Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Coronary Atherosclerosis Risk Stratification
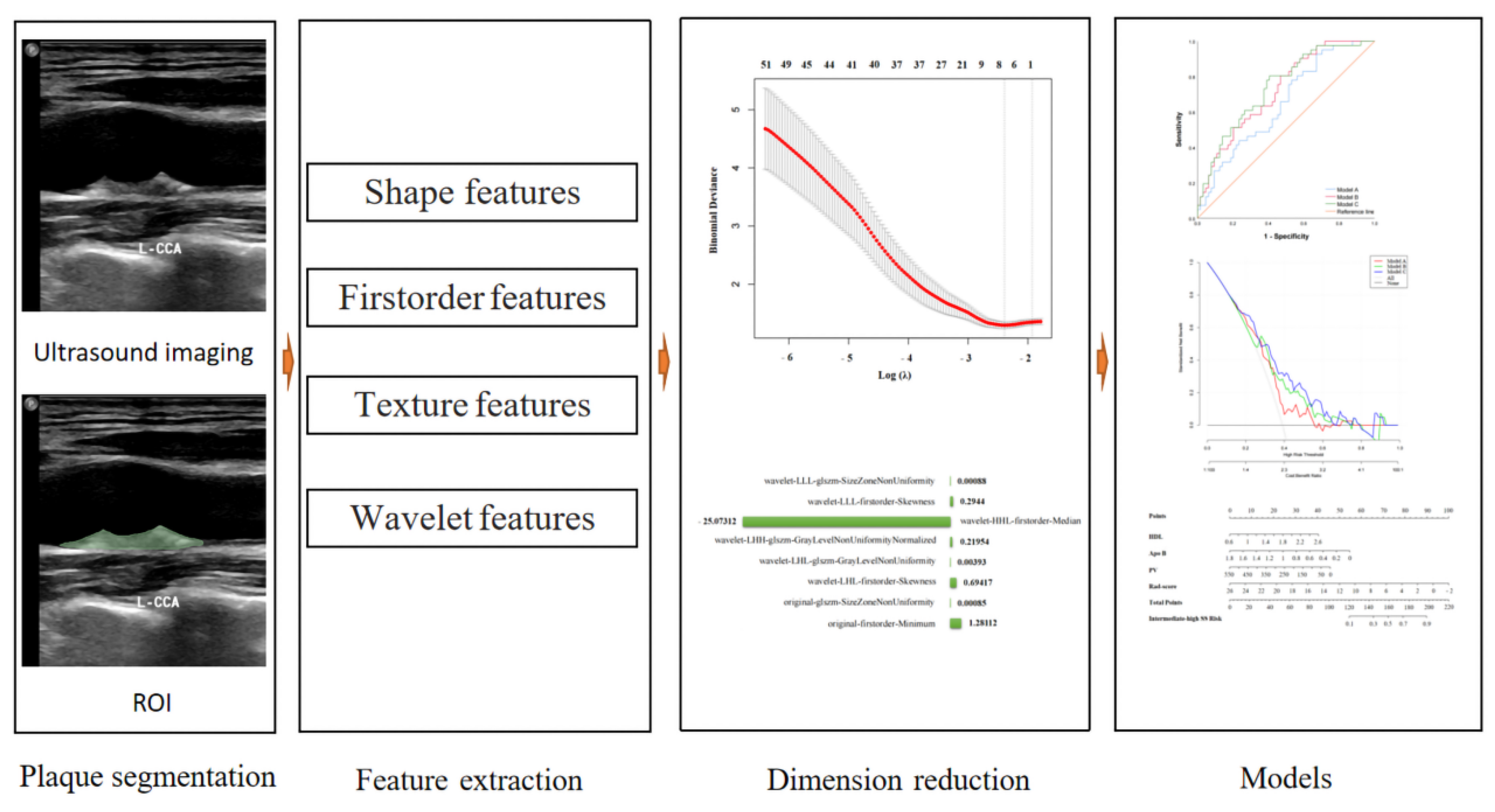
2.3. Imaging Acquisition and Carotid Plaque 3D-US Feature Extraction
2.4. Carotid Plaque Ultrasound Radiomics Feature Extraction, Dimension Reduction, and Radiomics Score
2.5. Models
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Characteristic Selection
3.3. Radiomics Score and 3D-US Characteristics
