Role of an Automated Deep Learning Algorithm for Reliable Screening of Abnormality in Chest Radiographs: A Prospective Multicenter Quality Improvement Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
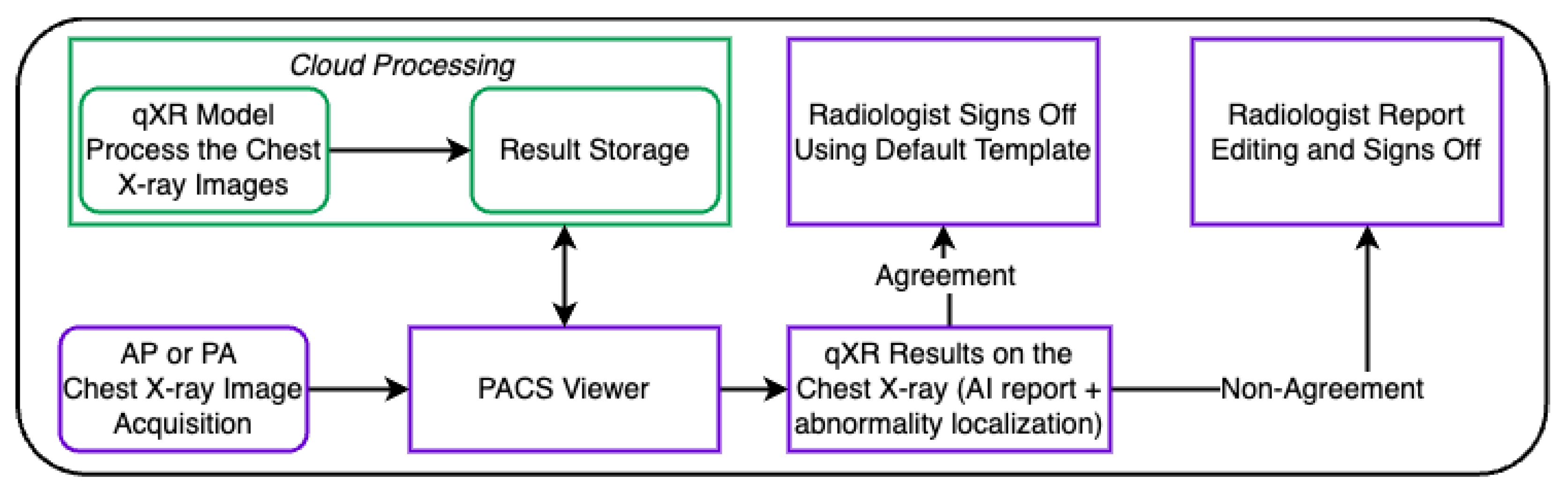
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
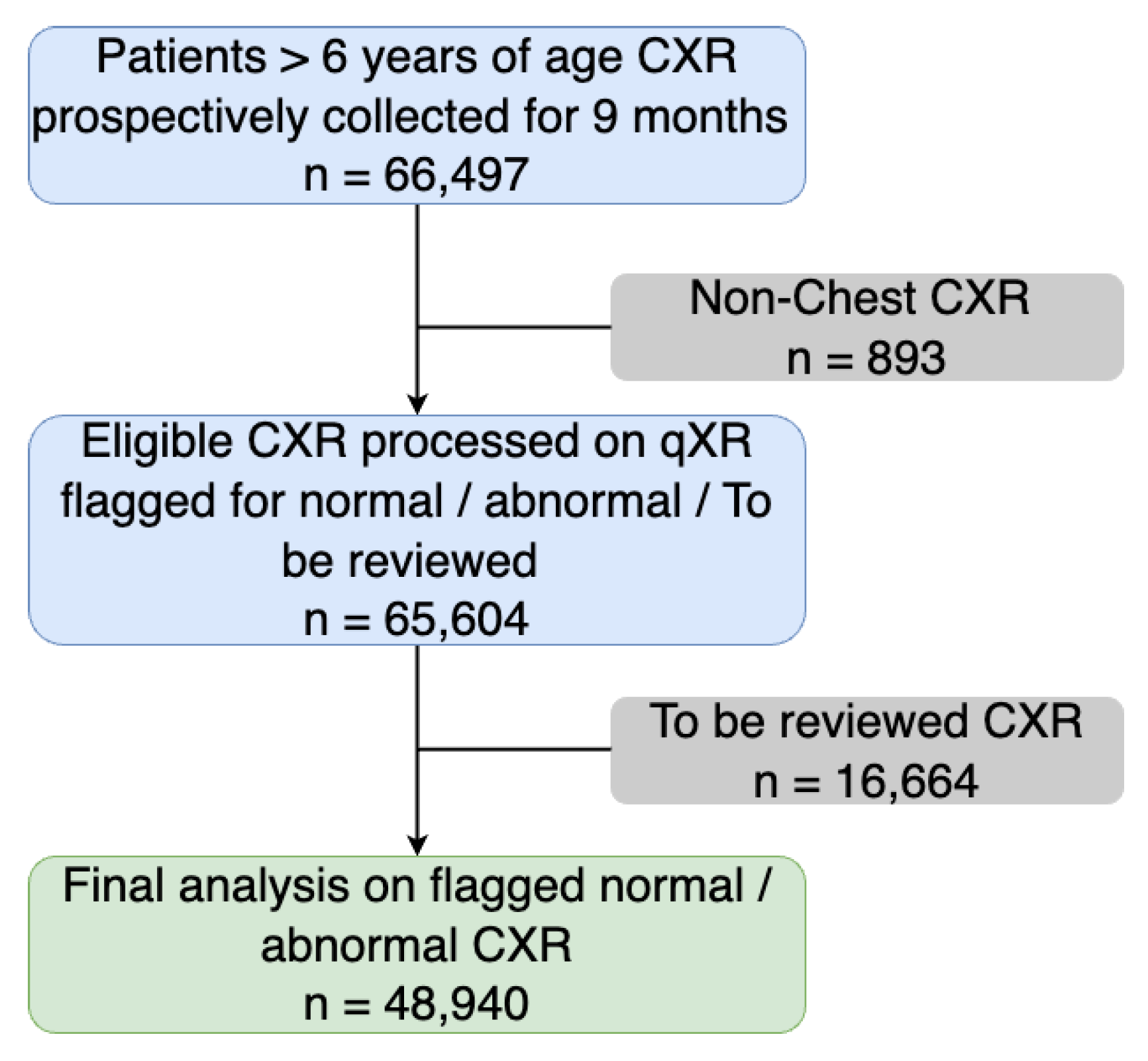
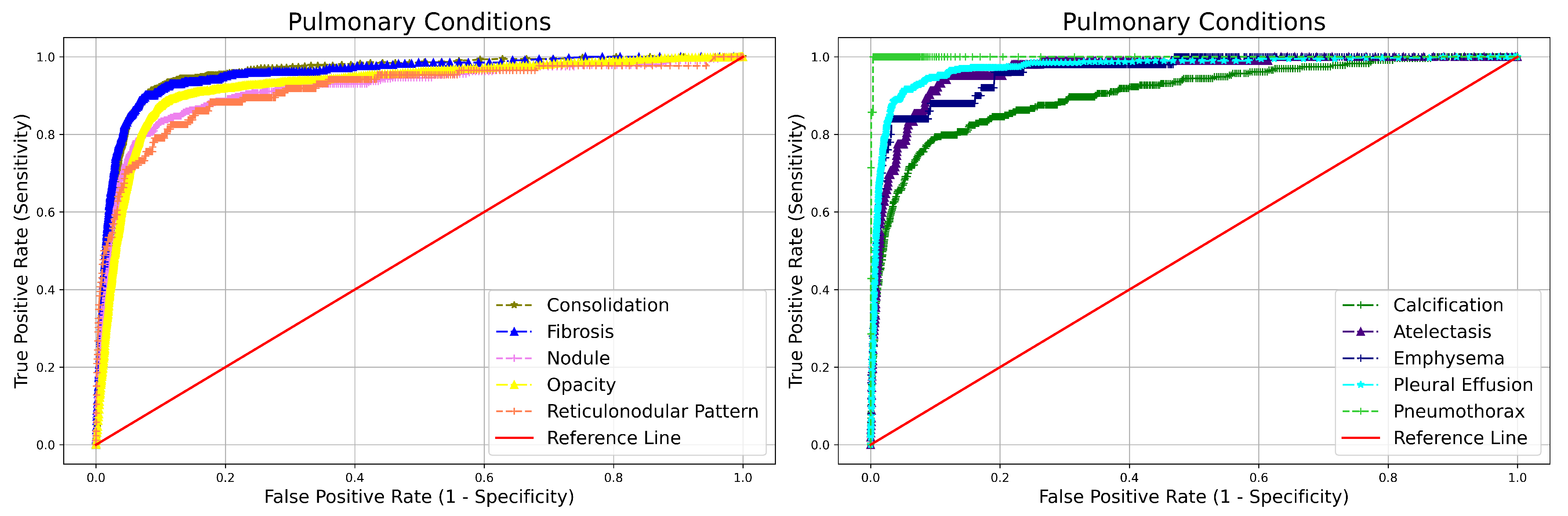
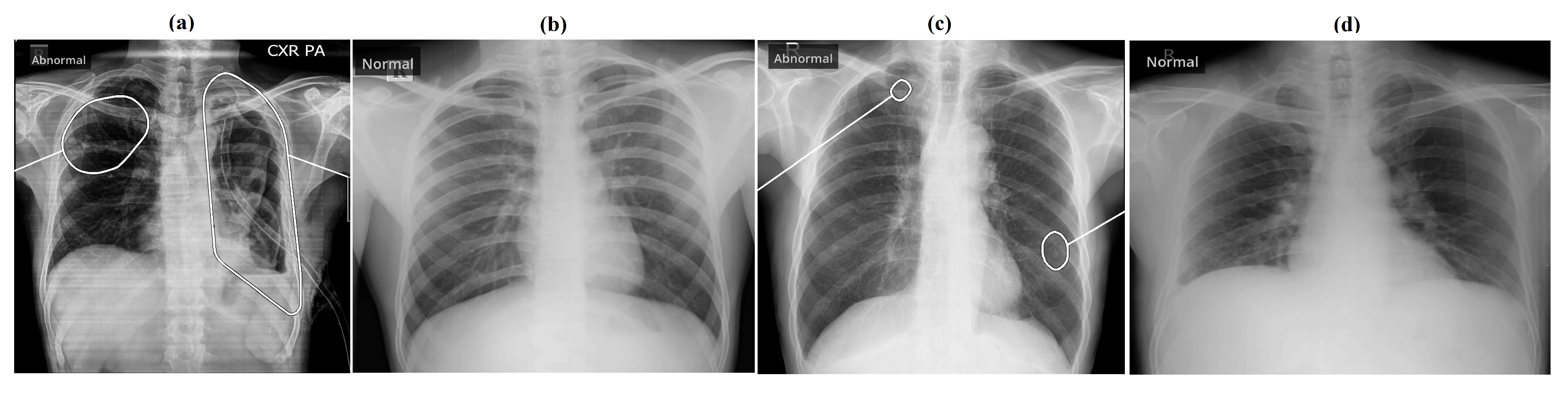
3. Results
Turnaround-Time Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raoof, S.; Feigin, D.S.; Sung, A.W.; Raoof, S.; Irugulpati, L.; Rosenow, E.C. Interpretation of plain chest roentgenogram. Chest 2012, 141, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corne, J.; Pointon, K. Comprar Chest X-ray Made Easy, 3rd ed.; Corne, J., Ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 9780443069222. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Kalra, M.K.; Nitiwarangkul, C.; Patti, J.A.; Homayounieh, F.; Padole, A.; Rao, P.; Putha, P.; Muse, V.; Sharma, A.; et al. Deep learning in chest radiography: Detection of findings and presence of change. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Z. Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majkowska, A.; Mittal, S.; Steiner, D.F.; Reicher, J.J.; McKinney, S.M.; Duggan, G.E.; Eswaran, K.; Chen, P.H.C.; Liu, Y.; Kalidindi, S.R.; et al. Chest Radiograph Interpretation with Deep Learning Models: Assessment with Radiologist-adjudicated Reference Standards and Population-adjusted Evaluation. Radiology 2019, 294, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, L.; Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, Z.; Hong, X.; Yu, J. Multi-resolution convolutional networks for chest X-ray radiograph based lung nodule detection. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pourpanah, F. Recent advances in deep learning. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sogancioglu, E.; Çalli, E.; van Ginneken, B.; van Leeuwen, K.G.; Murphy, K. Deep Learning for Chest X-ray Analysis: A Survey. Med Image Anal. 2021, 72, 102125. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Sun, H.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Hwang, E.J.