Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube—Predicting Insertion Depth and Tube Size Based on Patient’s Chest X-ray Image Data and 4 Other Body Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Double Lumen Endotracheal Tube
2.3. Chest Computed Tomography and X-ray Measurements
2.4. Final Set of 17 Parameters
3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Data
4.2. Ranking of 17 Body Parameters According to Correlation Coefficient with ‘Depth’ or ‘Size’
4.3. Exclusion of Statistical Outliers in Data from the Selected Four or Five Body Parameters
4.4. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Modeling Results
4.5. Modeling Results from Linear Regression Compared with SVM
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGrath, B.; Tennuci, C.; Lee, G. The History of One-Lung Anesthesia and the Double-Lumen Tube. J. Anesth. Hist. 2017, 3, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzon, D.; Alston, R.P.; Coley, E.; Montgomery, K. Lung Isolation for Thoracic Surgery: From Inception to Evidence-Based. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2017, 31, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, J.B. Con: A Bronchial Blocker Is Not a Substitute for a Double-Lumen Endobronchial Tube. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlens, E. A New Flexible Double-Lumen Catheter for Bronchospirometry. J. Thorac. Surg. 1949, 18, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertshaw, F.L. Low Resistance Double-Lumen Endobronchial Tubes. Br. J. Anaesth. 1962, 34, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaitan, P.G.; D’Amico, T.A. Milestones in Thoracic Surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, J.B.; Lemmens, H.J. Left Double-Lumen Tubes: Clinical Experience with 1170 Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2003, 17, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedoto, A. How to Choose the Double-Lumen Tube Size and Side: The Eternal Debate. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.H.; Massa, F.C.; Kernstine, K.H. The Incidence of Right Upper-Lobe Collapse When Comparing a Right-Sided Double-Lumen Tube versus a Modified Left Double-Lumen Tube for Left-Sided Thoracic Surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benumof, J.L.; Partridge, B.L.; Salvatierra, C.; Keating, J. Margin of Safety in Positioning Modern Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tubes. Anesthesiology 1987, 67, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, F.A. Tip of Polyvinyl Chloride Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Inadvertently Wedged in Left Lower Lobe Bronchus. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 1986, 64, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiqing, L.; Wenxu, Q.; Yuqiang, M.; Youjing, D. Predicting the Size of a Left Double-Lumen Tube for Asian Women Based on the Combination of the Diameters of the Cricoid Ring and Left Main Bronchus: A Randomized, Prospective, Controlled Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, J.B.; Macario, A.; Mark, J.B. Tracheal Diameter Predicts Double-Lumen Tube Size: A Method for Selecting Left Double-Lumen Tubes. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Son, J.-S.; Ko, S.; Jeong, W.; Lim, H. Measurements of the Length and Diameter of Main Bronchi on Three-Dimensional Images in Asian Adult Patients in Comparison with the Height of Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2014, 28, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiqing, L.; Wenxu, Q.; Jin, Z.; Youjing, D. The Combination of Diameters of Cricoid Ring and Left Main Bronchus for Selecting the “Best Fit” Double-Lumen Tube. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, P.; Hayon-Sonsino, D.; Convard, J.P.; Laloë, P.-A.; Fischler, M. Measurement of Left Mainstem Bronchus Using Multiplane CT Reconstructions and Relationship between Patient Characteristics or Tracheal Diameters and Left Bronchial Diameters. Chest 2006, 130, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S.; Mirjalili, V. Python Machine Learning: Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Python. Scikit-Learn TensorFlow, 2nd ed; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung So, E.; Chang, T.-R. Modeling Surgical Patients’ Tidal Volumes Set by Anesthesiologists—A Successful Regression Approach Based on 6 Body Parameters. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 77, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-521-78019-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schölkopf, B.; Platt, J.C.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Smola, A.J.; Williamson, R.C. Estimating the Support of a High-Dimensional Distribution. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 1443–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.-E.; Chen, P.