Angiogenetic Factors in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- What are the concentrations of the leading factors in neo-angiogenesis directly in the arterial blood in the vessels that feed the outer membrane of the CSDH capsule (MMA branches), and do they differ from the concentrations in the peripheral veins?
- -
- Are there any differences in the concentrations of angiogenesis factors in the bloods between patients who have repeated hemorrhages in the area of CSDH (rebleeding) and patients with a fairly homogeneous structure of the hematoma according to non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT)?
- -
- Are the hematoma volume, recidivation and side location related to the concentrations of angiogenesis factors in the blood?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Adherence to Ethical Standards
2.3. Participants and Enrolment Criteria
2.4. Variables
2.4.1. Volume Measurement of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
2.4.2. Determination of the Concentrations of Angiogenesis Factors
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tamura, R.; Sato, M.; Yoshida, K.; Toda, M. History and Current Progress of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 429, 118066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Huang, J. Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Epidemiology and Natural History. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, A.; Ivanov, A.; Rozhchenko, L.; Petrova, A.; Bhogal, P.; Cimpoca, A.; Henkes, H. Endovascular Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematomas through Embolization: A Pilot Study with a Non-Adhesive Liquid Embolic Agent of Minimal Viscosity (Squid). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virchow, R. Das Hämatom Der Dura Mater. Verh. Phys.-Med. Ges. Würzburg 1857, 7, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S.; Bae, W.K.; Park, Y.T.; Yun, I.G. The Pathogenesis and Fate of Traumatic Subdural Hygroma. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 8, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, J. Updates in Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Epidemiology, Etiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment, and Outcome; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 141, ISBN 4105025767. [Google Scholar]
- Edlmann, E.; Giorgi-Coll, S.; Whitfield, P.C.; Carpenter, K.L.H.; Hutchinson, P.J. Pathophysiology of Chronic Subdural Haematoma: Inflammation, Angiogenesis and Implications for Pharmacotherapy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jumah, F.; Osama, M.; Islim, A.I.; Jumah, A.; Patra, D.P.; Kosty, J.; Narayan, V.; Nanda, A.; Gupta, G.; Dossani, R.H. Efficacy and Safety of Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization in the Management of Refractory or Chronic Subdural Hematomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, I.; Park, H.S.; Kotsugi, M.; Wada, T.; Takeshima, Y.; Matsuda, R.; Nishimura, F.; Yamada, S.; Motoyama, Y.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Enhanced Hematoma Membrane on DynaCT Images During Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Persistently Recurrent Chronic Subdural Hematoma. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e473–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsan, A.; Mohanty, A.; Nascimento, F.A.; Hafeez, M.U.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Thomas, A.; Chen, S.R.; Johnson, J.N.; Kan, P. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Ohashi, T.; Watanabe, D.; Koyama, S.; Namatame, H.; Izawa, H.; Haraoka, R.; Okada, H.; Ichimasu, N.; Akimoto, J.; et al. Usefulness of Embolization of the Middle Meningeal Artery for Refractory Chronic Subdural Hematomas. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureb, M.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Shapiro, M.; Raz, E.; Nossek, E.; Haynes, J.; Farkas, J.; Riina, H.A.; Tanweer, O. DynaCT Enhancement of Subdural Membranes After Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization: Insights into Pathophysiology. World Neurosurg. 2020, 139, e265–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, T.W.; Rapoport, B.I.; Paine, S.M.; Kamel, H.; Knopman, J. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Endovascular Technique and Radiographic Findings. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2018, 24, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezami, P.; Boulos, A.; Paul, A.; Nourollahzadeh, E.; Dalfino, J. Contrast Enhancement of Chronic Subdural Hematomas after Embolization of the Middle Meningeal Artery. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2019, 25, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, D.; Merritt, H.H. Surgical Pathology of Subdural Hematoma. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1936, 35, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, R.; Schilling, L.; Schmiedek, P. Specific Pattern of Growth Factor Distribution in Chronic Subdural Hematoma (CSH): Evidence for an Angiogenic Disease. Acta Neurochir. 2001, 143, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Takano, S.; Nose, T.; Doi, M.; Ohashi, N. Increased Concentration of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Chronic Subdural Hematoma. J. Trauma 1999, 46, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozhchenko, L. v [Molecular Mechanisms of Growth and Relapse of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations]. Zh. Vopr. Neirokhir. Im N N Burdenko 2020, 84, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.-J.; Gao, J.; Wu, C.-W.; Zou, J.-F.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, D.-L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Huang, X.-J. Serum Levels of MMP-8 and MMP-9 as Markers in Chronic Subdural Hematoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Usuda, N.; Aoyama, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Takayasu, M. Eotaxin-3 Activates the Smad Pathway through the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Outer Membranes. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaji, T.; Osuka, K.; Ohmichi, Y.; Ohmichi, M.; Naito, M.; Nakano, T.; Iwami, K.; Miyachi, S. Expression of Angiopoietins and Angiogenic Signaling Pathway Molecules in Chronic Subdural Hematomas. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarius, T.; Kirkpatrick, P.J.; Kolias, A.G.; Hutchinson, P.J. Working toward Rational and Evidence-Based Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Clin. Neurosurg. 2010, 57, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asghar, M.; Adhiyaman, V.; Greenway, M.W.; Bhowmick, B.K.; Bates, A. Chronic Subdural Haematoma in the Elderly—A North Wales Experience. J. R. Soc. Med. 2002, 95, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.; Yan, Z.; She, L. Chronic Subdural Haematoma in Antithrombotic Cohorts: Characteristics, Surgical Outcomes, and Recurrence. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 34, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.; Mathieson, C.S.; Campbell, E.; Lindsay, K.W.; Murray, L. Treatment of Chronic Subdural Haematomas A Retrospective Comparison of Minicraniectomy versus Burrhole Drainage. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 24, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivamoto, H.S.; Lemos, H.P.; Atallah, A.N. Surgical Treatments for Chronic Subdural Hematomas: A Comprehensive Systematic Review; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 86, ISBN 5513327163. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, F.; Loos, F.; Dünisch, P.; Sakr, Y.; Al Safatli, D.; Kalff, R.; Ewald, C. Risk Factors for Reoperation after Initial Burr Hole Trephination in Chronic Subdural Hematomas. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 138, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher Hulou, M.; McLouth, C.J.; Hayden, C.S.; Sheldrake, A.K.; Parekh, M.; Dillen, W.L.; Wheeler, G.R.; Fraser, J.F. Predictors of Re-Operation in the Setting of Non-Acute Subdural Hematomas: A 12-Year Single Center Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 81, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torihashi, K.; Sadamasa, N.; Yoshida, K.; Narumi, O.; Chin, M.; Yamagata, S. Independent Predictors for Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Review of 343 Consecutive Surgical Cases. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.P.; Hwang, G.; Byoun, H.S.; Kim, T.; Lee, S.U.; Bang, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Kim, C.-Y.; Kwon, O.-K.; Oh, C.W. Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Radiology 2018, 286, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.I.; Kim, S.O.; Won, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.J.; Choi, C.S. Clinical Analysis of Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Chronic Subdural Hematoma Undergoing Burr Hole Trephination. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2014, 10, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamenova, M.; Lutz, K.; Schaedelin, S.; Fandino, J.; Mariani, L.; Soleman, J. Does Early Resumption of Low-Dose Aspirin after Evacuation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Burr-Hole Drainage Lead to Higher Recurrence Rates? Neurosurgery 2016, 79, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagatani, K.; Wada, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Nawashiro, H. Corticosteroid Suppression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, E1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Yamada, S.M.; Yamada, S.; Matsuno, A. Subdural Tension on the Brain in Patients with Chronic Subdural Hematoma Is Related to Hemiparesis but Not to Headache or Recurrence. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e518–e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.F.; Chen, J.H.; Leung, G.K.K.; Hao, S.Y.; Xu, L.; Hou, Z.G.; Mao, X.; Shi, G.Z.; Li, J.S.; Liu, B.Y. Quantitative Computer Tomography Analysis of Post-Operative Subdural Fluid Volume Predicts Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Haematoma. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Wen, L.; Yang, X. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, D.; Labadie, E.L. Physiopathogenesis of Subdural Hematomas. Part 2: Inhibition of Growth of Experimental Hematomas with Dexamethasone. J. Neurosurg. 