Proposals for Standardization of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring during Parotid Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
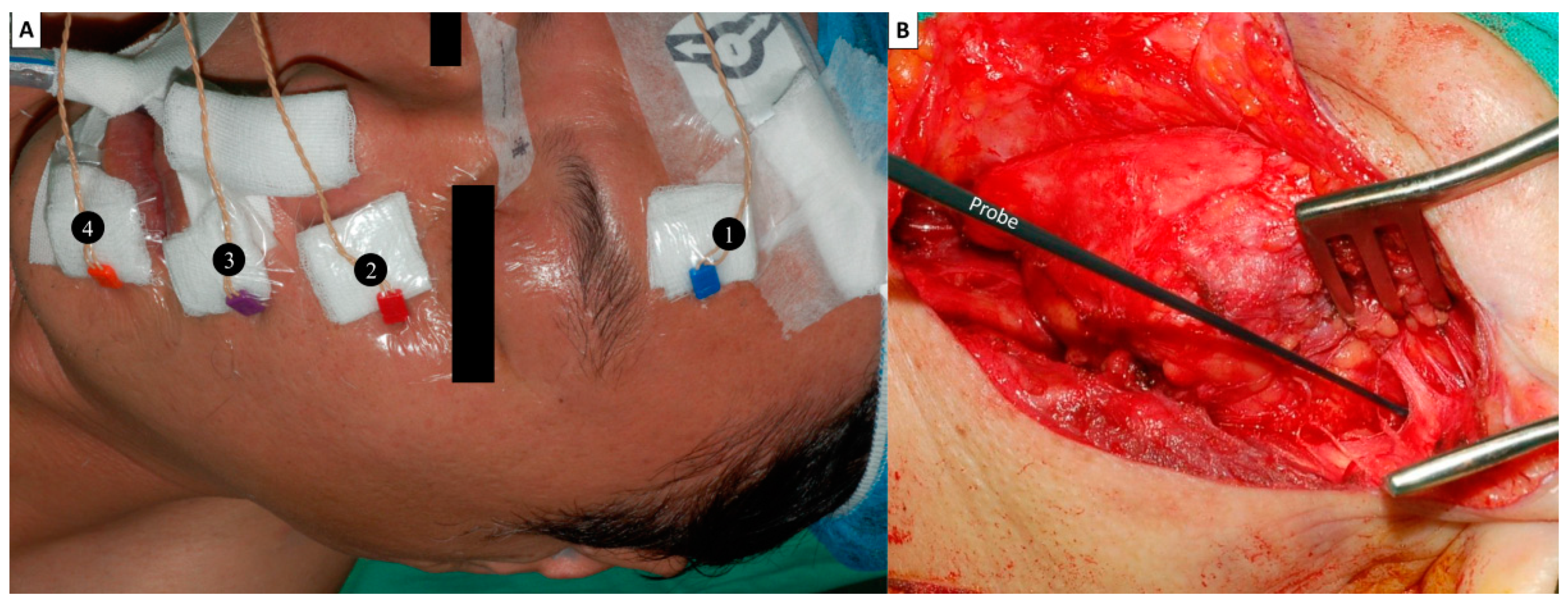
2. Standards in FNM Setup
3. Standards in General Anesthesia
4. Standards in FNM Procedures/Application of Stimulus Currents
5. Interpretation of EMG Signals/Prediction of the Facial Expression Outcome
6. Pre-/Post-Operative Assessment of Facial Expressions
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fliss, E.; Yanko, R.; Zaretski, A.; Tulchinsky, R.; Arad, E.; Kedar, D.J.; Fliss, D.M.; Gur, E. Facial Nerve Repair following Acute Nerve Injury. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.M.; Baba, H.O.; Saeed, Y.A.; Muhialdeen, A.S.; Kakamad, F.H.; Mohammed, S.H.; Hammood, Z.D.; Salih, K.M.; Salih, R.Q.; Hussein, D.A. Pattern of facial nerve palsy during parotidectomy: A single-center experience. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 03000605221108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Park, W.; Choi, S.; Chung, M.K.; Son, Y.-I.; Baek, C.-H.; Jeong, H.-S. Incidence of postoperative facial weakness in parotid tumor surgery: A tumor subsite analysis of 794 parotidectomies. BMC Surg. 2019, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, K.R. Socioemotional functioning with facial paralysis: Is there a congenital or acquired advantage? Health Psychol. 2020, 39, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, C.J. Current management of benign parotid tumors—The role of limited superficial parotidectomy. Head Neck J. Sci. Spec. Head Neck 2003, 25, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrell, J.E.; Kileny, P.R.; Yian, C.; Esclamado, R.M.; Bradford, C.R.; Pillsbury, M.S.; Wolf, G.T. Clinical outcome of continuous facial nerve monitoring during primary parotidectomy. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 123, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisele, D.W.; Wang, S.J.; Orloff, L.A. Electrophysiologic facial nerve monitoring during parotidectomy. Head Neck J. Sci. Spec. Head Neck 2010, 32, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulguerov, P.; Marchal, F.; Lehmann, W. Postparotidectomy facial nerve paralysis: Possible etiologic factors and results with routine facial nerve monitoring. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehle, M.E.; Kraus, D.H.; Wood, B.G.; Benninger, M.S.; Eliachar, I.; Levine, H.L.; Tucker, H.M.; Lavertu, P. Facial nerve morbidity following parotid surgery for benign disease: The Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience. Laryngoscope 1993, 103, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, L.P.; O’Brien, C.J. Facial nerve function after parotidectomy. Arch. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 1997, 123, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, R.L. Facial nerve function after partial superficial parotidectomy: An 11-year review (1987–1997). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 121, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mra, Z.; Komisar, A.; Blaugrund, S.M. Functional facial nerve weakness after surgery for benign parotid tumors: A multivariate statistical analysis. Head Neck 1993, 15, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Larruscain-Sarasola, E.; Lechien, J.R.; Mouawad, F.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Diom, E.S.; Ramirez, A.; Ayad, T. Facial nerve monitoring during parotid gland surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajisevi, M. Indications for Facial Nerve Monitoring During Parotidectomy. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 54, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graciano, A.J.; Fischer, C.A.; Coelho, G.V.; Steck, J.H.; Paschoal, J.R.; Chone, C.T. Facial nerve dysfunction after superficial parotidectomy with or without continuous intraoperative electromyographic neuromonitoring: A prospective randomized pilot study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballivet-de Régloix, S.; Grinholtz-Haddad, J.; Maurin, O.; Genestier, L.; Lisan, Q.; Pons, Y. Facial nerve monitoring during parotidectomy: A two-center retrospective study. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 28, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Grosheva, M.; Klussmann, J.P.; Grimminger, C.; Wittekindt, C.; Beutner, D.; Pantel, M.; Volk, G.F.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Electromyographic facial nerve monitoring during parotidectomy for benign lesions does not improve the outcome of postoperative facial nerve function: A prospective two-center trial. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvas, E.; Hillmann, S.; Weiss, D.; Koopmann, M.; Rudack, C.; Alberty, J. Association between facial nerve monitoring with postoperative facial paralysis in parotidectomy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.J.; Houlton, J.J.; Nguyen, S.A.; Gillespie, M.B. Facial nerve monitoring during parotidectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, K.; Akyildiz, S.; Gode, S.; Turhal, G.; Gursan, G.; Kirazli, T. The effect of partial superficial parotidectomy on amplitude, latency and threshold of facial nerve stimulation. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.D.; Wenig, B.L.; Manders, E.C.; Nenonene, E.K. Continuous intraoperative facial nerve monitoring in predicting postoperative injury during parotidectomy. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelle, E.; Bernat, I.; Pichon, S.; Granger, B.; Sain-Oulhen, C.; Lamas, G.; Tankéré, F. Supramaximal stimulation during intraoperative facial nerve monitoring as a simple parameter to predict early functional outcome after parotidectomy. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2013, 133, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, F.-Y.; Lee, K.-W.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lu, I.-C.; Kuo, W.-R.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Wu, C.-W. Standardization of intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid operation. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, G.W.; Dralle, H.; International Intraoperative Monitoring Study Group; Abdullah, H.; Barczynski, M.; Bellantone, R.; Brauckhoff, M.; Carnaille, B.; Cherenko, S.; Chiang, F.Y. Electrophysiologic recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery: International standards guideline statement. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lien, C.-F.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Hwang, T.-Z.; Shih, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-W.; Dionigi, G.; Huang, T.-Y.; Chiang, F.-Y. Necessity of Routinely Testing the Proximal and Distal Ends of Exposed Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve During Monitored Thyroidectomy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 923804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-W.; Huang, T.-Y.; Randolph, G.W.; Barczyński, M.; Schneider, R.; Chiang, F.-Y.; Karcioglu, A.S.; Wojtczak, B.; Frattini, F.; Gualniera, P. Informed Consent for Intraoperative Neural Monitoring in Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery–Consensus Statement of the International Neural Monitoring Study Group. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 795281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-W.; Randolph, G.W.; Barczyński, M.; Schneider, R.; Chiang, F.-Y.; Huang, T.-Y.; Karcioglu, A.S.; Konturek, A.; Frattini, F.; Weber, F. Training courses in laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid and parathyroid surgery-the INMSG consensus statement. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 708, 705346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Cheng, K.I.; Lu, I.C.; Chiang, F.Y. Influence of intravenous anesthetics on neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Hsu, H.T.; Tseng, K.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Lee, K.W.; Ho, K.Y.; Chiang, F.Y. A comparison between succinylcholine and rocuronium on the recovery profile of the laryngeal muscles during intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve: A prospective porcine model. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.-C.; Tsai, C.-J.; Wu, C.-W.; Cheng, K.-I.; Wang, F.-Y.; Tseng, K.-Y.; Chiang, F.-Y. A comparative study between 1 and 2 effective doses of rocuronium for intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroid surgery. Surgery 2011, 149, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiede, O.; Klüsener, T.; Sielenkämper, A.; Van Aken, H.; Stoll, W.; Schmäl, P.D.m.F. Interference between muscle relaxation and facial nerve monitoring during parotidectomy. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.-C.; Chang, P.-Y.; Su, M.-P.; Chen, P.-N.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chiang, F.-Y.; Wu, C.-W. The feasibility of sugammadex for general anesthesia and facial nerve monitoring in patients undergoing parotid surgery. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencke, T.; Echternach, M.; Kleinschmidt, S.; Lux, P.; Barth, V.; Plinkert, P.K.; Fuchs-Buder, T. Laryngeal morbidity and quality of tracheal intubation: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2003, 98, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrøm, L.; Møller, A.; Rosenstock, C.; Astrup, G.; Gätke, M.; Wetterslev, J.; Database, D.A. Avoidance of neuromuscular blocking agents may increase the risk of difficult tracheal intubation: A cohort study of 103 812 consecutive adult patients recorded in the Danish Anaesthesia Database. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 103, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, X.; Andriamifidy, L.; Dufresne, E.; Suen, P.; Sauvat, S.; Scherrer, E.; Feiss, P.; Marty, J.; Duvaldestin, P. Comparison of two induction regimens using or not using muscle relaxant: Impact on postoperative upper airway discomfort. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orebaugh, S.L. Succinylcholine: Adverse effects and alternatives in emergency medicine. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-W.; Lu, I.-C.; Chang, P.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lien, C.-F.; Wang, C.-C.; Huang, T.-Y.; Hwang, T.-Z. Correlation between Electrophysiological Change and Facial Function in Parotid Surgery Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behm, D.; Whittle, J.; Button, D.; Power, K. Intermuscle differences in activation. Muscle Nerve 2002, 25, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.J.; Gabaldón, A.M. Interpreting muscle function from EMG: Lessons learned from direct measurements of muscle force. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, W. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burres, S.; Fisch, U. The comparison of facial grading systems. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1986, 112, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, G.E.; Diver, J.P.; Kelly, P.J.; O’Donoghue, G.; Bradley, P.J. The Nottingham System: Objective assessment of facial nerve function in the clinic. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1994, 110, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxson, G.; May, M.; Mester, S.J. Grading facial nerve function: House-Brackmann versus Burres-Fisch methods. Am. J. Otol. 1990, 11, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, B.F.; Soraghan, J.J.; McGrenary, S.; He, S. Objective method of assessing and presenting the House-Brackmann and regional grades of facial palsy by production of a facogram. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stodulski, D.; Skorek, A.; Mikaszewski, B.; Wiśniewski, P.; Stankiewicz, C. Facial nerve grading after parotidectomy. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.G.; Fradet, G.; Nedzelski, J.M. Development of a sensitive clinical facial grading system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 114, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranhão-Filho, P.d.A.; Santos, I.C.; Luiz, R.R.; Vincent, M.B. Parotidectomy-related facial nerve lesions: Proposal for a modified Sunnybrook Facial Grading System. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2019, 77, 460–469. [Google Scholar]
