Beyond the In-Practice CBC: The Research CBC Parameters-Driven Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Early Differentiation among Leukemias
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Preparation and Methods
2.3. Classical Statistical Data Analysis
2.4. AI Based Approach
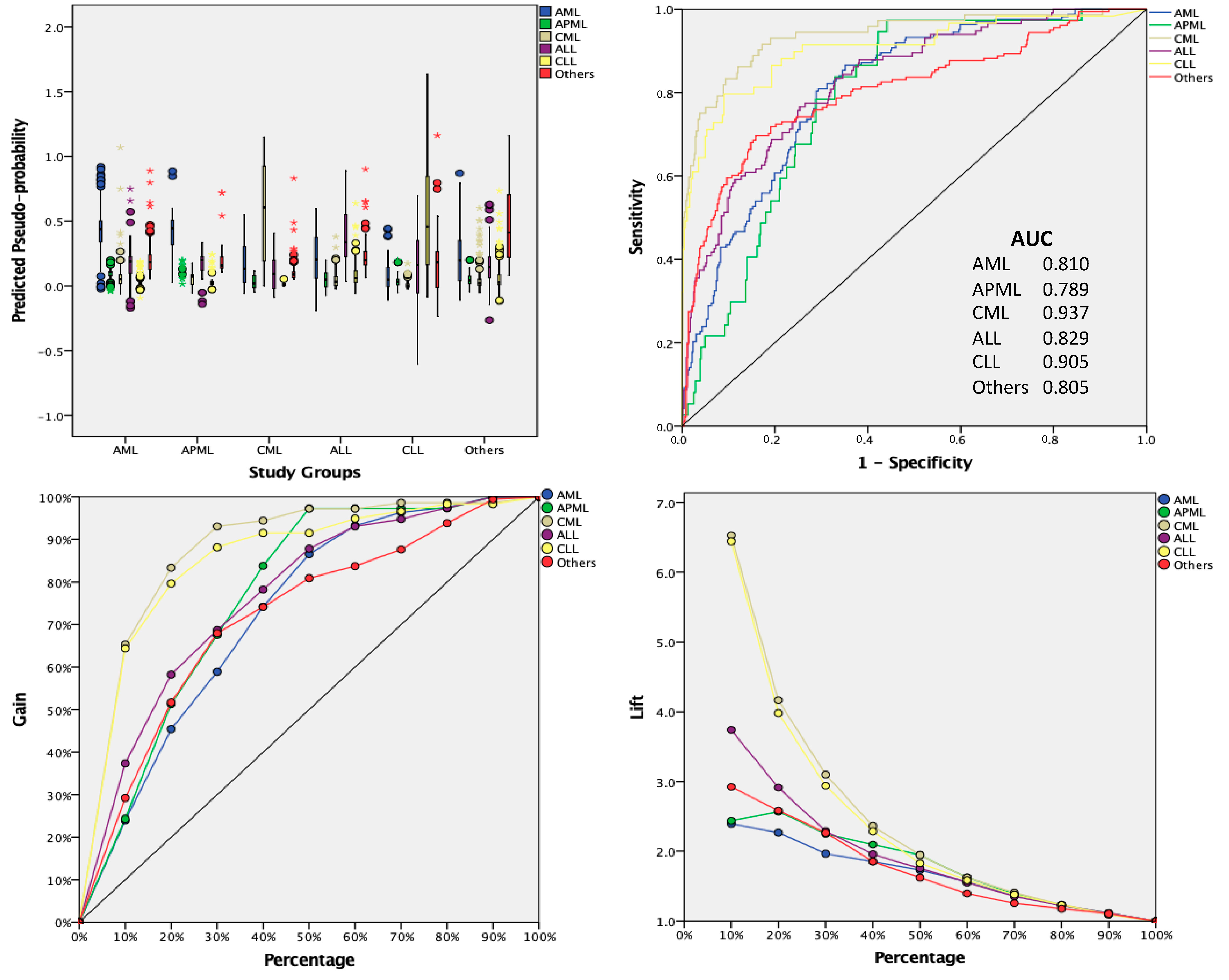
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolovits, P.; Patil, R.S.; Schwartz, W.B. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1988, 108, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, A.; Al-Jumeily, P.D.; Al-Jumaily, M.; Hussain, A.; Lamb, D. Medical Diagnosis: Are Artificial Intelligence Systems Able to Diagnose the Underlying Causes of Specific Headaches? In Proceedings of the 2013 Sixth International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 16–18 December 2013; pp. 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginneken, B. Fifty years of computer analysis in chest imaging: Rule-based, machine learning, deep learning. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2017, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bruijne, M. Machine learning approaches in medical image analysis: From detection to diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 33, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerr, W.; Lau, E.P.; Owens, G.E.; Trefler, A. The Future of Medical Diagnostics: Large Digitized Databases. Yale J. Boil. Med. 2012, 85, 363–377. [Google Scholar]
- Kukar, M.; Kononenko, I.; Grošelj, C. Modern parameterization and explanation techniques in diagnostic decision support system: A case study in diagnostics of coronary artery disease. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 52, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajn, L.; Kukar, M. Image processing and machine learning for fully automated probabilistic evaluation of medical images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2011, 104, e75–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Saito, A.; Tateishi, A.; Shimojo, H.; Kanno, H.; Tsuchiya, S.; Ito, K.-I.; Cosatto, E.; Graf, H.P.; Moraleda, R.R.; et al. Quantitative diagnosis of breast tumors by morphometric classification of microenvironmental myoepithelial cells using a machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrick, T. Evidence-Based Laboratory Medicine. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2013, 34, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Szolovits, P.; Dighe, A.S.; Baron, J.M. Using Machine Learning to Predict Laboratory Test Results. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, P.C. The CBC at the turn of the millennium: An overview. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-E.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Min, W.-S.; Han, K. Leukocyte Cell Population Analysis from the Coulter Automatic Blood Cell Analyzer DxH800 to Monitor the Effect of G-CSF. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2012, 26, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charafeddine, K.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Mahfouz, R.A.R.; Sarieddine, D.S.; Daher, R.T. Comparison of neutrophil volume distribution width to C-reactive protein and procalcitonin as a proposed new marker of acute infection. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 43, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Choi, J.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Song, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.-A. Delta neutrophil index: A promising diagnostic and prognostic marker for sepsis. Shock 2012, 37, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B.M.; Ragaller, M.; Hommel, K.; Tiebel, O.; Menschikowski, M.; Siegert, G. Novel Parameters of Extended Complete Blood Cell Count under Fluorescence Flow Cytometry in Patients with Sepsis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2014, 28, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoro, S.; Mecca, T.; Azzarà, G.; Esposito, S.A.; Seghezzi, M.; Vavassori, M.; Crippa, A.; Marchesi, G.; Castellucci, E.; Ottomano, C.; et al. Extended leukocyte differential count and C-reactive protein in septic patients with liver impairment: Diagnostic approach to evaluate sepsis in intensive care unit. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choccalingam, C. Volume, conductance, and scatter parameters of neoplastic and nonneoplastic lymphocytes using Coulter LH780. J. Lab. Physicians 2018, 10, 085–088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, E.; Boubaya, M.; Troussard, X. Contribution of the new XN-1000 parameters NEUT-RI and NEUT-WY for managing patients with immature granulocytes. