Serum microRNA Levels in Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Microperimetry
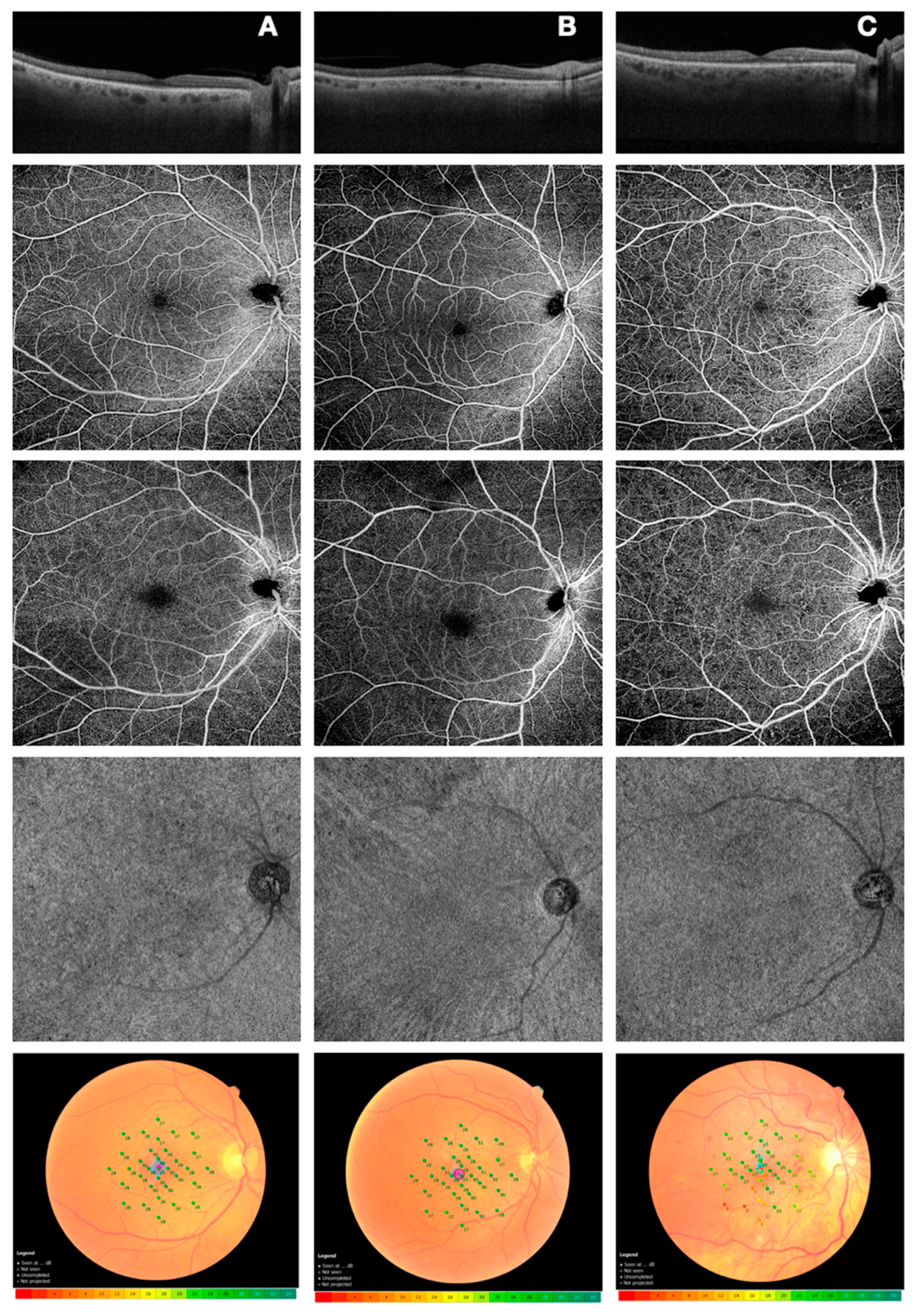
2.3. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography
2.4. Serum miRNAs Sampling and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anatomical/Perfusion and Functional Parameters
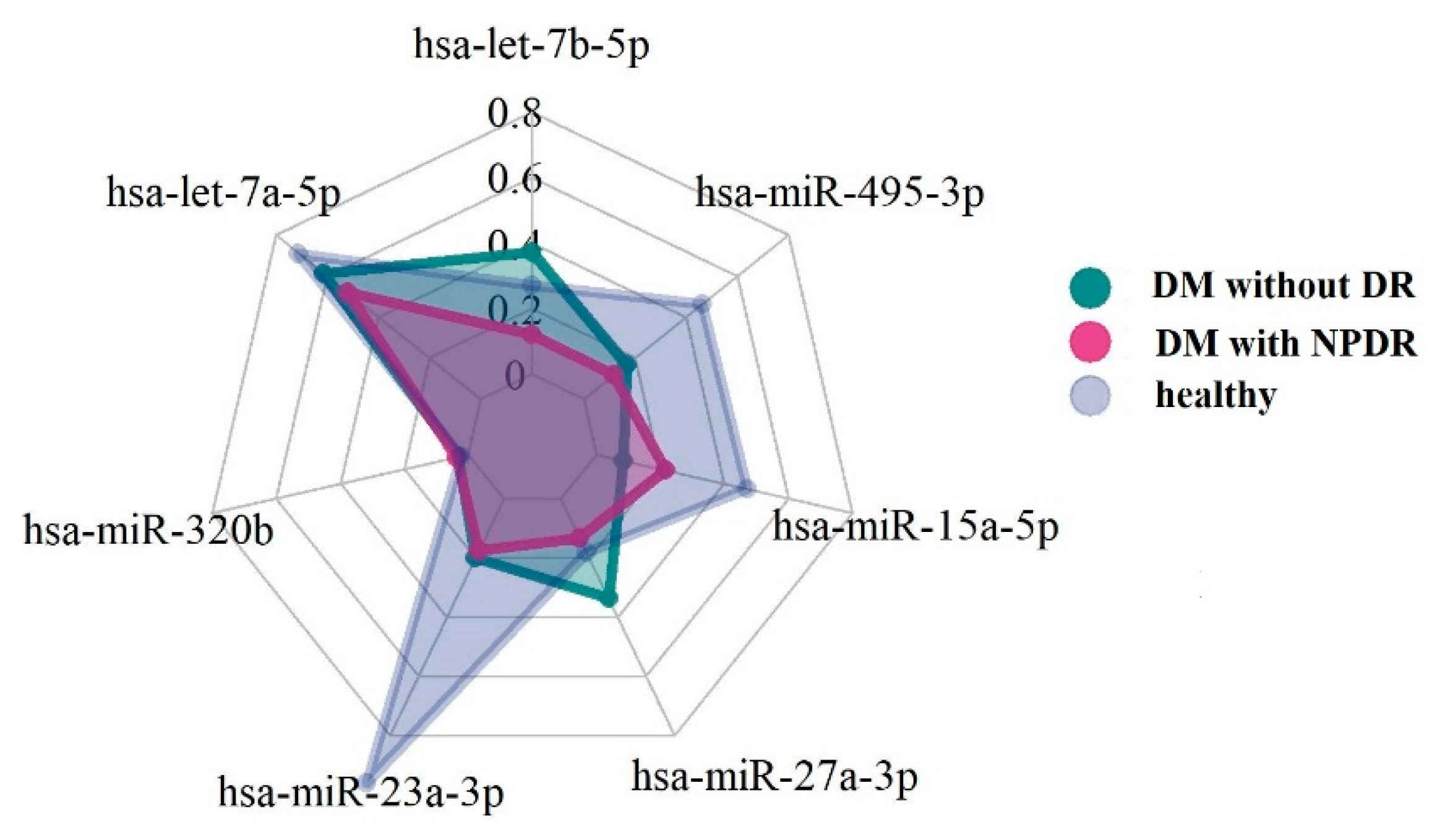
3.2. MicroRNA Expression Levels
3.3. Correlation analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivaprasad, S.; Pearce, E. The unmet need for better risk stratification of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó-Servat, O.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Diabetic Retinopathy in the Context of Patients with Diabetes. Ophthalmic. Res. 2019, 62, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Rezaei, K.A.; Saraf, S.S.; Chu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, R.K. Ultra-wide optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic retinopathy. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropasqua, R.; D’Aloisio, R.; Di Antonio, L.; Erroi, E.; Borrelli, E.; Evangelista, F.; D’Onofrio, G.; Di Nicola, M.; Di Martino, G.; Toto, L. Widefield optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, K.Y.; Teo, K.; Tan, A.C.; Devarajan, K.; Tan, B.; Tan, J.; Schmetterer, L.; Ang, M. Optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic retinopathy: A review of current applications. Eye Vis. 2019, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Yi, Q.; Chen, L.; Wong, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; et al. Circulating miR-3197 and miR-2116-5p as novel biomarkers for diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.G.; Abdelaleem, O.O.; Mahmoud, R.H.; Abdelghaffar, N.K.; Ahmed, T.I.; Said, O.M.; Zaki, O.M. Diagnostic and prognostic role of serum miR-20b, miR-17-3p, HOTAIR, and MALAT1 in diabetic retinopathy. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; D’Angelo, C.; Costantini, E.; Laus, M.; Moretti, A.; Croce, A. MicroRNA in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Their Potential Roles in Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7510174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, T.; Li, K.; Zheng, P.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Li, B.; Jin, L.; et al. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis Identified MicroRNA Coexpression Modules and Related Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 9567641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, G.E.; Brusco, N.; Licata, G.; Nigi, L.; Formichi, C.; Dotta, F.; Sebastiani, G. Targeting microRNAs as a Therapeutic Strategy to Reduce Oxidative Stress in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Halushka, M.K. Extracellular vesicle microRNA transfer in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.-Y.; Cao, J. MiRNA-138-5p protects the early diabetic retinopathy by regulating NOVA1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 7749–7756. [Google Scholar]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, M.; Martello, G.; Piccolo, S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastropasqua, R.; Toto, L.; Cipollone, F.; Santovito, D.; Carpineto, P.; Mastropasqua, L. Role of microRNAs in the modulation of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 43, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Qian, R.Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.F.; Jin, H.M.; Hu, R.M. MicroRNA-320 expression in myocardial microvascular endothelial cells and its relationship with insulin-like growth factor-1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2009, 36, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Chakrabarti, S. miR-320 Regulates Glucose-Induced Gene Expression in Diabetes. Int. Sch. Res. Netw. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 549875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Frost, R.J.; Anderson, C.; Zhao, F.; Ma, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, S. Let-7 contributes to diabetic retinopathy but represses pathological ocular angiogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00001-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houshmand-Oeregaard, A.; Schrölkamp, M.; Kelstrup, L.; Hansen, N.S.; Hjort, L.; Thuesen, A.C.B.; Broholm, C.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Clausen, T.D.; Vaag, A.; et al. Increased expression of microRNA-15a and microRNA-15b in skeletal muscle from adult offspring of women with diabetes in pregnancy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, E.A.; Steinle, J.J. Regulatory role of microRNA on inflammatory responses of diabetic retinopathy. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 580–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalden, T.A.; Macgregor-Das, A.M.; Kannan, S.M.; Dunkerly-Eyring, B.; Khaliddin, N.; Xu, Z.; Fusco, A.P.; Yazib, S.A.; Chow, R.C.; Duh, E.J.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNA-15a Transfer from the Pancreas Augments Diabetic Complications by Inducing Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, B.; Peplow, P.V. MicroRNAs as biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy and disease progression. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1858–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Markopoulos, G.S.; Roupakia, E.; Tokamani, M.; Alabasi, G.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Marcu, K.B.; Kolettas, E. Roles of NF-κB signaling in the regulation of miRNAs impacting on inflammation in cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elemeery, M.N.; Mohamed, M.A.; Madkour, M.A.; Shamseya, M.M.; Issa, N.M.; Badr, A.N.; Ghareeb, D.A.; Pan, C.H. MicroRNA signature in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma associated with type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6322–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Si, H.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Sheng, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhang, H. Serum miR-23a, a potential biomarker for diagnosis of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Z. Suppression of microRNA-495 alleviates high-glucose-induced retinal ganglion cell apoptosis by regulating Notch/PTEN/Akt signaling. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 106, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, E.