Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Quality Assessment
3. Results
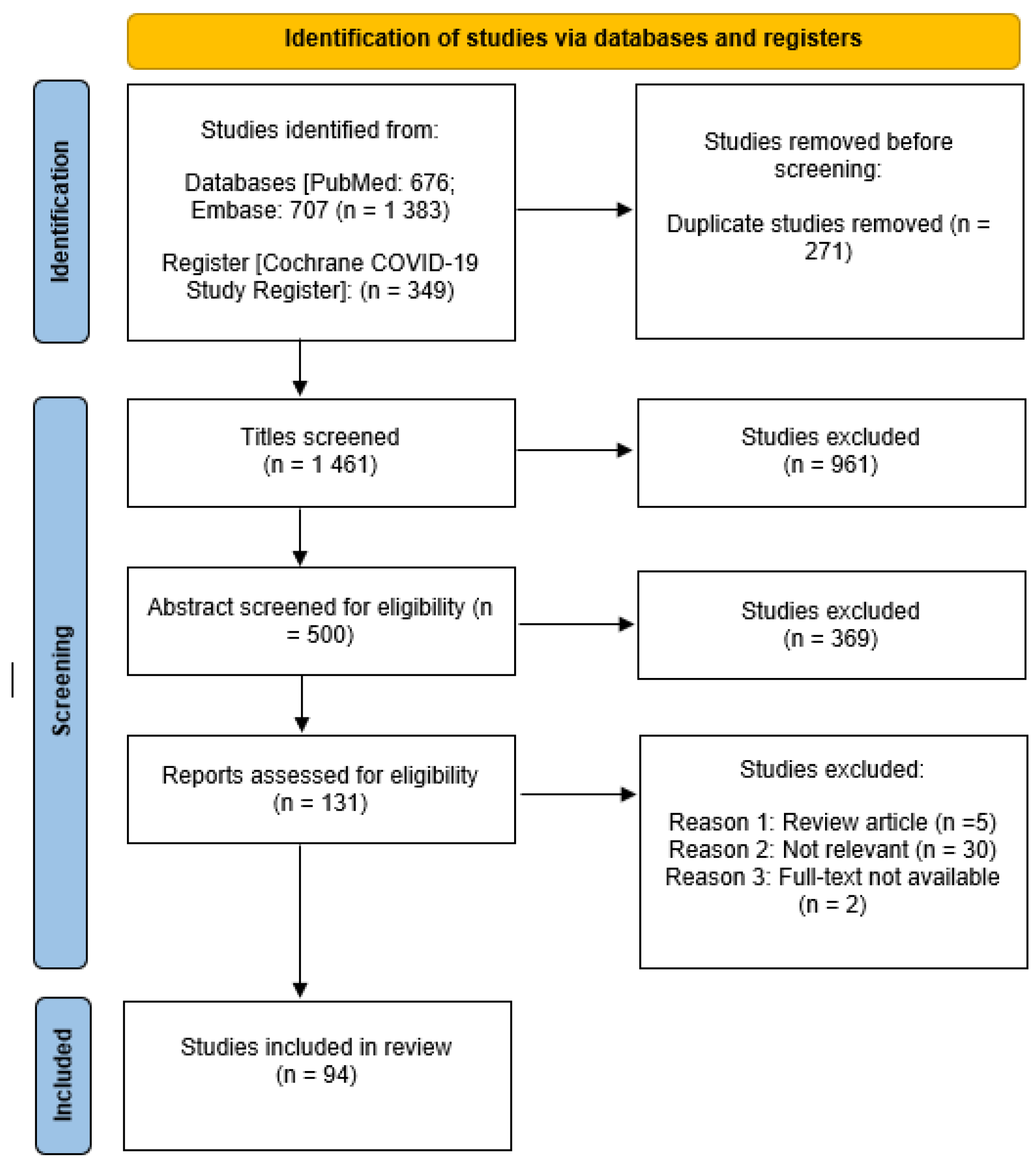
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
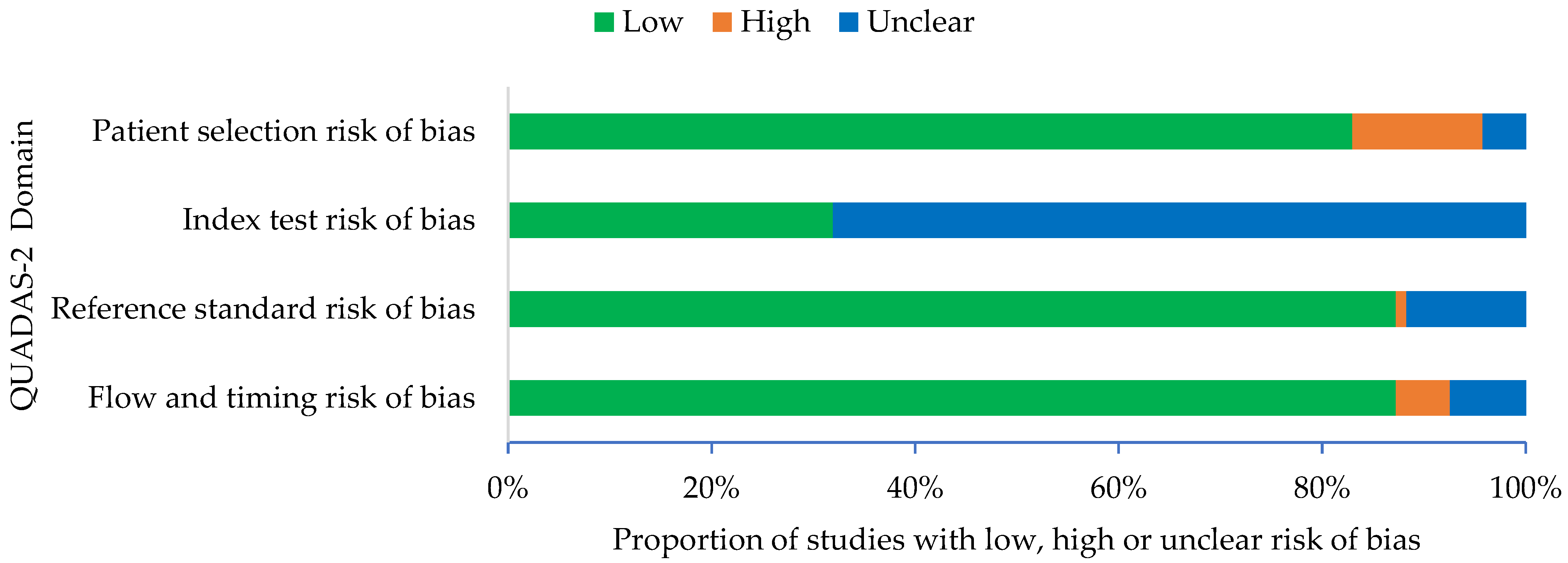
3.3. Quality of Articles
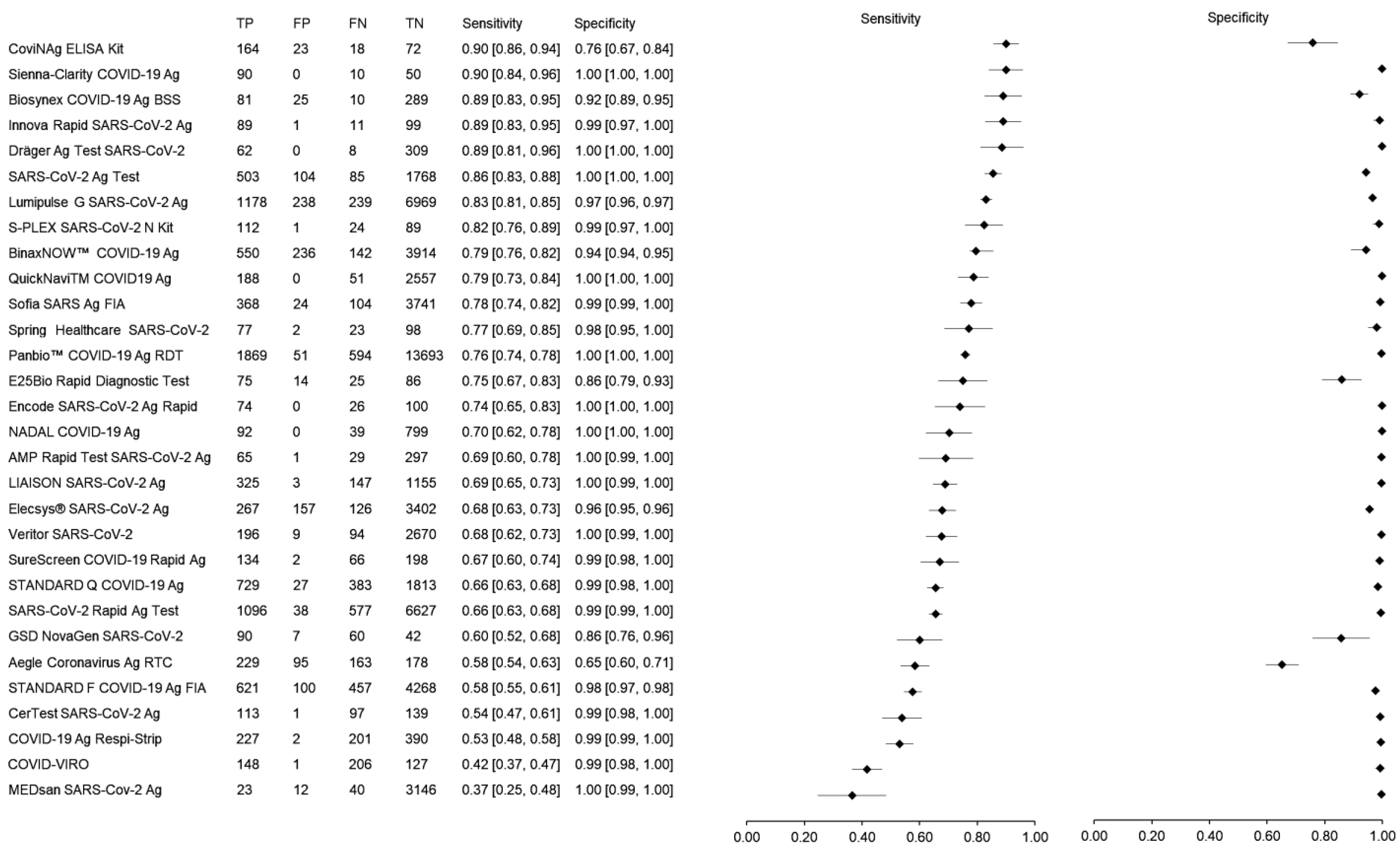
3.4. Meta-Analysis of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Rapid Antigen Tests
3.5. Performance of the Rapid Antigen Tests Based on Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saniasiaya, J.; Islam, M.A.; Abdullah, B. Prevalence of Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Meta-analysis of 27,492 Patients. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniasiaya, J.; Islam, M.A.; Abdullah, B. Prevalence and Characteristics of Taste Disorders in Cases of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of 29,349 Patients. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2021, 165, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subali, A.D.; Wiyono, L. Reverse Transcriptase Loop Mediated Isothermal AmplifiCation (RT-LAMP) for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2021, 115, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Qian, S.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.-S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Community Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Shenzhen, China, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Wong, S.-C.; Chen, J.H.K.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Chuang, V.W.M.; Tsang, O.T.Y.; Sridhar, S.; Chan, J.F.W.; Ho, P.-L.; Yuen, K.-Y. Escalating Infection Control Response to the Rapidly Evolving Epidemiology of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Hong Kong. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asadi, S.; Bouvier, N.; Wexler, A.S.; Ristenpart, W.D. The Coronavirus Pandemic and Aerosols: Does COVID-19 Transmit via Expiratory Particles? Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, K.-Y.; Kok, A.A.L.; Eikelenboom, M.; Horsfall, M.; Jörg, F.; Luteijn, R.A.; Rhebergen, D.; van Oppen, P.; Giltay, E.J.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. The Mental Health Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on People with and without Depressive, Anxiety, or Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: A Longitudinal Study of Three Dutch Case-Control Cohorts. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.; Hope, H.; Ford, T.; Hatch, S.; Hotopf, M.; John, A.; Kontopantelis, E.; Webb, R.; Wessely, S.; McManus, S.; et al. Mental Health before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Longitudinal Probability Sample Survey of the UK Population. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Alam, M.A.; Islam, A.B.M.S.; Ong, H.C.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Najafi, G.; Ahmed, S.F.; Uddin, M.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Impact of COVID-19 on the Social, Economic, Environmental and Energy Domains: Lessons Learnt from a Global Pandemic. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Whitaker, B.; Murray, J.; Kamili, S.; Lynch, B.; Malapati, L.; Burke, S.A.; Harcourt, J.; et al. US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, J.; Abdullah AL-maskri, A.A.; Kang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Cai, S. Recent Advances and Perspectives of Nucleic Acid Detection for Coronavirus. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbić, L.; Savić, V.; Bogdanić, M.; Antolašić, L.; Milašinčić, L.; Hruškar, Ž.; Sabadi, D.; Perić, L.; Tabain, I.; Stevanović, V.; et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Infektološki Glas 2020, 40, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Brümmer, L.E.; Katzenschlager, S.; Gaeddert, M.; Erdmann, C.; Schmitz, S.; Bota, M.; Grilli, M.; Larmann, J.; Weigand, M.A.; Pollock, N.R.; et al. Accuracy of Novel Antigen Rapid Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: A Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandker, S.S.; Nik Hashim, N.H.H.; Deris, Z.Z.; Shueb, R.H.; Islam, M.A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Rapid Antigen Test Kits for Detecting SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 17,171 Suspected COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Healthcare Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimayo, C.; Kaewnaphan, B.; Tanlieng, N.; Athipanyasilp, N.; Sirijatuphat, R.; Chayakulkeeree, M.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Sutthent, R.; Puangpunngam, N.; Tharmviboonsri, T.; et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection Assay in Comparison with Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Thailand. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.C.; Cheng, P.K.; Lau, S.S.; Wong, K.K.; Lau, C.; Lam, E.T.; Chan, R.C.; Tsang, D.N. Evaluation of Rapid Antigen Test for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scohy, A.; Anantharajah, A.; Bodéus, M.; Kabamba-Mukadi, B.; Verroken, A.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H. Low Performance of Rapid Antigen Detection Test as Frontline Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagura-Ikeda, M.; Imai, K.; Tabata, S.; Miyoshi, K.; Murahara, N.; Mizuno, T.; Horiuchi, M.; Kato, K.; Imoto, Y.; Iwata, M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Self-Collected Saliva by Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-QPCR), Direct RT-QPCR, Reverse Transcription—Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification, and a Rapid Antigen Test To Diagnose COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01438-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, L.; Legarraga, P.; Vollrath, V.; Aguilera, X.; Munita, J.M.; Araos, R.; Pizarro, G.; Vial, P.; Iruretagoyena, M.; Dittrich, S.; et al. Evaluation of a Novel Antigen-Based Rapid Detection Test for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüttgen, A.; Cornelissen, C.G.; Dreher, M.; Hornef, M.W.; Imöhl, M.; Kleines, M. Comparison of the SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test to the Real Star Sars-CoV-2 RT PCR Kit. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 288, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, E.; Torres, I.; Bueno, F.; Huntley, D.; Molla, E.; Fernández-Fuentes, M.Á.; Martínez, M.; Poujois, S.; Forqué, L.; Valdivia, A.; et al. Field Evaluation of a Rapid Antigen Test (PanbioTM COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) for COVID-19 Diagnosis in Primary Healthcare Centres. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 472.e7–472.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.; Poujois, S.; Albert, E.; Colomina, J.; Navarro, D. Evaluation of a Rapid Antigen Test (PanbioTM COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Asymptomatic Close Contacts of COVID-19 Patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 636.e1–636.