Role and Relevance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Diagnostics and Research: State-of-the-Art and Underutilized Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Challenge of Examining CSF Immune Cells—A History of Ups and Downs
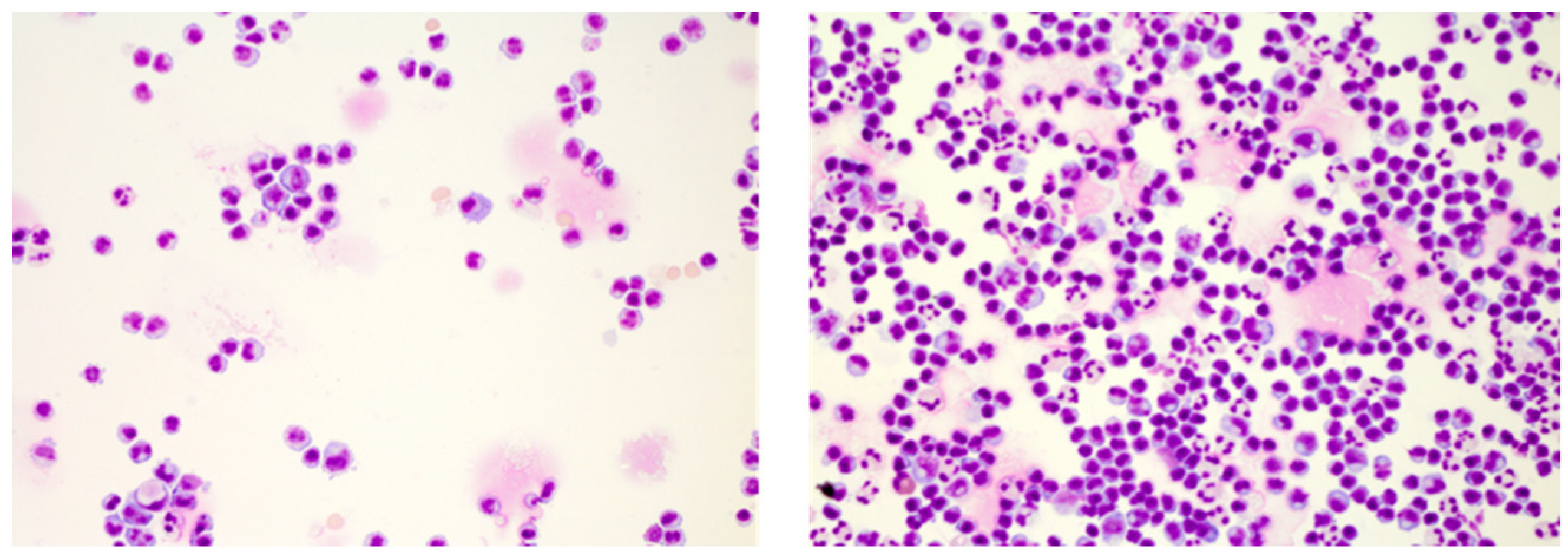
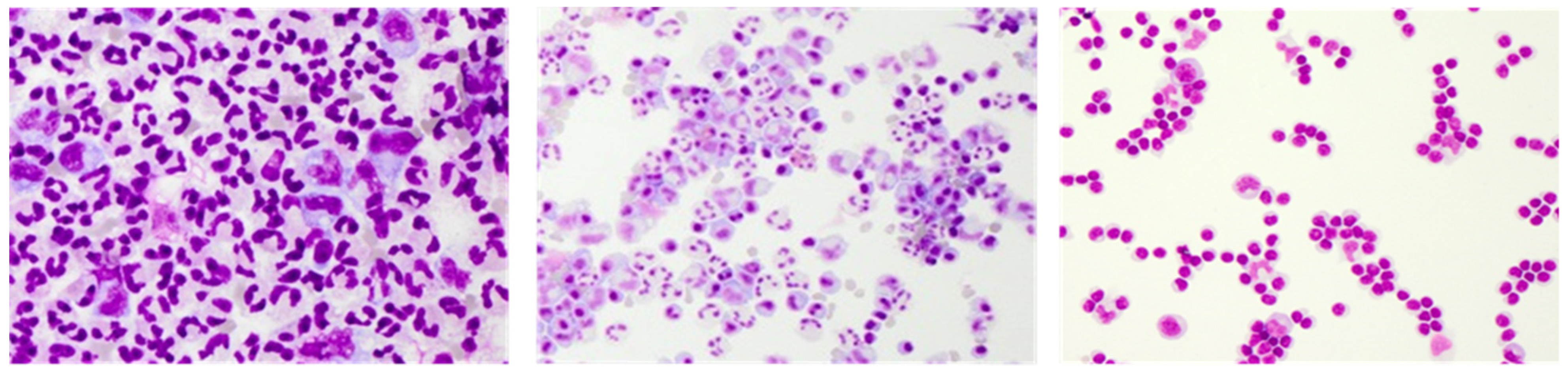
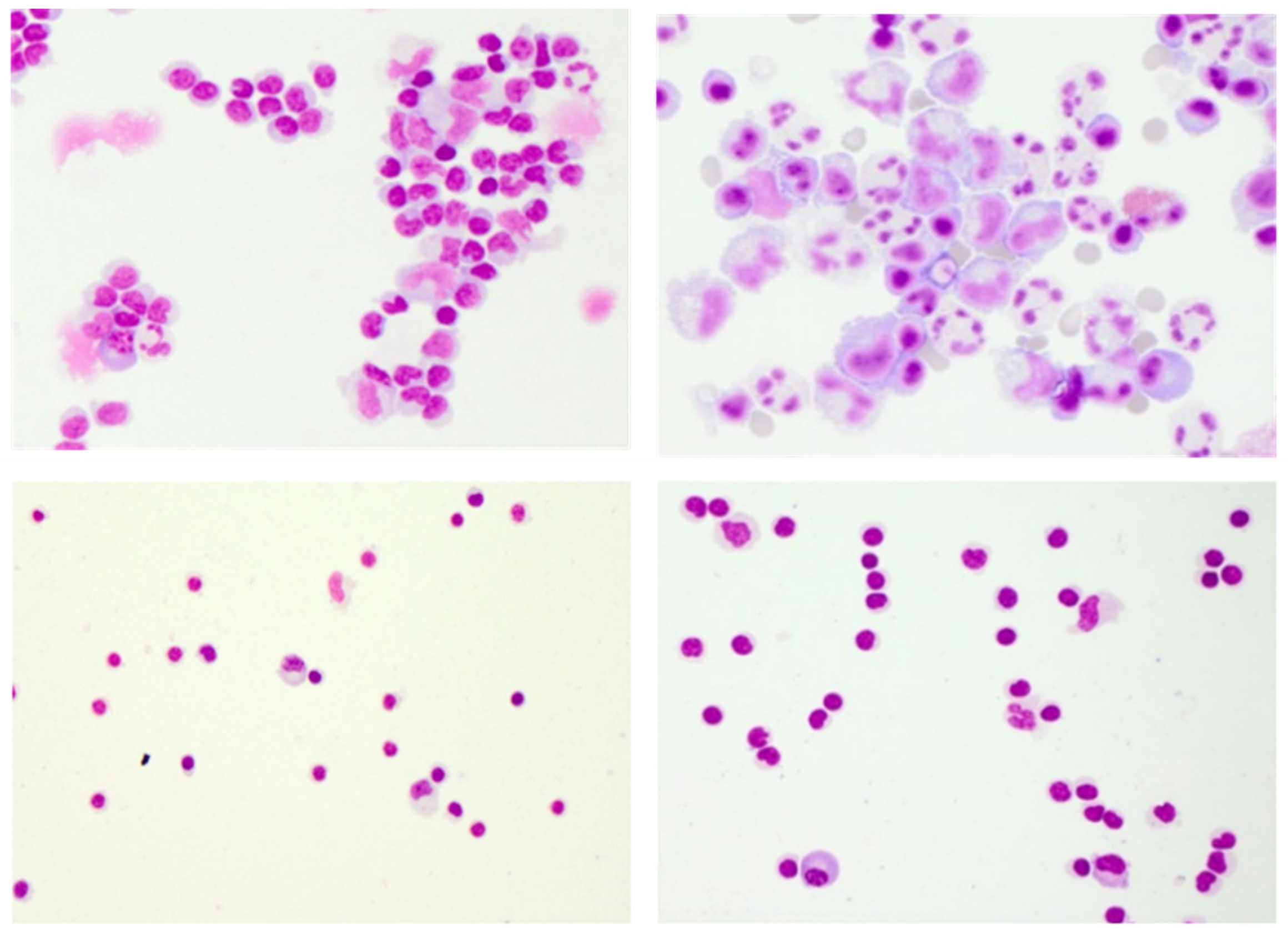
3. Conventional CSF Cell Diagnostics
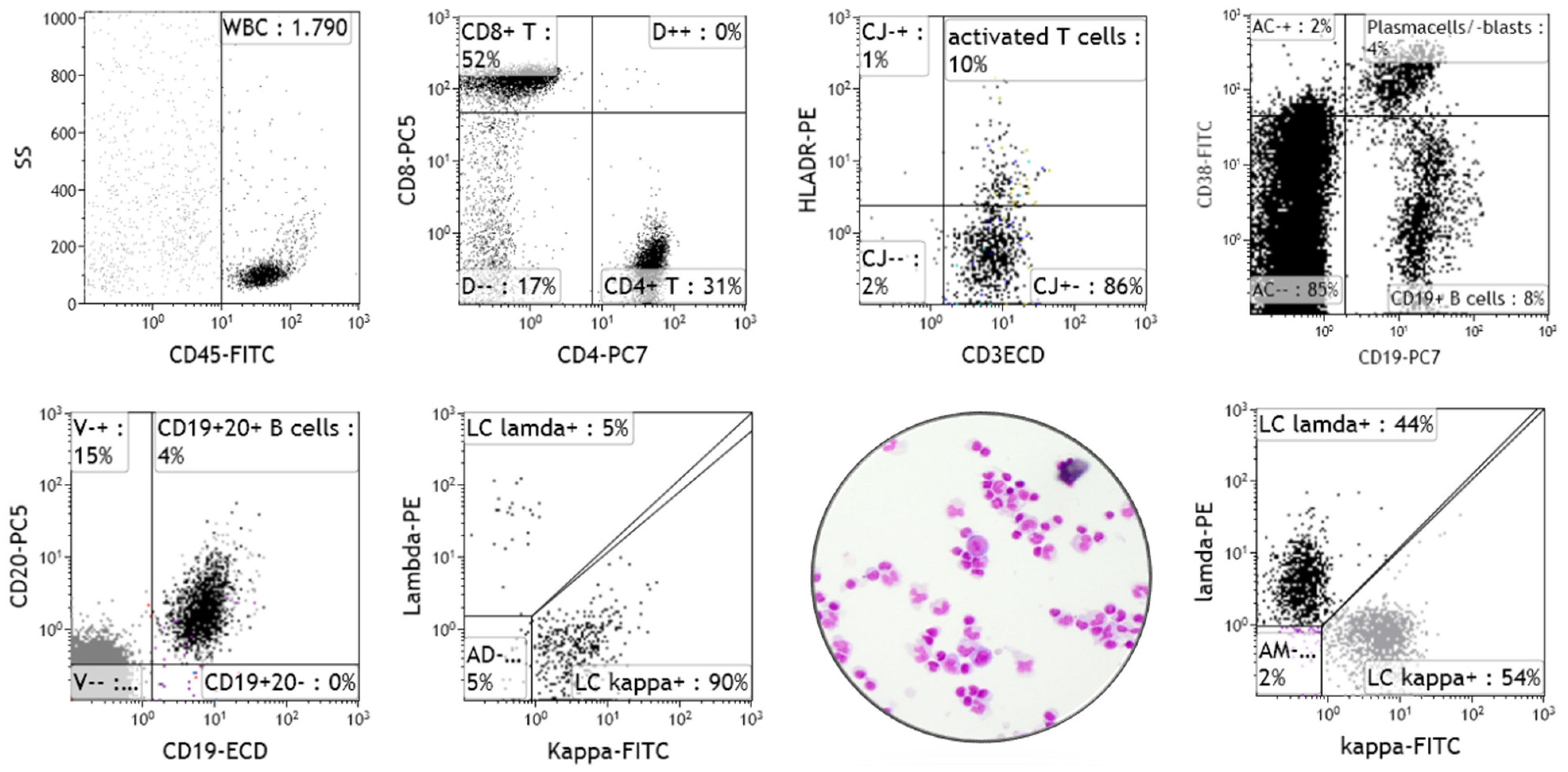
4. Clinical Relevance of Immune Phenotyping of CSF Cells by Flow Cytometry
5. CSF Cells in Research: Revisited
6. Perspectives for Translation into CSF Diagnostics
7. Final Comments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tashjian, R.S.; Vinters, H.V.; Yong, W.H. Biobanking of Cerebrospinal Fluid. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1897, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fame, R.M.; Lehtinen, M.K. Emergence and Developmental Roles of the Cerebrospinal Fluid System. Dev. Cell 2020, 52, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandy, W.E. Experimental Hydrocephalus. Ann. Surg. 1919, 70, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, H. Studies on the Cerebro-Spinal Fluid: I. Introduction. J. Med. Res. 1914, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, R.; Snodgrass, S.R.; Johanson, C.E. A balanced view of the cerebrospinal fluid composition and functions: Focus on adult humans. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 273, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negron, A.; Stüve, O.; Forsthuber, T.G. Ectopic Lymphoid Follicles in Multiple Sclerosis: Centers for Disease Control? Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 607766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.T.; Smitt, P.A.E.S.; Luitwieler, R.L.; van Velzen, C.; van den Broek, P.D.; Kraan, J.; Gratama, J.W. Central memory CD4+ T cells dominate the normal cerebrospinal fluid. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2011, 80, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, E.L.; Michel, B.A.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.-Z.; Bevan, C.J.; Abounasr, A.; Pierson, N.S.; Bischof, A.; Kazer, M.; Leitner, E.; et al. Clonal relationships of CSF B cells in treatment-naive multiple sclerosis patients. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivisäkk, P.; Mahad, D.J.; Callahan, M.K.; Trebst, C.; Tucky, B.; Wei, T.; Wu, L.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Lassmann, H.; Staugaitis, S.M.; et al. Human cerebrospinal fluid central memory CD4+T cells: Evidence for trafficking through choroid plexus and meninges via P-selectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8389–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Engelhardt, B. The anatomical and cellular basis of immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Büdingen, H.-C.; Kuo, T.C.; Sirota, M.; van Belle, C.J.; Apeltsin, L.; Glanville, J.; Cree, B.A.; Gourraud, P.-A.; Schwartzburg, A.; Huerta, G.; et al. B cell exchange across the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4533–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, R.; McGavern, D.B. Advances in Meningeal Immunity. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, B.; Ransohoff, R.M. The ins and outs of T-lymphocyte trafficking to the CNS: Anatomical sites and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumani, H.; Petereit, H.F.; Gerritzen, A.; Gross, C.C.; Huss, A.; Isenmann, S.; Jesse, S.; Khalil, M.; Lewczuk, P.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. S1 guidelines “lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis” (abridged and translated version). Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, M.-C.; Lenggenhager, L.; Schrenzel, J.; Cordey, S.; Kaiser, L. High-throughput sequencing for the aetiologic identification of viral encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, and meningitis. A narrative review and clinical appraisal. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, C.M.; Forbes, R.B. Diagnostic Lumbar Puncture. Ulst. Med. J. 2014, 83, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tumani, H.; Petereit, H.F. Lumbalpunktion und Liquor-diagnostik, S1-Leitlinie. 2019; In Leitlinien für Diagnostik und Therapie in der Neurologie; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Liquordiagnostik und Klinische Neurochemi (Hrsg); Available online: www.dgn.org/leitlinein.Abgerufenam (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- Delpech, B.; Lichtblau, E. Immunochemical estimation of IgG and albumin in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1972, 37, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, E. Immunophoretic studies on cerebrospinal fluid. Klin. Wochenschr. 1959, 37, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerus, J.M.; Brouwer, M.C.; van de Beek, D. Technological advances and changing indications for lumbar puncture in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H.; Peter, J.B. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: Disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 184, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A. Immune-mediated encephalitis for the infectious disease specialist. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincke, H. Die Lumbalpunktion des Hydrocephalus (German). Berl. Klin. Wochenschr. 1891, 32, 861–862. [Google Scholar]
- Wynter, W. Four cases of tubercular meningitis in which paracentesis was performed for the relief of fluid pressure. Lancet 1891, 137, 981–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, A. Ein neues Beleuchtungsverfahren für mikro-photographische Zwecke. Z. Wiss. Mikrosk. 1893, 10, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Widal, F.G.I.; Sicard, J.M.A.; Ravaut, P.J.F. Cytologie du liquide céphalo-rachidien au cours de quelques processes méninges chroniques (paralysis generale et tabes). Bull. Mem. Soc. Med. Hop. Paris 1901, 18, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, A.; Rosenthal, R. Physikalisch-chemische, zytologische und anderweitige Untersuchungen der Cerebrospinalflüssigkeit. Wien. Med. Presse 1904, 45, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann, N.; Zettl, U.K.; Kumbier, E. The Development of Sayk’s Cell Sedimentation Chamber: A Historical View on Clinical Cerebrospinal Fluid Diagnostics. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 77, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmitz, R.; Sayk, J.; Kretschmer, G. Zellsedimentation mit der Sorptionskammer—Vergleichende liquorzytologische Untersuchungen. Z. Med. Lab. Diagn. 1982, 22, 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf, M.T.; de Jongste, A.H.; Kraan, J.; Boonstra, J.G.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Gratama, J.W. Flow cytometric charac-terization of cerebrospinal fluid cells. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2011, 80, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, M.; Gross, C.C.; Tumani, H.; Wildemann, B.; Stangel, M.; Stangel, M. Automated Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells Using Commercially Available Blood Cell Analysis Devices—A Critical Appraisal. Cells 2021, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, H.; Luthe, H.; Nagel, I.; Ehrlich, B.; Bahr, M. Automated cerebrospinal fluid cytology: Limitations and reasonable applications. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 2005, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wick, M.; Gross, C.C.; Isenmann, S.; Strik, H. Cytology of cerebrospinal fluid: Standards, importance and modern methods. Nervenarzt 2016, 87, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Girón, R.; Pantanowitz, L. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in nonmalignant aseptic meningeal disorders. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2017, 45, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, J.; Woehrer, A. Overview of cerebrospinal fluid cytology. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 145, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Radkay, L.; Monaco, S.E.; Roth, C.G.; Pantanowitz, L. Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytology of Lyme Neuroborreliosis: A Report of 3 Cases with Literature Review. Acta Cytol. 2015, 59, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Grummel, V.; Wemlinger, S.; Buck, D.; Weber, M.S.; Berthele, A.; Hemmer, B. Immune cell subtyping in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological diseases. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granerod, J.; Ambrose, H.E.; Davies, N.W.S.; Clewley, J.P.; Walsh, A.L.; Morgan, D.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.J.; Solomon, T.; et al. Causes of encephalitis and differences in their clinical presentations in England: A multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleine, T.O.; Albrecht, J.; Zöfel, P. Flow Cytometry of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Lymphocytes: Alterations of Blood/CSF Ratios of Lymphocyte Subsets in Inflammation Disorders of Human Central Nervous System (CNS). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Mori, K.J.; Saida, T. Cellular immunoregulatory mechanisms in the central nervous system: Characterization of noninflammatory and inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytes. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, E.; Olsson, T.; Correale, J.; Baig, S.; Kostulas, V.; Olsson, O.; Link, H. B cells expressing CD5 are increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 79, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oreja-Guevara, C.; Sindern, E.; Raulf-Heimsoth, M.; Malin, J.P. Analysis of lymphocyte subpopulations in cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood in patients with multiple sclerosis and inflammatory diseases of the nervous system. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1998, 98, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenhammer, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Fitzner, B.; Zettl, U.K. The Cerebrospinal Fluid in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollender, A.; Kvaloy, S.; Nome, O.; Skovlund, E.; Lote, K.; Holte, H. Central nervous system involvement following diagnosis of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A risk model. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenk, L.; Alsadeq, A.; Schewe, D.M. Involvement of the central nervous system in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Opinions on molecular mechanisms and clinical implications based on recent data. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quijano, S.; López, A.; Manuel Sancho, J.; Panizo, C.; Debén, G.; Castilla, C.; Antonio García-Vela, J.; Salar, A.; Alonso-Vence, N.; González-Barca, E.; et al. Identification of leptomeningeal disease in aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Improved sensitivity of flow cytometry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, D.; Fanale, M.A.; Miranda, R.N.; Noorani, M.; Westin, J.R.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Fayad, L.E.; Romaguera, J.E.; Samaniego, F.; et al. The risk of central nervous system relapses in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurion, R.; Mehta, N.; Migliacci, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.; Moskowitz, A.; Lunning, M.; Moskowitz, C.; Hamlin, P.; Horwitz, S. Central nervous system involvement in T-cell lymphoma: A single center experience. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Baumgarten, L.; Illerhaus, G.; Korfel, A.; Schlegel, U.; Deckert, M.; Dreyling, M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary CNS Lymphoma. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2018, 115, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Bessell, E.; Bromberg, J.; Hottinger, A.F.; Preusser, M.; Rudà, R.; Schlegel, U.; Siegal, T.; Soussain, C.; Abacioglu, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: Guidelines from the European Association for Neuro-Oncology. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e322–e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepennetier, G.; Hracsko, Z.; Unger, M.; Van Griensven, M.; Grummel, V.; Krumbholz, M.; Berthele, A.; Hemmer, B.; Kowarik, M.C. Cytokine and immune cell profiling in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuro-inflammatory diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, A.; Pilz, G.; Wipfler, P.; Oppermann, K.; Sellner, J.; Hitzl, W.