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Joachims, T. Working Set Selection Using Second Order Information for Training Support Vector Machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 889–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Kecman, V.; Huang, T.-M.; Vogt, M. Iterative Single Data Algorithm for Training Kernel Machines from Huge Data Sets: Theory and Performance. In Support Vector Machines: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, W.S. What Is a Support Vector Machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.H.; Friedman, J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Scholkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Min, F.; Ma, F. Research on Diabetes Prediction Method Based on Machine Learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1684, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumaya, Z.; Drissi Taoufiq, B.; Benayad, N.; Yunus, K.; Abdelkrim, A. The Detection of Parkinson Disease Using the Genetic Algorithm and SVM Classifier. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 171, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumouchel, W.; O’Brien, F. Integrating a Robust Option into a Multiple Regression Computing Environment. In Proceedings of the Computer Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the 21st Symposium on the Interface; American Statistical Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1989; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, P.W.; Welsch, R.E. Robust Regression Using Iteratively Reweighted Least-Squares. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1977, 6, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, J.O.; Carroll, R.J.; Ruppert, D. A Note on Computing Robust Regression Estimates via Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 152–154. [Google Scholar]


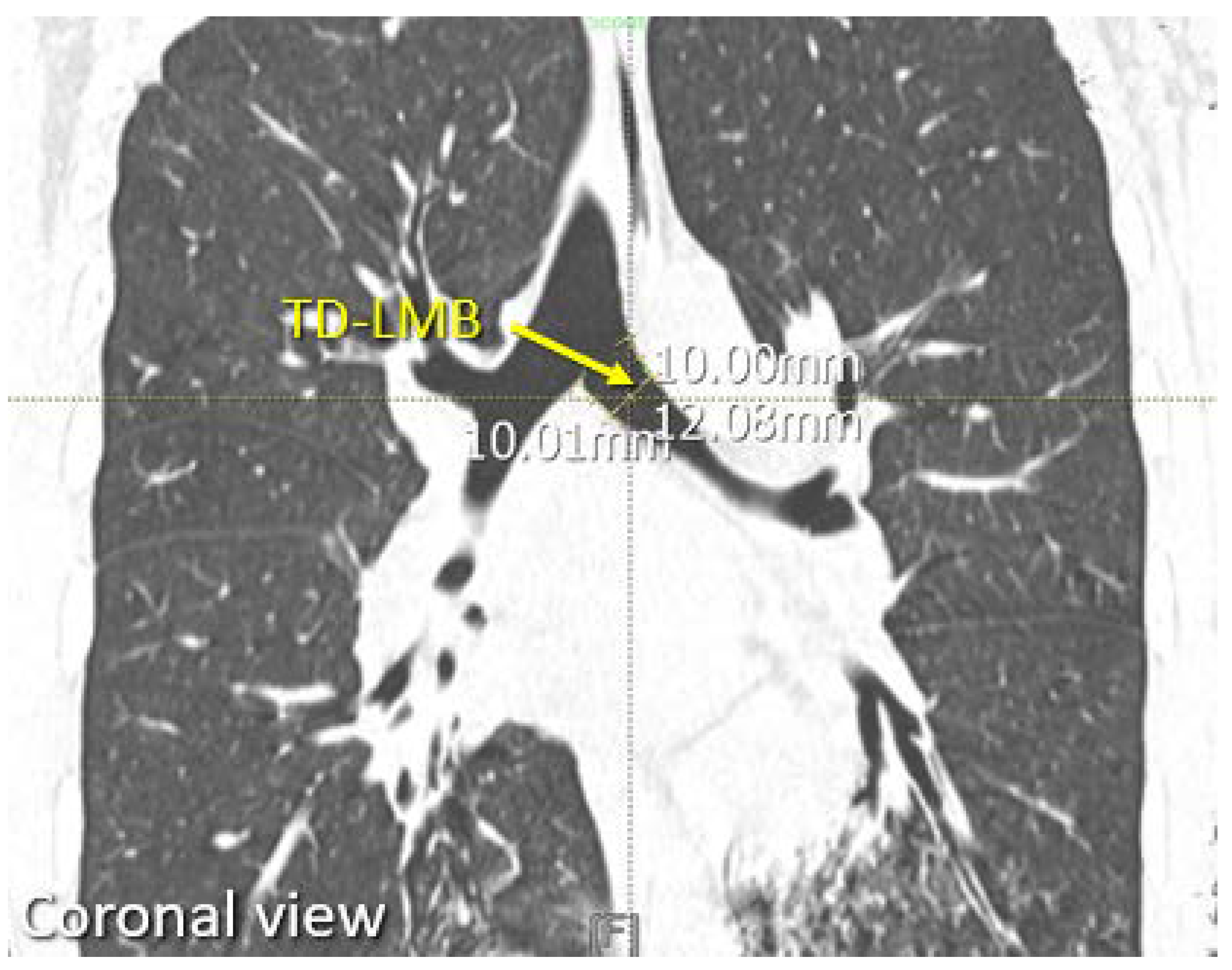


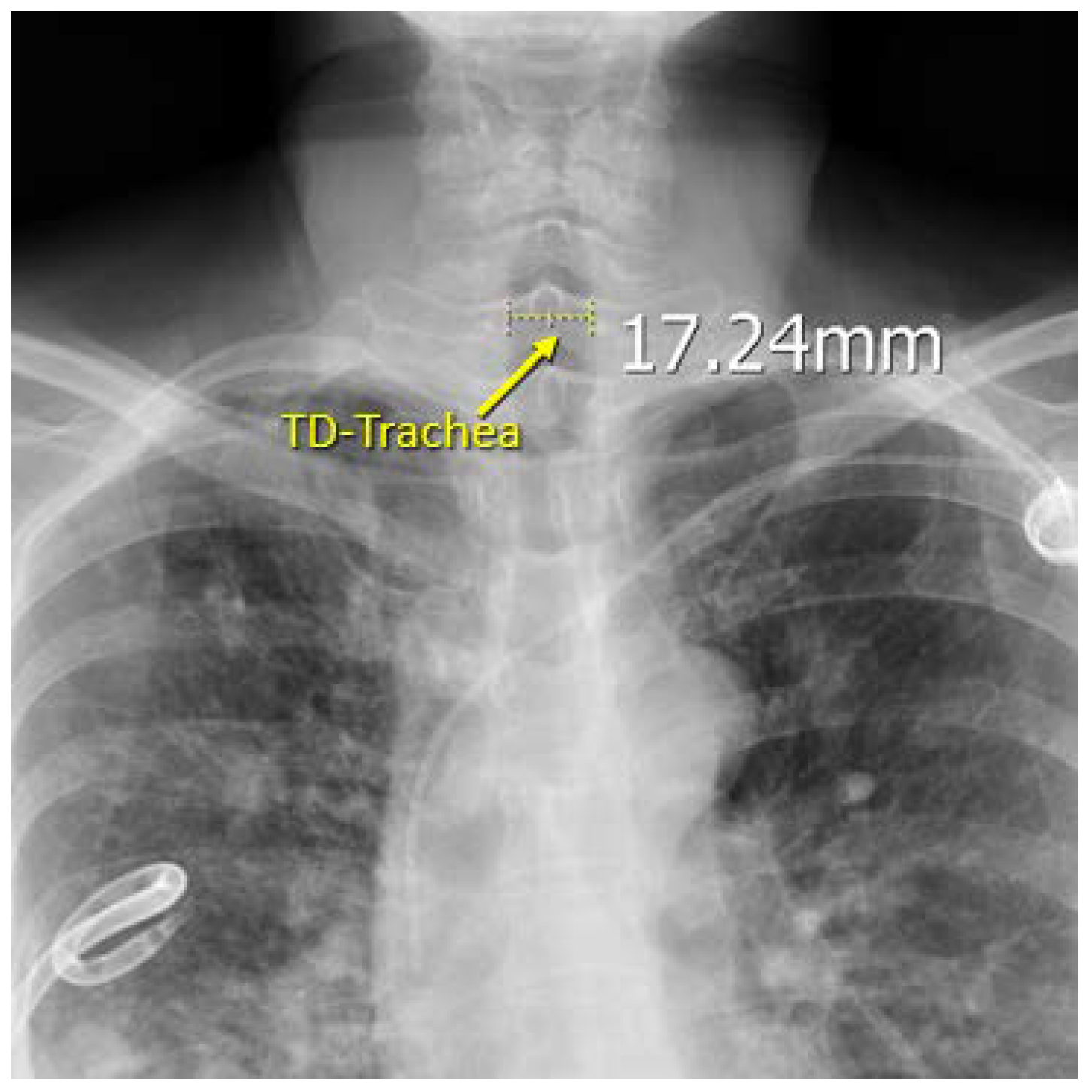


| No. | Parameter | Acquire Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SEX | Patient medical record |
| 2 | AGE | Patient medical record |
| 3 | WEIGHT | Patient medical record |
| 4 | HEIGHT | Patient medical record |
| 5 | BMI | Calculated (from WEIGHT and HEIGHT) |
| 6 | ASA | Patient medical record |
| 7 | TD-TRACHEA | Measured from X-ray |
| 8 | TD-CRICOID | Measured from CT |
| 9 | APD-CRICOID | Measured from CT |
| 10 | TD-LMB | Measured from CT |
| 11 | APD-LMB | Measured from CT |
| 12 | ED-LMB | Calculated (from TD-LMB and APD-LMB) |
