Association of Upper Lip Morphology Characteristics with Sagittal and Vertical Skeletal Patterns: A Cross Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
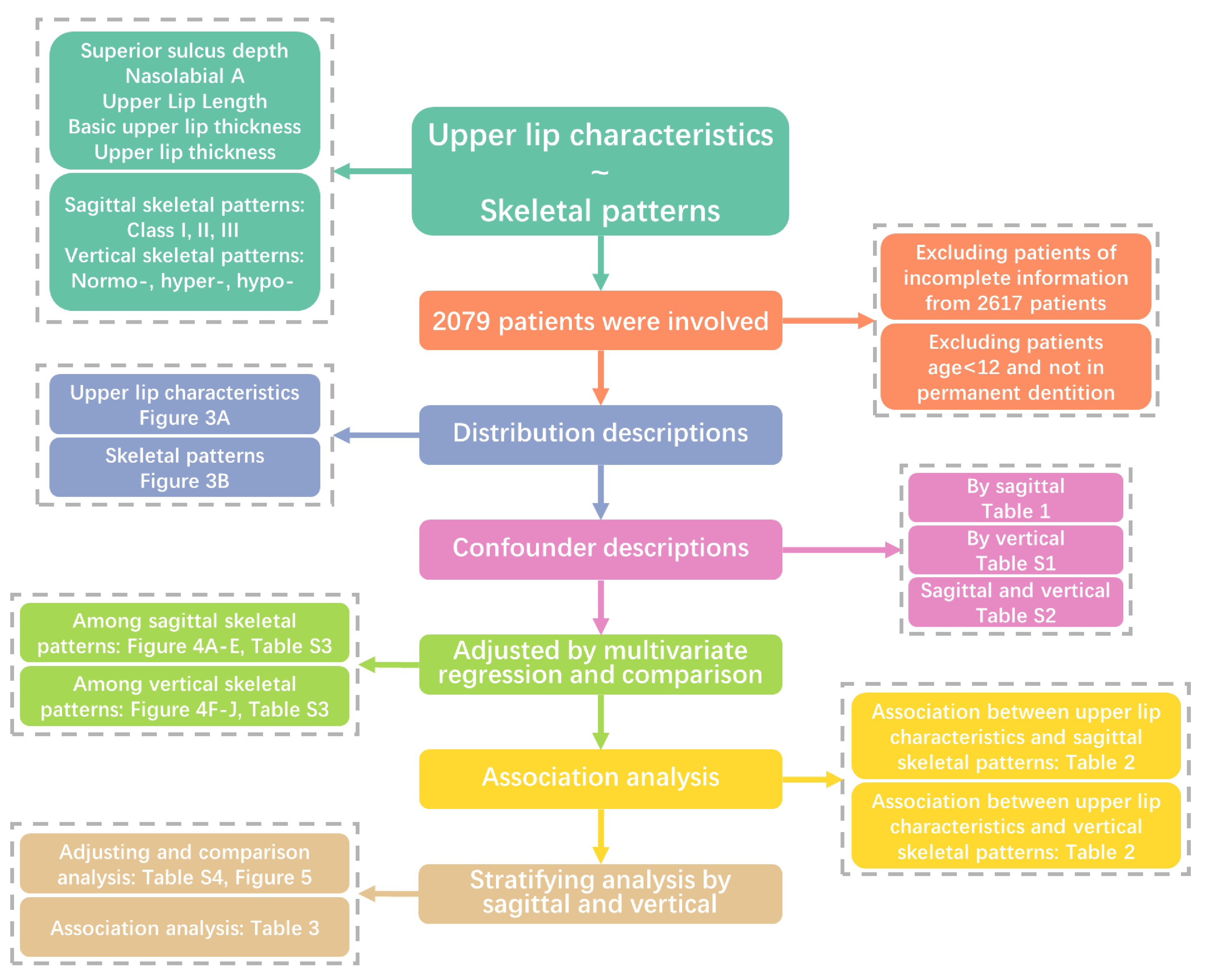
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Upper Lip Characteristics and Skeletal Patterns
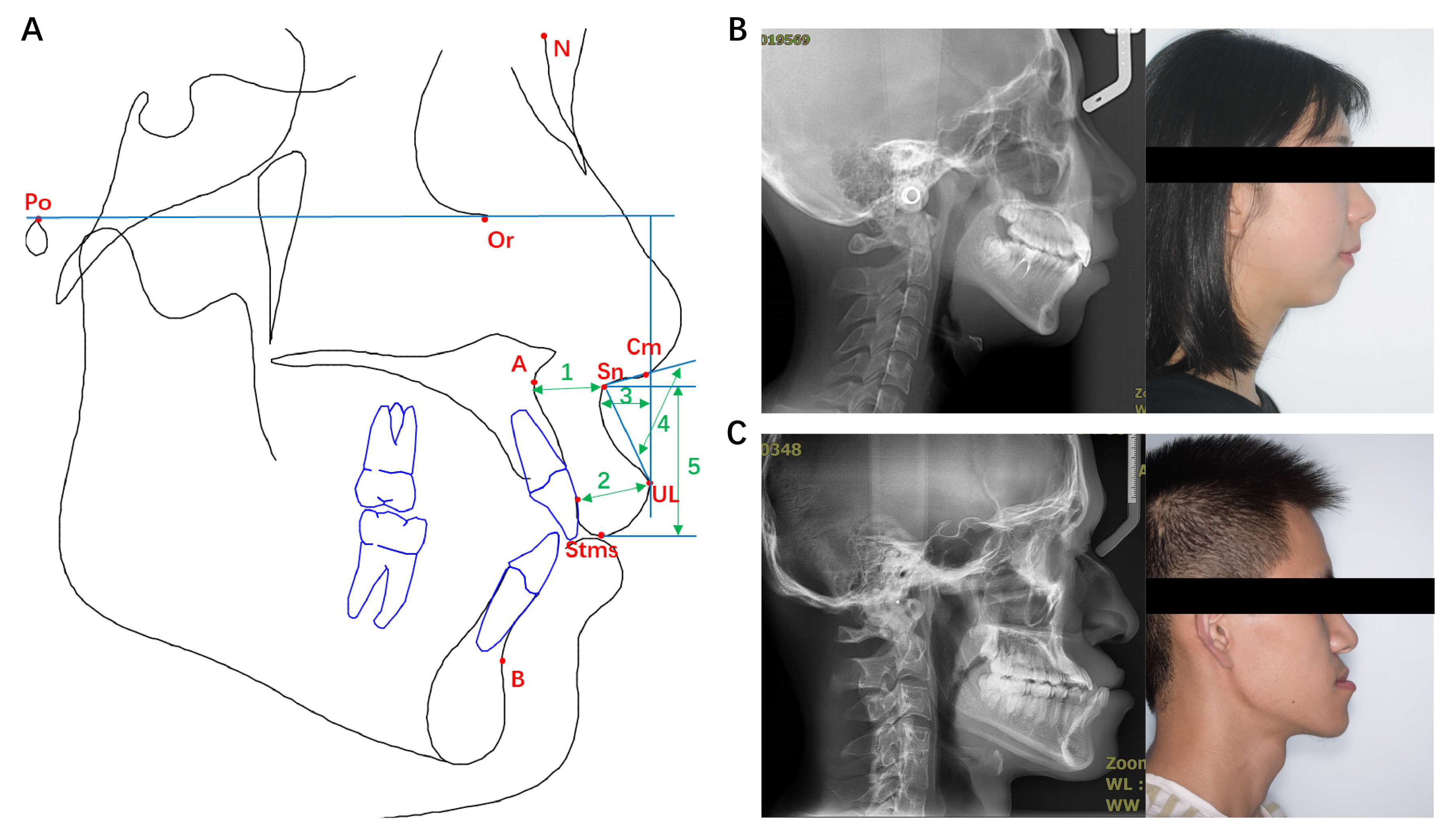
- Porion (Po): the midpoint of the upper contour of the external auditory canal.
- Orbitale (Or): the lowest point on the inferior margin of the orbit.
- Nasion (N): the most anterior point on midline of frontonasal suture.
- Columella (Cm): The most prominent point on the borderline between lower part of the nose contour and nasal tip.
- Subnasale (Sn): the deepest point on the curvature between the anterior nasal spine (ANS) and the prosthion on the anterior surface of the maxilla.
- Subspinale (point A): the innermost point on the contour of the premaxilla between ANS and the incisor tooth.
- Supramental (point B): the innermost point on the contour of the mandible between the incisor tooth and the bony chin.
- Labrale superius (UL): the most anterior and convex point of upper lip vermilion.
- Stomion superius (Stms): the lowest point of the margin of upper lip vermilion.
2.3. Demographics and Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participant Characteristics
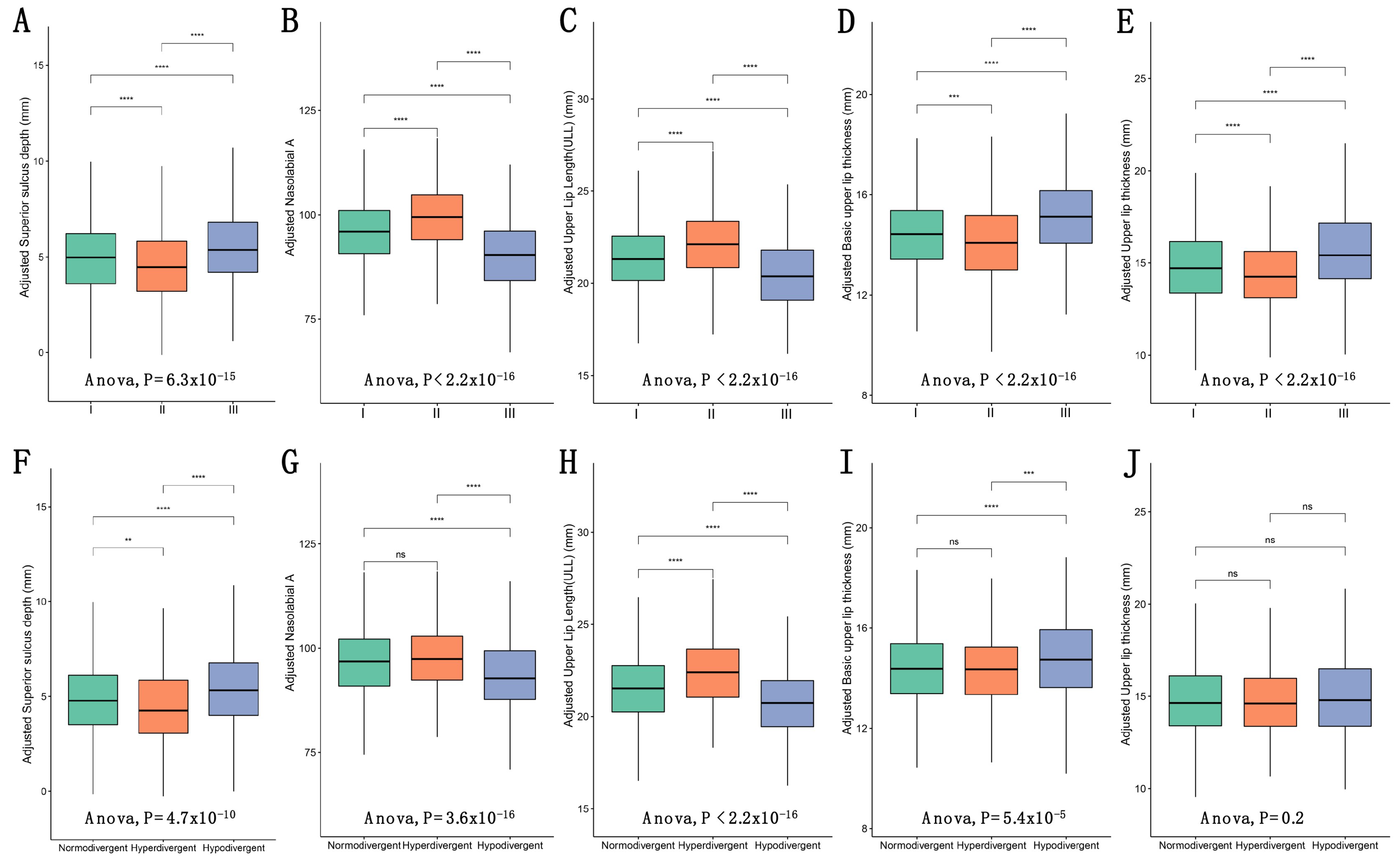
3.2. Comparison of Upper Lip Charactristics among Different Skeletal Patterns
3.3. Associations between Upper Lip Characteristics and Skeletal Patterns
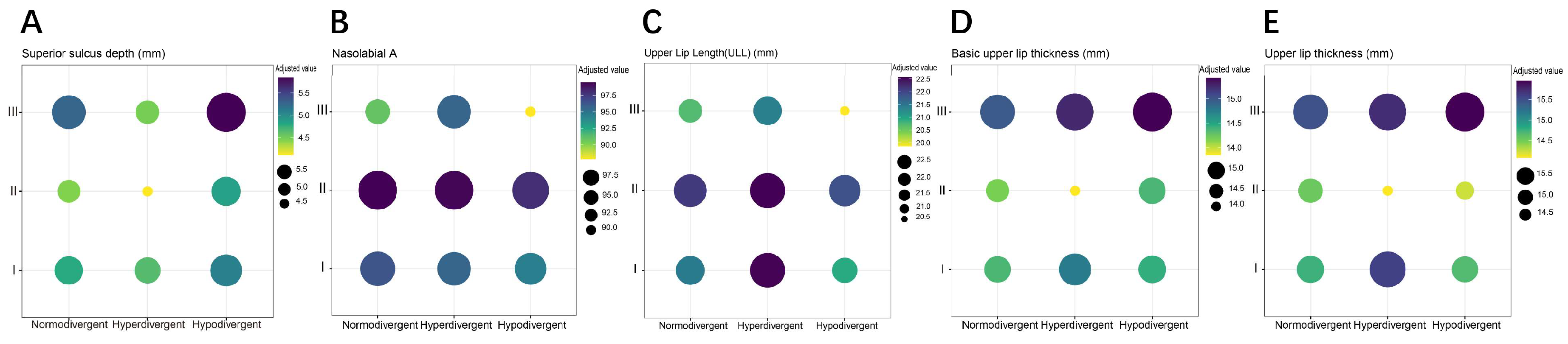
3.4. Stratified Associations between Upper Lip Characteristics and Skeletal Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The mean value of upper lip characteristics and prevalence of skeletal patterns were explored in Western China population, providing a race- and region-specific reference for Chinese orthodontists.
- Significant differences in upper lip characteristics were confirmed in various sagittal and vertical skeletal patterns, except for upper lip thickness among vertical skeletal patterns. This helps orthodontists make individualized treatment plans on the improvement of lip morphology according to patients with different skeletal patterns.
- The evaluation of independent correlation between upper lip characteristics and skeletal patterns provides guidance for a prognosis prediction of early intervention of skeletal growth patterns. Superior sulcus depth was negatively related to Class II, and positively related to Class III and the hypodivergent pattern regardless of age, gender, molar relationship, crowding, overbite, overjet, upper incisor position, and other upper lip characteristics, indicating that superior sulcus depth is the only upper lip index independently associated with skeletal patterns, and might be significantly corrected by intervention of skeletal growth. On the other hand, other upper lip characteristics may not be effectively improved by skeletal growth intervention, considering impacts of multiple covariates.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakosi, T.; Jonas, I.; Graber, T. Orthodontic Diagnosis; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, A.