The Potential Role of MUC16 (CA125) Biomarker in Lung Cancer: A Magic Biomarker but with Adversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MUC16 (CA 125) as a Lung Cancer Biomarker
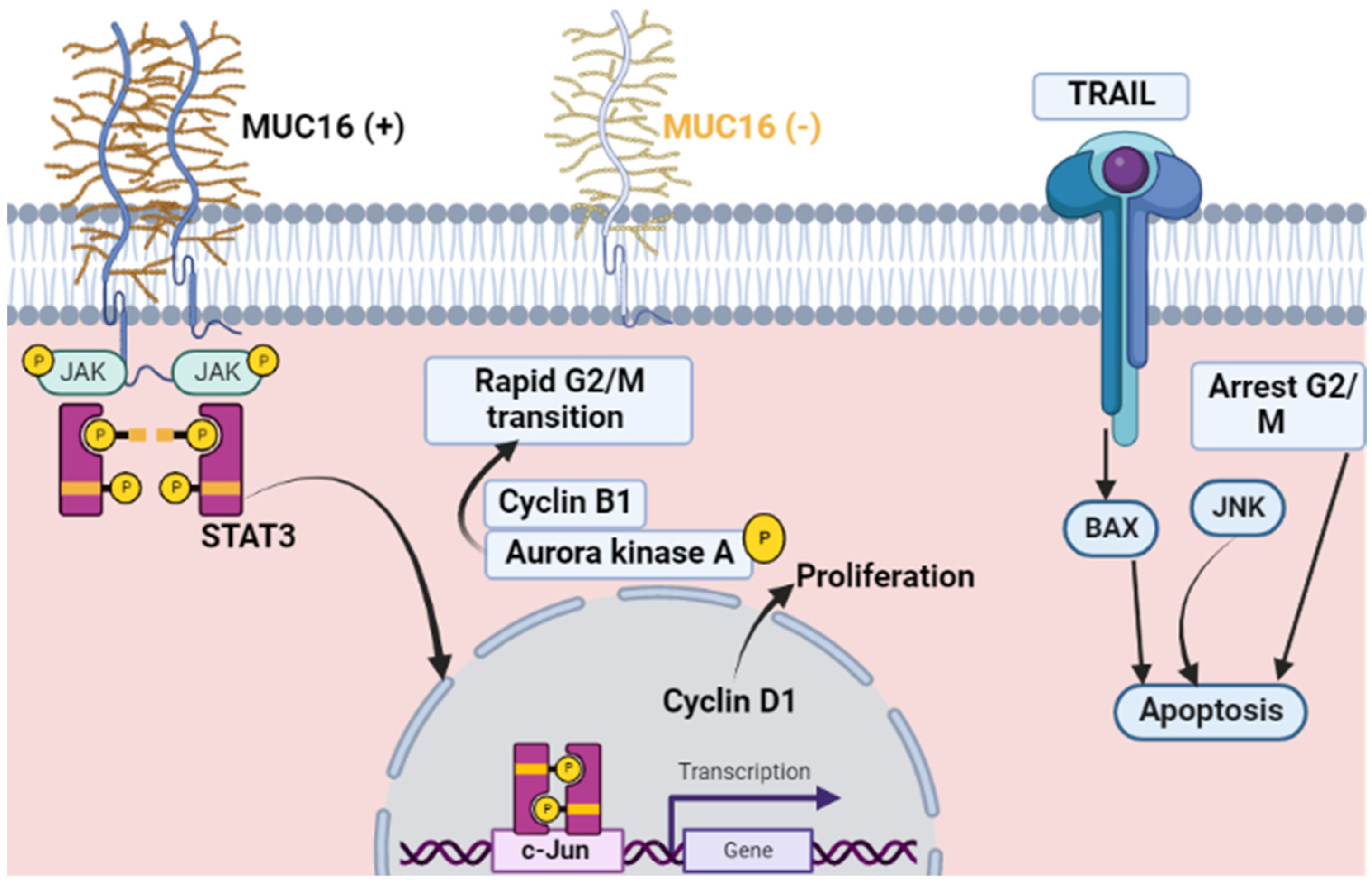
3. Muc16 (CA 125) and Malignant Proliferation
4. Muc16 (CA 125) and Metastasis
5. Mechanism of MUC16-Mediated Chemoresistance
6. Muc16 (CA 125) and Non-Malignant Proliferation
7. CA125, Proteomics, and Genomics Findings
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, T.R.; Im Choi, S.; Cho, E.W.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, I.G. TSPYL5 is involved in cell growth and the resistance to radiation in A549 cells via the regulation of p21WAF1/Cip1 and PTEN/AKT pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer progress and priorities: Lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter-Harris, L.; Slaven, J.E., Jr.; Monahan, P.O.; Shedd-Steele, R.; Hanna, N.; Rawl, S.M. Understanding lung cancer screening behavior: Racial, gender, and geographic differences among Indiana long-term smokers. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 10, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp. Oncol./Współczesna Onkol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Yin, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q. Trends in the incidence, treatment, and survival of patients with lung cancer in the last four decades. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. An electronic nose-based assistive diagnostic prototype for lung cancer detection with conformal prediction. Measurement 2020, 158, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Asada, K.; Takasawa, K.; Shimoyama, R.; Sakai, A.; Bolatkan, A.; Shinkai, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Komatsu, M.; Kaneko, S. Predicting deep learning based multi-omics parallel integration survival subtypes in lung cancer using reverse phase protein array data. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, V.M.L.; Carvalho, L. Heterogeneity in lung cancer. Pathobiology 2018, 85, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, B.D.; Shroff, G.S.; Truong, M.T.; Ko, J.P. Spectrum of lung adenocarcinoma. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2019, 40, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M.; Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer incidence in young women vs. young men: A systematic analysis in 40 countries. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmaully, J.; Tvardik, N.; Martin, D.; Billmann, R.; Cénée, S.; Antoine, M.; Blons, H.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Trédaniel, J.; Wislez, M. Risk of lung cancer among women in relation to lifetime history of tobacco smoking: A population-based case-control study in France (the WELCA study). BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.T.; Thomas, N.A.; Ward, R.; Rojewski, A.; Gebregziabher, M.; Toll, B.; Silvestri, G.A. Association of cigarette type with lung cancer incidence and mortality: Secondary analysis of the National lung screening trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, C.M.; Bora-Singhal, N.; Kumar, D.M.; Chellappan, S.P. Regulation of Sox2 and stemness by nicotine and electronic-cigarettes in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avino, P.; Scungio, M.; Stabile, L.; Cortellessa, G.; Buonanno, G.; Manigrasso, M. Second-hand aerosol from tobacco and electronic cigarettes: Evaluation of the smoker emission rates and doses and lung cancer risk of passive smokers and vapers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Phandthong, R.; Chaili, A.; Remark, G.; Talbot, P. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of A549 lung cancer cells exposed to electronic cigarettes. Lung Cancer 2018, 122, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlinden, K.D.; Lu, W.; Eapen, M.S.; Sohal, S.S. Electronic cigarettes: Modern instruments for toxic lung delivery and posing risk for the development of chronic disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 137, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): Updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The effect of advances in lung-cancer treatment on population mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Meng, W.-Y.; Li, R.-Z.; Wang, Y.-W.; Qian, X.; Chan, C.; Yu, Z.-F.; Fan, X.-X.; Pan, H.-D.; Xie, C. Early lung cancer diagnostic biomarker discovery by machine learning methods. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, R.; Li, Y.; Jin, R.; Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Che, Y.; Lu, Z.; Mao, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, C. Enhancement of diagnostic performance in lung cancers by combining CEA and CA125 with autoantibodies detection. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1625689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, M.R.; Kastelijn, E.A.; Peters, B.J.; Kelder, H.; Schramel, F.M. Evaluation of serum biomarker CEA and Ca-125 as immunotherapy response predictors in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, S.; Satoh, H.; Kagohashi, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Kamma, H.; Sekizawa, K. Production of CA125 by human lung cancer cell lines. Clin. Exp. Med. 2004, 4, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, M.; Kapur, A.; Gonzalez-Bosquet, J.; Horibata, S.; Heintz, J.; Albrecht, R.; Fass, L.; Kaur, J.; Hu, K.; Shojaei, H. MUC16 (CA125): Tumor biomarker to cancer therapy, a work in progress. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.-K.; Gu, C.-L.; Fan, J.-Q.; Zhang, X.-M. P-STAT3 and IL-17 in tumor tissues enhances the prognostic value of CEA and CA125 in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Gao, C.; Xing, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.-G.; Li, X. 5-Hydroxymethylome in circulating cell-free DNA as a potential biomarker for non-small-cell lung cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhang, L. Serum CA125 levels are decreased in rectal cancer but increased in fibrosis-associated diseases and in most types of cancers. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 162, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bottoni, P.; Scatena, R. The role of CA 125 as tumor marker: Biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv. Cancer Biomark. 2015, 867, 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Masahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, K.; Ohsawa, M.; Narita, O.; Asai, T.; Ishihara, M. Serum CA 125 levels in patients with endometriosis: Changes in CA 125 levels during menstruation. Obstet. Gynecol. 1988, 72, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kafali, H.; Artunc, H.; Erdem, M. Evaluation of factors that may be responsible for cyclic change of CA125 levels during menstrual cycle. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 275, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dochez, V.; Caillon, H.; Vaucel, E.; Dimet, J.; Winer, N.; Ducarme, G. Biomarkers and algorithms for diagnosis of ovarian cancer: CA125, HE4, RMI and ROMA, a review. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aithal, A.; Rauth, S.; Kshirsagar, P.; Shah, A.; Lakshmanan, I.; Junker, W.M.; Jain, M.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K. MUC16 as a novel target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shen, L.; Qian, N.; Chen, K. The prognostic values of CA125, CA19. 9, NSE, AND SCC for stage I NSCLC are limited. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, M.; Ding, X.-J.; Song, X.; Zhou, G.-B.; Cao, Y. MUC16 overexpression induced by gene mutations promotes lung cancer cell growth and invasion. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przepiorkowski, J.A. The Association between Serum Cancer Antigen 125 (CA 125) and Risk of Lung Cancer in Females: Assessing the Possibilities for Early Detection. 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10464/15097 (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Majewski, S.; Szewczyk, K.; Żal, A.; Białas, A.J.; Miłkowska-Dymanowska, J.; Piotrowski, W.J. Serial Measurements of Circulating KL-6, SP-D, MMP-7, CA19-9, CA-125, CCL18, and Periostin in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Receiving Antifibrotic Therapy: An Exploratory Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albogami, S.M.; Al-kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Maiahy, T.J.; Al-Buhadily, A.K.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alorabi, M.; Alotaibi, S.S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Saad, H.M.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Preeclampsia: A New Perspective. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, E.; Lavee, J.; Raanani, E.; Patel, J.; Peled, Y. Ca125 as an Early Marker for Graft Dysfunction in Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Guidance for Therapy. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K. MicroRNA-218-5p affects lung adenocarcinoma progression through targeting endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase 1 alpha. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 10061–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zang, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Mao, S.; Che, Y.; Wang, X. ERO1L promotes IL6/sIL6R signaling and regulates MUC16 expression to promote CA125 secretion and the metastasis of lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lycke, M.; Ulfenborg, B.; Lauesgaard, J.M.; Kristjansdottir, B.; Sundfeldt, K. Consideration should be given to smoking, endometriosis, renal function (eGFR) and age when interpreting CA125 and HE4 in ovarian tumor diagnostics. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2021, 59, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, S.; Zahan, R.; Yesmin, S.; Khan, A.; Mahmud, M.S.; Reza, M.A.; Albogami, S.M.; Alorabi, M.; De Waard, M.; Saad, H.M.; et al. Phytochemical Analysis and Understanding the Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties of Methanol Extract from Litsea glutinosa: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Bi, W.; Fan, T. Analysis on the Effects of CT-and Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Biopsy Combined with Serum CA125 and CEA on the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2289432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-F.; Peng, S.-J.; Liu, R.-Q.; Yu, Y.-J.; Ge, Q.-M.; Liang, R.-B.; Li, Q.-Y.; Li, B.; Shao, Y. The combination of CA125 and NSE is useful for predicting liver metastasis of lung cancer. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8850873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Feng, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, W. Deep learning model as a new trend in computer-aided diagnosis of tumor pathology for lung cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, I.; Salfity, S.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Rachagani, S.; Thomas, A.; Das, S.; Majhi, P.D.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Vengoji, R.; Lele, S.M. MUC16 Regulates TSPYL5 for Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Chemoresistance by Suppressing p53MUC16, TSPYL5, and Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3906–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashf, D.W.A.; Okasha, A.N.; Sahyoun, N.A.; El-Rabi, R.E.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Predicting DNA lung cancer using artificial neural network. Int. J. Acad. Dev. 2018, 2, 6–13. Available online: http://dstore.alazhar.edu.ps/xmlui/handle/123456789/321 (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Giamougiannis, P.; Martin-Hirsch, P.L.; Martin, F.L. The evolving role of MUC16 (CA125) in the transformation of ovarian cells and the progression of neoplasia. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, A.; Aghaie, A.; Vahedi, E.; Qazvini, A.; Ghanei, M.; Afkhami, A.; Hajian, A.; Bagheri, H. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of lung cancer biomarkers: A review. Talanta 2020, 206, 120251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.; Patterson, M.; Karnwal, S.; Brooks, C.L. Crystal structure of a human MUC16 SEA domain reveals insight into the nature of the CA125 tumor marker. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2022, 90, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhchi, P.; Cybulski, C.; Gronwald, J.; Wong, F.O.; Narod, S.A.; Akbari, M.R. CA125 and ovarian cancer: A comprehensive review. Cancers 2020, 12, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funston, G.; Hamilton, W.; Abel, G.; Crosbie, E.J.; Rous, B.; Walter, F.M. The diagnostic performance of CA125 for the detection of ovarian and non-ovarian cancer in primary care: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kanwal, M.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Niu, H.; Li, Z.; Ding, X. MUC16 in non-small cell lung cancer patients affected by familial lung cancer and indoor air pollution: Clinical characteristics and cell behaviors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Shi, Y. Association of MUC16 Mutation With Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2013201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Fennell, D.A.; De Ruysscher, D.K. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Goldstein, A.M.; Consonni, D.; Pesatori, A.C.; Wacholder, S.; Tucker, M.A.; Caporaso, N.E.; Goldin, L.; Landi, M.T. Family history of cancer and nonmalignant lung diseases as risk factors for lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Wever, B.; Mazzaschi, G.