Development and Validation of an Insulin Resistance Predicting Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Demographic, Anthropometric, and Biochemical Measurements
2.3. Genetic Variants for Insulin Resistance
2.4. Assessment of the Food and Nutrient Intake Using Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaires (SQFFQ)
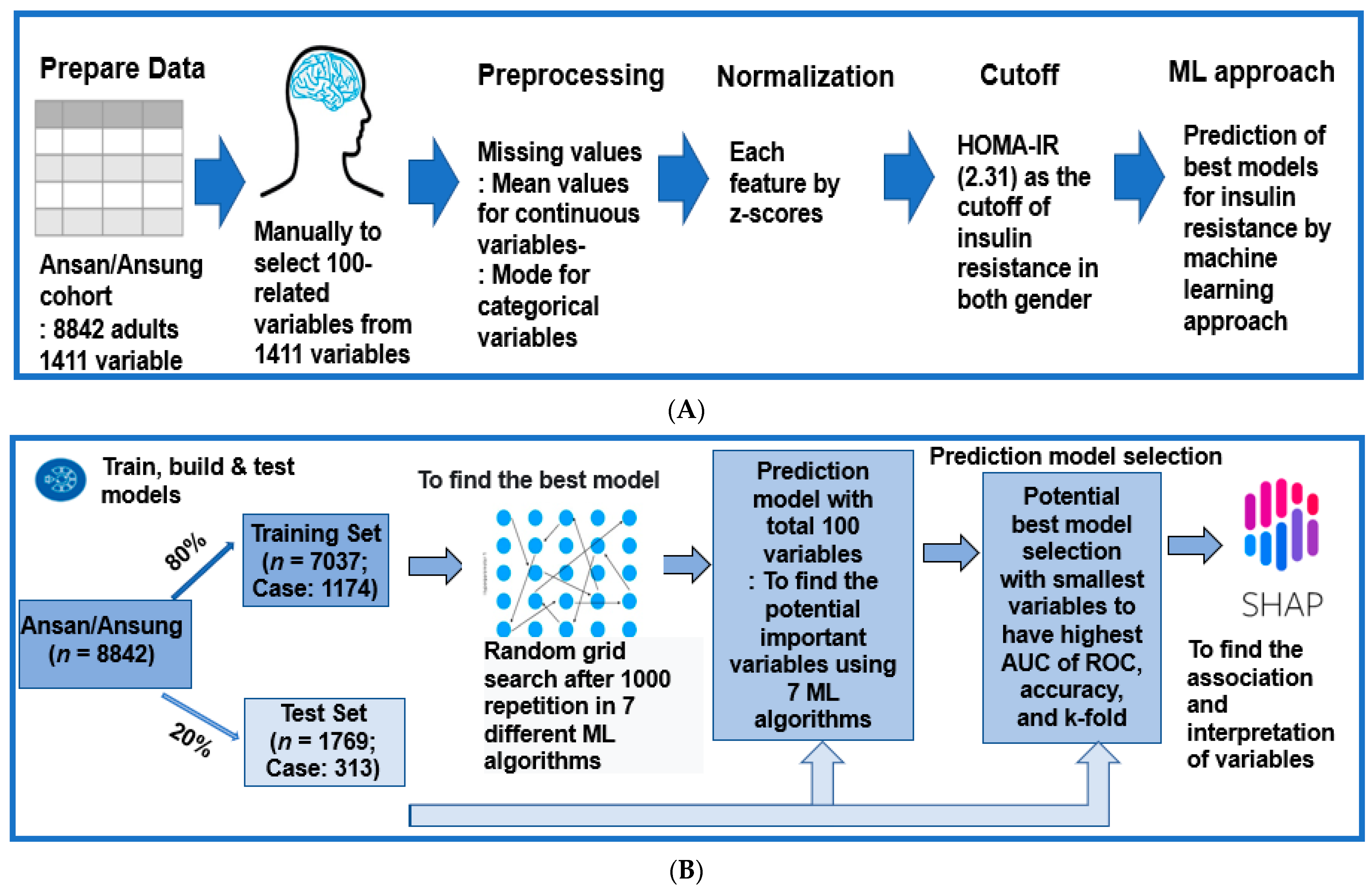
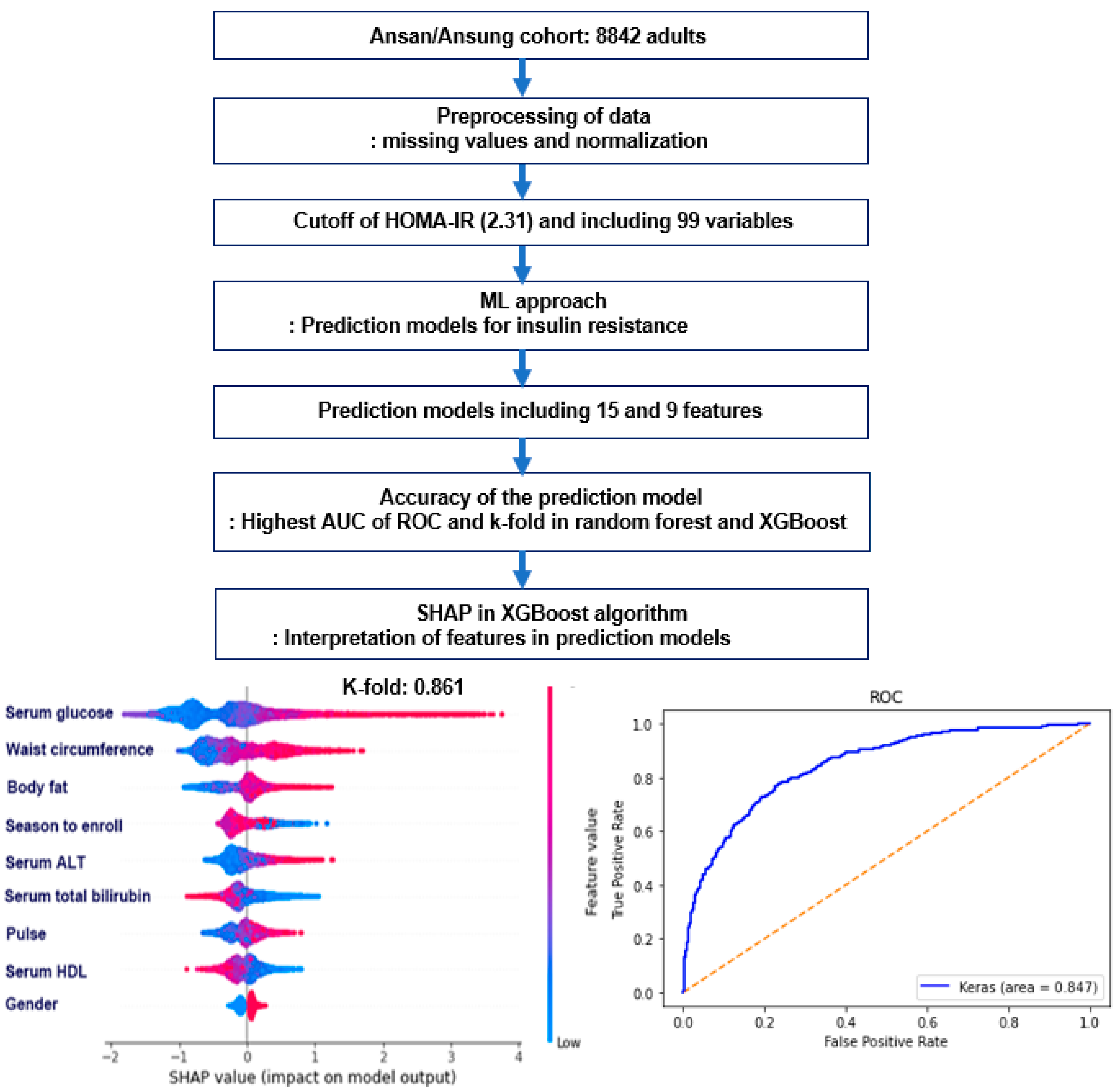
2.5. Experimental Design for Machine Learning for Predicting Insulin Resistance by HOMA-IR
2.6. Training for the Features for Generating Insulin Resistance Prediction Model and Testing the Models for Verifying the Prediction Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric and Biochemical Measurement of the Participants
3.2. Lifestyle-Related Variables
3.3. The Best Model for Explaining Insulin Resistance Using the Machine Learning (ML) Approach
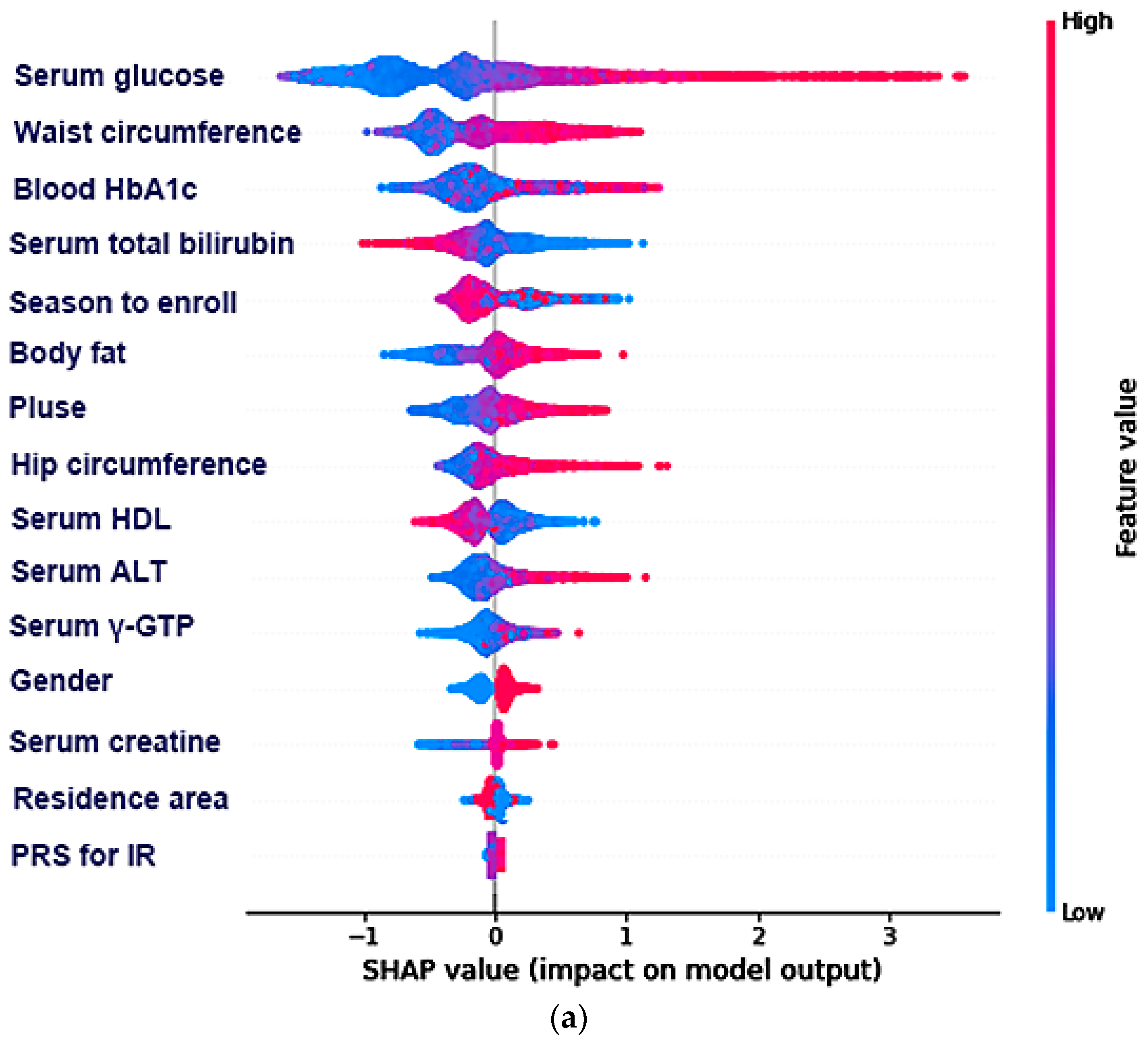
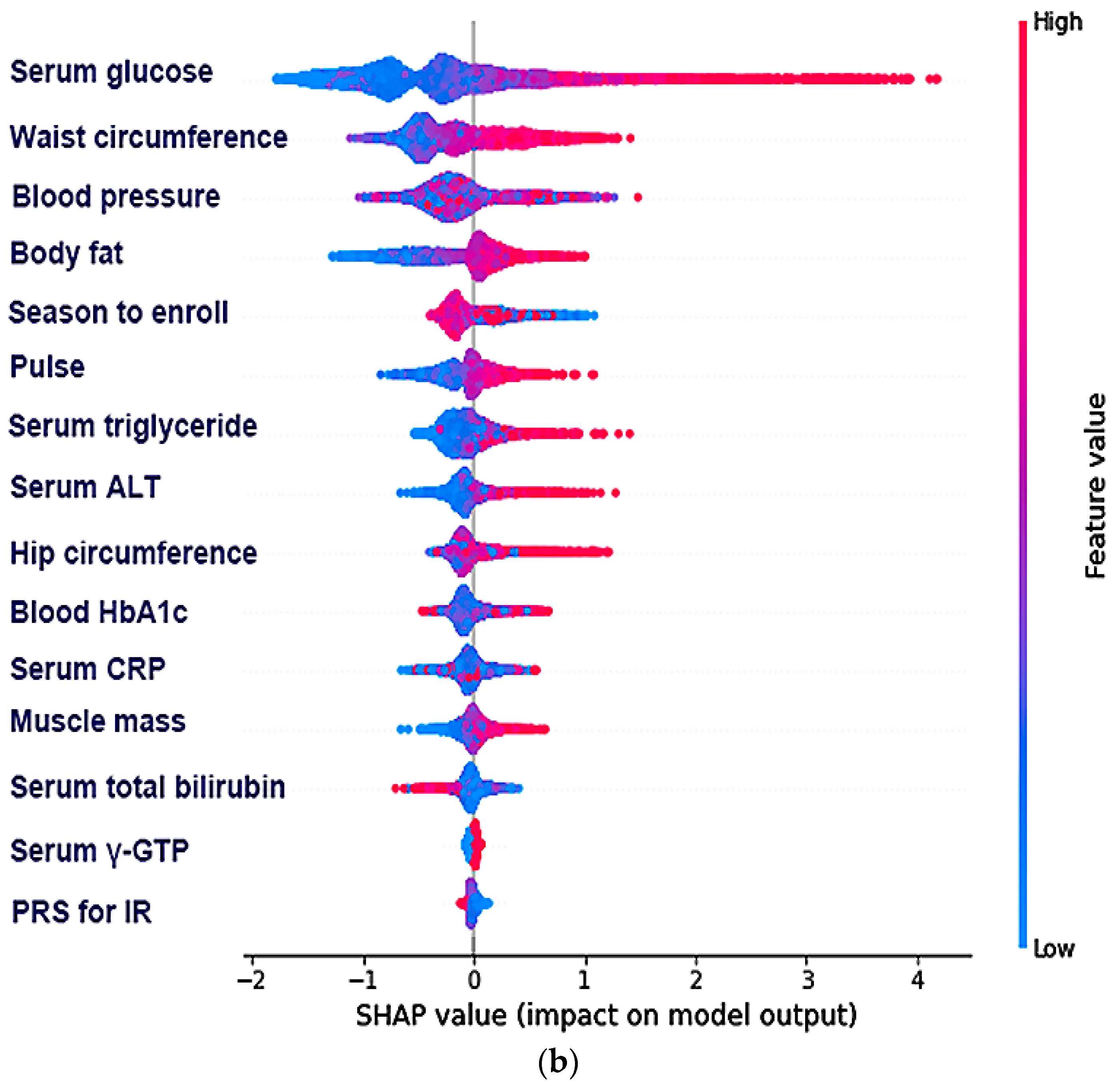
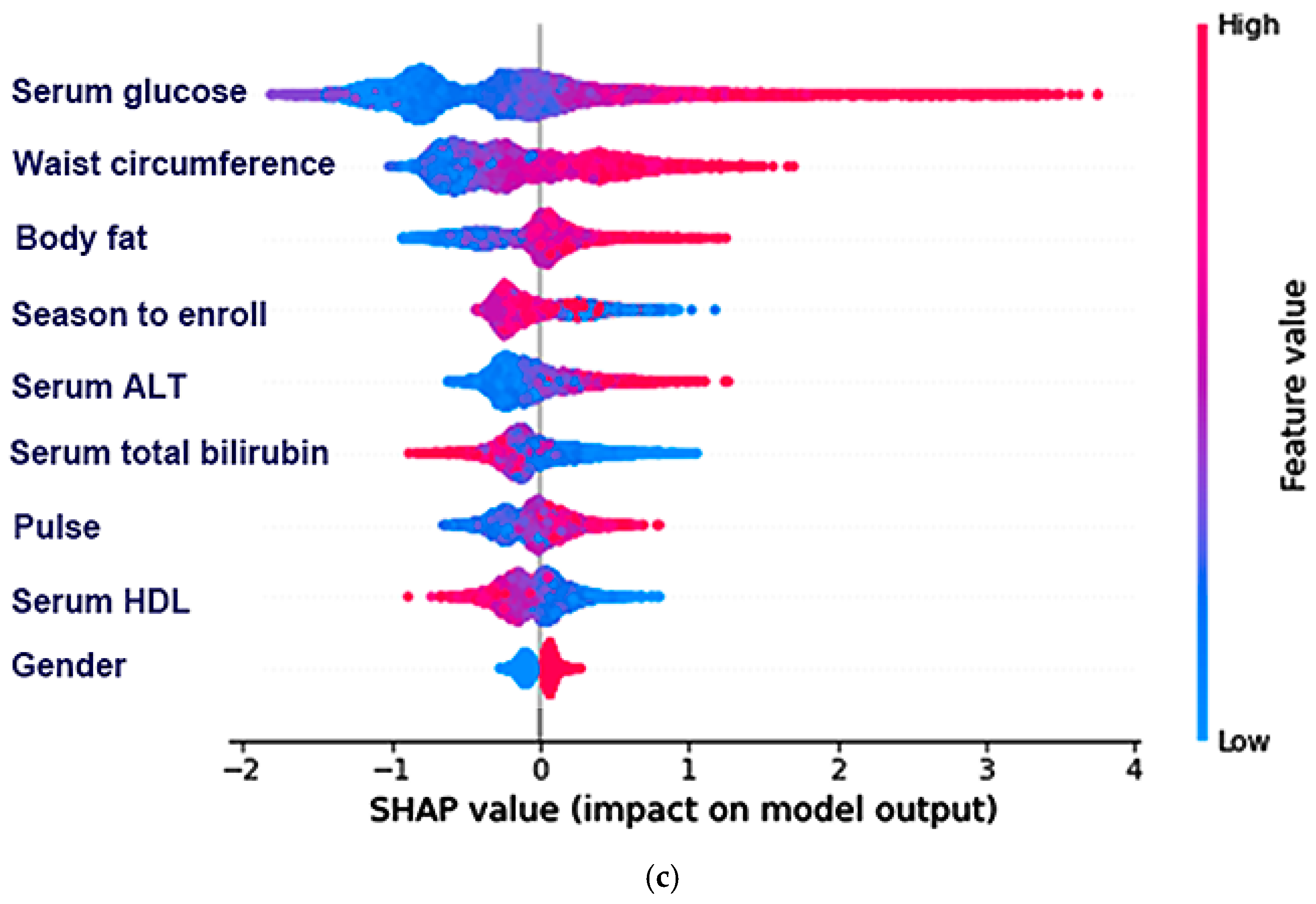
3.4. The Relative Importance of the Parameters in the Random Forest and XGBoost Prediction Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.; Park, S.; Lin, X.; Copps, K.; Yi, X.; White, M.F. Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Taguchi, A.; Park, S.; Kushner, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; White, M.F. Dysregulation of insulin receptor substrate 2 in beta cells and brain causes obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Vijayakumar, A.; Kahn, B.B. Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 19, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R. Insulin signaling in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Jung, J. Insulin resistance and the risk of diabetes and dysglycemia in Korean general adult population. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H. Relationship between metabolic syndrome, metabolic syndrome score, insulin resistance and beta cell function in korean adults with obesity. Korean J. