The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis with the Available Chairside Probing Tools
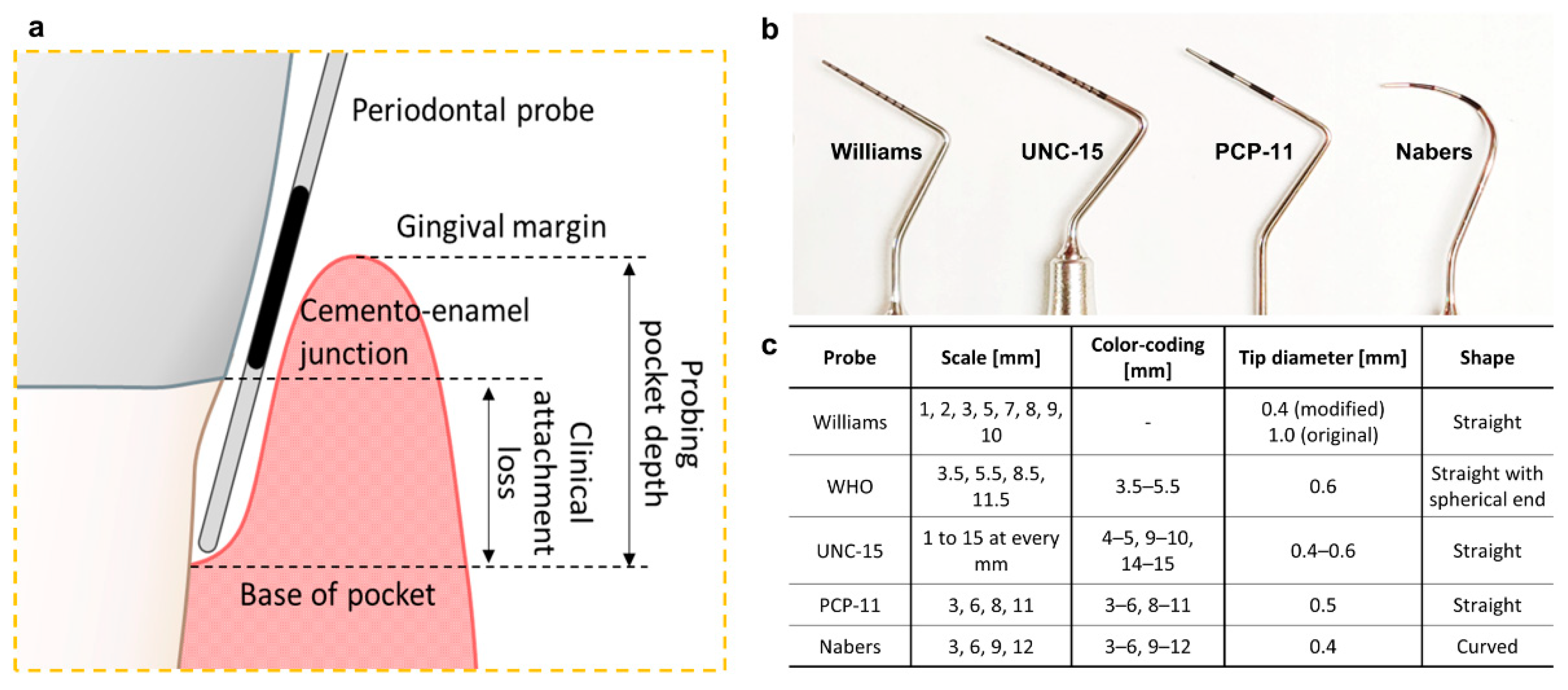
2.1. Pocket Depth and Clinical Attachment Loss
2.2. Bleeding on Probing
2.3. Tooth Mobility
2.4. Plaque and Calculus
2.5. Other Parameters with Diagnostic Potential
3. Diagnosis with the Imaging Tools
3.1. 2-Dimensional Imaging with Radiography
3.2. 3-Dimensional Imaging with Computed Tomography
3.3. Ultrasonography
3.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.5. Digital Dental Photography
3.6. Intraoral Scanners
3.7. Endoscopic Capillaroscopy
4. Chairside Biomarker Detection
4.1. Biochemical Assay Kits
4.2. Microbiological Assay Kits
4.3. Genetic Assay Kits
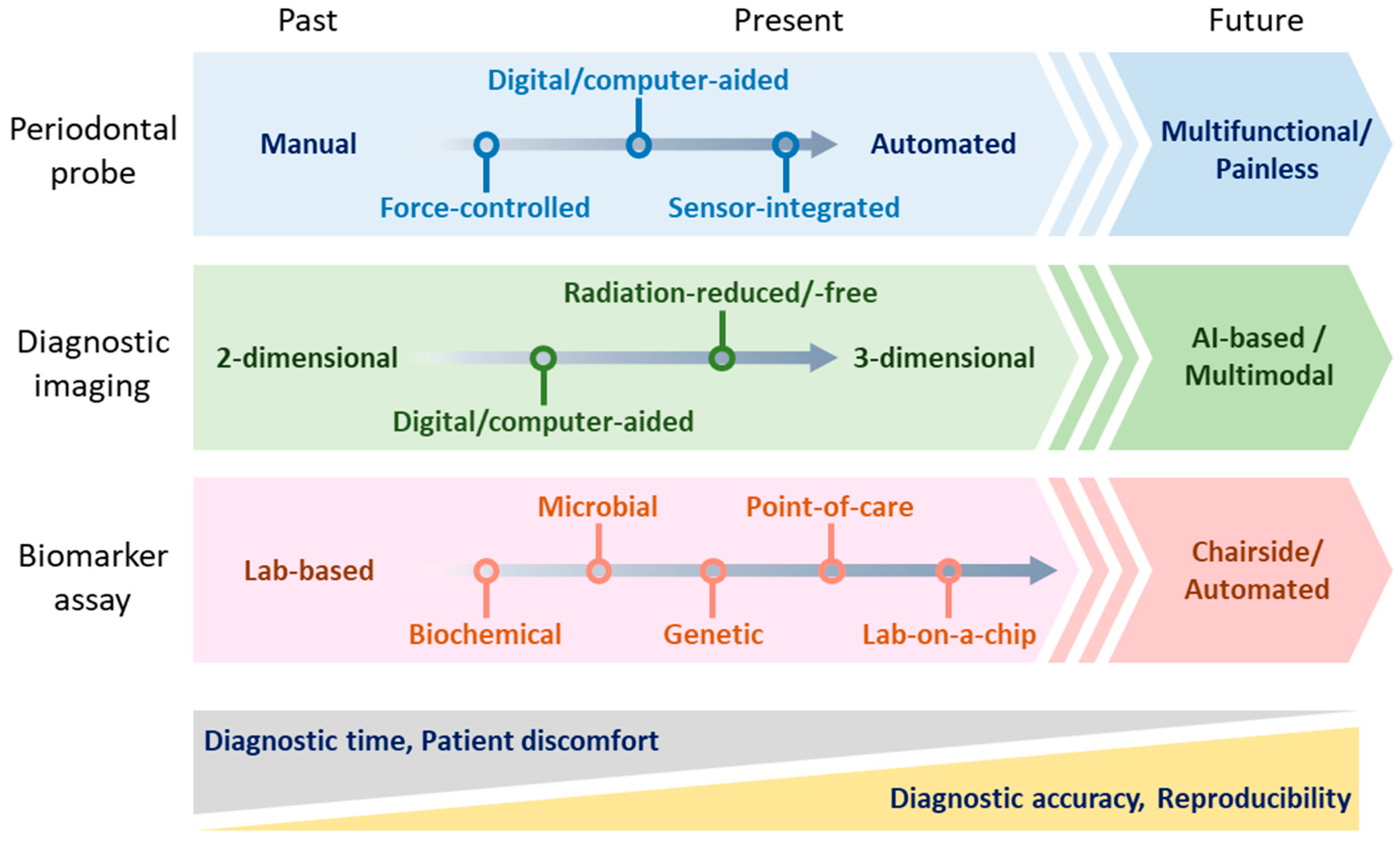
5. Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulkader, R.S.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abebo, T.A.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, D.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; Alonso, B.; Feres, M. Acute periodontal lesions (periodontal abscesses and necrotizing periodontal diseases) and endo-periodontal lesions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S78–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jepsen, S.; Caton, J.G.; Albandar, J.M.; Bissada, N.F.; Bouchard, P.; Cortellini, P.; Demirel, K.; de Sanctis, M.; Ercoli, C.; Fan, J. Periodontal manifestations of systemic diseases and developmental and acquired conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 3 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S219–S229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caton, J.G.; Armitage, G.; Berglundh, T.; Chapple, I.L.; Jepsen, S.; Kornman, K.S.; Mealey, B.L.; Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Tonetti, M.S. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions–Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Page, R.C.; Eke, P.I. Case Definitions for Use in Population-Based Surveillance of Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.S.; Abdulkareem, A.A.; Sha, A.M.; Rawlinson, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Oral Fluids Biomarker Profile to Determine the Current and Future Status of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Goodson, J.M.; Lindhe, J. New concepts of destructive periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1984, 11, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, Y.; Morozumi, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Sugaya, T.; Kawanami, M.; Suzuki, F.; Takahashi, K.; Abe, Y.; Sato, S.; Makino-Oi, A.; et al. Site-level progression of periodontal disease during a follow-up period. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steigmann, L.; Maekawa, S.; Sima, C.; Travan, S.; Wang, C.-W.; Giannobile, W.V. Biosensor and Lab-on-a-chip Biomarker-identifying Technologies for Oral and Periodontal Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 588480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, N.A. Diagnostic potential and future directions of biomarkers in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva of periodontal diseases: Review of the current evidence. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 87, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taba, M., Jr.; Kinney, J.; Kim, A.S.; Giannobile, W.V. Diagnostic biomarkers for oral and periodontal diseases. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 49, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostelc, J.G.; Zelson, P.R.; Preti, G.; Tonzetich, J. Quantitative differences in volatiles from healthy mouths and mouths with periodontitis. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgut, P. The relevance of pH to gingivitis and periodontitis. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2001, 3, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapple, I.L.C. Periodontal diagnosis and treatment—Where does the future lie? Periodontol. 2000 2009, 51, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, U.; Abbas, F.; Armand, S.; Loos, B.G.; Timmerman, M.F.; Van der Weijden, G.A.; Van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Winkel, E.G. Java project on periodontal diseases. The natural development of periodontitis: Risk factors, risk predictors and risk determinants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdala, I.; Olsen, I.; Haffajee, A.D.; Socransky, S.S.; Thoresen, M.; de Blasio, B.F. Comparing clinical attachment level and pocket depth for predicting periodontal disease progression in healthy sites of patients with chronic periodontitis using multi-state Markov models. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. Dentistry—Periodontal Probes—Part 1: General Requirements. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53649.html (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- International Organization for Standardization. Dentistry—Periodontal Probes—Part 2: Designation. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53650.html (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- Ramachandra, S.S.; Mehta, D.S.; Sandesh, N.; Baliga, V.; Amarnath, J. Periodontal probing systems: A review of available equipment. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2011, 32, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polson, A.M.; Caton, J.G.; Yeaple, R.N.; Zander, H.A. Histological determination of probe tip penetration into gingival sulcus of humans using an electronic pressure-sensitive probe. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1980, 7, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnick, J.; Keagle, J.; Searle, J.; King, G.; Thompson, W. Gingival Resistance to Probing Forces: II. The Effect of Inflammation and Pressure on Probe Displacement in Beagle Dog Gingivitis. J. Periodontol. 1989, 60, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, I.; Kaufman, H.W.; Wolff, M. Measurement of tooth hypersensitivity and oral factors involved in its development. Arch. Oral Biol. 1994, 39, S63–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, A.; Kumar, A.; Puri, K.; Khatri, M.; Bansal, M.; Gupta, G. Comparative evaluation of probing depth and clinical attachment level using a manual probe and Florida probe. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2016, 20, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renatus, A.; Trentzsch, L.; Schönfelder, A.; Schwarzenberger, F.; Jentsch, H. Evaluation of an Electronic Periodontal Probe Versus a Manual Probe. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZH03–ZH07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, J.B.; Stoltenberg, J.L.; Huso, B.A.; Aeppli, D.M.; Pihlstrom, B.L. Comparison of measurement variability in subjects with moderate periodontitis using a conventional and constant force periodontal probe. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.S.; Palcanis, K.G.; Geurs, N.C. A comparison of manual and controlled-force attachment-level measurements. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1997, 24, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, J.M. Diagnosis of Periodontitis by Physical Measurement: Interpretation From Episodic Disease Hypothesis. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.P.; Adler, R.; Joss, A.; Nyman, S. Absence of bleeding on probing An indicator of periodontal stability. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1990, 17, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Adler, R.; Lang, N.P. Bleeding on probing. A parameter for monitoring periodontal conditions in clinical practice. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1994, 21, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombelli, L.; Farina, R.; Silva, C.O.; Tatakis, D.N. Plaque-induced gingivitis: Case definition and diagnostic considerations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S44–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldredge, W.A. Bleeding on probing defined. Dimens. Dent. Hyg. 2012, 10, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Newbrun, E. Indices to Measure Gingival Bleeding. J. Periodontol. 1996, 67, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räisänen, I.T.; Sorsa, T.; Tervahartiala, T.; Raivisto, T.; Heikkinen, A.M. Low association between bleeding on probing propensity and the salivary aMMP-8 levels in adolescents with gingivitis and stage I periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Numabe, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Uehara, S.; Wu, Y.-H.; Ogawa, T. Usefulness of hemoglobin examination in gingival crevicular fluid during supportive periodontal therapy to diagnose the pre-symptomatic state in periodontal disease. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipioni, A.; Bruschi, G.B.; Giargia, M.; Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. Healing at implants with and without primary bone contact. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1997, 8, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laster, L.; Laudenbach, K.W.; Stoller, N.H. An evaluation of clinical tooth mobility measurements. J. Periodontol. 1975, 46, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Körber, K.H. Electronic registration of tooth movements. Int. Dent. J. 1971, 21, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mühlemann, H.R. Tooth Mobility: The Measuring Method. Initial and Secondary Tooth Mobility. J. Periodontol. 1954, 25, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, T.J. An instrument for measuring horizontal tooth mobility. Periodontics 1963, 1, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Wedendal, P.R.; Bjelkhagen, H.I. Dental holographic interferometry in vivo utilizing a ruby laser system: I. Introduction and development of methods for precision measurements on the functional dynamics of human teeth and prosthodontic appliances. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1974, 32, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedendal, P.R.; Bjelkhagen, H.I. Dental holographic interferometry in vivo utilizing a ruby laser system II. Clinical applications. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1974, 32, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, P.; Revel, G.M.; Scalise, L.; De Andrade, R.M. Experimental and numerical investigation on structural effects of laser pulses for modal parameter measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 1999, 32, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Saratani, K.; Shi, S.-G.; Kawazoe, T. Bender-type Tooth-Movement Transducer. IEEJ Trans. Sens. Micromach. 1998, 118, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, M.; Kobayashi, C.; Ogata, H.; Yamaoka, M.; Ogiso, B. A no-contact vibration device for measuring implant stability. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, M.; Yamaoka, M.; Hayashi, M.; Furutoyo, I.; Komori, N.; Ogiso, B. Measuring tooth mobility with a no-contact vibration device. J. Periodontal Res. 2008, 43, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Hayashi, M.; Yamaoka, M.; Yasukawa, T.; Ibi, H.; Ogiso, B. Evaluation of Qualitative Changes in Simulated Periodontal Ligament and Alveolar Bone Using a Noncontact Electromagnetic Vibration Device with a Laser Displacement Sensor. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9636513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulte, W.; D’Hoedt, B.; Lukas, D.; Maunz, M.; Steppeler, M. Periotest for measuring periodontal characteristics–Correlation with periodontal bone loss. J. Periodontal Res. 1992, 27, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Lukas, D. The Periotest method. Int. Dent. J. 1992, 42, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti, E.M.; Pascoletti, G.; Calì, M.; Bignardi, C.; Franceschini, G. Clinical Assessment of Dental Implant Stability During Follow-Up: What Is Actually Measured, and Perspectives. Biosensors 2018, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.-M.; Chiu, C.-L.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-T.; Lin, L.-H.; Lee, S.-Y. Early detection of implant healing process using resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-C.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, J.-H. Implant Stability-Measuring Devices and Randomized Clinical Trial for ISQ Value Change Pattern Measured from Two Different Directions by Magnetic RFA. In Implant Dentistry—A Rapidly Evolving Practice; Turkyilmaz, I., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 112–128. ISBN 978-953-307-658-4. [Google Scholar]
- The Forsyth Institute. Expanded Human Oral Microbiome Database. Available online: http://www.homd.org/index.php (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Paster, B.J.; Boches, S.K.; Galvin, J.L.; Ericson, R.E.; Lau, C.N.; Levanos, V.A.; Sahasrabudhe, A.; Dewhirst, F.E. Bacterial diversity in human subgingival plaque. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3770–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loesche, W.J. Microbiology of Dental Decay and Periodontal Disease. In Medical Microbiology; Baron, S., Ed.; The University of Texas Medical Branch: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-9631172-1-1. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.J. Dental calculus: Recent insights into occurrence, formation, prevention, removal and oral health effects of supragingival and subgingival deposits. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1997, 105, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingman, A.; Löe, H.; Ånerud, Å.; Boysen, H. Errors in Measuring Parameters Associated With Periodontal Health and Disease. J. Periodontol. 1991, 62, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, P.R.; Hutchens, L.H., Jr.; Jewson, L.G. The Effectiveness of Subgingival Scaling and Root Planing II. Clinical Responses Related to Residual Calculus. J. Periodontol. 1990, 61, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archana, V. Calculus detection technologies: Where do we stand now? J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sculean, A.; Schwarz, F.; Berakdar, M.; Romanos, G.E.; Arweiler, N.B.; Becker, J. Periodontal Treatment With an Er:YAG Laser Compared to UltrasonicInstrumentation: A Pilot Study. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, C.; Schander, K.; Dahlén, G.; Wennström, J.L. Short-Term Clinical and Microbiologic Effects of Pocket Debridement With an Er:YAG Laser During Periodontal Maintenance. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kung, R.T.V.; Ochs, B.; Goodson, J.M. Temperature as a periodontal diagnostic. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1990, 17, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedi, P.F., Jr.; Killoy, W.J. Temperature Differences at Periodontal Sites in Health and Disease. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunupati, S.; Sappiti, H.; Nagarakanti, S.; Reddy, B.R.; Chava, V.K. Validating gingival surface temperature as an alternative tool in the diagnosis of periodontal disease activity: An observational clinical trial. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2019, 13, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffajee, A.D.; Socransky, S.S.; Goodson, J.M. Subgingival temperature (I). Relation to baseline clinical parameters. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1992, 19, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederman, R.; Naleway, C.; Lu, B.