Diagnostic Properties of Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.3. Rapid Lateral Flow Test
2.4. Lumit™ Dx SARS-CoV-2 Immunoassay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
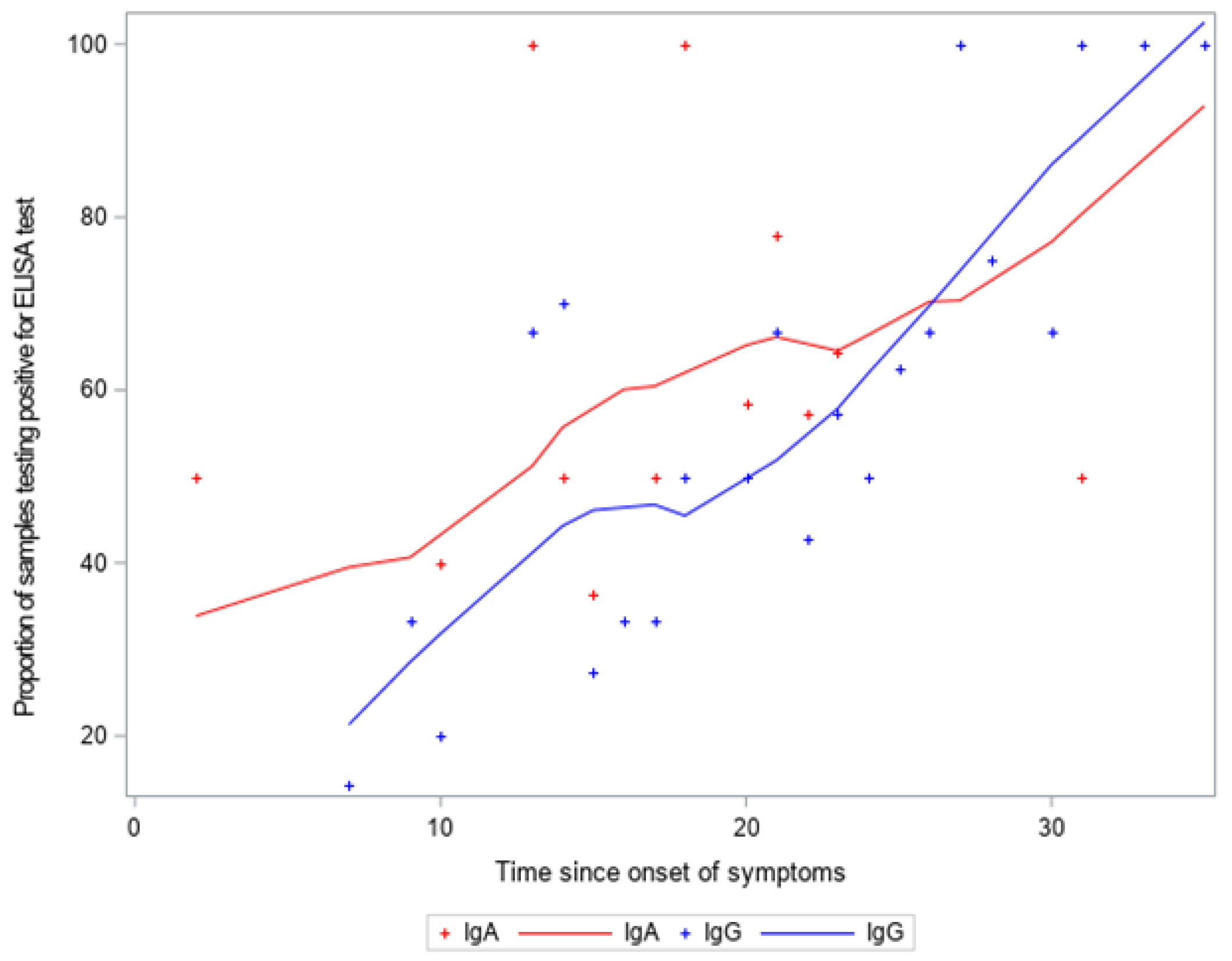
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohmer, N.; Westhaus, S.; Rühl, C.; Ciesek, S.; Rabenau, H.F. Brief Clinical Evaluation of Six High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibody Assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns Hopkins University. Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Manabe, Y.C.; Sharfstein, J.S.; Armstrong, K. The Need for More and Better Testing for COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—Symptoms. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Theel, E.S.; Slev, P.; Wheeler, S.; Couturier, M.R.; Wong, S.J.; Kadkhoda, K. The Role of Antibody Testing for SARS-CoV-2: Is There One? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00797-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazuck, T.; Colin, M.; Giachè, S.; Gubavu, C.; Seve, A.; Rzepecki, V.; Chevereau-Choquet, M.; Kiani, C.; Rodot, V.; Lionnet, E.; et al. Evaluation of Performance of Two SARS-CoV-2 Rapid IgM-IgG Combined Antibody Tests on Capillary Whole Blood Samples from the Fingertip. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candel González, F.J.; Viñuela-Prieto, J.M.; González del Castillo, J.; Barreiro García, P.; Fragiel Saavedra, M.; Hernández Píriz, A.; Jiménez Virumbrales, D.; Canora Lebrato, J.; García de Casasola, G.; Gil Prieto, R.; et al. Utility of Lateral Flow Tests in SARS-CoV-2 Infection Monitorization. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2020, 33, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, J.D.; Hiatt, J.; Mowery, C.T.; Shy, B.R.; Yu, R.; Yamamoto, T.N.; Rathore, U.; Goldgof, G.M.; Whitty, C.; Woo, J.M.; et al. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assays Reveals a Range of Test Performance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, B.; Daher, N.; François, C.; Lanoix, J.-P.; Duverlie, G.; Castelain, S.; Brochot, E. Dynamic Profile for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Using Four Immunochromatographic Assays. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e6–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, D.S.Y.; de Man, S.J.; Lindeboom, F.A.; Koeleman, J.G.M. Comparison of Diagnostic Accuracies of Rapid Serological Tests and ELISA to Molecular Diagnostics in Patients with Suspected Coronavirus Disease 2019 Presenting to the Hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1094.e7–1094.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA(IgA) Protocol. EUROIMMUN®. Available online: https://testecovid19.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Anti-SARS-CoV-2-ELISA-IgA.pdf?x45112 (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA(IgG) Protocol. EUROIMMUN®. Available online: https://testecovid19.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Anti-SARS-CoV-2-ELISA-IgG.pdf?x45112 (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Wondfo SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test (Lateral Flow Method) Protocol. WONDFO® (Catalog N°.: W195). Available online: https://www.zarenta.at/WNDF_EN_antikoerper_Rel20200528.