Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Imaging and Measurements
2.3. Observer Variability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
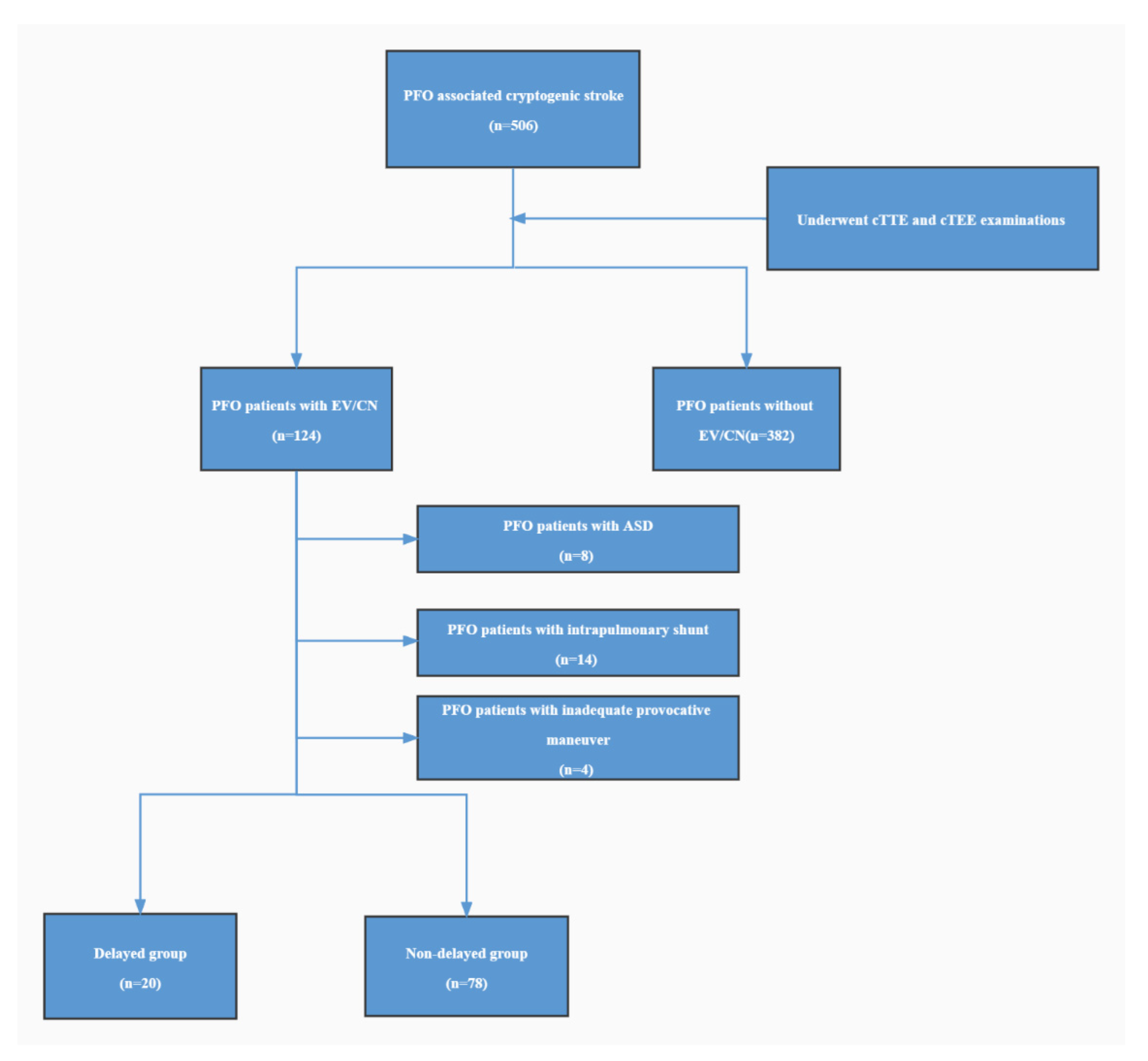
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
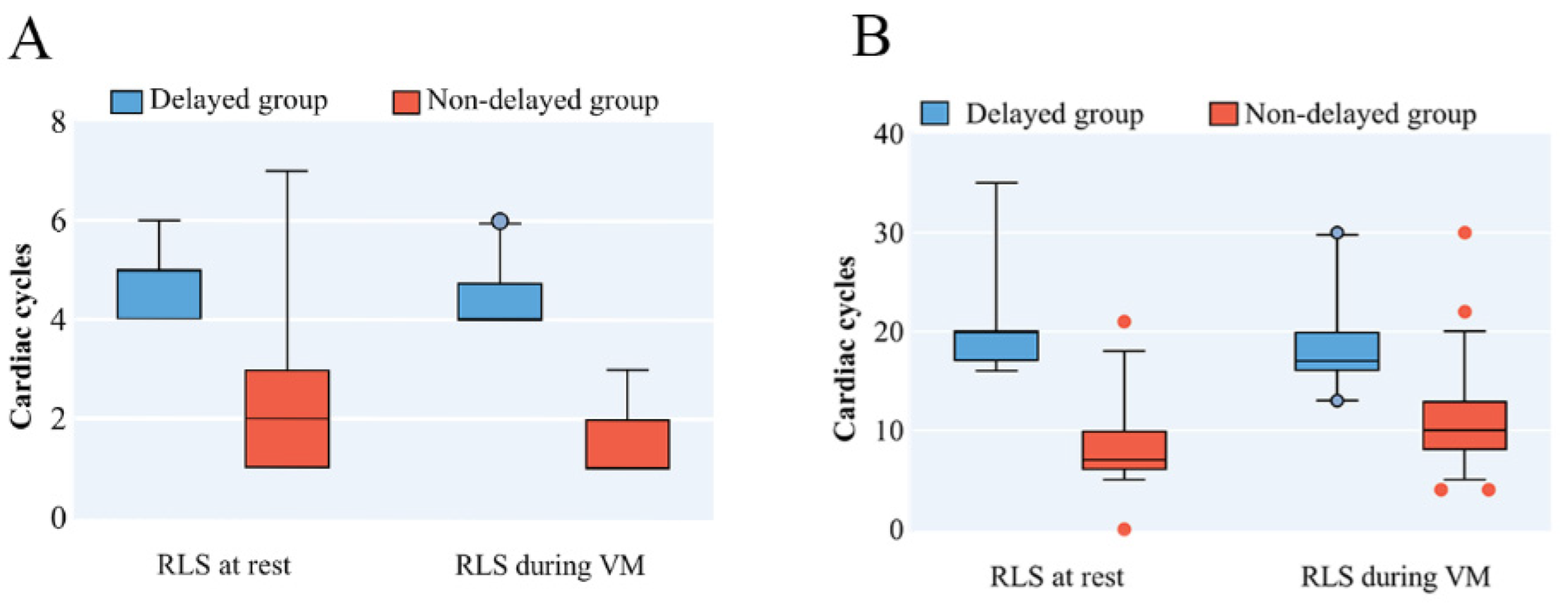
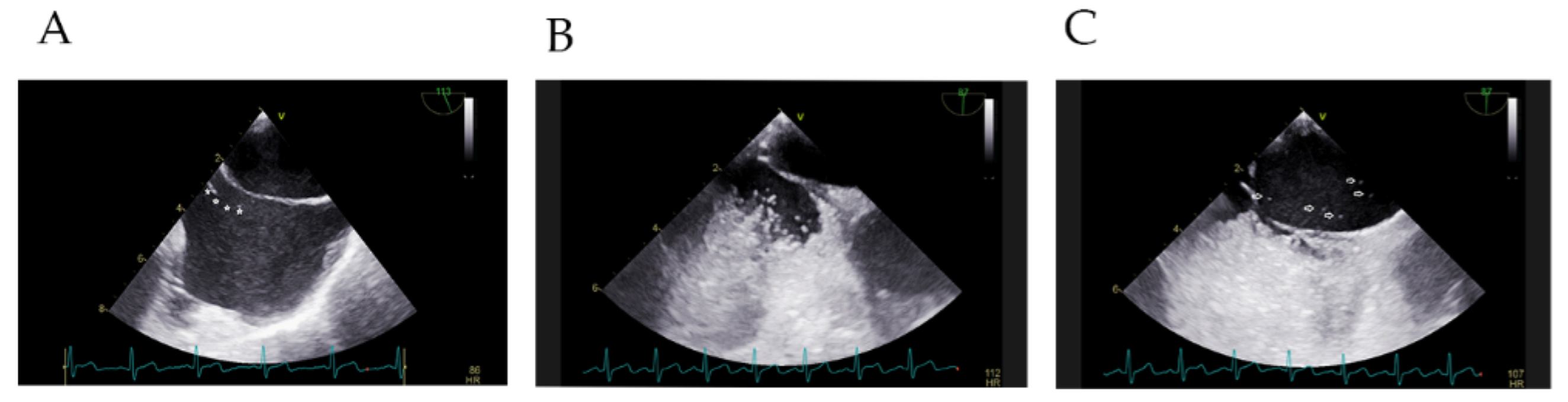
3.2. Characteristics of RLS in PFO Patients with Prominent EV/CN on cTTE
3.3. Factors Related to RLS
3.4. Observer Variability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Messé, S.R.; Gronseth, G.S.; Kent, D.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Homma, S.; Rosterman, L.; Carroll, J.D.; Ishida, K.; Sangha, N.; Kasner, S.E. Practice advisory update summary: Patent foramen ovale and secondary stroke prevention: Report of the Guideline Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2020, 94, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.J.; Ahmad, M. Eustachian valve, interatrial shunt, and paradoxical embolism. Echocardiography 2020, 37, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglessis, I.; Elmariah, S.; Rengifo-Moreno, P.A.; Margey, R.; O’Callaghan, C.; Cruz-Gonzalez, I.; Baron, S.; Mehrotra, P.; Tan, T.C.; Hung, J.; et al. Long-term experience and outcomes with transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’Avvocata, F.; Cardaioli, P.; Giordan, M.; Braggion, G.; Aggio, S.; Chinaglia, M.; Mandapaka, S.; Kuruvilla, J.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Permanent right-to-left shunt is the key factor in managing patent foramen ovale. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’avvocata, F.; Braggion, G.; Giordan, M.; Chinaglia, M.; Cardaioli, P. Persistent venous valves correlate with increased shunt and multiple preceding cryptogenic embolic events in patients with patent foramen ovale: An intracardiac echocardiographic study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 72, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhris, M.; Masson, J.B.; Potvin, J. Challenging Diagnosis of Patent Foramen Ovale in Presence of a Large Eustachian Valve. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2021, 33, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchlenz, H.W.; Weihs, W.; Hackl, E.; Rehak, P. A large Eustachian valve is a confounder of contrast but not of color Doppler transesophageal echocardiography in detecting a right-to-left shunt across a patent foramen ovale. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 109, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestry, F.E.; Cohen, M.S.; Armsby, L.B.; Burkule, N.J.; Fleishman, C.E.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Lang, R.M.; Rome, J.J.; Wang, Y.; American Society of Echocardiography; et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect and Patent Foramen Ovale: From the American Society of Echocardiography and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 910–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, S.; Churchill, T.W.; Namasivayam, M.; Bertrand, P.B. Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography in the Identification of Intra- and Extracardiac Shunts: Connecting the Dots. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2020, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, E.F.; Du, Y.J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.S. Modified Method of Contrast Transthoracic Echocardiography for the Diagnosis of Patent Foramen Ovale. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9828539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, E.; Murata, T.; Goto, E.; Fujiwara, T.; Sasaki, T.; Minami, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kumagai, K.; Naito, S.; Kario, K.; et al. Inferior Vena Cava Compression as a Novel Maneuver to Detect Patent Foramen Ovale: A Transesophageal Echocardiographic Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.M.; Bierig, M.; Devereux, R.B.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Pellikka, P.A.; Picard, M.H.; Roman, M.J.; Seward, J.; Shanewise, J.; et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2006, 7, 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, S.; Cartoni, D.; Fiorelli, M.; Rasura, M.; Anzini, A.; Zanette, E.M.; Beccia, M.; Colonnese, C.; Fedele, F.; Fieschi, C.; et al. Morphological and functional characteristics of patent foramen ovale and their embolic implications. Stroke 2000, 31, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, S.; Buscarini, E.; Gossage, J.R.; Snijder, R.J.; Mager, J.J.; Post, M.C. Clinical implications of pulmonary shunting on saline contrast echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Kuan, P.; Lien, W.P.; Lin, F.Y. Detection