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Rolfo, C.; Quaini, F.; Tiseo, M.; Giovannetti, E. Molecular basis and rationale for combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2019, 46, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Senan, S.; Paul, M.A.; Mehran, R.J.; Louie, A.V.; Balter, P.; Groen, H.J.; McRae, S.E.; Widder, J.; Feng, L. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmanaprabu, S.; Mohanty, S.N.; Shankar, K.; Arunkumar, N.; Ramirez, G. Optimal deep learning model for classification of lung cancer on CT images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, M.; Sugiyama, O.; Yakami, M.; Ueno, S.; Kubo, T.; Kuroda, T.; Togashi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule classification between benign nodule, primary lung cancer, and metastatic lung cancer at different image size using deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dammas, S.; Patz, E.F., Jr.; Goodman, P.C. Identification of small lung nodules at autopsy: Implications for lung cancer screening and overdiagnosis bias. Lung Cancer 2001, 33, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Song, S.-Y.; Ahn, H.-S.; An, B.C.; Choi, Y.-D.; Yang, E.G.; Na, K.-J.; Lee, S.-T.; Park, J.-I.; Kim, S.-Y. Integrative analysis for the discovery of lung cancer serological markers and validation by MRM-MS. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.-Q.; Huang, L.-S.; Zhu, B. Assessment of seven clinical tumor markers in diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Dis. Mrk. 2018, 2018, 9845123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.I.; Yoo, C.H.; Sohn, B.H.; Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.L.; Dai Kim, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, W.K.; Pae, W.K. Predictive value of preoperative serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA125 levels for peritoneal metastasis in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2004, 36, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. Blood protein biomarkers in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 551, 215886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chu, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X. Development of a prediction model with serum tumor markers to assess tumor metastasis in lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.-M.; Zou, Y.-T.; Shi, W.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Li, B.; Min, Y.-L.; Yuan, Q.; Shao, Y. Ocular Metastasis in Elderly Lung Cancer Patients: Potential Risk Factors of CA-125, CA-153 and TPSA. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wu, R.; Lu, K.; Zhou, H. Identifying the best marker combination in CEA, CA125, CY211, NSE, and SCC for lung cancer screening by combining ROC curve and logistic regression analyses: Is it feasible? Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 2082840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Tao, H.; Guo, D. Dynamics of serum tumor markers can serve as a prognostic biomarker for Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Hu, X.S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, P.; Xu, J.P.; He, X.H.; Hao, X.Z.; Jiang, P.D. Survival and pretreatment prognostic factors for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A comprehensive analysis of 358 patients. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Luanpitpong, S.; Chunhacha, P.; Promden, W.; Sriuranpong, V. Expression of CA125 and cisplatin susceptibility of pleural effusion-derived human lung cancer cells from a Thai patient. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, J. Clinical efficacy and safety of crizotinib and alectinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treatment and predictive value of CEA and CA125 for treatment efficacy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 13108. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Jia, L. LncRNA SNHG7 sponges miR-216b to promote proliferation and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer through upregulating GALNT1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Green, M.D.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Journey, S.N.; Choi, J.E.; Rizvi, S.M.; Qin, A.; Waninger, J.J.; Lang, X.; et al. Liver metastasis restrains immunotherapy efficacy via macrophage-mediated T cell elimination. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Song, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Huo, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Bao, H. The effect of CA125 on metastasis of ovarian cancer: Old marker new function. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.; Xiao, Z.; Long, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X. CA125 is superior to CA19-9 in predicting the resectability of pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Tian, B.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Sun, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jing, J. The diagnostic value of serum tumor markers CEA, CA19-9, CA125, CA15-3, and TPS in metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 470, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, N.D.; Cass, I.; Walsh, C.S.; Karlan, B.Y.; Li, A.J. CA125 surveillance increases optimal resectability at secondary cytoreductive surgery for recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.G.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, J.N.; Yu, Y.; Lu, K.H.; Diamandis, E.P.; Hellstrom, I.; Mok, S.C.; Liu, J.; Bast, R.C., Jr. Potential markers that complement expression of CA125 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 99, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.; Hollingworth, J.; Reynolds, T. The role of CA125 in clinical practice. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, M.; Klink, M. The Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in the Progression and Chemoresistance of Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G.J.; Baser, R.E.; Brady, M.F.; Bristow, R.E.; Markman, M.; Spriggs, D.; Thaler, H.T. CA125 regression in ovarian cancer patients treated with intravenous versus intraperitoneal platinum-based chemotherapy: A gynecologic oncology group study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatzemeier, U.; von Pawel, J.; Vynnychenko, I.; Zatloukal, P.; de Marinis, F.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Paz-Ares, L.; Schumacher, K.M.; Goddemeier, T.; O’Byrne, K.J.; et al. First-cycle rash and survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer receiving cetuximab in combination with first-line chemotherapy: A subgroup analysis of data from the FLEX phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pless, M.; Stupp, R.; Ris, H.B.; Stahel, R.A.; Weder, W.; Thierstein, S.; Gerard, M.A.; Xyrafas, A.; Früh, M.; Cathomas, R.; et al. Induction chemoradiation in stage IIIA/N2 non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Luft, A.V.; Szczesna, A.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Dediu, M.; Ramlau, R.; Galiulin, R.K.; Bálint, B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Necitumumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (SQUIRE): An open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epping, M.T.; Meijer, L.A.; Krijgsman, O.; Bos, J.L.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Bernards, R. TSPYL5 suppresses p53 levels and function by physical interaction with USP7. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van ’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.; Mao, M.; Peterse, H.L.; van der Kooy, K.; Marton, M.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002, 415, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.K.; Frankel, P.H.; Mortazavi, A.; Milowsky, M.; Vaishampayan, U.; Parikh, M.; Lyou, Y.; Weng, P.; Parikh, R.; Teply, B.; et al. Effect of Cisplatin and Gemcitabine With or Without Berzosertib in Patients With Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lyu, Q.; Luo, P.; Li, M.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Lyu, Q. Applications of Machine Learning to Predict Cisplatin Resistance in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 5911–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, Q.; Fei, X.; Li, C.; Li, B. Elevated tumor markers in a benign lung disease. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P. Tumor markers CA15-3, CA125, CEA and breast cancer survival by molecular subtype: A cohort study. Breast Cancer 2020, 27, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Du, K.; Liu, T.; Chen, G. Prognostic value of tumor markers, NSE, CA125 and SCC, in operable NSCLC Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11145–11156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Clinical evaluation and therapeutic monitoring value of serum tumor markers in lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2016, 31, e80–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, F.; Nath, R.; Sokolovsky, N.; Scaffidi, J.; Boley, J.; Mehra, G.; Sayanseh, A. Incidental finding of raised CA125: A cause for concern. Crit Care Obs. Gyne 2018, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sears, C.R.; Mazzone, P.J. Biomarkers in lung cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, X. Targeted therapies in gynecological cancers: A comprehensive review of clinical evidence. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.C.; Jia, B.; Hu, G.; Al Johani, L.I.; Fritz-Klaus, R.; Ham, J.D.; Fichorova, R.N.; Elias, K.M.; Cramer, D.W.; Patankar, M.S. Ovarian Cancer Ascites Inhibits Transcriptional Activation of NK Cells Partly through CA125. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Malukar, N.; Jain, S. Serum CA-125 and Serum CEA Ratio to Distinguish between Ovarian Malignancies and Non-ovarian Malignancies. Indian J. Med. Biochem. 2020, 24, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, A.H.; Tashie, C.; Wolf, S.; Troy, J.D.; Zafar, Y. Tumor marker response to SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, B.; Harper, S.L.; Goldman, A.R.; Bitler, B.G.; Aird, K.M.; Borowsky, M.E.; Cadungog, M.G.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Jean, S. CLIC1 and CLIC4 complement CA125 as a diagnostic biomarker panel for all subtypes of epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tansir, G.; Kumar, P.; Pius, A.; Sunny, S.; Soneja, M. Pseudo-pseudo Meigs’ syndrome: A rare presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Reumatismo 2019, 71, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, D.; Bai, W.; He, D.; Wang, D. Correlation between serum tumor marker levels and connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trape, J.; Filella, X.; Alsina-Donadeu, M.; Juan-Pereira, L.; Bosch-Ferrer, A.; Rigo-Bonnin, R.; Oncology Section of the Catalan Association of Clinical Laboratory Science. Increased plasma concentrations of tumour markers in the absence of neoplasia. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 1605–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsaa, K.; Gundestrup, S.; Jensen, J.-U.; Lange, P.; Løkke, A.; Roberts, N.B.; Shaker, S.B.; Sørensen, A.R.; Titlestad, I.L.; Thomsen, L.H. Danish respiratory society position paper: Palliative care in patients with chronic progressive non-malignant lung diseases. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 5, 1530029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, C.-H.; Tong, D.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Su, Z.-Q.; Luo, Y.-L.; Xing, J.; Bai, Y.-L.; Guo, S.-J.; Li, S.-Y. Performance evaluation of detecting circulating tumor cells and tumor cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in diagnosis of peripheral lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yu, X.; Li, S.; Lei, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Analysis of circulating tumor cells in ovarian cancer and their clinical value as a biomarker. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-X.; Neoh, K.H.; Chang, X.-H.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Ye, X.; Ma, R.-Q.; Han, R.P.; Cui, H. Diagnostic value of HE4+ circulating tumor cells in patients with suspicious ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Gao, L.; Jiang, X.; Fu, R.; Zhang, T.; Ren, T.; Hu, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, P. Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells and tumor markers in the diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3782–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Kou, T.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic models based on postoperative circulating tumor cells can predict poor tumor recurrence-free survival in patients with stage II-III colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doseeva, V.; Colpitts, T.; Gao, G.; Woodcock, J.; Knezevic, V. Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Wang, X.F.; Han, X.; Choi, H.; Seeley, M.; Scherer, R.; Doseeva, V. Evaluation of a Serum Lung Cancer Biomarker Panel. Biomark Insights 2018, 13, 1177271917751608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, R.; Marrades, R.M.; Augé, J.M.; Escudero, J.M.; Viñolas, N.; Reguart, N.; Ramirez, J.; Filella, X.; Molins, L.; Agustí, A. Assessment of a combined panel of six serum tumor markers for lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, L.M.; Peled, N.; Ajona, D.; Boeri, M.; Field, J.K.; Sozzi, G.; Pio, R.; Zulueta, J.J.; Spira, A.; Massion, P.P. Biomarkers in lung cancer screening: Achievements, promises, and challenges. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestri, G.A.; Tanner, N.T.; Kearney, P.; Vachani, A.; Massion, P.P.; Porter, A.; Springmeyer, S.C.; Fang, K.C.; Midthun, D.; Mazzone, P.J. Assessment of plasma proteomics biomarker’s ability to distinguish benign from malignant lung nodules: Results of the PANOPTIC (Pulmonary Nodule Plasma Proteomic Classifier) trial. Chest 2018, 154, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, F.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, N.; Chen, Z.; Lv, Y.; Shao, K.; Li, N.; Qiu, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Identification of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer by proteomic analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.008821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poschmann, G.; Sitek, B.; Sipos, B.; Ulrich, A.; Wiese, S.; Stephan, C.; Warscheid, B.; Klöppel, G.; Vander Borght, A.; Ramaekers, F.C.; et al. Identification of proteomic differences between squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and bronchial epithelium. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seike, M.; Kondo, T.; Fujii, K.; Okano, T.; Yamada, T.; Matsuno, Y.; Gemma, A.; Kudoh, S.; Hirohashi, S. Proteomic signatures for histological types of lung cancer. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.E.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, K.H.; Fung, E.T.; Bast, R.C., Jr. Proteomic biomarkers in combination with CA 125 for detection of epithelial ovarian cancer using prediagnostic serum samples from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Cancer 2012, 118, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Sokoll, L.J.; Rai, A.J.; Rosenzweig, J.M.; Cameron, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meng, X.Y.; et al. Three biomarkers identified from serum proteomic analysis for the detection of early stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5882–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Naka, T.; Serada, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Shima, Y.; Yamadori, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Proteomics-based identification of alpha-enolase as a tumor antigen in non-small lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanes, D.; Alcala, K.; Alcala, N.; Amos, C.; Arslan, A.; Bassett, J.; Brennan, P.; Cai, Q.; Chen, C.; Feng, X. The Blood Proteome of Imminent Lung Cancer Diagnosis. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Tang, W.-F.; Yang, L.-L.; Wu, M.; Bao, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hong, H.-Z.; Wu, Y.-L.; Zhong, W.-Z. EP16. 02-024 Plasma ctDNA Organ-Specific Genomic Patterns and Origination Analysis in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S581–S582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J. Circulating tumor DNA predicts the outcome of chemotherapy in patients with lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, H.M.; Tourky, G.F.; Al-kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Khattab, A.M.; Elmasry, S.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Hakami, Z.H.; Alsulimani, A.; Sabatier, J.-M.; et al. The Potential Role of MUC16 (CA125) Biomarker in Lung Cancer: A Magic Biomarker but with Adversity. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122985
Saad HM, Tourky GF, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Khattab AM, Elmasry SA, Alsayegh AA, Hakami ZH, Alsulimani A, Sabatier J-M, et al. The Potential Role of MUC16 (CA125) Biomarker in Lung Cancer: A Magic Biomarker but with Adversity. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122985
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, Hebatallah M., Ghada F. Tourky, Hayder M. Al-kuraishy, Ali I. Al-Gareeb, Ahmed M. Khattab, Sohaila A. Elmasry, Abdulrahman A. Alsayegh, Zaki H. Hakami, Ahmad Alsulimani, Jean-Marc Sabatier, and et al. 2022. "The Potential Role of MUC16 (CA125) Biomarker in Lung Cancer: A Magic Biomarker but with Adversity" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122985
APA StyleSaad, H. M., Tourky, G. F., Al-kuraishy, H. M., Al-Gareeb, A. I., Khattab, A. M., Elmasry, S. A., Alsayegh, A. A., Hakami, Z. H., Alsulimani, A., Sabatier, J.-M., Eid, M. W., Shaheen, H. M., Mohammed, A. A., Batiha, G. E.-S., & De Waard, M. (2022). The Potential Role of MUC16 (CA125) Biomarker in Lung Cancer: A Magic Biomarker but with Adversity. Diagnostics, 12(12), 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122985