| 13 | TD-CHEST | Measured from CT |
| 14 | APD-CHEST | Measured from CT |
| 15 | CHEST-CIRCUMFERENCE | Measured from CT |
| 16 | TRACHEA-LMB-ANGLE | Measured from CT |
| 17 | RMB-LMB-ANGLE | Measured from CT |
| Sex | Male: 161 (69.7%) | Female: 70 (30.3%) | Total: 231 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 57 ± 15.8 (14–86) | 59.5 ± 14.5 (17–88) | 57.7 ± 15.4 (14–88) |
| Weight (kg) | 66.2 ± 14.8 (31–130) | 57.4 ± 10.2 (38–83) | 63.5 ± 14.1 (31–130) |
| Height (cm) | 167.1 ± 6.3 (150–185) | 154.7 ± 5.4 (143.6–167) | 163.4 ± 8.3 (143.6–185) |
| BMI | 23.6 ± 4.8 (13.2–40) | 24 ± 4.4 (15.4–34.7) | 23.8 ± 4.7 (13.2–39.9) |
| DLT Size | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 28 Fr | 3 (1.9%) | 6 (8.6%) | 9 (3.9%) |
| 32 Fr | 12 (7.5%) | 40 (57.1%) | 52 (22.5%) |
| 35 Fr | 104 (64.6%) | 24 (34.3%) | 128 (55.4%) |
| 37 Fr | 42 (26.1%) | 0 (0%) | 42 (18.2%) |
| Intubation Depth (cm) | 29.7 ± 1.1 (27–35) | 27.2 ± 1.1 (23.5–29.5) | 29.0 ± 1.6 (23.5–35) |
| Male | Female | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TD-Trachea (mm) | 18.7 ± 1.8 (14.1–24.5) | 15.5 ± 1.7 (10.9–20.4) | 17.8 ± 2.3 (10.9–24.5) |
| TD-Cricoid (mm) | 17.1 ± 1.8 (10.9–22.2) | 13.5 ± 1.5 (9.9–16.5) | 16.0 ± 2.4 (9.9–22.2) |
| APD-Cricoid (mm) | 22.7 ± 2.6 (14–35.2) | 18.2 ± 1.7 (14.8–23.2) | 21.4 ± 3.1 (14.0–35.2) |
| TD-LMB (mm) | 14.5 ± 2 (9.9–22.1) | 12.4 ± 1.6 (8.5–19.2) | 13.9 ± 2.1 (8.5–22.1) |
| APD-LMB (mm) | 12.4 ± 2.1 (6.9–20.2) | 10.3 ± 2 (6.9–15.3) | 11.8 ± 2.3 (6.9–20.2) |
| ED-LMB (mm) | 13.5 ± 1.8 (8.4–20.5) | 11.4 ± 1.5 (8.1–15.1) | 12.9 ± 2.0 (8.1–20.5) |
| TD-Chest (mm) | 320.3 ± 26 (260.4–404.4) | 298.5 ± 28.3 (239.2–367.1) | 313.7 ± 28.5 (239.2–404.4) |
| APD-Chest (mm) | 225.9 ± 30.9 (153.8–336.1) | 211.1 ± 27 (138.9–260.3) | 221.4 ± 30.5 (138.9–336.1) |
| Chest Circumference (mm) | 877.3 ± 80.1 (695.4–1145.2) | 817.3 ± 80.1 (634.6–968.3) | 859.1 ± 84.6 (634.6–1145.24) |
| Trachea-LMB Angle (°) | 140.3 ± 10.5 (115.4–167.1) | 139.3 ± 10.8 (113.2–170.5) | 140 ± 10.6 (113.2–170.5) |
| RMB-LMB Angle (°) | 80.6 ± 15.3 (38.7–115.5) | 82.8 ± 17.3 (43.1–123.6) | 81.3 ± 16 (38.7–123.6) |
| Parameter | Correlation r with ‘Depth’ (FIX-DEPTH) | Parameter | Correlation r with ‘Size’ (TUBE-SIZE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEX | 0.84 | SEX | 0.74 |
| HEIGHT | 0.80 | TD-CRICOID | 0.71 |
| TD-CRICOID | 0.75 | HEIGHT | 0.70 |
| TD-TRACHEA | 0.71 | TD-TRACHEA | 0.67 |