of patent foramen ovale by contrast transesophageal echocardiography. Chest 1992, 101, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, P.S.; Telles-Hernandez, L.; Miller, R.; Hill, G.E.D.; Almassi, G.H. Selective Partial Obstruction of Inferior Vena Cava Blood Flow During Diastole: Cor Triatriatum Dexter, Large Eustachian Valve, or Chiari Network? J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerut, E.K.; Norfleet, W.T.; Plotnick, G.D.; Giles, T.D. Patent foramen ovale: A review of associated conditions and the impact of physiological size. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 38, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, K.G.; Huckell, V.F.; Pollick, C. Femoral vein delivery of contrast medium enhances transthoracic echocardiographic detection of patent foramen ovale. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.W. When to use femoral vein injection for diagnosis of patent foramen ovale-Effect of a persistent eustachian valve on right atrial flow patterns during contrast transesophageal echocardiography. Echocardiography 2017, 34, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | PFO with EV/CN Patients (N = 98) | PFO with EV/CN Patients | Pulmonary RLS (N = 42) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delayed Group (N = 20) | Non-Delayed Group (N = 78) | ||||
| Age, yrs | 42 ± 14 | 35 ± 7 * | 46(31–55) | 35 ± 11 * | 0.001 a |
| Male | 51(52) | 13(65) | 38(49) | 14(33) | 0.054 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26(23–28) | 25 ± 4 | 25 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 | 0.097 |
| History of DM | 8(8) | 2(10) | 6(6) | 4(9) | 0.915 |
| History of HTN | 24(24) | 3(15) | 21(27) | 6(14) | 0.206 |
| Parameter | Non-Delayed Group | Delayed Group | Pulmonary RLS | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of RLS Occurrence at Rest | 2.00 (1.00–3.00) | 5.00 (4.00–5.00) | 5.00 (4.00–5.00) | <0.001 a |
| Time of RLS Occurrence after VM | 1.00 (1.00–2.00) | 4.00 (4.00–4.75) | 4.00 (4.00–5.00) | <0.001 a |
| Duration at Rest | 7.00 (6.00–10.00) | 20.00 (17.00–20.00) | 20.00 (20.00–25.00) | <0.001 a |
| Duration after VM | 10.80 ± 4.31 | 17.00 (16.00–20.00) | 21.95 ± 5.99 | <0.001 a |
| Amount of RLS after VM | 50.00 (31.00–79.75) | 32.00 (26.25–45.50) | 50 (31.75–100.00) | 0.026 a |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value |