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pray, I.W.; Ford, L.; Cole, D.; Lee, C.; Bigouette, J.P.; Abedi, G.R.; Bushman, D.; Delahoy, M.J.; Currie, D.; Cherney, B.; et al. Performance of an Antigen-Based Test for Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Testing at Two University Campuses—Wisconsin, September–October 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 69, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, G.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y. Accuracy of a Nucleocapsid Protein Antigen Rapid Test in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 289.e1–289.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert-Niclot, S.; Cuffel, A.; Le Pape, S.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Roque-Afonso, A.-M.; Le Goff, J.; Delaugerre, C. Evaluation of a Rapid Diagnostic Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Nasopharyngeal Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00977-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, M.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Carrero, A.; Romanyk, J.; Pérez-García, F.; Gómez-Herruz, P.; Arroyo, T.; Cuadros, J. Panbio Antigen Rapid Test Is Reliable to Diagnose SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the First 7 Days after the Onset of Symptoms. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 133, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterman, A.; Baldauf, H.-M.; Eletreby, M.; Wettengel, J.M.; Afridi, S.Q.; Fuchs, T.; Holzmann, E.; Maier, A.; Döring, J.; Grzimek-Koschewa, N.; et al. Evaluation of Two Rapid Antigen Tests to Detect SARS-CoV-2 in a Hospital Setting. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Ishii, Y.; Yagi, S.; Okuma, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Maeda, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Yoshizawa, S.; Tateda, K. Clinical Validation of Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assays to Estimate SARS-CoV-2 Viral Loads in Nasopharyngeal Swabs. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalumansi, A.; Lutalo, T.; Kayiwa, J.; Watera, C.; Balinandi, S.; Kiconco, J.; Nakaseegu, J.; Olara, D.; Odwilo, E.; Serwanga, J.; et al. Field Evaluation of the Performance of a SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Test in Uganda Using Nasopharyngeal Samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, N.R.; Savage, T.J.; Wardell, H.; Lee, R.A.; Mathew, A.; Stengelin, M.; Sigal, G.B. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antigen and RNA Concentrations in Nasopharyngeal Samples from Children and Adults Using an Ultrasensitive and Quantitative Antigen Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e03077-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, S.; Domínguez-Rodríguez, S.; Sabrido, G.; Pérez-Jorge, C.; Plata, M.; Romero, M.P.; Grasa, C.D.; Jiménez, A.B.; Heras, E.; Broncano, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Panbio Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antigen Rapid Test Compared with Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing of Nasopharyngeal Samples in the Pediatric Population. J. Pediatr. 2021, 232, 287–289.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Murai, R.; Asanuma, K.; Fujiya, Y.; Takahashi, S. Evaluating a Novel, Highly Sensitive, and Quantitative Reagent for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blairon, L.; Cupaiolo, R.; Thomas, I.; Piteüs, S.; Wilmet, A.; Beukinga, I.; Tré-Hardy, M. Efficacy Comparison of Three Rapid Antigen Tests for SARS-CoV-2 and How Viral Load Impact Their Performance. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5783–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankova, Z.; Novakova, E.; Skerenova, M.; Holubekova, V.; Lucansky, V.; Dvorska, D.; Brany, D.; Kolkova, Z.; Strnadel, J.; Mersakova, S.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Detection by Rapid Antigen and by Three Commercial RT-QPCR Tests: A Study from Martin University Hospital in Slovakia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenkov, M.; Poopalasingam, N.; Madler, M.; Vanshylla, K.; Eggeling, R.; Wirtz, M.; Fish, I.; Dewald, F.; Gieselmann, L.; Lehmann, C.; et al. Evaluation of a Rapid Antigen Test To Detect SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Identify Potentially Infectious Individuals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0089621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, F.; Romanyk, J.; Gómez-Herruz, P.; Arroyo, T.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Linares, M.; Pérez Ranz, I.; Labrador Ballestero, A.; Moya Gutiérrez, H.; Ruiz-Álvarez, M.J.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of CerTest and Panbio Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Tests to Diagnose SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 137, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, V.; Bax, C.; Colantoni, L.; Peconi, C.; Termine, A.; Fabrizio, C.; Calvino, G.; Luzzi, L.; Panunzi, G.G.; Fusco, C.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Antigen and Molecular Tests for the Detection of Sars-CoV-2 and Related Variants: A Study on 4266 Samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayanskiy, N.; Brzhozovskaya, E.; Fedorova, N.; Lebedin, Y. Parallel Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and Nucleocapsid Antigen in Nasopharyngeal Specimens from a COVID-19 Patient Screening Cohort. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gili, A.; Paggi, R.; Russo, C.; Cenci, E.; Pietrella, D.; Graziani, A.; Stracci, F.; Mencacci, A. Evaluation of Lumipulse® G SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay Automated Test for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein (NP) in Nasopharyngeal Swabs for Community and Population Screening. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, S.; Batra, R.; Merrick, B.; Snell, L.B.; Nebbia, G.; Douthwaite, S.; Reid, F.; Patel, A.; Kia Ik, M.T.; Patel, B.; et al. Comparative Performance of SARS-CoV-2 Lateral Flow Antigen Tests and Association with Detection of Infectious Virus in Clinical Specimens: A Single-Centre Laboratory Evaluation Study. The Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e461–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Sugiura, H.; Maejima, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Tsutsui, T.; Kakizaki, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Omata, M. Comparison of Roche and Lumipulse Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test Performance Using Automated Systems for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, N.; Sakanashi, D.; Ohashi, W.; Nakamura, A.; Kawamoto, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Ohno, T.; Yamada, A.; Chida, S.; Shibata, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Validity of Automated Quantitative Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test from Saliva Specimen in the Diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo Nsoga, M.T.; Kronig, I.; Perez Rodriguez, F.J.; Sattonnet-Roche, P.; Da Silva, D.; Helbling, J.; Sacks, J.A.; de Vos, M.; Boehm, E.; Gayet- Ageron, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Panbio Rapid Antigen Tests on Oropharyngeal Swabs for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häuser, F.