Computed Tomography Texture Analysis of Carotid Plaque as Predictor of Unfavorable Outcome after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
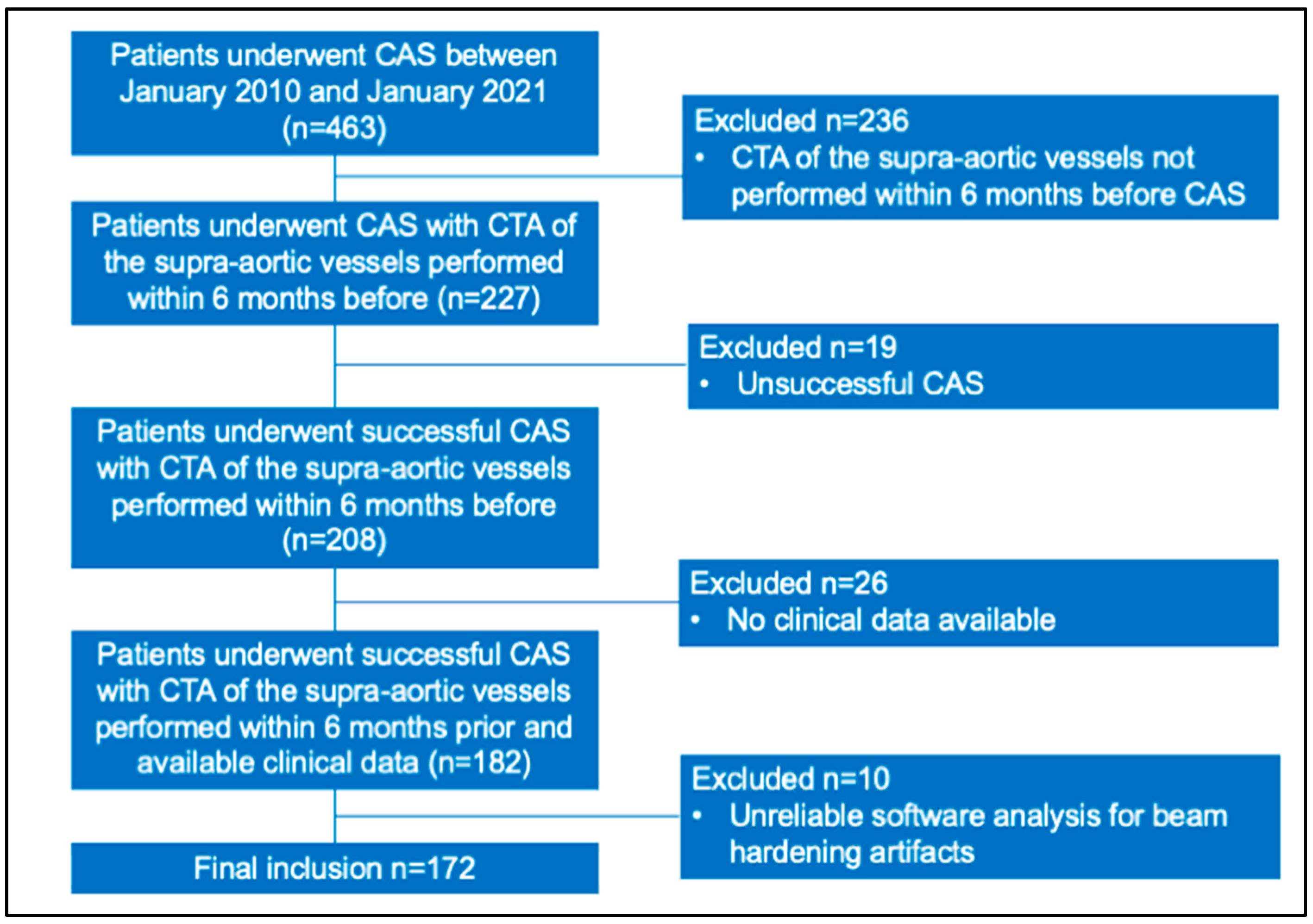
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. CT Angiography of the Supra-Aortic Vessels Protocol
2.3. CAS Procedure
2.4. Imaging Assessment
2.5. End-Point Definition
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Demographics, Clinical, Anatomical, and Procedural Findings
3.2. Plaque Visual Assessment and Texture Parameters
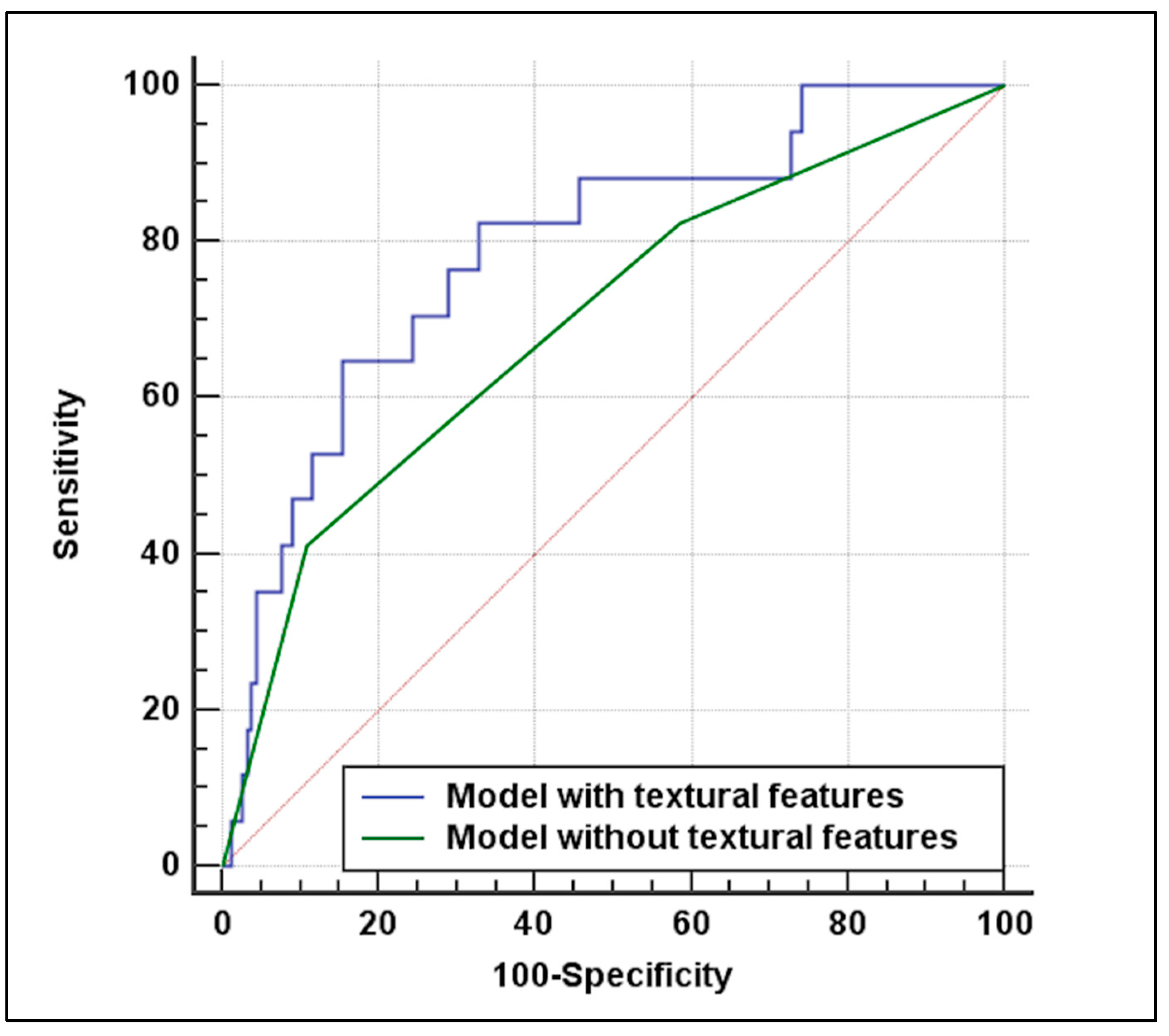
3.3. Predictive Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naghavi, M.; Wang, H.; Lozano, R.; Davis, A.; Liang, X.; Zhou, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Abbasoglu Ozgoren, A.; Abdalla, S.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Global, regional, and national age–sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immovilli, P.; Terracciano, C.; Zaino, D.; Marchesi, E.; Morelli, N.; Terlizzi, E.; De Mitri, P.; Vollaro, S.; Magnifico, F.; Colombi, D.; et al. Stroke in COVID-19 patients—A case series from Italy. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Aronow, H.D.; Kundu, A.; Ramchand, P.; Mukherjee, D.; Nairooz, R.; Gray, W.A.; White, C.; Jaff, M.R.; et al. Carotid Artery Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Stroke Prevention: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vaart, M.G.; Meerwaldt, R.; Reijnen, M.M.; Tio, R.A.; Zeebregts, C.J. Endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting: The quest continues. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 195, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brott, T.G.; Hobson, R.W., II; Howard, G.; Roubin, G.S.; Clark, W.M.; Brooks, W.; Mackey, A.; Hill, M.D.; Leimgruber, P.P.; Sheffet, A.J.; et al. Stenting versus Endarterectomy for Treatment of Carotid-Artery Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rots, M.L.; Meershoek, A.J.; Bonati, L.H.; Ruijter, H.M.D.; de Borst, G.J. Editor’s Choice—Predictors of New Ischaemic Brain Lesions on Diffusion Weighted Imaging After Carotid Stenting and Endarterectomy: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 58, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Setacci, C.; Chisci, E.; Setacci, F.; Iacoponi, F.; De Donato, G.; Rossi, A. Siena Carotid Artery Stenting Score: A Risk Modelling Study for Individual Patients. Stroke 2010, 41, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Kiura, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Shinagawa, K.; Ishii, D.; Ichinose, N.; Kurisu, K. Carotid artery stenting for vulnerable plaques on MR angiography and ultrasonography: Utility of dual protection and blood aspiration method. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, N.; Galyfos, G.; Sigala, F.; Thanopoulou, K.; De Borst, G.J.; Davidovic, L.; Eckstein, H.; Filipovic, N.; Grugni, R.; Kallmayer, M.; et al. The TAXINOMISIS Project: A multidisciplinary approach for the development of a new risk stratification model for patients with asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, A.; Balestrieri, A.; Crivelli, P.; Suri, J.S.; Conti, M.; Cademartiri, F.; Saba, L. Cardiac computed tomography radiomics: An emerging tool for the non-invasive assessment of coronary atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, K.; Fukuda, S.; Tanaka, A.; Nakanishi, K.; Taguchi, H.; Yoshikawa, J.; Shimada, K.; Yoshiyama, M. Napkin-Ring Sign on Coronary CT Angiography for the Prediction of Acute Coronary Syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saba, L.; Caddeo, G.; Sanfilippo, R.; Montisci, R.; Mallarini, G. CT and Ultrasound in the Study of Ulcerated Carotid Plaque Compared with Surgical Results: Potentialities and Advantages of Multidetector Row CT Angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Hippe, D.S.; Li, R.; Canton, G.M.; Sui, B.; Song, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, Y.; Sun, J.; Yamada, K.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Carotid Artery High-Risk Atherosclerotic Plaques in Chinese Patients With Cerebrovascular Symptoms: A Chinese Atherosclerosis Risk Evaluation II Study. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, L.; Micheletti, G.; Brinjikji, W.; Garofalo, P.; Montisci, R.; Balestrieri, A.; Suri, J.; DeMarco, J.; Lanzino, G.; Sanfilippo, R. Carotid Intraplaque-Hemorrhage Volume and Its Association with Cerebrovascular Events. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarco, J.K.; Huston, J., 3rd. Imaging of high-risk carotid artery plaques: Current status and future directions. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 36, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, L.; Mallarini, G. Fissured Fibrous Cap of Vulnerable Carotid Plaques and Symptomaticity: Are They Correlated? Preliminary Results by Using Multi-Detector-Row CT Angiography. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukadinovic, D.; Rozie, S.; Van Gils, M.; Van Walsum, T.; Manniesing, R.; Van Der Lugt, A.; Niessen, W.J. Automated versus manual segmentation of atherosclerotic carotid plaque volume and components in CTA: Associations with cardiovascular risk factors. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 28, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, K.A.; Ganeshan, B.; Hayball, M.P. CT texture analysis using the filtration-histogram method: What do the measurements mean? Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolossváry, M.; Karády, J.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ivanov, A.; Schlett, C.L.; Lu, M.T.; Foldyna, B.; Merkely, B.; Aerts, H.J.; Hoffmann, U.; et al. Radiomics versus Visual and Histogram-based Assessment to Identify Atheromatous Lesions at Coronary CT Angiography: An ex Vivo Study. Radiology 2019, 293, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermark, M.; Arora, S.; Tong, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Lau, B.C.; Ba, J.D.C.; Dillon, W.P.; Saloner, D. Carotid plaque computed tomography imaging in stroke and nonstroke patients. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaccagna, F.; Ganeshan, B.; Arca, M.; Rengo, M.; Napoli, A.; Rundo, L.; Groves, A.M.; Laghi, A.; Carbone, I.; Menezes, L.J. CT texture-based radiomics analysis of carotid arteries identifies vulnerable patients: A preliminary outcome study. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Zhu, C.; Degnan, A.J.; Tian, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Chen, C.; Lu, J.; et al. Identification of high-risk plaque features in intracranial atherosclerosis: Initial experience using a radiomic approach. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3912–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.; Lv, P.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Lin, J. Identification of high-risk carotid plaque with MRI-based radiomics and machine learning. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Engelen, A.; Wannarong, T.; Parraga, G.; Niessen, W.J.; Fenster, A.; Spence, J.D.; de Bruijne, M. Three-Dimensional Carotid Ultrasound Plaque Texture Predicts Vascular Events. Stroke 2014, 45, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madycki, G.; Staszkiewicz, W.; Gabrusiewicz, A. Carotid Plaque Texture Analysis Can Predict the Incidence of Silent Brain Infarcts Among Patients Undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2006, 31, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyman, E.; Lindqvist, P.; Näslund, U.; Grönlund, C. Risk Marker Variability in Subclinical Carotid Plaques Based on Ultrasound is Influenced by Cardiac Phase, Echogenicity and Size. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators; Barnett, H.; Taylor, D.; Haynes, R.; Sackett, D.; Peerless, S.; Ferguson, G.; Fox, A.; Rankin, R.; Hachinski, V.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Carotid Endarterectomy in Symptomatic Patients with High-Grade Carotid Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendera, M.; Aboyans, V.; Bartelink, M.-L.; Baumgartner, I.; Clement, D.L.; Collet, J.-P.; Cremonesi, A.; De Carlo, M.; Erbel, R.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; et al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries * The Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Hear. J. 2011, 32, 2851–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboyans, V.; Ricco, J.-B.; Bartelink, M.-L.E.L.; Björck, M.; Brodmann, M.; Cohnert, T.; Collet, J.-P.; Czerny, M.; De Carlo, M.; Debus, S.; et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): Document Covering Atherosclerotic Disease of Extracranial Carotid and Vertebral, Mesenteric, Renal, Upper and Lower Extremity Arteries Endorsed by: The European Stroke Organization (ESO) The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 763–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naylor, A.; Ricco, J.