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, e123–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, R.J.; Devi, A.; Hampson, P.; Wearn, C.M.; Bamford, A.L.; Hazeldine, J.; Bishop, J.; Ahmed, S.; Watson, C.; Lord, J.M.; et al. Changes in novel haematological parameters following thermal injury: A prospective observational cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furundarena, J.R.; Araiz, M.; Uranga, M.; Sainz, M.R.; Agirre, A.; Trassorras, M.; Uresandi, N.; Montes, M.C.; Argoitia, N. The utility of the Sysmex XE-2100 analyzer’s NEUT-X and NEUT-Y parameters for detecting neutrophil dysplasia in myelodysplastic syndromes. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2010, 32, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haschke-Becher, E.; Vockenhuber, M.; Niedetzky, P.; Totzke, U.; Gabriel, C. A new high-throughput screening method for the detection of chronic lymphatic leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriot, I.; Launay, E.; Boubaya, M.; Cremet, L.; Illiaquer, M.; Caillon, H.; Desjonquères, A.; Gillet, B.; Béné, M.; Eveillard, M. New parameters on the hematology analyzer XN-10 (SysmexTM) allow to distinguish childhood bacterial and viral infections. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J.; Kahng, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Han, K.; Lee, W. Evaluation of cell population data on the UniCel DxH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis system as a screening for viral infection in children. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2012, 34, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Yi, J.; Chang, C.L.; Lee, E.Y. Cell Population Data NE-SFL and MO-WX From Sysmex XN-3000 Can Provide Additional Information for Exclusion of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia from Other Acute Myeloid Leukemias: A Preliminary Study. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Park, C.-J.; Lee, B.-R.; Nam, K.-S.; Kim, M.-J.; Han, M.-Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, Y.-U.; Jang, S. Sepsis affects most routine and cell population data (CPD) obtained using the Sysmex XN-2000 blood cell analyzer: Neutrophil-related CPD NE-SFL and NE-WY provide useful information for detecting sepsis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2014, 37, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Fourcade, C.; Fartoukh, C.; Lenormand, B.; Buchonnet, G.; Callat, M.P.; Leclerc, C.; Basuyau, J.P.; Vasse, M. Lymphocyte volume and conductivity indices of the haematology analyser Coulter® GEN.STM in lymphoproliferative disorders and viral diseases. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2006, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, A.; Orero, M.; Simon, R.; Collado, R.; Perez, P.L.; Pacios, A.; Iglesias, R.; Martinez, A.; Carbonell, F. Automated Neutrophil Morphology and Its Utility in the Assessment of Neutrophil Dysplasia. Lab. Hematol. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Lab. Hematol. 2007, 13, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, H.-W.; Park, S.-G. Comparison of laboratory characteristics between acute promyelocytic leukemia and other subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood Res. 2013, 48, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz, M.A.; Grimwade, D.; Tallman, M.S.; Lowenberg, B.; Fenaux, P.; Estey, E.H.; Naoe, T.; Lengfelder, E.; Büchner, T.; Döhner, H.; et al. Management of acute promyelocytic leukemia: Recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European Leukemia. Net. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 1875–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.; Culp, N.; Davis, B.; D’Onofrio, G.; Zini, G.; Machin, S.J.; The International Council for Standardization of Haematology. ICSH guidelines for the evaluation of blood cell analysers including those used for differential leucocyte and reticulocyte counting. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2014, 36, 613–627. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Reference Leukocyte (WBC) Differential Count (Proportional) and Evaluation of Instrumental Methods; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Lim, J.; Kim, M.; Oh, E.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Park, Y.-J.; Min, W.S.; Cho, B.; Lee, K.; et al. Determination of acute leukemia lineage with new morphologic parameters available in the complete blood cell count. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2014, 44, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Virk, H.; Varma, N.; Naseem, S.; Bihana, I.; Sukhachev, D. Utility of cell population data (VCS parameters) as a rapid screening tool for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in resource-constrained laboratories. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syed-Abdul, S.; Firdani, R.-P.; Chung, H.