Ł.; Durak-Kozica, M.; Kamińska, A.; Targosz-Korecka, M.; Libera, M.; Tylko, G.; Opalińska, A.; Kapusta, M.; Solnica, B.; Georgescu, A.; et al. Circulating ectosomes: Determination of angiogenic microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3874–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liang, B.; Lin, J.; Kim, T.K.; Yu, H.; Hang, H.; Wang, K. A Systematic Study of Dysregulated MicroRNA in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Meng, X.; Che, H.; Shen, N.; Xiao, D.; Song, X.; Liang, M.; Fu, X.; Ju, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Regulation of Insulin Resistance by Multiple MiRNAs via Targeting the GLUT4 Signalling Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2063–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Midena, E.; Pilotto, E.; Radin, P.P.; Chiesa, L.; Cavarzeran, F. Diabetic macular edema: Correlation between microperimetry and optical coherence tomography findings. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3044–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vujosevic, S.; Bottega, E.; Casciano, M.; Pilotto, E.; Convento, E.; Midena, E. Microperimetry and fundus autofluorescence in diabetic macular edema: Subthreshold micropulse diode laser versus modified early treatment diabetic retinopathy study laser photocoagulation. Retina 2010, 30, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, S.A.; Mutalib, H.A.; Ngah, N.F. HbA1c and retinal sensitivity in diabetics using microperimetry. J. Optom. Publ. 2019, 12, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zang, P.; Jia, Y.; Huang, D. Extended axial imaging range, widefeld swept source optical coherence tomography angiography. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, O.; Ichiyama, Y.; Obata, S.; Ito, Y.; Kakinoki, M.; Sawada, T.; Saishin, Y.; Ohji, M. Comparison between wide-angle OCT angiography and ultra-wide feld fuorescein angiography for detecting non-perfusion areas and retinal neovascularization in eyes with diabetic retinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesper, P.L.; Roberts, P.K.; Onishi, A.C.; Chai, H.; Liu, L.; Jampol, L.M.; Fawzi, A.A. Quantifying Microvascular Abnormalities With Increasing Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, BIO307–BIO315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samara, W.A.; Shahlaee, A.; Adam, M.K.; Khan, M.A.; Chiang, A.; Maguire, J.I.; Hsu, J.; Ho, A.C. Quantification of Diabetic Macular Ischemia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography and Its Relationship with Visual Acuity. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.S.; Hagag, A.M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Smith, A.; Wilson, D.J.; Huang, D.; Jia, Y. Automated quantification of nonperfusion areas in 3 vascular plexuses with optical coherence tomography angiography in eyes of patients with diabetes. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Yang, D.