Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Types of EUS
3. EUS for Detecting PNENs
4. Precautions for EUS in Functional PNENs
5. Role of EUS Elastography
6. Role of Contrast-Enhanced EUS (CE-EUS)
7. Artificial Intelligence Analysis for Endoscopic Ultrasonography
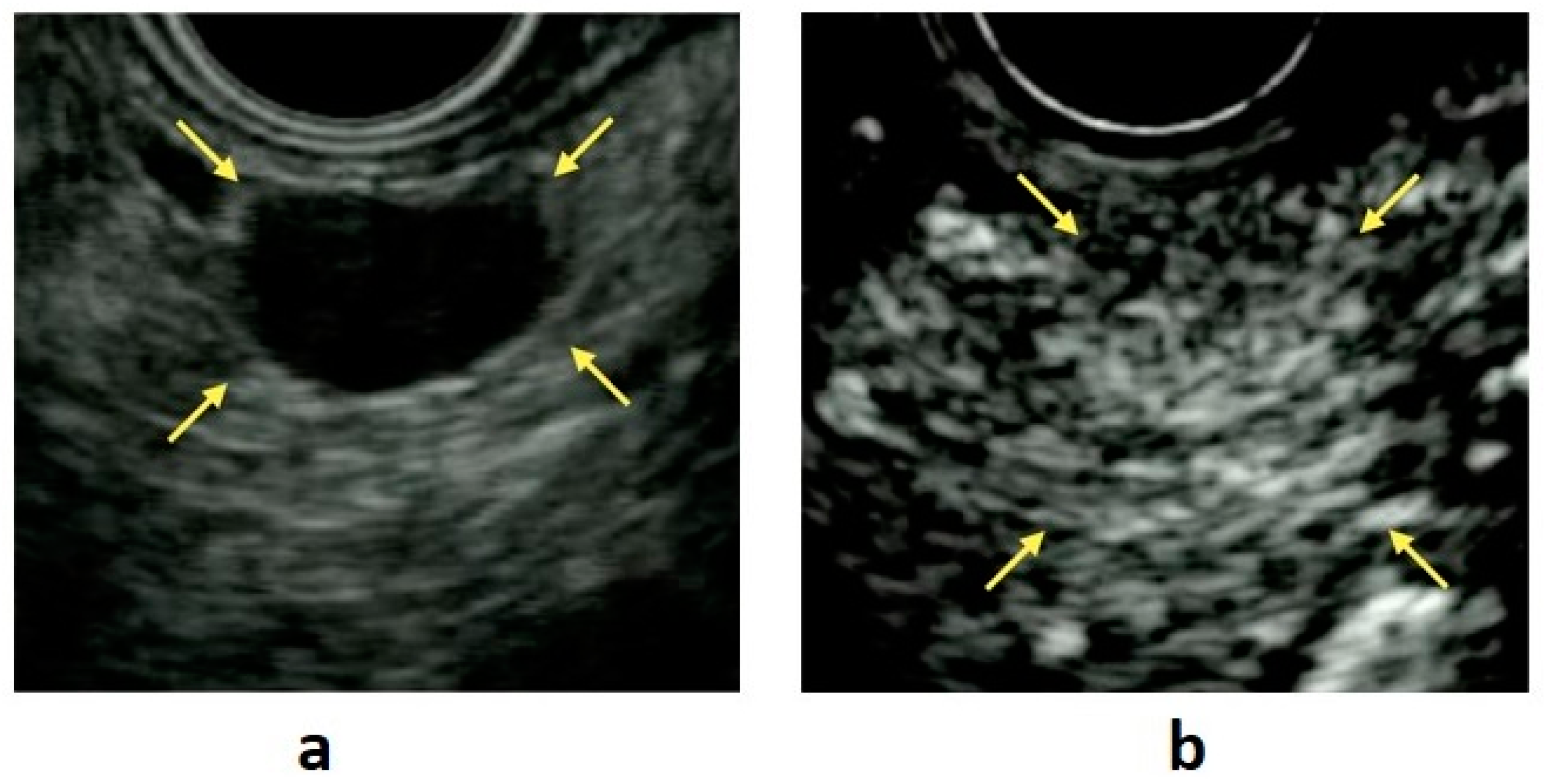
8. Features of EUS Findings in PNENs
8.1. Cystic Degeneration
8.2. Pancreatic Duct Stricture
8.3. Intraductal Invasion of the MPD
9. Features of Imaging Findings in PNEN G3 and Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (PNEC)
10. Tumors That Need to Be Differentiated from PNENs
10.1. SPNs
10.2. Serous Cystic Neoplasm (SCN)
10.3. Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen (IPAS)
10.4. Pancreatic Metastasis
11. Role of EUS-FNA in PNENs
11.1. Grading Diagnosis
11.2. EUS-FNA for Cystic PNENs
11.3. Genetic Analysis in PNENs
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rösch, T.; Lightdale, C.J.; Botet, J.F.; Boyce, G.A.; Sivak, M.V., Jr.; Yasuda, K.; Heyder, N.; Palazzo, L.; Dancygier, H.; Schusdziarra, V. Localization of pancreatic endocrine tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanuma, A.; Maguchi, H.; Osanai, M.; Takahashi, K. The difference in the capability of delineation between convex and radial arrayed echoendoscope for pancreas and biliary tract; case reports from the standpoint of both convex and radial arrayed echoendoscope. Dig. Endosc. 2011, 23, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Katanuma, A.; Maguchi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Osanai, M.; Yane, K.; Hashigo, S.; Harada, R.; Kato, S.; Kato, R. Prospective, randomized, comparative study of delineation capability of radial scanning and curved linear array endoscopic ultrasound for the pancreaticobiliary region. Endosc. Int. Open 2014, 2, E160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puli, S.R.; Kalva, N.; Bechtold, M.L.; Pamulaparthy, S.R.; Cashman, M.D.; Estes, N.C.; Pearl, R.H.; Volmar, F.-H.; Dillon, S.; Shekleton, M.F. Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A systematic review and meta analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manta, R.; Nardi, E.; Pagano, N.; Ricci, C.; Sica, M.; Castellani, D.; Bertani, H.; Piccoli, M.; Mullineris, B.; Tringali, A. Pre-operative diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors with endoscopic ultrasonography and computed tomography in a large series. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khashab, M.A.; Yong, E.; Lennon, A.M.; Shin, E.J.; Amateau, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Olino, K.; Giday, S.; Fishman, E.K.; Wolfgang, C.L. EUS is still superior to multidetector computerized tomography for detection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.D.; Tsolakis, A.V.; Zhang, M.; Belletrutti, P.J.; Mohamed, R.; Roberts, D.J.; Heitman, S.J. Incremental benefit of preoperative EUS for the detection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 848–856.e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asselt, S.J.; Brouwers, A.H.; van Dullemen, H.M.; van der Jagt, E.J.; Bongaerts, A.H.; Kema, I.P.; Koopmans, K.P.; Valk, G.D.; Timmers, H.J.; de Herder, W.W. EUS is superior for detection of pancreatic lesions compared with standard imaging in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 159–167.e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daskalakis, K.; Tsoli, M.; Alexandraki, K.I.; Angelousi, A.; Chatzellis, E.; Tsolakis, A.V.; Karoumpalis, I.; Kolomodi, D.; Kassi, E.; Kaltsas, G. Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Detection and Surveillance of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1? Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Asselt, S.J.; Brouwers, A.H.; van Dullemen, H.M.; van der Jagt, E.J.; Bongaerts, A.H.; Koopmans, K.P.; Kema, I.P.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Timmers, H.J.; de Herder, W.W.; et al. Potential value of EUS in pancreatic surveillance of VHL patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kann, P.H. Is endoscopic ultrasonography more sensitive than magnetic resonance imaging in detecting and localizing pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelle, W.F.; Valk, G.D.; Leenders, M.; Moons, L.M.; Bogte, A.; Siersema, P.D.; Vleggaar, F.P. Growth rate of small pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: Results from an endoscopic ultrasound based cohort study. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Igarashi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Sasano, H.; Okusaka, T.; Takano, K.; Komoto, I.; Tanaka, M.; Imamura, M.; Jensen, R.T. Epidemiological trends of pancreatic and gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors in Japan: A nationwide survey analysis. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.B.; Lattin, M., Jr.; Grant, E.; Paal, E. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: Radiologic-clinicopathologic correlation. Radiographics 2010, 30, 1445–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi, M.; Eriksson, B.; Kaltsas, G.; Bartsch, D.; Capdevila, J.; Caplin, M.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Kwekkeboom, D.; Rindi, G.; Klöppel, G. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the management of patients with functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamagno, G.; Scherer, V.; Caimo, A.; Bergmann, S.R.; Kann, P.H. Endoscopic Ultrasound Features of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1-Related versus Sporadic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Digestion 2018, 98, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Haba, S.; Okuno, N. Present status of ultrasound elastography for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumors: Review of the literature. J. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 47, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M.; Hookey, L.C.; Bories, E.; Pesenti, C.; Monges, G.; Delpero, J.R. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography: The first step towards virtual biopsy? Preliminary results in 49 patients. Endoscopy 2006, 38, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itokawa, F.; Itoi, T.; Sofuni, A.; Kurihara, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tsuji, S.; Ikeuchi, N.; Umeda, J.; Tanaka, R. EUS elastography combined with the strain ratio of tissue elasticity for diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawwas, M.F.; Taha, H.; Leeds, J.S.; Nayar, M.K.; Oppong, K.W. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative EUS elastography for discriminating malignant from benign solid pancreatic masses: A prospective, single-center study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Domínguez-Muñoz, J.E.; Castiñeira-Alvariño, M.; Luaces-Regueira, M.; Lariño-Noia, J. Quantitative elastography associated with endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 781–788. [Google Scholar]
- Havre, R.F.; Ødegaard, S.; Gilja, O.H.; Nesje, L.B. Characterization of solid focal pancreatic lesions using endoscopic ultrasonography with real-time elastography. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Itoh, A.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Matsubara, H.; Itoh, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Hayashi, K. Usefulness of EUS combined with contrast-enhancement in the differential diagnosis of malignant versus benign and preoperative localization of pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Kudo, M.; Yamao, K.; Takagi, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Komaki, T.; Kamata, K.; Imai, H.; Chiba, Y.; Okada, M. Characterization of small solid tumors in the pancreas: The value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, M.; Napoléon, B.; Gincul, R.; Pioche, M.; Pujol, B.; Lefort, C.; Fumex, F.; Hautefeuille, V.; Fabre, M.; Cros, J. Contrast harmonic EUS for the prediction of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor aggressiveness (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Kato, H.; Saragai, Y.; Muro, S.; Uchida, D.; Tomoda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Horiguchi, S.; Tanaka, N.; Okada, H. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound using time–intensity curve analysis predicts pathological grade of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm. J. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 46, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, K.; Takenaka, M.; Omoto, S.; Miyata, T.; Minaga, K.; Yamao, K.; Imai, H.; Sakurai, T.; Nishida, N.; Chikugo, T.; et al. Impact of avascular areas, as measured by contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS, on the accuracy of FNA for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Haba, S.; Okuno, N.; Koda, H.; Miyano, A.; Fumihara, D. Current status of artificial intelligence analysis for endoscopic ultrasonography. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Gheonea, D.I.; Gorunescu, M.; Ciurea, T.; Popescu, G.L.; Iordache, A.; Hassan, H.; Iordache, S. Neural network analysis of dynamic sequences of EUS elastography used for the differential diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Dietrich, C.F.