-J.; Uddin, M.; Hur, M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Gradišek, A.; Dovgan, E. Artificial intelligence based models for screening of hematologic malignancies using cell population data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, R.Z.; Ujjan, I.U.; Shamsi, T.S. Cell Population Data–Driven Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Flagging Through Artificial Neural Network Predictive Modeling. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
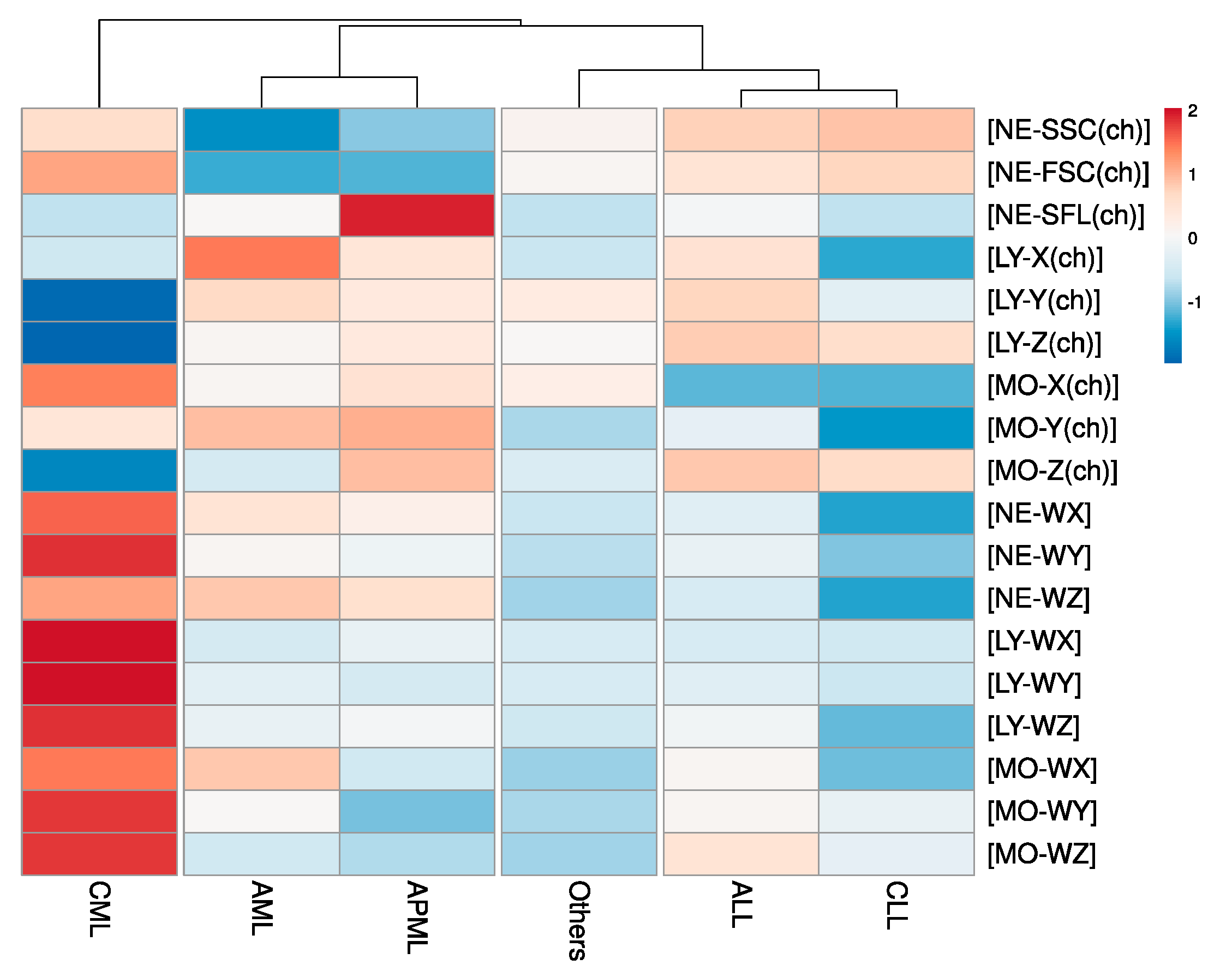


| Study Parameters | Study Groups | Sig. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML | APML | CML | ALL | CLL | Others | ||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Automated Classical CBC Parameters | |||||||
| Hb | 8.19 ± 2.10 | 8.56 ± 1.61 | 9.38 ± 1.87 | 8.17 ± 2.59 | 10.64 ± 2.47 | 9.69 ± 3.24 | <0.005 |
| RBC (1012/L) | 2.78 ± 0.82 | 2.93 ± 0.61 | 3.49 ± 0.8 | 3.02 ± 1.29 | 3.92 ± 0.99 | 3.68 ± 1.56 | <0.005 |
| PCV | 25.09 ± 8.09 | 25.6 ± 5.29 | 28.86 ± 6.24 | 24.73 ± 7.64 | 34.39 ± 7.51 | 30.27 ± 10.53 | <0.005 |
| MCV | 90.34 ± 10.47 | 88.18 ± 8.06 | 83.45 ± 10.14 | 83.94 ± 9.12 | 88.93 ± 9.01 | 85.47 ± 10.93 | <0.005 |
| MCH | 29.39 ± 3.53 | 29.01 ± 3.05 | 27.1 ± 3.9 | 27.36 ± 2.91 | 27.41 ± 3.29 | 27.15 ± 4.18 | <0.005 |
| MCHC | 32.35 ± 1.93 | 32.95 ± 2.34 | 32.15 ± 2.25 | 32.64 ± 1.93 | 30.81 ± 2.44 | 31.65 ± 1.92 | <0.005 |
| WBC (109/L) | 39.66 ± 66.75 | 26.8 ± 47.65 | 192.39 ± 142.46 | 70.91 ± 107.47 | 95.81 ± 123.45 | 16.99 ± 36.84 | <0.005 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 60.88 ± 83.18 | 53.73 ± 85.94 | 438.42 ± 292.94 | 53.74 ± 62.92 | 187.03 ± 105.8 | 304.35 ± 406.31 | <0.005 |
| NEUT# (103/μL) | 9.59 ± 29.59 | 10.35 ± 18.81 | 161.65 ± 125.42 | 3.25 ± 4.22 | 5.83 ± 4.49 | 8.39 ± 13.65 | <0.005 |
| LYMPH# (103/μL) | 9.07 ± 12.93 | 4.77 ± 11.01 | 9.62 ± 5.23 | 47.76 ± 77.4 | 82.74 ± 115.79 | 6.19 ± 31.27 | <0.005 |
| MONO# (103/μL) | 21.29 ± 42.93 | 12.05 ± 25.11 | 8.25 ± 8.81 | 20.09 ± 42.26 | 6.8 ± 17 | 1.91 ± 5.26 | <0.005 |
| EO# (103/μL) | 0.18 ± 0.99 | 0.07 ± 0.15 | 5.1 ± 5.24 | 0.13 ± 0.29 | 0.3 ± 0.42 | 0.36 ± 1.35 | <0.005 |
| BASO# (103/μL) | 0.07 ± 0.21 | 0.06 ± 0.13 | 5.32 ± 5.22 | 0.15 ± 0.39 | 0.15 ± 0.23 | 0.08 ± 0.15 | <0.005 |
| NEUT (%) | 22.16 ± 19.91 | 35.91 ± 19.93 | 81.92 ± 11.61 | 13.12 ± 17.24 | 12 ± 12.26 | 54.22 ± 23.9 | <0.005 |