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Grocholewicz, K. Nasal Morphology and Its Correlation to Craniofacial Morphology in Lateral Cephalometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perović, T.; Blažej, Z. Male and Female Characteristics of Facial Soft Tissue Thickness in Different Orthodontic Malocclusions Evaluated by Cephalometric Radiography. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridel, A.F.; Demeter, F.; Liebenberg, J.; L’Abbé, E.N.; Vandermeulen, D.; Oettlé, A.C. Skeletal dimensions as predictors for the shape of the nose in a South African sample: A cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarilita, E.; Rynn, C.; Mossey, P.A.; Black, S.; Oscandar, F. Facial average soft tissue depth variation based on skeletal classes in Indonesian adult population: A retrospective lateral cephalometric study. Leg. Med. 2020, 43, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perović, T.M.; Blažej, M.; Jovanović, I. The influence of mandibular divergence on facial soft tissue thickness in class I patients: A cephalometric study. Folia Morphol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macari, A.T.; Hanna, A.E. Comparisons of soft tissue chin thickness in adult patients with various mandibular divergence patterns. Angle Orthod. 2014, 84, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardani, I.; Willyanti, I.; Narmada, I.B. Correlation between vertical components and skeletal Class II malocclusion in ethnic Javanese. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2018, 10, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasserstein, A.; Shpack, N.; Yoseph, Y.B.; Geron, S.; Davidovitch, M.; Vardimon, A. Comparison of lateral photographic and radiographic sagittal analysis in relation to Angle’s classification. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2015, 76, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajwa, N.; Alkhars, F.A.; AlMubarak, F.H.; Aldajani, H.; AlAli, N.M.; Alhanabbi, A.H.; Alsulaiman, S.A.; Divakar, D.D. Correlation Between Sex and Facial Soft Tissue Characteristics Among Young Saudi Patients with Various Orthodontic Skeletal Malocclusions. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e919771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Asmar, R.; Akl, R.; Ghoubril, J.; El Khoury, E. Evaluation of the ideal position of the maxillary incisor relative to upper lip thickness. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, L.; McNamara Jr, J.A.; Ackerman, M.B.; Baccetti, T. Hard- and soft-tissue contributions to the esthetics of the posed smile in growing patients seeking orthodontic treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatienė, K.; Šidlauskas, A.; Vasiliauskas, A.; Čečytė, L.; Švalkauskienė, V.; Šidlauskas, M. Relationship between malocclusion, soft tissue profile, and pharyngeal airways: A cephalometric study. Medicina 2016, 52, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anić-Milosević, S.; Lapter-Varga, M.; Slaj, M. Analysis of the soft tissue facial profile by means of angular measurements. Eur. J. Orthod. 2008, 30, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronfman, C.N.; Janson, G.; Pinzan, A.; Rocha, T.L. Cephalometric norms and esthetic profile preference for the Japanese: A systematic review. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2015, 20, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldrees, A.M. Lateral cephalometric norms for Saudi adults: A meta-analysis. Saudi Dent. J. 2011, 23, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbanyjavadpour, F.; Rakhshan, V. Factors associated with the beauty of soft-tissue profile. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 155, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, G.; Dai, F.F.; Xu, T.M.; Jiang, R.P. Analysis of correlation of 3-dimensional lip vermilion morphology and dentoskeletal forms in young Chinese adults on the basis of sex and skeletal patterns. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e423–e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, C.; Nakamura, K.; Yagi, M.; Takada, K. Lip Vermilion Profile Patterns and Corresponding Dentoskeletal Forms in Female Adults. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, W163–W194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, M.; Lin, J. Orthodontics; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Orthodontics: Basic, Technical and Clinical Aspects; Chen, Y., Ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bartold, M.P.; Gronthos, S. Standardization of Criteria Defining Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, S.; Morice, A.; Picard, A.; Giudice, A. Surgery-first orthognathic approach vs conventional orthognathic approach: A systematic review of systematic reviews. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, Y.; Zamora, N.; Tarazona, B.; Bellot-Arcís, C.; Paredes-Gallardo, V. Cross-sectional human study of soft tissue chin (STC) thickness in adult patients in relation to sex, facial pattern and skeletal class. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, T.; Shaikh, A.; Fida, M. Comparison of nasal profiles in various skeletal patterns. J. Ayub. Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2013, 25, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, C.A.; Viana, G.; Anderson, N.K.; Giddon, D.B. Tolerance of deviations in eye and mouth position. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2005, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricketts, R.M. The value of cephalometrics and computerized technology. Angle Orthod. 1972, 42, 179–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bishara, E.S.; Hession, T.J.; Peterson, L.C. Longitudinal soft-tissue profile changes: A study of three analyses. Am. J. Orthod. 1985, 88, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.; Nalabothu, P.; Thanh, H.N.; Antonarakis, G.S. A Comparison of Craniofacial Characteristics between Two Different Adult Populations with Class II Malocclusion-A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. Biology 2021, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulsen, A.; Okay, C.; Aslan, B.I.; Uner, O.; Yavuzer, R. The relationship between craniofacial structures and the nose in Anatolian Turkish adults: A cephalometric evaluation. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 130, 131.e15–132.