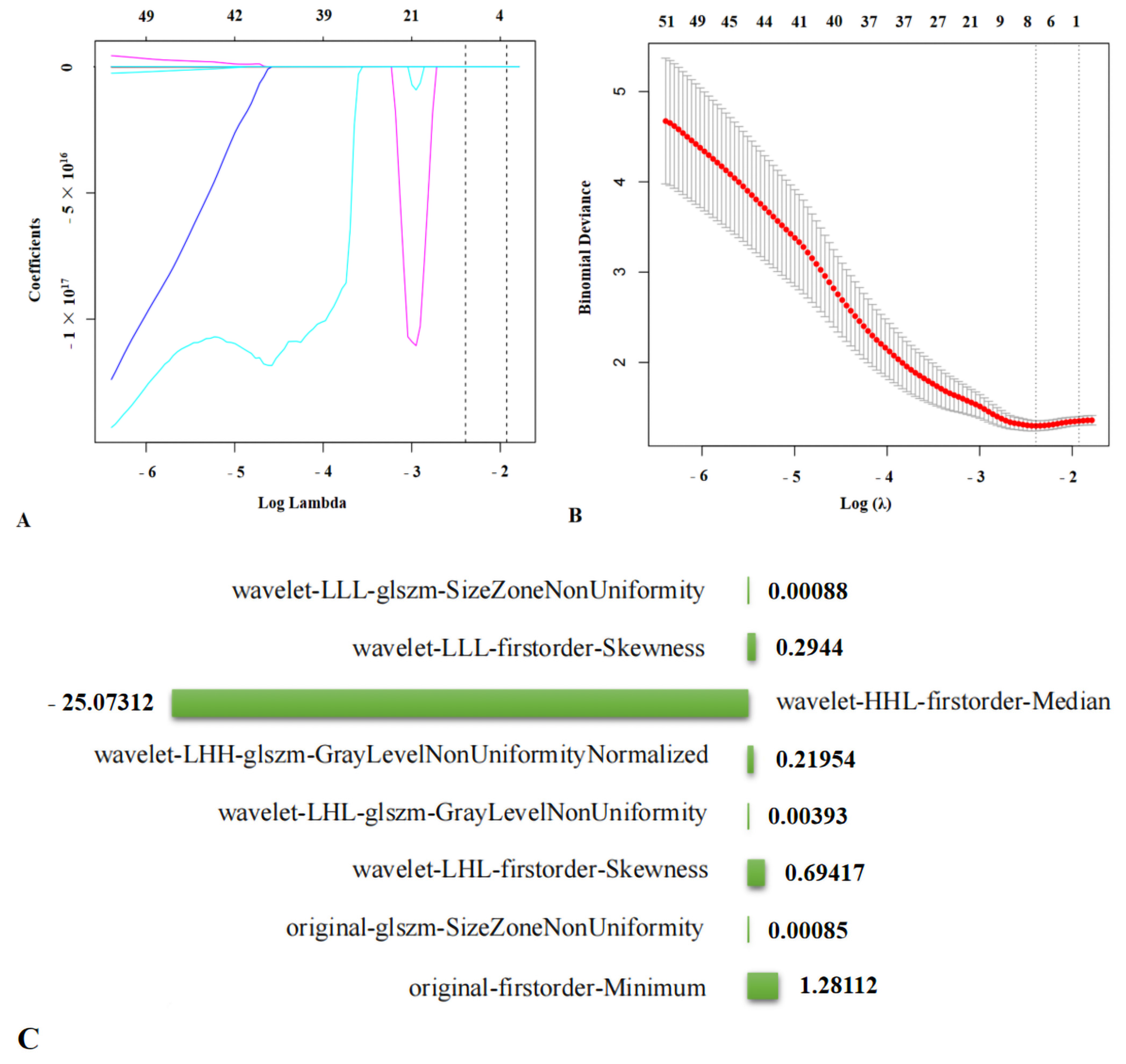
3.3.1. Screening for Ultrasound Radiomics Features and Radiomics Scores
glszm-SizeZoneNonUniformity + 0.69417 × wavelet-LHL-firstorder-Skewness
+ 0.00393 × wavelet-LHL-glszm-GrayLevelNonUniformity + 0.21954 ×
wavelet-LHH-glszm-GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized − 25.07312 ×
wavelet-HHL-firstorder-Median + 0.2944 × wavelet-LLL-firstorder-Skewness
+ 0.00088 × wavelet-LLL-glszm-SizeZoneNonUniformity.