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Optical coherence tomography angiography discerns preclinical diabetic retinopathy in eyes of patients with type 2 diabetes without clinical diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, G.; Chihara, E.; Takahashi, H.; Amano, H.; Okazaki, K. Quantitative retinal optical coherence tomography angiography in patients with diabetes without diabetic retinopathy. Investig Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, A.; Sacconi, R.; Corbelli, E.; Tomasso, L.; Querques, L.; Zerbini, G.; Scorcia, V.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography analysis of retinal vascular plexuses and choriocapillaris in patients with type 1 diabetes without diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonett, J.M.; Scarinci, F.; Picconi, F.; Giorno, P.; De Geronimo, D.; Di Renzo, A.; Varano, M.; Frontoni, S.; Parravano, M. Early microvascular retinal changes in optical coherence tomography angiography in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e751–e755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chao, J.R.; Rezaei, K.A.; Wang, R.K. Microvascular changes in the choriocapillaris of diabetic patients without retinopathy investigated by swept-source OCT angiography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fryczkowski, A.W.; Hodes, B.L.; Walker, J. Diabetic choroidal and iris vasculature scanning electron microscopy findings. Int. Ophthalmol. 1989, 13, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; McLeod, D.S.; Merges, C.A.; Lutty, G.A. Choriocapillaris Degeneration and Related Pathologic Changes in Human Diabetic Eyes. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1998, 116, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uji, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Lei, J.; Baghdasaryan, E.; Al-Sheikh, M.; Sadda, S.R. Impact of multiple en face image averaging on quantitative assessment from optical coherence tomography angiography images. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| miRNA Base ID | miRBase Accession: Mature miRNA Sequence |
|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-5p | MIMAT0000063: 5′UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUGUGGUU |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | MIMAT0000062: 5′UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU |
| hsa-miR-320b | MIMAT0005792: 5′AAAAGCUGGGUUGAGAGGGCAA |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | MIMAT0000078: 5′AUCACAUUGCCAGGGAUUUCC |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | MIMAT0000084: 5′UUCACAGUGGCUAAGUUCCGC |
| hsa-miR-15a-5p | MIMAT0000068: 5′UAGCAGCACAUAAUGGUUUGUG |
| hsa-miR-495-3p | MIMAT0002817: 5′AAACAAACAUGGUGCACUUCUU |
| hsa-miR-423-3p | MIMAT0001340: 5′AGCUCGGUCUGAGGCCCCUCAGU |
| Variable | Healthy (1) | DM without DR (2) | DM with NPRD (3) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCVA (logMAR) | 0.00 [0.00;0.00] | 0.01 [0.00;0.10] | 0.15 [0.10;0.27] | <0.001 * |
| CMT | 203 [201;204] | 228 [203;236] | 256 [223;276] | <0.001 * |
| HBA1c (%) | 4.7 [4.6;4.9] | 7.00 [6.8;7.0] | 8.4 [6.8;11.2] | <0.001 * |
| 4° MP (db) | 29.1 [28.5;29.4] | 25.1 [24.8;25.8] (1) | 23.4 [21.4;26.3] (1) | 0.002 |
| 8° MP(db) | 29.1 [28.9;29.7] | 26.1 [25.5;28.3] (1) | 23.9 [22.6;26.9] (1) | 0.002 |
| 20° MP (db) | 28.8 [28.6;29.5] | 26.1 [25.3;27.8] (1) | 23.6 [21.9;26.8] (1) | 0.002 |