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Afazel, S.; Rispens, T.; van der, K.D.; et al. High interindividual variability in the CD4/CD8 T cell ratio and natalizumab concentration levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, I.L.; Smith, B.R.; von Geldern, G.; Mateen, F.J.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated opportunistic infections of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Spudich, S.S. HIV-Associated Neurologic Disorders and Central Nervous System Opportunistic Infections in HIV. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, C.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Moloney, P.B.; Hutchinson, S.; Cryan, J.B.; Clarke, S.; Mulcahy, F.; Devitt, E. CD8 en-cephalitis with CSF EBV viraemia and HIV drug resistance, a case series. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2020, 9, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, S.; Andersson, B.; Malmeström, C. Cerebrospinal fluid CD4(+)/CD8(+) ratio in diagnosing neurosarcoidosis. Acta. Neurol. Scand 2020, 142, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazal, T.; Costopoulos, M.; Maillart, E.; Fleury, C.; Psimaras, D.; Legendre, P.; Pineton de Chambrun, M.; Haroche, J.; Lubetzki, C.; Amoura, Z.; et al. The cerebrospinal fluid CD4/CD8 ratio and interleukin-6 and -10 levels in neurosarcoidosis: A multicenter, pragmatic, comparative study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heming, M.; Lohmann, L.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Brix, T.; Gross, C.C.; Wiendl, H.; Klotz, L.; zu Hörste, G.M. Leukocyte profiles in blood and CSF distinguish neurosarcoidosis from multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 341, 577171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enose-Akahata, Y.; Azodi, S.; Smith, B.R.; Billioux, B.J.; Vellucci, A.; Ngouth, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohayon, J.; Cortese, I.; Nath, A.; et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of CSF B cells in virus-associated neuroinflammatory diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.C.; Meyer, C.; Bhatia, U.; Yshii, L.; Kleffner, I.; Bauer, J.; Tröscher, A.R.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Herich, S.; Schneider-Hohendorf, T.; et al. CD8(+) T cell-mediated endotheliopathy is a targetable mechanism of neuro-inflammation in Susac syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, T.; Salgado, A.D.; Mexhitaj, I.; Wuest, S.C.; Romm, E.; Ohayon, J.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Vanderver, A.; et al. Comprehensive Immunophenotyping of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Patients with Neuroimmunological Diseases. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrer, C.; Otto, F.; Pilz, G.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Trinka, E.; Hitzl, W.; Wipfler, P.; Harrer, A. The CXCL13/CXCR5-chemokine axis in neuroinflammation: Evidence of CXCR5+CD4 T cell recruitment to CSF. Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrate, A.E.; Ryman, D.C.; Ma, S.; Xiong, C.; Noble, J.M.; Ringman, J.M.; Morris, J.C.; Danek, A.; Müller-Sarnowski, F.; Clifford, D.B.; et al. Factors Associated with the Onset and Persistence of Post–Lumbar Puncture Headache. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bento, L.C.; Correia, R.P.; Alexandre, A.M.; Nosawa, S.T.; Pedro, E.C.; Vaz, A.D.C.; Schimidell, D.; Fernandes, G.B.P.; Duarte, C.A.S.; Barroso, R.S.; et al. Detection of Central Nervous System Infiltration by Myeloid and Lym-phoid Hematologic Neoplasms Using Flow Cytometry Analysis: Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, T.V.; Probstel, A.K.; Mildenberger, I.; Platten, M.; Schirmer, L. Single-Cell High-Throughput Technologies in Cerebrospinal Fluid Research and Diagnostics. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, M.H.; Nolan, G.P. Mass Cytometry: Single Cells, Many Features. Cell 2016, 165, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galli, E.; Hartmann, F.J.; Schreiner, B.; Ingelfinger, F.; Arvaniti, E.; Diebold, M.; Mrdjen, D.; Van Der Meer, F.; Krieg, C.; Al Nimer, F.A.; et al. GM-CSF and CXCR4 define a T helper cell signature in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, D.; Rauld, C.; Roux, J.; Regairaz, C.; Galli, E.; Callegari, I.; Raad, L.; Waldt, A.; Cuttat, R.; Roma, G.; et al. Mass Cytometry of CSF Identifies an MS-Associated B-cell Population. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafflick, D.; Xu, C.A.; Hartlehnert, M.; Cole, M.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Lautwein, T.; Wolbert, J.; Heming, M.; Meuth, S.G.; Kuhlmann, T.; et al. Integrated single cell analysis of blood and cerebrospinal fluid leukocytes in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhadian, S.F.; Mehta, S.S.; Zografou, C.; Robertson, K.; Price, R.W.; Pappalardo, J.; Chiarella, J.; Hafler, D.A.; Spudich, S.S. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals microglia-like cells in cerebrospinal fluid during virologically suppressed HIV. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palanichamy, A.; Apeltsin, L.; Kuo, T.C.; Sirota, M.; Wang, S.; Pitts, S.J.; Sundar, P.D.; Telman, D.; Zhao, L.Z.; Derstine, M.; et al. Immunoglobulin class-switched B cells form an active immune axis between CNS and periphery in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 248ra106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, J.N.H.; Yaari, G.; Vander Heiden, J.A.; Church, G.; Donahue, W.F.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Huttner, A.J.; Laman, J.D.; Nagra, R.M.; Nylander, A.; et al. B cells populating the multiple sclerosis brain mature in the draining cervical lymph nodes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 248ra107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lovato, L.; Willis, S.N.; Rodig, S.J.; Caron, T.; Almendinger, S.E.; Howell, O.W.; Reynolds, R.; O’Connor, K.C.; Hafler, D.A. Related B cell clones populate the meninges and parenchyma of patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain 2011, 134 Pt 2, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Astling, D.; Lepennetier, G.; Ritchie, A.; Hemmer, B.