Force-Invariant Improved Feature Extraction Method for Upper-Limb Prostheses of Transradial Amputees
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
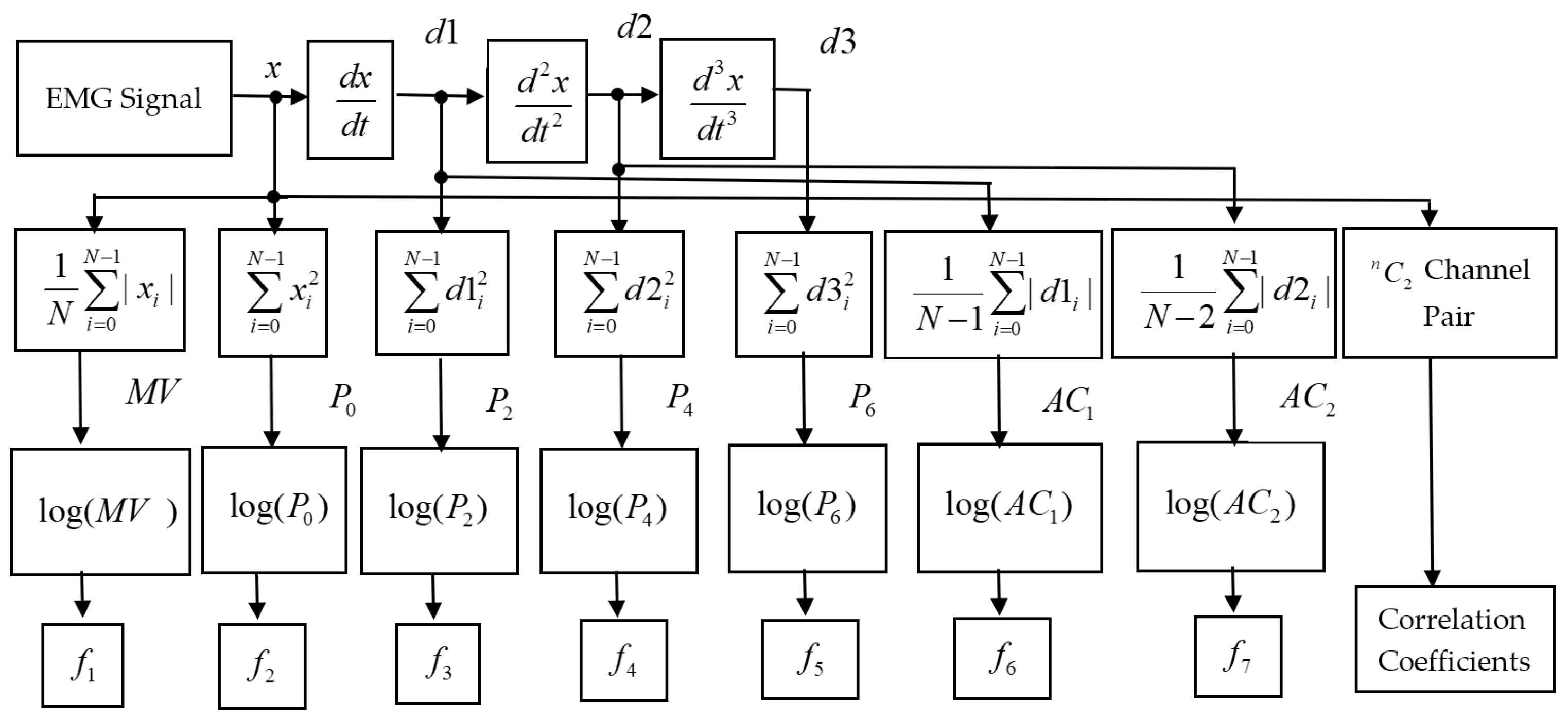
2.1. The Proposed Feature Extraction Method
2.2. Description of EMG Dataset
2.3. EMG Pattern Recognition
2.4. EMG Pattern Recognition Performance with Training Strategies of Various Force Level
2.5. Statistical Test
2.6. RES Index
3. Results
3.1. Signal Observation
3.2. Impact of Nonlinear Transformation
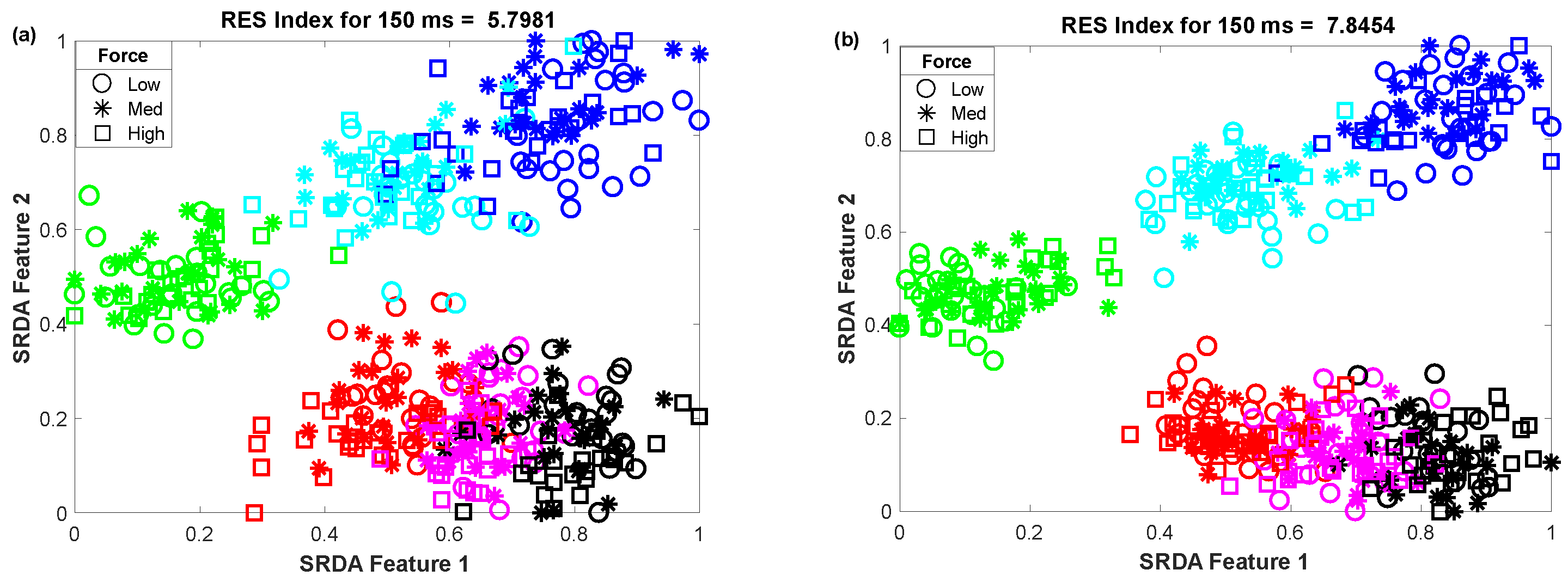
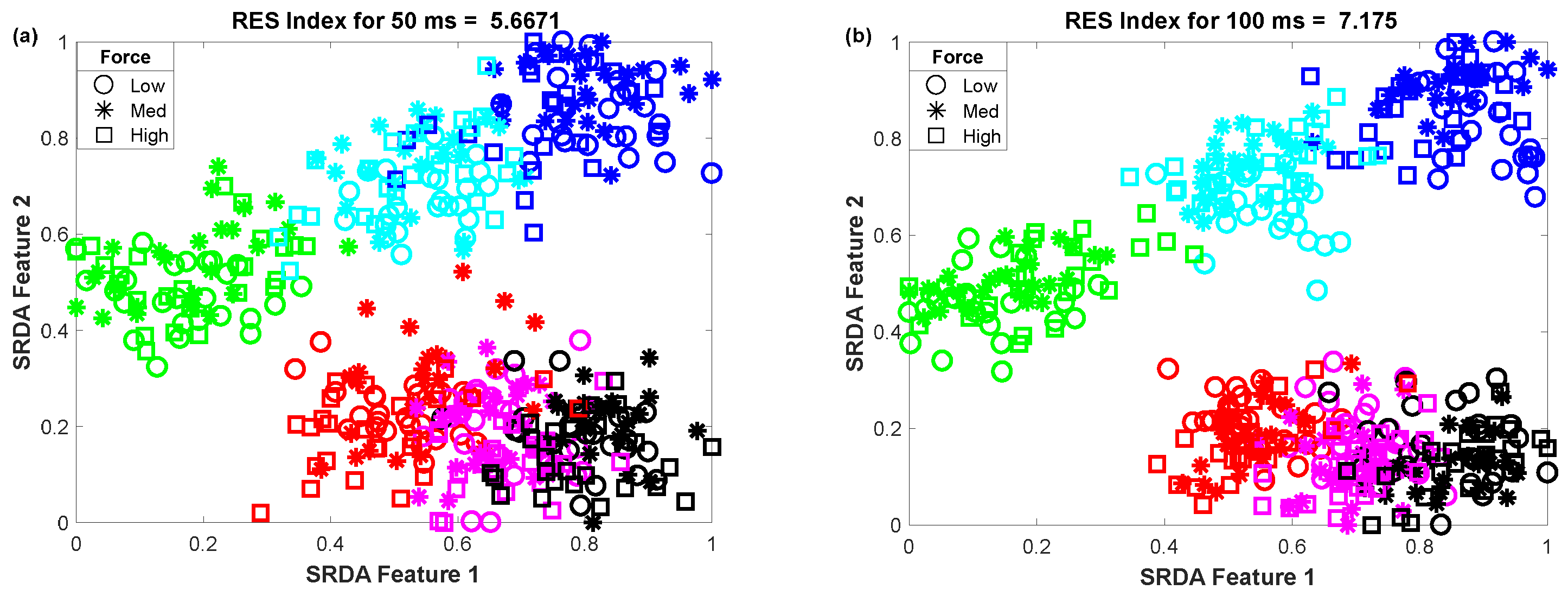
3.3. The Impact of Window Length on Clustering Performance
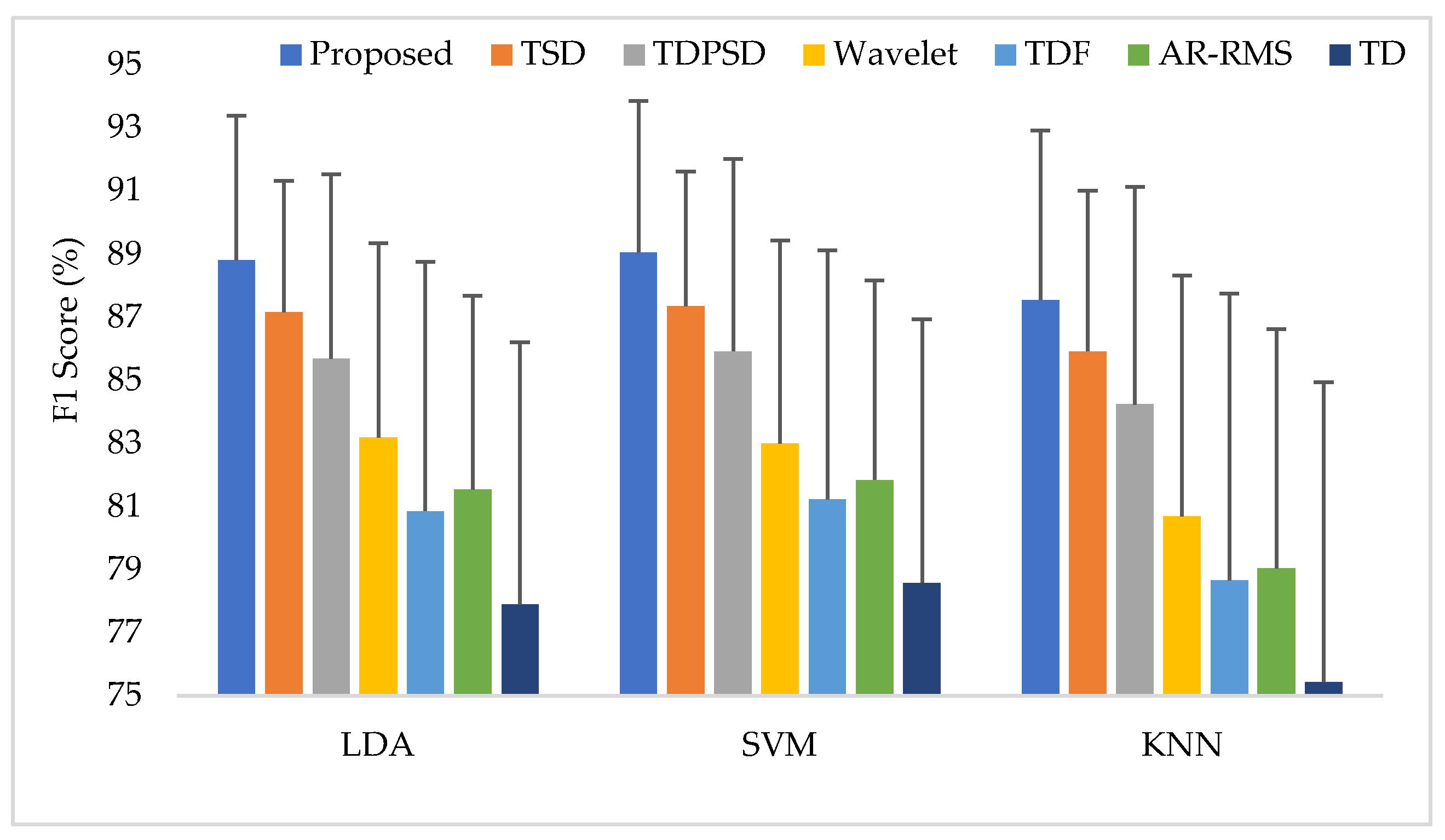
3.4. Training and Testing the Classifiers with Same Force Level (Case 1)
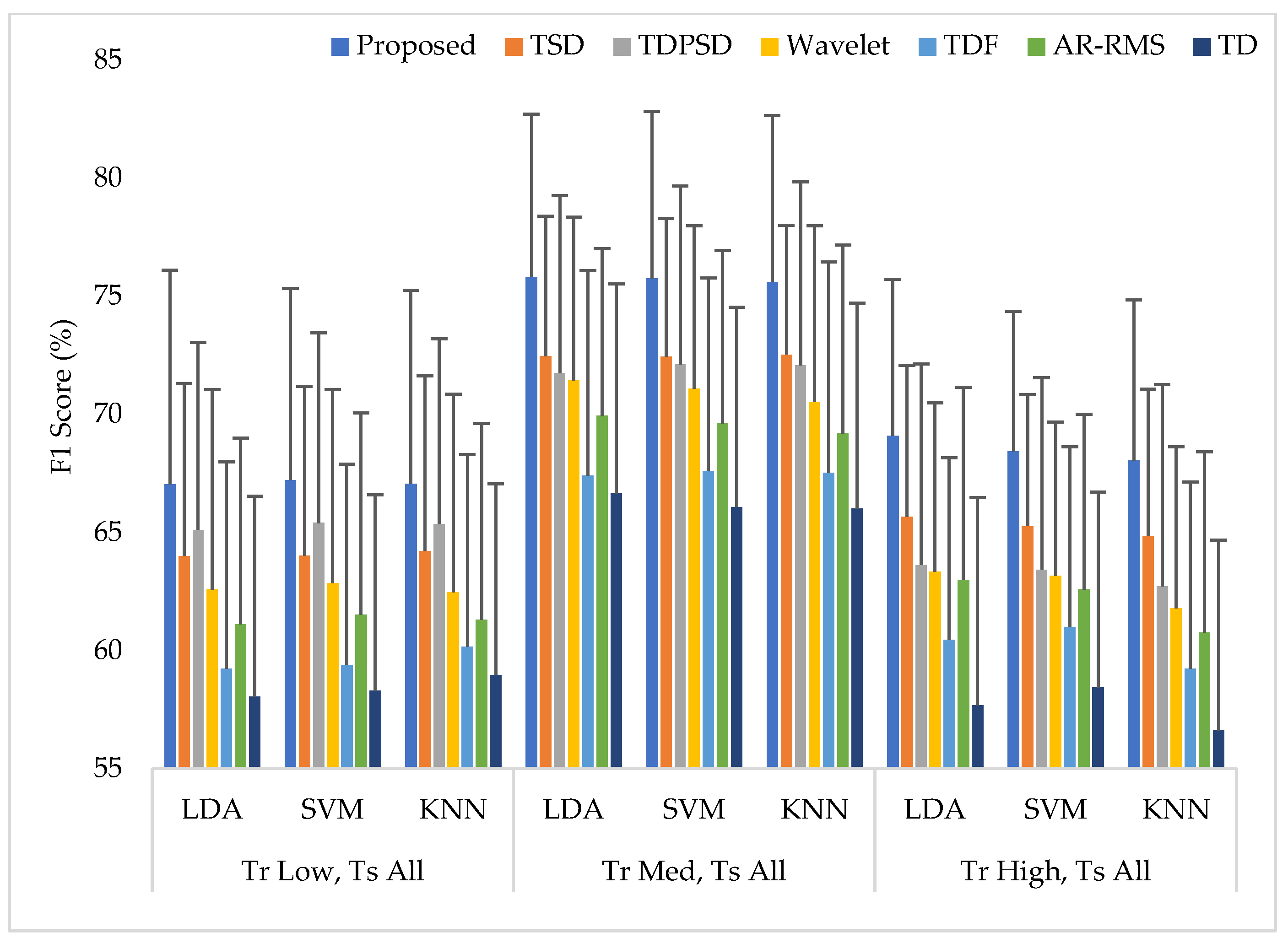
3.5. Training the Classifiers with a Single Force Level at a Time and Testing the Classifiers with All Three Force Levels (Case 2)
3.6. Training the Classifiers with Any Two Force Levels at a Time and Testing the Classifiers with All Three Force Levels (Case 3)
3.7. Training the Classifiers with all Three Force Levels and Testing the Classifiers with All Three Force Levels (Case 4)
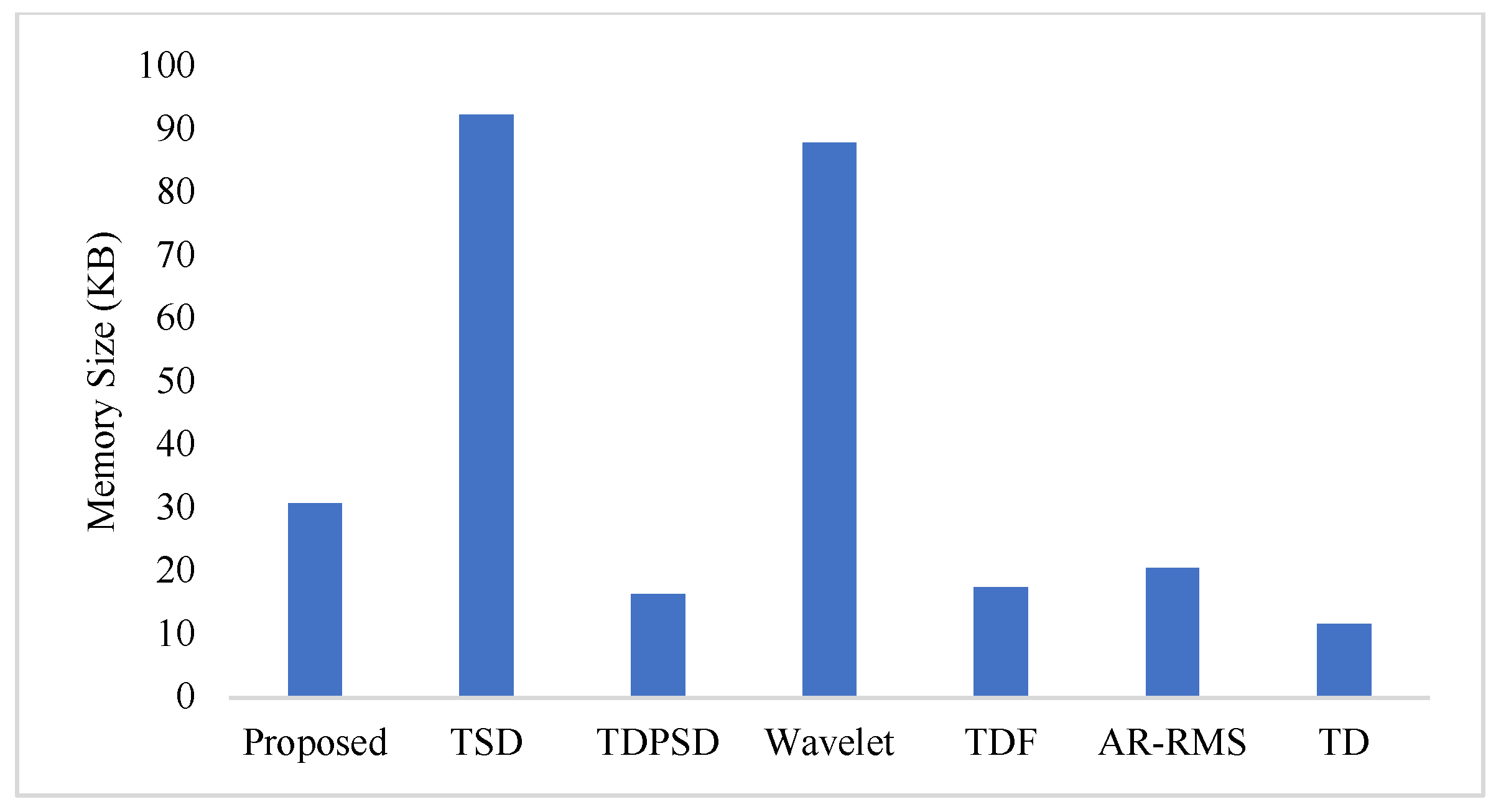
3.8. Computational Time and Memory Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
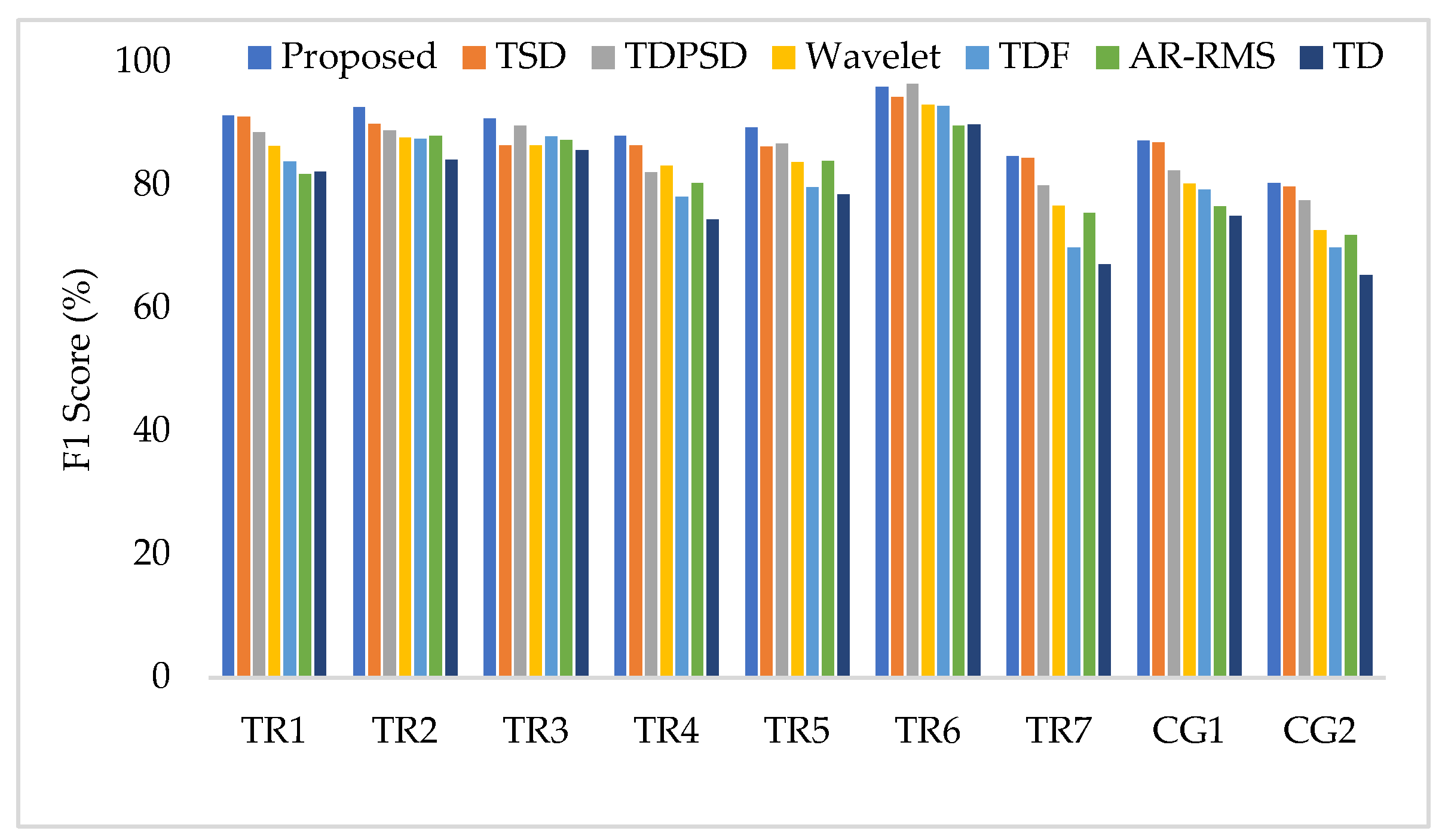
Appendix A. The EMG Pattern Recognition Performance for Different Training and Testing Cases
| Parameter | Classifier | Proposed | TSD | TDPSD | Wavelet | TDF | AR-RMS | TD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training and testing with low force | Accuracy | LDA | 97.86 ± 1.59 | 97.20 ± 1.65 | 96.97 ± 2.50 | 96.49 ± 2.73 | 95.88 ± 2.71 | 95.81 ± 2.69 | 95.17 ± 3.10 |
| SVM | 97.93 ± 1.70 | 97.36 ± 1.67 | 97.06 ± 2.57 | 96.41 ± 2.91 | 95.88 ± 2.83 | 95.80 ± 2.88 | 95.11 ± 3.19 | ||
| KNN | 97.78 ± 1.78 | 97.26 ± 1.86 | 96.87 ± 2.81 | 96.13 ± 3.13 | 95.55 ± 3.00 | 95.27 ± 3.28 | 94.69 ± 3.52 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 93.57 ± 4.77 | 91.60 ± 4.96 | 90.91 ± 7.50 | 89.46 ± 8.20 | 87.65 ± 8.14 | 87.43 ± 8.06 | 85.52 ± 9.31 | |
| SVM | 93.80 ± 5.09 | 92.09 ± 5.01 | 91.19 ± 7.72 | 89.22 ± 8.74 | 87.64 ± 8.48 | 87.39 ± 8.65 | 85.34 ± 9.56 | ||
| KNN | 93.34 ± 5.35 | 91.79 ± 5.59 | 90.60 ± 8.44 | 88.40 ± 9.39 | 86.64 ± 8.99 | 85.80 ± 9.84 | 84.06 ± 10.55 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 98.71 ± 0.92 | 98.32 ± 0.96 | 98.21 ± 1.45 | 97.90 ± 1.60 | 97.56 ± 1.50 | 97.47 ± 1.59 | 97.14 ± 1.74 | |
| SVM | 98.75 ± 1.00 | 98.42 ± 0.98 | 98.27 ± 1.52 | 97.86 ± 1.72 | 97.56 ± 1.62 | 97.46 ± 1.74 | 97.12 ± 1.79 | ||
| KNN | 98.65 ± 1.08 | 98.33 ± 1.12 | 98.12 ± 1.71 | 97.66 ± 1.89 | 97.32 ± 1.78 | 97.11 ± 2.04 | 96.82 ± 2.06 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 94.48 ± 4.18 | 92.47 ± 4.42 | 91.86 ± 6.83 | 90.52 ± 7.58 | 88.95 ± 7.33 | 88.81 ± 7.62 | 87.07 ± 8.48 | |
| SVM | 94.46 ± 4.41 | 93.03 ± 4.62 | 92.09 ± 7.04 | 90.12 ± 8.14 | 88.83 ± 7.85 | 88.56 ± 8.08 | 86.91 ± 8.73 | ||
| KNN | 93.95 ± 4.78 | 92.68 ± 5.17 | 91.43 ± 7.97 | 89.29 ± 8.89 | 87.69 ± 8.60 | 86.91 ± 9.54 | 85.47 ± 10.29 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 93.30 ± 4.91 | 91.28 ± 5.06 | 90.69 ± 7.65 | 89.29 ± 8.32 | 87.39 ± 8.15 | 87.14 ± 8.07 | 85.01 ± 9.51 | |
| SVM | 93.64 ± 5.18 | 91.89 ± 5.05 | 91.05 ± 7.87 | 89.07 ± 8.85 | 87.42 ± 8.52 | 87.25 ± 8.64 | 85.01 ± 9.76 | ||
| KNN | 93.22 ± 5.46 | 91.60 ± 5.69 | 90.44 ± 8.72 | 88.24 ± 9.55 | 86.39 ± 9.10 | 85.55 ± 10.0 | 83.67 ± 10.86 | ||
| Training and testing with medium force | Accuracy | LDA | 97.89 ± 1.05 | 97.30 ± 1.03 | 96.75 ± 1.68 | 96.21 ± 1.80 | 95.91 ± 1.79 | 96.00 ± 1.92 | 95.13 ± 2.21 |
| SVM | 97.91 ± 1.09 | 97.33 ± 1.06 | 96.96 ± 1.68 | 96.12 ± 1.85 | 95.95 ± 1.8 | 95.85 ± 1.98 | 95.10 ± 2.25 | ||
| KNN | 97.65 ± 1.20 | 97.17 ± 1.15 | 96.56 ± 1.87 | 95.75 ± 2.09 | 95.53 ± 2.17 | 95.53 ± 2.29 | 94.55 ± 2.52 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 93.66 ± 3.16 | 91.90 ± 3.09 | 90.25 ± 5.03 | 88.62 ± 5.40 | 87.72 ± 5.38 | 88.00 ± 5.77 | 85.40 ± 6.62 | |
| SVM | 93.72 ± 3.27 | 91.99 ± 3.19 | 90.87 ± 5.05 | 88.36 ± 5.55 | 87.84 ± 5.40 | 87.55 ± 5.94 | 85.31 ± 6.76 | ||
| KNN | 92.96 ± 3.61 | 91.52 ± 3.45 | 89.68 ± 5.61 | 87.24 ± 6.28 | 86.59 ± 6.50 | 86.58 ± 6.87 | 83.66 ± 7.57 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 98.82 ± 0.64 | 98.50 ± 0.61 | 98.17 ± 0.99 | 97.82 ± 1.09 | 97.62 ± 1.08 | 97.71 ± 1.13 | 97.18 ± 1.32 | |
| SVM | 98.81 ± 0.65 | 98.49 ± 0.63 | 98.29 ± 0.99 | 97.76 ± 1.12 | 97.61 ± 1.10 | 97.61 ± 1.16 | 97.14 ± 1.36 | ||