3.3.2. 3D-US Feature Selection
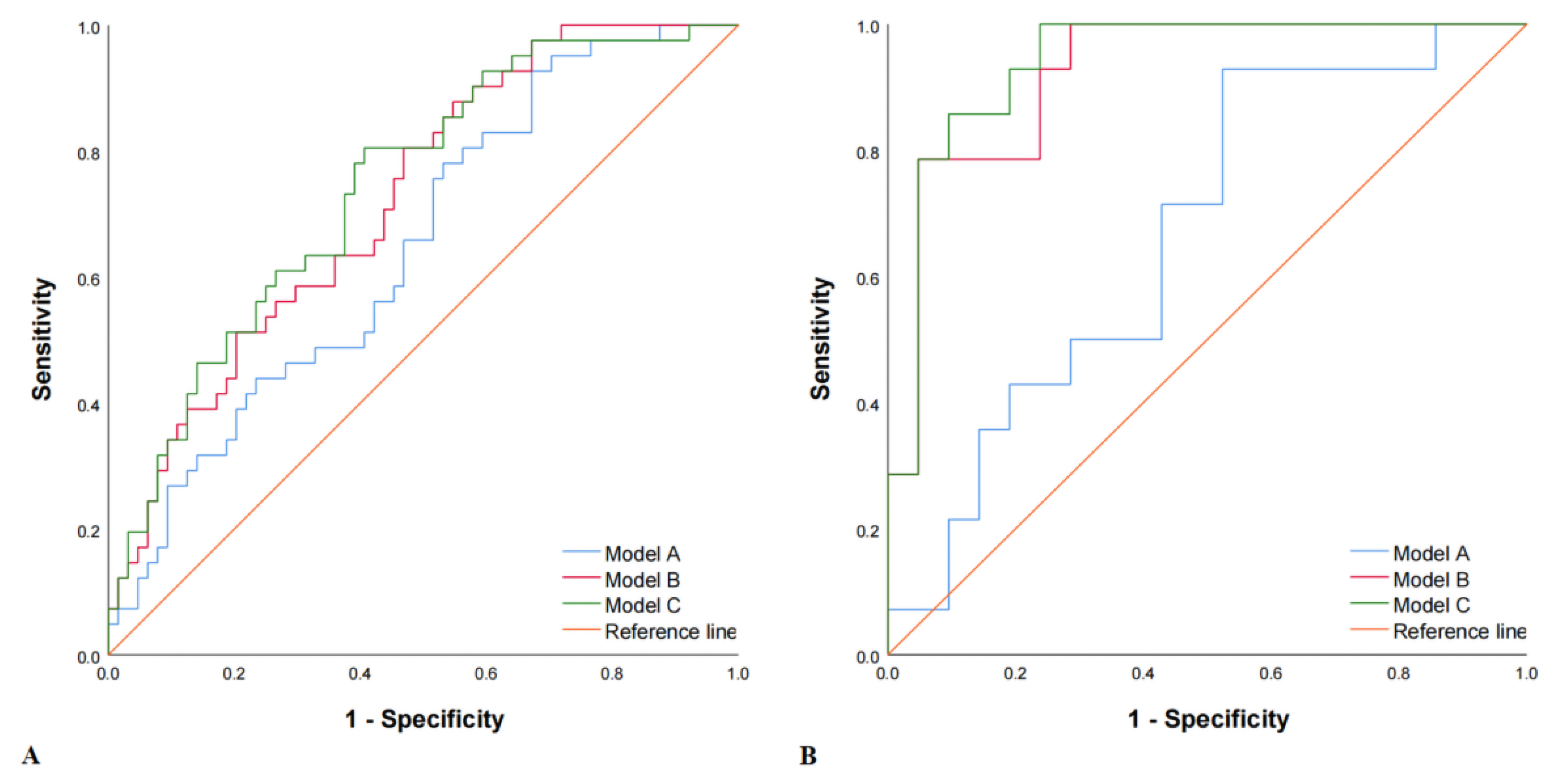
3.4. Models Construction
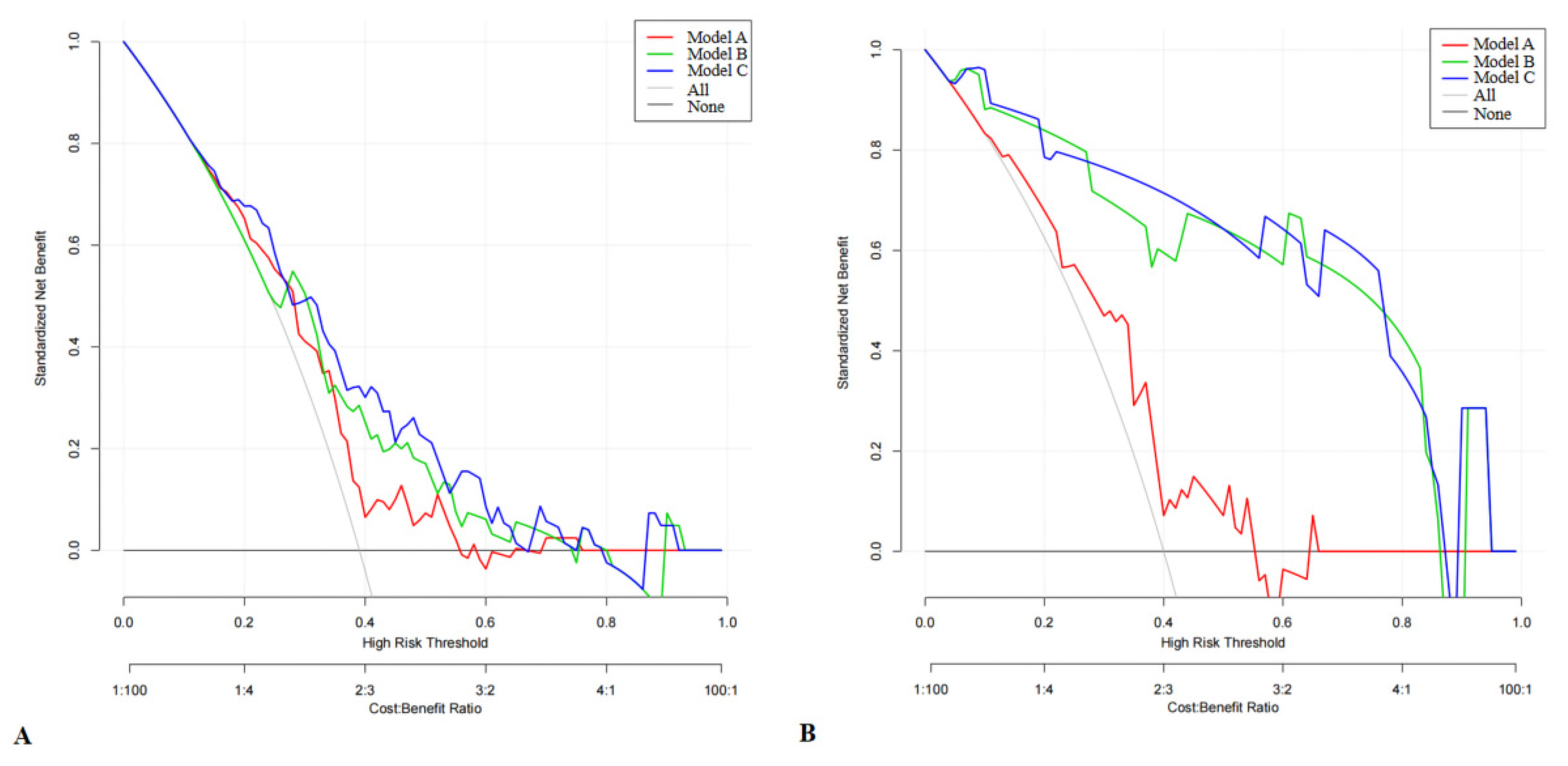
3.5. DCA
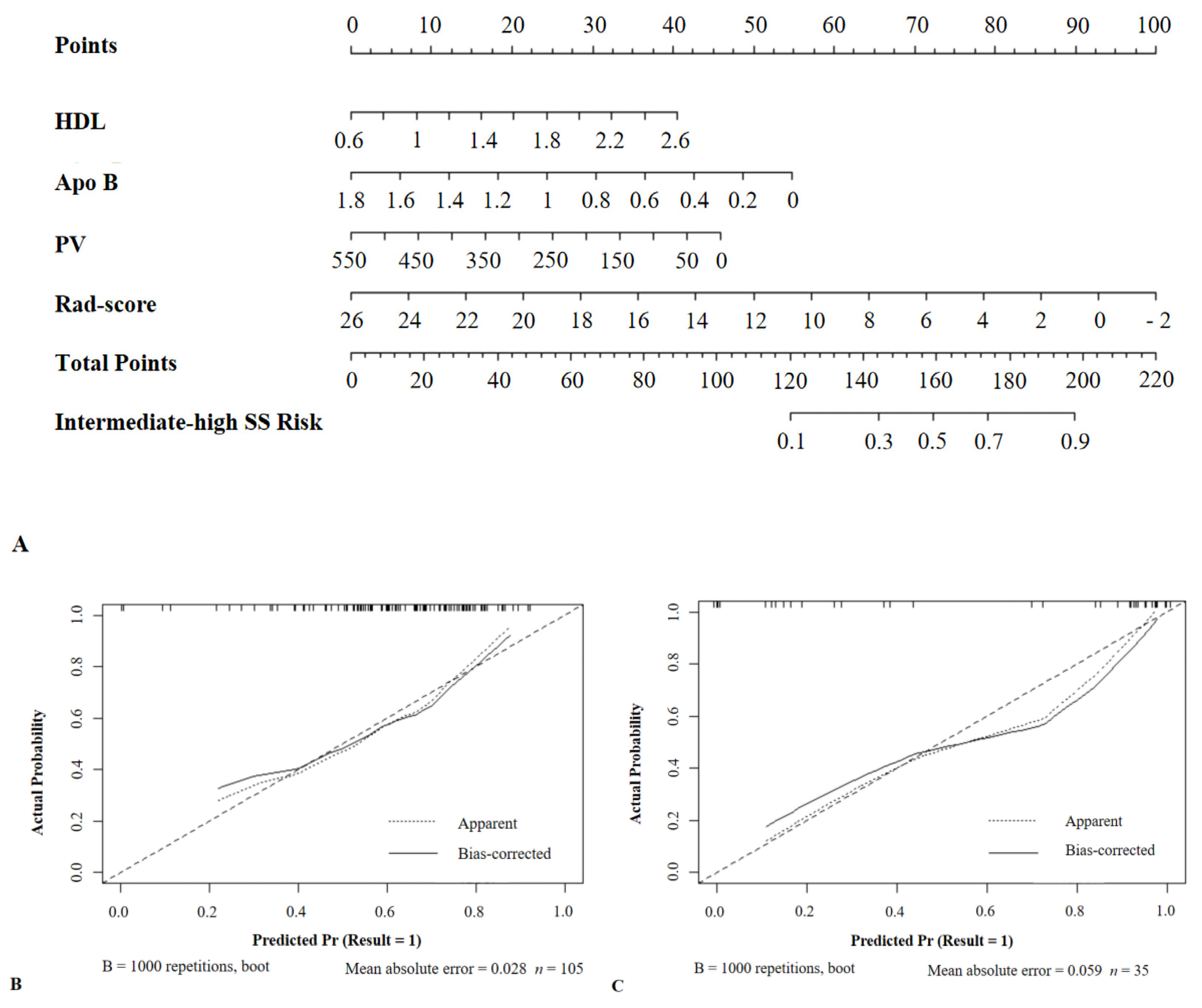
3.6. Development of a Nomogram
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knaapen, P. Computed Tomography to Replace Invasive Coronary Angiography? Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.E.; Handa, R. Contrast Nephropathy Associated with Percutaneous Coronary Angiography and Intervention. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danad, I.; Raijmaker, P.G.; Knaapen, P. Diagnosing coronary artery disease with hybrid PET/CT: It takes two to tango. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2013, 20, 874–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillesen, H.; Muntendam, P.; Adourian, A.; Entrekin, R.; Garcia, M.; Falk, E.; Fuster, V. Carotid plaque burden as a measure of subclinical atherosclerosis: Comparison with other tests for subclinical arterial disease in the High Risk Plaque BioImage study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Qiao, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Diagnosis of Ovarian Neoplasms Using Nomogram in Combination With Ultrasound Image-Based Radiomics Signature and Clinical Factors. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 753948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, C.L.; Luo, X.M.; Chuan, Z.-R.; Lv, W.-Z.; Li, X.; Cui, X.-W.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics in the assessment of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 147, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machicado, J.D.; Koay, E.J.; Krishna, S.G. Radiomics for the Diagnosis and Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J. Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkos, S.K.; Stevens, J.M.; Nicolaides, A.N.; Kyriacou, E.; Pattichis, C.S.; Geroulakos, G.; Thomas, D. Texture analysis of ultrasonic images of symptomatic carotid plaques can identify those plaques associated with ipsilateral embolic brain infarction. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2007, 33, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.; Yang, Y.; Lv, P.