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Dreis, K.J.; Renzaho, A.; Youhanen, S.; Kremer, W.M.; Podlech, J.; Galle, P.R.; Lackner, K.J.; Rossmann, H.; et al. Evaluation of a Laboratory-Based High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay for Non-COVID-19 Patient Screening at Hospital Admission. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Honacker, E.; Van Vaerenbergh, K.; Boel, A.; De Beenhouwer, H.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Cattoir, L. Comparison of Five SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Detection Tests in a Hospital Setting and Performance of One Antigen Assay in Routine Practice: A Useful Tool to Guide Isolation Precautions? J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 114, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Akashi, Y.; Kato, D.; Kuwahara, M.; Muramatsu, S.; Ueda, A.; Notake, S.; Nakamura, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Suzuki, H. Diagnostic Performance and Characteristics of Anterior Nasal Collection for the SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test: A Prospective Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Skvarč, M. Clinical Application of a New SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold) in the Detection of COVID-19. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, M.; Holtkamp, C.; Dittmer, U.; Anastasiou, O.E. Performance of the LIAISON® SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay vs. SARS-CoV-2-RT-PCR. Pathogens 2021, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leixner, G.; Voill-Glaninger, A.; Bonner, E.; Kreil, A.; Zadnikar, R.; Viveiros, A. Evaluation of the AMP SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test in a Hospital Setting. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, L.J.; Gaeddert, M.; Tobian, F.; Lainati, F.; Gottschalk, C.; Klein, J.A.F.; Schnitzler, P.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Nikolai, O.; Lindner, A.K.; et al. The Abbott PanBio WHO Emergency Use Listed, Rapid, Antigen-Detecting Point-of-Care Diagnostic Test for SARS-CoV-2—Evaluation of the Accuracy and Ease-of-Use. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboumba Bouassa, R.-S.; Veyer, D.; Péré, H.; Bélec, L. Analytical Performances of the Point-of-Care SIENNATM COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein in Nasopharyngeal Swabs: A Prospective Evaluation during the COVID-19 Second Wave in France. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 106, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, M.; Maurici, M.; Pieri, M.; Andreoni, M.; Bernardini, S. Performance of a Rapid Antigen Test in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2988–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwijck, E.; Brouwers-Boers, M.; Broertjes, J.; van Heeswijk, K.; Runderkamp, N.; Meijer, A.; Hermans, M.H.A.; Leenders, A.C.A.P. Validation and Implementation of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Symptomatic Hospital Healthcare Workers. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2021, 3, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Gianfilippi, G.; Bragantini, D.; Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Clinical Assessment of the Roche SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test. Diagnosis 2021, 8, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Boattini, M.; Barbui, A.M.; Scozzari, G.; Riccardini, F.; Coggiola, M.; Lupia, E.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. Evaluation of an Antigen-Based Test for Hospital Point-of-Care Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 139, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, M.; Ampuero, M.; Garcés, C.; Gaggero, A.; García, P.; Velasquez, M.S.; Luza, R.; Alvarez, P.; Paredes, F.; Acevedo, J.; et al. Performance of SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test Compared with Real-Time RT-PCR in Asymptomatic Individuals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 107, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Viera-Segura, O.; García-Chagollán, M.; Zepeda-Nuño, J.S.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Mora-Mora, J.; Espinoza-De León, G.; Bustillo-Armendáriz, G.; García-Cedillo, F.; Vega-Magaña, N. Performance Evaluation of a Lateral Flow Assay for Nasopharyngeal Antigen Detection for SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, M.; Nikolić, N.; Čabarkapa, V.; Turkulov, V.; Petrović, V. Validation of the STANDARD Q COVID-19 antigen test in Vojvodina, Serbia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, F.; Romanyk, J.; Moya Gutiérrez, H.; Labrador Ballestero, A.; Pérez Ranz, I.; González Arroyo, J.; González Ventosa, V.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Domingo Cruz, C.; Cuadros-González, J. Comparative Evaluation of Panbio and SD Biosensor Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5650–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaujia, R.; Ghosh, A.; Mohindra, R.; Singla, V.; Goyal, K.; Gudisa, R.; Sharma, V.; Mohan, L.; Kaur, N.; Mohi, G.K.; et al. Rapid Antigen Detection Kit for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2—Are We Missing Asymptomatic Patients? Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtellemont, L.; Guinard, J.; Guillaume, C.; Giaché, S.; Rzepecki, V.; Seve, A.; Gubavu, C.; Baud, K.; Le Helloco, C.; Cassuto, G.N.; et al. High Performance of a Novel Antigen Detection Test on Nasopharyngeal Specimens for Diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3152–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulilete, O.; Lorente, P.; Leiva, A.; Carandell, E.; Oliver, A.; Rojo, E.; Pericas, P.; Llobera, J. PanbioTM Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 Has Acceptable Accuracy in Symptomatic Patients in Primary Health Care. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Moeren, N.; Zwart, V.F.; Lodder, E.B.; Van den Bijllaardt, W.; Van Esch, H.R.J.M.; Stohr, J.J.J.M.; Pot, J.; Welschen, I.; Van Mechelen, P.M.F.; Pas, S.D.; et al. Evaluation of the Test Accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test in Symptomatic Community Dwelling Individuals in the Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, A.; Sberna, G.; Lalle, E.; Colavita, F.; Castilletti, C.; Menchinelli, G.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M.; Ippolito, G.; Bordi, L.; et al. Saliva Is a Valid Alternative to Nasopharyngeal Swab in Chemiluminescence-Based Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Nsoga, M.T.N.; Perez-Rodriguez, F.J.; Aad, Y.A.; Sattonnet-Roche, P.