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 52, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Park, S. Interactions among the variants of insulin-related genes and nutrients increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Res. 2018, 51, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Liu, M.; Kang, S. Alcohol intake interacts with CDKAL1, HHEX, and OAS3 genetic variants, associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes by lowering insulin secretion in Korean adults. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ham, J.O.; Lee, B.K. Effects of total vitamin A, vitamin C, and fruit intake on risk for metabolic syndrome in Korean women and men. Nutrition 2015, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.K.; Ahn, J. A healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin C is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome risk in korean adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.J.; Han, K.; Kim, M.K.; Park, Y.M.; Baek, K.H.; Song, K.H.; Kwon, H.S. Insulin resistance distribution and dut-off value in Koreans from the 2008–2010 Korean national health and nutrition examination survey. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, T1–T23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, C.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Hiratsuka, N.; Inabe, F.; Araida, N.; Takahashi, E. Optimal reference interval for homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in a Japanese population. J. Diab. Investig. 2011, 2, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horáková, D.; Štěpánek, L.; Janout, V.; Janoutová, J.; Pastucha, D.; Kollárová, H.; Petráková, A.; Štěpánek, L.; Husár, R.; Martiník, K. Optimal homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) cut-offs: A cross-sectional study in the Czech population. Medicina 2019, 55, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chitturi, S.; Abeygunasekera, S.; Farrell, G.C.; Holmes-Walker, J.; Hui, J.M.; Fung, C.; Karim, R.; Lin, R.; Samarasinghe, D.; Liddle, C.; et al. NASH and insulin resistance: Insulin hypersecretion and specific association with the insulin resistance syndrome. Hepatology 2002, 35, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Tang, L.; Shao, G.; Qiu, Q.; Lan, T.; Shao, J. A machine learning-based classification system for urban built-up areas using multiple classifiers and data sources. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, D.; Jeong, E.; Kim, H.; Pyun, H.W.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Jin, S.; Hong, D.; Lee, D.W.; et al. Machine learning-based three-month outcome prediction in acute ischemic stroke: A single cerebrovascular-specialty hospital study in South Korea. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Malavolti, M.; Severi, S.; Poli, M.; Mussi, C.; Fantuzzi, A.L.; Battistini, N. Accuracy of an eight-point tactile-electrode impedance method in the assessment of total body water. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downer, R.G.; Richardson, P.J. Illustrative Logistic Regression Examples Using PROC LOGISTIC: New Features in SAS/STAT 9.2; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, Y.-S.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.C.; Huh, K.B.; Kim, D.J. Cutoff values of surrogate measures of insulin resistance for metabolic syndrome in Korean non-diabetic adults. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S. Carrying minor allele of FADS1 and haplotype of FADS1 and FADS2 increased the risk of metabolic syndrome and moderate but not low-fat diets lowered the risk in two Korean cohorts. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Zhang, T. A positive association of overactivated immunity with metabolic syndrome risk and mitigation of its association by a plant-based diet and physical activity in a large cohort study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uma Jyothi, K.; Reddy, B.M. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the population of Hyderabad, India. Meta Gene 2015, 5, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, J.W.; Liu, M.; Park, S. High genetic risk scores of SLIT3, PLEKHA5 and PPP2R2C variants increased insulin resistance and interacted with coffee and caffeine consumption in middle-aged adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Daily, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.H. Interactions with the MC4R rs17782313 variant, mental stress and energy intake and the risk of obesity in genome epidemiology study. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Park, S. An inverse relation between hyperglycemia and skeletal muscle mass predicted by using a machine learning approach in middle-aged and older adults in large cohorts. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, M.; Shulman, G.I. The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes. Nature 2019, 576, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Paik, H.-Y.; Song, Y. The relationship between intake of nutrients and food groups and insulin resistance in Korean adults: Using the fourth korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES IV, 2007–2009). Korean J. Nutr. 2013, 46, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, N.E.; Jones, R.R.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Medgyesi, D.N.; Kahle, L.L.; Graubard, B.I. Insulin resistance in healthy U.S. adults: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Cepeda, M.; Muka, T.; Ikram, M.A.; Franco, O.H.; Schoufour, J.D. Seasonality of insulin resistance, glucose, and insulin among middle-aged and elderly population: The Rotterdam study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamezaki, F.; Sonoda, S.; Nakata, S.; Muraoka, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Tamura, M.; Abe, H.; Tekeuchi, M.; Otsuji, Y. Association of seasonal variation in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome with insulin resistance. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, L.; Berne, C.; Svärdsudd, K.; Garmo, H.; Melhus, H.; Zethelius, B. Seasonal variations of insulin sensitivity from a euglycemic insulin clamp in elderly men. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2012, 117, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reule, S.; Drawz, P.E. Heart rate and blood pressure: Any possible implications for management of hypertension? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaioannou, T.G.; Oikonomou, E.; Lazaros, G.; Christoforatou, E.; Vogiatzi, G.; Tsalamandris, S.; Chasikidis, C.; Kalambogias, A.; Mystakidi, V.X.; Galiatsatos, N.; et al. The influence of resting heart rate on pulse wave velocity measurement is mediated by blood pressure and depends on aortic stiffness levels: Insights from the Corinthia study. Physiol. Meas. 2019, 40, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, S.; Swenne, C.A.; Gast, K.B.; Maan, A.C.; le Cessie, S.; Jukema, J.W.; Rosendaal, F.R.; den Heijer, M.; de Mutsert, R. The role of insulin resistance in the association between body fat and autonomic function. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, K.M.; Kahn, S.E. The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 2006, 91, 4753–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, R.S.; Bril, F.; Cusi, K.; Newsome, P.N. Modulation of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2019, 70, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitade, H.; Chen, G.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: New insights and potential new treatments. Nutrients 2017, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lioudaki, E.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Liver enzymes: Potential cardiovascular risk markers? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3632–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, P.; Tarantino, G.; Conca, P.; Perrella, A.; Terracciano, M.L.; Vecchione, R.; Gargiulo, G.; Gennarelli, N.; Lobello, R. Silent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-a clinical-histological study. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Guo, H.; Ma, R.L.; Yan, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, K.; Mu, L.T.; et al. Association of total bilirubin and indirect bilirubin content with metabolic syndrome among Kazakhs in Xinjiang. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guan, W.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Guo, W.; Ma, Y.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liang, H.; Zhou, H. Relationship between serum indirect bilirubin level and insulin sensitivity: Results from two independent cohorts of obese patients with impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes mellitus in China. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 5681296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Yun, K.E.; Choi, H.J. Relationships between serum total bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzek, M.; Jakubowski, Z.; Bandosz, P.; Wyrzykowski, B.; Smoczyński, M.; Jabloiska, A.; Zdrojewski, T. Inverse association of serum bilirubin with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in Polish population. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2012, 66, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Men (n = 4183) | Women (n = 4659) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-IR (n = 3906) | High-IR (n = 677) | Low-IR (n = 3850) | High-IR (n = 809) | |
| Age (year) | 52.0 ± 0.15 b | 50.6 ± 0.34 c | 52.4 ± 0.14 a | 53.7 ± 0.31 a*** |
| HOMA-IR | 1.22 ± 0.03 c | 3.43 ± 0.08 a | 1.37 ± 0.03 b | 3.41 ± 0.07 a**### |
| BMI (mg/kg2) | 24.0 ± 0.06 d | 26.2 ± 0.13 b | 24.5 ± 0.05 c | 26.7 ± 0.12 a***### |
| Waist circumferences(cm) | 82.2 ± 0.21 c | 88.4 ± 0.54 a | 80.3 ± 0.22 d | 86.5 ± 0.46 b***### |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (%) | 35.4 ± 0.04 a | 33.9 ± 0.10 b | 30.8 ± 0.04 c | 29.4 ± 0.09 d***### |
| Fat mass (%) | 21.3 ± 0.09 d | 24.8 ± 0.21 c | 31.3 ± 0.09 b | 34.4 ± 0.20 a***### |
| MetS (%)9 | 558 (15.9) | 256 (37.8) *** | 813 (21.1) | 350 (43.3) *** |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 86.0 ± 0.34 c | 112.4 ± 0.77 a | 81.7 ± 0.33 d | 101.2 ± 0.70 b***### |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.71 ± 0.15 c | 6.44 ± 0.04 a | 5.69 ± 0.15 c | 6.30 ± 0.03 b**### |
| Serum total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 190 ± 0.61 b | 199 ± 1.38 a | 190 ± 0.58 b | 199 ± 1.26 a### |
| Serum HDL (mg/dL) | 44.1 ± 0.17 b | 41.0 ± 0.39 d | 46.1 ± 0.16 a | 43.0 ± 0.35 c***### |
| Serum LDL (mg/dL) | 105 ± 0.83 c | 103 ± 2.2 c | 113 ± 0.85 b | 118 ± 1.83 a*** |
| Serum Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 169 ± 1.74 c | 227 ± 3.96 a | 142 ± 1.66 d | 183 ± 3.62 b***### |
