Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnostic Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Clinical Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Trial Registration
2.2. CMT Spinal Diagnostic Panel
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (a)
- Adults aged 20–60 years
- (b)
- Patients who agreed to the clinical study plan and voluntarily signed the consent form approved by the IRB
- (c)
- Patients who could communicate during physical examination and X-ray imaging
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (a)
- History of injury or surgery that might cause structural problems in the lumbar spine
- (b)
- History of diseases that might cause deformation of the lumbar spine structure
- (c)
- Difficulty in palpation of the spine due to moderate or higher obesity (>30 kg/m2) based on body mass index (BMI)
- (d)
- Patients with psychotic disorders, alcoholism, or drug addiction
- (e)
- Women who were pregnant or were likely to become pregnant
- (f)
- Patients who were considered inappropriate to participate in this study according to the judgment of the principal investigator
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Sample Size Calculation
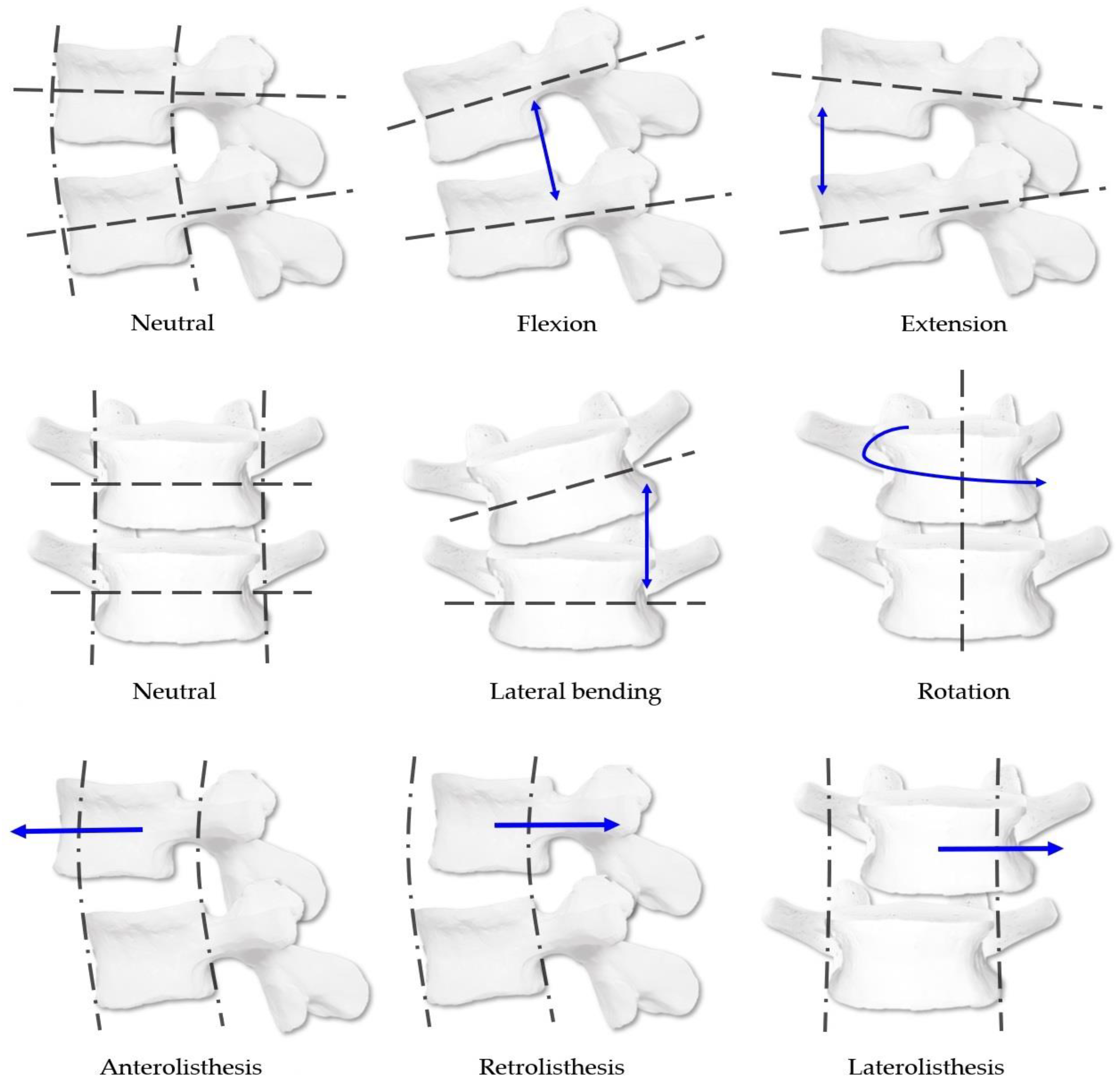
2.6. CMT Diagnostic Methods in This Study
2.6.1. CMT Spinal Diagnostic System
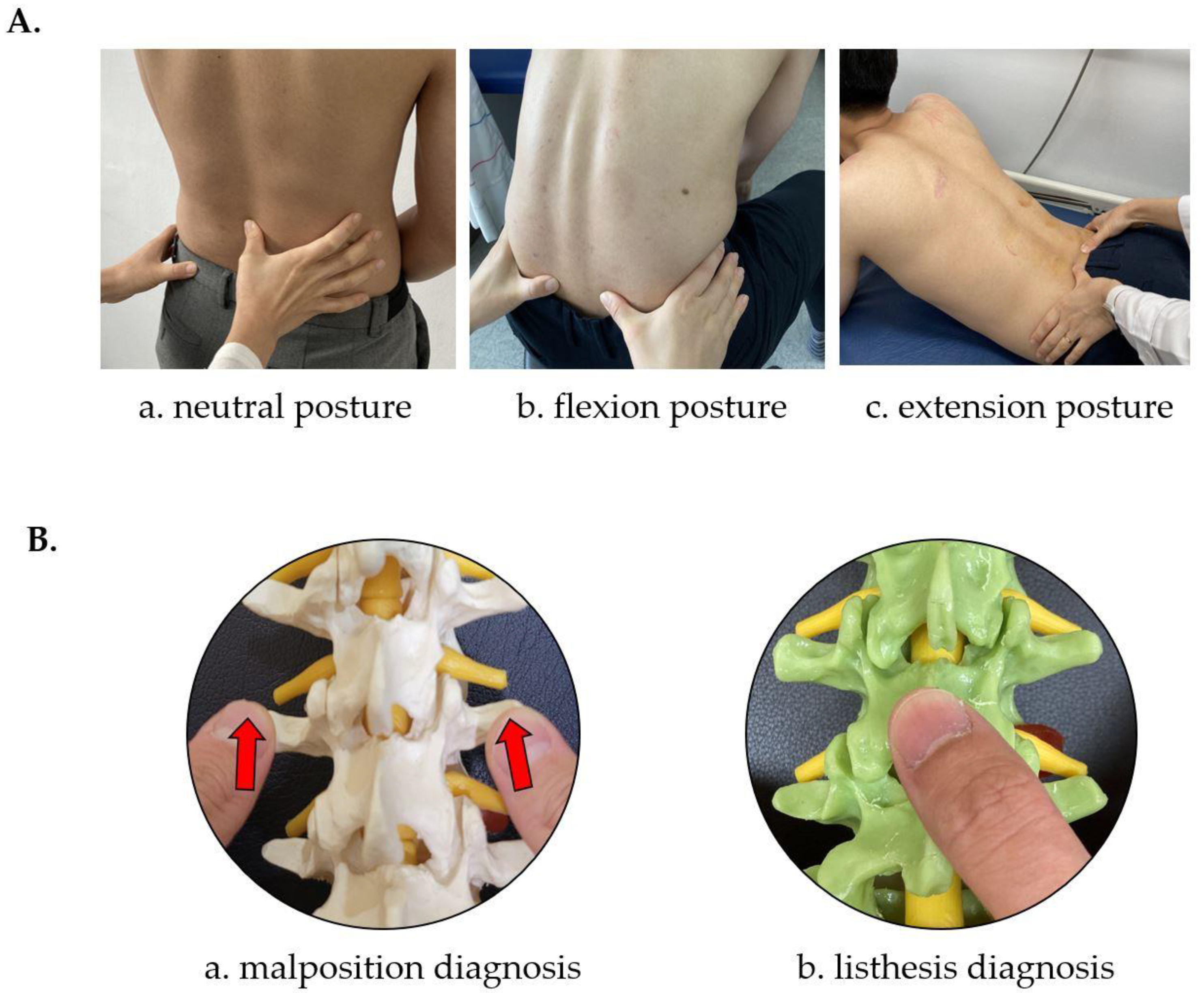
2.6.2. CMT Manual Diagnostic Method
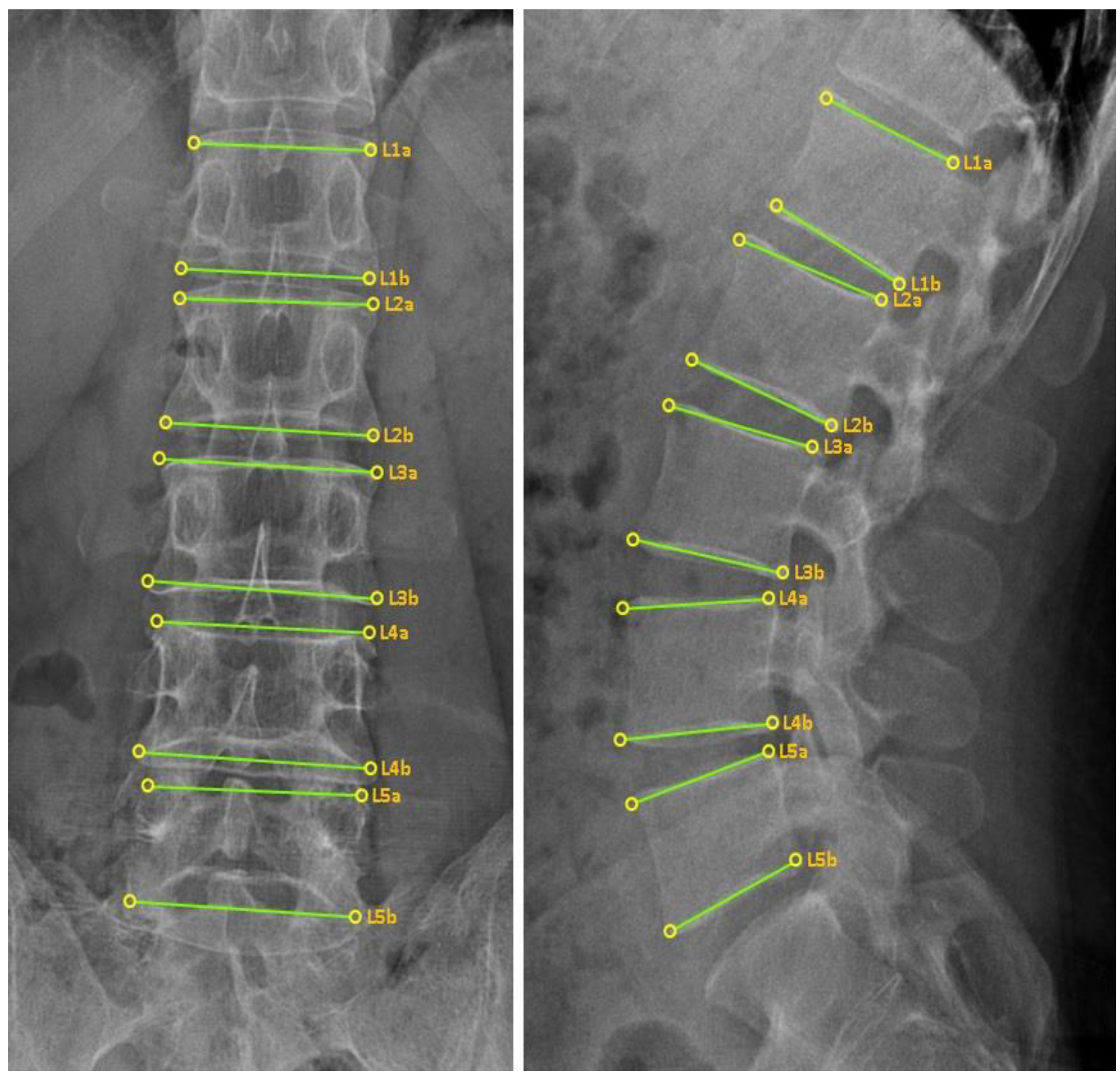
2.6.3. CMT X-ray Image-Based Diagnostic Method
2.6.4. CMT X-ray Image-Based Diagnostic Method Using the CMT-AI Program
2.7. Study Outcomes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Recruitment and Demographic Data
3.2. Comparison of Concordance in the MD Group
3.3. Comparison of Concordance in the XE Group
3.4. Comparison of Concordance in the XN Group
3.5. Comparison of Concordance in the AI Group
3.6. Comparison of Concordance among CMT Diagnostic Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, T.Y.; Moon, T.W.; Cho, D.C.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, Y.S.; Hwang, E.H.; Heo, K.H.; Choi, T.Y.; Shin, B.C. An introduction to Chuna manual medicine in Korea: History, insurance coverage, education, and clinical research in Korean literature. Integr. Med. Res. 2014, 3, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frass, M.; Strassl, R.P.; Friehs, H.; Müllner, M.; Kundi, M.; Kaye, A.D. Use and acceptance of complementary and alternative medicine among the general population and medical personnel: A systematic review. Ochsner J. 2012, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, H.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Chuna manual therapy vs usual care for patients with nonspecific chronic neck pain: A randomized clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2113757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.W.; Kim, G.H.; Heo, I.; Kim, K.W.; Ha, I.