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Lin, J. Identification of high-risk carotid plaque with MRI-based radiomics and machine learning. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sree, S.V.; Mookiah, M.R.K.; Saba, L.; Gao, H.; Mallarini, G.; Suri, J.S. Computed tomography carotid wall plaque characterization using a combination of discrete wavelet transform and texture features: A pilot study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2013, 227, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalashyan, H.; Shuaib, A.; Gibson, P.H.; Romanchuk, H.; Saqqur, M.; Khan, K.; Osborne, J.; Becher, H. Single sweep three-dimensional carotid ultrasound: Reproducibility in plaque and artery volume measurements. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Heo, R.; Lee, S.E.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; In Cho, J.; Chang, H.-J. Comparing the feasibility and accuracy of three-dimensional ultrasound to two-dimensional ultrasound and computed tomography angiography in the assessment of carotid atherosclerosis. Echocardiography 2019, 36, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianos, G.; Morel, M.A.; Kappetein, A.P.; Morice, M.-C.; Colombo, A.; Dawkins, K.; van den Brand, M.; Van Dyck, N.; Russell, M.E.; Mohr, F.W.; et al. The SYNTAX Score: An angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention 2005, 1, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Guo, D.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Yao, X.; Song, W.; Song, J.; Zhou, Z. Noncontrast Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Analysis in Discriminating Early Hematoma Expansion after Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Cai, J.; Zhou, Z. A clinical-radiomics nomogram may provide a personalized 90-day functional outcome assessment for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4949–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, H.; Batur, J.; Shi, Z.; Tuerxun, A.; Abulajiang, A.; Lu, S.; Kong, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, S.; et al. A multicenter study to develop a non-invasive radiomic model to identify urinary infection stone in vivo using machine-learning. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, X.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Tong, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Jiang, T.; et al. Deep learning Radiomics of shear wave elastography significantly improved diagnostic performance for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: A prospective multicentre study. Gut 2019, 68, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noflatscher, M.; Schreinlechner, M.; Sommer, P.; Kerschbaum, J.; Berggren, K.; Theurl, M.; Kirchmair, R.; Marschang, P. Influence of Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors on Carotid and Femoral Atherosclerotic Plaque Volume as Measured by Three-Dimensional Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, N.; Kogame, N.; Iijima, R.; Nakamura, M.; Sugi, K. Carotid artery intima-media thickness and plaque score can predict the SYNTAX score. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Guan, H.; Da Gao, J.P.; Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Alam, M.; Lian, J.; Zhou, J. Sex-specific association of monocyte count to high-density lipoprotein ratio with SYNTAX score in patients with suspected stable coronary artery disease. Medicine 2019, 98, e17536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Wei, M.; Li, G. Association Between Serum LDL-C and ApoB and SYNTAX Score in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Angiology 2018, 69, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, C.-J.; Zhu, C.-G.; Guo, Y.-L.; Wu, N.-Q.; Xu, R.-X.; Liu, G.; Dong, Q.; et al. Large HDL Subfraction But Not HDL-C Is Closely Linked With Risk Factors, Coronary Severity and Outcomes in a Cohort of Nontreated Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease: A Prospective Observational Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.D.; Chen, X.C.; Yang, Y.N.; Gao, X.-M.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.-M.; Gai, M.-T.; Liu, F.; Pan, S.; et al. Apolipoprotein A1 is associated with SYNTAX score in patients with a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, P.W.F.; Polonsky, T.S.; Miedema, M.D.; Khera, A.; Kosinski, A.S.; Kuvin, J.T. Systematic Review for the 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 3210–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolossváry, M.; Karády, J.