| LYMPH (%) | 37.9 ± 22.28 | 37.91 ± 26.65 | 7.19 ± 5.86 | 64.36 ± 22.07 | 80.56 ± 17.37 | 31.97 ± 22.22 | <0.005 |
| MONO (%) | 39.09 ± 23.61 | 25.37 ± 21.72 | 4.88 ± 4.61 | 21.07 ± 18.04 | 6.48 ± 10.98 | 11.35 ± 11.68 | <0.005 |
| EO (%) | 0.67 ± 2.07 | 0.71 ± 1.5 | 3.16 ± 5.5 | 0.5 ± 0.96 | 0.73 ± 1.5 | 1.96 ± 2.45 | <0.005 |
| BASO (%) | 0.18 ± 0.36 | 0.1 ± 0.16 | 2.85 ± 2.04 | 0.22 ± 0.3 | 0.23 ± 0.33 | 0.49 ± 0.75 | <0.005 |
| IG# (103/μL) | 1.86 ± 4.83 | 1.53 ± 3.76 | 65.04 ± 57.27 | 0.73 ± 1.51 | 0.45 ± 1.62 | 1.18 ± 3.61 | <0.005 |
| IG (%) | 4.38 ± 6.33 | 5.08 ± 7.77 | 30.31 ± 9.61 | 1.76 ± 2.93 | 0.54 ± 1.33 | 4.07 ± 6.64 | <0.005 |
| NRBC# (103/μL) | 0.35 ± 1.07 | 0.11 ± 0.22 | 2.16 ± 3.42 | 0.51 ± 1.56 | 0.05 ± 0.27 | 0.47 ± 4.46 | <0.005 |
| NRBC (%) | 1.61 ± 3.55 | 0.91 ± 1.35 | 1.15 ± 1.38 | 1.4 ± 3.87 | 0.28 ± 1.51 | 1.56 ± 8.43 | 0.549 |
| PDW (fL) | 8.76 ± 7.24 | 6.19 ± 7.35 | 11.09 ± 6.35 | 7.03 ± 6.72 | 11.92 ± 4.6 | 8.31 ± 6.58 | <0.005 |
| MPV (fL) | 7.23 ± 5.46 | 5.05 ± 5.67 | 8.83 ± 4.6 | 5.89 ± 5.35 | 9.93 ± 3.39 | 6.97 ± 5.25 | <0.005 |
| PCT (%) | 0.05 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 0.09 | 0.41 ± 0.35 | 0.04 ± 0.07 | 0.19 ± 0.12 | 0.28 ± 0.42 | <0.005 |
| Retic count | 1.93 ± 11.84 | 1.15 ± 1.51 | 3.13 ± 2.21 | 0.55 ± 1.07 | 0.2 ± 0.54 | 1.88 ± 1.63 | 0.015 |
| Automated Research CBC (CPD) Parameters | |||||||
| NE–SSC(ch) | 140.81 ± 14.05 | 143.08 ± 10.87 | 149.05 ± 6.53 | 149.64 ± 9.26 | 150.16 ± 7.89 | 147.15 ± 10.04 | <0.005 |
| NE–SFL(ch) | 51.43 ± 17.33 | 65.85 ± 22.71 | 45.86 ± 5.12 | 50.71 ± 8.3 | 45.81 ± 8.45 | 45.66 ± 7.27 | <0.005 |
| NE–FSC(ch) | 72.29 ± 11.15 | 72.59 ± 11.81 | 84.04 ± 5.57 | 80.89 ± 7.03 | 82.23 ± 5.73 | 78.92 ± 7.69 | <0.005 |
| LY–X(ch) | 87.33 ± 10.39 | 84.5 ± 10.35 | 81.63 ± 8.89 | 84.75 ± 7.25 | 79.58 ± 4.46 | 81.45 ± 4.49 | <0.005 |
| LY–Y(ch) | 68.65 ± 12.29 | 65.54 ± 9.37 | 42.89 ± 19.68 | 68.91 ± 16.15 | 59.04 ± 8.9 | 65.11 ± 6.06 | <0.005 |
| LY–Z(ch) | 56.68 ± 3.74 | 57.32 ± 3.02 | 52.44 ± 3.49 | 58.2 ± 3.79 | 57.78 ± 2.94 | 56.66 ± 2.39 | <0.005 |
| MO–X(ch) | 118.05 ± 8.27 | 120.75 ± 9.83 | 126.3 ± 6.91 | 110.2 ± 7.39 | 109.97 ± 6.14 | 119.14 ± 5.74 | <0.005 |
| MO–Y(ch) | 114.65 ± 23.51 | 115.35 ± 25.35 | 112.09 ± 24.26 | 108.43 ± 23.79 | 101.6 ± 9.56 | 105.47 ± 17.45 | <0.005 |
| MO–Z(ch) | 62.66 ± 4.97 | 65.49 ± 7.92 | 60.28 ± 2.89 | 65.29 ± 6.54 | 64.9 ± 3.53 | 62.82 ± 4.76 | <0.005 |
