Thicker Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer with Age among Schoolchildren: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Ocular and Physical Examinations
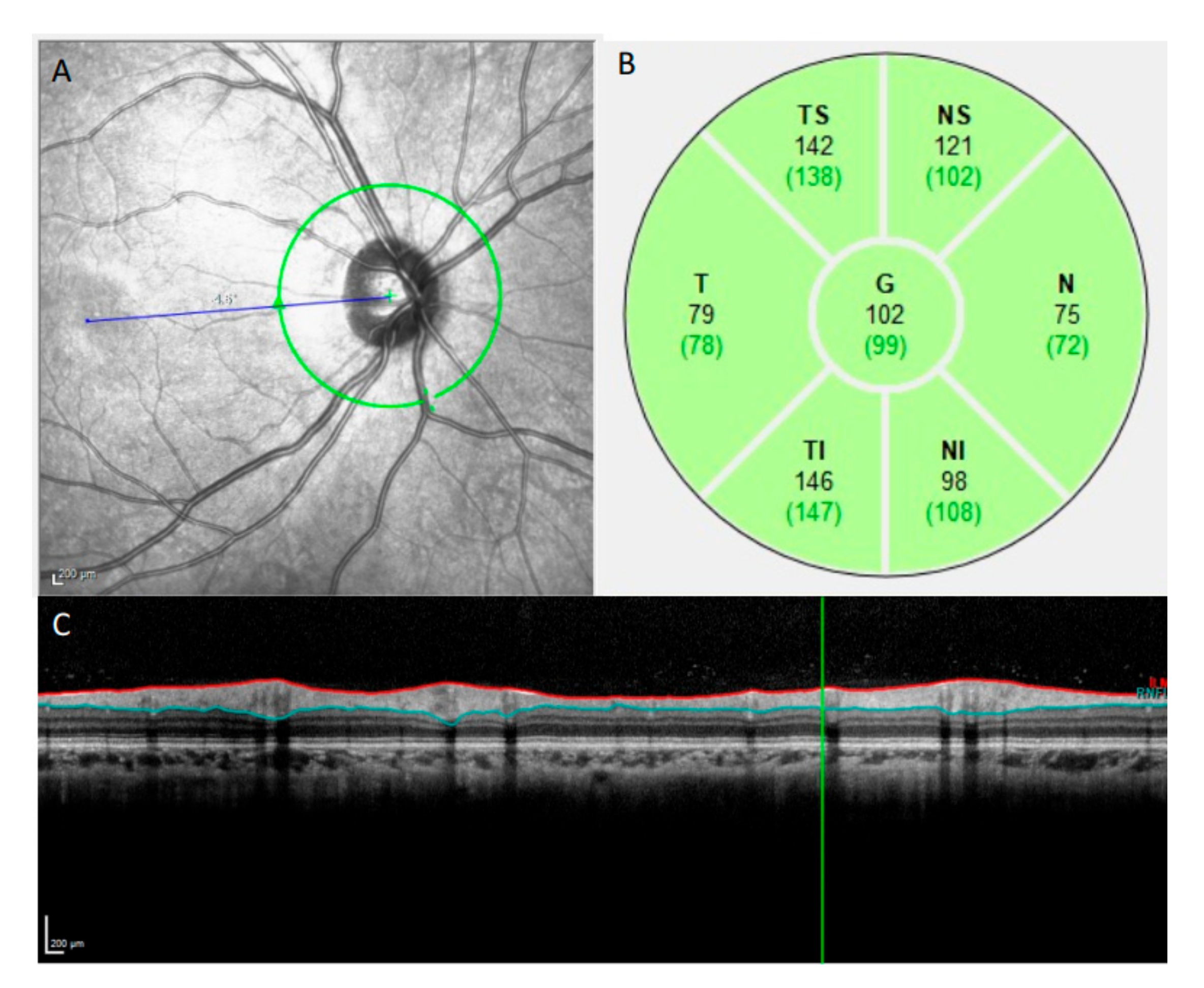
2.3. OCT Imaging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Normal Ranges of Global and Sectoral p-RNFL Thickness
3.3. Associations of Global and Sectoral p-RNFL Thickness with Age
3.4. Associations of Global and Sectoral p-RNFL Thickness with Other Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Age Correlation in Other Studies
4.2. Comparison of Mean p-RNFL Thickness with Other Studies
4.3. Other Factors with Significant Correlations with p-RNFL
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, C.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Dai, S.H. Causes of childhood low vision and blindness in New Zealand. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 47, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshigari, R.; Freidi, A.; Souru, C.; Edward, D.P.; Malik, R. Risk Factors for Blindness in Children with Primary Congenital Glaucoma-Follow-up of a Registry Cohort. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 224, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methe, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Pop, M.; Creasy, H.H.; Giglio, M.G.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; et al. A framework for human microbiome research. Nature 2012, 486, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Maccora, K.A.; Sheth, S.; Ruddle, J.B. Optical coherence tomography in paediatric clinical practice. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avery, R.A.; Rajjoub, R.D.; Trimboli-Heidler, C.; Waldman, A.T. Applications of optical coherence tomography in pediatric clinical neuroscience. Neuropediatrics 2015, 46, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hondur, G.; Goktas, E.; Al-Aswad, L.; Tezel, G. Age-related changes in the peripheral retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Y.; Huang, E.J.; Kuo, C.N.; Wu, P.L.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, P.C.; Wu, S.H.; King, Y.C.; Lai, C.H. The relationship between age, axial length and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in the normal elderly population in Taiwan: The Chiayi eye study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.X.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, L.; You, Q.S.; Xu, L.; Jonas, J.B. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. The Beijing Eye Study 2011. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, K.R.; Wollstein, G.; Bilonick, R.A.; Townsend, K.A.; Ishikawa, H.; Kagemann, L.; Noecker, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Schuman, J.S. Effects of age on optical coherence tomography measurements of healthy retinal nerve fiber layer, macula, and optic nerve head. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.W.; Ahn, Y.J.; Kang, N.Y. Relationship between Age and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Normal Children. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 32, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, C.; Barikian, A.; Jaroudi, M.; Massoud, V.; Tamim, H.; Noureddin, B. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography in children: Normative data and biometric correlations. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, B.; Meng, Z.W.; Hong, F.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, X.J.; Du, L.; Wang, I.Y.; Zhu, D.; et al. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Children: The Gobi Desert Children Eye Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 5285–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.T.; Li, S.M.