Federated Learning in Ocular Imaging: Current Progress and Future Direction
Abstract
1. Introduction
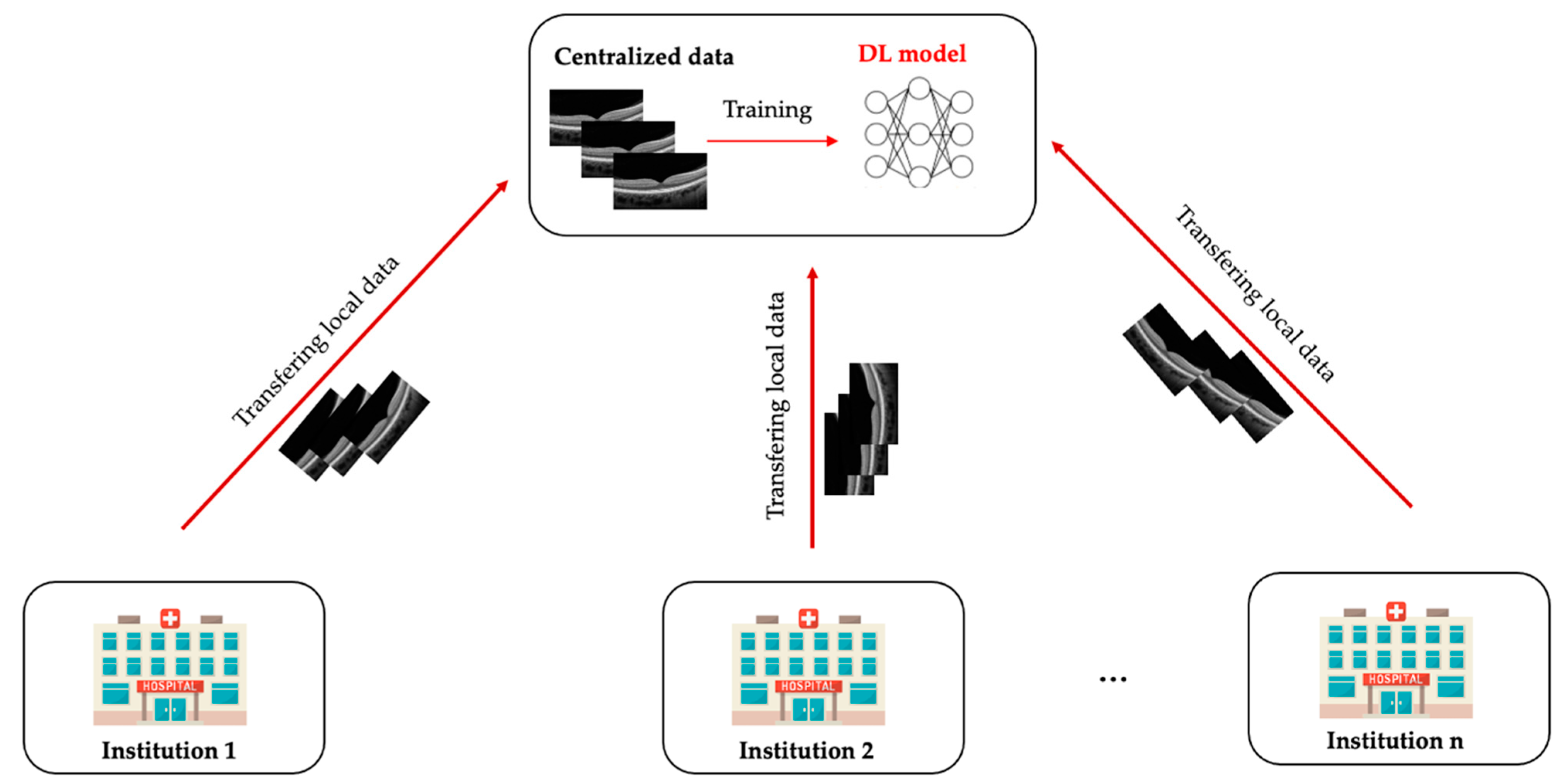
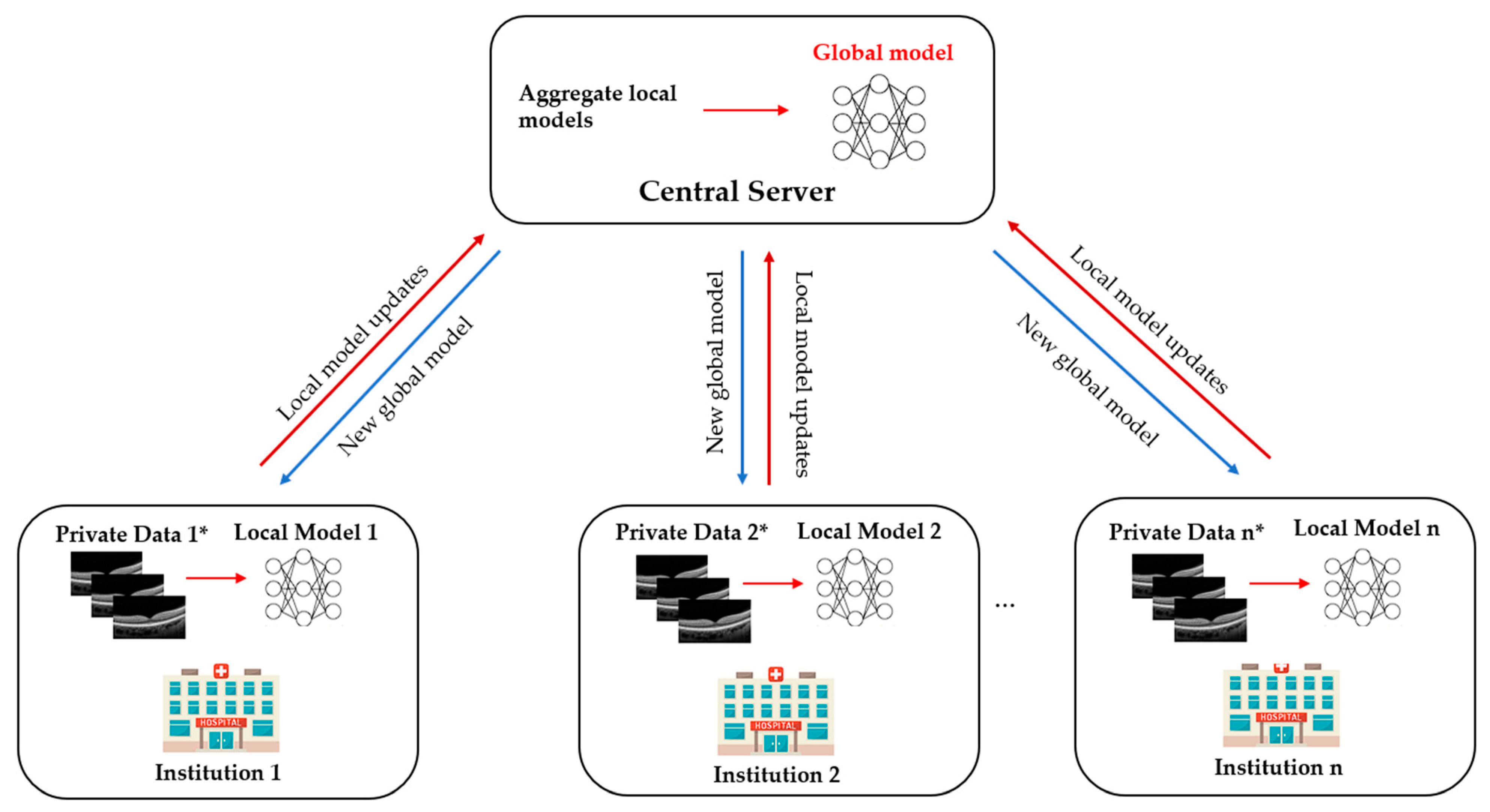
2. What Is Federated Learning?
3. Types of Federated Learning
4. Federated Learning Applications in Healthcare
4.1. Electronic Health Records
4.2. Internet of Things in Healthcare
4.3. Medical Image Analysis
5. Current FL Applications in Ophthalmology
5.1. Diabetic Retinopathy
5.2. Retinopathy of Prematurity
6. Challenges and Vulnerabilities
6.1. Data Heterogeneity
6.2. Bias
6.3. Privacy and Security
6.4. Communication Cost
7. Future Directions
7.1. Multi-Modal Federated Learning
7.2. Federated Learning and Rare Ocular Diseases
7.3. Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
7.4. Decentralised Federated Learning
7.5. Federated Learning and Fifth Generation (5G) and Beyond Technology
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul, V.; Enslin, S.; Gross, S.A. History of artificial intelligence in medicine. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamet, P.; Tremblay, J. Artificial intelligence in medicine. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2017, 69, S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.S.W.; Quang, N.D.; Gan, A.; Hamzah, H.; Garcia-Franco, R.; San Yeo, I.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images From Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 318, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Wang, X.; Ran, A.R.; Chan, C.K.M.; Ho, M.; Yip, W.; Young, A.L.; Lok, J.; Szeto, S.; Chan, J.; et al. A Multitask Deep-Learning System to Classify Diabetic Macular Edema for Different Optical Coherence Tomography Devices: A Multicenter Analysis. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, F.; Mengelkamp, J.; Brandl, C.; Harsch, S.; Zimmermann, M.E.; Linkohr, B.; Peters, A.; Heid, I.M.; Palm, C.; Weber, B.H.F. A Deep Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Age-Related Eye Disease Study Severity Scale for Age-Related Macular Degeneration from Color Fundus Photography. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, P.M.; Joshi, N.; Pekala, M.; Pacheco, K.D.; Freund, D.E.; Bressler, N.M. Automated Grading of Age-Related Macular Degeneration From Color Fundus Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Beers, A.; Chang, K.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Dy, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Ioannidis, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; et al. Automated Diagnosis of Plus Disease in Retinopathy of Prematurity Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Pasquale, L.R.; Peng, L.; Campbell, J.P.; Lee, A.Y.; Raman, R.; Tan, G.S.W.; Schmetterer, L.; Keane, P.A.; Wong, T.Y. Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; Keel, S.; Meng, W.; Chang, R.T.; He, M. Efficacy of a Deep Learning System for Detecting Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy Based on Color Fundus Photographs. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, A.R.; Cheung, C.Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Luo, L.Y.; Chan, P.P.; Wong, M.O.M.; Chang, R.T.; Mannil, S.S.; Young, A.L.; et al. Detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: A retrospective training and validation deep-learning analysis. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e172–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Yuan, J.; Cai, W.; Chen, T.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Nie, S.; Xu, X.; et al. Deep-learning models for the detection and incidence prediction of chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes from retinal fundus images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanayagam, C.; Xu, D.; Ting, D.S.W.; Nusinovici, S.; Banu, R.; Hamzah, H.; Lim, C.; Tham, Y.C.; Cheung, C.Y.; Tai, E.S.; et al. A deep learning algorithm to detect chronic kidney disease from retinal photographs in community-based populations. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e295–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, R.; Varadarajan, A.V.; Blumer, K.; Liu, Y.; McConnell, M.V.; Corrado, G.S.; Peng, L.; Webster, D.R. Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.Y.; Xu, D.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Sabanayagam, C.; Tham, Y.-C.; Yu, M.; Rim, T.H.; Chai, C.Y.; Gopinath, B.; Mitchell, P.; et al. A deep-learning system for the assessment of cardiovascular disease risk via the measurement of retinal-vessel calibre. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.Y.; Ran, A.R.; Wang, S.; Chan, V.T.T.; Sham, K.; Hilal, S.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Cheng, C.Y.; Sabanayagam, C.; Tham, Y.C.; et al. A deep learning model for detection of Alzheimer’s disease based on retinal photographs: A retrospective, multicentre case-control study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e806–e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.O.; Liu, H.; Ting, D.S.J.; Jeon, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Kim, J.E.; Sim, D.A.; Thomas, P.B.M.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Digital technology, tele-medicine and artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: A global perspective. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 82, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.P.; Lee, A.Y.; Abràmoff, M.; Keane, P.A.; Ting, D.S.W.; Lum, F.; Chiang, M.F. Reporting Guidelines for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Research. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Park, K.H.; Cheung, C.Y.; Tham, C.C.; Lam, D.S.C. Ocular Imaging Standardization for Artificial Intelligence Applications in Ophthalmology: The Joint Position Statement and Recommendations From the Asia-Pacific Academy of Ophthalmology and the Asia-Pacific Ocular Imaging Society. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 10, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Vettel, J.M.; Singh, A.; Poczos, B.; Grafton, S.T.; Erickson, K.I.; Tseng, W.-Y.I.; Verstynen, T.D. Quantifying Differences and Similarities in Whole-Brain White Matter Architecture Using Local Connectome Fingerprints. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigueoka, L.S.; Mariottoni, E.B.; Thompson, A.C.; Jammal, A.A.; Costa, V.P.; Medeiros, F.A. Predicting Age From Optical Coherence Tomography Scans With Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korot, E.; Pontikos, N.; Liu, X.; Wagner, S.K.; Faes, L.; Huemer, J.; Balaskas, K.; Denniston, A.K.; Khawaja, A.; Keane, P.A. Predicting sex from retinal fundus photographs using automated deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Shi, D.; Guankai, P.; Tan, Z.; Shang, X.; Hu, W.; Liao, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; et al. Retinal age gap as a predictive biomarker for mortality risk. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRullen, R.; Reddy, L. Reconstructing faces from fMRI patterns using deep generative neural networks. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.; Balachandar, N.; Lam, C.; Yi, D.; Brown, J.; Beers, A.; Rosen, B.; Rubin, D.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J. Distributed deep learning networks among institutions for medical imaging. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Kang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yu, H. Federated Learning. Synth. Lect. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. 2019, 13, 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Konečný, J.; McMahan, H.B.; Yu, F.X.; Richtárik, P.; Suresh, A.T.; Bacon, D. Federated Learning: Strategies for Improving Communication Efficiency. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.05492. [Google Scholar]
- Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.; Milletarì, F.; Roth, H.R.; Albarqouni, S.; Bakas, S.; Galtier, M.N.; Landman, B.A.; Maier-Hein, K.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Tong, Y. Federated Machine Learning: Concept and Applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q. Towards utilizing unlabeled data in federated learning: A survey and prospective. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11545. [Google Scholar]
- Deist, T.M.; Dankers, F.; Ojha, P.; Scott Marshall, M.; Janssen, T.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Masciocchi, C.; Valentini, V.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Distributed learning on 20 000+ lung cancer patients—The Personal Health Train. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 144, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Shamout, F.E.; Clifton, D.A. Preserving patient privacy while training a predictive model of in-hospital mortality. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.00354. [Google Scholar]
- Jaladanki, S.K.; Vaid, A.; Sawant, A.S.; Xu, J.; Shah, K.; Dellepiane, S.; Paranjpe, I.; Chan, L.; Kovatch, P.; Charney, A.W.; et al. Development of a federated learning approach to predict acute kidney injury in adult hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in New York City. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, A.; Jaladanki, S.K.; Xu, J.; Teng, S.; Kumar, A.; Lee, S.; Somani, S.; Paranjpe, I.; De Freitas, J.K.; Wanyan, T.; et al. Federated Learning of Electronic Health Records to Improve Mortality Prediction in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: Machine Learning Approach. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e24207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, E.; Van Velthoven, M.; Brindley, D.; Alturkistani, A.; Foley, K.; Rees, S.; Wells, G.; de Pennington, N. The Internet of Things in Health Care in Oxford: Protocol for Proof-of-Concept Projects. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2018, 7, e12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, W.; Qin, X. FedHealth: A Federated Transfer Learning Framework for Wearable Healthcare. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, E.; De Vos, M.; Boylan, G.; Ward, T. Estimation of Continuous Blood Pressure from PPG via a Federated Learning Approach. Sensors 2021, 21, 6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Milletarì, F.; Xu, D.; Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Zhu, W.; Baust, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J.; et al. Privacy-Preserving Federated Brain Tumour Segmentation. In Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop, MLMI 2019, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2019, Shenzhen, China, 13 October 2019; Springer: Shenzhen, China, 2019; pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Gu, Y.; Dvornek, N.; Staib, L.H.; Ventola, P.; Duncan, J.S. Multi-site fMRI analysis using privacy-preserving federated learning and domain adaptation: ABIDE results. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, I.; Vafaei Sadr, A.; Amini, M.; Salimi, Y.; Sanaat, A.; Akhavanallaf, A.; Razeghi, B.; Ferdowsi, S.; Saberi, A.; Arabi, H.; et al. Decentralized Distributed Multi-institutional PET Image Segmentation Using a Federated Deep Learning Framework. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; So, T.Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Q.; Vardhanabhuti, V.; Kaissis, G.; Li, Z.; Si, W.; Lee, H.H.C.; Yu, K.; et al. Federated deep learning for detecting COVID-19 lung abnormalities in CT: A privacy-preserving multinational validation study. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, I.; Ammar, S.; Kessentini, Y.; Muhammad, K. Federated learning for COVID-19 screening from Chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 106, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, I.; Roth, H.R.; Zhong, A.; Harouni, A.; Gentili, A.; Abidin, A.Z.; Liu, A.; Costa, A.B.; Wood, B.J.; Tsai, C.S.; et al. Federated learning for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Kong, D.; Lipkova, J.; Singh, R.