-B.; De Borst, G.; Debus, S.; De Haro, J.; Halliday, A.; Hamilton, G.; Kakisis, J.; Kakkos, S.; Lepidi, S.; et al. Editor’s Choice—Management of Atherosclerotic Carotid and Vertebral Artery Disease: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 3–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liapis, C.; Bell, S.P.; Mikhailidis, D.; Sivenius, J.; Nicolaides, A.; e Fernandes, J.F.; Biasi, G.; Norgren, L. ESVS Guidelines. Invasive Treatment for Carotid Stenosis: Indications, Techniques. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Waard, D.D.; Morris, D.; De Borst, G.J.; Bulbulia, R.; Halliday, A. Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: Who should be screened, who should be treated and how should we treat them? J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 58, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, D.; McClenny, T.E.; Cardella, J.F.; Lewis, C.A. Society of Interventional Radiology Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, S199–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboyans, V.; Ricco, J.-B.; Bartelink, M.-L.E.L.; Björck, M.; Brodmann, M.; Cohnert, T.; Naylor, A.R.; Roffi, M.; Tendera, M.; Vlachopoulos, C.; et al. Editor’s Choice—2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 305–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhwal, S.; Rajagopal, V.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bajzer, C.T.; Whitlow, P.; Kapadia, S.R. Predictors of difficult carotid stenting as determined by aortic arch angiography. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2008, 20, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, R.C.; Lin, S.C.; DeRubertis, B.; Hynecek, R.; Kent, K.C.; Faries, P.L. The impact of increasing age on anatomic factors affecting carotid angioplasty and stenting. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Schlett, C.; Alkadhi, H.; Nakano, M.; Otsuka, F.; Stolzmann, P.; Scheffel, H.; Ferencik, M.; Kriegel, M.; Seifarth, H.; et al. The Napkin-Ring Sign Indicates Advanced Atherosclerotic Lesions in Coronary CT Angiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, D.; Commandeur, F. Radiomics to Identify High-Risk Atherosclerotic Plaque From Computed Tomography: The Power of Quantification. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, E.P.V.; Rundo, L.; Tarkin, J.M.; Evans, N.R.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Coughlin, P.A.; Pavey, H.; Wall, C.; Zaccagna, F.; Gallagher, F.A.; et al. Assessing robustness of carotid artery CT angiography radiomics in the identification of culprit lesions in cerebrovascular events. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Brooks, W.H.; Mackey, A.; Clark, W.M.; Meschia, J.F.; Morrish, W.F.; Mohr, J.; Rhodes, J.D.; Popma, J.J.; Lal, B.K.; et al. Stroke After Carotid Stenting and Endarterectomy in the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST). Circulation 2012, 126, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brott, T.; Adams, H.P.; Olinger, C.P.; Marler, J.R.; Barsan, W.G.; Biller, J.; Spilker, J.; Holleran, R.; Eberle, R.; Hertzberg, V. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: A clinical examination scale. Stroke 1989, 20, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meschia, J.F.; Brott, T.G.; Chukwudelunzu, F.E.; Hardy, J.; Brown, J.R.D.; Meissner, I.; Hall, L.J.; Atkinson, E.J.; O’Brien, P.C. Verifying the Stroke-Free Phenotype by Structured Telephone Interview. Stroke 2000, 31, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rautaharju, P.M.; MacInnis, P.J.; Warren, J.W.; Wolf, H.K.; Rykers, P.M.; Calhoun, H.P. Methodology of ECG Interpretation in the Dalhousie Program; NOVACODE ECG Classification Procedures for Clinical Trials and Population Health Surveys. Methods Inf. Med. 1990, 29, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delong, E.R.; Delong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.D.; Lyrer, P.A.; Brown, M.M.; Bonati, L.H. Carotid Artery Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Treatment of Carotid Artery Stenosis. Stroke 2020, 52, e3–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, L.; Sanfilippo, R.; Sannia, S.; Anzidei, M.; Montisci, R.; Mallarini, G.; Suri, J.S. Association Between Carotid Artery Plaque Volume, Composition, and Ulceration: A Retrospective Assessment With MDCT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doonan, R.; Dawson, A.; Kyriacou, E.; Nicolaides, A.; Corriveau, M.; Steinmetz, O.; Mackenzie, K.; Obrand, D.; Daskalopoulos, M.; Daskalopoulou, S. Association of Ultrasonic Texture and Echodensity Features Between Sides in Patients with Bilateral Carotid Atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2013, 46, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steven, A.J.; Zhuo, J.; Melhem, E.R. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: An Emerging Technique for Evaluating the Microstructural Environment of the Brain. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, W26–W33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doonan, R.J.; Gorgui, J.; Veinot, J.P.; Lai, C.; Kyriacou, E.; Corriveau, M.M.; Steinmetz, O.K.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Plaque echodensity and textural features are associated with histologic carotid plaque instability. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 671–677.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Variables | Overall (n = 172) | Good Outcome (n = 155) | Unfavorable Outcome (n = 17) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Gender
| 112 (65%) 60 (35%) | 100 (65%) 55 (35%) | 12 (70%) 5 (30%) | 0.790 |
| Age | 77 (70–82) | 77 (70–82) | 79 (72–83) | 0.243 |
| Ipsilateral neurological ischemic event within 6 months before CAS | 90 (52%) | 83 (53%) | 7 (41%) | 0.444 |
| Cardiac disease | 71 (41%) | 60 (38%) | 11 (64%) | 0.066 |
| Diabetes | 53 (30%) | 47 (30%) | 6 (35%) | 0.782 |
| Arch type II-III | 66 (38%) | 63 (40%) | 3 (17%) | 0.071 |
| Bovine arch | 51 (30%) | 43 (27%) | 8 (47%) | 0.158 |
| Arch calcifications | 131 (76%) | 115 (74%) | 16 (94%) | 0.076 |
| Procedural time (min) | 18 (15–22) | 18 (16–22) | 15 (15–20) | 0.098 |