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Lumit™ Dx SARS-CoV-2 Immunoassay protocol. PROMEGA®. Available online: https://www.promega.com/-/media/files/resources/protocols/technical-manuals/500/lumit-dx-sars-cov-2-immunoassay-protocol-tm636.pdf?la=en (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, M.A.; Shen, G.; Feng, X.; Garcia Beltran, W.F.; Feng, Y.; Vasudevaraja, V.; Allison, D.; Lin, L.H.; Gindin, T.; Astudillo, M.; et al. Analytical Performance of Lateral Flow Immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2 Exposure Screening on Venous and Capillary Blood Samples. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 489, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, D.; Newton, D.; Evans, P.; Osman, H.; Baretto, R. Preanalytical Issues Affecting the Diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongchen, Z.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Gu, B. Different Longitudinal Patterns of Nucleic Acid and Serology Testing Results Based on Disease Severity of COVID-19 Patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Ong, C.W.; Chan, M.Y.; Ang, L.W.; Leo, Y.S.; Chen, M.I.; Lye, D.C.B.; Young, B.E. Diagnostic Performance of COVID-19 Serological Assays during Early Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 11 516 Samples. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2021, 15, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traugott, M.; Aberle, S.W.; Aberle, J.H.; Griebler, H.; Karolyi, M.; Pawelka, E.; Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Zoufaly, A.; Weseslindtner, L. Performance of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antibody Assays in Different Stages of Infection: Comparison of Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays and Rapid Tests. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Elslande, J.; Houben, E.; Depypere, M.; Brackenier, A.; Desmet, S.; André, E.; Van Ranst, M.; Lagrou, K.; Vermeersch, P. Diagnostic Performance of Seven Rapid IgG/IgM Antibody Tests and the Euroimmun IgA/IgG ELISA in COVID-19 Patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, T.; Lefeuvre, C.; Serri, O.; Pivert, A.; Joubaud, F.; Dubée, V.; Kouatchet, A.; Ducancelle, A.; Lunel-Fabiani, F.; Le Guillou-Guillemette, H. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 through the Evaluation of Three Immunoassays: Two Automated Immunoassays (Euroimmun and Abbott) and One Rapid Lateral Flow Immunoassay (NG Biotech). J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Patients With Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ding, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Jin, T.; Gao, Y.; et al. Characteristics of Patients with Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Confirmed Using an IgM-IgG Antibody Test. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévost, J.; Gasser, R.; Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Richard, J.; Duerr, R.; Laumaea, A.; Anand, S.P.; Goyette, G.; Benlarbi, M.; Ding, S.; et al. Cross-Sectional Evaluation of Humoral Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, B.; Song, S.; et al. Human Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nature 2020, 584, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.M.; Goodwin, E.C.; Verma, A.; Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; McAllister, C.