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Jaksic, C.; Torriani, G.; Boehm, E.; Kronig, I.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Two Commercial SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Tests at the Point of Care in Community-Based Testing Centers. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanodja, B.; Budde, K.; Zickler, D.; Naik, M.G.; Hofmann, J.; Gertler, M.; Hülso, C.; Rössig, H.; Horn, P.; Seybold, J.; et al. Accuracy of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Test from Standardized Self-Collected Anterior Nasal Swabs. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenhäuser, I.; Knies, K.; Rauschenberger, V.; Eisenmann, M.; McDonogh, M.; Petri, N.; Andres, O.; Flemming, S.; Gawlik, M.; Papsdorf, M.; et al. Clinical Performance Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Testing in Point of Care Usage in Comparison to RT-QPCR. EBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, A.E.; Ahava, M.J.; Jokela, P.; Szirovicza, L.; Pohjala, S.; Vapalahti, O.; Lappalainen, M.; Hepojoki, J.; Kurkela, S. Evaluation of Three Rapid Lateral Flow Antigen Detection Tests for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 137, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeleman, J.G.M.; Brand, H.; de Man, S.J.; Ong, D.S.Y. Clinical Evaluation of Rapid Point-of-Care Antigen Tests for Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, S.; Indevuyst, C.; Cuypers, L.; Dewaele, K.; Yin, N.; Cotton, F.; Padalko, E.; Oyaert, M.; Descy, J.; Cavalier, E.; et al. Comparison of the Quantitative DiaSorin Liaison Antigen Test to Reverse Transcription-PCR for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Outpatients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0037421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglὁi, Z.; Velzing, J.; van Beek, J.; van de Vijver, D.; Aron, G.; Ensing, R.; Benschop, K.; Han, W.; Boelsums, T.; Koopmans, M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Roche SD Biosensor Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Health Service Testing Site, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriou, I.; Dasoula, F.; Dimopoulou, D.; Lebessi, E.; Serafi, E.; Spyridis, N.; Tsolia, M. Real-life Evaluation of a COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Detection Test in Hospitalized Children. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6040–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyasu, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Akashi, Y.; Kato, D.; Kuwahara, M.; Muramatsu, S.; Notake, S.; Ueda, A.; Nakamura, K.; Ishikawa, H.; et al. Prospective Analytical Performance Evaluation of the QuickNaviTM-COVID19 Ag for Asymptomatic Individuals. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferté, T.; Ramel, V.; Cazanave, C.; Lafon, M.-E.; Bébéar, C.; Malvy, D.; Georges-Walryck, A.; Dehail, P. Accuracy of COVID-19 Rapid Antigenic Tests Compared to RT-PCR in a Student Population: The StudyCov Study. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 141, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, N.R.; Jacobs, J.R.; Tran, K.; Cranston, A.E.; Smith, S.; O’Kane, C.Y.; Roady, T.J.; Moran, A.; Scarry, A.; Carroll, M.; et al. Performance and Implementation Evaluation of the Abbott BinaxNOW Rapid Antigen Test in a High-Throughput Drive-Through Community Testing Site in Massachusetts. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00083-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilarowski, G.; Lebel, P.; Sunshine, S.; Liu, J.; Crawford, E.; Marquez, C.; Rubio, L.; Chamie, G.; Martinez, J.; Peng, J.; et al. Performance Characteristics of a Rapid Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antigen Detection Assay at a Public Plaza Testing Site in San Francisco. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegerlehner, S.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Jent, P.; Bittel, P.; Nagler, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test in Real-Life Clinical Settings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Haage, V.C.; Bleicker, T.; Schmidt, M.L.; Mühlemann, B.; Zuchowski, M.; Jo, W.K.; Tscheak, P.; Möncke-Buchner, E.; Müller, M.A.; et al. Comparison of Seven Commercial SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Point-of-Care Antigen Tests: A Single-Centre Laboratory Evaluation Study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e311–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiro, V.; Gupta, A.; Singh, P.; Sharad, N.; Khurana, S.; Parakash, S.; Dar, L.; Malhotra, R.; Wig, N.; Kumar, A.; et al. Evaluation of COVID-19 Antigen Fluorescence Immunoassay Test for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2021, 13, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Nörz, D.; Olearo, F.; Perisic, S.; Bauer, M.F.; Riester, E.; Schneider, T.; Schönfeld, K.; Laengin, T.; Lütgehetmann, M. Multicenter Evaluation of a Fully Automated High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Immunoassay. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartard, C.; Berger, S.; Josse, T.; Schvoerer, E.; Jeulin, H. Performance Evaluation of an Automated SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection on Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Sahuquillo, S.; Lázaro-Carreño, M.I.; Camacho, J.; Barrés-Fernández, A.; Albert, E.; Torres, I.; Bretón-Martínez, J.R.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Navarro, D. Evaluation of a Rapid Antigen Detection Test (PanbioTM COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) as a Point-of-care Diagnostic Tool for COVID-19 in a Pediatric Emergency Department. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6803–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Levy, C.; Varon, E.; Biscardi, S.; Batard, C.; Wollner, A.; Deberdt, P.; Sellam, A.; Hau, I.; Cohen, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection Test in Children: A Real-Life Study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 647274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterman, A.; Iglhaut, M.; Lehner, A.; Späth, P.; Stern, M.; Autenrieth, H.; Muenchhoff, M.; Graf, A.; Krebs, S.; Blum, H.; et al. Comparison of Four Commercial, Automated Antigen Tests to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Montero, A.; Argemi, J.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Ariño, A.H.; Moreno-Galarraga, L. Validation of a Rapid Antigen Test as a Screening Tool for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Asymptomatic Populations. Sensitivity, Specificity and Predictive Values. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, L.J.; Klein, J.A.F.; Tobian, F.; Gaeddert, M.; Lainati, F.; Klemm, S.; Schnitzler, P.; Bartenschlager, R.; Cerikan, B.; Neufeldt, C.J.; et al. Evaluation of Accuracy, Exclusivity, Limit-of-Detection and Ease-of-Use of LumiraDxTM: An Antigen-Detecting Point-of-Care Device for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv 2021, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Baccani, I.; Morecchiato, F.; Chilleri, C.; Cervini, C.; Gori, E.; Matarrese, D.; Bassetti, A.; Bonizzoli, M.; Mencarini, J.; Antonelli, A.; et al. Evaluation of Three Immunoassays for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 101, 115434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.D.; Johnson, J.K.; Clay, C.; Girio-Herrera, L.; Stevens, D.; Abraham, M.; Zimand, P.; Ahlman, M.; Gimigliano, S.; Zhao, R.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Sofia Rapid Antigen Assay for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) among Emergency Department to Hospital Admissions. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.; Kompatscher, J.; La Guardia, M. Diagnostic Performance of the Elecsys SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in the Clinical Routine of a Tertiary Care Hospital: Preliminary Results from a Single-center Evaluation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremmels, H.; Winkel, B.M.F.; Schuurman, R.; Rosingh, A.; Rigter, N.A.M.; Rodriguez, O.; Ubijaan, J.; Wensing, A.M.J.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Hofstra, L.M. Real-Life Validation of the PanbioTM COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test (Abbott) in Community-Dwelling Subjects with Symptoms of Potential SARS-CoV-2 Infection. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrivá, B.F.; Mochón, M.D.O.; González, R.M.; García, C.S.; Pla, A.T.; Ricart, A.S.; García, M.M.; Aranda, I.T.; García, F.G.; Cardona, C.G. “The Effectiveness of Rapid Antigen Test-Based for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Nursing Homes in Valencia, Spain”. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 143, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favresse, J.; Gillot, C.; Oliveira, M.; Cadrobbi, J.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Laffineur, K.; Rosseels, C.; Van Eeckhoudt, S.; Nicolas, J.-B.; et al. Head-to-Head Comparison of Rapid and Automated Antigen Detection Tests for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassuto, N.G.; Gravier, A.; Colin, M.; Theillay, A.; Pires-Roteira, D.; Pallay, S.; Serreau, R.; Hocqueloux, L.; Prazuck, T. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-detecting Rapid Diagnostic Test as a Self-test: Diagnostic Performance and Usability. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6686–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, L.; Legarraga, P.; Iruretagoyena, M.; Vollrath, V.; Pizarro, G.; Munita, J.; Araos, R.; Weitzel, T. Evaluation of Two Fluorescence Immunoassays for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen—New Tool to Detect Infective COVID-19 Patients. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömer, A.; Rose, R.; Schäfer, M.; Schön, F.; Vollersen, A.; Lorentz, T.; Fickenscher, H.; Krumbholz, A. Performance of a Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchinelli, G.; De Angelis, G.; Cacaci, M.; Liotti, F.M.; Candelli, M.; Palucci, I.; Santangelo, R.; Sanguinetti, M.; Vetrugno, G.; Franceschi, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection to Expand Testing Capacity for COVID-19: Results from a Hospital Emergency Department Testing Site. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, P.N.; Cheung, B.; Kustra, J.; Pidduck, T.; Mak, A.; Tsang, F.; Petric, M.; Krajden, M. Evaluation of a High Volume Antigen Test for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 142, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, A.K.; Nikolai, O.; Rohardt, C.; Kausch, F.; Wintel, M.; Gertler, M.; Burock, S.; Hörig, M.; Bernhard, J.; Tobian, F.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy and Feasibility of Patient Self-Testing with a SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Test. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 141, 104874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Moeren, N.; Zwart, V.F.; Goderski, G.; Rijkers, G.T.; van den Bijllaardt, W.; Veenemans, J.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W.; Pas, S.D.; Meijer, A.; Verweij, J.J.; et al. Performance of the Diasorin SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection Assay on the LIAISON XL. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 141, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilarowski, G.; Marquez, C.; Rubio, L.; Peng, J.; Martinez, J.; Black, D.; Chamie, G.; Jones, D.; Jacobo, J.; Tulier-Laiwa, V.; et al. Field Performance and Public Health Response Using the BinaxNOWTM Rapid Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Antigen Detection Assay During Community-Based Testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e3098–e3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leli, C.; Di Matteo, L.; Gotta, F.; Cornaglia, E.; Vay, D.; Megna, I.; Pensato, R.E.; Boverio, R.; Rocchetti, A. Performance of a SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Immunoassay in Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 110, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruana, G.; Croxatto, A.; Kampouri, E.; Kritikos, A.; Opota, O.; Foerster, M.; Brouillet, R.; Senn, L.; Lienhard, R.; Egli, A.; et al. Implementing SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Testing in the Emergency Ward of a Swiss University Hospital: The INCREASE Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhi, S.; Tayler, N.; Hoang, T.; Ballard, S.A.; Graham, M.; Rojek, A.; Kwong, J.C.; Trubiano, J.A.; Smibert, O.; Drewett, G.; et al. Multi-Site Assessment of Rapid, Point-of-Care Antigen Testing for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Low-Prevalence Setting: A Validation and Implementation Study. Lancet Reg. Health-West. Pac. 2021, 9, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, R.M.; Samir, M.; Gaber, O.A.; EL-Deeb, N.A.; Abdelmoaty, A.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Samy, W.; Atta, A.H.; Walaa, M.; Anis, R.H. Diagnostic Performance of Rapid Antigen Test for COVID-19 and the Effect of Viral Load, Sampling Time, Subject’s Clinical and Laboratory Parameters on Test Accuracy. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuit, E.; Veldhuijzen, I.K.; Venekamp, R.P.; van den Bijllaardt, W.; Pas, S.D.; Lodder, E.B.; Molenkamp, R.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Velzing, J.; Huisman, R.C.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Rapid Antigen Tests in Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic Close Contacts of Individuals with Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Cross Sectional Study. BMJ 2021, 374, n1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, P.; Guinea, J.; Muñoz-Gallego, I.; González-Donapetry, P.; Galán, J.C.; Antona, N.; Cilla, G.; Hernáez-Crespo, S.; Díaz-de Tuesta, J.L.; Gual-de Torrella, A.