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsuno, H.; Kageyama, T.; Uchida, K.; Yoshino, M.; Oohigashi, S.; Miyazawa, H.; Inoue, K. Pilot study of facial soft tissue thickness differences among three skeletal classes in Japanese females. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 195, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, K.; Bulut, O.; Hizliol, I.; Hekimoglu, B.; Gurcan, S. Variations of midline facial soft tissue thicknesses among three skeletal classes in Central Anatolian adults. Leg. Med. 2015, 17, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstone, C.J. The integumental profile. Am. J. Orthod. 1958, 44, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perović, M.T.; Blažej, Z.; Jovanović, I. The influence of antero-posterior dentoskeletal pattern on the value of nasal soft tissue angles: A cephalometric study. Folia Morphol. 2020, 80, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, D.; Prasad, S.; Antoun, J.S.; Mei, L.; Farella, M. Biomechanical properties of the lips in a pre-orthodontic sample of adolescents and young adults. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikoglu, M.; Buyuk, S.K.; Ekizer, A.; Sekerci, A.E.; Sisman, Y. Assessment of the soft tissue thickness at the lower anterior face in adult patients with different skeletal vertical patterns using cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, W.; Fida, M.; Shaikh, A. Facial soft tissue thickness among various vertical facial patterns in adult Pakistani subjects. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 517.e1–517.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.P.; Goorhuis, J.; Kapila, S.; Nanda, R.S. Growth changes in the nasal profile from 7 to 18 years of age. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1988, 94, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Barone, S.; Belhous, K.; Morice, A.; Soupre, V.; Bennardo, F.; Boddaertc, N.; Vazquezd, M.-P.; Abadiee, V.; Picardd, A. Pierre Robin sequence: A comprehensive narrative review of the literature over time. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 119, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Kojima, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Ohbora, A.; Kato, T.; Nakamura, N.; Fukui, M. Association between serum γ-glutamyltranspeptidase and atherosclerosis: A population-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, G.; Liao, S.; Gong, D.; Qiu, H. Association of acrylamide and glycidamide haemoglobin adduct levels with diabetes mellitus in the general population. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zheng, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Feng, W.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Association of Depressive Symptoms with Incident Cardiovascular Diseases in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1916591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Level | Overall | I | II | III | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 2079 | 968 | 691 | 420 | |
| Age (%) | |||||
| Adolescent | 734 (35.3) | 373 (38.5) | 248 (35.9) | 113 (26.9) | <0.001 |
| Young adult | 1272 (61.2) | 566 (58.5) | 409 (59.2) | 297 (70.7) | |
| Middle age | 73 (3.5) | 29 (3.0) | 34 (4.9) | 10 (2.4) | |
| Gender (%) | |||||
| Male | 623 (30.0) | 271 (28.0) | 199 (28.8) | 153 (36.4) | 0.005 |