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Hocke, M.; Seicean, A.; Ignee, A.; Hassan, H.; Streba, C.T.; Ioncică, A.M. Quantitative contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS in differential diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux, S.; Tang, L.; Klimstra, D.; Gonen, M.; Brennan, M.F.; D’Angelica, M.; DeMatteo, R.; Fong, Y.; Jarnagin, W.; Allen, P.J. The outcome of resected cystic pancreatic endocrine neoplasms: A case-matched analysis. Surgery 2012, 151, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.-X.; Chok, A.-Y.; Zheng, H.-L.; Tan, C.-S.; Goh, B.K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinicopathologic characteristics of cystic versus solid pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Surgery 2014, 156, 83–96. e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridtitid, W.; Halawi, H.; DeWitt, J.M.; Sherman, S.; LeBlanc, J.; McHenry, L.; Coté, G.A.; Al-Haddad, M.A. Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Outcomes of preoperative endosonography-guided fine needle aspiration, and recurrence during long-term follow-up. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, H.; Yamao, K.; Salem, A.A.; Sawaki, A.; Takahashi, K.; Mizuno, N.; Kawai, H.; Tajika, M.; Isaka, T.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Pancreatic endocrine neoplasm can mimic serous cystadenoma. Int. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2005, 35, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, C.M.; Shi, C.; Klein, A.P.; Konukiewitz, B.; Edil, B.H.; Ellison, T.A.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Schulick, R.D.; Klöppel, G.; Hruban, R.H. Serotonin expression in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors correlates with a trabecular histologic pattern and large duct involvement. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawamoto, S.; Shi, C.; Hruban, R.H.; Choti, M.A.; Schulick, R.D.; Fishman, E.K.; Siegelman, S.S. Small serotonin-producing neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas associated with pancreatic duct obstruction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, W482–W488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, S.; Partelli, S.; Petrone, M.C.; Zilli, A.; Conte, D.; Falconi, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G. Endoscopic ultrasound appearance of pancreatic serotonin-staining neuroendocrine neoplasms. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyonaga, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Mori, H.; Yamada, Y.; Takaji, R.; Hijiya, N.; Yoshizumi, F.; Aramaki, M. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with extensive intraductal invasion of the main pancreatic duct: A case report. JOP 2014, 15, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Chen, J.; Chan, T.; Lin, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.P.; Feng, S.T. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: Correlation between MSCT features and pathological classification. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2945–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Assignies, G.; Couvelard, A.; Bahrami, S.; Vullierme, M.P.; Hammel, P.; Hentic, O.; Sauvanet, A.; Bedossa, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Vilgrain, V. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: Tumor blood flow assessed with perfusion CT reflects angiogenesis and correlates with prognostic factors. Radiology 2009, 250, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K.; Kurihara, K.; Itoi, T.; Katanuma, A.; Sasaki, T.; Hara, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kimura, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; et al. Clinical and Pathological Features of Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A Nationwide Multicenter Study in Japan. Pancreas 2018, 47, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, S.; Hua, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.J.; Yu, X.J. Differentiation of solid-pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by using endoscopic ultrasound. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Saito, H.; Kato, H.; Kojima, T.; Ito, M.; Ishiyama, S.; Fujiwara, A.; Niguma, T.; Yoshioka, M.; Shiode, J.; et al. Diagnosis of a solid pseudopapillary neoplasm using EUS-FNA. Intern. Med. 2013, 52, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardengh, J.C.; Lopes, C.V.; Venco, F.E.; Machado, M.A. Diagnosis of pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasms using cell-blocks and immunohistochemical evaluation of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy specimens. Cytopathology 2021, 32, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; Byun, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.G. Hypervascular solid-appearing serous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: Differential diagnosis with neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutiani, N.; Egger, M.E.; Doughtie, C.A.; Burkardt, E.S.; Scoggins, C.R.; Martin, R.C., 2nd; McMasters, K.M. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen (IPAS): A single-institution experience and review of the literature. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 213, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.E.; Morris, J.D.; Anand, N.; DePalma, F.; Greenwald, B.D.; Kim, R.E.; Laczek, J.; Lee, W.J.; Papadopoulas, I.; Uradomo, L.; et al. Recognizing intrapancreatic accessory spleen via EUS: Interobserver variability. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, M.S.; Singh, B.S.; Cazacu, I.M.; Saftoiu, A. Differentiating intrapancreatic accessory spleen from a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor or metastasis by the “bridge sign”. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.; Sun, S.-Y. Endoscopic ultrasonography elastography in the diagnosis of intrapancreatic ectopic spleen: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renno, A.; Hill, M.; Abdel-Aziz, Y.; Meawad, H.; Lenhard, A.; Nawras, A. Diagnosis of intrapancreatic accessory spleen by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration mimicking a pancreatic neoplasm: A case report and review of literature. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, C.; Luigiano, C.; Maimone, A.; Tarantino, I.; Baccarini, P.; Fornelli, A.; Liotta, R.; Polifemo, A.; Barresi, L.; Traina, M.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy of small solid pancreatic lesions using a 22-gauge needle with side fenestration. Surg. Endosc. 2015, 29, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Hijioka, S.; Masui, T.; Kasajima, A.; Nakamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Komoto, I.; Hijioka, M.; Lee, L.; Igarashi, H.; et al. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.H.; Cramer, H. EUS-guided FNA cytology of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour (PanNET): A retrospective study of 132 cases over an 18-year period in a single institution. Cytopathology 2014, 25, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.G.; Bhattacharya, A.; Li, F.; Ross, W.A.; Ladha, H.; Porter, K.; Atiq, M.; Bhutani, M.S.; Lee, J.H. Diagnostic Differentiation of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor from Other Neoplastic Solid Pancreatic Lesions During Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration. Pancreas 2016, 45, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidsma, C.M.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Rocha, F.; Abbott, D.E.; Fields, R.; Smith, P.M.; Poultsides, G.A.; Cho, C.; van Eijck, C.; van Dijkum, E.N.; et al. Clinical relevance of performing endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors less than 2 cm. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 122, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijioka, S.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Imaoka, H.; Bhatia, V.; Mekky, M.A.; Yoshimura, K.; Yoshida, T.; Okuno, N.; Hieda, N.; et al. Diagnostic performance and factors influencing the accuracy of EUS-FNA of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedenström, P. The best approach for sampling of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors—EUS-FNA or EUS-FNB? Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E1400–E1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Thorburn, D.; Toumpanakis, C.; Frazzoni, L.; Johnson, G.; Vessal, S.; Luong, T.V.; Caplin, M.; Pereira, S.P. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration vs fine-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E1393–E1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witt, B.L.; Factor, R.E.; Chadwick, B.E.; Caron, J.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Adler, D.G. Evaluation of the SharkCore(®) needle for EUS-guided core biopsy of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endosc. Ultrasound. 2018, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeds, J.S.; Nayar, M.K.; Bekkali, N.L.H.; Wilson, C.H.; Johnson, S.J.; Haugk, B.; Darne, A.; Oppong, K.W. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy is superior to fine-needle aspiration in assessing pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E1281–E1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.S.; Kim, Y.; An, S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, D.W.