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M. Performance of a Deep Learning Algorithm Compared with Radiologic Interpretation for Lung Cancer Detection on Chest Radiographs in a Health Screening Population. Radiology 2020, 297, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Agrawal, R.; Ansari, M.A.M.H. Diagnosis of hypercritical chronic pulmonary disorders using dense convolutional network through chest radiography. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 7625–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, U.; Greenspan, H.; Konen, E.; Sharon, M.; Goldberger, J. X-ray Categorization and Retrieval on the Organ and Pathology Level, Using Patch-Based Visual Words. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, N.M.; Rijal, O.M.; Yunus, A.; Mahayiddin, A.A.; Gan, C.P.; Ong, E.L.; Bakar, S.A.R.S.A. Texture-Based Statistical Detection and Discrimination of Some Respiratory Diseases Using Chest Radiograph. In Advances in Medical Diagnostic Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cicero, M.D.; Bilbily, A.; Colak, E.; Dowdell, T.; Gray, B.G.; Perampaladas, K.; Barfett, J. Training and Validating a Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Computer-Aided Detection and Classification of Abnormalities on Frontal Chest Radiographs. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.P.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets and Fully Connected CRFs. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Candemir, S.; Jaeger, S.; Lin, W.; Xue, Z.; Antani, S.K.; Thoma, G.R. Automatic heart localization and radiographic index computation in chest x-rays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Diagnose like a Radiologist: Attention Guided Convolutional Neural Network for Thorax Disease Classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.09927. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.T.; Wong, K.C.L.; Gur, Y.; Ansari, N.; Karargyris, A.; Sharma, A.; Morris, M.; Saboury, B.; Ahmad, H.M.; Boyko, O.B.; et al. Comparison of Chest Radiograph Interpretations by Artificial Intelligence Algorithm vs Radiology Residents. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2022779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Zhou, X.H. Prospective studies of diagnostic test accuracy when disease prevalence is low. Biostatistics 2002, 3, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putha, P.; Tadepalli, M.; Reddy, B.; Raj, T.; Chiramal, J.A.; Govil, S.; Sinha, N.; Manjunath, K.; Reddivari, S.; Rao, P.; et al. Can Artificial Intelligence Reliably Report Chest X-Rays?: Radiologist Validation of an Algorithm trained on 1.2 Million X-Rays. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.07455. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.Z.; Ahmed, S.; Sarker, M.S.; Paul, K.K.; Adel, A.S.S.; Naheyan, T.; Barrett, R.; Banu, S.; Creswell, J. Tuberculosis detection from chest x-rays for triaging in a high tuberculosis-burden setting: An evaluation of five artificial intelligence algorithms. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e543–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, P.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Bizzo, B.C.; Reddy, B.; Tadepalli, M.; Putha, P.; Jagirdar, A.; Ebrahimian, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Dreyer, K.J. Performance of a Chest Radiography AI Algorithm for Detection of Missed or Mislabeled Findings: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimian, S.; Homayounieh, F.; Rockenbach, M.A.B.C.; Putha, P.; Raj, T.; Dayan, I.; Bizzo, B.C.; Buch, V.; Wu, D.; Kim, K.; et al. Artificial intelligence matches subjective severity assessment of pneumonia for prediction of patient outcome and need for mechanical ventilation: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, B.M.; Tadepalli, M.; Raj, T.; Santhanakrishnan, R.; Hachim, M.Y.; Bastaki, U.M.A.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Haider, E.A.; Alabousi, A. Identifying malignant nodules on chest X-rays: A validation study of radiologist versus artificial intelligence diagnostic accuracy. Adv. Biomed. Health Sci. 2022, 1, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, D.; Bryant, T.; Altman, D.; Gardner, M. Statistics with Confidence: Confidence Intervals and Statistical Guidelines; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboen, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.B. Probable Inference, the Law of Succession, and Statistical Inference. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1927, 22, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxton, G.D. The unequal variance t-test is an underused alternative to Student’s t-test and the Mann–Whitney U test. Behav. Ecol. 2006, 17, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Joshi, A.; Pareek, A.; Chen, P.; Kiani, A.; Irvin, J.A.; Ng, A.; Lungren, M.P. CheXpedition: Investigating Generalization Challenges for Translation of Chest X-ray Algorithms to the Clinical Setting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11379. [Google Scholar]
- Albahli, S.; Rauf, H.T.; Algosaibi, A.A.; Balas, V.E. AI-driven deep CNN approach for multi-label pathology classification using chest X-Rays. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, E.; Gabrielian, A.E.; Long, A.; Hurt, D.E.; Rosenthal, A. Performance of Qure.ai automatic classifiers against a large annotated database of patients with diverse forms of tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bejnordi, B.E.; Veta, M.; van Diest, P.J.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.J.S.; van der Laak, J.A.; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; Balkenhol, M.C.A.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women With Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, E.J.; Park, S.; Jin, K.N.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Aum, J.; Yim, J.J.; Cohen, J.G.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning–Based Automated Detection Algorithm for Major Thoracic Diseases on Chest Radiographs. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e191095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, E.J.; Park, S.; Jin, K.N.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Aum, J.; Yim, J.J.; Park, C.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning–based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis on Chest Radiographs. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2018, 69, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppola, F.; Faggioni, L.; Gabelloni, M.; Vietro, F.D.; Mendola, V.; Cattabriga, A.; Cocozza, M.A.; Vara, G.; Piccinino, A.; Monaco, S.L.; et al. Human, All Too Human? An All-Around Appraisal of the “Artificial Intelligence Revolution” in Medical Imaging. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 710982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Evaluation Metrics | Point Estimate (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.879 (0.867–0.889) |