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhu, B.D.; Guo, Y.Q.; Meng, B.; Sun, Y.Y.; Ran, A.; et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and its association with refractive error in Chinese children: The Anyang Childhood Eye Study. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 44, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.W.; Ahn, M.D.; Kang, S.H.; Im, S.K. Analysis of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber distribution in normal young adults. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, S.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Rochtchina, E.; Mitchell, P. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in a population of 6-year-old children: Findings by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, J.C.; Tang, S.M.; Kam, K.W.; Chen, L.J.; Yu, M.; Law, A.K.; Yip, B.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Cheung, C.Y.L.; Ng, D.S.C.; et al. High prevalence of myopia in children and their parents in Hong Kong Chinese Population: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e639–e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.X.; Xu, L.; Jonas, J.B. Retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measured by Spectralis spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: The Beijing Eye Study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, e35–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Akhtar, N.; Afzal, F.; Ali, K. Effect of refractive errors/axial length on peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness (RNFL) measured by Topcon SD-OCT. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Yanni, S.E.; Wang, J.; Cheng, C.S.; Locke, K.I.; Wen, Y.; Birch, D.G.; Birch, E.E. Normative reference ranges for the retinal nerve fiber layer, macula, and retinal layer thicknesses in children. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 354–360.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salchow, D.J.; Oleynikov, Y.S.; Chiang, M.F.; Kennedy-Salchow, S.E.; Langton, K.; Tsai, J.C.; Al-Aswad, L.A. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal children measured with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.C.; Huang, N.; Hwu, J.J.; Jueng, R.N.; Chou, P. Estimating retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal schoolchildren with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 56, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banc, A.; Ungureanu, M.I. Normative data for optical coherence tomography in children: A systematic review. Eye 2021, 35, 714–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Zou, H.; Xue, W.; Ma, Y.; He, X.; Lu, L.; Zhu, J. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal Chinese students aged 6 to 17 years. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7990–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.D.; Li, S.M.; Li, H.; Liu, L.R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.Y.; Kang, M.T.; Fu, J.; Qi, Y.H.; et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in a population of 12-year-old children in central China measured by iVue-100 spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: The Anyang Childhood Eye Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 8104–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bendschneider, D.; Tornow, R.P.; Horn, F.K.; Laemmer, R.; Roessler, C.W.; Juenemann, A.G.; Kruse, F.E.; Mardin, C.Y. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normals measured by spectral domain OCT. J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Hong, S.W.; Im, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, M.D. Effect of myopia on the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4075–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, E.Y.; Leung, C.K.; Musch, D.C.; Tang, X.; Zheng, C.; He, M.; Chang, D.F.; Lam, D.S. Prevalence of visual impairment and outcomes of cataract surgery in Chaonan, South China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonas, J.B.; Muller-Bergh, J.A.; Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U.M.; Naumann, G.O. Histomorphometry of the human optic nerve. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1990, 31, 736–744. [Google Scholar]