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, E.H.; Shin, B.C. Chuna (or Tuina) Manual therapy for musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 8218139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roh, J.A.; Kim, K.I.; Jung, H.J. The efficacy of manual therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.T.; Hwang, E.H.; Kim, B.J.; Park, I.H.; Heo, I. chuna manual therapy for essential hypertension: A systematic review. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2017, 12, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Han, C.H. Chuna manual therapy for stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2019, 14, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Society of Chuna Manual Medicine for Spine and Nerves. Chuna Manual Medicine, 2.5th ed.; Korean Society of Chuna Manual Medicine for Spine and Nerves: Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, B.C.; Cho, H.W.; Hwang, E.H.; Sul, J.U.; Shin, M.S.; Nam, H.W. An literatural study of listing system of spinal subluxation. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2011, 6, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- May, S.; Littlewood, C.; Bishop, A. Reliability of procedures used in the physical examination of non-specific low back pain: A systematic review. Aust. J. Physiother. 2006, 52, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hestbaek, L.; Leboeuf-Yde, C. Are chiropractic tests for the lumbo-pelvic spine reliable and valid? A systematic critical literature review. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2000, 23, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, A.; Darbois, N.; Monvoisin, R.; Pinsault, N. Reliability of diagnosis and clinical efficacy of visceral osteopathy: A systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holt, K.; Russell, D.; Cooperstein, R.; Young, M.; Sherson, M.; Haavik, H. Interexaminer reliability of a multidimensional battery of tests used to assess for vertebral subluxations. Chiropr. J. Aust. 2018, 46, 100–117. [Google Scholar]
- Nolet, P.S.; Yu, H.; Côté, P.; Meyer, A.-L.; Kristman, V.L.; Sutton, D.; Murnaghan, K.; Lemeunier, N. Reliability and validity of manual palpation for the assessment of patients with low back pain: A systematic and critical review. Chiropr. Man. Therap. 2021, 29, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.A.; Coleman, R.R.; Cremata, E.J. Radiography and clinical decision-making in chiropractic. Dose Response 2021, 19, 15593258211044844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Maddox, J.; Berg, E.; Kim, K.; Messier, S.; Swanson, L.; Dobrusin, R.; Stein, A.B.; Nakken, G.N.; Noble, J.; et al. Evaluating for a correlation between osteopathic examination and ultrasonography on thoracic spine asymmetry. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 122, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.G.; Jo, D.C.; Moon, S.J.; Park, T.Y.; Ko, Y.S.; Nam, H.W.; Lee, J.H. Diagnostic X-ray from the Perspective of Chuna Manual Medicine, Based on the Listing System of Spinal and Pelvic Subluxation. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2014, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Horng, M.H.; Kuok, C.P.; Fu, M.J.; Lin, C.J.; Sun, Y.N. Cobb Angle Measurement of Spine from X-Ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 6357171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, R.S.; Haddad, A.F.; Lau, D.; Ames, C.P. Artificial Intelligence for Adult Spinal Deformity. Neurospine 2019, 16, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, A.; Fairbank, J.; Harding, I.; Kadir, T.; Peters, T.J.; Zisserman, A.; Clark, E.M. Identifying Scoliosis in Population-Based Cohorts: Automation of a Validated Method Based on Total Body Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Scans. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galbusera, F.; Niemeyer, F.; Wilke, H.-J.; Bassani, T.; Casaroli, G.; Anania, C.; Costa, F.; Brayda-Bruno, M.; Sconfienza, L.M. Fully automated radiological analysis of spinal disorders and deformities: A deep learning approach. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Weng, C.H.; Huang, Y.J.; Fu, C.J.; Tsai, T.T.; Yeh, C.Y. Deep learning approach for automatic landmark detection and alignment analysis in whole-spine lateral radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Gao, P.; Xie, G. Automated vertebral landmarks and spinal curvature estimation using non-directional part affinity fields. Neurocomputing 2021, 438, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, K.; Ning, Z.; Wang, K.; Dong, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, C.; Yu, Q.; et al. Deep learning of lumbar spine X-ray for osteopenia and osteoporosis screening: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. Bone 2020, 140, 115561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaludin, A.; Kadir, T.; Zisserman, A. SpineNet: Automated classification and evidence visualization in spinal MRIs. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, P.; Yazdanian, T.; Benzel, E.C.; Aghaei, H.N.; Azhari, S.; Sadeghi, S.; Montazeri, A. A review on the use of artificial intelligence in spinal diseases. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 543–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yao, H.; Ma, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Ji, H.; He, L.; Luo, M.; Guo, Y. Artificial intelligence X-ray measurement technology of anatomical parameters related to lumbosacral stability. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 146, 110071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.S. A Study on Lumbar vertebrae landmark detection using convolutional neural networks. JNCIST 2020, 9, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Research Information Service. Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnosis Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional, Prospective Observational Study. Available online: https://cris.nih.go.kr/cris/search/detailSearch.do/20613 (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Lee, J.H.; Woo, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.I.; Jang, J.S.; Na, Y.C.; Kim, K.R.; Park, T.Y. Comparison of concordance between Chuna manual therapy diagnosis methods (palpation, X-ray, artificial intelligence program) in lumbar spine: An exploratory, cross-sectional, prospective observational study protocol. Medicine 2021, 100, e28177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.H.; Min, S.J.; Kim, B.S.; Song, Y.S.; Lee, S.K.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, J.H. Correlation Analysis of Body Parameters between Chuna Posture Analysis System and X-ray. J. Korean Med. Rehabil. 2014, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano, L.A. Greenman’s Principles of Manual Medicine, 5th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Regulations on Approval of Clinical Trial Plans for Medical Devices [Korean]. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/admRulLsInfoP.do?admRulSeq=2100000065809 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation. Guidelines for Clinical Efficacy Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence [AI] Based Medical Devices [Korean]. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_1060/view.do?seq=13613&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=0&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&multi_itm_seq=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&Data_stts_gubun=C1004&page=1 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Lee, J.M.; Koog, G.H.; Choi, B.m.; Jeong, H.A.; Hong, S.Y. The Comparative Study between Leg Length Analysis and X-ray on Diagnosis of Pelvic Malpositions—According to Positions and Valuation Bases. J. CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2010, 5, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Y. Computer-Aided Cobb Measurement Based on Automatic Detection of Vertebral Slopes Using Deep Neural Network. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2017, 2017, 9083916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, K.; Jhun, H.-J. New physical examination tests for lumbar spondylolisthesis and instability: Low midline sill sign and interspinous gap change during lumbar flexion-extension motion. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nichols, T.R.; Wisner, P.M.; Cripe, G.; Gulabchand, L. Putting the Kappa Statistic to Use. Qual. Assur. J. 2010, 13, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Wright, C.C. The Kappa Statistic in Reliability Studies: Use, Interpretation, and Sample Size Requirements. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falotico, R.; Quatto, P. Fleiss’ kappa statistic without paradoxes. Qual. Quant. 2015, 49, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, T.B.; Vasiliadis, E.; Malakasis, M.; Mouzakis, V.; Segos, D. Intervertebral disc biomechanics in the pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2006, 123, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crisco, J.J.; Panjabi, M.M.; Yamamoto, I.; Oxland, T.R. Euler stability of the human ligamentous lumbar spine. Part II: Experiment. Clin. Biomech. 1992, 7, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, E.F., Jr.; Hosek, R.S.; Sullivan, S.G.; Russell, B.S.; Mullin, L.E.; Dever, L.L. Establishing force and speed training targets for lumbar spine high-velocity, low-amplitude chiropractic adjustments. J. Chiropr. Educ. 2016, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, S.; Marras, W.S. Tolerance of the lumbar spine to shear: A review and recommended exposure limits. Clin. Biomech. 2012, 27, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Ehsani, N.N.; Harrison, D.E. Repeat radiography in monitoring structural changes in the treatment of spinal disorders in chiropractic and manual medicine practice: Evidence and safety. Dose Response 2019, 17, 1559325819891043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wall, B.F.; Kendall, G.M.; Edwards, A.A.; Bouffler, S.; Muirhead, C.R.; Meara, J.R. What are the risks from medical X-rays and other low dose radiation? Br. J. Radiol. 2006, 79, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, R. Chiropractic spinography and postural Roentgenology. Part I: History of development. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1980, 3, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.G.; Gi, Y.M.; Yang, K.J.; Lee, K.B.; Jo, H.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Ha, I.H. The Implications of X-ray Use in Chuna Manual Therapy from the Viewpoint of Korean Medicine Doctors. J. Acupunct. Res. 2018, 35, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, B.F.; Snider, K.T.; Snider, E.J.; Johnson, J.C. Interobserver reliability of osteopathic palpatory diagnostic tests of the lumbar spine: Improvements from consensus training. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2005, 105, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeaux, Z.; Eland, D.; Chila, A.; Pheley, A.; Tate, M. Measurement challenges in physical diagnosis: Refining inter-rater palpation, perception and communication. J. Body Mov. Ther. 2001, 5, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, T.F.; Peterson, D.H. Chiropractic Technique, 3rd ed.