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.C.; et al. Grading by the Ki-67 Labeling Index of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Specimens of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Can Be Underestimated. Pancreas 2018, 47, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, M.; Poliani, L.; Rahal, D.; Auriemma, F.; Anderloni, A.; Ridolfi, C.; Spaggiari, P.; Capretti, G.; Di Tommaso, L.; Preatoni, P.; et al. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound Biopsy in Diagnosis and Grading Based on the WHO 2017 Classification. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, K.; Ashida, R.; Yasukawa, S.; Chiba, Y.; Fukutake, N.; Nebiki, H.; Kurita, A.; Takaoka, M.; Ogura, T.; Shiomi, H.; et al. Histological diagnosis and grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy using a 25-gauge needle with a core trap: A multicenter prospective trial. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Osamura, R.Y.; Klöppel, G.N.; Rosai, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs; WHO: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.C.; Grant, C.S.; Salomao, D.R.; Fletcher, J.G.; Takahashi, N.; Fidler, J.L.; Levy, M.J.; Huebner, M. Small, nonfunctioning, asymptomatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): Role for nonoperative management. Surgery 2012, 152, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, Y.; Hara, K.; Kuwahara, T.; Mizuno, N.; Okuno, N.; Haba, S.; Okuno, M.; Natsume, S.; Senda, Y.; Kubota, K.; et al. Comparison of prognosis between observation and surgical resection groups with small sporadic non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms without distant metastasis. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piani, C.; Franchi, G.M.; Cappelletti, C.; Scavini, M.; Albarello, L.; Zerbi, A.; Giorgio Arcidiacono, P.; Bosi, E.; Manzoni, M.F. Cytological Ki-67 in pancreatic endocrine tumours: An opportunity for pre-operative grading. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaklamanos, M.; Karoumpalis, I.; Salla, C.; Thomas, D.; Kanakis, G.; Alexandraki, K.; Sougioultzis, S.; Diakatou, E.; Kontogeorgos, G.; Kaltsas, G. Diagnostic accuracy and clinical significance of the fine needle aspiration Ki-67 labelling index in pancreatic endocrine tumours. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, L1-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larghi, A.; Capurso, G.; Carnuccio, A.; Ricci, R.; Alfieri, S.; Galasso, D.; Lugli, F.; Bianchi, A.; Panzuto, F.; De Marinis, L.; et al. Ki-67 grading of nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors on histologic samples obtained by EUS-guided fine-needle tissue acquisition: A prospective study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yamao, K.; Hijioka, S.; Bhatia, V.; Mizuno, N.; Hara, K.; Imaoka, H.; Niwa, Y.; Tajika, M.; Kondo, S.; et al. Evaluation of Ki-67 index in EUS-FNA specimens for the assessment of malignancy risk in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weynand, B.; Borbath, I.; Bernard, V.; Sempoux, C.; Gigot, J.F.; Hubert, C.; Lannoy, V.; Deprez, P.H.; Jouret-Mourin, A. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour grading on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: High reproducibility and inter-observer agreement of the Ki-67 labelling index. Cytopathology 2014, 25, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlinfante, G.; Baccarini, P.; Berretti, D.; Cassetti, T.; Cavina, M.; Conigliaro, R.; De Pellegrin, A.; Di Tommaso, L.; Fabbri, C.; Fornelli, A.; et al. Ki-67 cytological index can distinguish well-differentiated from poorly differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A comparative cytohistological study of 53 cases. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.M.; Pang, J.C.; Kim, G.E.; Tabatabai, Z.L. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Accurate grading with Ki-67 index on fine-needle aspiration specimens using the WHO 2010/ENETS criteria. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unno, J.; Kanno, A.; Masamune, A.; Kasajima, A.; Fujishima, F.; Ishida, K.; Hamada, S.; Kume, K.; Kikuta, K.; Hirota, M.; et al. The usefulness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors based on the World Health Organization classification. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Takagi, T.; Hikichi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamura, J.; Kikuchi, H.; Konno, N.; Waragai, Y.; Asama, H.; et al. Efficacy of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor grading. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8118–8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, N.; Osoegawa, T.; Lee, L.; Tachibana, Y.; Aso, A.; Kubo, H.; Kawabe, K.; Igarashi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Oda, Y.; et al. Efficacy of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis and grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Arco, C.D.; Pérez, J.Á.D.; Medina, L.O.; Valera, J.S.; Aceñero, M.J.F. Reliability of Ki-67 Determination in FNA Samples for Grading Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Endocr. Pathol. 2016, 27, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskiewicz, L.; Jamshed, S.; Gong, Y.; Ainechi, S.; LaFemina, J.; Wang, X. The diagnostic value of FNA biopsy in grading pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutsen, L.; Jouret-Mourin, A.; Borbath, I.; van Maanen, A.; Weynand, B. Accuracy of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumour Grading by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration: Analysis of a Large Cohort and Perspectives for Improvement. Neuroendocrinology 2018, 106, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, V.L.; Kiernan, C.; Wright, J.; Merchant, N.B.; Coogan, A.C.; Shi, C. Fine-Needle Aspiration-Based Grading of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms Using Ki-67: Is Accurate WHO Grading Possible on Cytologic Material? J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2018, 7, 154–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, C.; Noack, P.; Silye, R. Accuracy of grading pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms with Ki-67 index in fine-needle aspiration cellblock material. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Khanna, L.G.; Saqi, A.; Crapanzano, J.P.; Mitchell, J.M.; Sethi, A.; Gonda, T.A.; Kluger, M.D.; Schrope, B.A.; Allendorf, J.; et al. The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Ki67 in the Management of Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalantri, S.; Bakshi, P.; Verma, K. Grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration using Ki-67 index and 2017 World Health Organization criteria: An analysis of 32 cases. Cytojournal 2020, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiella, S.; Landoni, L.; Rota, R.; Valenti, M.; Elio, G.; Crinò, S.F.; Manfrin, E.; Parisi, A.; Cingarlini, S.; D’Onofrio, M.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis and grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A retrospective analysis of 110 cases. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebours, V.; Cordova, J.; Couvelard, A.; Fabre, M.; Palazzo, L.; Vullierme, M.P.; Hentic, O.; Sauvanet, A.; Aubert, A.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Can pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour biopsy accurately determine pathological characteristics? Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzilli, R.; Partelli, S.; Cannizzaro, R.; Pagano, N.; Crippa, S.; Pagnanelli, M.; Falconi, M. Ki-67 prognostic and therapeutic decision driven marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs): A systematic review. Adv. Med. Sci. 2016, 61, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumoto, S.; Kodama, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Katanuma, A.; Maguchi, H. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: Correlation between computed tomography enhancement patterns and prognostic factors of surgical and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy specimens. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, F.A.; Giovannini, M.; Monges, G.; Bories, E.; Pesenti, C.; Caillol, F.; Delpero, J.R. EUS-FNA predicts 5-year survival in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, A.; Couvelard, A.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Costa, F.; Borbath, I.; Delle Fave, G.; Gorbounova, V.; Gross, D.; Grossma, A.; Jense, R.T.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the Standards of Care in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Pathology: Diagnosis and Prognostic Stratification. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 105, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, C.; Krishna, S.G. Advanced diagnostics for pancreatic cysts: Confocal endomicroscopy and molecular analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2734–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.G.; Hart, P.A.; Malli, A.; Kruger, A.J.; McCarthy, S.T.; El-Dika, S.; Walker, J.P.