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the PanbioTM COVID-19 Rapid Antigen-Detection Test for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.; Salvatore, P.P.; Ford, L.; Kamitani, E.; Whaley, M.J.; Mitchell, K.; Currie, D.W.; Morgan, C.N.; Segaloff, H.E.; Lecher, S.; et al. Performance of Repeat BinaxNOW Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antigen Testing in a Community Setting, Wisconsin, November 2020–December 2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, S54–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.C.K.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Chow, N.L.S.; Lau, C.S.; Lam, E.T.K.; Chan, R.C.W.; Tsang, D.N.C. Evaluation of Rapid Antigen Detection Kit from the WHO Emergency Use List for Detecting SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 134, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjit, M.; Lal, S.K. The SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid Protein: A Protein with Multifarious Activities. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, N.N.Y.; So, H.C.; Ng, K.Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Leung, G.M.; Ip, D.K.M. Diagnostic Performance of Different Sampling Approaches for SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Testing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, B. Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Molecular Weight and Size Distribution of Gluten. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, V.P.; Farah, W.H.; Hill, J.C.; Hassett, L.C.; Binnicker, M.J.; Yao, J.D.; Murad, M.H. Association Between SARS-CoV-2 Cycle Threshold Values and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Domains | Criteria for Low Risk Assessment |
|---|---|
| Patient selection | Patient enrolment strategy is specified and free of bias. A case–control design and inappropriate exclusions are avoided. |
| Index test | The index test results are interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard. The conduct or interpretation of the index test does not introduce bias. |
| Reference standard | The reference standard correctly classifies the target condition. The reference standard results are interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test. The reference standard, its conduct or its interpretation do not introduce bias. |
| Flow and timing | There is an appropriate interval between the index test(s) and reference standard. All patients receive the same reference standard. All patients included in the analysis and patient flow do not introduce bias. |
| Tests Investigate | Target | Sample | Sample Size | Sensitivity | Specificity | Location | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS and TS | 454 | 98.33% | 98.73% | Thailand | [20] |
| 2 | Biocredit Covid-19 Ag Detection Kit (RapiGEN, Gyeonggi-do, Korea) | N | NPS and TS | 35 | 34.30% | NR | Hong Kong | [21] |
| SP | 45 | 11.10% | NR | |||||
| S | 45 | 40.00% | NR | |||||
| 3 | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip (Coris BioConcept, Gembloux, Belgium) | N | NPS | 148 | 30.20% | 100% | Belgium | [22] |
| 4 | Espline SARS-CoV-2 (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | S | 103 | 11.70% | NR | Japan | [23] |
| 5 | Sofia SARS Ag FIA (Quidel, San Diego, USA) | N | NPS and TS | 127 | 93.90% | 100% | Chile | [24] |
| 6 | SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 150 | 70.70% | 96.00% | Germany | [25] |
| 7 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 412 | 79.60% | 100% | Spain | [26] |
| 8 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 634 | 48.10% | 100% | Spain | [27] |
| 9 | Sofia SARS Ag FIA (Quidel, San Diego, USA) | N | NPS (asymptomatic) | 871 | 41.20% | 98.40% | United States | [28] |
| NPS (symptomatic) | 227 | 80.00% | 98.90% | |||||
| 10 | In house | N | NPS | 251 | 75.60% | 100% | China | [29] |
| 11 | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip (Coris BioConcept, Gembloux, Belgium) | N | NPS | 138 | 50.00% | 100% | France | [30] |
| 12 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 255 | 73.30% | NR | Spain | [31] |
| 13 | STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS and TS | 741 | 45.40% | 97.80% | Germany | [32] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS and TS | 831 | 50.30% | 97.70% | |||
| 14 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 548 | 91.70% | 98.50% | Japan | [33] |
| 15 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 262 | 70.00% | 92.00% | Uganda | [34] |
| 16 | S-PLEX SARS-CoV-2 N Kit (MesoScale Diagnostics, Maryland, USA) | N | NPS | 226 | 82.00% | 99.00% | United States | [35] |
| 17 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 1620 | 45.40% | 99.80% | Spain | [36] |
| 18 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 274 | 75.70% | 96.00% | Japan | [37] |
| 19 | Aegle Coronavirus Ag RTC (Bio-Rad, California, United States) | N | NPS | 199 | 59.30% | 100% | Belgium | [38] |
| GSD NovaGen SARS-CoV-2 (Eurofins Technologies, Budapest, Hungary) | N | NPS | 199 | 60.00% | 85.70% | |||
| Aegle Coronavirus Ag RTC (Bio-Rad, California, United States) | N | NPS | 199 | 61.10% | 100% | |||
| 20 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 1223 | 37.84% | 100% | Slovakia | [39] |
| 21 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS and TS | 2032 | 42.86% | 99.89% | Germany | [40] |
| 22 | CerTest SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Certest Biotec, Zaragoza, Spain) | N | NPS | 320 | 53.50% | 100% | Spain | [41] |
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 320 | 60.00% | 100% | |||
| 23 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS and TS | 4266 | 86.60% | 97.30% | Italy | [42] |
| 24 | CoviNAg ELISA Kit (XEMA, Moscow, Russia) | N | NPS | 277 | 90.10% | 75.80% | Russia | [43] |
| 25 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 226 | 92.60% | 90.80% | Italy | [44] |
| Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 1738 | 100% | 94.80% | |||
| 26 | Innova Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test (Xiamen Biotime Biotechnology, Fujian, China) | N | NPS and TS | 200 | 89.00% | 99.00% | United Kingdom | [45] |
| Spring Healthcare SARS-CoV-2 Ag RTC (Shanghai ZJ Bio-Tech, Shanghai, China) | N | NPS | 200 | 77.00% | 98.00% | |||
| E25Bio Rapid Diagnostic Test (E25Bio, Cambridge, USA) | N | NPS | 200 | 75.00% | 86.00% | |||
| Encode SARS-CoV-2 Ag Rapid Test Encode SARS-CoV-2 Ag Rapid Test Device (Zhuhai Encode Medical Engineering, Zhuhai, China) | N | NS and TS | 200 | 74.00% | 100% | |||
| SureScreen COVID-19 Rapid Ag Test (SureScreen Diagnostics, Derby, UK) | N | NPS | 200 | 69.00% | 98.00% | |||
| 27 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 529 | 84.80% | 97.90% | Japan | [46] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 637 | 70.00% | 100% | |||