| Specificity | 0.829 (0.825–0.832) |
| NPV | 0.989 (0.981–0.990) |
| AUC | 0.871 (0.866–0.877) |
| Attributes | NPV | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Carestream Health | 0.988 (0.987–0.990) | 0.878(0.862–0.892) | 0.831 (0.826–0.836) | 0.872 (0.862–0.883) |
| AGFA | 0.987 (0.985–0.989) | 0.865 (0.840–0.887) | 0.836 (0.829–0.843) | 0.878 (0.862–0.893) | |
| Fujifilm | 0.991 (0.989–0.993) | 0.894 (0.870–0.914) | 0.817 (0.810–0.824) | 0.868 (0.851–0.884) | |
| Age (years) | 16 and less | 0.995(0.988–0.997) | 0.901 (0.790–0.957) | 0.819 (0.797–0.840) | 0.886 (0.826–0.946) |
| 16–45 | 0.993 (0.992–0.994) | 0.792 (0.763–0.819) | 0.922 (0.919–0.925) | 0.878 (0.862–0.893) | |
| 45 and above | 0.981 (0.978–0.983) | 0.905 (0.893–0.916) | 0.694 (0.688–0.701) | 0.809 (0.798–0.819) | |
| Gender | Male | 0.990 (0.989–0.991) | 0.884 (0.869–0.897) | 0.833 (0.829–0.838) | 0.875 (0.865–0.885) |
| Female | 0.987 (0.985–0.989) | 0.871 (0.853–0.888) | 0.821 (0.815–0.826) | 0.866 (0.854–0.878) |
| Abonrmality | NPV | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blunted CP angle | 0.995 (0.995–0.996) | 0.484 (0.435–0.534) | 0.990 (0.989–0.991) | 0.973 (0.709–0.766) | |
| Hilar Dysmorphism | 0.999 (0.999–0.999) | 0.216 (0.113–0.371) | 0.992 (0.991–0.993) | 0.864 (0.789–0.939) | |
| Extra Pulmonary | Cardiomegaly | 0.997 (0.997–0.997) | 0.804 (0.770–0.835) | 0.962 (0.960–0.964) | 0.965 (0.955–0.975) |
| Reticulonodular Pattern | 0.999 (0.998–0.999) | 0.511 (0.407–0.614) | 0.983 (0.981–0.984) | 0.913 (0.872–0.954) | |
| Rib Fracture | 0.999 (0.999–0.999) | 0.840 (0.653–0.935) | 0.991 (0.991–0.992) | 0.984 (0.951–1.000) | |
| Scoliosis | 0.999 (0.999–0.999) | 0.698 (0.593–0.786) | 0.995 (0.995–0.996) | 0.981 (0.961–1.000) | |
| Atelectasis | 0.999 (0.998–0.999) | 0.607 (0.5108–0.697) | 0.982 (0.980–0.983) | 0.962 (0.936–0.987) | |
| Calcification | 0.997 (0.997–0.997) | 0.804 (0.770–0.835) | 0.962(0.960–0.964) | 0.965 (0.955–0.975) | |
| Consolidation | 0.996 (0.995–0.996) | 0.702 (0.663–0.737) | 0.967 (0.966–0.969) | 0.956 (0.944–0.967) | |
| Emphysema | 0.999 (0.999–0.999) | 0.580 (0.442–0.706) | 0.988 (0.987–0.989) | 0.960 (0.922–0.998) | |