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. Differential Effects of Fingolimod and Natalizumab on B Cell Repertoires in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.; Leventhal, O.; Channappa, D.; Henderson, V.W.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Lehallier, B.; Gate, D. Methods to investigate intrathecal adaptive immunity in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvermann, S.; Hennig, C.; Stuve, O.; Wiendl, H.; Stangel, M. Immunophenotyping of cerebrospinal fluid cells in multiple sclerosis: In search of biomarkers. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielekova, B.; Pranzatelli, M.R. Promise, Progress, and Pitfalls in the Search for Central Nervous System Biomarkers in Neu-roimmunological Diseases: A Role for Cerebrospinal Fluid Immunophenotyping. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 24, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Spidlen, J.; Boyce, K.; Cai, J.; Crosbie, N.; Dalphin, M.; Furlong, J.; Gasparetto, M.; Goldberg, M.; Goralczyk, E.M.; et al. MIFlowCyt: The minimum information about a flow cytometry experiment. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2008, 73, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subirá, D.; Castañón, S.; Román, A.; Aceituno, E.; Jiménez-Garófano, C.; Jiménez, A.; García, R.; Bernácer, M. Flow cytometry and the study of central nervous disease in patients with acute leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 112, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.T.; van den Broek, P.D.; Kraan, J.; Luitwieler, R.L.; van den Bent, M.J.; Boonstra, J.G.; Schmitz, P.I.M.; Gratama, J.W.; Smitt, P.A.S. Addition of serum-containing medium to cerebrospinal fluid prevents cellular loss over time. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Jongste, A.H.; de Graaf, M.T.; van den Broek, P.D.; Kraan, J.; Smitt, P.A.; Gratama, J.W. Elevated numbers of regulatory T cells, central memory T cells and class-switched B cells in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with anti-Hu antibody associated paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 258, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, V.; Schmid, S.; Gelderblom, M.; Hackbusch, R.; Kolster, M.; Schuster, S.; Thomalla, G.; Keminer, O.; Pleß, O.; Bernreuther, C.; et al. IL-17 production by CSF lymphocytes as a biomarker for cerebral vasculitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melzer, N.; Golombeck, K.S.; Gross, C.C.; Meuth, S.G.; Wiendl, H. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and CD138+ plasma cells prevail in cerebrospinal fluid in non-paraneoplastic cerebellar ataxia with contactin-associated protein-2 antibodies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dale, R.C.; Tantsis, E.; Merheb, V.; Brilot, F. Cerebrospinal fluid B-cell expansion in longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis associated with neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.C.; Pillai, S.; Brilot, F. Cerebrospinal fluid CD19(+) B-cell expansion in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Kleffner, I.; Beuker, C.; Wirth, T.; Hartwig, M.; Schmidt-Pogoda, A.; Klotz, L.; Hansen, W.