| Serum CRP (mg/dL) | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| Pulse | 62.8 ± 0.13 | 64.8 ± 0.29 | 64.0 ± 0.12 | 67.3 ± 0.27 ***### |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119 ± 0.46 b | 125 ± 1.18 a | 119 ± 0.47 b | 127 ± 1.01 a### |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.5 ± 0.27 | 80.7 ± 0.70 | 74.9 ± 0.28 | 80.0 ± 0.60 **### |
| Serum AST (U/L) | 32.4 ± 0.31 b | 34.5 ± 0.70 a | 27.0 ± 0.29 c | 28.0 ± 0.64 c***## |
| Serum ALT(U/L) | 31.8 ± 0.45 b | 43.6 ± 1.02 a | 22.4 ± 0.43 d | 27.8 ± 0.94 c***### |
| Men (n = 4183) | Women (n = 4659) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-IR (n = 3906) | High-IR (n = 677) | Low-IR (n = 3850) | High-IR (n = 809) | |
| Energy (EER%) | 96.8 ± 0.66 b | 97.1 ± 1.49 b | 106 ± 0.62 a | 109 ± 1.38 a*** |
| CHO (En%) | 69.7 ± 0.12 b | 68.8 ± 0.27 b | 71.7 ± 0.11 a | 72.4 ± 0.25 a***++ |
| Fat (En%) | 15.3 ± 0.09 a | 15.9 ± 0.21 a | 13.6 ± 0.09 b | 13.0 ± 0.19 c***++ |
| SFA (En%) | 3.76 ± 0.04 a | 3.96 ± 0.09 a | 3.15 ± 0.04 b | 2.93 ± 0.08 b***++ |
| MUFA (En%) | 4.88 ± 0.04 a | 5.04 ± 0.09 a | 4.00 ± 0.04 b | 3.76 ± 0.09 b***++ |
| PUFA (En%) | 2.29 ± 0.02 a | 2.37 ± 0.04 a | 1.94 ± 0.02 b | 1.90 ± 0.03 b***+ |
| Protein (En%) | 13.7 ± 0.04 b | 14.1 ± 0.09 a | 13.5 ± 0.04 c | 13.4 ± 0.09 c***++ |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 6.92 ± 0.08 | 7.11 ± 0.16 | 7.16 ± 0.07 | 7.31 ± 0.15 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 121 ± 2.17 b | 126 ± 4.57 b | 136 ± 2.09 a | 141 ± 4.30 a*** |
| Calcium (mg) | 486 ± 5.86 | 481 ± 12.3 | 482 ± 5.63 | 477 ± 11.6 |
| Sodium (g) | 3.37 ± 0.04 a | 3.39 ± 0.07 a | 3.02 ± 0.03 b | 3.03 ± 0.07 b*** |
| Alcohol intake (g/day) | 19.1 ± 0.35a | 19.5 ± 0.80 a | 1.29 ± 0.33 b | 1.48 ± 0.73 b*** |
| Smoking | ||||
| Former smoker | 166 (4.8) | 33 (4.9) | 46 (1.22) | 13 (1.65) |
| Smoker | 1567 (44.9) | 298 (44.1) | 86 (2.28) | 19 (2.41) |
| Regular exercise (yes, %) | 1043 (73.9) | 144 (68.3) | 933 (71.9) | 213 (77.2) |
| 99 Features | Logistic Regression | XGBoost | Decision Tree | KNN | SVM | Random Forest | ANN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC of ROC | 0.866 (0.865–0.867) | 0.866 (0.865–0.867) | 0.647 (0.646–0.647) | 0.662 (0.661–0.663) | 0.597 (0.596–0.597) | 0.836 (0.835–0.836) | 0.816 |