| KNN | 98.66 ± 0.72 | 98.41 ± 0.69 | 98.05 ± 1.09 | 97.53 ± 1.26 | 97.36 ± 1.32 | 97.42 ± 1.36 | 96.79 ± 1.53 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 94.25 ± 3.16 | 92.87 ± 3.08 | 91.24 ± 4.97 | 89.64 ± 5.43 | 88.88 ± 5.28 | 88.83 ± 5.76 | 86.77 ± 6.29 | |
| SVM | 94.17 ± 3.21 | 92.75 ± 3.16 | 91.62 ± 4.96 | 89.33 ± 5.55 | 88.86 ± 5.35 | 88.49 ± 5.88 | 86.68 ± 6.57 | ||
| KNN | 93.45 ± 3.52 | 92.26 ± 3.45 | 90.51 ± 5.52 | 88.08 ± 6.26 | 87.57 ± 6.39 | 87.38 ± 6.90 | 84.97 ± 7.40 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 93.55 ± 3.21 | 91.70 ± 3.22 | 90.11 ± 5.07 | 88.51 ± 5.45 | 87.49 ± 5.42 | 87.87 ± 5.83 | 85.12 ± 6.69 | |
| SVM | 93.62 ± 3.31 | 91.85 ± 3.33 | 90.81 ± 5.08 | 88.23 ± 5.62 | 87.65 ± 5.46 | 87.44 ± 5.96 | 85.12 ± 6.82 | ||
| KNN | 92.84 ± 3.67 | 91.39 ± 3.59 | 89.58 ± 5.67 | 87.07 ± 6.37 | 86.35 ± 6.57 | 86.44 ± 6.99 | 83.39 ± 7.65 | ||
| Training and testing with high force | Accuracy | LDA | 97.44 ± 1.10 | 96.69 ± 1.60 | 96.34 ± 1.75 | 95.56 ± 1.70 | 95.40 ± 1.98 | 95.69 ± 1.50 | 94.89 ± 1.88 |
| SVM | 97.32 ± 1.22 | 96.63 ± 1.67 | 96.32 ± 1.70 | 95.47 ± 1.77 | 95.36 ± 1.94 | 95.52 ± 1.50 | 94.89 ± 1.99 | ||
| KNN | 97.13 ± 1.25 | 96.44 ± 1.86 | 95.95 ± 1.90 | 95.10 ± 1.85 | 94.99 ± 2.16 | 95.07 ± 1.75 | 94.39 ± 2.17 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 92.33 ± 3.30 | 90.07 ± 4.80 | 89.01 ± 5.24 | 86.69 ± 5.09 | 86.20 ± 5.94 | 87.07 ± 4.50 | 84.68 ± 5.63 | |
| SVM | 91.97 ± 3.66 | 89.90 ± 5.01 | 88.96 ± 5.09 | 86.41 ± 5.31 | 86.08 ± 5.81 | 86.57 ± 4.50 | 84.68 ± 5.97 | ||
| KNN | 91.38 ± 3.75 | 89.31 ± 5.57 | 87.84 ± 5.69 | 85.30 ± 5.55 | 84.97 ± 6.49 | 85.21 ± 5.24 | 83.18 ± 6.51 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 98.54 ± 0.65 | 98.11 ± 0.91 | 97.90 ± 1.01 | 97.43 ± 0.99 | 97.33 ± 1.17 | 97.52 ± 0.92 | 97.06 ± 1.14 | |
| SVM | 98.48 ± 0.71 | 98.07 ± 0.97 | 97.90 ± 0.99 | 97.38 ± 1.03 | 97.31 ± 1.15 | 97.41 ± 0.92 | 97.07 ± 1.20 | ||
| KNN | 98.36 ± 0.72 | 97.94 ± 1.09 | 97.67 ± 1.12 | 97.14 ± 1.10 | 97.05 ± 1.32 | 97.13 ± 1.09 | 96.73 ± 1.33 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 92.97 ± 3.11 | 90.97 ± 4.29 | 90.11 ± 4.21 | 87.74 ± 4.73 | 87.35 ± 5.15 | 87.98 ± 4.38 | 86.06 ± 4.90 | |
| SVM | 92.79 ± 3.52 | 90.79 ± 4.61 | 90.03 ± 4.13 | 87.51 ± 4.93 | 87.28 ± 5.06 | 87.46 ± 4.26 | 86.01 ± 5.36 | ||
| KNN | 92.24 ± 3.52 | 90.24 ± 5.11 | 88.93 ± 4.80 | 86.31 ± 5.25 | 86.09 ± 6.01 | 86.25 ± 5.06 | 84.48 ± 5.95 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 92.07 ± 3.40 | 89.77 ± 4.87 | 88.67 ± 5.12 | 86.37 ± 5.03 | 85.78 ± 5.87 | 86.75 ± 4.45 | 84.23 ± 5.53 | |
| SVM | 91.67 ± 3.78 | 89.58 ± 5.08 | 88.61 ± 4.94 | 86.13 ± 5.28 | 85.70 ± 5.80 | 86.23 ± 4.41 | 84.26 ± 5.94 | ||
| KNN | 91.09 ± 3.84 | 88.96 ± 5.72 | 87.47 ± 5.61 | 84.94 ± 5.54 | 84.61 ± 6.46 | 84.89 ± 5.16 | 82.74 ± 6.53 |
| Parameter | Classifier | Proposed | TSD | TDPSD | Wavelet | TDF | AR-RMS | TD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training with low force | Accuracy | LDA | 89.07 ± 3.15 | 88.04 ± 2.61 | 88.48 ± 2.78 | 87.63 ± 2.91 | 86.52 ± 3.04 | 87.23 ± 2.71 | 86.18 ± 2.92 |
| SVM | 89.10 ± 2.79 | 88.01 ± 2.57 | 88.57 ± 2.73 | 87.70 ± 2.83 | 86.46 ± 3.00 | 87.28 ± 2.94 | 86.15 ± 2.87 | ||
| KNN | 89.02 ± 2.82 | 88.06 ± 2.64 | 88.55 ± 2.64 | 87.57 ± 2.86 | 86.84 ± 2.82 | 87.27 ± 2.84 | 86.50 ± 2.70 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 67.22 ± 9.44 | 64.13 ± 7.84 | 65.43 ± 8.33 | 62.90 ± 8.74 | 59.57 ± 9.13 | 61.69 ± 8.12 | 58.55 ± 8.76 | |
| SVM | 67.29 ± 8.38 | 64.03 ± 7.71 | 65.72 ± 8.19 | 63.11 ± 8.49 | 59.37 ± 8.99 | 61.83 ± 8.82 | 58.46 ± 8.60 | ||
| KNN | 67.07 ± 8.45 | 64.17 ± 7.91 | 65.64 ± 7.92 | 62.72 ± 8.58 | 60.53 ± 8.45 | 61.81 ± 8.51 | 59.50 ± 8.11 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 93.72 ± 1.75 | 93.11 ± 1.49 | 93.34 ± 1.59 | 92.87 ± 1.68 | 92.17 ± 1.77 | 92.59 ± 1.58 | 92.00 ± 1.69 | |
| SVM | 93.70 ± 1.64 | 93.11 ± 1.47 | 93.4 ± 1.53 | 92.91 ± 1.71 | 92.07 ± 1.85 | 92.62 ± 1.75 | 91.87 ± 1.75 | ||
| KNN | 93.65 ± 1.65 | 93.12 ± 1.54 | 93.36 ± 1.5 | 92.82 ± 1.69 | 92.30 ± 1.70 | 92.59 ± 1.76 | 92.11 ± 1.69 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 75.51 ± 5.90 | 72.35 ± 4.97 | 73.37 ± 7.31 | 70.74 ± 6.72 | 67.70 ± 7.93 | 69.21 ± 6.65 | 66.75 ± 7.87 | |
| SVM | 74.63 ± 5.92 | 72.21 ± 5.51 | 73.21 ± 6.62 | 70.49 ± 6.57 | 67.55 ± 7.98 | 69.06 ± 7.45 | 66.55 ± 8.55 | ||
| KNN | 74.21 ± 5.94 | 72.06 ± 5.85 | 72.81 ± 6.96 | 69.84 ± 7.07 | 66.83 ± 7.42 | 67.49 ± 7.71 | 65.42 ± 8.22 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 67.04 ± 9.07 | 64.00 ± 7.31 | 65.10 ± 7.95 | 62.58 ± 8.48 | 59.23 ± 8.76 | 61.11 ± 7.90 | 58.05 ± 8.48 | |