| Female | 1456 (70.0) | 697 (72.0) | 492 (71.2) | 267 (63.6) | |
| Molar Relationship (%) | |||||
| I | 654 (31.5) | 376 (38.8) | 186 (26.9) | 92 (21.9) | <0.001 |
| II-1 | 654 (31.5) | 288 (29.8) | 318 (46.0) | 48 (11.4) | |
| II-2 | 205 (9.9) | 77 (8.0) | 120 (17.4) | 8 (1.9) | |
| III | 506 (24.3) | 197 (20.4) | 52 (7.5) | 257 (61.2) | |
| IV | 60 (2.9) | 30 (3.1) | 15 (2.2) | 15 (3.6) | |
| Upper crowding (%) | |||||
| I | 1275 (61.3) | 590 (61.0) | 446 (64.5) | 239 (56.9) | 0.108 |
| II | 507 (24.4) | 245 (25.3) | 152 (22.0) | 110 (26.2) | |
| III | 297 (14.3) | 133 (13.7) | 93 (13.5) | 71 (16.9) | |
| Lower crowding (%) | |||||
| I | 1325 (63.7) | 608 (62.8) | 392 (56.7) | 325 (77.4) | <0.001 |
| II | 557 (26.8) | 270 (27.9) | 210 (30.4) | 77 (18.3) | |
| III | 197 (9.5) | 90 (9.3) | 89 (12.9) | 18 (4.3) | |
| Overbite (%) | |||||
| Normal | 1302 (62.6) | 647 (66.8) | 463 (67.0) | 192 (45.7) | <0.001 |
| Deep | 246 (11.8) | 91 (9.4) | 112 (16.2) | 43 (10.2) | |
| Open | 117 (5.6) | 40 (4.1) | 39 (5.6) | 38 (9.0) | |
| Shallow | 414 (19.9) | 190 (19.6) | 77 (11.1) | 147 (35.0) | |
| Overjet (%) | |||||
| Normal | 1125 (54.1) | 638 (65.9) | 299 (43.3) | 188 (44.8) | <0.001 |
| Cross | 234 (11.3) | 36 (3.7) | 5 (0.7) | 193 (46.0) | |
| Deep | 690 (33.2) | 284 (29.3) | 385 (55.7) | 21 (5.0) | |
| Shallow | 30 (1.4) | 10 (1.0) | 2 (0.3) | 18 (4.3) | |
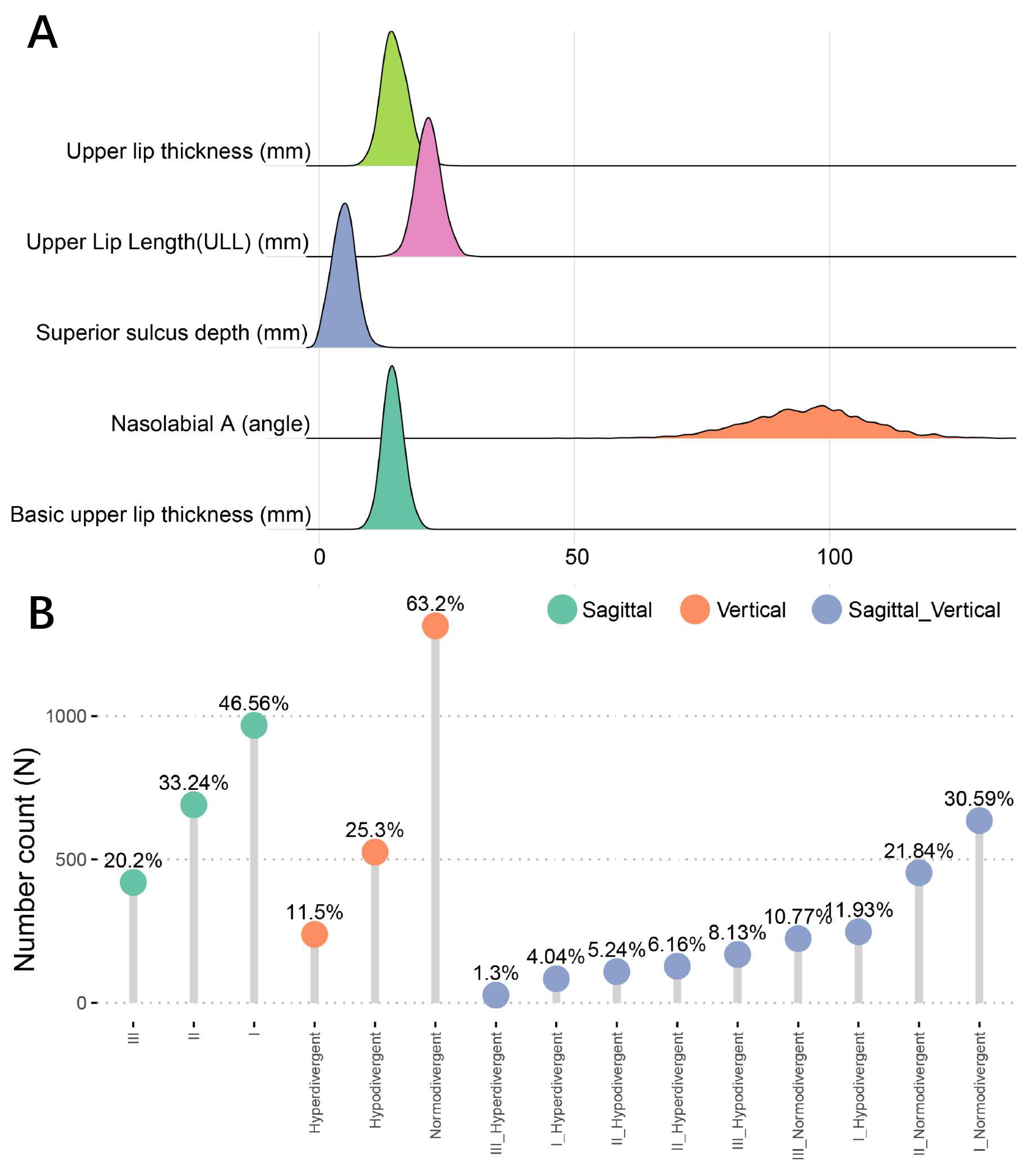
| Vertical skeletal pattern (%) | |||||
| Normodivergent | 1314 (63.2) | 636 (65.7) | 454 (65.7) | 224 (53.3) | <0.001 |
| Hyperdivergent | 239 (11.5) | 84 (8.7) | 128 (18.5) | 27 (6.4) | |
| Hypodivergent | 526 (25.3) | 248 (25.6) | 109 (15.8) | 169 (40.2) | |
| U1-ANS (mm) (mean (SD)) | 27.60 (3.08) | 27.54 (2.93) | 28.50 (2.91) | 26.29 (3.21) | <0.001 |
| U1-OP (mean (SD)) | 54.09 (7.65) | 54.18 (7.42) | 54.33 (8.28) | 53.47 (7.06) | 0.168 |
| U1-PP (mm) (mean (SD)) | 27.28 (3.12) | 27.22 (2.97) | 28.18 (2.96) | 25.94 (3.22) | <0.001 |
| U1-NA (mean (SD)) | 27.92 (8.76) | 28.06 (8.12) | 24.92 (9.08) | 32.55 (7.49) | <0.001 |
| U1-NA (mm) (mean (SD)) | 5.65 (2.85) | 5.72 (2.76) | 4.78 (2.61) | 6.92 (2.93) | <0.001 |
| U1-SN (mean (SD)) | 108.46 (9.48) | 108.40 (8.99) | 106.34 (10.12) | 112.08 (8.37) | <0.001 |
| U1-PP (mean (SD)) | 119.54 (8.88) | 119.36 (8.54) | 117.94 (9.43) | 122.57 (7.93) | <0.001 |
| U1-NPo (mm) (mean (SD)) | 9.86 (4.92) | 9.42 (3.71) | 13.60 (4.16) | 4.74 (3.17) | <0.001 |
| UL-EL (mm) (mean (SD)) | 0.53 (2.85) | 0.45 (2.32) | 2.35 (2.32) | −2.28 (2.39) | <0.001 |
| UL-SL (mean (SD)) | 4.60 (2.64) | 4.65 (2.57) | 4.24 (2.52) | 5.07 (2.90) | <0.001 |
| Upper Lip Length (ULL) (mm) (mean (SD)) | 21.46 (2.40) | 21.41 (2.24) | 22.16 (2.30) | 20.41 (2.52) | <0.001 |
| Basic upper lip thickness (mm) (mean (SD)) | 14.48 (1.97) | 14.42 (1.82) | 14.14 (2.00) | 15.18 (2.07) | <0.001 |
| Nasolabial A (mean (SD)) | 95.74 (11.83) | 95.80 (11.34) | 99.17 (11.02) | 89.96 (12.01) | <0.001 |
| Upper lip thickness (mm) (mean (SD)) | 14.85 (2.50) | 14.80 (2.43) | 14.40 (2.36) | 15.69 (2.67) | <0.001 |
| Superior sulcus depth (mm) (mean (SD)) | 4.84 (2.17) | 4.85 (2.16) | 4.44 (2.14) | 5.45 (2.11) | <0.001 |
| β (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 4 d | |
| Superior sulcus depth (mm) | ||||