| APD-CRICOID | 0.68 | APD-CRICOID | 0.66 |
| TD-LMB | 0.63 | TD-CHEST | 0.65 |
| ED-LMB | 0.62 | CHEST-CIRCUMFERENCE | 0.65 |
| WEIGHT | 0.56 | WEIGHT | 0.64 |
| APD-LMB | 0.55 | ED-LMB | 0.60 |
| TD-CHEST | 0.52 | TD-LMB | 0.59 |
| CHEST-CIRCUMFERENCE | 0.50 | APD-CHEST | 0.56 |
| APD-CHEST | 0.43 | APD-LMB | 0.55 |
| AGE | −0.37 | BMI | 0.46 |
| RMB-LMB-ANGLE | −0.24 | TRACHEA-LMB-ANGLE | 0.36 |
| TRACHEA-LMB-ANGLE | 0.13 | ASA | 0.33 |
| ASA | 0.12 | AGE | 0.16 |
| BMI | 0.04 | RMB-LMB-ANGLE | 0.13 |
| Depth | Linear Regression | Cubic SVM |
|---|---|---|
| 4 Parameters | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| 3 Parameters (no Sex) | 0.79 | 0.87 |
| 3 Parameters (no Height) | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| 3 Parameters (no TD-Trachea) | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| 3 Parameters (no Weight) | 0.85 | 0.77 |
| Size | Linear Regression | Cubic SVM |
| 5 Parameters | 0.68 | 0.82 |
| 4 Parameters (no Sex) | 0.66 | 0.78 |
| 4 Parameters (no Height) | 0.67 | 0.68 |
| 4 Parameters (no TD-Trachea) | 0.67 | 0.75 |
| 4 Parameters (no Chest circumference) | 0.68 | 0.66 |
| 4 Parameters (no Weight) | 0.67 | 0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, T.-R.; Yuan, M.-K.; Pan, S.-F.; Chuang, C.-C.; So, E.C. Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube—Predicting Insertion Depth and Tube Size Based on Patient’s Chest X-ray Image Data and 4 Other Body Parameters. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123162
Chang T-R, Yuan M-K, Pan S-F, Chuang C-C, So EC. Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube—Predicting Insertion Depth and Tube Size Based on Patient’s Chest X-ray Image Data and 4 Other Body Parameters. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123162
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Tsai-Rong, Mei-Kang Yuan, Shao-Fang Pan, Chia-Chun Chuang, and Edmund Cheung So. 2022. "Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube—Predicting Insertion Depth and Tube Size Based on Patient’s Chest X-ray Image Data and 4 Other Body Parameters" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123162
APA StyleChang, T.-R., Yuan, M.-K., Pan, S.-F., Chuang, C.-C., & So, E. C. (2022). Double-Lumen Endotracheal Tube—Predicting Insertion Depth and Tube Size Based on Patient’s Chest X-ray Image Data and 4 Other Body Parameters. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123162