| SVM | 67.22 ± 8.12 | 64.02 ± 7.17 | 65.40 ± 8.05 | 62.85 ± 8.21 | 59.40 ± 8.49 | 61.52 ± 8.54 | 58.30 ± 8.30 | ||
| KNN | 67.07 ± 8.19 | 64.22 ± 7.41 | 65.35 ± 7.86 | 62.47 ± 8.39 | 60.16 ± 8.14 | 61.31 ± 8.31 | 58.96 ± 8.11 | ||
| Training with medium force | Accuracy | LDA | 91.99 ± 2.35 | 90.86 ± 2.05 | 90.66 ± 2.63 | 90.57 ± 2.41 | 89.20 ± 2.97 | 90.03 ± 2.40 | 88.96 ± 3.03 |
| SVM | 91.94 ± 2.44 | 90.82 ± 2.07 | 90.78 ± 2.56 | 90.45 ± 2.39 | 89.26 ± 2.82 | 89.91 ± 2.49 | 88.78 ± 2.90 | ||
| KNN | 91.89 ± 2.42 | 90.86 ± 1.92 | 90.76 ± 2.67 | 90.27 ± 2.56 | 89.22 ± 3.06 | 89.81 ± 2.65 | 88.76 ± 2.92 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 75.97 ± 7.06 | 72.58 ± 6.14 | 71.97 ± 7.88 | 71.70 ± 7.22 | 67.61 ± 8.91 | 70.10 ± 7.20 | 66.89 ± 9.09 | |
| SVM | 75.81 ± 7.33 | 72.46 ± 6.21 | 72.35 ± 7.68 | 71.34 ± 7.17 | 67.79 ± 8.47 | 69.74 ± 7.46 | 66.34 ± 8.70 | ||
| KNN | 75.67 ± 7.26 | 72.57 ± 5.77 | 72.27 ± 8.00 | 70.80 ± 7.68 | 67.67 ± 9.19 | 69.44 ± 7.95 | 66.29 ± 8.76 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 95.29 ± 1.44 | 94.61 ± 1.30 | 94.49 ± 1.59 | 94.41 ± 1.49 | 93.55 ± 1.81 | 94.11 ± 1.44 | 93.38 ± 1.85 | |
| SVM | 95.24 ± 1.50 | 94.57 ± 1.31 | 94.54 ± 1.57 | 94.34 ± 1.49 | 93.56 ± 1.74 | 94.02 ± 1.50 | 93.26 ± 1.78 | ||
| KNN | 95.21 ± 1.50 | 94.58 ± 1.23 | 94.52 ± 1.65 | 94.22 ± 1.61 | 93.52 ± 1.91 | 93.95 ± 1.62 | 93.23 ± 1.83 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 78.70 ± 5.93 | 75.77 ± 4.91 | 75.12 ± 6.73 | 74.03 ± 6.54 | 70.41 ± 8.26 | 72.37 ± 7.12 | 69.18 ± 8.73 | |
| SVM | 78.57 ± 6.02 | 75.71 ± 4.76 | 75.05 ± 6.94 | 73.45 ± 6.49 | 70.63 ± 7.90 | 72.03 ± 7.17 | 69.03 ± 8.24 | ||
| KNN | 78.27 ± 6.10 | 75.55 ± 4.51 | 74.69 ± 7.39 | 72.77 ± 7.06 | 70.11 ± 8.51 | 71.31 ± 8.17 | 68.33 ± 8.51 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 75.83 ± 6.89 | 72.47 ± 5.94 | 71.75 ± 7.53 | 71.44 ± 6.92 | 67.42 ± 8.68 | 69.94 ± 7.08 | 66.64 ± 8.90 | |
| SVM | 75.76 ± 7.08 | 72.46 ± 5.85 | 72.13 ± 7.55 | 71.09 ± 6.91 | 67.61 ± 8.18 | 69.61 ± 7.34 | 66.09 ± 8.46 | ||
| KNN | 75.61 ± 7.05 | 72.54 ± 5.48 | 72.08 ± 7.78 | 70.53 ± 7.47 | 67.52 ± 8.95 | 69.20 ± 7.98 | 66.01 ± 8.70 | ||
| Training with high force | Accuracy | LDA | 89.93 ± 2.26 | 88.76 ± 2.21 | 88.31 ± 2.70 | 88.11 ± 2.29 | 87.20 ± 2.47 | 87.92 ± 2.65 | 86.24 ± 2.90 |
| SVM | 89.72 ± 2.11 | 88.65 ± 2.03 | 88.21 ± 2.61 | 88.04 ± 2.10 | 87.32 ± 2.47 | 87.76 ± 2.44 | 86.40 ± 2.73 | ||
| KNN | 89.53 ± 2.38 | 88.47 ± 2.16 | 87.95 ± 2.76 | 87.55 ± 2.18 | 86.76 ± 2.55 | 87.19 ± 2.46 | 85.80 ± 2.63 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 69.79 ± 6.79 | 66.28 ± 6.64 | 64.93 ± 8.09 | 64.32 ± 6.88 | 61.60 ± 7.42 | 63.76 ± 7.94 | 58.73 ± 8.70 | |
| SVM | 69.17 ± 6.33 | 65.94 ± 6.09 | 64.64 ± 7.84 | 64.12 ± 6.29 | 61.95 ± 7.42 | 63.28 ± 7.32 | 59.21 ± 8.19 | ||
| KNN | 68.60 ± 7.13 | 65.42 ± 6.47 | 63.84 ± 8.27 | 62.64 ± 6.55 | 60.29 ± 7.66 | 61.57 ± 7.39 | 57.40 ± 7.88 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 93.90 ± 1.32 | 93.18 ± 1.29 | 92.85 ± 1.63 | 92.75 ± 1.34 | 92.11 ± 1.57 | 92.61 ± 1.57 | 91.56 ± 1.69 | |
| SVM | 93.77 ± 1.23 | 93.10 ± 1.20 | 92.76 ± 1.57 | 92.67 ± 1.28 | 92.12 ± 1.58 | 92.50 ± 1.46 | 91.59 ± 1.65 | ||
| KNN | 93.63 ± 1.41 | 92.97 ± 1.31 | 92.54 ± 1.68 | 92.35 ± 1.32 | 91.78 ± 1.66 | 92.12 ± 1.49 | 91.22 ± 1.60 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 74.84 ± 5.30 | 72.18 ± 4.89 | 70.51 ± 7.23 | 69.12 ± 6.66 | 66.68 ± 7.46 | 68.12 ± 7.14 | 63.70 ± 8.82 | |
| SVM | 74.36 ± 4.89 | 71.89 ± 4.11 | 70.85 ± 6.47 | 68.84 ± 6.32 | 66.73 ± 7.20 | 68.17 ± 6.58 | 65.00 ± 8.29 | ||
| KNN | 73.82 ± 5.34 | 71.18 ± 5.10 | 70.60 ± 7.21 | 67.79 ± 6.46 | 66.36 ± 8.11 | 66.38 ± 7.18 | 63.85 ± 8.82 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 69.10 ± 6.63 | 65.67 ± 6.42 | 63.63 ± 8.51 | 63.35 ± 7.15 | 60.46 ± 7.70 | 62.99 ± 8.17 | 57.69 ± 8.79 | |
| SVM | 68.43 ± 5.93 | 65.27 ± 5.57 | 63.43 ± 8.12 | 63.16 ± 6.51 | 60.99 ± 7.65 | 62.58 ± 7.43 | 58.42 ± 8.30 | ||
| KNN | 68.05 ± 6.80 | 64.86 ± 6.21 | 62.72 ± 8.54 | 61.80 ± 6.84 | 59.23 ± 7.91 | 60.77 ± 7.65 | 56.60 ± 8.07 |
| Parameter | Classifier | Proposed | TSD | TDPSD | Wavelet | TDF | AR-RMS | TD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training with low and medium forces | Accuracy | LDA | 94.21 ± 1.83 | 93.30 ± 1.66 | 93.06 ± 2.34 | 92.80 ± 2.23 | 91.53 ± 2.69 | 92.06 ± 1.86 | 91.05 ± 2.52 |
| SVM | 94.20 ± 1.84 | 93.22 ± 1.63 | 93.12 ± 2.32 | 92.75 ± 2.26 | 91.76 ± 2.59 | 92.02 ± 2.16 | 91.12 ± 2.82 | ||