| SSP-Class I | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| SSP-Class II | −0.300 ** (−0.516, −0.084) | −0.587 *** (−0.827, −0.346) | −0.471 *** (−0.569, −0.372) | −0.195 *** (−0.302, −0.087) |
| SSP-Class III | 0.301 * (0.011, 0.590) | 0.613 *** (0.331, 0.896) | 0.752 *** (0.630, 0.875) | 0.253 *** (0.117, 0.389) |
| VSP-Normodivergent | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| VSP-Hyperdivergent | −0.134 (−0.427, 0.159) | 0.150 (−0.141, 0.441) | −0.114 (−0.241, 0.014) | 0.185 ** (0.058, 0.313) |
| VSP-Hypodivergent | 0.307 ** (0.086, 0.527) | 0.143 (−0.088, 0.375) | 0.267 *** (0.171, 0.362) | 0.050 (−0.052, 0.151) |
| Nasolabial A | ||||
| SSP-Class I | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| SSP-Class II | 2.729 *** (1.544, 3.914) | 2.255 ** (0.839, 3.670) | −1.446 ** (−2.378, −0.515) | −0.922 (−1.998, 0.154) |
| SSP-Class III | −3.754 *** (−5.341, −2.168) | −3.907 *** (−5.565, −2.248) | 1.219 * (0.050, 2.387) | 0.524 (−0.839, 1.887) |
| VSP-Normodivergent | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| VSP-Hyperdivergent | −0.103 (−1.712, 1.506) | −1.346 (−3.056, 0.365) | −1.389 * (−2.568, −0.210) | −0.346 (−1.622, 0.930) |
| VSP-Hypodivergent | −1.888 ** (−3.097, −0.678) | −1.014 (−2.375, 0.347) | 0.165 (−0.723, 1.053) | −0.582 (−1.599, 0.434) |
| Upper Lip Length (ULL) (mm) | ||||
| SSP-Class I | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| SSP-Class II | 0.536 *** (0.318, 0.754) | −0.011 (−0.233, 0.210) | 0.427 *** (0.197, 0.657) | −0.043 (−0.236, 0.150) |
| SSP-Class III | −0.901 *** (−1.193, −0.609) | −0.148 (−0.407, 0.111) | −0.732 *** (−1.020, −0.445) | −0.176 (−0.421, 0.068) |
| VSP-Normodivergent | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| VSP-Hyperdivergent | 0.772 *** (0.476, 1.068) | −0.019 (−0.286, 0.248) | 0.723 *** (0.432, 1.013) | −0.069 (−0.298, 0.160) |
| VSP-Hypodivergent | −0.689 *** (−0.911, −0.466) | 0.315 ** (0.102, 0.527) | −0.629 *** (−0.846, −0.411) | 0.203 * (0.021, 0.386) |
| Basic upper lip thickness (mm) | ||||
| SSP-Class I | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| SSP-Class II | −0.457 *** (−0.639, −0.275) | 0.060 (−0.174, 0.294) | −0.741 *** (−0.912, −0.570) | −0.141 (−0.297, 0.015) |
| SSP-Class III | 0.721 *** (0.477, 0.964) | 0.299 * (0.025, 0.573) | 1.333 *** (1.123, 1.543) | 0.194 (−0.004, 0.392) |
| VSP-Normodivergent | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| VSP-Hyperdivergent | 0.278 * (0.032, 0.525) | 0.0001 (−0.282, 0.283) | −0.376 *** (−0.595, −0.157) | 0.179 (−0.005, 0.364) |
| VSP-Hypodivergent | −0.069 (−0.254, 0.117) | 0.278 * (0.053, 0.503) | 0.588 *** (0.425, 0.751) | 0.111 (−0.036, 0.258) |
| Upper lip thickness (mm) | ||||
| SSP-Class I | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| SSP-Class II | −0.250 * (−0.485, −0.015) | −0.480 ** (−0.769, −0.191) | 0.159 (−0.074, 0.392) | −0.109 (−0.298, 0.079) |
| SSP-Class III | 0.193 (−0.122, 0.508) | 0.959 *** (0.620, 1.298) | −0.178 (−0.470, 0.114) | 0.194 (−0.045, 0.433) |
| VSP-Normodivergent | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| VSP-Hyperdivergent | 0.422 ** (0.102, 0.741) | −0.052 (−0.401, 0.298) | 0.386 * (0.092, 0.680) | −0.089 (−0.313, 0.135) |