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, C.N.R. The basis for spinal manipulation: Chiropractic perspective of indications and theory. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, C.A.; Volpon, J.B. Development and evaluation of thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis during growth. J. Child. Orthop. 2007, 1, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-C.; Wang, Y.-X.J.; Gong, J.-S.; Griffith, J.F.; Zeng, X.-J.; Kwok, A.W.L.; Leung, J.C.S.; Kwok, T.; Ahuja, A.T.; Leung, P.C. Prevalence and risk factors of lumbar spondylolisthesis in elderly Chinese men and women. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iguchi, T.; Wakami, T.; Kurihara, A.; Kasahara, K.; Yoshiya, S.; Nishida, K. Lumbar multilevel degenerative spondylolisthesis: Radiological evaluation and factors related to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2002, 15, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.R.; Russell, D.G.; Hoffmann, N.J.; Bruce, B.I.; Bushell, P.M.; Taylor, H.H. Interexaminer reliability of a leg length analysis procedure among novice and experienced practitioners. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2009, 32, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Item | (n = 100) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years; mean ± SD) | 32.5 ± 11.3 | |
| Sex | Male [n (%)] | 36 (36) |
| Female [n (%)] | 64 (64) | |
| Height (cm; mean ± SD) | 165.0 ± 8.2 | |
| Weight (kg; mean ± SD) | 62.8 ± 10.8 | |
| BMI (kg/m2; mean ± SD) | 22.9 ± 2.7 | |
| BP | Systolic (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 120.6 ± 10.5 |
| Diastolic (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 75.6 ± 8.5 | |
| HR (bpm; mean ± SD) | 78.9 ± 10.6 | |
| BT (°C; mean ± SD) | 36.7 ± 0.3 | |
| LBP (NRS; mean ± SD) | 2.4 ± 1.6 | |
| MD Group | XE Group | XN Group | AI Group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Item * | Kappa | Z | p-Value | Kappa | Z | p-Value | Kappa | Z | p-Value | Kappa | Z | p-Value |
| L1 | Mal † | −0.104 | −1.8 | 0.073 | 0.587 | 10.2 | 0.000 | 0.295 | 5.1 | 0.000 | 0.465 | 8.1 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.064 | −1.4 | 0.152 | 0.553 | 10.1 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.2 | 0.808 | 0.470 | 8.6 | 0.000 | |
| Axi § | −0.042 | −1.0 | 0.324 | 0.826 | 19.5 | 0.000 | 0.625 | 14.7 | 0.000 | 0.803 | 19.2 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | −0.078 | −1.8 | 0.067 | 0.840 | 19.4 | 0.000 | 0.432 | 9.9 | 0.000 | 0.647 | 15.2 | 0.000 | |
| L2 | Mal † | 0.018 | 0.3 | 0.751 | 0.790 | 13.7 | 0.000 | 0.428 | 7.4 | 0.000 | 0.476 | 8.2 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.004 | −0.1 | 0.927 | 0.860 | 17.2 | 0.000 | 0.151 | 3.4 | 0.001 | 0.662 | 13.4 | 0.000 | |