| NE–WX | 435.71 ± 127.01 | 419.16 ± 119.61 | 501.29 ± 76.69 | 386.73 ± 108.58 | 323.69 ± 61.47 | 368.47 ± 88.09 | <0.005 |
| NE–WY | 1388.88 ± 755.01 | 1262.53 ± 829.7 | 2467.69 ± 693.2 | 1226.47 ± 616.41 | 740.42 ± 279.96 | 897.1 ± 471.45 | <0.005 |
| NE–WZ | 825.5 ± 257.67 | 801.79 ± 213.15 | 847.02 ± 109.49 | 721.08 ± 203.64 | 650.14 ± 154.81 | 691.02 ± 156.02 | <0.005 |
| LY–WX | 533.66 ± 118.75 | 550.86 ± 136.81 | 695.52 ± 168.56 | 535.53 ± 119.29 | 530.33 ± 115.78 | 536.78 ± 109.45 | <0.005 |
| LY–WY | 1069.66 ± 267.76 | 994.91 ± 184.93 | 1929.71 ± 1070.73 | 1060.03 ± 231.82 | 960.37 ± 169.92 | 1007.77 ± 220.04 | <0.005 |
| LY–WZ | 568.06 ± 115.83 | 586.67 ± 142.48 | 801.74 ± 165.36 | 578.5 ± 138.35 | 460.95 ± 102.18 | 527.32 ± 122.95 | <0.005 |
| MO–WX | 340.51 ± 75.02 | 301.81 ± 104.41 | 357.22 ± 65.23 | 319.04 ± 90.03 | 285.66 ± 66.46 | 291.38 ± 73.36 | <0.005 |
| MO–WY | 873.84 ± 282.05 | 701.67 ± 446.57 | 1146.88 ± 346.87 | 878.07 ± 317.66 | 832.36 ± 218.58 | 736.74 ± 258.89 | <0.005 |
| MO–WZ | 616.05 ± 112.94 | 601.16 ± 204.8 | 767.94 ± 100.79 | 681.88 ± 226.76 | 636 ± 255.98 | 597.25 ± 156.62 | <0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haider, R.Z.; Ujjan, I.U.; Khan, N.A.; Urrechaga, E.; Shamsi, T.S. Beyond the In-Practice CBC: The Research CBC Parameters-Driven Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Early Differentiation among Leukemias. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010138
Haider RZ, Ujjan IU, Khan NA, Urrechaga E, Shamsi TS. Beyond the In-Practice CBC: The Research CBC Parameters-Driven Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Early Differentiation among Leukemias. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010138
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaider, Rana Zeeshan, Ikram Uddin Ujjan, Najeed Ahmed Khan, Eloisa Urrechaga, and Tahir Sultan Shamsi. 2022. "Beyond the In-Practice CBC: The Research CBC Parameters-Driven Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Early Differentiation among Leukemias" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010138
APA StyleHaider, R. Z., Ujjan, I. U., Khan, N. A., Urrechaga, E., & Shamsi, T. S. (2022). Beyond the In-Practice CBC: The Research CBC Parameters-Driven Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Early Differentiation among Leukemias. Diagnostics, 12(1), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010138







