A Cascaded Neural Network for Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Pre-Treatment CT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohorts and Imaging Data
2.2. Data Preprocessing
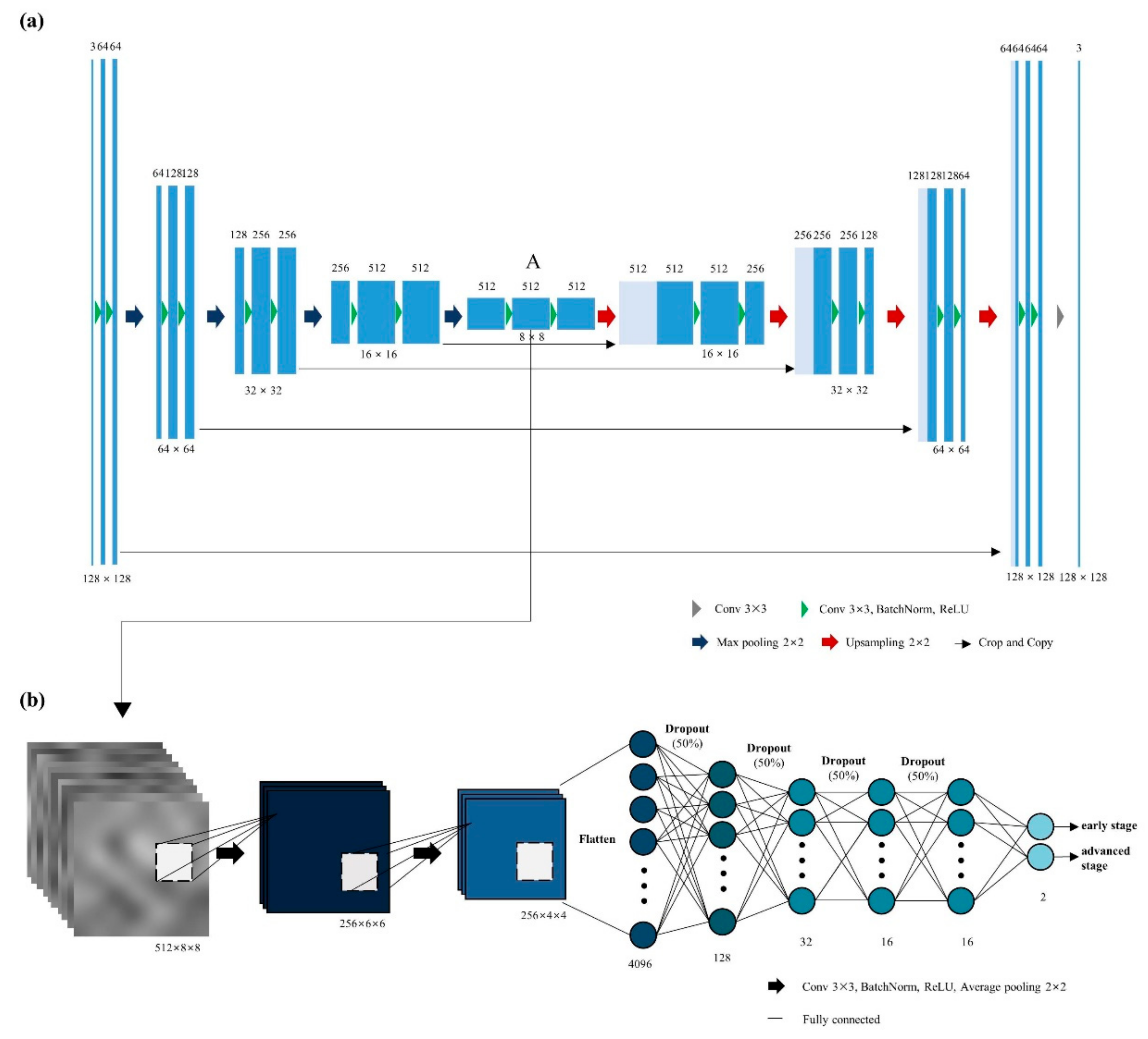
2.3. Autoencoder Network to Extract Latent Variables
2.4. Classification Network for Staging
2.5. Comparison with Other Models
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Training Setup
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Cohorts
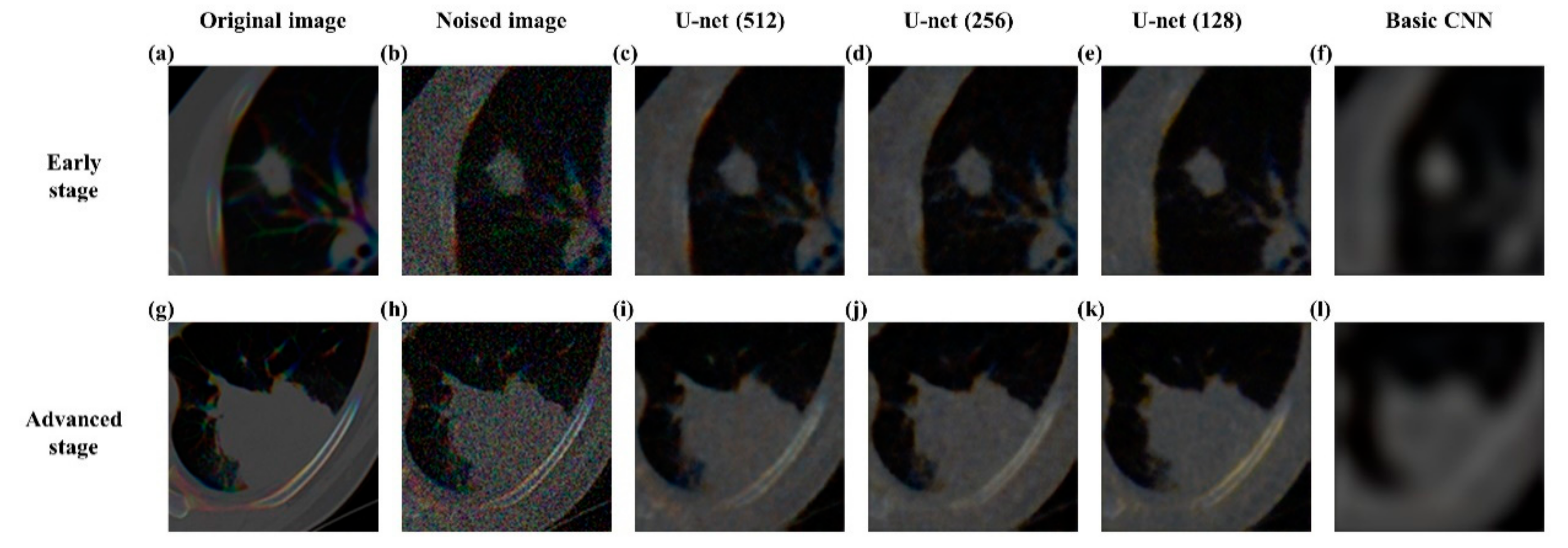
3.2. Reconstructing Images Using U-Net Autoencoder
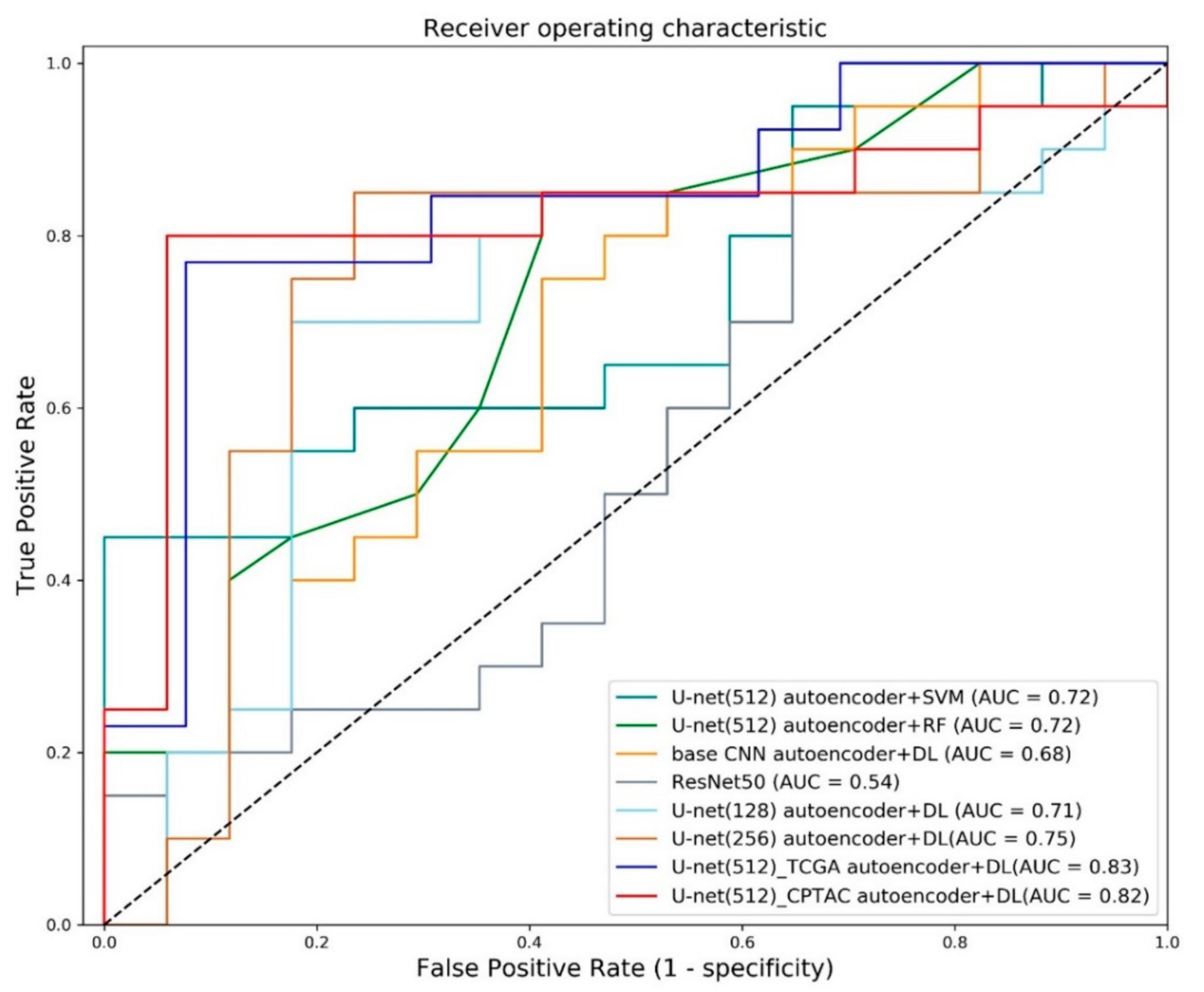
3.3. Classification of Early and Advanced Stages
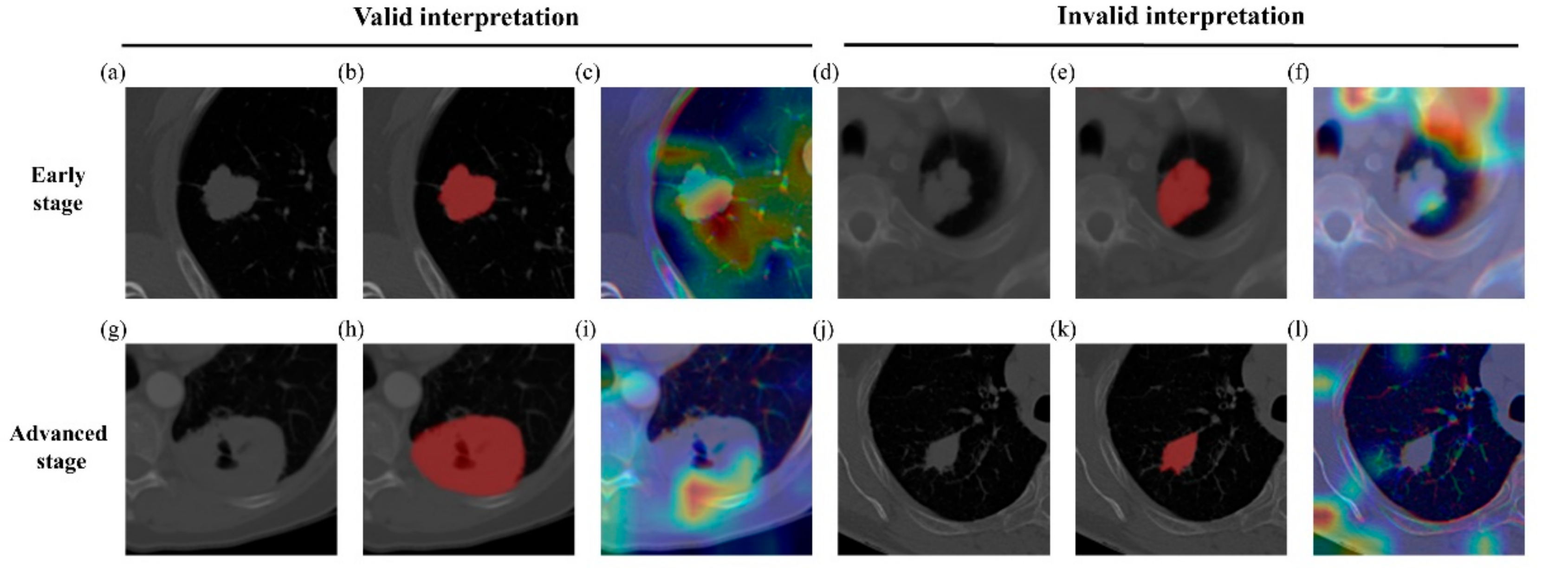
3.4. Possible Confirmation Using Activation Maps
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.; Adjei, A.A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, S.; Takashima, S.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.; Honda, T.; Maruyama, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Yamanda, T.; Kubo, K.; Hanamura, K.; et al. Mass screening for lung cancer with mobile spiral computed tomography scanner. Lancet 1998, 351, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Byrd, D.R.; Compton, C.C.; Fritz, A.G.; Greene, F.L.; Trotti, A. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardi, U.; Filippi, A.R.; Guarneri, A.; Giglioli, F.R.; Ciammella, P.; Franco, P.; Mantovani, C.; Borasio, P.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Ragona, R. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a prospective trial. Lung Cancer 2010, 68, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, L.; Weder, W.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Felip, E. Early stage and locally advanced (non-metastatic) non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, v103–v115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, S.S.F.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palumbo, B.; Bianconi, F.; Palumbo, I.; Fravolini, M.L.; Minestrini, M.; Nuvoli, S.; Stazza, M.L.; Rondini, M.; Spanu, A. Value of Shape and Texture Features from 18F-FDG PET/CT to Discriminate between Benign and Malignant Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: An Experimental Evaluation. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; He, Y.; Allen, B.G.; Buatti, J.M.; Smith, B.J.; Tong, L.; Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Diehn, M.; Loo, B.W.; et al. Deep segmentation networks predict survival of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, F.; Fravolini, M.L.; Pizzoli, S.; Palumbo, I.; Minestrini, M.; Rondini, M.; Nuvoli, S.; Spanu, A.; Palumbo, B. Comparative evaluation of conventional and deep learning methods for semi-automated segmentation of pulmonary nodules on CT. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 3286–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paing, M.P.; Hamamoto, K.; Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Pintavirooj, C. Automatic Detection and Staging of Lung Tumors using Locational Features and Double-Staged Classifications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nibali, A.; He, Z.; Wollersheim, D. Pulmonary nodule classification with deep residual networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciompi, F.; de Hoop, B.; van Riel, S.J.; Chung, K.; Scholten, E.T.; Oudkerk, M.; de Jong, P.A.; Prokop, M.; van Ginneken, B. Automatic classification of pulmonary peri-fissural nodules in computed tomography using an ensemble of 2D views and a convolutional neural network out-of-the-box. Med. Image Anal. 2015, 26, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Halpenny, D.; Hellmann, M.D.; Deasy, J.O.; Mageras, G.; Veeraraghavan, H. Multiple Resolution Residually Connected Feature Streams for Automatic Lung Tumor Segmentation from CT Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, S.; Gevaert, O.; Echegaray, S.; Ayers, K.; Zhou, M.; Shafiq, M.; Zheng, H.; Benson, J.A.; Zhang, W.; Leung, A.N.C.; et al. Data for NSCLC Radiogenomics Collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, S.; Gevaert, O.; Echegaray, S.; Ayers, K.; Zhou, M.; Shafiq, M.; Zheng, H.; Benson, J.A.; Zhang, W.; Leung, A.N.C.; et al. A radiogenomic dataset of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, O.; Xu, J.; Hoang, C.D.; Leung, A.N.; Xu, Y.; Quon, A.; Rubin, D.L.; Napel, S.; Plevritis, S.K. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Identifying Prognostic Imaging Biomarkers by Leveraging Public Gene Expression Microarray Data—Methods and Preliminary Results. Radiology 2012, 264, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Rios Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Data From NSCLC-Radiomics-Genomics. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC). Radiology Data from the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium Lung Adenocar-cinoma [CPTAC-LUAD] collection [Data set]. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC). Radiology Data from the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma [CPTAC-LSCC] Collection [Data set]. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertina, B.; Watson, M.; Holback, C.; Jarosz, R.; Kirk, S.; Lee, Y.; Lemmerman, J. Radiology Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas Lung Adenocarcinoma [TCGA-LUAD] collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, S.; Lee, Y.; Kumar, P.; Filippini, J.; Albertina, B.; Watson, M.; Lemmerman, J. Radiology Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma [TCGA-LUSC] collection. Cancer Imaging Arch. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cham, Switzerland, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Staging Using Deep Restricted Boltzmann Machine. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 1175–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Tao, G.; Zhu, L.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Ye, J.; Chen, Q. Prediction of pathologic stage in non-small cell lung cancer using machine learning algorithm based on CT image feature analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Why did you say that? Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2016, 17, 331–336. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02391 (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Bussink, J.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Machine Learning methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Luo, Y.; Tseng, H.; Haken, R.K.T.; El Naqa, I. Combining handcrafted features with latent variables in machine learning for prediction of radiation-induced lung damage. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 2497–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Lai, K.K.; Wang, S.; Huang, W. A Bias-Variance-Complexity Trade-Off Framework for Complex System Modeling. In Transactions on Petri Nets and Other Models of Concurrency XV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 3980, pp. 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-H.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, H. Marginal radiomics features as imaging biomarkers for pathological invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2984–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, D.; Ma, Z.; Liang, C.; Tian, J.; Liang, C. Radiomics Signature: A Potential Biomarker for the Prediction of Disease-Free Survival in Early-Stage (I or II) Non—Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiology 2016, 281, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, J.; Wu, H.; Wen, Z.; Qin, J. Memory-Efficient Automatic Kidney and Tumor Segmentation Based on Non-local Context Guided 3D U-Net; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12264, pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, N.; Isensee, F.; Maier-Hein, K.H.; Hou, X.; Xie, C.; Li, F.; Nan, Y.; Mu, G.; Lin, Z.; Han, M.; et al. The state of the art in kidney and kidney tumor segmentation in contrast-enhanced CT imaging: Results of the KiTS19 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Goyal, L.M.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, I.; Verma, A.; Hemanth, D.J. Deep learning based enhanced tumor segmentation approach for MR brain images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 78, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Training and Validation | CPTAC-Test | TCGA-Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCLC-Radio-Genomics | NSCLC-Radiomics-Genomics | CPTAC- LUAD | CPTAC- LSCC | TCGA- LUAD | TCGA- LUSC | p-Value | |
| n | 65 | 33 | 17 | 20 | 13 | 13 | |
| Age mean (STD) | 68.97 (9.1532) | N/A | 68.47 (6.30) | 68.05 (6.36) | 68.08 (10.56) | 68 (11.53) | 0.9023 |
| Sex | 0.6943 | ||||||
| Male | 49 | 25 | 10 | 13 | 8 | 9 | |
| Female | 16 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | |
| N stage | |||||||
| N0 | 54 | 24 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 9 | |
| N1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 4 | - | 3 | |