| Axi § | 0.001 | 0.0 | 0.986 | 0.876 | 20.8 | 0.000 | 0.597 | 14.1 | 0.000 | 0.718 | 17.2 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | −0.037 | −0.9 | 0.369 | 0.834 | 19.8 | 0.000 | 0.561 | 13 | 0.000 | 0.711 | 17.3 | 0.000 | |
| L3 | Mal † | −0.081 | −1.4 | 0.162 | 0.747 | 12.9 | 0.000 | 0.428 | 7.4 | 0.000 | 0.492 | 8.5 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | 0.081 | 1.8 | 0.066 | 0.769 | 16.9 | 0.000 | 0.086 | 1.8 | 0.066 | 0.193 | 4.2 | 0.000 | |
| Axi § | −0.059 | −1.4 | 0.173 | 0.842 | 19.8 | 0.000 | 0.598 | 14.1 | 0.000 | 0.753 | 17.7 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | −0.079 | −1.9 | 0.061 | 0.751 | 17.0 | 0.000 | 0.394 | 8.8 | 0.000 | 0.670 | 15.7 | 0.000 | |
| L4 | Mal † | 0.006 | 0.1 | 0.919 | 0.715 | 12.4 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 8.2 | 0.000 | 0.485 | 8.4 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.007 | −0.2 | 0.866 | 0.721 | 16.1 | 0.000 | 0.190 | 4.0 | 0.000 | 0.312 | 7.0 | 0.000 | |
| Axi § | −0.052 | −1.2 | 0.222 | 0.903 | 20.6 | 0.000 | 0.594 | 13.7 | 0.000 | 0.588 | 13.5 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | −0.017 | −0.4 | 0.683 | 0.711 | 16.3 | 0.000 | 0.349 | 8.0 | 0.000 | 0.636 | 14.9 | 0.000 | |
| L5 | Mal † | −0.097 | −1.7 | 0.092 | 0.629 | 10.9 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 2.3 | 0.020 | 0.572 | 9.9 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.056 | −1.3 | 0.180 | 0.607 | 13.6 | 0.000 | 0.061 | 1.3 | 0.185 | 0.477 | 10.1 | 0.000 | |
| Axi § | −0.111 | −2.6 | 0.008 | 0.861 | 18.7 | 0.000 | 0.220 | 4.9 | 0.000 | 0.352 | 8.0 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | −0.144 | −3.4 | 0.001 | 0.694 | 15.1 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 2.2 | 0.030 | 0.543 | 12.3 | 0.000 | |
| Level | Item * | Kappa | Z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Mal † | 0.286 | 7.0 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | 0.116 | 3.2 | 0.001 | |
| Axi § | 0.493 | 16.5 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | 0.396 | 13.1 | 0.000 | |
| L2 | Mal † | 0.262 | 6.4 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | 0.103 | 3.3 | 0.001 | |
| Axi § | 0.414 | 14 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | 0.406 | 13.8 | 0.000 | |
| L3 | Mal † | 0.222 | 5.4 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | 0.041 | 1.3 | 0.194 | |
| Axi § | 0.528 | 17.6 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | 0.250 | 8.1 | 0.000 | |
| L4 | Mal † | 0.173 | 4.2 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.026 | 0.8 | 0.421 | |
| Axi § | 0.238 | 7.9 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | 0.245 | 8.1 | 0.000 | |
| L5 | Mal † | 0.142 | 3.5 | 0.000 |