| 28 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | S | 305 | 77.80% | 99.60% | Japan | [47] |
| 29 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 402 | 81.00% | 99.10% | Switzerland | [48] |
| 30 | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy) | N | NPS | 196 | 40.20% | 100% | Germany | [49] |
| 31 | Biosynex COVID-19 Ag BSS Test (Biosynex, Strasbourg, France) | N | NPS | 97 | 89.70% | 46.20% | Belgium | [50] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Ag Card (Biotical Health, Madrid, Spain) | N | NPS | 98 | 67.20% | 100% | |||
| Aegle Coronavirus Ag RTC (Bio-Rad, California, United States) | N | NPS | 98 | 82.80% | 92.50% | |||
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 97 | 78.90% | 100% | |||
| STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 98 | 82.80% | 100% | |||
| 32 | QuickNaviTM COVID19 Ag (Otsuka, Japan) | N | NS | 862 | 72.50% | 100% | Japan | [51] |
| 33 | COVID-19 Ag Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold-CG) | N | NPS | 358 | 89.47% | 99.59% | Slovenia | [52] |
| 34 | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy) | N | NPS | 182 | 70.00% | 100% | Germany | [53] |
| 35 | AMP Rapid Test SARS-CoV-2 Ag (AMP Diagnostics, Graz, Austria) | N | NPS | 392 | 69.15% | 99.66% | Austria | [54] |
| 36 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 1108 | 86.80% | 99.90% | Germany | [55] |
| 37 | Sienna-Clarity COVID-19 Ag RTC (Salofa Oy, Salo, Finland) | N | NPS | 150 | 90.00% | 100% | France | [56] |
| 38 | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip (Coris BioConcept, Gembloux, Belgium) | N | NPS | 50 | 30.70% | 100% | Italy | [57] |
| 39 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 433 | 86.70% | 100% | The Netherlands | [58] |
| 40 | SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 321 | 73.15% | 100% | Italy | [59] |
| 41 | SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test (LumiraDx GmbH, Cologne, Germany) | N | NPS and NS | 907 | 90.30% | 92.10% | Italy | [60] |
| 42 | STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 842 | 69.86% | 99.61% | Chile | [61] |
| 43 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 369 | 75.90% | 100% | Mexico | [62] |
| 44 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | TS | 402 | 81.00% | 99.00% | United States | [48] |
| 45 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 120 | 58.10% | 100% | Serbia | [63] |
| 46 | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip (Coris BioConcept, Gembloux, Belgium) | N | NPS | 484 | 71.96% | 99.32% | India | [64] |
| 47 | COVID-VIRO (AAZ-LMB Boulogne-Billancourt, France) | N | NPS | 248 | 96.70% | 100% | France | [65] |
| 48 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 1362 | 71.40% | 99.80% | Spain | [66] |
| 49 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 356 | 60.00% | 100% | Spain | [67] |
| STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 356 | 66.50% | 97.30% | |||
| 50 | Veritor SARS-CoV-2 (BectonDickinson, New Jersey, USA) | N | TS | 351 | 94.12% | 100% | The Netherlands | [68] |
| 51 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | S | 127 | 52.40% | 94.10% | Italy | [69] |
| 52 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 535 | 85.50% | 100% | United States | [70] |
| STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 529 | 89.00% | 100% | |||
| 53 | Dräger Ag Test SARS-CoV-2 (Dräger, Lübeck, Germany) | N | NS | 379 | 88.60% | 99.70% | Germany | [71] |
| 54 | MEDsan SARS-Cov-2 Ag (MEDsan GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) | N | NPS | 806 | 36.51% | 99.61% | Germany | [72] |
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 1029 | 46.67% | 99.62% | |||
| NADAL COVID-19 Ag (Nal Von Minden GmbH, Moers, Germany) | N | NPS | 3221 | 56.62% | 100% | |||
| 55 | Sofia SARS Ag FIA (Quidel, San Diego, USA) | N | NPS | 188 | 80.00% | 100% | Finland | [73] |
| STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 198 | 81.00% | 100% | |||
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 190 | 83.00% | 100% | |||
| 56 | CerTest SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Certest Biotec, Zaragoza, Spain) | N | NPS | 80 | 55.00% | 97.50% | The Netherlands | [74] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 80 | 62.50% | 87.50% | |||
| Romed SARS-CoV-2 Ag RTC (Oostveen Medical BV Van, Wilnis, The Netherlands) | N | NPS | 80 | 80.00% | 100% | |||
| Veritor SARS-CoV-2 (BectonDickinson, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS | 40 | 77.50% | NR | |||
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 40 | 70.00% | NR | |||
| 57 | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy) | N | NPS | 414 | 67.70% | 100% | Belgium | [75] |
| 58 | SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS and TS | 970 | 84.90% | 99.50% | The Netherlands | [76] |
| 59 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 744 | 82.35% | 100% | Greece | [77] |
| 60 | QuickNaviTM COVID19 Ag (Otsuka, Japan) | N | NPS | 1934 | 80.30% | 100% | Japan | [78] |
| 61 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 692 | 63.50% | 100% | France | [79] |
| 62 | BinaxNOW™ COVID-19 Ag Self-Test (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 2308 | 66.70% | 95.20% | United States | [80] |
| 63 | BinaxNOW™ COVID-19 Ag Self-Test (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 878 | 93.30% | 99.90% | United States | [81] |
| 64 | SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 1465 | 65.30% | 99.90% | Switzerland | [82] |
| 65 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS and TS | 105 | NR | 99·30% | Germany | [83] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 115 | NR | 98.50% | |||
| 66 | STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 354 | 38.00% | 99.00% | India | [84] |
| 67 | Elecsys® SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS and TS | 3139 | 60.20% | 99.90% | Germany | [85] |
| 68 | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy) | N | NPS | 378 | 84.80% | 99.40% | France | [86] |
| 69 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 357 | 70.50% | 100% | Spain | [87] |
| 70 | Biosynex COVID-19 Ag BSS Test (Biosynex, Strasbourg, France) | N | NPS | 308 | 87.90% | 98.50% | China | [88] |
| 71 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 410 | 91.70% | 97.30% | Germany | [89] |
| LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy) | N | NPS | 408 | 99.10% | 98.70% | |||
| Elecsys® SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 410 | 65.50% | 99.80% | |||
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 410 | 93.60% | 100% | |||
| 72 | SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS and TS | 2288 | 71.43% | 99.68% | Spain | [90] |
| 73 | SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test (LumiraDx GmbH, Cologne, Germany) | N | NPS | 761 | 82.20% | 99.30% | Germany | [91] |