| KNN | 93.90 ± 1.97 | 93.03 ± 1.74 | 92.85 ± 2.47 | 92.37 ± 2.46 | 91.49 ± 2.81 | 91.72 ± 2.28 | 90.86 ± 2.90 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 82.64 ± 5.50 | 79.90 ± 4.97 | 79.18 ± 7.03 | 78.40 ± 6.70 | 74.60 ± 8.07 | 76.18 ± 5.59 | 73.14 ± 7.57 | |
| SVM | 82.60 ± 5.52 | 79.66 ± 4.89 | 79.37 ± 6.95 | 78.24 ± 6.79 | 75.28 ± 7.76 | 76.06 ± 6.48 | 73.36 ± 8.45 | ||
| KNN | 81.70 ± 5.90 | 79.09 ± 5.22 | 78.54 ± 7.42 | 77.11 ± 7.38 | 74.47 ± 8.44 | 75.15 ± 6.85 | 72.57 ± 8.69 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 96.64 ± 1.05 | 96.07 ± 0.95 | 95.95 ± 1.37 | 95.79 ± 1.31 | 95.00 ± 1.60 | 95.32 ± 1.11 | 94.68 ± 1.50 | |
| SVM | 96.63 ± 1.06 | 96.03 ± 0.92 | 95.97 ± 1.35 | 95.75 ± 1.34 | 95.12 ± 1.52 | 95.30 ± 1.26 | 94.72 ± 1.67 | ||
| KNN | 96.44 ± 1.14 | 95.90 ± 1.01 | 95.80 ± 1.46 | 95.51 ± 1.48 | 94.93 ± 1.71 | 95.09 ± 1.39 | 94.53 ± 1.76 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 84.45 ± 4.98 | 81.95 ± 4.49 | 81.28 ± 6.79 | 80.19 ± 6.37 | 76.89 ± 7.89 | 77.98 ± 5.72 | 75.26 ± 7.81 | |
| SVM | 84.37 ± 4.96 | 81.8 ± 4.27 | 81.28 ± 6.70 | 80.03 ± 6.43 | 77.24 ± 7.44 | 77.90 ± 6.18 | 75.55 ± 8.14 | ||
| KNN | 83.29 ± 5.59 | 80.98 ± 4.93 | 80.24 ± 7.34 | 78.53 ± 7.41 | 75.91 ± 8.58 | 76.34 ± 7.18 | 73.94 ± 9.00 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 82.63 ± 5.40 | 79.91 ± 4.92 | 79.13 ± 6.96 | 78.30 ± 6.59 | 74.64 ± 7.85 | 76.11 ± 5.58 | 73.04 ± 7.57 | |
| SVM | 82.60 ± 5.39 | 79.72 ± 4.75 | 79.36 ± 6.85 | 78.21 ± 6.65 | 75.26 ± 7.62 | 76.05 ± 6.36 | 73.34 ± 8.35 | ||
| KNN | 81.69 ± 5.83 | 79.10 ± 5.16 | 78.49 ± 7.37 | 77.02 ± 7.35 | 74.38 ± 8.38 | 75.02 ± 6.90 | 72.32 ± 8.85 | ||
| Training with low and high forces | Accuracy | LDA | 95.34 ± 1.70 | 94.80 ± 1.61 | 94.17 ± 2.12 | 93.39 ± 2.12 | 92.55 ± 2.64 | 92.81 ± 2.24 | 91.57 ± 2.86 |
| SVM | 95.37 ± 1.78 | 94.80 ± 1.70 | 94.25 ± 2.16 | 93.30 ± 2.17 | 92.49 ± 2.74 | 92.77 ± 2.35 | 91.60 ± 2.89 | ||
| KNN | 94.98 ± 1.92 | 94.41 ± 1.87 | 93.72 ± 2.40 | 92.58 ± 2.48 | 91.77 ± 2.95 | 91.92 ± 2.60 | 90.73 ± 3.16 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 86.03 ± 5.10 | 84.41 ± 4.82 | 82.52 ± 6.35 | 80.18 ± 6.35 | 77.66 ± 7.93 | 78.43 ± 6.71 | 74.72 ± 8.58 | |
| SVM | 86.12 ± 5.34 | 84.39 ± 5.11 | 82.74 ± 6.49 | 79.89 ± 6.52 | 77.47 ± 8.23 | 78.31 ± 7.06 | 74.81 ± 8.68 | ||
| KNN | 84.94 ± 5.75 | 83.23 ± 5.60 | 81.16 ± 7.21 | 77.74 ± 7.43 | 75.32 ± 8.84 | 75.75 ± 7.79 | 72.20 ± 9.47 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 97.25 ± 1.00 | 96.90 ± 0.95 | 96.55 ± 1.24 | 96.07 ± 1.24 | 95.53 ± 1.61 | 95.67 ± 1.34 | 94.94 ± 1.71 | |
| SVM | 97.26 ± 1.07 | 96.90 ± 1.02 | 96.58 ± 1.26 | 96.01 ± 1.29 | 95.49 ± 1.68 | 95.65 ± 1.42 | 94.97 ± 1.74 | ||
| KNN | 97.02 ± 1.16 | 96.66 ± 1.12 | 96.25 ± 1.42 | 95.57 ± 1.50 | 95.03 ± 1.83 | 95.12 ± 1.59 | 94.41 ± 1.93 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 86.81 ± 5.11 | 85.22 ± 4.78 | 83.61 ± 6.29 | 81.16 ± 6.36 | 78.61 ± 8.04 | 79.39 ± 6.60 | 76.00 ± 8.62 | |
| SVM | 86.92 ± 5.37 | 85.26 ± 5.03 | 83.85 ± 6.31 | 80.84 ± 6.55 | 78.54 ± 8.25 | 79.33 ± 6.91 | 76.15 ± 8.63 | ||
| KNN | 85.69 ± 5.82 | 84.00 ± 5.73 | 82.11 ± 7.18 | 78.63 ± 7.55 | 76.30 ± 9.08 | 76.61 ± 7.81 | 73.37 ± 9.63 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 85.92 ± 5.17 | 84.27 ± 4.90 | 82.33 ± 6.43 | 80.06 ± 6.39 | 77.49 ± 8.02 | 78.31 ± 6.75 | 74.51 ± 8.74 | |
| SVM | 86.05 ± 5.38 | 84.31 ± 5.15 | 82.62 ± 6.52 | 79.82 ± 6.53 | 77.43 ± 8.23 | 78.27 ± 7.06 | 74.79 ± 8.72 | ||
| KNN | 84.84 ± 5.84 | 83.11 ± 5.72 | 81.02 ± 7.26 | 77.63 ± 7.52 | 75.21 ± 8.95 | 75.64 ± 7.89 | 72.08 ± 9.63 | ||
| Training with medium and high forces | Accuracy | LDA | 94.27 ± 1.83 | 93.20 ± 1.54 | 93.00 ± 2.23 | 92.57 ± 2.24 | 91.71 ± 2.87 | 92.06 ± 2.29 | 90.82 ± 2.78 |
| SVM | 94.18 ± 1.86 | 93.24 ± 1.49 | 93.16 ± 2.30 | 92.45 ± 2.29 | 91.95 ± 2.88 | 91.92 ± 2.29 | 91.11 ± 2.72 | ||
| KNN | 93.88 ± 1.91 | 92.95 ± 1.60 | 92.82 ± 2.34 | 91.97 ± 2.43 | 91.24 ± 3.06 | 91.23 ± 2.45 | 90.29 ± 2.93 | ||
| Sensitivity | LDA | 82.81 ± 5.50 | 79.60 ± 4.61 | 79.01 ± 6.70 | 77.72 ± 6.71 | 75.14 ± 8.62 | 76.18 ± 6.86 | 72.46 ± 8.33 | |
| SVM | 82.53 ± 5.58 | 79.71 ± 4.48 | 79.49 ± 6.91 | 77.34 ± 6.87 | 75.86 ± 8.64 | 75.75 ± 6.87 | 73.33 ± 8.15 | ||
| KNN | 81.64 ± 5.72 | 78.86 ± 4.80 | 78.46 ± 7.01 | 75.91 ± 7.30 | 73.71 ± 9.18 | 73.68 ± 7.35 | 70.87 ± 8.78 | ||
| Specificity | LDA | 96.62 ± 1.09 | 95.95 ± 0.94 | 95.83 ± 1.33 | 95.55 ± 1.38 | 95.00 ± 1.80 | 95.24 ± 1.37 | 94.44 ± 1.72 | |
| SVM | 96.55 ± 1.11 | 95.97 ± 0.91 | 95.92 ± 1.39 | 95.48 ± 1.41 | 95.13 ± 1.79 | 95.16 ± 1.38 | 94.61 ± 1.69 | ||
| KNN | 96.37 ± 1.15 | 95.79 ± 0.99 | 95.70 ± 1.42 | 95.18 ± 1.50 | 94.68 ± 1.93 | 94.71 ± 1.49 | 94.09 ± 1.83 | ||