-Y.; Buyle-Bodin, Y.; Robinson, P. Subgingival temperature as a gingival inflammatory indicator. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Kumar, G. Comparison of the subgingival temperature of smokers and nonsmokers in healthy and diseased sites of gingiva in association with sublingual body temperature. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 3166–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, P.; Vandana, K.L.; Khatri, M. A comparative assessment of subgingival temperature in bleeding and non-bleeding sites before and after periodontal treatment. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2001, 12, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiden, M.F.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Macuch, P.J.; Murray, L.; Kent, R.L., Jr. Subgingival temperature and microbiota in initial periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, P.E.; Khan, K.A.M. PerioTemp® vs. Infrared Thermometer for Measuring Gingival Temperature. In Proceedings of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR) Southeast Asian Division Meeting, Malacca, Malaysia, 5 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pavolotskaya, A.; McCombs, G.; Darby, M.; Marinak, K.; Dayanand, N.N. Sulcular Sulfide Monitoring: An Indicator of Early Dental Plaque-Induced Gingival Disease. J. Dent. Hyg. 2006, 80, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Alasqah, M.; Sanaa, M.S.; Gufran, K. The Relationship between Volatile Sulfur Compounds and the Severity of Chronic Periodontitis: A Cross-sectional Study. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, S268–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Wang, H.-L. Relationship of Sulcular Sulfide Level to Severity of Periodontal Disease and BANA Test. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; McCombs, G.; Darby, M.; Marinak, K. Sulphur by-product: The relationship between volatile sulphur compounds and dental plaque-induced gingivitis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2004, 5, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Chou, H.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Yang, Y.-H.; Ho, K.-Y.; Wu, Y.-M.; Ho, Y.-P. The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2008, 43, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, Y.; Yamaga, T.; Yoshihara, A.; Nohno, K.; Miyazaki, H. Association between Volatile Sulfur Compounds and Periodontal Disease Progression in Elderly Non-Smokers. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaira, N.; Palmer, R.; Wilson, R.; Scott, D.; Wade, W. Production of volatile sulphur compounds in diseased periodontal pockets is significantly increased in smokers. Oral Dis. 2000, 6, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresyap, G.; Haffajee, A.; Uzel, N.; Socransky, S. Relationship between periodontal pocket sulfide levels and subgingival species. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.D.; Papapanou, P.N.; Philips, K.H.; Offenbacher, S. Periodontal Medicine: 100 Years of Progress. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Bansal, N.; Logani, A. Recent advances in imaging technologies in dentistry. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kripal, K.; Dileep, A. Role of Radiographic Evolution: An Aid to Diagnose Periodontal Disease. In Periodontal Disease—Diagnostic and Adjunctive Non-Surgical Considerations; Yussif, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-1-78984-461-0. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Morgado, M.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Accuracy of Panoramic Radiograph for Diagnosing Periodontitis Comparing to Clinical Examination. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, L.H.; Nguyen, K.-C.T.; Kaipatur, N.R.; Major, P.W. Ultrasound for Periodontal Imaging. In Dental Ultrasound in Periodontology and Implantology: Examination, Diagnosis and Treatment Outcome Evaluation; Chan, H.-L., Kripfgans, O.D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 115–129. ISBN 978-3-030-51288-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Rajani, S.; Wang, B.-Y. Comparison of periodontal evaluation by cone-beam computed tomography, and clinical and intraoral radiographic examinations. Oral Radiol. 2018, 34, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, B.; Jalowski, S.; Górska, R.; Zaremba, M. Treatment of intrabony defects with modified perforated membranes in aggressive periodontitis: Subtraction radiography outcomes, prognostic variables, and patient morbidity. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 3005–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Song, I.-S.; Jung, K.-H. DeNTNet: Deep Neural Transfer Network for the detection of periodontal bone loss using panoramic dental radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, E.; Ho, D.; Lai, S. Radiographs in periodontal disease diagnosis and management. Aust. Dent. J. 2009, 54, S27–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashiry, M.; Meghil, M.M.; Kalathingal, S.; Buchanan, A.; Elrefai, R.; Looney, S.; Rajendran, M.; Ochieng, M.; Young, N.; Elawady, A.; et al. Application of radiopaque micro-particle fillers for 3-D imaging of periodontal pocket analogues using cone beam CT. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Mark, R.; Sing, I.; Jain, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of CBCT for Aggressive Periodontitis. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2014, 4, 2:1–2:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakrapani, S.; Sirisha, K.; Srilalitha, A.; Srinivas, M. Choice of diagnostic and therapeutic imaging in periodontics and implantology. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, S. Digital Imaging in Dentistry: A Review. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2017, 8, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, D.; Fisch, S. Dental technology: Knocking at high-tech’s door. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1989, 118, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannucci, J.M.; Howerton, L.J. Dental Radiography: Principles and Techniques, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-0-3232-9742-4. [Google Scholar]
- Brägger, U.; Pasquali, L.; Rylander, H.; Carnes, D.; Kornman, K.S. Computer-assisted densitometric image analysis in periodontal radiography. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1988, 15, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräegger, U.; Pasquali, L.; Weber, H.; Kornman, K.S. Computer-assisted densitometric image analysis (CADIA) for the assessment of alveolar bone density changes in furcations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1989, 16, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, I.; Kumar, Y.; Rao, S. Use of Computer-Assisted Densitometric Image Analysis (CADIA) in Assessing Bone Density Changes in Extraction Socket. Indian J. Stomatol. 2011, 2, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Krois, J.; Ekert, T.; Meinhold, L.; Golla, T.; Kharbot, B.; Wittemeier, A.; Dörfer, C.; Schwendicke, F. Deep Learning for the Radiographic Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.-N.; Choi, S.-H. Diagnosis and prediction of periodontally compromised teeth using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eickholz, P.; Kim, T.-S.; Benn, D.K.; Staehle, H.J. Validity of radiographic measurement of interproximal bone loss. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, R.A.W.; Bücker, A.; Diedrich, P.R. Assessment of alveolar bone loss with high resolution computed tomography. J. Periodontal Res. 1995, 30, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, D.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Geenty, J.P.; Darendeliler, M. Comparison of radiation levels from computed tomography and conventional dental radiographs. Aust. Orthod. J. 2003, 19, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen, A.; Kiljunen, T.; Käser, Y.; Peltola, J.; Kortesniemi, M. Dosimetry and image quality of four dental cone beam computed tomography scanners compared with multislice computed tomography scanners. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2009, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, B.; Jacobs, R.; Bosmans, H. Modern dental imaging: A review of the current technology and clinical applications in dental practice. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 2637–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, H.; Mah, P.; Dove, S.B.; McDavid, W.D. Evaluation of image quality parameters of representative intraoral digital radiographic systems. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 116, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.-H.; Choi, B.-R.; Choi, J.-W.; Huh, K.-H.; Yi, W.-J.; Heo, M.-S.; Choi, S.-C.; Lee, S.-S. Reference line-pair values of panoramic radiographs using an arch-form phantom stand to assess clinical image quality. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2013, 43, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brüllmann, D.; Schulze, R.K.W. Spatial resolution in CBCT machines for dental/maxillofacial applications-what do we know today? Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. The use of cone-beam computed tomography in dentistry: An advisory statement from the American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Gantes, B.; Riggs, M.; Crigger, M. Bone density assessments of dental implant sites: 3. Bone quality evaluation during osteotomy and implant placement. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe, B.; Jacobs, R.; Yang, J. Diagnostic validity (or acuity) of 2D CCD versus 3D CBCT-images for assessing periodontal breakdown. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2007, 104, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengel, R.; Candir, M.; Shiratori, K.; Flores-de-Jacoby, L. Digital Volume Tomography in the Diagnosis of Periodontal Defects: An In Vitro Study on Native Pig and Human Mandibles. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noujeim, M.; Prihoda, T.; Langlais, R.; Nummikoski, P. Evaluation of high-resolution cone beam computed tomography in the detection of simulated interradicular bone lesions. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2009, 38, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, R.L.; Horton, R.A.; Tyndall, D.A.; Ludlow, J.B. Tuned-aperture computed tomography (TACT). Theory and application for three-dimensional dento-alveolar imaging. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 1997, 26, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.K.; Seyedain, A.; Agarwal, S.; Webber, R.L.; Nair, U.P.; Piesco, N.P.; Mooney, M.P.; Grondahl, H.G. Tuned Aperture Computed Tomography to Evaluate Osseous Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyndall, D.; Kohltfarber, H. Application of cone beam volumetric tomography in endodontics. Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, C.E. Quantitative CT for determination of bone mineral density: A review. Radiology 1988, 166, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.S.; Rabelo, G.D.; Spin-Neto, R.; Dechichi, P.; Borges, J.S.; Soares, P.B.F. Use of Micro-Computed Tomography for Bone Evaluation in Dentistry. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baum, G.; Greenwood, I.; Slawski, S.; Smirnow, R. Observation of Internal Structures of Teeth by Ultrasonography. Science 1963, 139, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Ngan, P.; Crout, R.; Mukdadi, O.M. High-Resolution 3D Ultrasound Jawbone Surface Imaging for Diagnosis of Periodontal Bony Defects: An In Vitro Study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3409–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, B.J.; Longsine, W.; Sabonghy, E.P.; Han, A.; Tasciotti, E.; Weiner, B.K.; Ferrari, M.; Righetti, R. Characterization of controlled bone defects using 2D and 3D ultrasound imaging techniques. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 4839–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimbran, A.; Dudea, S.M.; Dudea, D. Evaluation of Periodontal Tissues Using 40MHz Ultrasonography. Preliminary report. Med. Ultrason. 2013, 15, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzetti, R.; Vitali, S.; Aringhieri, G.; Caramella, D.; Nisi, M.; Oranges, T.; Dini, V.; Graziani, F.; Gabriele, M. The efficacy of Ultra-High Frequency Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of intraoral lesions. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 129, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.E.; Hinders, M.K.; McCombs, G.B. Clinical comparison of an ultrasonographic periodontal probe to manual and controlled-force probing. Measurement 2006, 39, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.-C.T.; Le, L.H.; Kaipatur, N.R.; Zheng, R.; Lou, E.H.; Major, P.W. High-Resolution Ultrasonic Imaging of Dento-Periodontal Tissues Using a Multi-Element Phased Array System. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Luijk, J.A. NMR: Dental imaging without X-rays? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1981, 52, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. ICNIRP Statement on Diagnostic Devices Using Non-ionizing Radiation: Existing Regulations and Potential Health Risks. Health Phys. 2017, 112, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, A.T.; Zrnc, T.A.; Remus, C.C.; Schönfeld, M.; Habermann, C.R.; Riecke, B.; Friedrich, R.E.; Fiehler, J.; Heiland, M.; Sedlacik, J. Evaluation of four different optimized magnetic-resonance-imaging sequences for visualization of dental and maxillo-mandibular structures at 3 T. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niraj, L.K.; Patthi, B.; Singla, A.; Gupta, R.; Ali, I.; Dhama, K.; Kumar, J.K.; Prasad, M. MRI in Dentistry—A Future towards Radiation Free Imaging—Systematic Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZE14–ZE19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, M.; Heiland, S.; Gareis, D.; Hilgenfeld, T.; Bendszus, M.; Gaudino, C. Dental MRI using a dedicated RF-coil at 3 Tesla. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schara, R.; Sersa, I.; Skaleric, U. T1 relaxation time and magnetic resonance imaging of inflamed gingival tissue. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2009, 38, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetters, M.; Juerchott, A.; El Sayed, N.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Kim, T.S. Dental magnetic resonance imaging for periodontal indication—A new approach of imaging residual periodontal bone support. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2019, 77, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudino, C.; Cosgarea, R.; Heiland, S.; Csernus, R.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Pham, M.; Kim, T.-S.; Bendszus, M.; Rohde, S. MR-Imaging of teeth and periodontal apparatus: An experimental study comparing high-resolution MRI with MDCT and CBCT. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geibel, M.A.; Schreiber, E.S.; Bracher, A.K.; Hell, E.; Ulrici, J.; Sailer, L.K.; Ozpeynirci, Y.; Rasche, V. Assessment of Apical Periodontitis by MRI: A Feasibility Study. Rofo 2015, 187, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geibel, M.A.; Schreiber, E.; Bracher, A.K.; Hell, E.; Ulrici, J.; Sailer, L.K.; Rasche, V. Characterisation of apical bone lesions: Comparison of MRI and CBCT with histological findings—A case series. Eur. J. Oral. Implantol. 