Fluorescence-Linked Aptamer Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein: A Step-by-Step Performance Analysis in Clinical Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oligonucleotides
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.3. Fluorophore-Linked Aptamer Assay (FLAA)
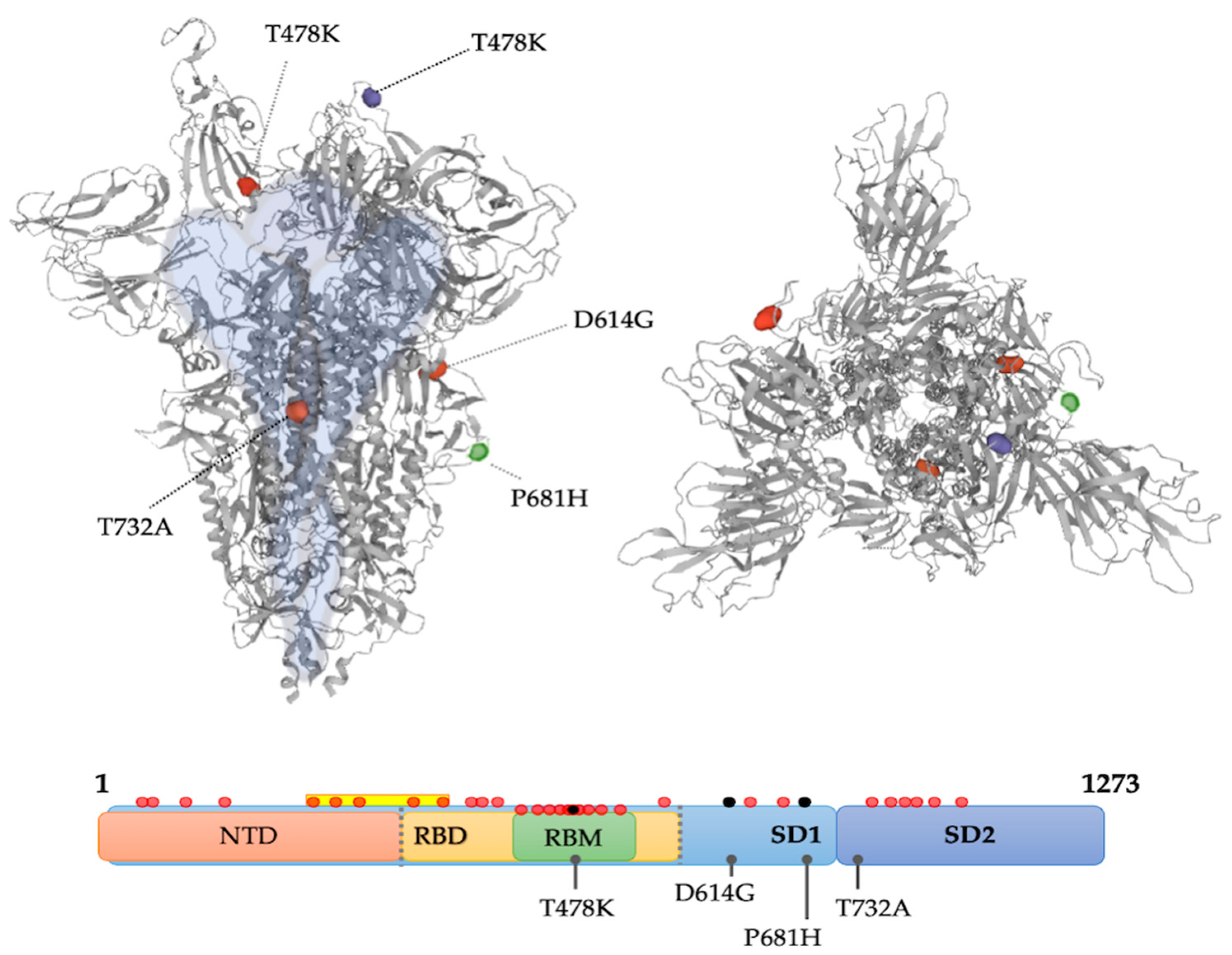
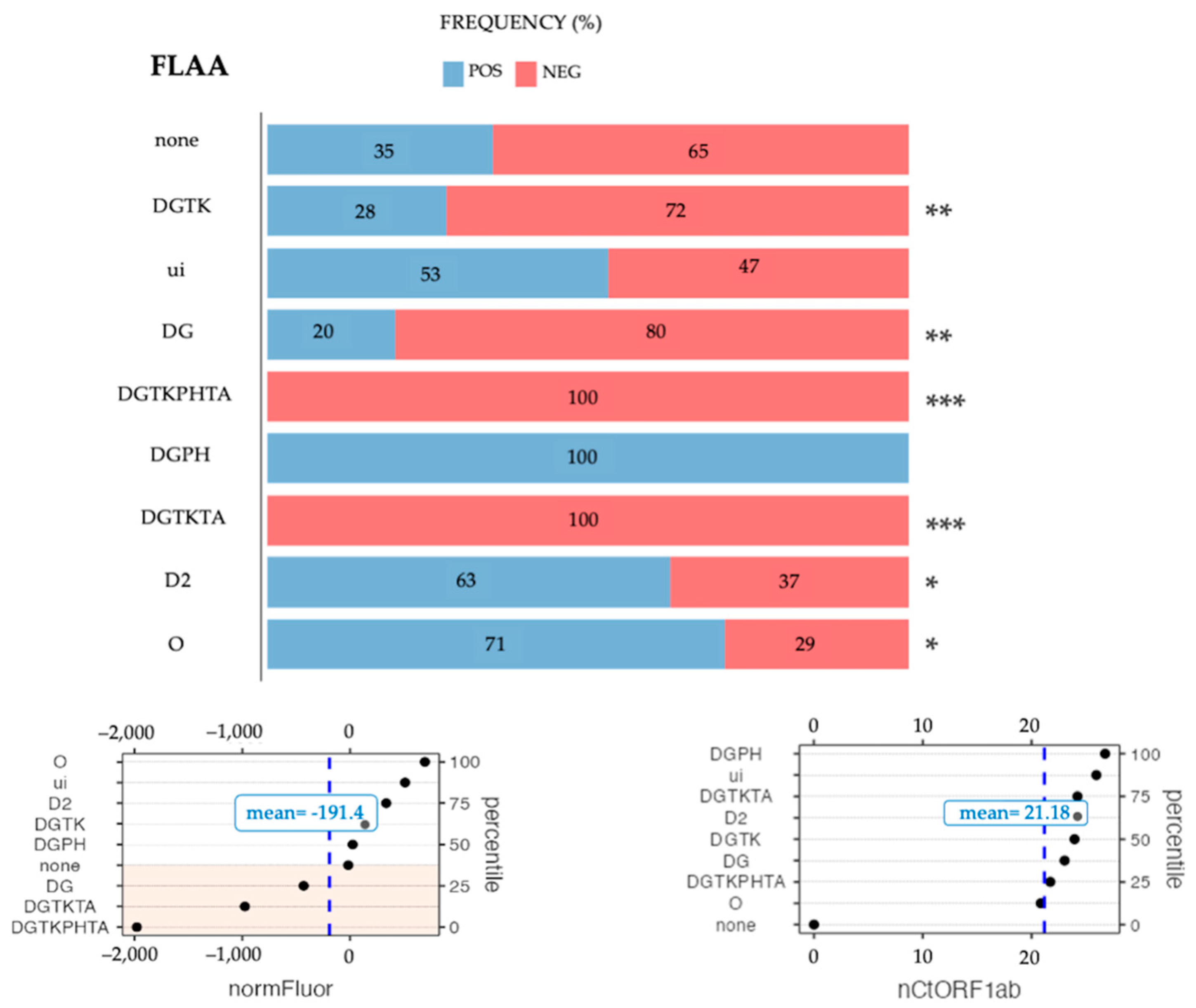
2.4. Mutation Analysis
2.5. Normalization
2.6. Diagnostic Accuracy Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
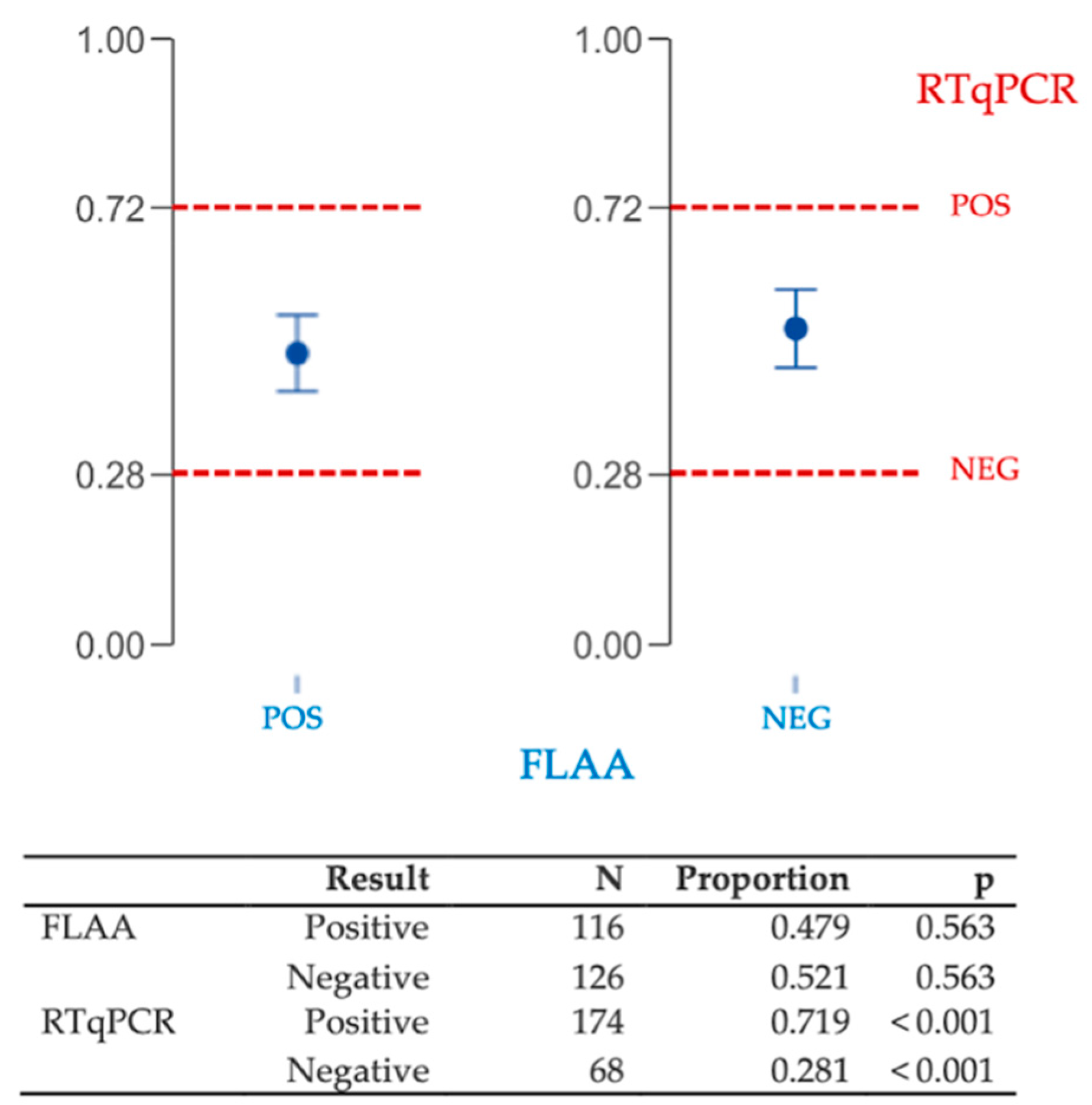
3.1. First Step: Inner Consistency
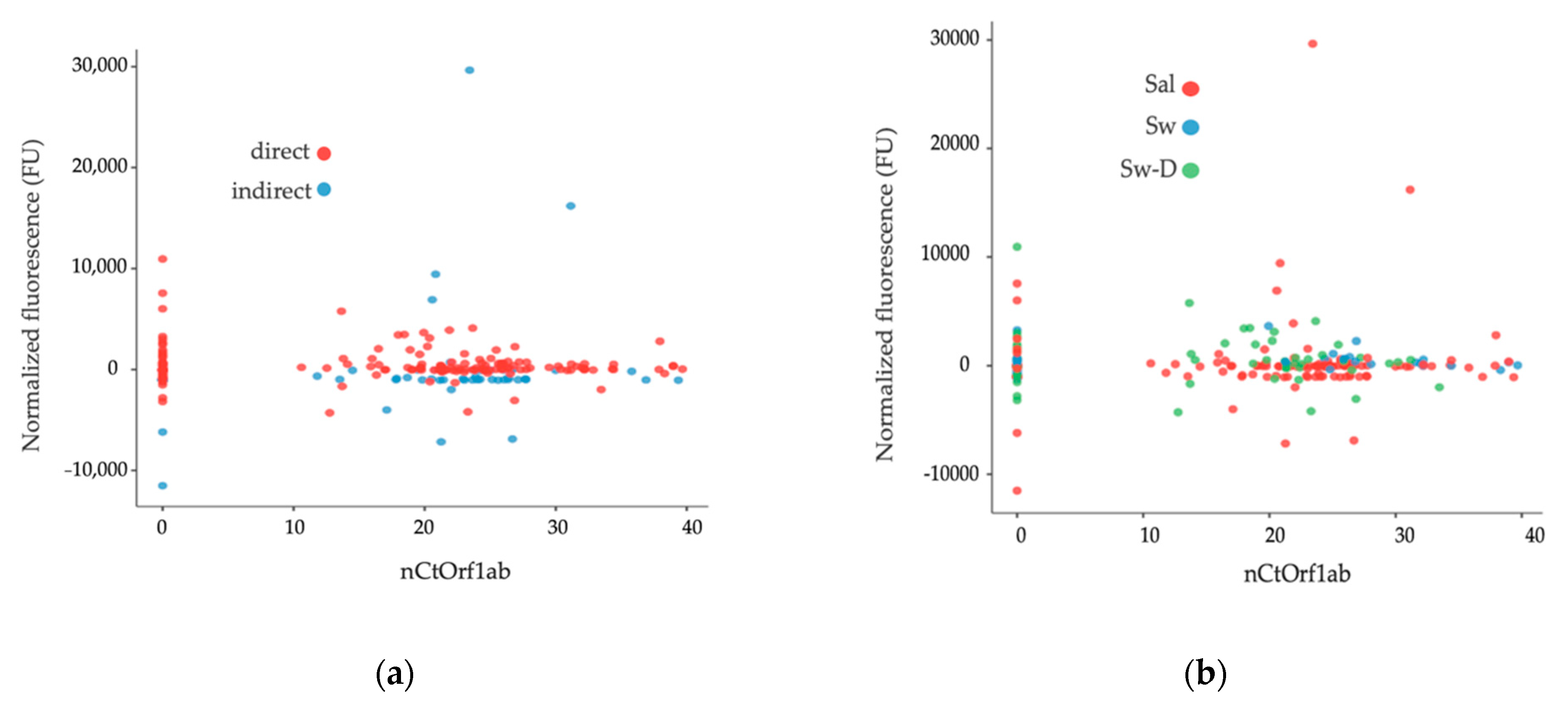
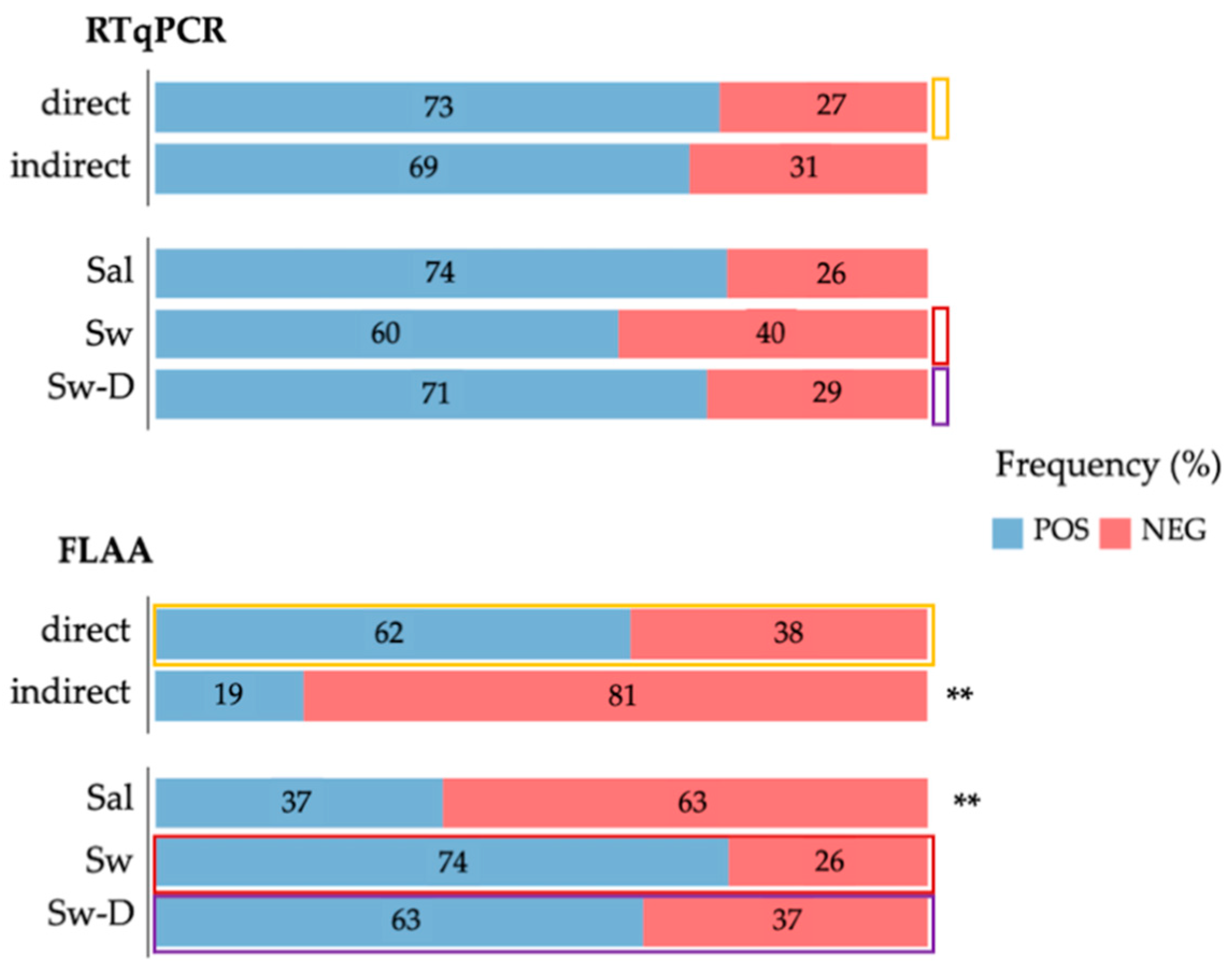
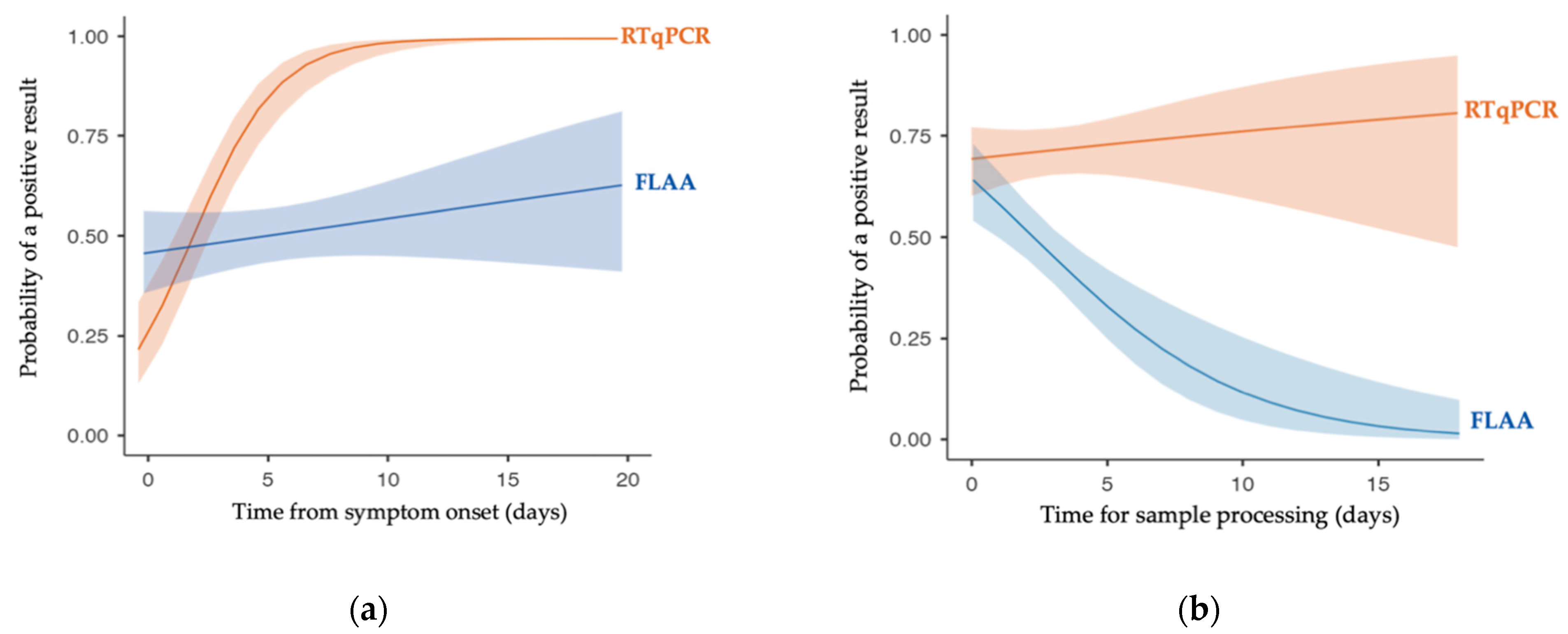
3.2. Second Step: Data Distribution for Preliminary Visualization
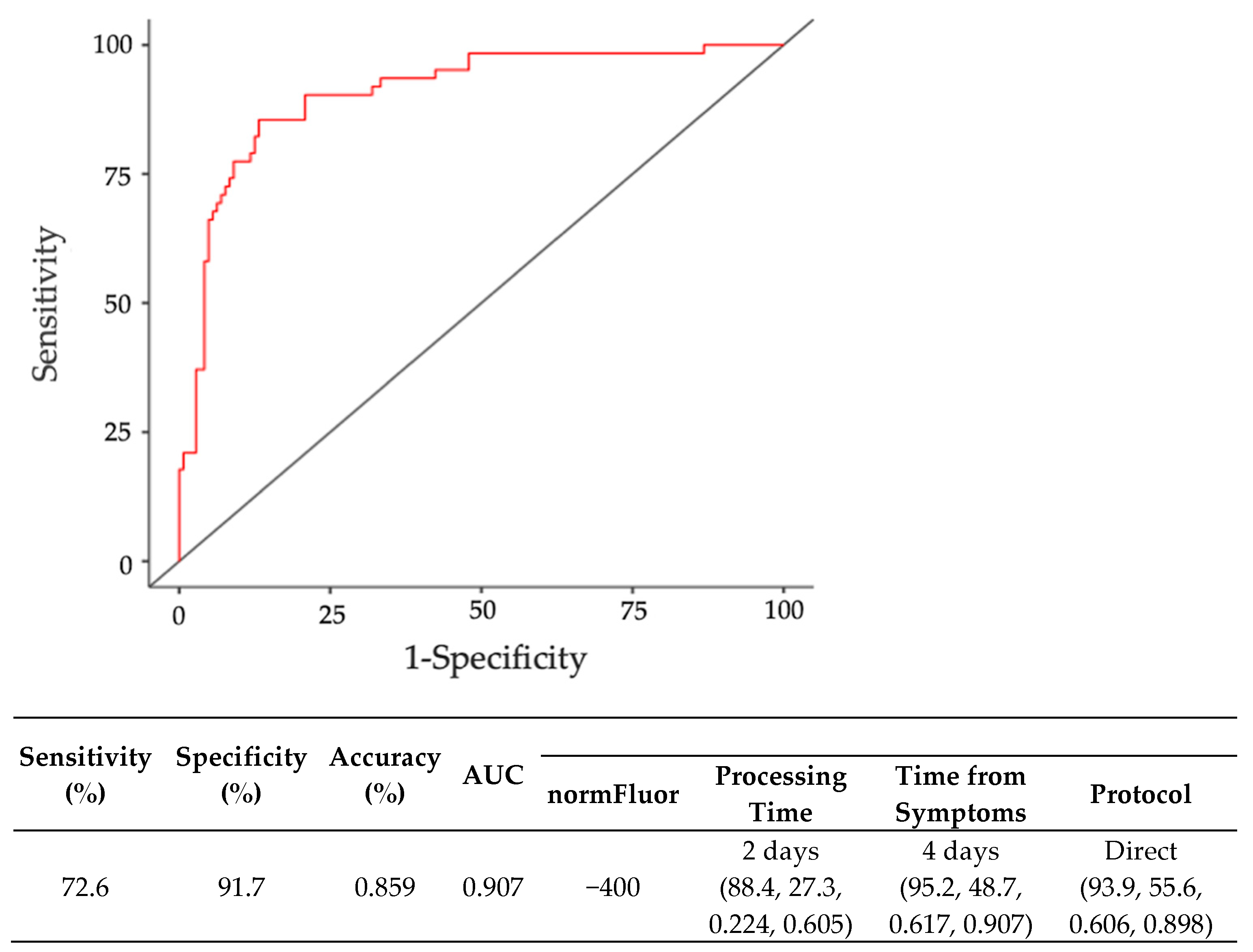
3.3. Third Step: Diagnostic Accuracy Analysis by Binomial Regression
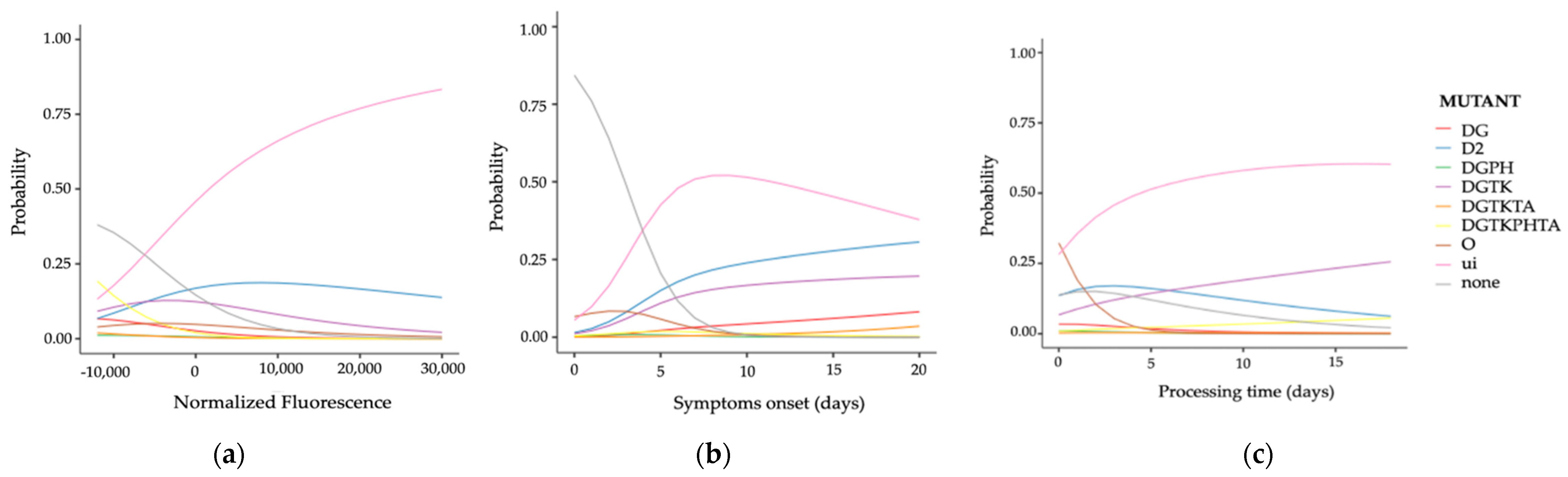
3.4. Fourth Step: Analyzing Influential Factors by Multinomial Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alpdagtas, S.; Ilhan, E.; Uysal, E.; Sengor, M.; Ustundag, C.B.; Gunduz, O. Evaluation of Current Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19. APL Bioeng. 2020, 4, 41506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleghani, N.; Taghipour, F. Diagnosis of COVID-19 for Controlling the Pandemic: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Saatchi, M.; Zadeh, S.S.T.; Aghamir, Z.S.; Shabestari, A.N.; Reis, L.O.; Aghamir, S.M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Accuracy and Sensitivity of Chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 Diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Anand, A.; Jain, N.; Goswami, S.; Anantharaj, A.; Patil, S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Shrivastava, T.; Bhatnagar, S.; et al. A Novel G-Quadruplex Aptamer-Based Spike Trimeric Antigen Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.; Kobokovich, A.; Connell, N.; Gronvall, G.K. COVID-19 Antibody Tests: A Valuable Public Health Tool with Limited Relevance to Individuals. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, M.J.; Parker, R.; Larremore, D.B. Rethinking Covid-19 Test Sensitivity—A Strategy for Containment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ni, X.; Dai, J. A DNA Aptamer Based Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Juhas, M.; Kwok, C.K. Aptamers Targeting SARS-COV-2: A Promising Tool to Fight against COVID-19. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment: RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In Vitro Selection of RNA Molecules That Bind Specific Ligands. Natrue 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino-Jarquin, G.; Toscano-Garibay, J.D. RNA Aptamer Evolution: Two Decades of SELEction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9155–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, A.T.H.; Krylova, S.M.; Kanoatov, M.; Desai, S.; Krylov, S.N. Ideal-Filter Capillary Electrophoresis (IFCE) Facilitates the One-Step Selection of Aptamers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2739–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S. SELEX-Based DNA Aptamer Selection: A Perspective from the Advancement of Separation Techniques. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Gu, J.; Brennan, J.D.; Li, Y. Aptamers for SARS-CoV-2: Isolation, Characterization, and Diagnostic and Therapeutic Developments. Anal. Sens. 2022, 2022, e202200012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Ray, P.; Carlin, A.F.; Magallanes, C.; Morgan, S.C.; Laurent, L.C.; Aronoff-Spencer, E.S.; Hall, D.A. Hitting the Diagnostic Sweet Spot: Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Salivary Antigen Testing with an off-the-Shelf Glucometer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pandey, R.; Li, J.; Gu, J.; White, D.; Stacey, H.D.; Ang, J.C.; Steinberg, C.; Capretta, A.; Filipe, C.D.M. High-Affinity Dimeric Aptamers Enable the Rapid Electrochemical Detection of Wild-Type and B. 1.1. 7 SARS-CoV-2 in Unprocessed Saliva. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24266–24274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Tian, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Fu, T.; Sun, J.; Tan, W. Rapid One-Step Detection of Viral Particles Using an Aptamer-Based Thermophoretic Assay. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7261–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, M.; Skouridou, V.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Viéitez, I.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Cabrera Alvargonzalez, J.J.; Poveda, E.; Bofill, C.B.; Sans, T.; Bashammakh, A. Aptamer Sandwich Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Antigen. ACS omega 2021, 6, 35657–35666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Roque, M.A.; Franco-Urquijo, P.A.; García-Velásquez, V.M.; Choukeife, M.; Mayer, G.; Molina-Ramírez, S.R.; Figueroa-Miranda, G.; Mayer, D.; Alvarez-Salas, L.M. DNA Aptamer Selection for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Detection. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 645, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Malah, S.S.; Saththasivam, J.; Jabbar, K.A.; K.K., A.; Gomez, T.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Mohamoud, Y.A.; Malek, J.A.; Abu Raddad, L.J.; Abu Halaweh, H.A.; et al. Application of Human RNase P Normalization for the Realistic Estimation of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Wastewater: A Perspective from Qatar Wastewater Surveillance. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Jamovi Project. 2021. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Disease Screening—Statistics Teaching Tools—New York State Department of Health. Available online: https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/chronic/discreen.htm (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Shreffler, J.; Huecker, M.R. Diagnostic Testing Accuracy: Sensitivity, Specificity, Predictive Values and Likelihood Ratio; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brü, L.E.; Katzenschlager, S.; Mcgrath Id, S.; Schmitz Id, S.; Gaeddert Id, M.; Erdmann Id, C.; Id, M.B.; Grilli, M.; Larmann, J.; Weigand, M.A.; et al. Accuracy of Rapid Point-of-Care Antigen-Based Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Meta-Regression Analyzing Influencing Factors. PLOS Med. 2022, 19, e1004011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Mohammed, I.; Zhao, L.; Wei, W.; Xiao, H.; Guo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, F.; Huang, Y. Identification of SARS-CoV-2-against Aptamer with High Neutralization Activity by Blocking the RBD Domain of Spike Protein 1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Stacey, H.D.; Ang, J.C.; Capretta, A.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Mossman, K.L.; Balion, C.; Salena, B.J. Diverse High-Affinity DNA Aptamers for Wild-Type and B. 1.1. 7 SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins from a Pre-Structured DNA Library. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 7267–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacherovsky, N.; Yang, L.F.; Dang, H.V.; Cheng, E.L.; Cardle, I.I.; Walls, A.C.; McCallum, M.; Sellers, D.L.; DiMaio, F.; Salipante, S.J. Discovery and Characterization of Spike N-terminal Domain-binding Aptamers for Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 21381–21385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakashansky, J.A.; Imamura, A.H.; Salgado, D.F.; Mercieca, H.C.R.; Aguas, R.F.L.; Lao, A.M.; Pariser, J.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Khine, M. Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in Saliva with Shrinky-Dink© Electrodes. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Liang, Z.; Hu, O.; He, Q.; Sun, D.; Chen, Z. An Electrochemical Dual-Aptamer Biosensor Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks MIL-53 Decorated with Au@Pt Nanoparticles and Enzymes for Detection of COVID-19 Nucleocapsid Protein. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 387, 138553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.A.; Nazari, L.; Acedo, P. A Photo-Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Determination of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Receptor-Binding Domain by Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride-Cadmium Sulfide Quantum Dots Nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; He, L.; Hu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J. A Serological Aptamer-Assisted Proximity Ligation Assay for COVID-19 Diagnosis and Seeking Neutralizing Aptamers. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 12157–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Giroux, E.; Jovic, M.; Martic-Milne, S. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Aptasensor for Selective Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein. Analyst 2021, 146, 7207–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhao, H.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Ge, M.; Qin, M.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Construction of Optimal SERS Hotspots Based on Capturing the Spike Receptor-Binding Domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 for Highly Sensitive and Specific Detection by a Fish Model. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16086–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wan, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Frequency, N (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Female | Male | |
| Gender | 242 (100) | 131 (54) | 111 (46) |
| Sal | 158 (65) | 90 (37) | 68 (28) |
| Sw | 35 (14) | 19 (8) | 16 (7) |
| Sw-D | 49 (20) | 22 (9) | 27 (11) |
| Direct | 164 (68) | 84 (35) | 80 (33) |
| Indirect | 78 (32) | 47 (19) | 31 (13) |
| N | Mean | SD | |
| Age (years) | 232 | 40.55 | 17.21 |
| Symptoms onset (days) | 213 | 5.65 | 4.64 |
| Sample processing (days) | 235 | 3.03 | 3.00 |
| RTqPCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FLAA | Positive | Negative | Total |
| Positive | 92 | 25 | 117 |
| Negative | 82 | 43 | 125 |
| Total | 174 | 68 | 242 |
| Parameters | |||
| Sensitivity | 52.9% | ||
| Specificity | 63.2% | ||
| Accuracy | 55.8% | ||
| Prevalence | 71.9% | ||
| Positive Predictive Value | 78.6% | ||
| Negative Predictive Value | 34.4% | ||
| Positive likelihood ratio | 1.438 | ||
| Negative likelihood ratio | 0.745 | ||
| Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Youden Index | AUC | Cutoff Point | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sal | 70.1 | 53.7 | 81.2 | 38.6 | 0.237 | 0.619 | −103 |
| Sw | 100 | 42.9 | 72.4 | 100.0 | 0.429 | 0.646 | −398 |
| Sw-D | 50 | 77.4 | 77.4 | 38.9 | 0.186 | 0.510 | 160 |
| Indirect (10%) | 54.7 | 72 | 80.6 | 42.9 | 0.267 | 0.655 | −884 |
| Direct (20%) | 93.3 | 25.0 | 77.2 | 57.9 | 0.183 | 0.531 | −404 |
| Overall | 71.1 | 50.7 | 78.3 | 41.2 | 0.218 | 0.587 | −78 |
| Ranges | Ct range | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy(%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlapped | <20; 0–20 | 89 | 52 | 76 | 85 |
| <25 | 79 | 83 | 81 | 89 | |
| <30 | 73 | 90 | 84 | 90 | |
| Independent | 20–25 | 90 | 80 | 86 | 91 |