| Sag ‡ | −0.043 | −1.4 | 0.163 | |
| Axi § | 0.122 | 3.9 | 0.000 | |
| Cor ∥ | 0.154 | 5.0 | 0.000 |
| Level | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item * | Mal † | Sag ‡ | Axi § | Cor ∥ | Mal † | Sag ‡ | Axi § | Cor ∥ | Mal † | Sag ‡ | Axi § | Cor ∥ | Mal † | Sag ‡ | Axi § | Cor ∥ | Mal † | Sag ‡ | Axi § | Cor ∥ | |
| CI | MD1 | 0.212 (0.025) | −0.053 (0.427) | 0.411 (0.000) | 0.359 (0.000) | 0.079 (0.000) | −0.053 (0.390) | 0.202 (0.003) | 0.255 (0.000) | 0.042 (0.677) | −0.073 (0.216) | 0.231 (0.001) | 0.193 (0.007) | −0.088 (0.368) | −0.053 (0.314) | −0.100 (0.115) | 0.057 (0.393) | 0.071 (0.307) | 0.036 (0.370) | 0.085 (0.005) | 0.159 (0.000) |
| ++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - | ++ | ++ | + | - | ++ | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| XN3 | 0.541 (0.000) | 0.149 (0.003) | 0.680 (0.000) | 0.589 (0.000) | 0.498 (0.000) | 0.310 (0.000) | 0.641 (0.000) | 0.559 (0.000) | 0.602 (0.000) | 0.340 (0.000) | 0.793 (0.000) | 0.416 (0.000) | 0.529 (0.000) | 0.064 (0.224) | 0.782 (0.000) | 0.551 (0.000) | 0.318 (0.000) | 0.093 (0.002) | 0.522 (0.000) | 0.311 (0.000) | |
| +++ | + | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++++ | +++ | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | ||
| AI3 | 0.442 (0.000) | 0.553 (0.000) | 0.667 (0.000) | 0.656 (0.000) | 0.508 (0.000) | 0.668 (0.000) | 0.703 (0.000) | 0.725 (0.000) | 0.430 (0.000) | 0.310 (0.000) | 0.783 (0.000) | 0.558 (0.000) | 0.495 (0.000) | 0.259 (0.001) | 0.692 (0.000) | 0.611 (0.000) | 0.506 (0.000) | 0.457 (0.000) | 0.446 (0.000) | 0.655 (0.000) | |
| +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Woo, H.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, J.I.; Na, Y.C.; Kim, K.-R.; Cho, E.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, T.-Y. Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnostic Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112732
Lee J-H, Woo H, Jang J-S, Kim JI, Na YC, Kim K-R, Cho E, Lee J-H, Park T-Y. Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnostic Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112732
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin-Hyun, Hyeonjun Woo, Jun-Su Jang, Joong Il Kim, Young Cheol Na, Kwang-Ryeol Kim, Eunbyul Cho, Jung-Han Lee, and Tae-Yong Park. 2022. "Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnostic Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Clinical Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112732
APA StyleLee, J.-H., Woo, H., Jang, J.-S., Kim, J. I., Na, Y. C., Kim, K.-R., Cho, E., Lee, J.-H., & Park, T.-Y. (2022). Comparison of Concordance between Chuna Manual Therapy Diagnostic Methods (Palpation, X-ray, Artificial Intelligence Program) in Lumbar Spine: An Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112732