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ivanov, A.; Schlett, C.L.; Lu, M.T.; Foldyna, B.; Merkely, B.; Aerts, H.J.; Hoffmann, U.; et al. Radiomics versus Visual and Histogram-based Assessment to Identify Atheromatous Lesions at Coronary CT Angiography: An ex Vivo Study. Radiology 2019, 293, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Lin, A.; Yuvaraj, J.; Nicholls, S.; Wong, D. Cardiac Computed Tomography Radiomics for the Non-Invasive Assessment of Coronary Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayounieh, F.; Yan, P.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Kruger, U.; Wang, G.; Kalra, M.K. Prediction of Coronary Calcification and Stenosis: Role of Radiomics from Low-Dose CT. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Clinical Features | Low SSs (64) | Intermediate-High SSs (41) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.051 | ||
| Man | 40 (38.1%) | 33 (31.6%) | |
| Female | 24 (22.9%) | 8 (7.4%) | |
| Age (y) | 64.9 ± 10.1 | 65.5 ± 10.7 | 0.776 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.39 (1.56, 3.06) | 2.31 (1.85, 3.17) | 0.354 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.19 (0.95, 1.36) | 1.02 (0.93, 1.26) | 0.047 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.38 (1.05, 1.86) | 1.31 (1.01, 1.98) | 0.963 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4,45 (3.42, 5.25) | 4.32 (3.75, 5.78) | 0.524 |
| non-HDL (mmol/L) | 3.15 (2.19, 4.06) | 3.24 (2.47, 4.61) | 0.201 |
| HS-CRP (mg/L) | 2.66 (0.86, 5.00) | 2.69 (1.20, 5.00) | 0.687 |
| BP status | 0.080 | ||
| 0 | 28 (26.7%) | 11 (10.5%) | |
| 1 | 36 (34.3%) | 30 (28.5%) | |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 132 ± 16 | 132 ± 19 | 0.858 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 80 ± 11 | 81 ± 10 | 0.664 |
| Smoking | 0.080 | ||
| 0 | 28 (26.7%) | 11 (10.5%) | |
| 1 | 36 (34.3%) | 30 (28.5%) | |
| Diabetes status | 0.631 | ||
| 0 | 45 (42.9%) | 27 (25.7%) | |
| 1 | 19 (18.1%) | 14 (13.3%) | |