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Mahmood, F. Federated learning for computational pathology on gigapixel whole slide images. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 76, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.T.L.; Lo, J.; Ma, D.; Zang, P.; Owen, J.; Wang, R.K.; Lee, A.Y.; Jia, Y.; Sarunic, M.V. Collaborative Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Classification of Optical Coherence Tomography Data through Federated Learning. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 1029. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, A.; Lu, C.; Chang, K.; Singh, P.; Coyner, A.S.; Brown, J.M.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Rubin, D.; Chiang, M.F.; et al. Federated Learning for Multicenter Collaboration in Ophthalmology: Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Disease Epidemiology. Ophthalmol. Retina 2022, 6, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Hanif, A.; Singh, P.; Chang, K.; Coyner, A.S.; Brown, J.M.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Rubin, D.; Chiang, M.F.; et al. Federated Learning for Multicenter Collaboration in Ophthalmology: Improving Classification Performance in Retinopathy of Prematurity. Ophthalmol. Retina 2022, 6, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, B.W.; Williams, C.; Juszczak, E.; Cocker, K.; Stenson, B.J.; Darlow, B.A.; Dai, S.; Gole, G.A.; Quinn, G.E.; Wallace, D.K.; et al. An international comparison of retinopathy of prematurity grading performance within the Benefits of Oxygen Saturation Targeting II trials. Eye 2018, 32, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Talwalkar, A.; Smith, V. Federated Learning: Challenges, Methods, and Future Directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Lai, L.; Suda, N.; Civin, D.; Chandra, V. Federated learning with non-iid data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, B. Towards Optimal Multi-Modal Federated Learning on Non-IID Data with Hierarchical Gradient Blending. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, London, UK, 2–5 May 2022; pp. 1469–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Hong, J.; Zhou, J. Data-free knowledge distillation for heterogeneous federated learning. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 139, 12878–12889. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, N.; Nishio, T.; Morikura, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Yonetani, R. Hybrid-FL: Cooperative Learning Mechanism Using Non-IID Data in Wireless Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.07210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Mathews, R.; Kiddon, C.; Eichner, H.; Beaufays, F.; Ramage, D. Federated evaluation of on-device personalization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.10252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Jin, Y. Federated learning on non-IID data: A survey. Neurocomputing 2021, 465, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.B.; Teeple, S.; Navathe, A.S. Addressing Bias in Artificial Intelligence in Health Care. JAMA 2019, 322, 2377–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, P.; Joshi, N.; Paul, W.; Pacheco, K.D.; Bressler, N.M. Addressing Artificial Intelligence Bias in Retinal Diagnostics. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Hw, X.; Lee, L.-H.; Fang, P.; Hui, P. Are You Left Out? An Efficient and Fair Federated Learning for Personalized Profiles on Wearable Devices of Inferior Networking Conditions. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Pei, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fedfair: Training fair models in cross-silo federated learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.05662. [Google Scholar]