| Precision | LDA | 84.54 ± 4.81 | 81.72 ± 3.94 | 80.95 ± 6.42 | 79.06 ± 6.72 | 76.90 ± 8.29 | 77.50 ± 6.83 | 74.29 ± 8.25 | |
| SVM | 84.38 ± 4.70 | 81.79 ± 3.66 | 81.37 ± 6.51 | 78.77 ± 6.64 | 77.42 ± 8.33 | 77.17 ± 6.82 | 74.92 ± 8.24 | ||
| KNN | 83.43 ± 4.94 | 80.95 ± 4.05 | 80.12 ± 6.81 | 77.19 ± 7.17 | 75.29 ± 9.02 | 74.93 ± 7.62 | 72.51 ± 8.95 | ||
| F1 Score | LDA | 82.65 ± 5.47 | 79.42 ± 4.58 | 78.65 ± 6.85 | 77.41 ± 6.85 | 74.71 ± 8.75 | 75.86 ± 7.18 | 72.07 ± 8.49 | |
| SVM | 82.40 ± 5.50 | 79.57 ± 4.41 | 79.18 ± 6.99 | 77.10 ± 6.92 | 75.49 ± 8.72 | 75.48 ± 7.09 | 72.96 ± 8.36 | ||
| KNN | 81.54 ± 5.61 | 78.71 ± 4.77 | 78.10 ± 7.13 | 75.64 ± 7.37 | 73.36 ± 9.32 | 73.34 ± 7.66 | 70.47 ± 9.07 |
| Parameter | Classifier | Proposed | TSD | TDPSD | Wavelet | TDF | AR-RMS | TD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | LDA | 96.30 ± 1.52 | 95.75 ± 1.38 | 95.28 ± 1.94 | 94.45 ± 2.03 | 93.69 ± 2.60 | 93.89 ± 2.02 | 92.71 ± 2.74 |
| SVM | 96.37 ± 1.60 | 95.80 ± 1.42 | 95.34 ± 2.03 | 94.37 ± 2.14 | 93.78 ± 2.62 | 93.98 ± 2.09 | 92.91 ± 2.77 | |
| KNN | 95.88 ± 1.77 | 95.33 ± 1.68 | 94.79 ± 2.28 | 93.62 ± 2.51 | 92.95 ± 2.99 | 93.07 ± 2.48 | 91.88 ± 3.10 | |
| Sensitivity | LDA | 88.89 ± 4.55 | 87.24 ± 4.13 | 85.83 ± 5.81 | 83.34 ± 6.10 | 81.07 ± 7.81 | 81.68 ± 6.06 | 78.12 ± 8.22 |
| SVM | 89.11 ± 4.80 | 87.41 ± 4.25 | 86.02 ± 6.09 | 83.10 ± 6.43 | 81.35 ± 7.87 | 81.93 ± 6.28 | 78.72 ± 8.30 | |
| KNN | 87.63 ± 5.32 | 86.00 ± 5.04 | 84.36 ± 6.85 | 80.86 ± 7.52 | 78.84 ± 8.96 | 79.21 ± 7.43 | 75.65 ± 9.31 | |
| Specificity | LDA | 97.82 ± 0.90 | 97.51 ± 0.81 | 97.22 ± 1.14 | 96.71 ± 1.23 | 96.24 ± 1.60 | 96.36 ± 1.22 | 95.63 ± 1.67 |
| SVM | 97.86 ± 0.95 | 97.53 ± 0.83 | 97.26 ± 1.20 | 96.66 ± 1.29 | 96.29 ± 1.59 | 96.41 ± 1.27 | 95.77 ± 1.67 | |
| KNN | 97.56 ± 1.07 | 97.24 ± 1.01 | 96.91 ± 1.35 | 96.19 ± 1.54 | 95.76 ± 1.85 | 95.84 ± 1.52 | 95.11 ± 1.90 | |
| Precision | LDA | 89.31 ± 4.50 | 87.85 ± 4.04 | 86.50 ± 5.79 | 83.86 ± 6.16 | 81.59 ± 8.02 | 82.20 ± 6.19 | 78.79 ± 8.44 |
| SVM | 89.54 ± 4.71 | 88.01 ± 4.13 | 86.71 ± 5.96 | 83.62 ± 6.46 | 81.90 ± 7.86 | 82.43 ± 6.31 | 79.36 ± 8.34 | |
| KNN | 88.01 ± 5.31 | 86.51 ± 5.04 | 84.92 ± 6.86 | 81.21 ± 7.73 | 79.32 ± 9.12 | 79.56 ± 7.64 | 76.19 ± 9.59 | |
| F1 Score | LDA | 88.81 ± 4.58 | 87.16 ± 4.17 | 85.69 ± 5.85 | 83.20 ± 6.16 | 80.86 ± 7.91 | 81.54 ± 6.15 | 77.90 ± 8.31 |
| SVM | 89.06 ± 4.81 | 87.36 ± 4.27 | 85.93 ± 6.09 | 83.00 ± 6.44 | 81.23 ± 7.89 | 81.85 ± 6.33 | 78.59 ± 8.35 | |
| KNN | 87.56 ± 5.37 | 85.93 ± 5.09 | 84.24 ± 6.89 | 80.69 ± 7.64 | 78.67 ± 9.09 | 79.04 ± 7.58 | 75.44 ± 9.50 |
References
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bin Mohd Ali, M.A.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T.G. Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: Detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol. Proced. Online. 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.L.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. A low noise capacitive electromyography monitoring system for remote healthcare applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3333–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Ali, S.H.M.; Arsad, N.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. Performance analysis of noninvasive electrophysiological methods for the assessment of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical research: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.L.; Reaz, M.B.I. Evolution of a capacitive electromyography contactless biosensor: Design and modelling techniques. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2019, 145, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.L.; Reaz, M.B.I. Impact of skin-electrode capacitance on the performance of cemg biosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 2636–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.L.; Reaz, M.B.I. Characterization of textile-insulated capacitive biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A.D.; Rehbaum, H.; Farina, D.; Aszmann, O.C. Prosthetic myoelectric control strategies: A clinical perspective. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2014, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G. The bionic hand with a human touch. CNN 2013. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2013/02/01/tech/bionic-hand-ilimb-prosthetic/index.html (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Pu, J. The influence of common component on myoelectric pattern recognition. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powar, O.S.; Chemmangat, K. Reducing the effect of wrist variation on pattern recognition of Myoelectric hand prostheses control through dynamic time warping. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 55, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougner, A.; Scheme, E.; Chan, A.D.C.; Englehart, K.; Stavdahl, Ø. Resolving the limb position effect in myoelectric pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Takruri, M.; Miro, J.V.; Kodagoda, S. Towards limb position invariant myoelectric pattern recognition using time-dependent spectral features. Neural Netw. 2014, 55, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.J.; Hargrove, L.J.; Kuiken, T.A. The effects of electrode size and orientation on the sensitivity of myoelectric pattern recognition systems to electrode shift. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, A.J.; Hargrove, L.J.; Kuiken, T.A. Improving myoelectric pattern recognition robustness to electrode shift by changing interelectrode distance and electrode configuration. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, N. Position identification for robust myoelectric control against electrode shift. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrain, T.; Jiang, N.; Farina, D. Influence of the training set on the accuracy of surface EMG classification in dynamic contractions for the control of multifunction prostheses. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogbon, M.G.; Samuel, O.W.; Geng, Y.; Oluwagbemi, O.; Ning, J.; Chen, S.; Ganesh, N.; Feng, P.; Li, G. Towards resolving the co-existing impacts of multiple dynamic factors on the performance of EMG-pattern recognition based prostheses. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 184, 105278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Timemy, A.H.; Khushaba, R.N.; Bugmann, G.; Escudero, J. Improving the performance against force variation of EMG controlled multifunctional upper-limb prostheses for transradial amputees. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 650–661. [Google Scholar]
- Scheme, E.; Englehart, K. Electromyogram pattern recognition for control of powered upper-limb prostheses: State of the art and challenges for clinical use. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 643–660. [Google Scholar]
- Onay, F.; Mert, A. Phasor represented EMG feature extraction against varying contraction level of prosthetic control. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 59, 101881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, T.W.; Chapman, A.E. The relationship between the surface EMG and force transients in muscle: Simulation and experimental studies. Proc. IEEE 1977, 65, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.L. The relationship between electromyogram and muscle force. Sportverletz. –Sportschaden. 1997, 11, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, D.; Huang, H.; Kuiken, T.A. Study of stability of time-domain features for electromyographic pattern recognition. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2010, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Englehart, K.B.; Hudgins, B.; Chan, A.D.C. A Gaussian mixture model based classification scheme for myoelectric control of powered upper limb prostheses. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Al-Ani, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. A framework of temporal-spatial descriptors-based feature extraction for improved myoelectric pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, D.; Sheng, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, X. Invariant surface EMG feature against varying contraction level for myoelectric control based on muscle coordination. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2015, 19, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simao, M.; Mendes, N.; Gibaru, O.; Neto, P. A review on electromyography decoding and pattern recognition for human-machine interaction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 39564–39582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Bao, S. A review of the key technologies for sEMG-based human-robot interaction systems. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remeseiro, B.; Bolon-Canedo, V. A review of feature selection methods in medical applications. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.W.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Li, G. Pattern recognition of electromyography signals based on novel time domain features for amputees’ limb motion classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Kodagoda, S.; Lal, S.; Dissanayake, G. Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Shyu, L.Y.; Chen, T. Portable hand motion classifier for multi-channel surface electromyography recognition using grey relational analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4283–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.; Scott, R.N. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Martinez-Luna, C.; Li, J.; McDonald, B.E.; Dai, C.; Huang, X.; Farrell, T.R.; Clancy, E.A. EMG-Force and EMG-Target models during force-varying bilateral hand-wrist contraction in able-bodied and limb-absent subjects. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 3040–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, D.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Improving myoelectric control for amputees through transcranial direct current stimulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, B. EEG analysis based on time domain properties. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1970, 29, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, T.R.; Weir, R.F. The optimal controller delay for myoelectric prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J.; Donald Gilmore, L.; Kuznetsov, M.; Roy, S.H. Filtering the surface EMG signal: Movement artifact and baseline noise contamination. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, S.; Raoof, K. Power line interference rejection from surface electromyography signal using an adaptive algorithm. Irbm 2008, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; He, X.; Han, J. SRDA: An efficient algorithm for large scale discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2008, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Triwiyanto, T.; Pawana, I.P.A.; Purnomo, M.H. An improved performance of deep learning based on convolution neural network to classify the hand motion by evaluating hyper parameter. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanoi, Y.; Ogiri, Y.; Kato, R. EMG-based posture classification using a convolutional neural network for a myoelectric hand. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 55, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleari, M.; Di Girolamo, M.; Celadon, N.; Favetto, A.; Ariano, P. On optimal electrode configuration to estimate hand movements from forearm surface electromyography. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conferences IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6086–6089. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Continuous estimation of finger joint angles under different static wrist motions from surface EMG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Morimoto, J. Bilinear modeling of EMG signals to extract user-independent features for multiuser myoelectric interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskoei, M.A.; Hu, H. Support vector machine-based classification scheme for myoelectric control applied to upper limb. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Kodagoda, S.; Takruri, M.; Dissanayake, G. Toward improved control of prosthetic fingers using surface electromyogram (EMG) signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10731–10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Ani, A.; Al-Timemy, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. A fusion of time-domain descriptors for improved myoelectric hand control. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Athens, Greece, 6–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pinzón-Arenas, J.O.; Jiménez-Moreno, R.; Rubiano, A. Percentage estimation of muscular activity of the forearm by means of EMG signals based on the gesture recognized using CNN. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Timemy, A.H.; Bugmann, G.; Escudero, J.; Outram, N. Classification of finger movements for the dexterous hand prosthesis control with surface electromyography. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2013, 17, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Dehnbostel, F.O.; Preissner, R. Prediction is a balancing act: Importance of sampling methods to balance sensitivity and specificity of predictive models based on imbalanced chemical data sets. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.W.; Asogbon, M.G.; Geng, Y.; Jiang, N.; Mzurikwao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wong, K.K.L.; Vollero, L.; Li, G. Decoding movement intent patterns based on spatiotemporal and adaptive filtering method towards active motor training in stroke rehabilitation systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Limsakul, C.; Phukpattaranont, P. Application of wavelet analysis in EMG feature extraction for pattern classification. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2011, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Ju, Z.; Sun, Y.; Kong, J. A novel feature extraction method for machine learning based on surface electromyography from healthy brain. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 9013–9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.V.; Subramaniam, K.; Asmi, P.S. Robust feature sets for contraction level invariant control of upper limb myoelectric prosthesis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 51, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Paper | Subject Type | Muscle Force Level | Feature | Classifier | Training Force | Accuracy (%) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tkach et al. [24] | Intact | Low and high | Mean absolute value, zero crossings, slope sign change, waveform length, Wilson amplitude, variance, v-order, log detector, EMG histogram, AR, and cepstrum coefficients. | LDA | Low and high | 82 with AR | Time-domain features are not stable with muscle force variation. |
| Huang et al. [25] | Intact | --- | Mean absolute value, zero crossings, slope sign change, waveform length, AR, and RMS | Gaussian mixture model | --- | 96 AR + RMS | AR and RMS can be grouped for better EMG pattern recognition performance. |
| Scheme et al. [20] | Intact | 20% to 80% of MVC at 10% interval | Time-domain features | LDA | 20% to 80% | 84 | Time-domain features are not reliable with muscle force variation. |
| Al-Timemy et al. [19] | Amputee | Low, medium, and high | TDPSD includes root squared zero-order, second-order, and fourth-order moments; sparseness; irregularity factor; and waveform length ratio | LDA | All | 90 | TDPSD improves the performance with muscle force variation. |
| Khushaba et al. [26] | Intact and amputee | --- | TSD, which includes root squared zero-order, second-order, and fourth-order moments; sparseness; irregularity factor; coefficient of variation; and Teager–Kaiser energy operator | LDA | --- | 99 (128 channel EMG) | TSD improves the EMG pattern recognition performance |
| He et al. [27] | Intact | Low, medium, and high | Global normalized discrete Fourier transform-based features | LDA | Medium | 91 | Force-invariant EMG pattern recognition performance is satisfactory, but the electrode position is specific. |
| Khushaba et al. [32] | Intact (driver drowsiness detection) | --- | Symmlet-8 decomposition-based Wavelet features including energy, variance, standard deviation, waveform length, and entropy | LDA | --- | 97 | Performance is better in another field, so the features may be applicable for force-invariant EMG pattern recognition. |
| Du et al. [33] | Intact | --- | Time-domain features (TDF) including the integral of EMG, waveform length, variance, zero-crossing, slope sign change, and Wilson amplitude | Grey relational analysis | --- | 96 | Performance is better, so these features may be utilized for force-invariant EMG pattern recognition. |
| Hudgin et al. [34] | Intact and amputee | --- | Mean absolute value, mean absolute value slope, zero crossings, slope sign change, and waveform length | Neural Network | --- | 91.2 for intact subject and 85.5 for amputee | Performance is not satisfactory for amputees, but the features are fundamental. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.J.; Ahmad, S.; Haque, F.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Islam, M.R. Force-Invariant Improved Feature Extraction Method for Upper-Limb Prostheses of Transradial Amputees. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050843
Islam MJ, Ahmad S, Haque F, Reaz MBI, Bhuiyan MAS, Islam MR. Force-Invariant Improved Feature Extraction Method for Upper-Limb Prostheses of Transradial Amputees. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(5):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050843
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md. Johirul, Shamim Ahmad, Fahmida Haque, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Mohammad Arif Sobhan Bhuiyan, and Md. Rezaul Islam. 2021. "Force-Invariant Improved Feature Extraction Method for Upper-Limb Prostheses of Transradial Amputees" Diagnostics 11, no. 5: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050843
APA StyleIslam, M. J., Ahmad, S., Haque, F., Reaz, M. B. I., Bhuiyan, M. A. S., & Islam, M. R. (2021). Force-Invariant Improved Feature Extraction Method for Upper-Limb Prostheses of Transradial Amputees. Diagnostics, 11(5), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050843