| Vessel Density | ||||
| Inferior ring_DCP | 44.5 [42.5;47.9] | 41.1 [33.5;41.5] | 37.6 [31.9;40.1] (1)(2) | 0.033 |
| Foveal ring_CC | 74.4 [72.3;75.5] | 72.3 [71.1;74.0] | 67.9 [66.3;71.0] (1)(2) | 0.001 |
| Parafoveal ring_CC | 75.5 [72.9;76.7] | 73.9 [71.8;75.0] | 68.9 [67.3;70.6] (1)(2) | <0.001 |
| Perifoveal ring_CC | 75.7 [73.1;76.3] | 74.2 [72.3;75.2] | 68.5 [67.5;70.9] (1)(2) | <0.001 |
| Superior ring_CC | 73.2 [71.8;75.2] | 74.6 [72.8;75.9] | 68.6 [66.2;69.8] (1)(2) | <0.001 |
| Inferior ring_CC | 75.3 [74.9;77.1] | 74.8 [73.0;75.3] | 69.7 [67.3;71.2] | <0.001 * |
| Temporal ring_CC | 75.1 [73.4;76.6] | 74.7 [72.7;76.3] | 72.1 [68.2;73.8] (1)(2) | 0.019 |
| miRNA | Healthy (1) | DM without DR (2) | DM with NPRD (3) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-5p | 0.34 [0.18;0.44] | 0.46 [0.29;0.74] | 0.15 [0.12;0.24] | 0.217 |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | 0.89 [0.56;2.06] | 0.86 [0.35;1.19] | 0.65 [0.35;0.94] | 0.625 |
| hsa-miR-320b | 0.03 [0.03;0.03] | 0.04 [0.03;0.10] | 0.04 [0.02;0.07] | 0.519 |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | 1.20 [0.57;1.37] | 0.29 [0.13;0.33] (1) | 0.22 [0.10;0.30] (1) | 0.013 |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 0.22 [0.19;0.52] | 0.42 [0.22;0.74] | 0.16 [0.11;0.29] | 0.230 |
| hsa-miR-15a-5p | 0.59 [0.46;0.68] | 0.11 [0.06;0.52] (1) | 0.27 [0.16;0.35] (1) | 0.027 |
| hsa-miR-495-3p | 0.58 [0.22;0.96] | 0.18 [0.08;0.22] (1) | 0.15 [0.07;0.21] (1) | 0.049 |
| miRNA | Ophthalmological Variables |
|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-5p | Foveal ring VD_SCP |
| Rho = 0.888 * | |
| hsa-miR-15a-5p | Temporal ring VD_CC |
| Rho = 0.895 * | |
| hsa-miR-320b | BCVA (logMAR) |
| Rho = 0.894 * | |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | Inferior ring VD_CC |
| Rho = −0.963 ** | |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | Superior ring VD_CC |
| Rho = −0.945 * | |
| hsa-miR-495-3p | Superior ring VD-SCP |
| Rho = 0.972 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastropasqua, R.; D’Aloisio, R.; Costantini, E.; Porreca, A.; Ferro, G.; Libertini, D.; Reale, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Viggiano, P.; Falconio, G.; et al. Serum microRNA Levels in Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020284
Mastropasqua R, D’Aloisio R, Costantini E, Porreca A, Ferro G, Libertini D, Reale M, Di Nicola M, Viggiano P, Falconio G, et al. Serum microRNA Levels in Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020284
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastropasqua, Rodolfo, Rossella D’Aloisio, Erica Costantini, Annamaria Porreca, Giada Ferro, Daniele Libertini, Marcella Reale, Marta Di Nicola, Pasquale Viggiano, Gennaro Falconio, and et al. 2021. "Serum microRNA Levels in Diabetes Mellitus" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020284
APA StyleMastropasqua, R., D’Aloisio, R., Costantini, E., Porreca, A., Ferro, G., Libertini, D., Reale, M., Di Nicola, M., Viggiano, P., Falconio, G., & Toto, L. (2021). Serum microRNA Levels in Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics, 11(2), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020284