| Height (cm) | 162.5 (155.0, 168.0) | 165.0 (160.0, 168.0) | 0.240 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.7 ± 10.1 | 64.0 ± 10.1 | 0.524 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 ± 2.6 | 23.9 ± 3.0 | 0.883 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.90 (5.60, 6.95) | 6.15 (5.60, 6.75) | 0.585 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 90.85 (75.58, 99.33) | 84.90 (63.70, 99.45) | 0.231 |
| Apo B (g/L) | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.039 |
| Lp(a) (mg/L) | 141.50 (73.00, 279.75) | 254.00 (107.00, 490.00) | 0.094 |
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) | 6.79 (5.41, 8.20) | 5.93 (5.18, 9.41) | 0.852 |
| Plaque volume (mm3) | 47.50 (23.25, 94.00) | 74.00 (39.00, 159.50) | 0.014 |
| Wall area (mm2) | 19.20 (15.88, 24.65) | 19.10 (16.10, 28.30) | 0.452 |
| Median gray scale (dB) | 54.50 (41.13, 66.75) | 50.00 (40.00, 58.50) | 0.404 |
| Maximum area reduction rate (%) | 14.00 (8.00, 20.75) | 15.00 (11.50, 29.50) | 0.061 |
| Normalized wall index | 0.32 (0.28, 0.39) | 0.35 (0.30, 0.46) | 0.070 |
| Plaque thickness (mm) | 1.92 (1.58, 2.53) | 2.20 (1.64, 2.96) | 0.147 |
| Plaque area (mm2) | 5.95 (3.43, 10.18) | 7.80 (4.20, 13.50) | 0.179 |
| Lumen area (mm2) | 38.05 (27.23, 49.93) | 34.40 (25.10, 46.15) | 0.419 |
| Mean (dB) | 28.90 (21.00, 40.13) | 24.60 (20.15, 40.40) | 0.501 |
| Median (dB) | 17.65 (13.53, 20.00) | 16.50 (13.15, 19.25) | 0.389 |
| Standard deviation (dB) | 33.00 (23.25, 46.98) | 29.10 (23.05, 48.65) | 0.653 |
| Clinical Features | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Gender | 2.48 (0.98, 6.23) | 0.054 | ||
| Age | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 0.774 | ||
| LDL | 1.32 (0.89, 1.94) | 0.166 | ||
| HDL | 0.22 (0.05, 0.98) | 0.047 | 0.21 (0.04, 0.96) | 0.045 |
| TG | 1.29 (0.90, 1.84) | 0.174 | ||
| TC | 1.23 (0.92, 1.66) | 0.166 | ||
| non-HDL | 1.34 (0.98, 1.82) | 0.062 | ||
| HS-CRP | 1.02 (0.97, 1.06) | 0.443 | ||
| BP | 0.47 (0.20, 1.10) | 0.082 | ||
| Systolic BP | 1.00 (0.98, 1.03) | 0.856 | ||
| Diastolic BP | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 0.661 | ||
| Smoking status | 0.47 (0.20, 1.10) | 0.083 | ||
| Diabetes status | 0.81 (0.35, 1.88) | 0.631 | ||
| Height | 1.03 (0.98, 1.08) | 0.217 | ||
| Weight | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 0.520 | ||