| Pulmonary | Fibrosis | 0.997 (0.996–0.997) | 0.650 (0.598–0.698) | 0.977 (0.976–0.978) | 0.955 (0.940–0.970) |
| Nodule | 0.998 (0.997–0.998) | 0.719 (0.667–0.766) | 0.955 (0.953–0.956) | 0.915 (0.894–0.936) | |
| Opacity | 0.992 (0.991–0.993) | 0.828 (0.811–0.844) | 0.921 (0.919–0.924) | 0.925 (0.917–0.933) | |
| Pleural Effusion | 0.997 (0.996–0.997) | 0.667 (0.619–0.712) | 0.986 (0.985–0.987) | 0.972 (0.961–0.984) | |
| Pneumothorax | 0.999 (0.999–0.999) | 0.857 (0.486–0.974) | 0.998 (0.998–0.998) | 0.999 (0.983–1.000) |
| Attributes | Pre-qXR (minutes) | Post-qXR (minutes) |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 11.547 | 6.249 |
| Mean | 83.028 | 50.287 |
| Maximum | 24,918.617 | 14,290.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Govindarajan, A.; Govindarajan, A.; Tanamala, S.; Chattoraj, S.; Reddy, B.; Agrawal, R.; Iyer, D.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, P.; Putha, P. Role of an Automated Deep Learning Algorithm for Reliable Screening of Abnormality in Chest Radiographs: A Prospective Multicenter Quality Improvement Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112724
Govindarajan A, Govindarajan A, Tanamala S, Chattoraj S, Reddy B, Agrawal R, Iyer D, Srivastava A, Kumar P, Putha P. Role of an Automated Deep Learning Algorithm for Reliable Screening of Abnormality in Chest Radiographs: A Prospective Multicenter Quality Improvement Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112724
Chicago/Turabian StyleGovindarajan, Arunkumar, Aarthi Govindarajan, Swetha Tanamala, Subhankar Chattoraj, Bhargava Reddy, Rohitashva Agrawal, Divya Iyer, Anumeha Srivastava, Pradeep Kumar, and Preetham Putha. 2022. "Role of an Automated Deep Learning Algorithm for Reliable Screening of Abnormality in Chest Radiographs: A Prospective Multicenter Quality Improvement Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112724
APA StyleGovindarajan, A., Govindarajan, A., Tanamala, S., Chattoraj, S., Reddy, B., Agrawal, R., Iyer, D., Srivastava, A., Kumar, P., & Putha, P. (2022). Role of an Automated Deep Learning Algorithm for Reliable Screening of Abnormality in Chest Radiographs: A Prospective Multicenter Quality Improvement Study. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112724