1976, 45, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Cao, X.D.; Ren, Y.M.; Zhou, L.X.; Yang, C.H. Risk Factors for Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Single Center Experience. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e506–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Hirashima, Y.; Hamada, H.; Hayashi, N.; Origasa, H.; Endo, S. Independent Predictors of Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Results of Multivariate Analysis Performed Using a Logistic Regression Model. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.E.; Rozhchenko, L.V.; Ivanov, A.A.; Bobinov, V.V.; Henkes, H. The First Experience of Endovascular Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematomas with Non-Adhesive Embolization Materials of Various Viscosities: Squid 12 and 18. Voprosy Neirokhirurgii Imeni N.N. Burdenko 2021, 85, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollherbst, D.F.; Chapot, R.; Bendszus, M.; Möhlenbruch, M.A. Glue, Onyx, Squid or PHIL? Liquid Embolic Agents for the Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2021, 32, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Qian, Y.; Nie, M.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, H.; Yuan, J.; et al. Hematoma-Derived Exosomes of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Promote Abnormal Angiogenesis and Inhibit Hematoma Absorption through MiR-144-5p. Aging 2019, 11, 12147–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Zhao, G.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Song, H.; Bie, L. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Development of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, D. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Transformation of Subdural Effusion into Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2010, 30, 1188–1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bokka, S.; Trivedi, A. Histopathological Study of the Outer Membrane of the Dura Mater in Chronic Sub Dural Hematoma: Its Clinical and Radiological Correlation. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2016, 11, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandhoke, G.S.; Kaif, M.; Choi, L.; Williamson, R.W.; Nakaji, P. Histopathological Features of the Outer Membrane of Chronic Subdural Hematoma and Correlation with Clinical and Radiological Features. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaguchi, H.; Tanishima, T.; Yoshimasu, N. Factors in the Natural History of Chronic Subdural Hematomas That Influence Their Postoperative Recurrence. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heula, A.-L.; Ohlmeier, S.; Sajanti, J.; Majamaa, K. Characterization of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Fluid Proteome. Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, D.; Rao, C.; Li, Y.; Rong, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Atorvastatin Combined with Low-Dose Dexamethasone Treatment Protects Endothelial Function Impaired by Chronic Subdural Hematoma via the Transcription Factor KLF-2. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Usuda, N.; Aoyama, M.; Kawaguchi, R.; Watabe, T.; Takayasu, M. Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Endothelial Cells of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Outer Membranes. World Neurosurg. 2016, 91, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Usuda, N.; Aoyama, M.; Kawaguchi, R.; Takeuchi, M.; Takayasu, M. Activation of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B in Endothelial Cells of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Outer Membranes. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, R.; Hohenstein, A.; Schilling, L. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Concentration in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Fluid Is Related to Computed Tomography Appearance and Exudation Rate. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokmak, M.; Iplikcioglu, A.C.; Bek, S.; Gökduman, C.A.; Erdal, M. The Role of Exudation in Chronic Subdural Hematomas. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Hua, C.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Bie, L. Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor with Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Chronic Subdural Hematomas. J. Neurol Sci. 2017, 377, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
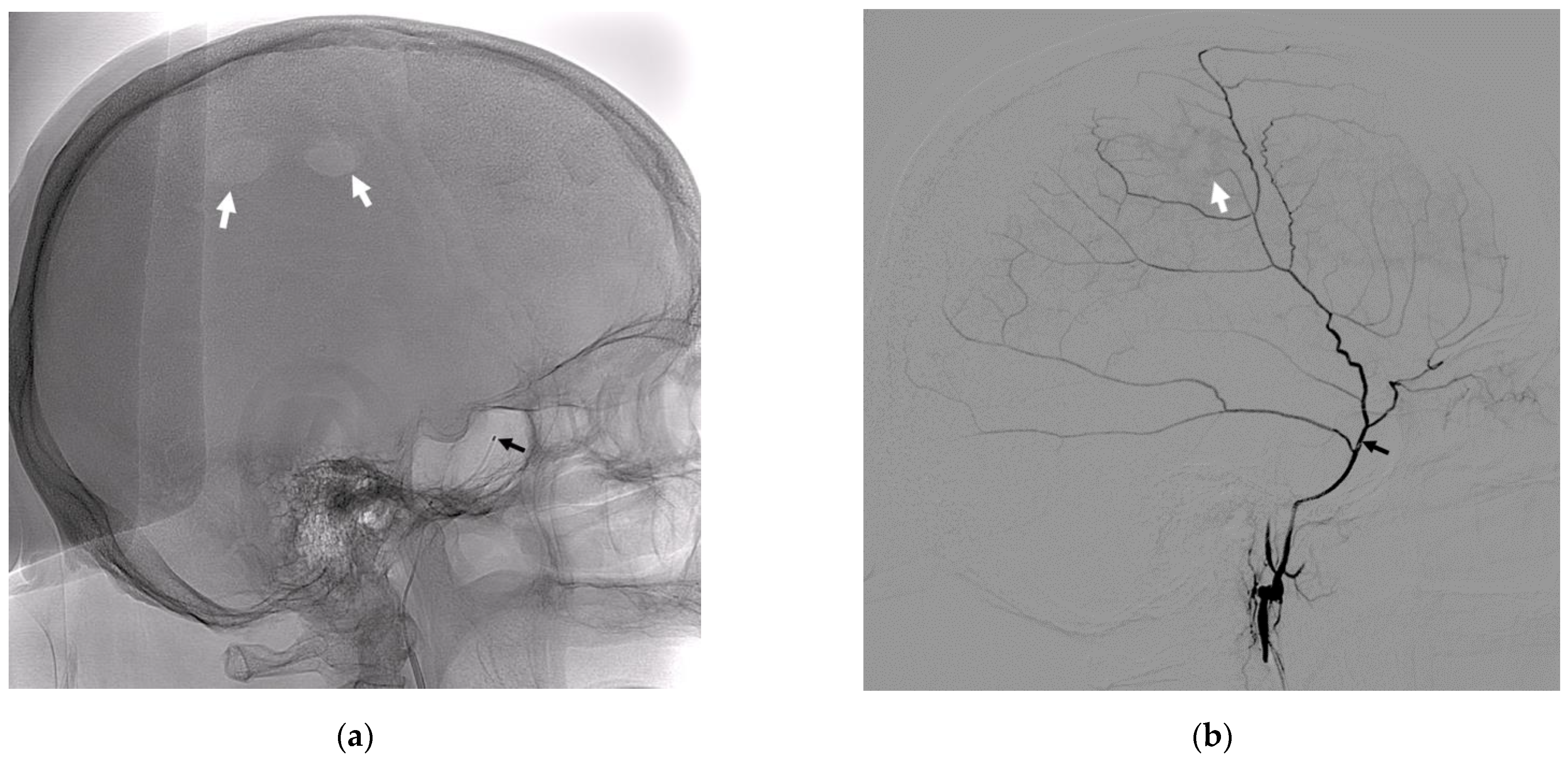




| Patient # Age (Years) Gender | Side | Rebleeding on NCCT Scans | Surgery Status before MMA Embolization | Volume Pre-Embol (mL) | Total Volume Pre-Embol (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 57, m | Left unilateral | rebled | none | 170 | 170 |
| 2, 66, m | Left unilateral | none | Pre-embol left-side craniectomy | 70 | 70 |
| 3, 43, m | Right unilateral | none | none | 53 | 53 |
| 4, 60, m | Left unilateral | rebled | none | 57 | 57 |
| 5, 44, f | Bilateral | none | none | right 44 left 54 | 98 |
| 6, 58, m | Left unilateral | rebled | pre-embol burr hole | 70 | 70 |
| 7, 82, m | Bilateral | rebled | pre-embol right- and left-side burr hole | right 170 left 67 | 237 |
| 8, 77, m | Right unilateral | none | pre-embol burr hole | 65 | 65 |
| Mean (M ± SD/Me) Healthy Volunteers (n) | Mean (M ± SD/Me) Patients (n) | Comparison Patients’ Venous Blood Samples/Healthy Volunteers’ Venous Blood Samples (Applied Method) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| venous blood | venous blood | ||
| VEGF (pg/mL) | 271 ± 41 (n = 33) | 39 (n = 8) | p = 0.004 * (Mann–Whitney U-test) |
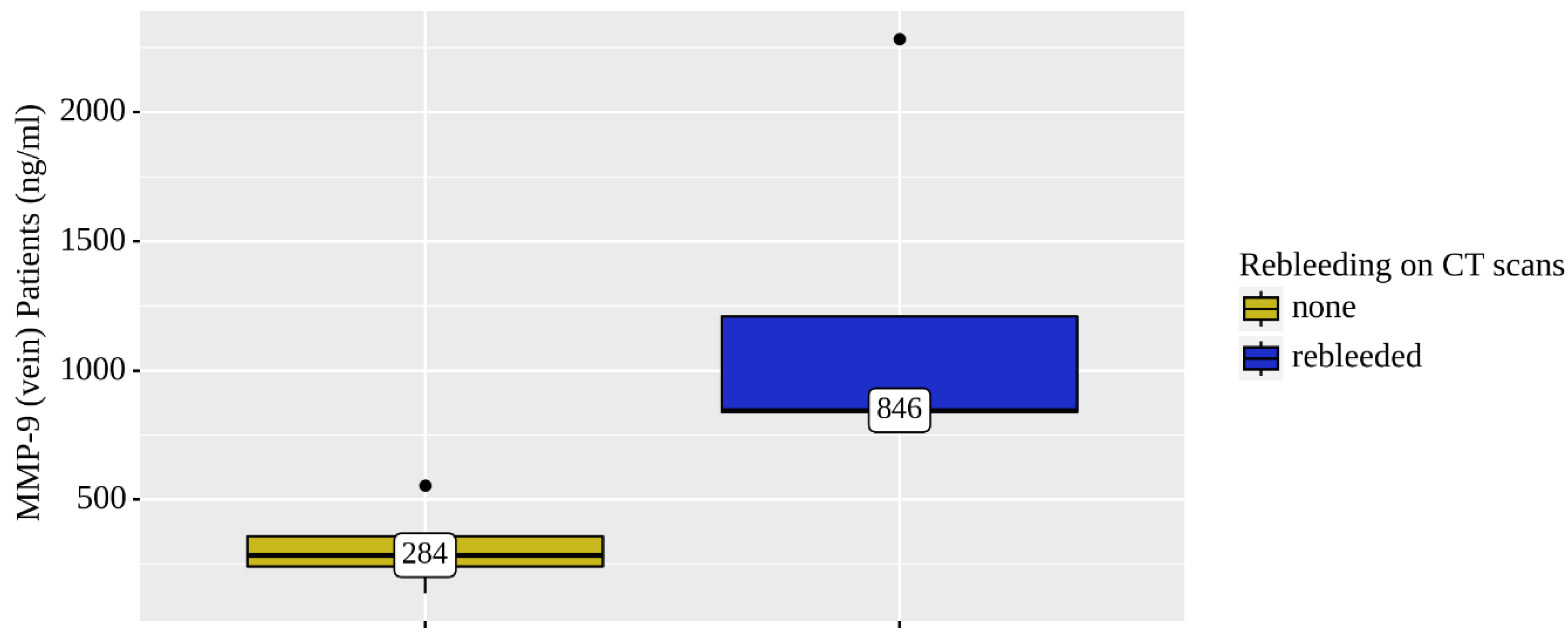
| MMP-9 (ng/mL) | 432 ± 48 (n = 33) | 692 (n = 8) | p = 0.278 (Mann–Whitney U-test) |
| Angio-2 (pg/mL) | 2198 ± 248 (n = 33) | 2608 (n = 8) | p = 0.023 * (Mann–Whitney U-test) |
| TGF-β1 (pg/mL) | 10,936 ± 411 (n = 21) | 7462 ± 3497 (n = 8) | p = 0.026 * (Welch’s t-test) |
| PDGFβ- (pg/mL) | 3611 ± 371 (n = 21) | 2372 ± 1371 (n = 8) | p = 0.038 * (Welch’s t-test). |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrov, A.; Ivanov, A.; Dryagina, N.; Petrova, A.; Samochernykh, K.; Rozhchenko, L. Angiogenetic Factors in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Development. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112787
Petrov A, Ivanov A, Dryagina N, Petrova A, Samochernykh K, Rozhchenko L. Angiogenetic Factors in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Development. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112787
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrov, Andrey, Arkady Ivanov, Natalia Dryagina, Anna Petrova, Konstantin Samochernykh, and Larisa Rozhchenko. 2022. "Angiogenetic Factors in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Development" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112787
APA StylePetrov, A., Ivanov, A., Dryagina, N., Petrova, A., Samochernykh, K., & Rozhchenko, L. (2022). Angiogenetic Factors in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Development. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112787