| Variables | Overall (n = 172) | Good Outcome (n = 155) | Unfavorable Outcome (n = 17) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Side
| 92 (53%) 80 (47%) | 81 (52%) 74 (48%) | 11 (64%) 6 (36%) | 0.443 |
Visual plaque classification
| 166 (96%) 6 (4%) | 150 (97%) 5 (3%) | 16 (94%) 1 (6%) | 0.469 |
| Plaque ulceration | 58 (33%) | 48 (30%) | 10 (58%) | 0.029 |
| Ostial plaque | 91 (52%) | 83 (53%) | 8 (47%) | 0.620 |
| Angiographic stenosis (%) | 68 (60–75) | 69 (60–75) | 64 (51–74) | 0.232 |
| Plaque length ≥15 mm | 85 (49%) | 80 (51%) | 5 (29%) | 0.123 |
| Recurrent plaque | 18 (10%,) | 16 (10%) | 2 (11%) | 0.693 |
| Plaque mean density (HU) | 225 (146–353) | 222 (144–349) | 244 (158–389) | 0.570 |
| Plaque standard deviation density (HU) | 229 (142–340) | 228 (141–336) | 254 (146–365) | 0.713 |
| Plaque kurtosis | 5.75 (3.91–9.31) | 5.84 (3.96–9.97) | 5.37 (3.27–6.32) | 0.048 |
| Plaque skewness | 1.63 (1.13–2.26) | 1.67 (1.14–2.36) | 1.53 (0.96–1.68) | 0.093 |
| Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariable analysis without textural features | |||
| Coefficient | OR (95%CI) | p-value | |
| Cardiac disease | 1.09 | 3 (1.03–8.71) | 0.042 |
| Plaque ulceration | 1.19 | 3.28 (1.16–9.31) | 0.025 |
| Multivariable analysis with textural features | |||
| Cardiac disease | 1.11 | 3.05 (1.02–9.09) | 0.045 |
| Plaque ulceration | 1.37 | 3.96 (1.34–11.72) | 0.012 |
| Plaque kurtosis | −0.22 | 0.79 (0.65–0.97) | 0.029 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colombi, D.; Bodini, F.C.; Rossi, B.; Bossalini, M.; Risoli, C.; Morelli, N.; Petrini, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Michieletti, E. Computed Tomography Texture Analysis of Carotid Plaque as Predictor of Unfavorable Outcome after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122214
Colombi D, Bodini FC, Rossi B, Bossalini M, Risoli C, Morelli N, Petrini M, Sverzellati N, Michieletti E. Computed Tomography Texture Analysis of Carotid Plaque as Predictor of Unfavorable Outcome after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(12):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122214
Chicago/Turabian StyleColombi, Davide, Flavio Cesare Bodini, Beatrice Rossi, Margherita Bossalini, Camilla Risoli, Nicola Morelli, Marcello Petrini, Nicola Sverzellati, and Emanuele Michieletti. 2021. "Computed Tomography Texture Analysis of Carotid Plaque as Predictor of Unfavorable Outcome after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Preliminary Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 12: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122214
APA StyleColombi, D., Bodini, F. C., Rossi, B., Bossalini, M., Risoli, C., Morelli, N., Petrini, M., Sverzellati, N., & Michieletti, E. (2021). Computed Tomography Texture Analysis of Carotid Plaque as Predictor of Unfavorable Outcome after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics, 11(12), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122214