- Jammal, A.A.; Thompson, A.C.; Mariottoni, E.B.; Estrela, T.; Shigueoka, L.S.; Berchuck, S.I.; Medeiros, F.A. Impact of Intraocular Pressure Control on Rates of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Loss in a Large Clinical Population. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Li, K.; Ding, X.; Hu, D.; Li, K.; Ge, J. Relationship between intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fibre thickness loss in a monkey model of chronic ocular hypertension. Eye 2019, 33, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, J.Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.X.; You, Q.S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, M.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Fan, Y.Y.; et al. Localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects and arterial hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baran, R.T.; Baran, S.O.; Toraman, N.F.; Filiz, S.; Demirbilek, H. Evaluation of intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fiber layer, retinal ganglion cell, central macular thickness, and choroidal thickness using optical coherence tomography in obese children and healthy controls. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozen, B.; Ozturk, H.; Catli, G.; Dundar, B. An Assessment of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Non-Diabetic Obese Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2018, 10, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangwani, R.A.; Lee, J.W.Y.; Mo, H.Y.; Sum, R.; Kwong, A.S.K.; Wang, J.H.L.; Tsui, W.W.S.; Chan, J.C.H.; Lai, J.S.M. The Correlation of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness with Blood Pressure in a Chinese Hypertensive Population. Medicine 2015, 94, e947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.L.; Wu, J.F.; Ye, X.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, W.; Guo, D.D.; Wang, X.R.; Bi, H.S.; Jonas, J.B. Axial Length and Associated Factors in Children: The Shandong Children Eye Study. Ophthalmologica 2016, 235, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rauscher, F.G.; Choi, E.Y.; Wang, M.; Baniasadi, N.; Wirkner, K.; Kirsten, T.; Thiery, J.; Engel, C.; Loeffler, M.; et al. Sex-Specific Differences in Circumpapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex | |
|---|---|
| Male, N (%) | 2067 (51.2%) |
| Female, N (%) | 1967 (48.8%) |
| Age (mean ± SD), years | 7.61 ± 0.98 |
| Body mass index (mean ± SD), kg/m2 | 16.14 ± 2.88 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mean ± SD), mm Hg | 101.51 ± 11.13 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mean ± SD), mm Hg | 64.50 ± 9.03 |
| Visual acuity, logMAR unit | |
| Right eyes (Mean ± SD) | 0.01 ± 0.05 |
| Left eyes (Mean ± SD) | 0.02 ± 0.05 |
| Axial length (mm) | |
| Right eyes (Mean ± SD) | 23.14 ± 0.94 |
| Left eyes (Mean ± SD) | 23.13 ± 0.94 |
| Spherical equivalent, D | |
| Right eyes (Mean ± SD) | 0.13 ± 1.56 |
| Left eyes (Mean ± SD) | 0.17 ± 1.57 |
| Central corneal thickness, μm | |
| Right eyes (Mean ± SD) | 549.50 ± 32.51 |
| Left eyes (Mean ± SD) | 551.27 ± 31.83 |
| Intraocular Pressure, mmHg | |
| Right eyes (Mean ± SD) | 15.57 ± 2.53 |
| Left eyes (Mean ± SD) | 15.86 ± 2.77 |
| logMAR, logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution |
| p-RNFL Thickness, μm | Right Eyes | Left Eyes | Both Eyes | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentiles | Percentiles | Percentiles | ||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | Range | 1st | 5th | 95th | 99th | Mean (SD) | Range | 1st | 5th | 95th | 99th | Mean (SD) | Range | 1st | 5th | 95th | 99th | |