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Weaver, J.; et al. Seasonal Human Coronavirus Antibodies Are Boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 Infection but Not Associated with Protection. Cell 2021, 184, 1858–1864.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W.; Faulkner, N.; Cornish, G.H.; Rosa, A.; Harvey, R.; Hussain, S.; Ulferts, R.; Earl, C.; Wrobel, A.G.; Benton, D.J.; et al. Preexisting and de Novo Humoral Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Humans. Science 2020, 370, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; He, W.; Callaghan, S.; Anzanello, F.; Huang, D.; Ricketts, J.; Torres, J.L.; Beutler, N.; Peng, L.; Vargas, S.; et al. Cross-Reactive Serum and Memory B-Cell Responses to Spike Protein in SARS-CoV-2 and Endemic Coronavirus Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | RT-PCR Positive N (%) | RT-PCR Negative N (%) | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | p < 0.01 | ||
| Male | 50 (52.6%) | 29 (33.0%) | |
| Female | 45 (47.4%) | 59 (67.0%) | |
| Age (years) | p < 0.05 * | ||
| 20–35 | 21 (22.1%) | 20 (22.7%) | |
| 36–45 | 19 (20.0%) | 34 (38.6%) | |
| 46–59 | 25 (26.3%) | 19 (21.6%) | |
| 60+ | 30 (31.6%) | 15 (17.1%) | |
| Ethnicity | p = 0.01 * | ||
| White | 91 (96.8%) | 81 (92.1%) | |
| Black | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| Brown | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (6.8%) | |
| Other | 3 (3.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Education level | p = 0.34 | ||
| Elementary school | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| Secondary school | 5 (5.3%) | 2 (2.3%) | |
| Graduate | 90 (94.7%) | 85 (96.6%) | |
| Symptoms | |||
| Fever | 48 (50.5%) | 21 (24.1%) | p < 0.01 * |
| Sore throat | 36 (37.9%) | 43 (50.0%) | p = 0.13 |
| Cough | 48 (51.6%) | 38 (44.2%) | p = 0.37 |
| Cougar in cough | 13 (27.1%) | 8 (23.5%) | p = 0.80 |
| Difficulty breathing | 30 (31.6%) | 24 (27.6%) | p = 0.63 |
| Stuffy nose | 14 (41.2%) | 14 (58.3%) | p = 0.29 |
| Vomiting | 6 (6.5%) | 9 (10.5%) | p = 0.42 |
| Diarrhea | 39 (41.1%) | 33 (37.5%) | p = 0.65 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes | 5 (5.3%) | 2 (2.3%) | p = 0.45 |
| Asthma | 9 (9.6%) | 16 (18.4%) | p = 0.13 |
| Hypertension | 12 (12.6%) | 9 (10.5%) | p = 0.82 |
| Test | Overall | Time from Symptoms Onset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <15 Days | 15 to 21 Days | >21 Days | ||
| ELISA (Euroimmun) | (n = 138) | (n = 36) | (n = 47) | (n = 55) |
| IgA or IgG | 89.5% | 92.9% | 75.9% | 97.0% |
| IgA | 85.3% | 78.6% | 75.9% | 94.0% |
| IgG | 80.0% | 85.7% | 62.1% | 97.0% |
| LUMIT (Promega) | (n = 80) | (n = 17) | (n = 27) | (n = 36) |
| IgG | 77.4% | 76.9% | 73.9% | 90.6% |
| RT (Wondfo) | (n = 138) | (n = 36) | (n = 47) | (n = 55) |
| IgM or IgG | 77.9% | 78.6% | 75.9% | 81.8% |
| Overall % (95% CI) | Time from Symptoms Onset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <15 Days % (95% CI) | 15 to 21 Days % (95% CI) | >21 Days % (95% CI) | ||
| RT vs. ELISA | (n = 138) | (n = 36) | (n = 47) | (n = 55) |
| Sensitivity | 88.0 (78.0–94.0) | 83.0 (52.0–98.0) | 100.0 (82.0–100.0) | 85.0 (68.0–95.0) |