- Adour, K.; Swanson, P., Jr. Facial paralysis in 403 consecutive patients: Emphasis on treatment response in patients with Bell’s palsy. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1971, 75, 1284–1301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pillsbury, H.C.; Fisch, U. Extratemporal facial nerve grafting and radiotherapy. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1979, 105, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.W. Facial nerve grading systems. Laryngoscope 1983, 93, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, T.L.; Driscoll, C.L.; Lalwani, A.K. Significance of House-Brackmann facial nerve grading global score in the setting of differential facial nerve function. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, S.E.; Croxson, G.R.; Adams, R.D.; O’Dwyer, N.J. Reliability of the “Sydney,”“Sunnybrook,” and “House Brackmann” facial grading systems to assess voluntary movement and synkinesis after facial nerve paralysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagihara, N. Grading of facial palsy. In Proceedings of the Facial Nerve Surgery, Third International Symposium on Facial Nerve Surgery, Aesculapius, Zurich, Switzerland, 9–12 August 1976. [Google Scholar]



| Phases | Procedures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-operative | Pre-operative video recording of facial expression | Four dynamic facial movements: wrinkling foreheads, tightly closing eyes, whistling and a wide smile |
| Intra-operative | FNM setup | Recording electrodes are inserted into the muscles over lower forehead, infraorbital area, superolateral upper lip and inferolateral lower lip |
| General anesthesia (NMBA use) | (1) A small dose of non-depolarizing NMBA (rocuronium, 0.3 mg/kg or mivacurium, 0.2 mg/kg), (2) standard dose of rocuronium combined with reversal agent (sugammadex, 1–2 mg/kg) | |
| FNM procedures (V-L-F1-F2) | ||
| V—Verification (10 mA) | Stimulus for mandibular angle area and verification of the functional FNM system before parotid gland dissection | |
| L—Localization (5 mA) | Stimulus for FN trunk during parotid gland dissection and facilitate the identification of the FN trunk | |
| F1—Pre-dissection FN signal (3–5 mA) | Signals were obtained when the FN trunk is first identified | |
| F2—Post-dissection FN signal (3–5 mA) | Signals were obtained after dissecting the FN branches and resecting the parotid tumor | |
| Interpretation of EMG signals (F1/F2 ratio) | Prediction of facial expression outcome | |
| Unchanged or Increased | Intact FN branch function | |
| Decreased (>20%↓) | Neural injury point mapping procedure—Mapping the injured area of the corresponding FN branch from the distal to proximal end with 1 mA | |
| Post-operative | Post-operative video recording of facial expression | The dynamic movements of individual muscle groups over four separate facial regions are recorded and the total score of the patient’s facial function was 12, registered as T(0–3)Z(0–3)B(0–3)M(0–3) |
| 0 (Severe facial dysfunction) | A complete lack of dynamic movement | |
| 1 (Moderate facial dysfunction) | Obvious asymmetrical dynamic movement, but movement is observable | |
| 2 (Mild facial dysfunction) | Slightly asymmetrical dynamic movement, but symmetrical expression can be achieved after the movement is completed | |
| 3 (Normal facial function) | Fully symmetrical dynamic movement of the facial area |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiang, F.-Y.; Lien, C.-F.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Hwang, T.-Z.; Shih, Y.-C.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-C.; Huang, T.-Y. Proposals for Standardization of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring during Parotid Surgery. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102387
Chiang F-Y, Lien C-F, Wang C-C, Wang C-C, Hwang T-Z, Shih Y-C, Tseng H-Y, Wu C-W, Huang Y-C, Huang T-Y. Proposals for Standardization of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring during Parotid Surgery. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102387
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiang, Feng-Yu, Ching-Feng Lien, Chih-Chun Wang, Chien-Chung Wang, Tzer-Zen Hwang, Yu-Chen Shih, Hsin-Yi Tseng, Che-Wei Wu, Yaw-Chang Huang, and Tzu-Yen Huang. 2022. "Proposals for Standardization of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring during Parotid Surgery" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102387
APA StyleChiang, F.-Y., Lien, C.-F., Wang, C.-C., Wang, C.-C., Hwang, T.-Z., Shih, Y.-C., Tseng, H.-Y., Wu, C.-W., Huang, Y.-C., & Huang, T.-Y. (2022). Proposals for Standardization of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring during Parotid Surgery. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102387