| 74 | Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan) | N | NPS | 201 | 87.90% | 95.80% | Italy | [92] |
| STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 93 | 35.70% | 100% | |||
| 75 | Sofia SARS Ag FIA (Quidel, San Diego, USA) | N | NPS | 2887 | 76.60% | 99.70% | United States | [93] |
| 76 | Elecsys® SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 403 | 26.00% | 100% | Italy | [94] |
| 77 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 1577 | 76.80% | 100% | The Netherlands | [95] |
| 78 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 448 | 85.00% | 100% | Spain | [96] |
| 79 | SARS-CoV-2 Ag Card (Biotical Health, Madrid, Spain) | N | NPS | 188 | 66.70% | 98.90% | Belgium | [97] |
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 188 | 67.70% | 100% | |||
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS | 188 | 69.80% | 100% | |||
| VITROS SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Ortho, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS | 188 | 83.30% | 100% | |||
| 80 | COVID-VIRO (AAZ-LMB Boulogne-Billancourt, France) | N | NPS | 234 | 96.88% | 100% | France | [98] |
| 81 | Sofia SARS Ag FIA (Quidel, San Diego, USA) | N | NPS | 64 | 93.80% | 96.90% | Chile | [99] |
| STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 64 | 90.60% | 96.90% | |||
| 82 | NADAL COVID-19 Ag (Nal Von Minden GmbH, Moers, Germany) | N | NPS | 124 | 73.10% | 100% | Germany | [100] |
| 83 | STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 2898 | 54.95% | 97.80% | Italy | [101] |
| 84 | VITROS SARS-CoV-2 Ag (Ortho, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS | 24 | 84.20% | 100% | China | [102] |
| 85 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 146 | 82.50% | 100% | Germany | [103] |
| 86 | Veritor SARS-CoV-2 (BectonDickinson, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS | 248 | 73.00% | 100% | The Netherlands | [104] |
| 87 | BinaxNOW™ COVID-19 Ag Self-Test (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NS | 3302 | 100% | 98.60% | Brazil | [105] |
| 88 | SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test (LumiraDx GmbH, Cologne, Germany) | N | NPS | 792 | 95.20% | 79.20% | Italy | [106] |
| 89 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS | 532 | 41.20% | 99.70% | Switzerland | [107] |
| Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 532 | 41.20% | 99.50% | |||
| Veritor SARS-CoV-2 (BectonDickinson, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS | 532 | 41.20% | 99.70% | |||
| 90 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 2413 | NR | 99.96% | Australia | [108] |
| 91 | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Home Test (SD Biosensor, Seoul, South Korea) | N | NPS and TS | 83 | 78.20% | 64.20% | Egypt | [109] |
| 92 | Veritor SARS-CoV-2 (BectonDickinson, New Jersey, USA) | N | NPS and TS | 2678 | 63.90% | 99.60% | The Netherlands | [110] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Ag Test (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) | N | NPS and TS | 1370 | 62.90% | 99.50% | |||
| 93 | Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag RDT (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NPS | 958 | 90.50% | 98.80% | Spain | [111] |
| 94 | BinaxNOW™ COVID-19 Ag Self-Test (Abbott, Jena, Germany) | N | NS | 2110 | 77.2% | 99.6% | United States | [112] |
| Subgroups | Number of Studies | Total Number of Patients | Sensitivity [95% CI] | Specificity [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All studies | 94 | 74445 | 0.70 [0.69–0.71] | 0.98 [0.98–0.98] |
| Specimens | ||||
| Nasopharyngeal swabs | 58 | 38548 | 0.71 [0.70–0.72] | 0.98 [0.98–0.99] |
| Nasal swabs | 4 | 4258 | 0.83 [0.80–0.86] | 0.98 [0.98–0.99] |
| Throat swabs | 2 | 3623 | 0.69 [0.63–0.75] | 0.99 [0.99–1.00] |
| Saliva | 2 | 432 | 0.68 [0.59–0.77] | 0.97 [0.95–0.99] |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Symptomatic | 30 | 24726 | 0.82 [0.82–0.82] | 0.98 [0.98–0.98] |
| Asymptomatic | 14 | 14926 | 0.68 [0.65–0.71] | 0.99 [0.99–0.99] |
| Ct values | ||||
| Ct value ≤25 | 13 | 5378 | 0.96 [0.95–0.97] | 0.99 [0.98–0.99] |
| Ct value >25 | 12 | 6139 | 0.69 [0.67–0.71] | 0.97 [0.96–0.97] |
| Countries | ||||
| Germany | 14 | 14179 | 0.58 [0.56–0.60] | 0.98 [0.98–0.98] |
| Spain | 11 | 9391 | 0.71 [0.68–0.73] | 0.99 [0.99–1.00] |
| Italy | 10 | 11752 | 0.81 [0.79–0.83] | 0.96 [0.96–0.97] |
| United States | 8 | 10605 | 0.77 [0.75–0.79] | 0.97 [0.97–0.97] |
| Japan | 7 | 5192 | 0.72 [0.70–0.75] | 0.99 [0.99–1.00] |
| Netherlands | 7 | 8073 | 0.72 [0.70–0.75] | 1.00 [0.99–1.00] |
| France | 6 | 1858 | 0.58 [0.54–0.62] | 1.00 [0.99–1.00] |
| Belgium | 5 | 1634 | 0.73 [0.70–0.76] | 0.84 [0.81–0.86] |
| Switzerland | 3 | 2399 | 0.65 [0.61–0.70] | 1.00 [1.00–1.00] |
| Chile | 3 | 906 | 0.77 [0.69–0.85] | 1.00 [0.99–1.00] |
| China | 3 | 332 | 0.87 [0.77–0.97] | 0.99 [0.97–1.00] |
| India | 2 | 838 | 0.58 [0.52–0.63] | 0.99 [0.98–1.00] |
| Subgroups | Number of Studies | Total Number of Patients | Sensitivity [95% CI] | Specificity [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All studies | 78 | 47415 | 0.72 [0.71–0.73] | 0.98 [0.98–0.98] |
| Specimens | ||||
| Nasopharyngeal swabs | 49 | 37646 | 0.71 [0.70–0.72] | 0.98 [0.97–0.99] |
| Nasal swabs | 3 | 3879 | 0.83 [0.80–0.85] | 0.98 [0.98–0.99] |
| Throat swabs | 2 | 3623 | 0.69 [0.63–0.75] | 0.99 [0.99–1.00] |
| Saliva | 2 | 432 | 0.68 [0.59–0.77] | 0.97 [0.95–0.99] |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Symptomatic | 24 | 21029 | 0.80 [0.78–0.81] | 0.99 [0.99–0.99] |
| Asymptomatic | 14 | 14926 | 0.68 [0.65–0.71] | 0.99 [0.99–0.99] |
| Ct values | ||||
| Ct value ≤25 | 13 | 5378 | 0.96 [0.95–0.97] | 0.99 [0.98–0.99] |
| Ct value >25 | 10 | 5693 | 0.69 [0.67–0.71] | 0.97 [0.96–0.97] |
| Subgroups | Number of Studies | Total Number of Patients | Sensitivity [95% CI] | Specificity [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies (blinded the index test) | 30 | 24,470 | 0.72 [0.71–0.73] | 0.97 [0.97–0.98] |
| Studies (did not blind the index test) | 64 | 49,975 | 0.69 [0.68–0.70] | 0.99 [0.99–0.99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, M.F.; Selvam, K.; Jeffry, A.J.N.; Salmi, M.F.; Najib, M.A.; Norhayati, M.N.; Aziah, I. Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010110
Khalid MF, Selvam K, Jeffry AJN, Salmi MF, Najib MA, Norhayati MN, Aziah I. Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010110
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Muhammad Fazli, Kasturi Selvam, Alfeq Jazree Nashru Jeffry, Mohamad Fazrul Salmi, Mohamad Ahmad Najib, Mohd Noor Norhayati, and Ismail Aziah. 2022. "Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010110
APA StyleKhalid, M. F., Selvam, K., Jeffry, A. J. N., Salmi, M. F., Najib, M. A., Norhayati, M. N., & Aziah, I. (2022). Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 12(1), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010110