- Mohri, M.; Sivek, G.; Suresh, A.T. Agnostic Federated Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.00146. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzeldin, Y.H.; Yan, S.; He, C.; Ferrara, E.; Avestimehr, S. Fairfed: Enabling group fairness in federated learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.00857. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, H.; Lee, K. Improving Fairness via Federated Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.15545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Kou, Z.; Wang, D. FairFL: A Fair Federated Learning Approach to Reducing Demographic Bias in Privacy-Sensitive Classification Models. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–13 December 2020; pp. 1051–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraguig, L.; Djebrouni, Y.; Bouchenak, S.; Marangozova, V. Survey of Bias Mitigation in Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference Francophone d’Informatique en Parallélisme, Architecture et Système, Virtuel, Lyon, France, 5–9 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Xian, M. Privacy-Preserving Distributed Deep Learning via Homomorphic Re-Encryption. Electronics 2019, 8, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugunthan, V.; Polychroniadou, A.; Byrd, D.; Balch, T.H. SMPAI: Secure Multi-Party Computation for Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2019 Workshop on Robust AI in Financial Services, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Phong, L.T.; Aono, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Wang, L.; Moriai, S. Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning via Additively Homomorphic Encryption. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Chu, A.; Goodfellow, I.; McMahan, H.B.; Mironov, I.; Talwar, K.; Zhang, L. Deep learning with differential privacy. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.00133. [Google Scholar]
- Bouacida, N.; Mohapatra, P. Vulnerabilities in Federated Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63229–63249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, S.; Konečny, J.; McMahan, H.B.; Talwalkar, A. Expanding the reach of federated learning by reducing client resource requirements. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.07210. [Google Scholar]
- Rothchild, D.; Panda, A.; Ullah, E.; Ivkin, N.; Stoica, I.; Braverman, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Arora, R. FetchSGD: Communication-Efficient Federated Learning with Sketching. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. pp. 8253–8265. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Lyu, L.; Huang, Y.; Xie, X. Communication-efficient federated learning via knowledge distillation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, F.; Song, D.; Tang, G.; He, J.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.; Song, Y.; Lin, F.; et al. Multimodal Machine Learning Using Visual Fields and Peripapillary Circular OCT Scans in Detection of Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.; Yan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Lou, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J. Multimodal deep learning with feature level fusion for identification of choroidal neovascularization activity in age-related macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022, 100, e512–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Barnaghi, P.; Haddadi, H. Multimodal federated learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.04833. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, A.; Ahmad, K.; Ahsan, M.A.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Qadir, J. Collaborative federated learning for healthcare: Multi-modal covid-19 diagnosis at the edge. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.07511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadilek, A.; Liu, L.; Nguyen, D.