| Global | 106.60 (9.41) | (72 to 171) | 85.34 | 92.00 | 122.00 | 131.25 | 105.99 (9.30) | (76 to 163) | 84.84 | 91.50 | 121.50 | 130.16 | 106.29 (9.36) | (72 to 171) | 85.25 | 91.75 | 121.75 | 131.00 |
| Temporal superior | 154.22 (20.53) | (65 to 269) | 103.00 | 122.00 | 188.00 | 207.00 | 155.12 (19.42) | (61 to 258) | 111.00 | 124.00 | 187.00 | 206.65 | 154.67 (19.99) | (61 to 269) | 106.00 | 123.00 | 187.55 | 207.00 |
| Temporal | 83.98 (13.13) | (51 to 214) | 60.00 | 66.00 | 106.00 | 123.00 | 81.99 (12.40) | (41 to 198) | 58.00 | 64.00 | 104.00 | 118.65 | 82.99 (12.81 | (41 to 214) | 59.00 | 65.00 | 105.00 | 121.00 |
| Temporal inferior | 155.65 (19.11) | (88 to 271) | 114.00 | 127.00 | 188.00 | 204.65 | 154.60 (19.72) | (68 to 235) | 106.35 | 124.00 | 187.00 | 201.00 | 155.12 (19.42) | (68 to 271) | 111.00 | 125.00 | 188.00 | 203.31 |
| Nasal inferior | 117.26 (23.69) | (46 to 231) | 68.00 | 80.75 | 156.00 | 181.65 | 115.83 (23.45) | (38 to 247) | 67.00 | 80.00 | 156.00 | 175.65 | 116.51 (23.47) | (38 to 247) | 67.00 | 80.00 | 156.00 | 178.00 |
| Nasal | 68.34 (14.15) | (32 to 199) | 40.00 | 48.00 | 92.00 | 107.65 | 63.88 (13.73) | (32 to 177) | 39.00 | 45.00 | 87.00 | 101.00 | 66.11 (14.12) | (32 to 177) | 39.69 | 46.00 | 90.00 | 104.00 |
| Nasal superior | 121.14 (20.75) | (45 to 212) | 76.00 | 89.00 | 156.00 | 177.00 | 130.46 (22.45) | (41 to 234) | 80.35 | 96.00 | 168.00 | 190.00 | 125.77 (22.01) | (41 to 234) | 78.00 | 92.00 | 163.00 | 187.00 |
| Parameters | β | 95% CI | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.509 | 0.21 | 0.80 | 0.001 |
| Sex * | 1.013 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.140 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.013 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | −0.011 | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.547 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | −0.001 | −0.04 | 0.04 | 0.946 |
| Axial length, mm | −2.917 | −3.23 | −2.61 | <0.001 |
| Intraocular Pressure, mmHg | −0.115 | −0.18 | −0.06 | <0.001 |
| CCT, μm | 0.000 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.898 |
| Temporal Superior | Temporal | Temporal Inferior | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | β | 95% CI | p Values | β | 95% CI | p Values | β | 95% CI | p Values | |||
| Age | 0.953 | 0.35 | 1.56 | 0.002 | −0.210 | −0.61 | 0.19 | 0.305 | 1.372 | 0.76 | 1.99 | 0.000 |
| Sex * | 1.568 | 0.36 | 2.77 | 0.011 | −2.637 | −3.42 | −1.85 | 0.000 | −0.982 | −2.19 | 0.22 | 0.110 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.133 | −0.08 | 0.35 | 0.223 | 0.093 | −0.05 | 0.23 | 0.195 | 0.190 | −0.02 | 0.40 | 0.081 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | −0.053 | −0.12 | 0.02 | 0.134 | −0.005 | −0.05 | 0.04 | 0.822 | −0.011 | −0.08 | 0.06 | 0.765 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 0.058 | −0.02 | 0.14 | 0.163 | 0.009 | −0.04 | 0.06 | 0.745 | −0.013 | −0.10 | 0.07 | 0.761 |
| Axial length, mm | −2.294 | −2.96 | −1.63 | 0.000 | 3.186 | 2.75 | 3.62 | 0.000 | −2.682 | −3.36 | −2.00 | 0.000 |
| Intraocular Pressure, mmHg | −0.228 | −0.40 | -0.05 | 0.011 | −0.069 | −0.18 | 0.04 | 0.229 | −0.208 | −0.38 | −0.03 | 0.019 |
| CCT, μm | −0.004 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.667 | −0.002 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.707 | 0.000 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.970 |
| Age | 0.772 | 0.06 | 1.48 | 0.034 | 0.175 | −0.25 | 0.60 | 0.425 | 0.955 | 0.29 | 1.62 | 0.005 |