| VSP-Hypodivergent | −0.332 ** (−0.572, −0.092) | 0.115 (−0.164, 0.393) | −0.455 *** (−0.676, −0.234) | −0.077 (−0.256, 0.101) |
| β (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 4 d | |
| Superior sulcus depth (mm) | ||||
| I-Norm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| I-Hyper | −0.037 (−0.506, 0.433) | 0.341 (−0.109, 0.791) | −0.089 (−0.297, 0.119) | 0.190 (−0.004, 0.384) |
| I-Hypo | 0.241 (−0.067, 0.548) | 0.024 (−0.280, 0.327) | 0.232 *** (0.098, 0.366) | 0.007 (−0.125, 0.139) |
| II-Norm | −0.378 (−0.782, 0.027) | −0.446 * (−0.878, −0.014) | −0.686 *** (−0.868, −0.504) | −0.035 (−0.224, 0.153) |
| II-Hyper | −0.047 (−0.480, 0.385) | −0.487 * (−0.902, −0.073) | −0.149 (−0.334, 0.037) | −0.173 (−0.357, 0.010) |
| II-Hypo | −0.317 * (−0.575, −0.058) | −0.570 *** (−0.845, −0.295) | −0.469 *** (−0.587, −0.352) | −0.196 ** (−0.317, −0.074) |
| III-Norm | −0.515 (−1.344, 0.314) | 0.185 (−0.582, 0.953) | 0.978 *** (0.623, 1.333) | 0.471 ** (0.128, 0.813) |
| III-Hyper | 0.709 *** (0.317, 1.101) | 0.907 *** (0.506, 1.308) | 1.016 *** (0.842, 1.191) | 0.355 *** (0.172, 0.537) |
| III-Hypo | 0.277 (−0.070, 0.623) | 0.510 ** (0.167, 0.853) | 0.708 *** (0.558, 0.858) | 0.198 * (0.041, 0.354) |
| Nasolabial A | ||||
| I-Norm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| I-Hyper | −0.940 (−3.510, 1.631) | −2.155 (−4.797, 0.488) | −1.699 (−3.622, 0.224) | −1.041 (−2.981, 0.900) |
| I-Hypo | −1.830 * (−3.514, −0.145) | −0.758 (−2.540, 1.025) | −0.241 (−1.481, 1.000) | −1.348 * (−2.670, −0.026) |
| II-Norm | 2.006 (−0.210, 4.222) | 0.088 (−2.449, 2.626) | −3.719 *** (−5.414, −2.024) | −1.751 (−3.635, 0.133) |
| II-Hyper | 1.528 (−0.843, 3.899) | 2.085 (−0.349, 4.519) | −0.267 (−1.984, 1.450) | −0.891 (−2.725, 0.944) |
| II-Hypo | 2.645 *** (1.228, 4.063) | 1.995 * (0.378, 3.611) | −1.696 ** (−2.797, −0.594) | −1.432 * (−2.652, −0.213) |
| III-Norm | 1.417 (−3.127, 5.962) | 0.052 (−4.456, 4.559) | 3.714 * (0.412, 7.016) | 2.049 (−1.377, 5.475) |
| III-Hyper | −6.291 *** (−8.439, −4.143) | −5.712 *** (−8.068, −3.356) | 0.970 (−0.694, 2.635) | −0.013 (−1.846, 1.820) |
| III-Hypo | −3.855 *** (−5.755, −1.956) | −3.565 *** (−5.577, −1.552) | 0.923 (−0.490, 2.337) | 0.029 (−1.539, 1.597) |
| Upper Lip Length (ULL) (mm) | ||||
| I-Norm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| I-Hyper | 1.031 *** (0.558, 1.505) | 0.108 (−0.305, 0.521) | 0.997 *** (0.523, 1.471) | −0.032 (−0.380, 0.316) |
| I-Hypo | −0.663 *** (−0.973, −0.353) | 0.210 (−0.069, 0.488) | −0.575 *** (−0.881, −0.270) | 0.104 (−0.133, 0.341) |
| II-Norm | 1.097 *** (0.689, 1.505) | −0.196 (−0.592, 0.200) | 0.966 *** (0.547, 1.385) | −0.237 (−0.575, 0.102) |
| II-Hyper | 0.102 (−0.335, 0.539) | 0.664 *** (0.284, 1.044) | 0.154 (−0.270, 0.579) | 0.434 ** (0.106, 0.763) |
| II-Hypo | 0.574 *** (0.313, 0.835) | −0.117 (−0.369, 0.136) | 0.443 ** (0.170, 0.715) | −0.141 (−0.360, 0.078) |
| III-Norm | 0.306 (−0.531, 1.143) | −0.062 (−0.766, 0.641) | 0.311 (−0.506, 1.128) | −0.103 (−0.718, 0.512) |
| III-Hyper | −1.688 *** (−2.084, −1.293) | 0.060 (−0.308, 0.427) | −1.544 *** (−1.950, −1.137) | −0.055 (−0.384, 0.273) |
| III-Hypo | −0.805 *** (−1.155, −0.456) | −0.051 (−0.365, 0.264) | −0.549 ** (−0.898, −0.200) | −0.128 (−0.409, 0.153) |