| N2 | 7 | 2 | - | - | 3 | 1 | |
| Early stage | |||||||
| Stage Ⅰ | 45 | 17 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 5 | |
| Advanced-stage | |||||||
| Stage Ⅱ | 9 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 6 | |
| Stage Ⅲ | 9 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Stage Ⅳ | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | |
| Training | Validation | CPTAC-Test | TCGA-Test | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | 0.5777 | ||||
| Early- | 57 | 5 | 20 | 13 | |
| Advanced- | 33 | 3 | 17 | 13 | |
| Total | 90 | 8 | 37 | 26 |
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-net autoencoder + SVM | 0.62 | 0.80 | 0.41 | 0.72 |
| U-net autoencoder + random forest | 0.62 | 1.0 | 0.18 | 0.72 |
| Basic CNN reconstruction + DL | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| Sun et al. (2018) [25] | - | - | - | 0.67 |
| Single-stage ResNet50 | 0.62 | 0.85 | 0.35 | 0.54 |
| U-net (128) autoencoder + DL | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.82 | 0.71 |
| U-net (256) autoencoder + DL | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| Proposed U-net (512) autoencoder + DL (TCGA) | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.83 |
| Proposed U-net (512) autoencoder + DL (CPTAC) | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.; Cho, H.-h.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, H. A Cascaded Neural Network for Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Pre-Treatment CT. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061047
Choi J, Cho H-h, Kwon J, Lee HY, Park H. A Cascaded Neural Network for Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Pre-Treatment CT. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061047
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jieun, Hwan-ho Cho, Junmo Kwon, Ho Yun Lee, and Hyunjin Park. 2021. "A Cascaded Neural Network for Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Pre-Treatment CT" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061047
APA StyleChoi, J., Cho, H.-h., Kwon, J., Lee, H. Y., & Park, H. (2021). A Cascaded Neural Network for Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Pre-Treatment CT. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061047