| Sex * | 3.633 | 2.24 | 5.02 | 0.000 | 2.375 | 1.54 | 3.21 | 0.000 | 4.486 | 3.17 | 5.80 | 0.000 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.214 | −0.03 | 0.46 | 0.083 | 0.137 | −0.01 | 0.28 | 0.060 | 0.123 | −0.11 | 0.36 | 0.309 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | −0.015 | −0.09 | 0.06 | 0.704 | 0.016 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.535 | −0.021 | −0.09 | 0.05 | 0.568 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | −0.003 | −0.09 | 0.09 | 0.957 | −0.027 | −0.08 | 0.03 | 0.331 | −0.014 | −0.10 | 0.07 | 0.746 |
| Axial length, mm | −10.003 | −10.77 | −9.23 | 0.000 | −4.071 | −4.53 | −3.61 | 0.000 | −6.305 | −7.04 | −5.57 | 0.000 |
| Intraocular Pressure, mmHg | −0.275 | −0.47 | −0.08 | 0.005 | −0.192 | −0.32 | −0.07 | 0.003 | 0.024 | −0.17 | 0.22 | 0.807 |
| CCT, μm | 0.000 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.989 | −0.004 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.496 | 0.008 | −0.01 | 0.03 | 0.391 |
| Study | Ethnicity | Age, Years (Mean ± SD; Range) | Type of OCT | Mean Global RNFL Thickness (μm) | Correlation with Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present study | Chinese (n = 4034) | 7.61 ± 0.98; 6–8 | SD-OCT | 106.29 ± 9.36 | Positively correlated |
| Wang CY, et al. (2018) [12] | Chinese and Mongolian (n = 1565) | 11.9 ± 3.5; 6–21 | SD-OCT | 101.3 ± 9.2 | No correlation |
| Hong SW, et al. (2017) [10] | Korean (n = 198) | 8.61 ± 3.12; 2–18 | Stratus OCT | 107.71 ± 11.83 | Positively correlated |
| Kang MT, et al. (2016) [13] | Chinese (n = 2893) | 7.1 ± 0.4; 5.7–9.1 | SD OCT | 102.01 ± 8.02 | Not reported |
| Chen L, et al. (2013) [23] | Chinese (n = 2324) | 12.82 ± 3.11; 6–17 | OCT-iVue100 | 106.89 ± 12.84 | No correlation |
| Yanni SE, et al. (2013) [21] | non-Hispanic, African American, Hispanic, and Asian (n = 83) | 9.14; 5–15 | SD OCT | 107.6 ± 1.2 | Negatively correlated |
| Zhu BD, et al. (2013) [22] | Chinese (n = 2105) | 12.34 ± 0.58; 10–16 | SD-OCT | 103.08 ± 9.01 | No correlation |
| Tsai DC, et al. (2011) | Taiwanese (n = 470) | 7–12 | SD-OCT | 109.4 ± 10.0 | No correlation |
| Huynh SC, et al. (2006) | Caucasian, African American, Asian, and Hispanic (n = 1369) | 6.71 ± 0.4 | Stratus OCT | 103.7 ± 11.4 | No correlation |
| Salchow DJ, et al. (2005) [22] | Hispanic, African American, Caucasian (n = 92) | 9.7 ± 2.7; 4–17 | Stratus OCT | 107.0 ± 11.1 | Negatively correlated |
| Neelam, P, et al. (2014) | Indian (n = 120) | 10.8 ± 3.24 years (range 5–17) | Stratus OCT | 106.11 ± 9.5 | No correlation |
| Leung, et al. (2010) | Chinese (n = 104) | 9.75; (6.08–17.58) | Optical OCT | 113 | No correlation |
| Al-haddad Christiane | Middle Eastern (n = 108) | 10.7 ± 3.1 | Cirrus OCT | 95.6 ± 8.7 | No correlation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.-J.; Lau, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chan, H.-N.; Chan, P.P.; Kam, K.-W.; Ip, P.; Zhang, W.; Young, A.L.; Tham, C.C.; et al. Thicker Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer with Age among Schoolchildren: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020500
Zhang X-J, Lau Y-H, Wang Y-M, Chan H-N, Chan PP, Kam K-W, Ip P, Zhang W, Young AL, Tham CC, et al. Thicker Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer with Age among Schoolchildren: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020500
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiu-Juan, Yi-Han Lau, Yu-Meng Wang, Hei-Nga Chan, Poemen P. Chan, Ka-Wai Kam, Patrick Ip, Wei Zhang, Alvin L. Young, Clement C. Tham, and et al. 2022. "Thicker Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer with Age among Schoolchildren: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020500
APA StyleZhang, X.-J., Lau, Y.-H., Wang, Y.-M., Chan, H.-N., Chan, P. P., Kam, K.-W., Ip, P., Zhang, W., Young, A. L., Tham, C. C., Pang, C.-P., Chen, L.-J., & Yam, J. C. (2022). Thicker Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer with Age among Schoolchildren: The Hong Kong Children Eye Study. Diagnostics, 12(2), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020500