| BMI | 0.99 (0.86, 1.14) | 0.881 | ||
| HbA1c | 0.95 (0.69, 1.30) | 0.741 | ||
| eGFR | 0.99 (0.97, 1.01) | 0.219 | ||
| Apo B | 4.37 (1.05, 18.19) | 0.043 | 4.60 (1.07, 19.82) | 0.041 |
| Lp(a) | 1.0012 (0.9997, 1.0027) | 0.105 | ||
| Blood glucose | 1.04 (0.94, 1.15) | 0.434 | ||
| Three-Dimensional Ultrasonic Features | Univariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Plaque volume | 1.0046 (0.9998, 1.0093) | 0.014 |
| Wall area | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 0.352 |
| Median gray scale | 0.99 (0.98, 1.01) | 0.569 |
| Maximum area reduction rate | 1.02 (1.00, 1.05) | 0.107 |
| Normalized wall index | 4.93 (0.25, 97.10) | 0.294 |
| Plaque thickness | 1.37 (0.87, 2.16) | 0.178 |
| Plaque area | 1.02 (0.98, 1.07) | 0.303 |
| Lumen area | 0.99 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.530 |
| Mean | 1.00 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.758 |
| Median | 0.98 (0.93, 1.04) | 0.507 |
| Standard deviation | 1.00 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.845 |
| Training Set | Verification Set | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | ACC (%) | Y | AUC | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | ACC (%) | Y | |
| Method A | 0.648 | 31.7 | 84.4 | 63.8 | 0.161 | 0.667 | 42.9 | 76.2 | 62.9 | 0.191 |
| Method B | 0.723 | 24.4 | 93.8 | 66.7 | 0.182 | 0.922 | 78.6 | 90.5 | 85.7 | 0.691 |
| Method C | 0.741 | 41.5 | 85.9 | 68.6 | 0.274 | 0.939 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 0.714 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Luo, P.; Du, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wan, L.; Zhao, B.; Ren, J. Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020256
Wang X, Luo P, Du H, Li S, Wang Y, Guo X, Wan L, Zhao B, Ren J. Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoting, Peng Luo, Huaan Du, Shiyu Li, Yi Wang, Xun Guo, Li Wan, Binyi Zhao, and Jianli Ren. 2022. "Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020256
APA StyleWang, X., Luo, P., Du, H., Li, S., Wang, Y., Guo, X., Wan, L., Zhao, B., & Ren, J. (2022). Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics, 12(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020256