2017, 10, 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Juerchott, A.; Sohani, M.; Schwindling, F.S.; Jende, J.M.E.; Kurz, F.T.; Rammelsberg, P.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Hilgenfeld, T. In vivo accuracy of dental magnetic resonance imaging in assessing maxillary molar furcation involvement: A feasibility study in humans. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenfeld, T.; Juerchott, A.; Jende, J.M.E.; Rammelsberg, P.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Schwindling, F.S. Use of dental MRI for radiation-free guided dental implant planning: A prospective, in vivo study of accuracy and reliability. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6392–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarín, J.M.; Díaz-Caballero, E.; Borreguero, J.; Galve, F.; Grau-Ruiz, D.; Rigla, J.P.; Bosch, R.; González, J.M.; Pallás, E.; Corberán, M.; et al. Simultaneous imaging of hard and soft biological tissues in a low-field dental MRI scanner. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I. Digital dental photography. Part 2: Purposes and uses. Br. Dent. J. 2009, 206, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I. Digital dental photography. Part 1: An overview. Br. Dent. J. 2009, 206, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, L.; Sharland, M. Dental photography: A practical guide. Dent. Update 2020, 47, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting-shu, S.; Jian, S. Intraoral Digital Impression Technique: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suese, K. Progress in digital dentistry: The practical use of intraoral scanners. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Luan, Q. Digital assessment of gingiva morphological changes and related factors after initial periodontal therapy. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 63, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icen, M.; Orhan, K.; Şeker, Ç.; Geduk, G.; Özlü, F.C.; Cengiz, M.İ. Comparison of CBCT with different voxel sizes and intraoral scanner for detection of periodontal defects: An in vitro study. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2020, 49, 20190197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, L.; Siqueira, R.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Yu, S.-H.; Chan, H.-L.; Wang, H.-L. Quantitative tooth mobility evaluation based on intraoral scanner measurements. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deferm, J.T.; Schreurs, R.; Baan, F.; Bruggink, R.; Merkx, M.A.W.; Xi, T.; Bergé, S.J.; Maal, T.J.J. Validation of 3D documentation of palatal soft tissue shape, color, and irregularity with intraoral scanning. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-S.; Strauss, F.-J.; Jung, H.-I.; Gruber, R. Digital scanning is more accurate than using a periodontal probe to measure the keratinized tissue width. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedelcu, R.; Olsson, P.; Nyström, I.; Rydén, J.; Thor, A. Accuracy and precision of 3 intraoral scanners and accuracy of conventional impressions: A novel in vivo analysis method. J. Dent. 2018, 69, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.; Francesco, D. Periodontal Capillary Imaging in vivo by Endoscopic Capillaroscopy. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2010, 30, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Buduneli, N.; Kinane, D.F. Host-derived diagnostic markers related to soft tissue destruction and bone degradation in periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Periodontology: Past, present, perspectives. Periodontol. 2000 2013, 62, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.J. Protein biomarkers of periodontitis in saliva. ISRN Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 593151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alassy, H.; Parachuru, P.; Wolff, L. Peri-Implantitis Diagnosis and Prognosis Using Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nwhator, S.O.; Ayanbadejo, P.O.; Umeizudike, K.A.; Opeodu, O.I.; Agbelusi, G.A.; Olamijulo, J.A.; Arowojolu, M.O.; Sorsa, T.; Babajide, B.S.; Opedun, D.O. Clinical Correlates of a Lateral-Flow Immunoassay Oral Risk Indicator. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, A.M.; Nwhator, S.O.; Rathnayake, N.; Mäntylä, P.; Vatanen, P.; Sorsa, T. Pilot Study on Oral Health Status as Assessed by an Active Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Chairside Mouthrinse Test in Adolescents. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, T.; Alassiri, S.; Grigoriadis, A.; Räisänen, I.T.; Pärnänen, P.; Nwhator, S.O.; Gieselmann, D.-R.; Sakellari, D. Active MMP-8 (aMMP-8) as a grading and staging biomarker in the periodontitis classification. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Majid, A.; Alassiri, S.; Rathnayake, N.; Tervahartiala, T.; Gieselmann, D.-R.; Sorsa, T. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 as an inflammatory and prevention biomarker in periodontal and peri-implant diseases. Int. J. Dent. 2018, 2018, 7891323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; You, M.; Wan, W.; Xu, F.; Li, F.; Li, A. Point-of-Care Periodontitis Testing: Biomarkers, Current Technologies, and Perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1127–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Usui, M.; Ariyoshi, W.; Nakashima, K.; Nagai-Yoshioka, Y.; Inoue, M.; Nishihara, T. A Preliminary Study on the Ability of the Trypsin-Like Peptidase Activity Assay Kit to Detect Periodontitis. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flügge, T.; Hövener, J.B.; Ludwig, U.; Eisenbeiss, A.K.; Spittau, B.; Hennig, J.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Nelson, K. Magnetic resonance imaging of intraoral hard and soft tissues using an intraoral coil and FLASH sequences. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 4616–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, S.-N.; Choi, S.-H. Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Dent. 2018, 77, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, J.; Jeong, S.; Jin, H.; Lee, U.; Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, S.C. Periodontal Disease Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Okinawa, Japan, 11–13 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, T.K.; Dheeba, J. Digitalization in Dental problem diagnosis, Prediction and Analysis: A Machine Learning Perspective of Periodontitis. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2020, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
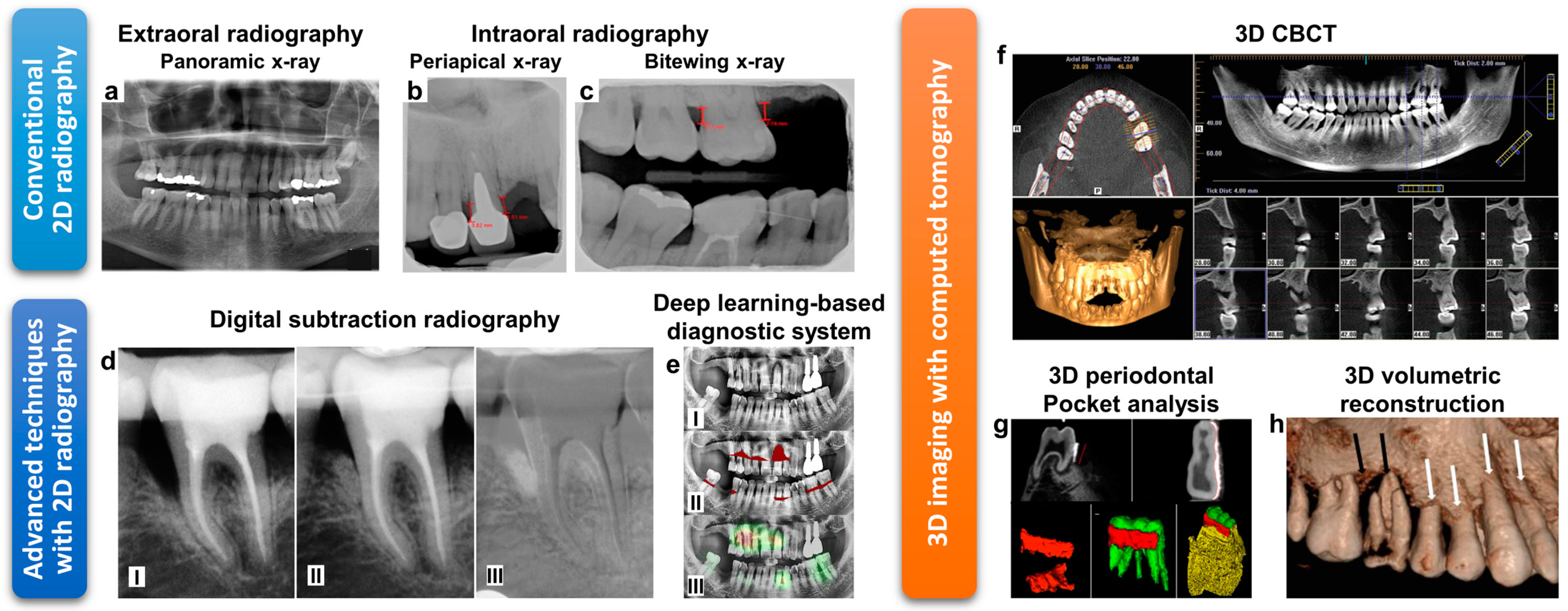
| 2D Dental Radiography | Techniques | 3D CBCT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Intraoral X-ray | 2D Panoramic X-ray | ||
| ~20 lp/mm (Film) [105] 6–15 lp/mm (Digital) [105] | 1–4 lp/mm [106] | Resolution (lp/mm) | 0.6–2.8 lp/mm [107] |
| 0.005 mSv (Bitewing) [108] 0.035–0.171 mSv (Full-mouth series) [108] | 0.003–0.024 mSv [108] | Effective radiation dose | 0.011–0.674 mSv (Dentoalveolar CBCT with small and medium field view) [108] 0.030–1.073 mSv (Maxillofacial CBCT with large field of view) [108] |
| Periapical view- Visualize the root apex, assess severe bone loss Bitewing-Evaluate bone height, assess moderate to severe bone loss | Provides overall view (bird’s-eye view) of the periodontium with the minimized radiation exposure. | Features | Provides axial, coronal, and sagittal multiplanar images with reconstructed form without magnification. Pre-surgical bone quality assessment for osteotomy and implant insertion [109] Assessing crater defects and furcation involvements [110] |
| 2D imaging Superpositions, distortion, and magnification | Imaging method | 3D imaging Cross-sectional and volumetric models No image deformation | |
| Lower cost, lower radiation dose, relatively small device | Advantages | High accuracy for detecting periodontal bone defects [111,112] | |
| Biomarker Classification | Sampling From | Product Name | Detecting Target | Detecting Principle | Analyzing in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochemical assay | GCF | Periocheck | Neutral proteases | Enzymatic digestion reaction (Colorimetric assays) | Chairside |
| GCF | PocketWatch | AST | Enzymatic catalysis reaction (Colorimetric assays) | ||
| GCF | PerioGard | AST | Enzymatic catalysis reaction (Colorimetric assays) | ||
| Oral rinse | PerioSafe | aMMP-8 | Lateral flow test with digital reader (OraLyzer®) | ||
| GCF | ImplantSafe | ||||
| Oral rinse | SillHa ST-4910 | Blood, leukocytes, and protein | Lateral flow test with dual-wavelength reflectometry | ||
| Microbiological assay | Subgingival plaque | Evalusite | Aa, Pg, Pi | Sandwich enzyme immunoassay (Colorimetric assays) | Chairside |
| Subgingival plaque | BANA-Enzymatic test kit | Pg, Td, Tf | BANA hydrolysis reaction (Colorimetric assays) | ||
| Gums and plaque | OMNIgene ORAL/ OMR-110 | Characterization of virus species of all genome type including Aa, Pg, Pt, Fn, Td, Ec | DNA hybridization | Company or research laboratory | |
| Saliva | OMNIgene ORAL/ OM-501, 505 | ||||
| Subgingival plaque | Carpegen® Perio Diagnostik | Aa, Pg, Tf, Td, Fn, Pi | Real-time qPCR | ||
| Oral rinse | MyPerioPath® | Aa, Pg, Td, Tf, En, Fn, Pi, Cr, Pm, Ec, Cs | DNA hybridization | ||
| Microbiological samples/subgingival plaque | iai Pado Test | Aa, Pg, Pi, Td, Tf, Fa | DNA hybridization | ||
| Subgingival plaque | micro-IDent®plus11 | Aa, Pg, Pi, Tf, Td, Pm, Fn, Cr, En, Ec, Cs | DNA hybridization | ||
| Genetic assay | Cheek swab | PerioPredict™ | genes for IL-1 | DNA hybridization | Company laboratory |
| Oral rinse | MyPerioID® IL-6 or IL-1 | genes for IL-6 or IL-1 | Genetic polymorphisms detection |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, T.-J.; Byrd, K.M.; Kim, S.A. The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060932
Ko T-J, Byrd KM, Kim SA. The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060932
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Tae-Jun, Kevin M. Byrd, and Shin Ae Kim. 2021. "The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060932
APA StyleKo, T.-J., Byrd, K. M., & Kim, S. A. (2021). The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future. Diagnostics, 11(6), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060932