| Prevalence of EV | 1.545 (0.570–4.188) | 0.392 | ||
| Length of EV/CN (>19 mm) | 5.176 (1.585–16.906) | 0.006 a | 8.412 (1.544–45.820) | 0.014 a |
| The diameter of PFO at left atrium aspect (<1.2 mm) | 12.013 (3.221–44.804) | <0.001 a | 14.806 (2.415–90.780) | 0.004 a |
| The diameter of PFO at right atrium aspect (<1.0 mm) | 12.000 (3.582–40.205) | <0.001 a | ||
| Length of tunnel | 0.959 (0.833–1.103) | 0.556 | ||
| The angle between IVC and PFO flap | 1.014 (0.981–1.047) | 0.421 | ||
| The angle between EV/CN and PFO flap | 0.998 (0.973–1.024) | 0.862 | ||
| Prevalence of LRS | 0.436 (0.339–0.561) | <0.001 a | ||
| Hypermobile primary septum | 0.859 (0.785–0.940) | 0.166 | ||
| Age | 0.955 (0.918–0.933) | 0.02 a | ||
| Outcomes Compared | ICC | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance at Rest Intraobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O1(second outcome) | 0.951 | 0.864–0.983 |
| Appearance at Rest Interobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O2 | 0.951 | 0.864–0.983 |
| Duration at Rest Intraobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O1(second outcome) | 1.000 | 1.000–1.000 |
| Duration at Rest Interobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O2 | 0.979 | 0.938–0.993 |
| Appearance at VM Intraobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O1(second outcome) | 0.951 | 0.864–0.983 |
| Appearance at VM Interobserver | O1(first outcome) vs O2 | 1.000 | 1.000–1.000 |
| Duration at VM Intraobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O1(second outcome) | 0.971 | 0.917–0.990 |
| Duration at VM Interobserver | O1(first outcome) vs. O2 | 0.945 | 0.845–0.981 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102283
Zhang H, Liu W, Ma J, Liu H, Li L, Zhou J, Wang S, Li S, Wang W, Wang Y. Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102283
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Han, Weiwei Liu, Jie Ma, Huanling Liu, Lin Li, Jinling Zhou, Shanshan Wang, Shanshan Li, Wei Wang, and Yueheng Wang. 2022. "Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102283
APA StyleZhang, H., Liu, W., Ma, J., Liu, H., Li, L., Zhou, J., Wang, S., Li, S., Wang, W., & Wang, Y. (2022). Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102283