| Accuracy | 0.867 (0.867–0.868) | 0.868 (0.868–0.869) | 0.793 (0.792–0.793) | 0.826 (0.825–0.827) | 0.859 (0.858–0.859) | 0.841 (0.840–0.841) | |
| k-fold | 0.858 (0.853–0.863) | 0.859 (0.856–0.863) | 0.786 (0.764–0.786) | 0.821 (0.818–0.825) | 0.851 (0.848–0.854) | 0.833 (0.831–0.834) | |
| Top 15 features | |||||||
| AUC of ROC | 0.849 (0.848–0.850) | 0.853 (0.853–0.854) | 0.639 (0.638–0.640) | 0.694 (0.693–0.695) | 0.574 (0.574–0.575) | 0.831 (0.830–0.832) | 0.822 |
| Accuracy | 0.868 (0.867–0.868) | 0.877 (0.876–0.877) | 0.798 (0.797–0.798) | 0.837 (0.836–0.837) | 0.855 (0.854–0.856) | 0.860 (0.859–0.860) | |
| k-fold | 0.856 (0.850–0.862) | 0.861 (0.853–0.870) | 0.777 (0.768–0.785) | 0.827 (0.818–0.831) | 0.850 (0.846–0.852) | 0.856 (0.853–0.859) | |
| Top 9 features | |||||||
| AUC of ROC | 0.849 (0.848–0.850) | 0.853 (0.852–0.853) | 0.636 (0.635–0.636) | 0.691 (0.690–0.692) | 0.561 (0.560–0.561) | 0.836 (0.835–0.837) | 0.862 |
| Accuracy | 0.867 (0.867–0.868) | 0.868 (0.867–0.868) | 0.791 (0.790–0.792) | 0.834 (0.833–0.834) | 0.853 (0.852–0.853) | 0.862 (0.862–0.863) | |
| k-fold | 0.856 (0.851–0.861) | 0.861 (0.857–0.864) | 0.779 (0.764–0.795) | 0.828 (0.824–0.835) | 0.848 (0.843–0.853) | 0.857 (0.853–0.859) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, C.; Wu, X. Development and Validation of an Insulin Resistance Predicting Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010212
Park S, Kim C, Wu X. Development and Validation of an Insulin Resistance Predicting Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010212
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sunmin, Chaeyeon Kim, and Xuangao Wu. 2022. "Development and Validation of an Insulin Resistance Predicting Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010212
APA StylePark, S., Kim, C., & Wu, X. (2022). Development and Validation of an Insulin Resistance Predicting Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach in a Population-Based Cohort in Korea. Diagnostics, 12(1), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010212







