposure. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, D.; König, B.; Blex, S.; Zensen, S.; Opitz, M.; Maier, S.; Forsting, M.; Zylka, W.; Kühl, H.; Wetter, A.; et al. Experimental Examination of Radiation Doses Of Dual- and Single-Energy Computed Tomography in Chest And Upper Abdomen in a Phantom Study. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2021, 193, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler, T.; Fink, C.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Schoepf, U.J. Dual-Energy CT: Radiation Dose Aspects. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, S16–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenzle, J.C.; Sommer, W.H.; Neumaier, K.; Michalski, G.; Lechel, U.; Nikolaou, K.; Becker, C.R.; Reiser, M.F.; Johnson, T.R.C. Dual Energy CT of the Chest. Investig. Radiol. 2010, 45, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, J.; Rehani, M. Diagnostic Reference Levels. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W1–W3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CT Scanner | Siemens SOMATOM Definition AS+ | Siemens SOMATOM Definition Flash | Siemens SOMATOM Force 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collimation | 128 × 0.6 mm | 128 × 0.6 mm | 192 × 0.6 mm | ||
| No. of examinations | 44 | 15 | 48 | 48 | 28 |
| Dual-source mode | N/A | off | off | off | on |
| Tube voltage (kV) | 100 | 100 | 110 | 150 | 100/Sn150 2 |
| Reference effective tube current-time product (mAs) | 316 | 273 | 171 | 81 | 190/380 |
| Automatic tube current modulation | on | on | on | on | on |
| Rotation time (s) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 |
| CTDIvol [mGy] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Location | CT Scanner * | No. of Scans | Min | 25th Percentile | Median | 75th Percentile | Max | Mean | SD |
| (A) Whole spine | Total | 31 | 4.25 | 6.01 | 7.44 | 11.17 | 16.15 | 8.81 | 3.75 |
| AS+ | 4 | 10.13 | 11.16 | 14.84 | 15.97 | 16.15 | 13.99 | 2.69 | |
| Flash | 1 | - | - | 7.97 | - | - | - | - | |
| Force | 26 | 4.25 | 5.67 | 6.91 | 10.02 | 15.74 | 8.04 | 3.32 | |
| (B) Cervical spine | Total | 23 | 5.42 | 7.20 | 9.31 | 14.64 | 18.44 | 10.44 | 4.05 |
| AS+ | 4 | 7.57 | 7.96 | 9.85 | 10.66 | 10.69 | 9.49 | 1.47 | |
| Flash | 2 | 9.31 | - | 12.84 | - | 16.36 | 12.84 | 4.99 | |
| Force | 17 | 5.42 | 6.60 | 8.88 | 14.76 | 18.44 | 10.38 | 4.43 | |
| (C) Thoracic spine | Total | 10 | 5.66 | 6.14 | 6.80 | 8.26 | 24.58 | 8.74 | 5.72 |
| AS+ | 3 | 5.66 | - | 10.31 | - | 24.58 | 13.52 | 9.86 | |
| Flash | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Force | 7 | 5.75 | 6.27 | 6.60 | 7.25 | 7.58 | 6.69 | 0.63 | |
| (D) Lumbar spine | Total | 119 | 5.36 | 7.97 | 11.02 | 14.89 | 26.34 | 11.52 | 4.37 |
| AS+ | 33 | 6.91 | 8.88 | 13.35 | 17.20 | 26.34 | 13.63 | 5.15 | |
| Flash | 12 | 5.75 | 7.33 | 10.67 | 15.85 | 19.34 | 11.34 | 4.68 | |
| Force | 74 | 5.36 | 7.45 | 10.09 | 13.53 | 17.83 | 10.62 | 3.62 | |
| DLP [mGy·cm] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Location | CT Scanner * | No. of Scans | Min | 25th Percentile | Median | 75th Percentile | Max | Mean | SD |
| (A) Whole spine | Total | 31 | 279.6 | 382.4 | 509.7 | 682.9 | 1033.0 | 542.9 | 199.1 |
| AS+ | 4 | 530.5 | 606.5 | 893.9 | 1013.0 | 1033.0 | 837.8 | 220.5 | |
| Flash | 1 | - | - | 530.2 | - | - | - | - | |
| Force | 26 | 279.6 | 367.7 | 481.6 | 583.6 | 850.6 | 498.1 | 160.4 | |
| (B) Cervical spine | Total | 23 | 115.5 | 153.7 | 214.5 | 308.2 | 611.5 | 241.5 | 115.4 |
| AS+ | 4 | 137.6 | 150.8 | 209.1 | 275.7 | 291.6 | 211.9 | 64.8 | |
| Flash | 2 | 237.5 | - | 314.8 | - | 392.1 | 314.8 | 109.3 | |
| Force | 17 | 115.5 | 143.9 | 185.9 | 312.1 | 611.5 | 239.9 | 126.0 | |
| (C) Thoracic spine | Total | 10 | 123.8 | 222.8 | 365.4 | 432.4 | 500.8 | 340.1 | 119.8 |
| AS+ | 3 | 123.8 | - | 416.3 | - | 500.8 | 347.0 | 197.8 | |
| Flash | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Force | 7 | 199.2 | 230.6 | 356.3 | 431.6 | 434.7 | 337.1 | 91.83 | |
| (D) Lumbar spine | Total | 119 | 114.3 | 224.7 | 308.0 | 413.7 | 841.5 | 325.9 | 134.2 |
| AS+ | 33 | 156.1 | 219.2 | 329.1 | 423.2 | 698.0 | 337.2 | 136.8 | |
| Flash | 12 | 124.8 | 223.1 | 313.6 | 436.5 | 841.5 | 353.2 | 193.0 | |
| Force | 74 | 114.3 | 224.0 | 303.8 | 404.9 | 674.1 | 316.4 | 122.6 | |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) | Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | ||
| Anatomical location | |||||
| (A) Whole spine (B) Cervical spine (C) Thoracic spine (D) Lumbar spine | 40 | 34 | 80 | 148 | |
| 25 | 46 | 54 | 50 | ||
| 25 | 49 | 57 | 120 | ||
| 26 | 23 | 48 | 58 | ||
| CT scanner * | |||||
| AS+ Flash Force (110 kV protocol) Force (150 kV protocol) Force (100/Sn150 kV protocol) | 26 | 26 | 33 | 31 | |
| 23 | 19 | 21 | 20 | ||
| 34 | 38 | 74 | 57 | ||
| 24 | 24 | 51 | 66 | ||
| 27 | 17 | 50 | 46 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zensen, S.; Bos, D.; Opitz, M.; Forsting, M.; Guberina, N.; Deuschl, C.; Wetter, A. Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography: Comparison of Radiation Exposure and Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101809
Zensen S, Bos D, Opitz M, Forsting M, Guberina N, Deuschl C, Wetter A. Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography: Comparison of Radiation Exposure and Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101809
Chicago/Turabian StyleZensen, Sebastian, Denise Bos, Marcel Opitz, Michael Forsting, Nika Guberina, Cornelius Deuschl, and Axel Wetter. 2021. "Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography: Comparison of Radiation Exposure and Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101809
APA StyleZensen, S., Bos, D., Opitz, M., Forsting, M., Guberina, N., Deuschl, C., & Wetter, A. (2021). Single- and Dual-Source CT Myelography: Comparison of Radiation Exposure and Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101809