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Serghiou, S.; Rader, B.; Ingerman, A.; Mellem, S.; Kairouz, P.; Nsoesie, E.O.; et al. Privacy-first health research with federated learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheller, M.J.; Edwards, B.; Reina, G.A.; Martin, J.; Pati, S.; Kotrotsou, A.; Milchenko, M.; Xu, W.; Marcus, D.; Colen, R.R.; et al. Federated learning in medicine: Facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujinami-Yokokawa, Y.; Ninomiya, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Pontikos, N.; Yoshitake, K.; Iwata, T.; Sato, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Tsunoda, K.; et al. Prediction of causative genes in inherited retinal disorder from fundus photography and autofluorescence imaging using deep learning techniques. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Blockchain technology applications in healthcare: An overview. Int. J. Intell. Netw. 2021, 2, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.Y.; Tan, T.-E.; Xiao, Z.; Movva, P.V.H.; Foo, F.S.S.; Yun, D.; Chen, W.; Wong, T.Y.; Lin, H.T.; Ting, D.S.W. Blockchain Technology for Ophthalmology: Coming of Age? Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 10, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.-E.; Anees, A.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lei, X.; Ang, M.; et al. Retinal photograph-based deep learning algorithms for myopia and a blockchain platform to facilitate artificial intelligence medical research: A retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e317–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Blockchain-based Federated Learning: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02182. [Google Scholar]
- Warnat-Herresthal, S.; Schultze, H.; Shastry, K.L.; Manamohan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Garg, V.; Sarveswara, R.; Händler, K.; Pickkers, P.; Aziz, N.A.; et al. Swarm Learning for decentralized and confidential clinical machine learning. Nature 2021, 594, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairouz, P.; McMahan, H.B.; Avent, B.; Bellet, A.; Bennis, M.; Bhagoji, A.N.; Bonawitz, K.; Charles, Z.; Cormode, G.; Cummings, R. Advances and open problems in federated learning. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2021, 14, 1–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, O.L.; Quirke, P.; West, N.P.; James, J.A.; Loughrey, M.B.; Grabsch, H.I.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Alwers, E.; Cifci, D.; Ghaffari Laleh, N. Swarm learning for decentralized artificial intelligence in cancer histopathology. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects-A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Li, N.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Xiong, W.; Lu, L.; Li, W.; Zhou, D. Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences From Western China. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pan, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, J.; Qin, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Ting, D.; Chen, Y. Application of 5G Technology to Conduct Real-Time Teleretinal Laser Photocoagulation for the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021, 139, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.X.; Ran, A.R.; Hu, X.; Yang, D.; Jiang, M.; Dou, Q.; Cheung, C.Y. Federated Learning in Ocular Imaging: Current Progress and Future Direction. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112835
Nguyen TX, Ran AR, Hu X, Yang D, Jiang M, Dou Q, Cheung CY. Federated Learning in Ocular Imaging: Current Progress and Future Direction. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112835
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Truong X., An Ran Ran, Xiaoyan Hu, Dawei Yang, Meirui Jiang, Qi Dou, and Carol Y. Cheung. 2022. "Federated Learning in Ocular Imaging: Current Progress and Future Direction" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112835
APA StyleNguyen, T. X., Ran, A. R., Hu, X., Yang, D., Jiang, M., Dou, Q., & Cheung, C. Y. (2022). Federated Learning in Ocular Imaging: Current Progress and Future Direction. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112835