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Manilchuk, A.; Schmidt, C.R.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Increases Accuracy of Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 432–440.e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, A.K.; Swanson, B.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Conwell, D.L.; Krishna, S.G. Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Correlation of in vivo needle-based confocal endomicroscopic findings by ex vivo analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacelli, M.; Celsa, C.; Magro, B.; Barchiesi, M.; Barresi, L.; Capurso, G.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Cammà, C.; Crinò, S.F. Diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasound through-the-needle microforceps biopsy of pancreatic cystic lesions: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Facciorusso, A.; Del Prete, V.; Antonino, M.; Buccino, V.R.; Wani, S. Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle biopsy in pancreatic cysts: A meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 1–8.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Calderón, E.; Martinez-Moreno, B.; Casellas, J.A.; de Madaria, E.; Aparicio, J.R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided, through-the-needle forceps biopsy for diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1123–E1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerveld, D.R.; Ponniah, S.A.; Draganov, P.V.; Yang, D. Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy versus EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E656–E667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trikudanathan, G.; Snover, D.; Mallery, S.J. Microforceps-Assisted Diagnosis of Cystic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheesman, A.R.; Zhu, H.; Liao, X.; Szporn, A.H.; Kumta, N.A.; Nagula, S.; DiMaio, C.J. Impact of EUS-guided microforceps biopsy sampling and needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy on the diagnostic yield and clinical management of pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Biase, D.; Visani, M.; Acquaviva, G.; Fornelli, A.; Masetti, M.; Fabbri, C.; Pession, A.; Tallini, G. The role of next-generation sequencing in the cytologic diagnosis of pancreatic lesions. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gleeson, F.C.; Kerr, S.E.; Kipp, B.R.; Voss, J.S.; Minot, D.M.; Tu, Z.J.; Henry, M.R.; Graham, R.P.; Vasmatzis, G.; Cheville, J.C. Targeted next generation sequencing of endoscopic ultrasound acquired cytology from ampullary and pancreatic adenocarcinoma has the potential to aid patient stratification for optimal therapy selection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VandenBussche, C.J.; Allison, D.B.; Graham, M.K.; Charu, V.; Lennon, A.M.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Hruban, R.H.; Heaphy, C.M. Alternative lengthening of telomeres and ATRX/DAXX loss can be reliably detected in FNAs of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackeng, W.M.; Morsink, F.H.; Moons, L.M.; Heaphy, C.M.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Dreijerink, K.M.; Brosens, L.A. Assessment of ARX expression, a novel biomarker for metastatic risk in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, in endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspiration. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2020, 48, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, A.; Kebebew, E. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pea, A.; Yu, J.; Marchionni, L.; Noe, M.; Luchini, C.; Pulvirenti, A.; De Wilde, R.F.; Brosens, L.A.; Rezaee, N.; Javed, A. Genetic analysis of small well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors identifies subgroups with differing risks of liver metastases. Ann. Surg. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejas, P.; Drier, Y.; Dreijerink, K.M.; Brosens, L.A.; Deshpande, V.; Epstein, C.B.; Conemans, E.B.; Morsink, F.H.; Graham, M.K.; Valk, G.D. Enhancer signatures stratify and predict outcomes of non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Lawlor, R.T.; Ragulan, C.; Patil, Y.; Mafficini, A.; Bersani, S.; Antonello, D.; Mansfield, D.; Cingarlini, S.; Landoni, L. Immune landscape, evolution, hypoxia-mediated viral mimicry pathways and therapeutic potential in molecular subtypes of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Mamlouk, S.; Riemer, P.; Bormann, F.; Klinger, B.; Menne, A.; Teichmann, D.; Wanke-Moehr, K.; Pacyna-Gengelbach, M.; Khouja, S. An Integrative Genetic, Epigenetic and Proteomic Characterization of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (PanNENs) defines Distinct Molecular Features of α-and β-cell like Subgroups. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Findings | Differential Disease | |