| Specificity | 91.0 (84.0–96.0) | 92.0 (73.0–99.0) | 86.0 (67.0–96.0) | 100.0 (85.0–100.0) |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | 89.0 (79.0–95.0) | 83.0 (52.0–98.0) | 83.0 (61.0–95.0) | 100.0 (85.0–100.0) |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | 90.0 (83.0–95.0) | 92.0 (73.0–99.0) | 100.0 (86.0–100.0) | 81.0 (62.0–94.0) |
| LUMIT vs. ELISA | (n = 80) | (n = 17) | (n = 27) | (n = 36) |
| Sensitivity | 86.0 (76.0-93.0) | 83.0 (52.0–98.0) | 95.0 (74.0–100.0) | 94.0 (79.0–99.0) |
| Specificity | 100.0 (85.0-100.0) | 100.0 (48.0–100.0) | 100.0 (63.0–100.0) | 100.0 (40.0–100.0) |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | 100.0 (85.0-100.0) | 100.0 (69.0–100.0) | 100.0 (81.0–100.0) | 100.0 (88.0–100.0) |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | 67.0 (48.0-82.0) | 71.0 (29.0–96.0) | 89.0 (52.0–100.0) | 67.0 (22.0–96.0) |
| RT vs. LUMIT | (n = 80) | (n = 17) | (n = 27) | (n = 36) |
| Sensitivity | 93.0 (83.0–98.0) | 90.0 (55.0–100) | 100.0 (81.0–100.0) | 90.0 (73.0–98.0) |
| Specificity | 64.0 (45.0–80.0) | 57.0 (18.0–91.0) | 56.0 (21.0–86.0) | 100.0 (54.0–100.0) |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | 84.0 (73.0–91.0) | 75.0 (43.0–95.0) | 82.0 (60.0–95.0) | 100.0 (87.0–100.0) |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | 81.0 (61.0–93.0) | 80.0 (28.0–99.0) | 100.0 (48.0–100.0) | 67.0 (30.0–93.0) |
| RT vs. ELISA % (95% CI) (n = 95) | LUMIT vs. ELISA % (95% CI) (n = 84) | RT vs. LUMIT % (95% CI) (n = 84) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 88.0 (79.0–94.0) | 88.0 (78.0–94.0) | 92.0 (83.0–97.0) |
| Specificity | 63.0 (38.0–84.0) | 100.0 (69.0–100.0) | 47.0 (24.0–71.0) |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | 91.0 (81.0–96.0) | 100.0 (94.0–100.0) | 86.0 (75.0–93.0) |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | 57.0 (34.0–78.0) | 53.0 (29.0–76.0) | 64.0 (35.0–87.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basgalupp, S.; dos Santos, G.; Bessel, M.; Garcia, L.; de Moura, A.C.; Rocha, A.C.; Brito, E.; de Miranda, G.; Dornelles, T.; Dartora, W.; et al. Diagnostic Properties of Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081441
Basgalupp S, dos Santos G, Bessel M, Garcia L, de Moura AC, Rocha AC, Brito E, de Miranda G, Dornelles T, Dartora W, et al. Diagnostic Properties of Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(8):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081441
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasgalupp, Suelen, Giovana dos Santos, Marina Bessel, Lara Garcia, Ana Carolina de Moura, Ana Carolina Rocha, Emerson Brito, Giovana de Miranda, Thayane Dornelles, William Dartora, and et al. 2021. "Diagnostic Properties of Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests" Diagnostics 11, no. 8: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081441
APA StyleBasgalupp, S., dos Santos, G., Bessel, M., Garcia, L., de Moura, A. C., Rocha, A. C., Brito, E., de Miranda, G., Dornelles, T., Dartora, W., Pellanda, L., Hallal, P., & Wendland, E. (2021). Diagnostic Properties of Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests. Diagnostics, 11(8), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081441