| 25–30 | 97 | 78 | 90 | 94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco-Urquijo, P.A.; Sierra-Martínez, M.; Jarquín-Martínez, M.; Martínez-Roque, M.A.; García-Velásquez, V.M.; Acosta-Altamirano, G.; Ruiz-Pérez, N.J.; Toscano-Garibay, J.D.; Alvarez-Salas, L.M. Fluorescence-Linked Aptamer Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein: A Step-by-Step Performance Analysis in Clinical Samples. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112829
Franco-Urquijo PA, Sierra-Martínez M, Jarquín-Martínez M, Martínez-Roque MA, García-Velásquez VM, Acosta-Altamirano G, Ruiz-Pérez NJ, Toscano-Garibay JD, Alvarez-Salas LM. Fluorescence-Linked Aptamer Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein: A Step-by-Step Performance Analysis in Clinical Samples. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112829
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco-Urquijo, Pablo Alberto, Mónica Sierra-Martínez, Mariana Jarquín-Martínez, Mateo Alejandro Martínez-Roque, Victor Miguel García-Velásquez, Gustavo Acosta-Altamirano, Nancy Jannet Ruiz-Pérez, Julia Dolores Toscano-Garibay, and Luis Marat Alvarez-Salas. 2022. "Fluorescence-Linked Aptamer Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein: A Step-by-Step Performance Analysis in Clinical Samples" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112829
APA StyleFranco-Urquijo, P. A., Sierra-Martínez, M., Jarquín-Martínez, M., Martínez-Roque, M. A., García-Velásquez, V. M., Acosta-Altamirano, G., Ruiz-Pérez, N. J., Toscano-Garibay, J. D., & Alvarez-Salas, L. M. (2022). Fluorescence-Linked Aptamer Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Protein: A Step-by-Step Performance Analysis in Clinical Samples. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112829