|---|---|---|
| PNENs (G1, G2) | Well-rounded, hypoechoic lesions with a homogeneous pattern and clear regular margins | SCN (solid type), SPN, metastic tumor, IPAS |
| Cystic degeneration | SCN (macrocystic type), SPN | |
| Calcification | SPN | |
| PNENs (G3, NEC) | Unclear irregular margins, hypovascular, and internal necrosis of the tumor | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, acinar cell carcinoma |
| Intraductal invasion of the main pancreatic duct | Acinar cell carcinoma |
| First Author | Year | Study Design | Number of Patients Analyzed for the Concordance Rate, n | Ki-67 Concordance Rate | Mean Lesion Size (Range), mm | Percentage of Functioning Tumor | Needle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piani C [67] | 2008 | Retrospective | 18 | 78–89% a | 30 (10–100) | 38.9% | 22-, or 25-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Kaklamatos M [68] | 2011 | Retrospective | 26 | 54% | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. |
| Larghi A [69] | 2012 | Prospective | 12 | 83.3% | 16.9 (7–100) | 0% | 19-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Hasegawa T [70] | 2014 | Retrospective | 27 | 77.8% | 28.1 (5–130) | 10.3% | 25-, or 22-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Weynand B [71] | 2014 | Retrospective | 33 | 57.6% | 33 (2–110) | n.r. | 22-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Carlinfante G [72] | 2014 | Retrospective | 53 | 86.8% | 17 (n.r.) | n.r. | 25-, 19-, or 22-gauge EUS-FNA or EUS-FNB needles |
| Farrell JM [73] | 2014 | Retrospective | 22 | 86% | 30 (15–82) | 24% | 25-, 22-, or 19-gauge needles (details unknown) |
| Unno J [74] | 2014 | Retrospective | 19 | 89.5% | 22.3 (7–100) | 31.6% | 22-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Sugimoto M [75] | 2015 | Retrospective | 8 | 87.5% | 25.7 (4.4–10) | n.r. | 25-, 22-, or 19-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Fujimori N [76] | 2016 | Retrospective | 13 | 69.2% | 20.5 (8–67) | 13.1% | 25-, or 22-gauge EUS-FNA needles |
| Díaz Del Arco C [77] | 2016 | Retrospective | 10 | 70% | 32 (12–120) | 20% | n.r. |
| Laskiewicz L [78] | 2018 | Retrospective | 26 | 84.6% | 21 (8–140) | n.r. | n.r. |
| Boutsen L [79] | 2018 | Retrospective | 57 | 72% | 28.5 (2–110) | 18.9% | n.r. |
| Weiss VL [80] | 2018 | Retrospective | 49 | 61% | 30 (n.r.) | 6.1% | n.r. |
| Hwang HS [61] | 2018 | Retrospective | 33 | 75.8% | 33 (n.r.) | 0% | 25-, 22-, or 19-gauge EUS-FNB needles |
| Grosse C [81] | 2019 | Retrospective | 15 | 100% | 39 (9–75) | 0% | n.r. |
| Di Leo M [62] | 2019 | Retrospective | 25 | 84% | 21 (n.r.) | n.r. | 25- or 22-gauge EUS-FNA or 25-gauge EUS-FNB needles |
| Cui Y [82] | 2020 | Retrospective | 37 | 73% | 40 (7–170) | 0 | 25-, 22-, or 19-gauge needles (details unknown) |
| Heidsma CM [55] | 2020 | Retrospective | 63 | 81% | 13 (n.r.) | 14% | NA |
| Kalantri S [83] | 2020 | Retrospective | 6 b | 100% b | n.r. (11–70) | n.r. | 22-gauge needles (details unknown) |
| Paiella S [84] | 2020 | Prospective | 77 | 81.8% | 24.5 (n.r.) | 11.8% | 25-gauge EUS-FNA needle |
| Kamata K [63] | 2020 | Prospective | 23 | 82.6% | 12.8 (n.r.) | n.r. | 25-gauge EUS-FNB needle |
| Resected Tumor Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUS-FNAB Tumor Grade | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Total |
| Grade 1 | 338 | 88 | 5 | 431 |
| Grade 2 | 32 | 111 | 12 | 155 |
| Grade 3 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 23 |
| Total | 370 | 199 | 40 | 609 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishii, T.; Katanuma, A.; Toyonaga, H.; Chikugo, K.; Nasuno, H.; Kin, T.; Hayashi, T.; Takahashi, K. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020316
Ishii T, Katanuma A, Toyonaga H, Chikugo K, Nasuno H, Kin T, Hayashi T, Takahashi K. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020316
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshii, Tatsuya, Akio Katanuma, Haruka Toyonaga, Koki Chikugo, Hiroshi Nasuno, Toshifumi Kin, Tsuyoshi Hayashi, and Kuniyuki Takahashi. 2021. "Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020316
APA StyleIshii, T., Katanuma, A., Toyonaga, H., Chikugo, K., Nasuno, H., Kin, T., Hayashi, T., & Takahashi, K. (2021). Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Diagnostics, 11(2), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020316