| Basic upper lip thickness (mm) | ||||
| I-Norm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| I-Hyper | 0.464 * (0.070, 0.858) | 0.278 (−0.159, 0.715) | −0.297 (−0.655, 0.062) | 0.234 (−0.048, 0.515) |
| I-Hypo | −0.155 (−0.414, 0.103) | 0.175 (−0.119, 0.470) | 0.420 *** (0.189, 0.650) | 0.071 (−0.121, 0.263) |
| II-Norm | −0.378 * (−0.718, −0.038) | −0.147 (−0.567, 0.272) | −1.242 *** (−1.555, −0.929) | 0.025 (−0.249, 0.299) |
| II-Hyper | −0.551 ** (−0.914, −0.187) | 0.338 (−0.064, 0.741) | −0.107 (−0.427, 0.213) | −0.121 (−0.387, 0.145) |
| II-Hypo | −0.411 *** (−0.629, −0.194) | 0.108 (−0.159, 0.375) | −0.778 *** (−0.981, −0.575) | −0.114 (−0.291, 0.063) |
| III-Norm | 1.269 *** (0.573, 1.966) | 0.384 (−0.361, 1.129) | 0.962 ** (0.347, 1.576) | 0.273 (−0.224, 0.770) |
| III-Hyper | 0.804 *** (0.475, 1.133) | 0.728 *** (0.339, 1.118) | 2.032 *** (1.735, 2.330) | 0.405 ** (0.140, 0.670) |
| III-Hypo | 0.599 *** (0.308, 0.891) | 0.184 (−0.148, 0.517) | 1.194 *** (0.935, 1.452) | 0.117 (−0.110, 0.345) |
| Upper lip thickness (mm) | ||||
| I-Norm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| I-Hyper | 0.899 *** (0.389, 1.410) | 0.464 (−0.075, 1.003) | 0.869 *** (0.390, 1.349) | −0.018 (−0.359, 0.324) |
| I-Hypo | −0.247 (−0.582, 0.087) | −0.059 (−0.422, 0.305) | −0.396 * (−0.705, −0.087) | −0.119 (−0.352, 0.113) |
| II-Norm | −0.001 (−0.441, 0.439) | −0.748 ** (−1.265, −0.230) | 0.284 (−0.141, 0.709) | −0.251 (−0.582, 0.080) |
| II-Hyper | −0.747 ** (−1.217, −0.276) | −0.506 * (−1.003, −0.009) | −0.393 (−0.822, 0.036) | −0.185 (−0.507, 0.137) |
| II-Hypo | −0.070 (−0.351, 0.211) | −0.361 * (−0.691, −0.031) | 0.336 * (0.060, 0.611) | −0.105 (−0.320, 0.109) |
| III-Norm | 0.436 (−0.466, 1.338) | 0.440 (−0.480, 1.359) | 0.428 (−0.398, 1.254) | 0.090 (−0.513, 0.692) |
| III-Hyper | 0.061 (−0.365, 0.488) | 1.413 *** (0.932, 1.894) | −0.468 * (−0.884, −0.053) | 0.168 (−0.154, 0.490) |
| III-Hypo | 0.197 (−0.180, 0.574) | 0.731 *** (0.321, 1.142) | −0.205 (−0.559, 0.148) | 0.159 (−0.116, 0.435) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Long, H.; Lai, W. Association of Upper Lip Morphology Characteristics with Sagittal and Vertical Skeletal Patterns: A Cross Sectional Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091713
Yan X, Zhang X, Chen Y, Long H, Lai W. Association of Upper Lip Morphology Characteristics with Sagittal and Vertical Skeletal Patterns: A Cross Sectional Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(9):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091713
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xinyu, Xiaoqi Zhang, Yiyin Chen, Hu Long, and Wenli Lai. 2021. "Association of Upper Lip Morphology Characteristics with Sagittal and Vertical Skeletal Patterns: A Cross Sectional Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 9: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091713
APA StyleYan, X., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Long, H., & Lai, W. (2021). Association of Upper Lip Morphology Characteristics with Sagittal and Vertical Skeletal Patterns: A Cross Sectional Study. Diagnostics, 11(9), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091713