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Immunophenotyping of cerebrospinal fluid cells in ischaemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueg, G.; Gross, C.C.; Lohmann, H.; Johnen, A.; Kemmling, A.; Deppe, M.; Groger, J.; Minnerup, J.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Clinical relevance of specific T-cell activation in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenbruch, L.; Bleß, L.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Sundermann, B.; Brix, T.; Elger, C.E.; Melzer, N.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Gross, C.C.; et al. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid immune cell profiles in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy of different etiologies. Epilepsia 2020, 61, e153–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczylowski, K.; Grygorczuk, S.; Osada, J.; Wojtkowska, M.; Bojkiewicz, E.; Wozinska-Klepadlo, M.; Potocka, P.; Sulik, A. Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid CXCL13 concentrations and lymphocyte subsets in tick-borne encephalitis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heming, M.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Brix, T.; Wolbert, J.; Ruland, T.; Klotz, L.; Meuth, S.G.; Gross, C.C.; Wiendl, H.; Zu Hörste, G.M. Immune Cell Profiling of the Cerebrospinal Fluid Provides Pathogenetic Insights Into Inflammatory Neuropathies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Njemini, R.; Onyema, O.O.; Renmans, W.; Bautmans, I.; De Waele, M.; Mets, T. Shortcomings in the Application of Multicolour Flow Cytometry in Lymphocyte Subsets Enumeration. Scand. J. Immunol. 2014, 79, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otto, F.; Harrer, C.; Pilz, G.; Wipfler, P.; Harrer, A. Role and Relevance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Diagnostics and Research: State-of-the-Art and Underutilized Opportunities. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010079
Otto F, Harrer C, Pilz G, Wipfler P, Harrer A. Role and Relevance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Diagnostics and Research: State-of-the-Art and Underutilized Opportunities. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtto, Ferdinand, Christine Harrer, Georg Pilz, Peter Wipfler, and Andrea Harrer. 2022. "Role and Relevance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Diagnostics and Research: State-of-the-Art and Underutilized Opportunities" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010079
APA StyleOtto, F., Harrer, C., Pilz, G., Wipfler, P., & Harrer, A. (2022). Role and Relevance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells in Diagnostics and Research: State-of-the-Art and Underutilized Opportunities. Diagnostics, 12(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010079





